TDOA-AOA Localization Algorithm for 5G Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces
Abstract
1. Introduction
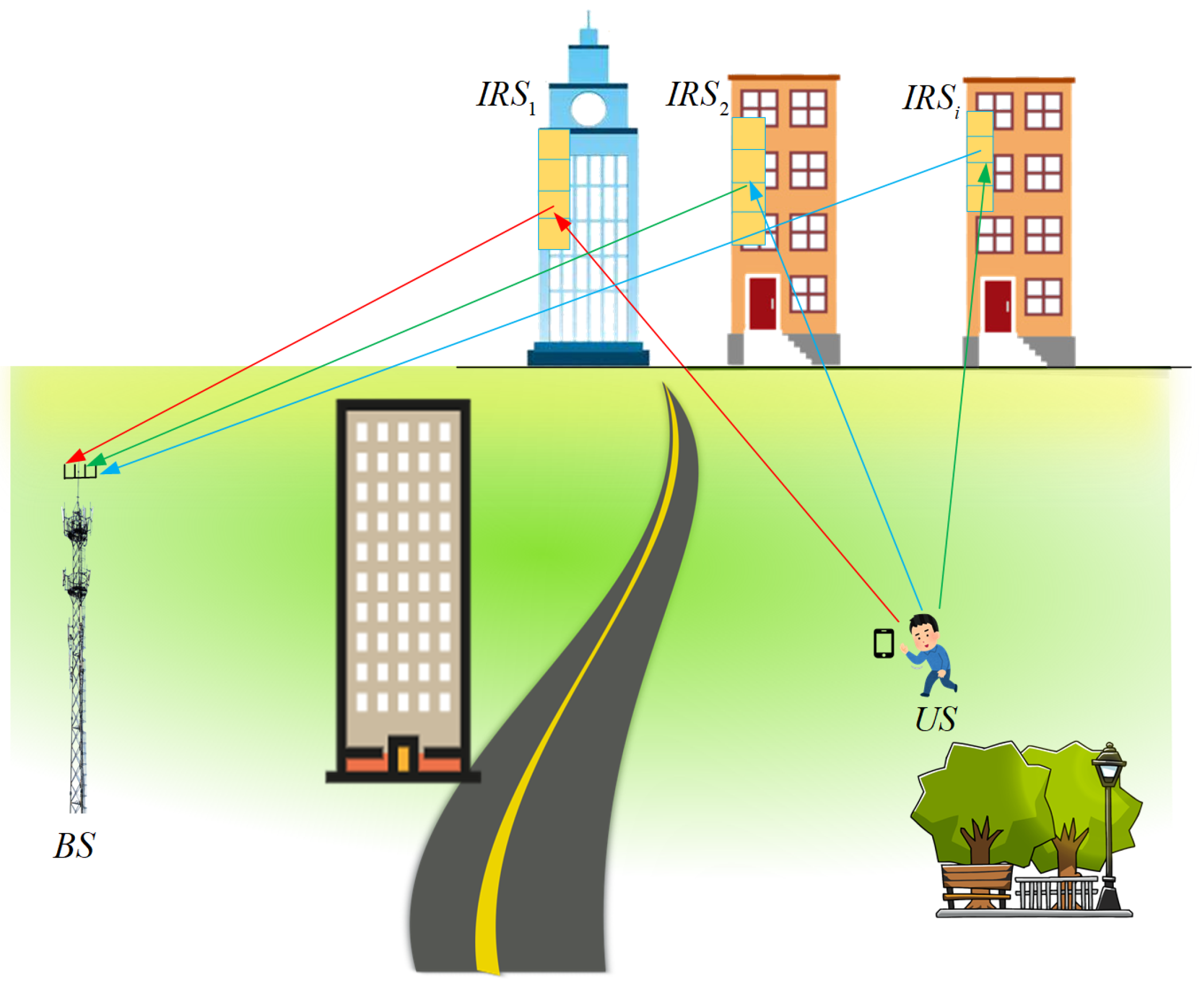
- We developed a 5G IRS localization (GIL) system model, consisting of a BS, multiple IRSs, and a user to be located (US). In GIL, the BS and the US do not have a LOS link, and signals can only be reflected via IRSs to the BS, effectively overcoming issues with poor positioning in the NLOS link.
- We propose an IRS NLOS TDOA-AOA localization (INTAL) algorithm. By combining the MUSIC and Chan algorithms, this method estimates the three-dimensional positions of US. It formulates an optimization problem that minimizes the distance between each estimated coordinate and the actual coordinate.
