Abstract
The existence of camouflage targets is widespread in the natural world, as they blend seamlessly or closely resemble their surrounding environment, making it difficult for the human eye to identify them accurately. In camouflage target segmentation, challenges often arise from the high similarity between the foreground and background, resulting in segmentation errors, imprecise edge detection, and overlooking of small targets. To address these issues, this paper presents a robust localization-guided dual-branch network for the recognition of camouflaged targets. Two crucial branches, i.e., a localization branch and an overall refinement branch are designed and incorporated. The localization branch achieves accurate preliminary localization of camouflaged targets by incorporating the robust localization module, which integrates different high-level feature maps in a partially decoded manner. The overall refinement branch optimizes segmentation accuracy based on the output predictions of the localization branch. Within this branch, the edge refinement module is devised to effectively reduce false negative and false positive interference. By conducting context exploration on each feature layer from top to bottom, this module further enhances the precision of target edge segmentation. Additionally, our network employs five jointly trained output prediction maps and introduces attention-guided heads for diverse prediction maps in the overall refinement branch. This design adjusts the spatial positions and channel weights of different prediction maps, generating output prediction maps based on the emphasis of each output, thereby further strengthening the perception and feature representation capabilities of the model. To improve its ability to generate highly confident and accurate prediction candidate regions, tailored loss functions are designed to cater to the objectives of different prediction maps. We conducted experiments on three publicly available datasets for camouflaged object detection to assess our methodology and compared it with state-of-the-art network models. On the largest dataset COD10K, our method achieved a Structure-measure of 0.827 and demonstrated superior performance in other evaluation metrics, outperforming recent network models.
1. Introduction
In biological evolution, some organisms develop self-protective mechanisms to enhance their survival rates, and camouflage is a common strategy. Camouflage targets refer to objects that can naturally blend into their surrounding backgrounds. These creatures achieve self-concealment by increasing their similarity to the environment [1]. For example, lions living in tropical grasslands have body colors that help them better hide in their environment, aiding their hunting and survival. The body structure and coloration of dead leaf mantises (Deroplatys) closely resemble withered leaves, providing them a significant advantage in predation and evading predators, enabling them to thrive. Flatfish, such as flounders, have a flattened body shape, one side of their body with colored patterns, usually orange spots and patches, allowing them to blend in with the seabed. Some flatfish species can even change their coloration to match the environment, further enhancing their concealment. These are self-protective mechanisms that organisms have developed through natural evolution. In addition to natural camouflage in the animal kingdom, there is also artificial camouflage, such as the camouflage uniforms worn by soldiers in forest combat. The camouflage strategies of disguised targets involve enhancing their similarity to the surrounding environment in terms of texture, color, shape, and other aspects, making detecting the target within its environment difficult. Due to the unique characteristics of camouflage targets, segmenting them is more challenging and complex compared to general salient object detection tasks.
In recent years, camouflage object segmentation (COS) is gaining an increasing research focus for its wide applications in various fields. For example, COS techniques can effectively identify the pathological tissues or lesion areas that are difficult to spot in traditional medical image analysis, providing valuable references for doctors [2]. In the military domain, COS techniques can assist in the detection of military targets hidden in the surrounding environment, which is of great significance to battlefield situation assessment. In the wilderness, COS technology can enhance the discovery rate of rare species, playing a crucial role in biodiversity conservation [3]. Moreover, in complex rescue missions conducted in challenging environments, COS technology can be utilized for target localization, thereby improving the success rate of rescue operations.
In summary, camouflage object segmentation techniques have broad applications in various fields and hold significant research and practical value. Due to the inherent characteristics of camouflage targets, precise localization and segmentation pose considerable difficulties and challenges. This drives researchers to continuously explore more efficient and advanced COS techniques, fostering COS technology’s continuous development and innovation in practice.
With the introduction and rapid development of deep learning methods, they have demonstrated superior performance in camouflage object segmentation tasks compared to traditional algorithms [4,5,6]. Traditional methods primarily rely on manually crafted low-level features, such as texture and color, for foreground and background discrimination [7,8,9]. However, these methods often need help with feature extraction and better transferability, resulting in inaccurate identification of camouflage targets. The similarity between camouflage targets and their surrounding environment in terms of color, texture, and structure makes detection tasks more difficult, presenting a greater challenge compared to general object detection. Qin et al. proposed the BASNet [10], which aims to refine coarse predictions by learning the differences between rough prediction maps and true segmentation results. Simultaneously, Mei et al. introduced a distraction mining strategy that effectively identifies and eliminates the influence of distracting regions [11]. Although the development of deep learning has significantly improved the performance of camouflage object segmentation, there is still room for further improvement. Continuous research and exploration are necessary to enhance the performance of camouflage object segmentation.
In this work, a Robust Localization-Guided Dual-Branch Network is proposed (RLGDBNet). This model is inspired by the process of recognizing camouflaged objects by humankind. This identification process of camouflaged organisms can be summarized into two key steps. Firstly, through naked-eye observation and leveraging personal life experiences and subtle incongruities, humans can roughly identify the approximate location of camouflaged targets. Secondly, starting from this position, humans gradually expand their field of view to observe the surroundings, determining the contours of the camouflaged target, and further refining its edge features. Based on these observation methods, the proposed model in this work aims to simulate and implement these two key steps. Firstly, by designing the localization branch, the model can preliminarily locate camouflaged targets and fuse deep semantic information and shallow geometric information to improve the accuracy of localization. Secondly, the overall refinement branch is designed to progressively diffuse and refine edge information, allowing the model to better reveal the contour features of camouflaged targets. Our primary objective is to address challenges faced by traditional methods, including issues such as blurred edges of camouflaged objects and complex and varied backgrounds. Through the research presented in this paper, we aim to achieve more accurate segmentation of camouflaged objects to enhance the performance of target detection and recognition. We compare the model proposed in this paper with recent typical methods, achieving excellent results on three publicly available datasets. Particularly on COD10K, the largest dataset, our model achieved a Structure-measure of 0.827 and outperformed recent network models on other evaluation metrics as well. Additionally, we conducted ablation experiments to validate the effectiveness of various key components of our network.
