Road to Efficiency: V2V Enabled Intelligent Transportation System
Abstract
1. Introduction
- We present a review that contributes to this dynamic field by providing a comprehensive synthesis by critically analyzing the state of the art and aiming to identify trends, challenges, and emerging research areas of ITSs;
- Additionally, we seek to offer insights into the transformative potential of intelligent hybrid V2V communication systems in enhancing sustainable road cooperation, safety, and overall transportation efficiency;
- With this contribution, we aim to guide future research and developments in connected and cooperative vehicle systems for the ITS;
- We analyze and deliberate on the most advanced, sustainable V2V communication architectures;
- We thoroughly examine the advantages of V2V communication architectures, their contributions, and their limitations for ITS network environments.
2. Motivations
3. Related Studies
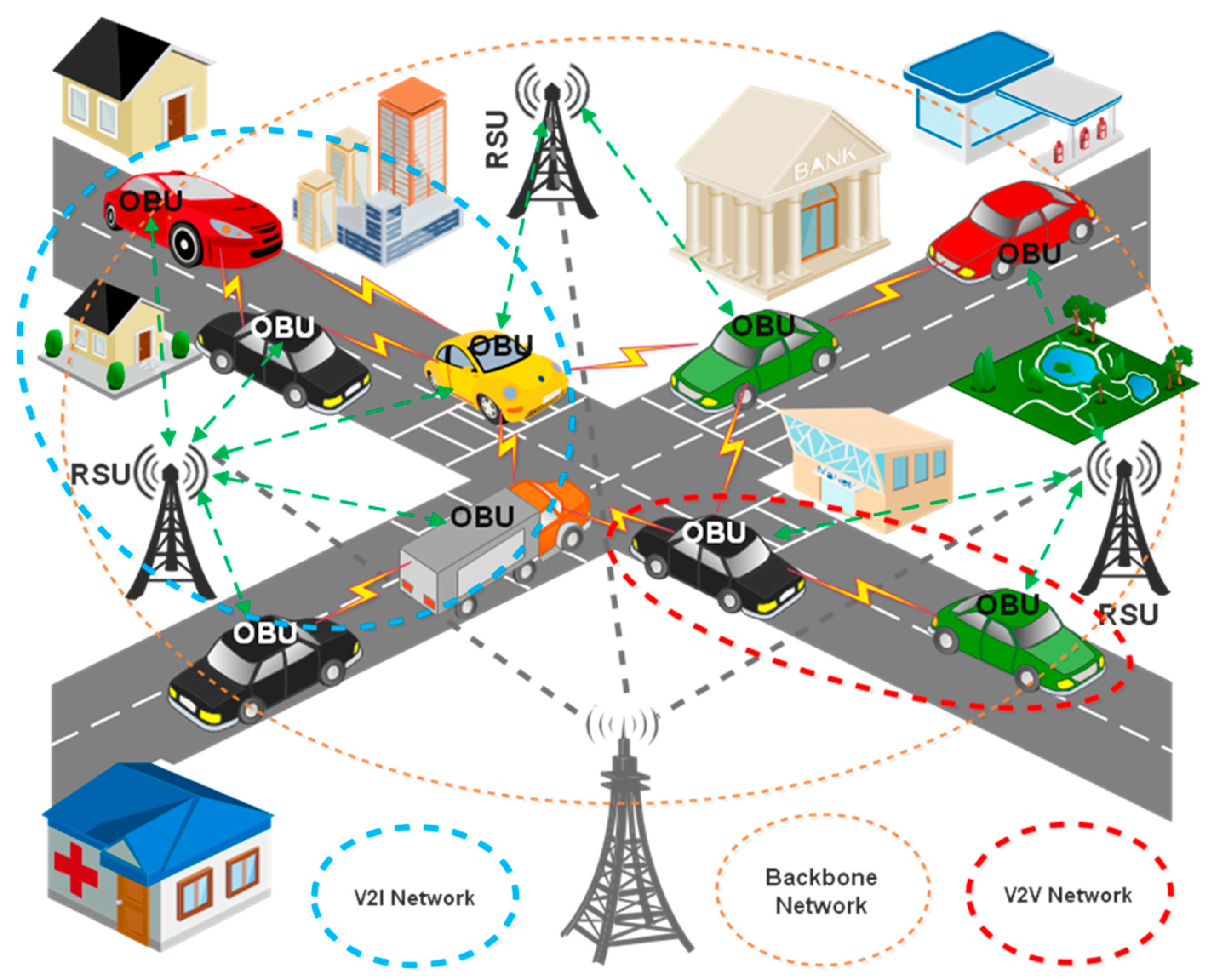
4. V2V Communication Architectures
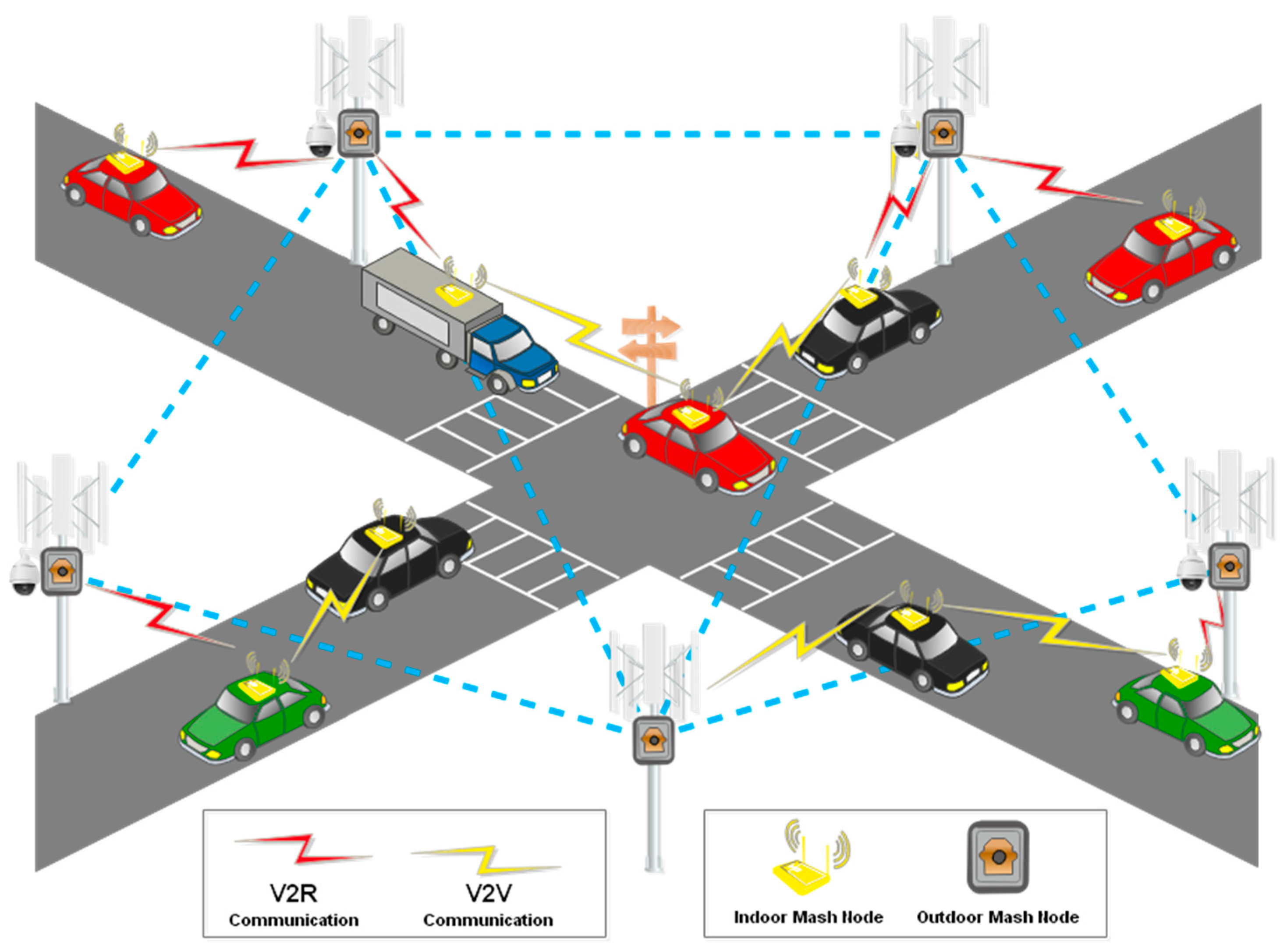
4.1. Decentralized Mesh Network
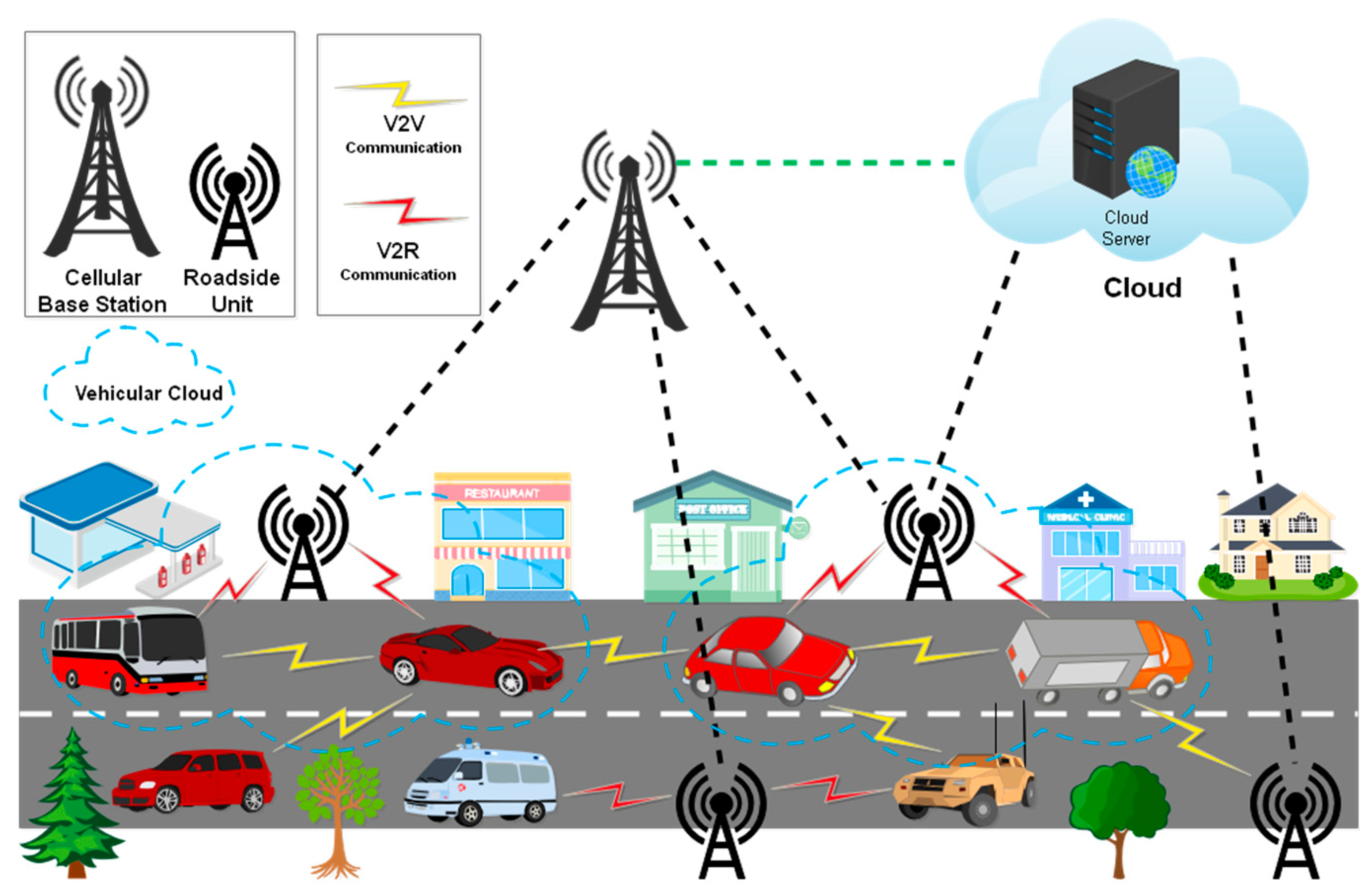
4.2. V2V-Based Cloud-Integrated Hub
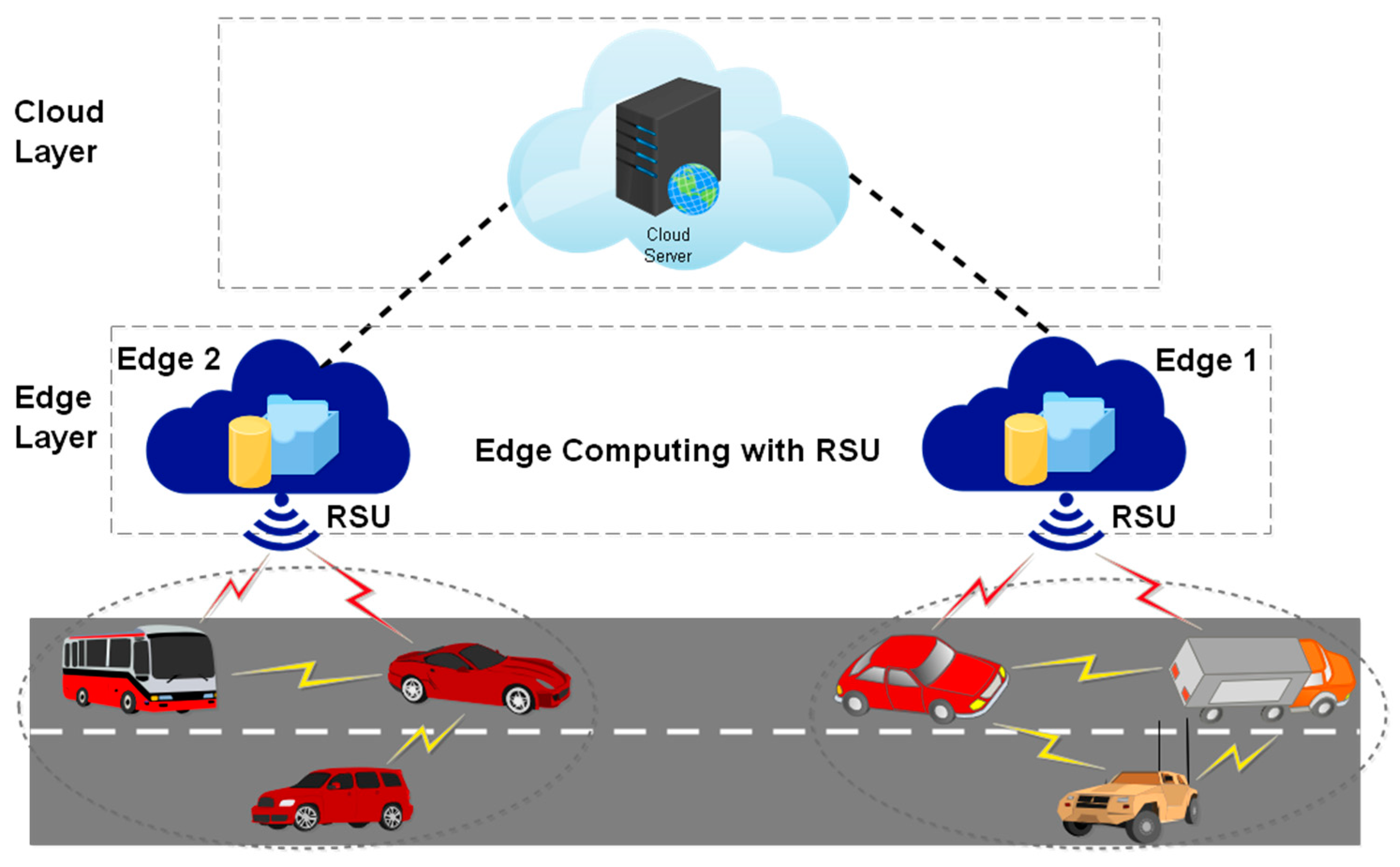
4.3. Edge Computing-Based V2V Architecture
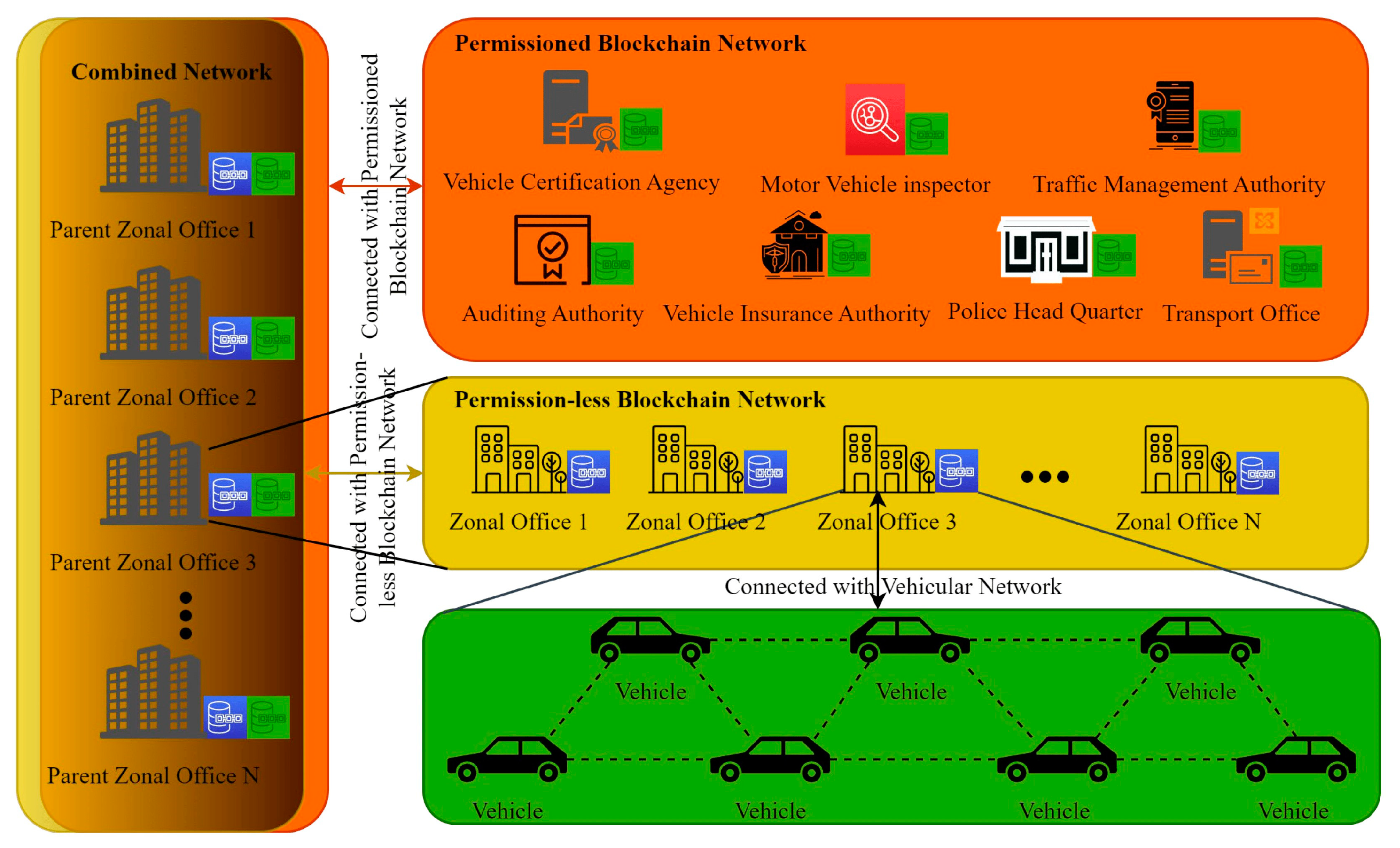
4.4. Blockchain-Enabled V2V Network
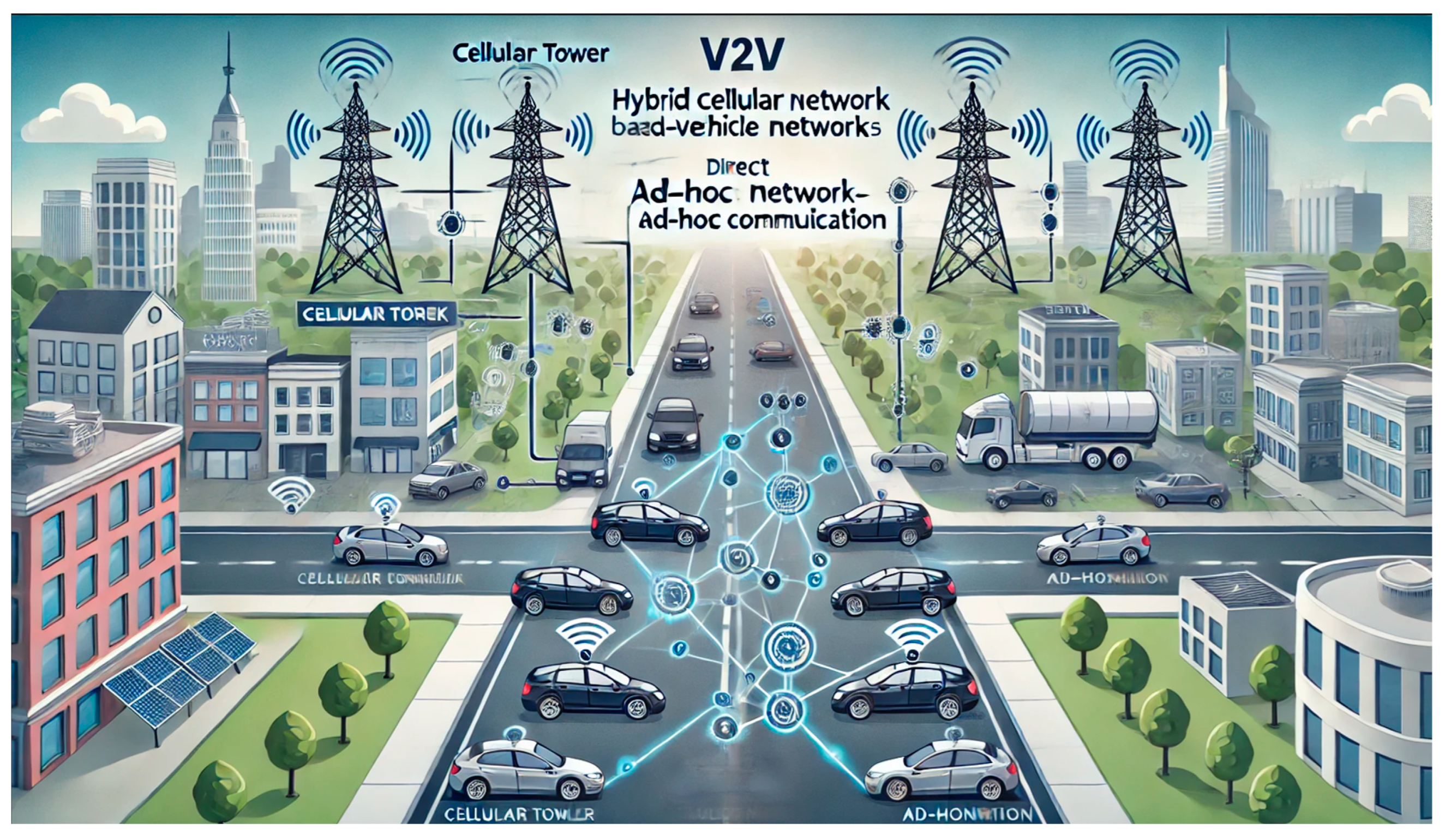
4.5. Hybrid Cellular and Ad-Hoc Network-Based V2V
4.6. AI-Driven Dynamic Network for V2V Communication
5. V2V Aids toward Sustainable Transportation Systems
5.1. V2V DMN Contributions in ITS