- A tent–snake optimization (tent–SO) algorithm is used to solve the optimization problem. Initially, tent chaos mapping is introduced to distribute the initial positions of the population uniformly, addressing the issue of local optima; subsequently, an improved dimensional strategy selection is used to overcome the stagnation of individual positions in the later stages of iterations; finally, improved mating selection is used to prevent premature convergence and balance the exploration and exploitation capabilities of the algorithm, helping to reduce goodness of fit.
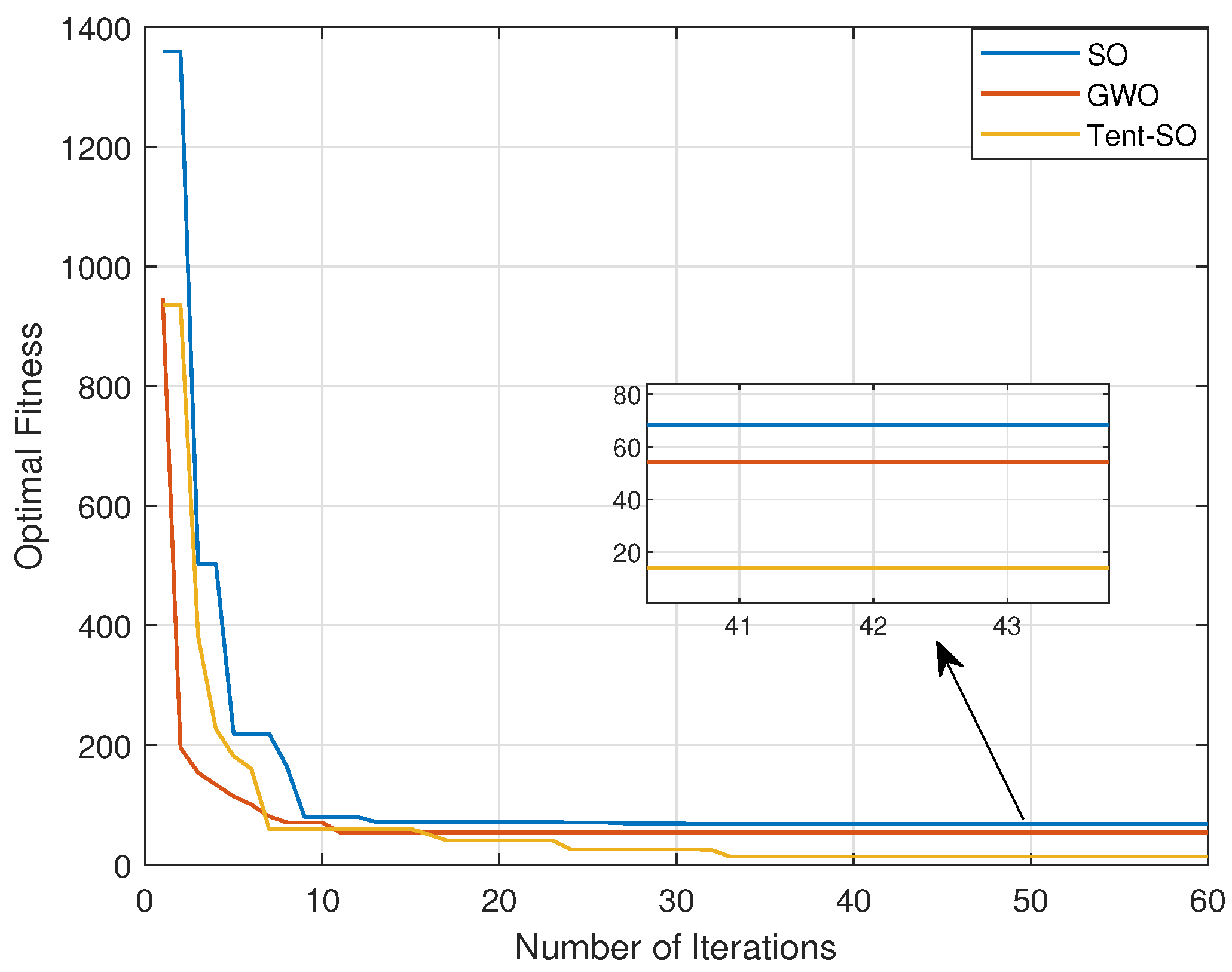
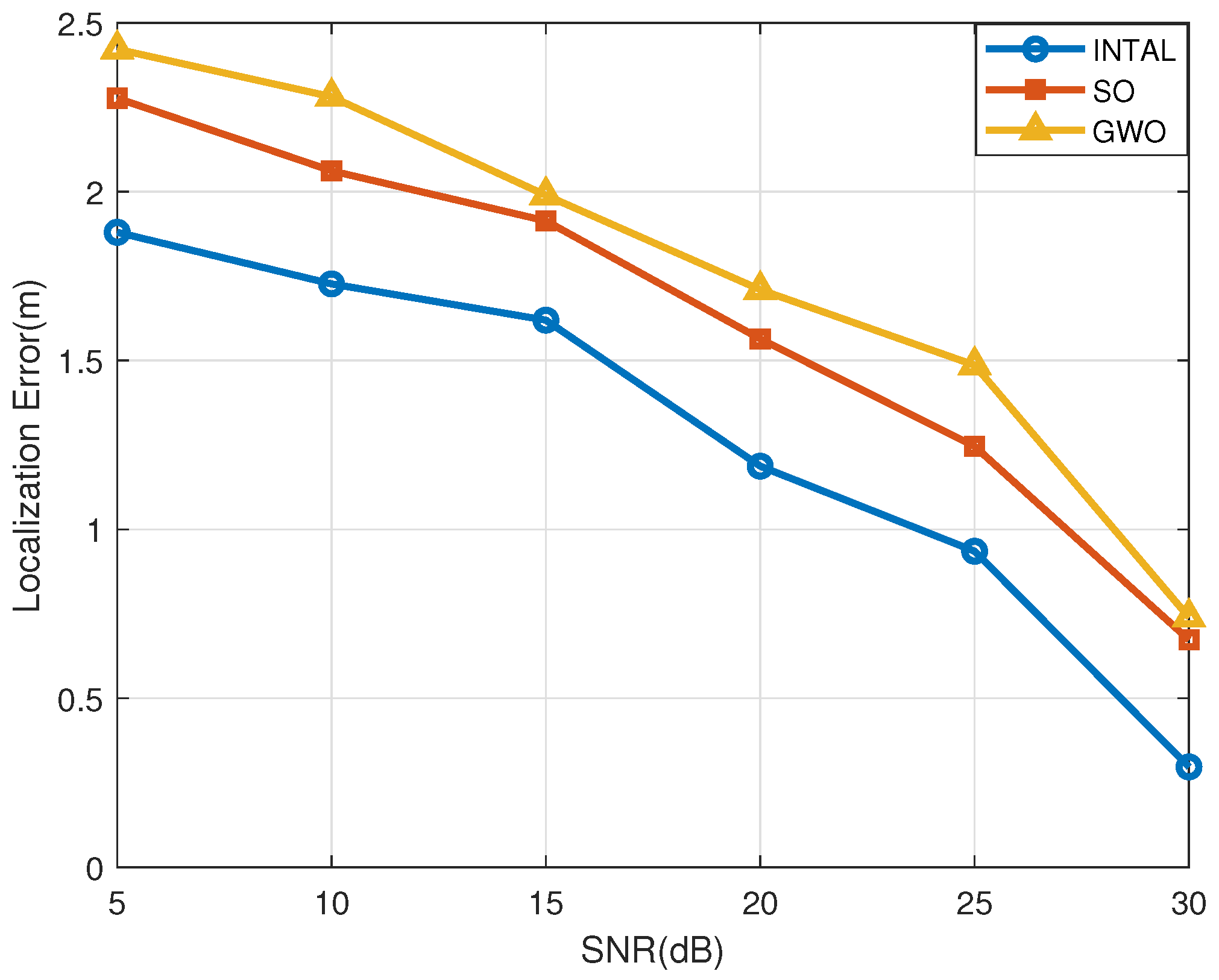
- In the simulation section, it can be seen that the INTAL algorithm has superior performance to both SO and gray wolf optimization (GWO) algorithms and reduces the localization error by 56% and 60% on average, respectively, under the same conditions.