In summary, this paper makes the following contributions:
- (1)
- We designed a comprehensive camouflaged object segmentation network that mimics the process of humans recognizing camouflaged targets by performing initial localization and distinguishing details between the background and foreground, enhancing the model’s performance in complex backgrounds.
- (2)
- We designed dual branches to address both initial localization and detailed analysis of the background and foreground. In the localization branch, a robust localization module (RLM) is employed, which introduces Atrous Spatial Pyramid Pooling (ASPP) [12] to jointly explore contextual information and perform multi-scale high-level feature fusion for more accurate localization of camouflaged targets. In the overall refinement branch, an edge refinement module (ERM) is designed to decode from top to bottom, using an improved SPP to remove noise from features and highlight detailed edge information of the target.
- (3)
- We designed an attention-guided head (AG-Head) to guide the predictions in the overall refinement branch, aiding the model in learning and utilizing important features more effectively. Additionally, joint loss functions are designed for training with five predictions from both branches. Comparative experiments on publicly available COS datasets against 13 state-of-the-art models demonstrate that our model exhibits the best overall performance. Furthermore, we conducted ablation experiments to validate the effectiveness of each key component.
2. Related Work
Currently, the field of computer vision primarily focuses on salient object detection (SOD) [13,14,15]. In comparison to these SOD tasks, less attention has been paid to research on visual tasks related to disguised targets, resulting in a research gap. However, research on SOD also influences the development of COS. The camouflage object task requires accurate segmentation of concealed targets, which poses higher challenges and demands stronger perceptual capabilities and robustness. Drawing insights and absorbing the research achievements of SOD can provide valuable inspiration and reference for the advancement of COS. Despite the relatively limited research on disguised targets, through cross-research with other tasks, exploration of the application and extension of general feature representations and target localization methods can be conducted, thereby enhancing the segmentation performance and accuracy of disguised targets.
SOD refers to the detection of salient objects in an image. Salient objects are regions in the image that attract attention and are significantly different from the surrounding environment. In recent years, deep learning has been widely applied in the field of SOD, with many scholars aiming to improve the accuracy of SOD through various methods such as attention mechanisms [16], focusing on object edges [17] and multi-scale or multi-level feature fusion [18,19]. However, unlike the human visual mechanism, there are significant differences between camouflaged objects and salient objects; hence, SOD methods cannot be directly applied to the detection of camouflaged objects.
In images, detecting camouflaged objects is more challenging compared to SOD. The task of camouflaged object segmentation (COS) involves segmenting objects that share similar features (such as color and texture) with the surrounding environment, making it significantly more difficult. In recent years, some scholars have released multiple camouflaged object datasets and introduced deep learning into the COS field, leading to in-depth research and the proposal of many excellent networks. Some core ideas and techniques from SOD algorithms [20,21] can be transferred to COS. For example, employing state-of-the-art object detection algorithms as the foundation module of COS can enhance the detection performance and robustness of camouflaged targets. Fan et al. [22] first released a relatively complete camouflaged object dataset, COD10K, and proposed SINet based on a cascade partial decoder [23]. Some studies [6,24] also focus on extracting the edges around camouflaged objects more accurately. Furthermore, some research adopts a multi-task learning framework, introducing tasks such as object ordering [5] or edge detection [25] to facilitate robust camouflaged object segmentation. Unsupervised camouflaged object segmentation [26,27,28] has also received attention. Due to domain differences between generic objects and camouflaged objects, exploring unsupervised camouflaged object segmentation still requires effort, with its performance showing some gap compared to supervised camouflaged object segmentation. Unlike the aforementioned work, our network focuses more on the initial localization of camouflaged targets to penetrate them more deeply, thereby achieving more accurate results.
3. Methodology
3.1. Overall Introduction
Figure 1 illustrates the overall structure of the Robust Localization-Guided Dual-Branch Network (RLGDBNet). This network is designed to mimic the human observation approach towards camouflaged organisms that seamlessly blend into the natural environment. Both branches use Res2Net-50 [29] as the backbone network for feature extraction, and Res2Net-50 demonstrates excellent performance in tasks such as object detection, semantic segmentation, and SOD. The input images are uniformly resized to three different scales for training, employing a multi-scale training strategy. The images are fed into the backbone network to extract features at different scales, denoted as , collectively referred to as low-level features, before entering the branches. In the localization branch, features extracted are denoted as , with sizes of .
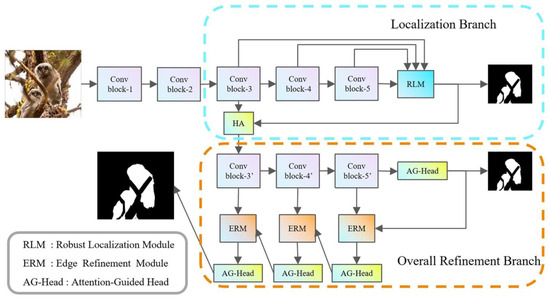
Figure 1.
Overall framework of the proposed method in this paper.