5.2. Cloud-Integrated V2V Network Contributions in ITS
5.3. V2V Edge Computing Contributions in ITSs
5.4. Blockchain-Enabled V2V Network Contributions in ITSs
5.5. V2V Enabled Hybrid Cellular and Ad-Hoc Network Contributions in ITSs
5.6. V2V AI-Driven Dynamic Network Contributions in ITSs
6. Open Research Challenges and Future Research Directions
6.1. Frequent Topological Changes
6.2. Coherence
6.3. Accuracy
6.4. Security and Privacy Challenges
6.5. Integration of 5G and Beyond
6.6. Edge Intelligence and Edge Computing
6.7. Scalability and Reliability
6.8. Autonomous and Cooperative Driving
6.9. Dynamic Spectrum Access and Resource Management
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mao, J.; Sun, Q.; Wang, X.; Muthu, B.; Krishnamoorthy, S. The importance of public support in the implementation of green transportation in the smart cities. Comput. Intell. 2024, 40, e12326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gontarz, M.; Sulich, A. The sustainable transportation solutions: Smart shuttle example. Vision 2025, 10833–10840. [Google Scholar]
- Elassy, M.; Al-Hattab, M.; Takruri, M.; Badawi, S. Intelligent Transportation Systems for Sustainable Smart Cities. Transp. Eng. 2024, 16, 100252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zoghlami, C.; Kacimi, R.; Dhaou, R. 5g-enabled v2x communications for vulnerable road users safety applications: A review. Wirel. Netw. 2023, 29, 1237–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Naeem, M.A.; Ali, R.; Zikria, Y.B.; Kim, S.W. DCS: Distributed caching strategy at the edge of vehicular sensor