2. System Model
3. INTAL Algorithm
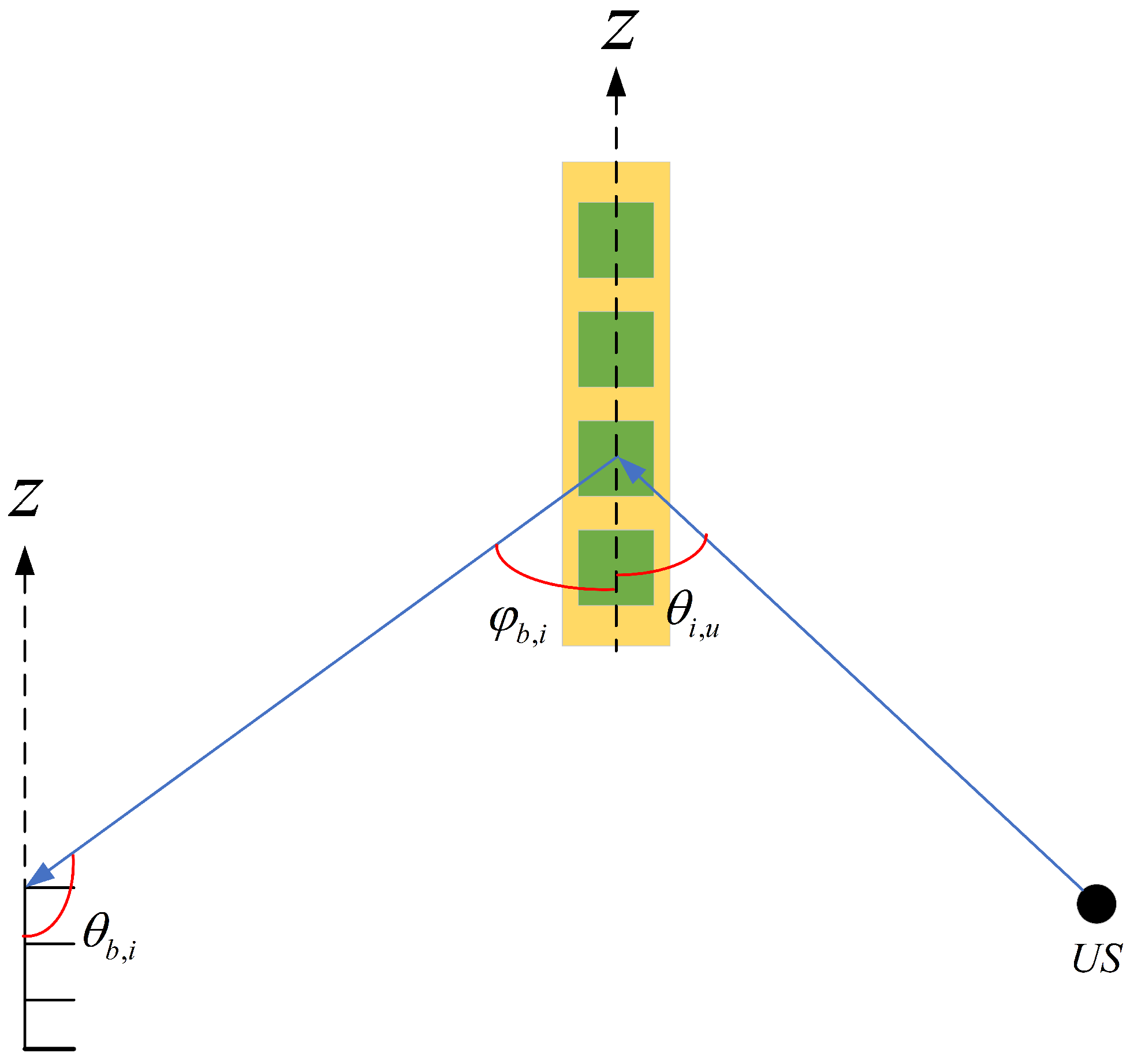
3.1. Angle and Delay Estimation
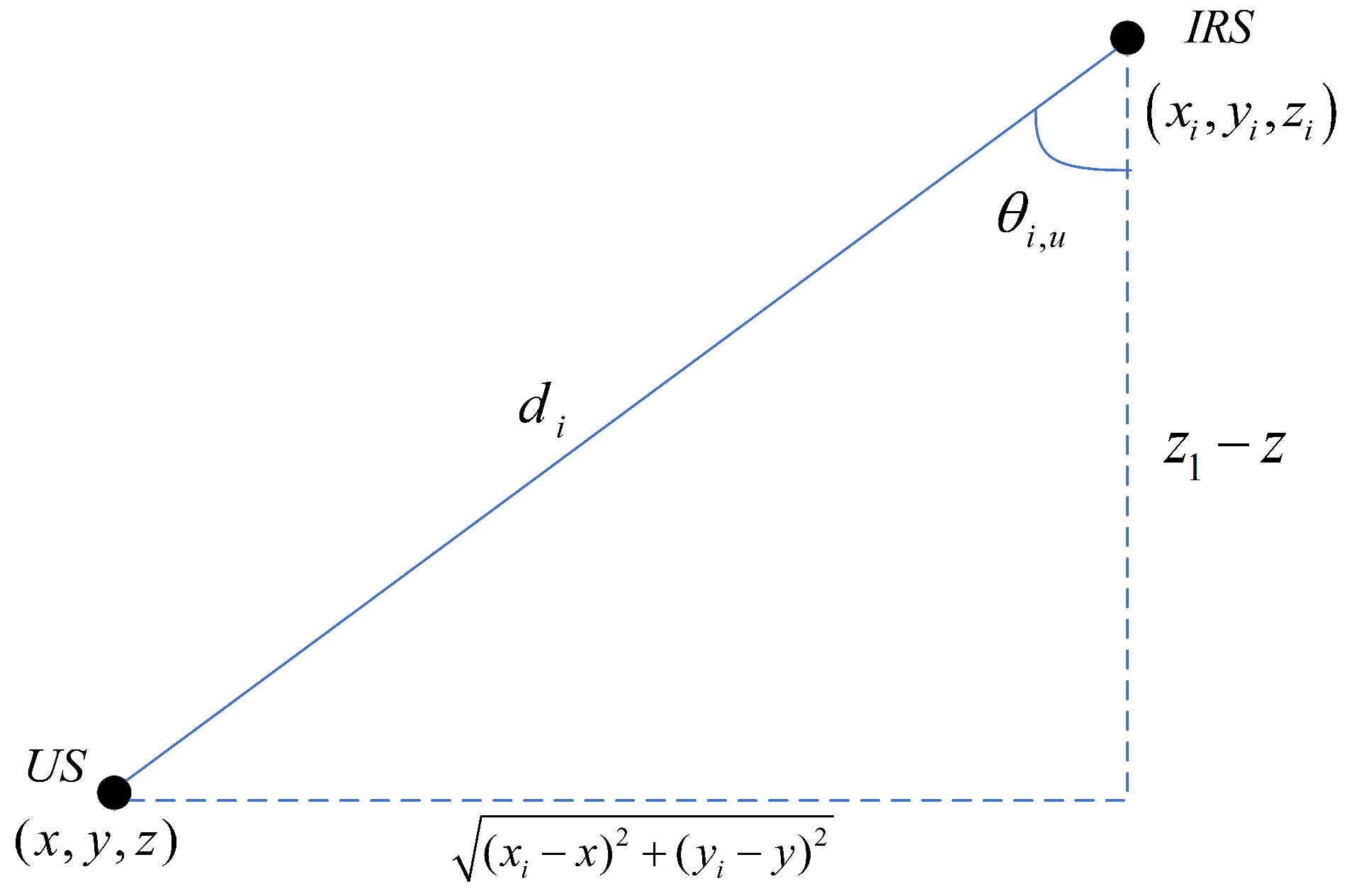
3.2. Calculation of US-Estimated Coordinates
3.3. Tent–Snake Optimization
3.3.1. Initial Population Position
3.3.2. Exploration Phase
3.3.3. Development Phase
- (1)
- Foraging ()
- (2)
- Enter Combat or Mating Mode ()
| Algorithm 1 INTAL algorithm |
|
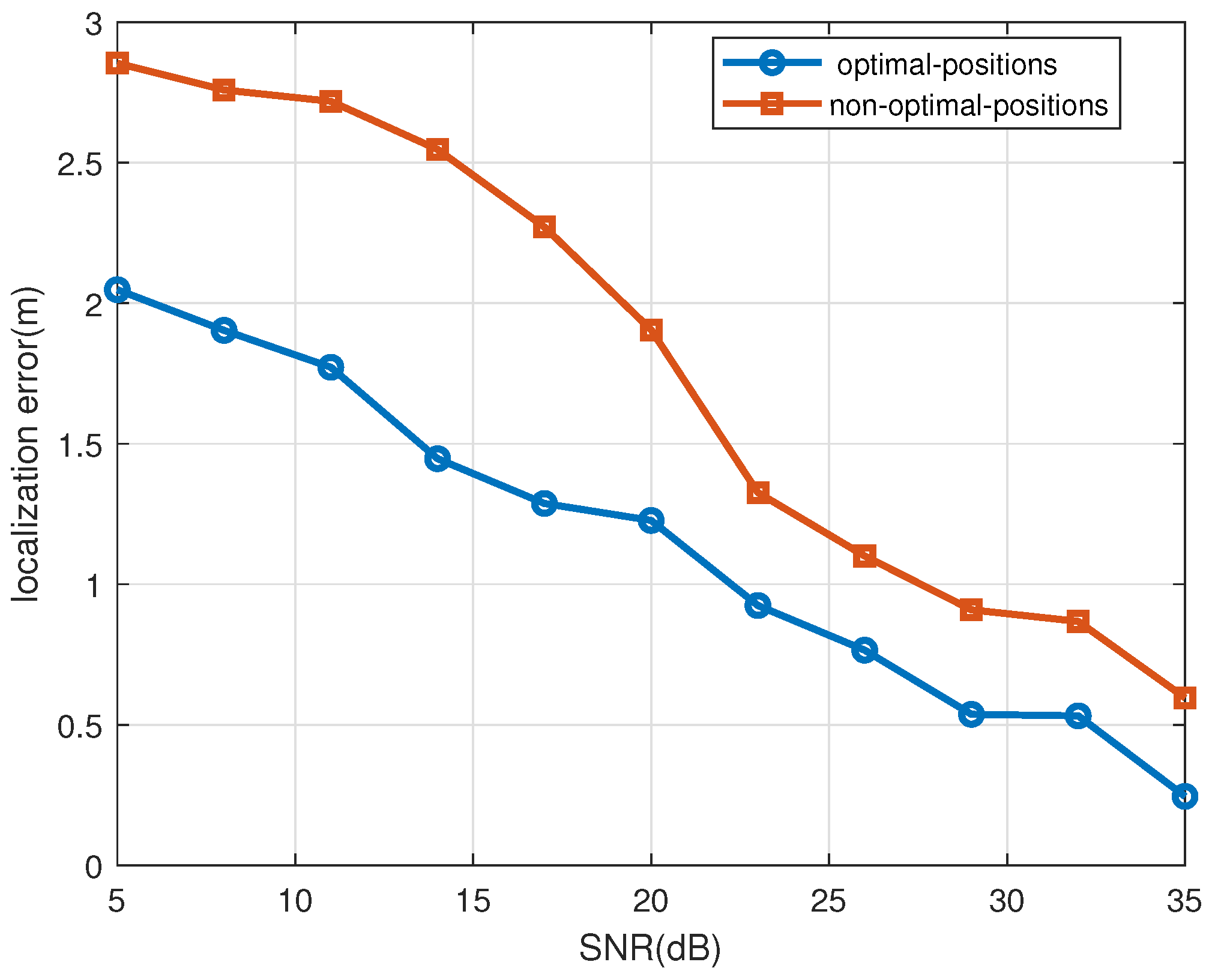
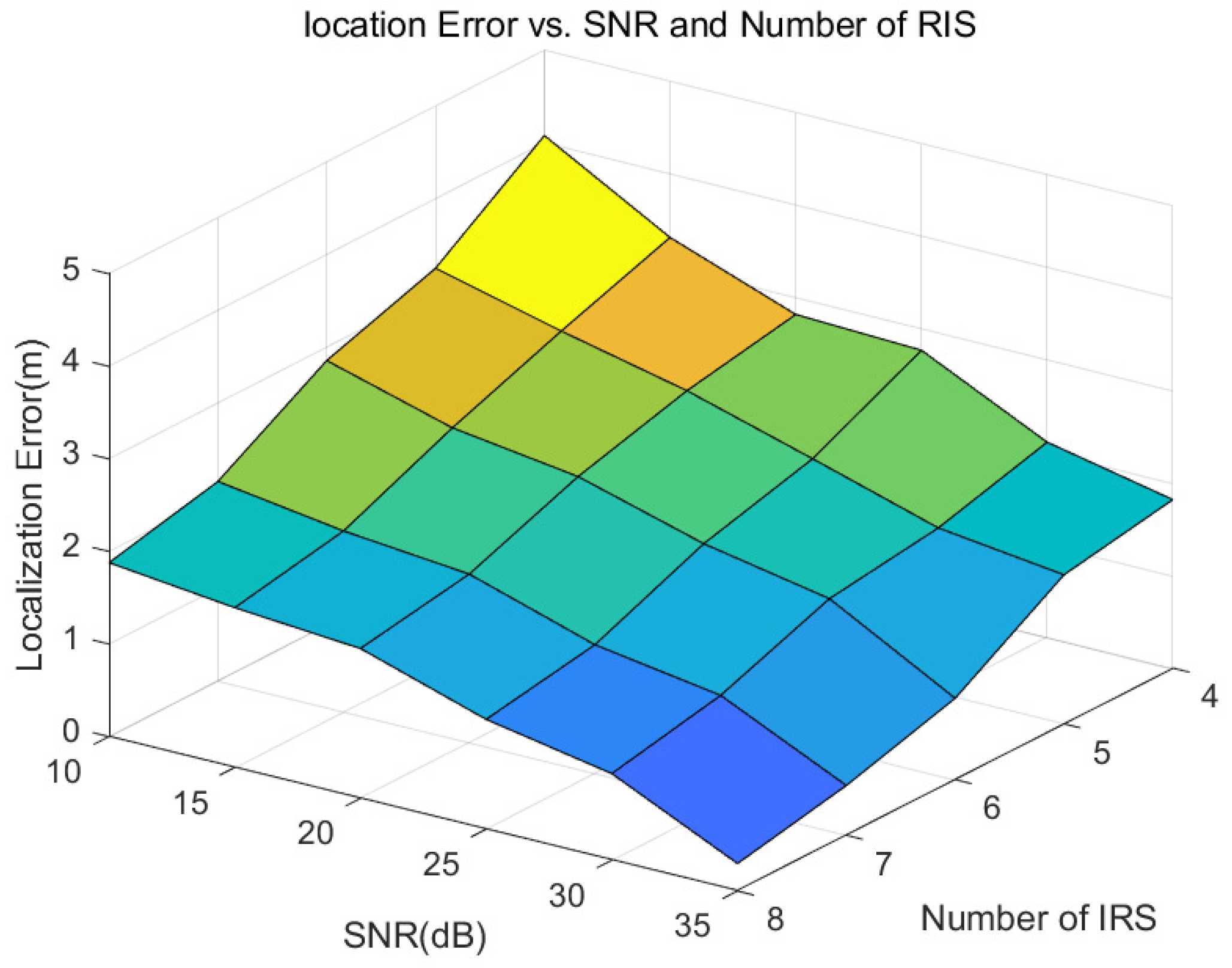
4. Simulation Results and Analysis
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Huang, Y.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J. From Terahertz Imaging to Terahertz Wireless Communications. Engineering 2023, 22, 106–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, S.; Ho, C.K.; Zhang, R. Wireless powered communication: Opportunities and challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2015, 53, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, J.; Zhao, M.; Yao, G. PSOSVRPos: WiFi indoor positioning using SVR optimized by PSO. Expert Syst. Appl. 2023, 222, 119–778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, H.; Wang, X.; Lin, X. Placing wireless chargers with limited mobility. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2021, 22, 3589–3603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Li, Z.; Hu, J. OTFS enabled LEO satellite communications: A promising solution to severe doppler effects. IEEE Netw. 2024, 38, 203–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Chen, R.; Cai, C. An onboard magnetic integration-based WPT system for UAV misalignment-tolerant charging with constant current output. IEEE Trans. Transp. Electrif. 