Due to the minimal difference between camouflaged targets and the background, relying solely on shallow feature extraction, such as color and texture information, is insufficient [15,30]. Shallow feature computation is not only computationally intensive but also susceptible to significant noise. Deep feature maps contain more semantic information, and for camouflaged targets, the semantic information from deep feature maps is more effective than the local information from shallow features. However, shallow features should not be disregarded, as , relative to lower-level features and , not only retains edge information but also includes semantic information. In the localization branch, the RLM is employed to partially parallel decode [23] and fuse high-level features, achieving preliminary localization. The output of the localization branch is used as attention to generate more informative and context-aware feature representations for the overall refinement branch.
The overall refinement branch further utilizes Res2Net-50 for feature extraction, and the AG-Head is applied for output prediction in spatial and channel dimensions. The features at each level and high-level features are collectively used as inputs to the ERM. This approach enhances the local features of the shallow network. Inspired by the FM [11], ERM can better segment the edge of the camouflaged target accurately. The ERM requires the use of features at each scale and supports pyramid operations from bottom to top and then top to bottom. This approach enables better integration of pixel information from shallow layers and effectively addresses false positive and false negative interference issues. Detailed introductions to each branch and module will be provided in the following sections.
3.2. Localization Branch
The localization branch of this network is designed to mimic the process of a human preliminarily determining the position of camouflaged targets, serving as a prerequisite for further refining the segmentation of the edges of camouflaged targets. The overall refinement branch relies on localization feature maps to eliminate false positives and false negatives, enhancing the effectiveness of the localization branch crucial to the overall performance of the network. The localization branch decodes and fuses high-level features, and Figure 2 illustrates the structure of the RLM. High-level semantic features can guide the model to more accurately localize the position and boundaries of the target. Additionally, feature contributes to the model’s better understanding of the spatial arrangement of the target. Integrating high-level features enables the model to effectively leverage the advantages of both semantic and geometric information [22,23]. This module abandons the use of low-level high-resolution features to enhance operational speed. By fusing features , , and , the RLM enriches deep abstract semantic information, provides more extensive contextual information, and better understands the position and semantics of the target throughout the entire image. It also retains shallow geometric information, thereby improving the segmentation accuracy for small or complex-shaped targets and effectively suppressing noise in the features.
As depicted in Figure 2, the ASPP module is applied to high-level features , , and . ASPP can capture features within different receptive field ranges, enhancing the model’s perception of object-scale variations. Through experimentation, the final dilation rates are adjusted to {3, 6, 12, 18}.
where is the feature obtained from after ASPP operation, represents the convolution operation, denotes element-wise multiplication, denotes the concatenation operation, refers to the combination of convolution, batch normalization, and ReLU, represents the bilinear upsampling. Specifically, as the network depth increases, the scale of high-level features gradually diminishes, necessitating upsampling and convolution operations on to obtain feature maps with the same spatial dimensions as , followed by element-wise multiplication with . Due to the semantic importance of deep features, needs to be concatenated with the aforementioned result. Through this process, can be obtained, and a similar method is used to obtain . Specifically, element-wise multiplication of with and is performed, followed by concatenation with . It is noteworthy that feeding the concatenated result into CBAM yields . As for the localization prediction map , it is obtained through convolution on . Figure 3 presents the visualization of the output features from RLM.
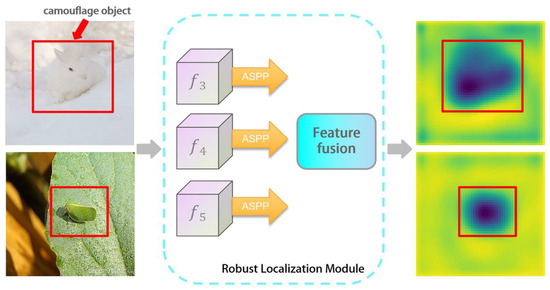
Figure 3.
Output feature visualization of RLM.
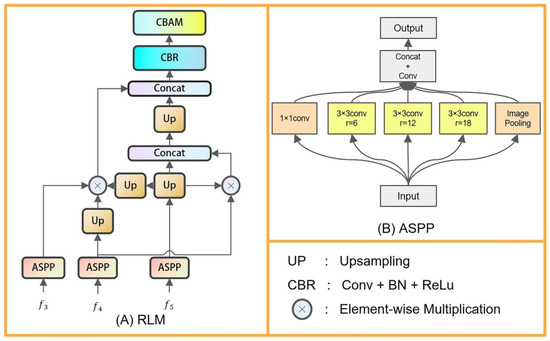
Figure 2.
(A) Overview of the robust localization module and (B) ASPP module.
3.3. Overall Refinement Branch
The localization branch not only outputs the localization prediction map P but also utilizes P as the Holistic Attention (HA) to enhance . After attention enhancement, is integrated into the overall refinement branch, producing a more informative and context-aware feature representation, denoted as . Based on , further feature extraction is performed using Res2Net to obtain and . We introduce an AG-Head as an output head based on the attention mechanism, placed after . As shown in Figure 4, the AG-Head combines channel attention and spatial attention mechanisms, adaptively adjusting the importance of different channels and spatial positions in the feature map. It further enhances the model’s perceptual and feature representation capabilities before generating output prediction maps, thus improving segmentation task accuracy and precision.
where denotes element-wise multiplication, represents the convolution operation of the prediction map with the Gaussian kernel, denotes taking the per-channel maximum values of the convolution result.
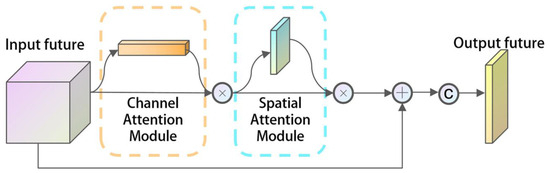
Figure 4.
Attention-guided head.
Subsequently, we employ the ERM, a module that establishes the relationship between region and boundary cues to provide more accurate segmentation of foreground contours and edges. As illustrated in Figure 5, ERM requires features from the previous level, current-level features, and prediction maps as inputs. We feed the feature map m and the prediction map p outputted by AG-Head into ERM, and the output of ERM is then fed back into AG-Head for generating output prediction maps and refined feature maps . The dual output of AG-Head is designed to facilitate the preparation of the refined feature map for the next level of edge refinement, and the upsampled prediction map P serves as input to ERM and contributes to the loss function computation. Due to the significant noise impact on low-level features, an improved Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) module is applied to filter out noisy features. SPP utilizes pooling operations at different scales on different regions of the input feature map, capturing information at various scales to provide a more comprehensive and rich image representation. The filtered features are then inputted into ERM for edge refinement.
ERM performs upsampling on the prediction map from a higher level and uses this upsampled prediction map, along with the inverted version of the prediction map, to perform element-wise multiplication with the feature map from the current level. These two sets of features are then fed in parallel into the context exploration block to identify false positive and false negative interference further. Subsequently, element-wise subtraction and multiplication are applied separately to suppress these interferences, thus eliminating false positives and negatives. The specific formulas are as follows:
where represent the output features of the edge refinement. denotes the combination of convolution, batch normalization (BN), and ReLU. denotes bilinear upsampling. Additionally, and are learnable parameters initialized to 1. To extract background interference information and foreground interference information separately, we first remove noise from through the SPP module. Subsequently, we perform element-wise multiplication between the processed feature and the higher-level prediction map and , respectively. Then, context exploration is conducted using the CE module to better focus on information at different scales in the feature map, resulting in false negative interference and false positive interference . represents the higher-level feature obtained through and upsampling. To reduce false negative interference and false positive interference, we use element-wise subtraction to suppress blurry backgrounds and element-wise addition to enhance missing foregrounds, ultimately yielding . serves as the input to the AG-Head, where attention is applied to to generate the final refined edge features and prediction map in the AG-Head.
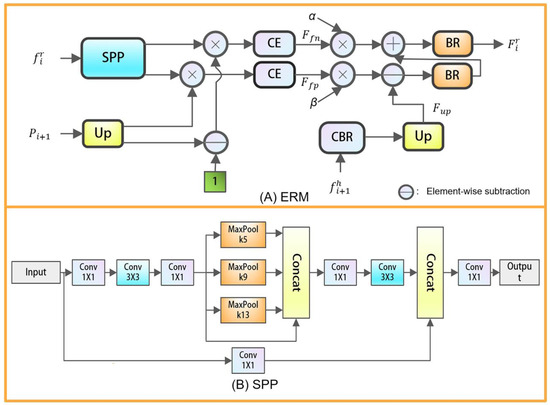
Figure 5.
(A) Edge refinement module and (B) Spatial Pyramid Pooling module.
We designed four predictions in the overall refinement branch. In order to demonstrate the actual effects, we compared the results of these four predictions in Figure 6. It is evident that edge refinement is a gradual process in different environments, and the effect is significant for various types of camouflage targets. As shown in the first row of the figure, fish hidden in the sand have their body surfaces partially covered by sand. Through the computations of the refinement module, the sand on the fish’s body can be effectively distinguished. In the image of a soldier holding a gun in the fourth row, the refinement process of the firearm clearly demonstrates a highly noticeable effect on edge refinement.
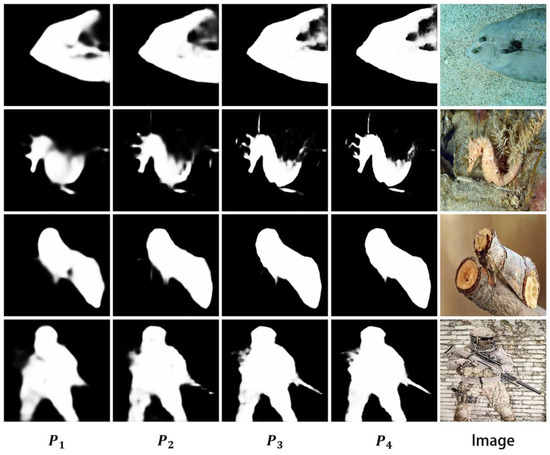
Figure 6.
Comparison of the four prediction results in the overall refinement branch.
3.4. Loss Function
Commonly used loss functions for semantic segmentation include Dice loss [31], IoU loss, cross-entropy loss, and others. In our model, there are multiple predictions, namely, the predictions from the localization branch and the overall refinement branch, resulting in a total of 5 output prediction maps. Each prediction is trained independently with separate parameters. Since each module has different objectives, the localization branch focuses less on edge details, and thus, the cross-entropy loss and IoU loss are sufficient for accurate foreground localization. Therefore, for the RLM, the loss function is defined as follows:
For predictions of the overall refinement branch, a combination of weighted binary cross-entropy loss, weighted IoU loss, and uncertainty-aware loss (UAL) are employed to supervise the model. The weighted cross-entropy loss assigns higher weights to hard pixels. Similarly, the weighted IoU loss focuses more on hard pixels than uniformly distributing weights, emphasizing foreground edge pixels more, as demonstrated by its effectiveness [32]. In addition, uncertainty-aware loss (UAL) [33] is introduced due to the minimal differences between the camouflaged target and the background, making accurate target localization and segmentation challenging. To reduce prediction uncertainty and enhance the model’s decision confidence, UAL is incorporated. By applying the sigmoid function, the pixel values during prediction are constrained to the range of , where values close to 0 represent the background and values close to 1 represent the foreground, with values around 0.5 indicating uncertainty. Pixels with values close to 0.5 represent high uncertainty, and to address these challenging samples, the blurriness is used as an additional loss for these problematic samples. The direct approach is to assign the highest loss to pixels with a prediction value of 0.5 and the lowest loss to values of 0 and 1, given by , where represents the pixel value.