2022, 9, 1973–1984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhang, Z.; Peng, Z. Energy minimization in RIS-assisted UAV-enabled wireless power transfer systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 10, 5794–5809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, Z.; Wu, M.; Zhao, C. Free-rotation wireless power transfer system based on composite anti-misalignment method for AUVs. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2023, 38, 4262–4266. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, S.; Yi, J.; Wan, X. Illuminator of opportunity localization for digital broadcast-based passive radar in moving platforms. IEEE Trans. Aerosp. Electron. Syst. 2022, 59, 3539–3549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Yan, T.; Sun, W. Polynomial fitting and interpolation method in tdoa estimation of sensors network. IEEE Sens. J. 2023, 23, 3837–3847. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, C.; AlSubki, L.; Yamaya, A. Poor ovarian response in assisted reproductive technology cycles is associated with anti-ovarian antibody and pro-inflammatory immune responses. J. Reprod. Immunol. 2023, 160, 104–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hassanin, O.; Wang, X.; Wu, X. Efficiency performance and safety evaluation of the responsibility-sensitive safety in freeway car-following scenarios using automated longitudinal controls. Accid. Anal. Prev. 2022, 177, 106–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, X.; He, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhou, X.; Chen, Y.; Pan, X. TOA positioning algorithm of LBL system for underwater target based on PSO. J. Syst. Eng. Electron. 2023, 34, 1319–1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Chen, C.; Wang, Y. Range-Independent TDOA Localization using Stepwise Accuracy Enhancement under Speed Uncertainty. IEEE Signal Process. Lett. 2023, 30, 1372–1376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, K.; Wang, T.; Liu, J. A learning-based AOA estimation method for device-free localization. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 1264–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Qian, Z.; Liu, G. NQRELoc: AP selection via nonuniform quantization RSSI entropy for indoor localization. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 9724–9732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Shen, S.; Nerini, M. Reconfigurable intelligent surfaces 2.0: Beyond diagonal phase shift matrices. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2023, 62, 102–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Z.; Yue, X.; Dai, B. Reconfigurable intelligent surface assisted unified NOMA framework. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2023, 72, 10617–10632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, S.; Tang, W.; Chen, W. Rank Optimization for MIMO Channel with RIS: Simulation and Measurement. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2023, 13, 437–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dash, S.P.; Mallik, R.K.; Pandey, N. Performance analysis of an index modulation-based receive diversity RIS-assisted wireless communication system. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 768–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Q.; Wen, M.; Xu, L. Reconfigurable-intelligent-surface-aided number modulation for symbiotic active/passive transmission. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 10, 19356–19367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Tang, W.; Li, X. CSI acquisition in RIS-assisted mobile communication systems. Natl. Sci. Rev. 2023, 10, nwad127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luan, M.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y. Phase design and near-field target localization for RIS-assisted regional localization system. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 71, 1766–1777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keykhosravi, K.; Denis, B.; Alexandropoulos, G.C. Leveraging RIS-enabled smart signal propagation for solving infeasible localization problems: Scenarios, key research directions, and open challenges. IEEE Veh. Technol. Mag. 2023, 18, 20–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Junaid, F.; Ibrahim, E. Monostatic Sensing for Passive RIS Localization and Tracking. IEEE Wirel. Commun. Lett. 2024, 13, 1260–1264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rinchi, O.; Elzanaty, A.; Alouini, M.S. Compressive near-field localization for multipath RIS-aided environments. IEEE Commun. Lett. 2022, 26, 1268–1272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dardari, D.; Decarli, N.; Guerra, A. LOS/NLOS near-field localization with a large reconfigurable intelligent surface. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2021, 21, 4282–4294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Zheng, Z.; Fei, Z. Energy-efficient multiuser localization in the RIS-assisted IoT networks. IEEE Internet Things J. 2022, 9, 20651–20665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Yang, J.; Tang, W. Joint localization and environment sensing by harnessing NLOS components in RIS-aided mmWave communication systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2023, 22, 8797–8813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Wang, B.; Zhao, Y. Near-field RSS-based localization algorithms using reconfigurable intelligent surface. IEEE Sens. J. 2022, 22, 3493–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, C.L.; Georgiou, O.; Gradoni, G.; Di Renzo, M. Wireless fingerprinting localization in smart environments using reconfigurable intelligent surfaces. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 135526–135541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Wu, J.; Yang, S.; Lu, W. DOA estimation method based on EMD and MUSIC for mutual interference in FMCW automotive radars. IEEE Geosci. Remote Sens. Lett. 2021, 19, 1–5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakshmi, Y.V.; Singh, P.; Abouhawwash, M.; Mahajan, S.; Pandit, A.K.; Ahmed, A.B. Improved Chan algorithm based optimum UWB sensor node localization using hybrid particle swarm optimization. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 32546–32565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Simulation Parameters | Specific Values |
|---|---|
| The number of antennas at the BS | |
| The carrier frequency | |
| The number of IRS | |
| The number of elements at the IRS | |
| The number of subcarriers | 16 |
| The bandwidth | 20 MHz |
| Amplitude reflection coefficient | |
| The number of population iterations | |
| Threshold values | , |
| The population size |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Gang, Y.; Wang, Y. TDOA-AOA Localization Algorithm for 5G Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces. Electronics 2024, 13, 4347. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13224347
Zhang Y, Liu C, Gang Y, Wang Y. TDOA-AOA Localization Algorithm for 5G Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces. Electronics. 2024; 13(22):4347. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13224347
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Yuexia, Changbao Liu, Yuanshuo Gang, and Yu Wang. 2024. "TDOA-AOA Localization Algorithm for 5G Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces" Electronics 13, no. 22: 4347. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13224347
APA StyleZhang, Y., Liu, C., Gang, Y., & Wang, Y. (2024). TDOA-AOA Localization Algorithm for 5G Intelligent Reflecting Surfaces. Electronics, 13(22), 4347. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13224347