The loss function used for the predictions in the refinement module is defined as follows:
where λ is the balance coefficient, an incremental cosine strategy is adopted to adjust its value during training.
The overall loss function is defined as follows, considering that the edges of camouflage targets provide more valuable information for segmentation and should receive more attention:
4. Experiments
4.1. Experiment Setup
Dataset: We conducted experiments on three COS datasets, namely, CAMO [4], CHAMELEON [34], and COD10K [22]. These datasets are specifically designed for camouflaged object segmentation tasks. CAMO comprises 8 categories with a total of 1250 images, including 1000 images for training and 250 for testing. Each CAMO image contains at least one camouflaged object, which exhibits variable shapes and appearances within complex scenes. CHAMELEON consists of 76 high-resolution images of camouflaged targets, where animals blend into natural environments through skin color or body shape. COD10K is currently the largest benchmark dataset for camouflage, consisting of 5066 images, with 3040 used for training and 2026 for testing. The dataset includes both natural and artificial camouflaged images, covering 10 super-classes and 78 sub-classes. Our training set consists of the training sets of COD10K and CAMO, totaling 4040 images with a combined size of 1.01 GB. Other datasets are used as the test set, as shown specifically in Figure 7.

Figure 7.
Dataset visualization.
4.2. Evaluation Criteria
The following metrics were used to evaluate our proposed method in this study:
- Structure-measure: It includes region-aware structural similarity measure and object-aware structural similarity measure .
- 2.
- The Mean Absolute Error (MAE) is a widely used metric for evaluating image segmentation results. It measures the average absolute difference between predicted values and ground truth.
- 3.
- The weighted F-measure is a comprehensive evaluation metric based on precision and recall [36].
- 4.
- The adaptive E-measure () considers both pixel-level matching and image-level statistics to accurately evaluate the overall and local accuracy of the segmentation results [37]. Pixel-level matching involves comparing and matching the pixel values between the algorithm’s segmentation result and the ground truth segmentation result to determine their differences. On the other hand, image-level statistics involve analyzing and summarizing features such as pixel regions, shapes, and positions in the segmentation result to obtain a more comprehensive and detailed evaluation. The adaptive E-measure combines information from both aspects, enabling a more accurate assessment of the algorithm’s precision and performance, and providing strong support for the improvement and optimization of image segmentation algorithms. The adaptive E-measure is an effective tool for evaluating image segmentation techniques in practical applications, including medical image segmentation, scene understanding, and object detection. By incorporating pixel-level and image-level information, it provides a comprehensive and accurate evaluation that aligns with human perception and judgment. This contributes to the advancement and refinement of image segmentation techniques, benefiting various computer vision tasks.
4.3. Implementation Details
The proposed model in this paper is implemented using the PyTorch framework. The training and testing are performed on an NVIDIA Tesla V100S-PCIE-32GB GPU. The parameters of the backbone network are initialized with a pre-trained Res2Net-50 model on the ImageNet dataset, while the remaining parameters are initialized with PyTorch’s default settings. During training, the input image sizes were adjusted to 264 × 264, 352 × 352 and 440 × 440, respectively. Data augmentation is applied using random horizontal flipping. The batch size is set to 16. The optimization uses the stochastic gradient descent (SGD) optimizer with a weight decay of 5e-4 and a momentum of 0.9. The initial learning rate is set to 1 × 10−3 and is adjusted using the poly learning rate policy with a decay factor of 0.9. The model is trained for a total of 65 epochs.
4.4. Experimental Results and Comparisons
This study explores emerging techniques in the field of camouflage object segmentation. To demonstrate the effectiveness of our proposed method, we compared it with several recent state-of-the-art approaches, including FPN [21] (a deep learning architecture for object detection and semantic segmentation), NLDF [30] (a complex image processing method), PraNet [38] (a medical image segmentation method), PiCANet [39], BASNet [10], CPD [23] (methods for SOD), SINet [22], PFNet [11], SINet-V2 [40], C2FNet [41], ZoomNet [33], SegMaR (S-1) [42], and FLCNet [43] (methods for natural camouflage object segmentation). To ensure fairness and comparability of the prediction results, we obtained the predicted maps through two methods: first, by acquiring them from publicly available sources on the internet, and second, by running retrained models using open-source code. For the predicted maps obtained from public sources, we ensured their reliability and availability. These maps were directly downloaded from the websites where the respective method’s researchers or teams have made them publicly accessible. The second method involved retraining the models using the official open-source code with the same settings and parameters. This ensured we used the same code and training methodology, making the predicted maps directly comparable. Additionally, all predicted maps were evaluated using the same code. By following this approach, we ensured the reliability and effectiveness of our research.
The experimental results of our proposed method and eight other methods are shown in Table 1. The results demonstrate that our method consistently outperforms the other detection models regarding all four evaluation metrics across different datasets. Our method exhibits superior performance across various evaluation metrics compared to other detection models. For instance, when compared to C2FNet on the CHAMELEON-Test, COD10K-Test, and CAMO-Test datasets, our method shows an improvement of 1.3%, 1.4%, and 2.4% in , respectively. Additionally, it can be observed that our method performs similarly to SINet-V2 on the CAMO-Test dataset but exhibits improved metrics on the CHAMELEON-Test and COD10K-Test. As indicated in Table 2, in terms of testing speed, we employed the hardware configuration mentioned in Section 4.3 for experimentation. During testing, we achieved a frame rate of 28.2 FPS, indicating an overall relatively favorable performance.

Table 1.
Experimental results of the proposed method and other 13 methods.

Table 2.
Comparison of testing speed and FLOPS.
We compared the performance of our model with other methods on the CHAMELEON, CAMO, and COD10K datasets, and the PR curve is shown in Figure 8. The higher the curve, the better the performance of the model, and our method has better performance than other methods.
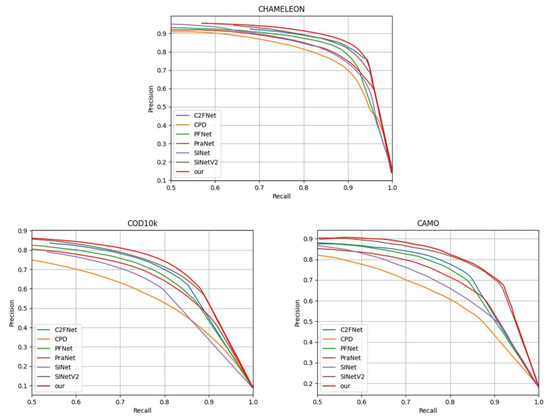
Figure 8.
PR curves of the proposed method and other six methods on the CHAMELEON, CAMO, and COD10K datasets.
The visual comparison of our proposed model with different-sized camouflage objects is presented in Figure 9. The visual comparison shows that our method excels at segmenting objects in various complex environments. Our predicted results exhibit more evident, more complete object regions, and more distinct boundaries. This indicates that our method accurately locates and segments the objects. In the last row of Figure 9, our model demonstrates superior recognition results for multiple objects. Our model accurately segments all five cicadas and performs more precisely regarding edge details. In contrast, other methods struggle to achieve satisfactory recognition results for the cicada in the top-right corner.
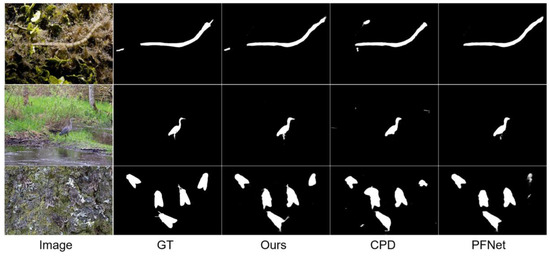
Figure 9.
Visual comparison with different methods.
4.5. Ablation Experiments
To validate the effectiveness of the key components within our network, this section conducts a detailed ablation experiment analysis. All experiments in this section utilize the evaluation metrics from Section 4.2 to assess the model’s performance, with bold font in the tables indicating the optimal results.
Localization Branch. Recognizing the crucial role of rich semantic information in high-level features for capturing internal details of camouflaged targets, we introduced the RLM. Specifically, we enhanced these high-level features by introducing the ASPP module to cover different scales of receptive fields, followed by partial decoding. This approach allows the model to gather contextual information from local to global on relatively small-sized feature maps, thereby improving the model’s recognition capability for objects of different scales. Such an extension further enhances the model’s expressive power and perception range. Through this strategy, we can globally and multi-scale analyze the features extracted by Res2Net, extracting more discriminative features. Our objective is to further enhance the model’s recognition capability for camouflaged targets.
To validate the effectiveness of RLM, as shown in Table 3, we conducted relevant experiments on the COD10K-text dataset. The high-level features used by the partial decoders were ,, and . Different scales of ASPP were applied to these high-level features, with the selected scales being {3, 6, 12, 18}. Due to the numerous scale choices for ASPP, only the experiment data based on this selected scale is presented in the table. In the table, BA, PD1, PD2, and PD3 represent the baseline model, the partial decoder on , the partial decoder on , and the partial decoder on , respectively. Experimental results demonstrate that BASIC + PD2 + ASPP yields the best performance.

Table 3.
Relevant experiments of the localization branch on the COD10K-text dataset.
Overall Refinement Branch. In this branch, we drew inspiration from the structure of Feature Pyramid Network (FPN) and further refined and improved it using the ERM. Through this module, we can fuse feature maps from different levels from top to bottom, generating a multi-scale feature representation. This feature fusion method contributes to providing richer multi-scale information, enhancing the detection capability for small targets by merging low-level and high-level features. Simultaneously, we preserved the spatial dimension during the feature fusion process, aiding in accurate target localization and boundary detection. Additionally, we introduced lateral connections to facilitate information exchange between high-level and low-level features. This cross-level feature transfer not only assists in extracting semantic information from low-level features but also captures retained high-level semantic information, further boosting the performance of our model. Through ablation experiments, we obtained satisfactory results. Detailed experimental results are shown in Table 4, where specific experiments include the use of ERM on different layers, improvement of ERM by adding the Spatial Pyramid Pooling (SPP) module for denoising features fi. In Table 4, 2 × ERM, 3 × ERM, and ERM-I respectively represent using ERM on , using ERM on , and incorporating SPP into ERM.

Table 4.
Relevant experiments of ELM on the COD10K-text dataset.
5. Conclusions
In this study, we proposed a comprehensive camouflage target segmentation network aimed at improving segmentation performance in complex backgrounds. The RLM was employed in the localization branch to expand the receptive fields of each high-level feature, followed by the fusion of three different scales of high-level features. The localization predictions guided the overall refinement branch. The localization predictions, serving as coarse predictions with numerous false positives and negatives, were refined by the overall refinement branch from top to bottom. The branch effectively identified and eliminated these erroneous pixels, incorporating the AG-Head to enhance attention mechanisms and further refine edge features.
We compared our model with recent typical methods in this paper and achieved excellent performance on three commonly used public datasets. Particularly, on the largest-scale COD10K dataset, our model achieved a Structure-measure of 0.827, outperforming recent network models on other evaluation metrics as well.
Our future research is inspired by recent articles, such as MRR-Net [44], which emphasizes the role of different receptive fields. We consider incorporating more diverse receptive fields in the overall refinement branch to better prepare for matching candidate regions. Drawing from the methodology of SegMaR [42], we can establish appropriate amplification mechanisms and employ multiple iterations to further enhance accuracy. Regarding camouflaged objects, we not only utilize binary ground truth data but also introduce additional training information, such as ranking information and relevant masks [45]. Large Language Models (LLMs) and Visual Language Models (VLMs) [46,47] can provide rich semantic information to models, including object names, context, and more. By integrating this information, we can gain a deeper understanding of the model’s decision-making process and interpret the model’s understanding and reasoning about scenes, thereby endowing our model with stronger semantic scene understanding capabilities. Our study provides new ideas and methods for the field of disguised target segmentation, aiming to advance its development and application.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, Y.L. and C.W.; methodology, Y.L.; software, Y.L. and G.W.; validation and formal analysis, Y.L., X.H. and C.W.; resources and data curation, Y.L. and X.S.; writing—original draft preparation, Y.L.; writing—review and editing, C.W. and X.S.; project administration, Y.L. and X.S.; funding acquisition, X.S. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The research was supported by the Key Science and Technology Innovation Programs in Shandong Province (No. 2017CXGC0919) and the Shandong Province Key Research and Development Plan (No. 2016GSF201197).
Data Availability Statement
The dataset used in this study is available on demand.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Stevens, M.; Merilaita, S. Animal camouflage: Current issues and new perspectives. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. Ser. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 423–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perez-de la Fuente, R.; Delclos, X.; Penalver, E.; Speranza, M.; Wierzchos, J.; Ascaso, C.; Engel, M.S. Early evolution and ecology of camouflage in insects. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 21414–21419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, D.-P.; Zhou, T.; Ji, G.-P.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, G.; Fu, H.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Inf-Net: Automatic COVID-19 Lung Infection Segmentation From CT Images. IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2020, 39, 2626–2637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trung-Nghia, L.; Nguyen, T.V.; Nie, Z.; Minh-Triet, T.; Sugimoto, A. Anabranch network for camouflaged object segmentation. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2019, 184, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, A.; Liu, B.; Barnes, N.; Fan, D.-P. Simultaneously Localize, Segment and Rank the Camouflaged Objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 11586–11596. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, Q.; Li, X.; Yang, F.; Chen, C.; Cheng, H.; Fan, D.-P. Mutual Graph Learning for Camouflaged Object Detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 12992–13002. [Google Scholar]
- Tankus, A.; Yeshurun, Y. Convexity-Based Visual Camouflage Breaking. Comput. Vis. Image Underst. 2001, 82, 208–237. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhajantri, N.U.; Nagabhushan, P. Camouflage defect identification: A novel approach. In Proceedings of the 9th International Conference on Information Technology (ICIT’06), Bhubaneswar, India, 18–21 December 2006; pp. 145–148. [Google Scholar]
- Song, L.; Geng, W. A new camouflage texture evaluation method based on WSSIM and nature image features. In Proceedings of the 2010 International Conference on Multimedia Technology, Ningbo, China, 29–31 October 2010; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Qin, X.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, C.; Gao, C.; Dehghan, M.; Jagersand, M. Basnet: Boundary-aware salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 7479–7489. [Google Scholar]
- Mei, H.Y.; Ji, G.P.; Wei, Z.Q.; Yang, X.; Wei, X.P.; Fan, D.P. Camouflaged Object Segmentation with Distraction Mining. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Nashville, TN, USA, 19–25 June 2021; pp. 8768–8777. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, L.-C.; Papandreou, G.; Kokkinos, I.; Murphy, K.; Yuille, A.L. DeepLab: Semantic Image Segmentation with Deep Convolutional Nets, Atrous Convolution, and Fully Connected CRFs. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2017, 40, 834–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.Y.; Tai, Y.W.; Kim, J.M. Deep Saliency with Encoded Low level Distance Map and High Level Features. In Proceedings of the 2016 IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition (CVPR), Seattle, WA, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 660–668. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.P.; Cheng, M.M.; Liu, J.J.; Gao, S.H.; Hou, Q.B.; Borji, A. Salient Objects in Clutter: Bringing Salient Object Detection to the Foreground. In Proceedings of the 15th European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 196–212. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, P.; Wang, D.; Lu, H.; Wang, H.; Ruan, X. Amulet: Aggregating Multi-level Convolutional Features for Salient Object Detectionn. In Proceedings of the 16th IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 202–211. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, H.; Li, Y. Three-stream attention-aware network for RGB-D salient object detection. IEEE Trans. Image Process. 2019, 28, 2825–2835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wan, B.; Zhou, X.; Zheng, B.; Yin, H.; Zhu, Z.; Wang, H.; Sun, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yan, C. LFRNet: Localizing, Focus, and Refinement Network for Salient Object Detection of Surface Defects. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2023, 72, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Multi-scale interactive network for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 9413–9422. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Z.; Xu, Q.; Cong, R.; Huang, Q. Global context-aware progressive aggregation network for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York City, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 10599–10606. [Google Scholar]
- Uijlings, J.R.R.; van de Sande, K.E.A.; Gevers, T.; Smeulders, A.W.M. Selective Search for Object Recognition. Int. J. Comput. Vis. 2013, 104, 154–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, T.-Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.-P.; Ji, G.-P.; Sun, G.; Cheng, M.-M.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 13–19 June 2020; pp. 2777–2787. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, Z.; Su, L.; Huang, Q. Cascaded partial decoder for fast and accurate salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 3907–3916. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Zhang, J.; Barnes, N. Confidence-aware learning for camouflaged object detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2106.11641. [Google Scholar]
- Ji, G.-P.; Zhu, L.; Zhuge, M.; Fu, K. Fast Camouflaged Object Detection via Edge-based Reversible Re-calibration Network. Pattern Recognit. 2022, 123, 108414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Wu, C. Unsupervised camouflaged object segmentation as domain adaptation. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Paris, France, 2–3 October 2023; pp. 4334–4344. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, G.; Albanie, S.; Xie, W. Unsupervised salient object detection with spectral cluster voting. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 3971–3980. [Google Scholar]
- Siméoni, O.; Sekkat, C.; Puy, G.; Vobecký, A.; Zablocki, É.; Pérez, P. Unsupervised object localization: Observing the background to discover objects. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Vancouver, BC, Canada, 17–24 June 2023; pp. 3176–3186. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, S.-H.; Cheng, M.-M.; Zhao, K.; Zhang, X.-Y.; Yang, M.-H.; Torr, P. Res2Net: A New Multi-Scale Backbone Architecture. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 43, 652–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Mishra, A.; Achkar, A.; Eichel, J.; Li, S.; Jodoin, P.-M. Non-local deep features for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 6609–6617. [Google Scholar]
- Milletari, F.; Navab, N.; Ahmadi, S.-A. V-net: Fully convolutional neural networks for volumetric medical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the 2016 Fourth International Conference on 3D Vision (3DV), Stanford, CA, USA, 25–28 October 2016; pp. 565–571. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, J.; Wang, S.; Huang, Q. F3Net: Fusion, feedback and focus for salient object detection. In Proceedings of the AAAI Conference on Artificial Intelligence, New York, NY, USA, 7–12 February 2020; pp. 12321–12328. [Google Scholar]
- Pang, Y.; Zhao, X.; Xiang, T.-Z.; Zhang, L.; Lu, H. Zoom in and out: A mixed-scale triplet network for camouflaged object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 2160–2170. [Google Scholar]
- Skurowski, P.; Abdulameer, H.; Błaszczyk, J.; Depta, T.; Kornacki, A.; Kozieł, P. Animal Camouflage Analysis: Chameleon Database; Politechniki Śląskiej: Gliwice, Poland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.-P.; Cheng, M.-M.; Liu, Y.; Li, T.; Borji, A. Structure-measure: A new way to evaluate foreground maps. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Venice, Italy, 22–29 October 2017; pp. 4548–4557. [Google Scholar]
- Margolin, R.; Zelnik-Manor, L.; Tal, A. How to evaluate foreground maps? In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Columbus, OH, USA, 23–28 June 2014; pp. 248–255. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.-P.; Gong, C.; Cao, Y.; Ren, B.; Cheng, M.-M.; Borji, A. Enhanced-alignment measure for binary foreground map evaluation. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1805.10421. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.-P.; Ji, G.-P.; Zhou, T.; Chen, G.; Fu, H.; Shen, J.; Shao, L. Pranet: Parallel reverse attention network for polyp segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Lima, Peru, 4–8 October 2020; pp. 263–273. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, N.; Han, J.; Yang, M.-H. Picanet: Learning pixel-wise contextual attention for saliency detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 3089–3098. [Google Scholar]
- Fan, D.-P.; Ji, G.-P.; Cheng, M.-M.; Shao, L. Concealed object detection. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2021, 44, 6024–6042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Chen, G.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, N. Context-aware cross-level fusion network for camouflaged object detection. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2105.12555. [Google Scholar]
- Jia, Q.; Yao, S.; Liu, Y.; Fan, X.; Liu, R.; Luo, Z. Segment, magnify and reiterate: Detecting camouflaged objects the hard way. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, New Orleans, LA, USA, 18–24 June 2022; pp. 4713–4722. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Wang, R. Camouflaged Object Detection with a Feature Lateral Connection Network. Electronics 2023, 12, 2570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, X.; Sun, M.; Han, Y.; Wang, Z.J.I.T.o.N.N.; Systems, L. Camouflaged object segmentation based on matching–recognition–refinement network. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2023, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lv, Y.; Zhang, J.; Dai, Y.; Li, A.; Barnes, N.; Fan, D.-P. Toward Deeper Understanding of Camouflaged Object Detection. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Video Technol. 2023, 33, 3462–3476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Curtò, J.; de Zarzà, I.; Calafate, C.T. Semantic scene understanding with large language models on unmanned aerial vehicles. Drones 2023, 7, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Li, D.; Savarese, S.; Hoi, S. Blip-2: Bootstrapping language-image pre-training with frozen image encoders and large language models. arXiv 2023, arXiv:2301.12597. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).