networks in information-centric networking. Sensors 2019, 19, 4407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashingaidze, N.; Mutonhodza, C. The Search for Sustainable Transport Infrastructure in Harare: Integrating Intelligent Transport Systems. In Urban Infrastructure in Zimbabwe: Departures, Divergences and Convergences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 53–71. [Google Scholar]
- Yan, H.; Lv, Z. A survey of sustainable development of intelligent transportation system based on urban travel demand. Sustain. Soc. Dev. 2024, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Giannaros, A.; Karras, A.; Theodorakopoulos, L.; Karras, C.; Kranias, P.; Schizas, N.; Kalogeratos, G.; Tsolis, D. Autonomous vehicles: Sophisticated attacks, safety issues, challenges, open topics, blockchain, and future directions. J. Cybersecur. Priv. 2023, 3, 493–543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, D.; Banerjee, S.; Chatterjee, P.; Ghosh, U.; Biswas, U. Blockchain for intelligent transportation systems: Applications, challenges, and opportunities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oladimeji, D.; Gupta, K.; Kose, N.A.; Gundogan, K.; Ge, L.; Liang, F. Smart transportation: An overview of technologies and applications. Sensors 2023, 23, 3880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwin, M.; Eniyan, M.; Saranya Nair, M.; Antony Miraculas, G. Multi-Energy Management Schemes for the Sustainability of Intelligent Interconnected Transportation Systems. In Interconnected Modern Multi-Energy Networks and Intelligent Transportation Systems: Towards a Green Economy and Sustainable Development; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2024; pp. 325–343. [Google Scholar]
- Ameen, H.A.; Zaidan, B.B.; Zaidan, A.A.; Saon, S.; Nor, D.M.; Malik, R.Q.; Kareem, Z.H.; Garfan, S.; Zaidan, R.A.; Mohammed, A. A deep review and analysis of data exchange in vehicle-to-vehicle communications systems: Coherent taxonomy, challenges, motivations, recommendations, substantial analysis and future directions. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 158349–158378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, B.; Zhang, X.; Mumtaz, S.; Han, C.; Li, C.; Wen, H.; Wang, D. Survey on the internet of vehicles: Network architectures and applications. IEEE Commun. Stand. Mag. 2020, 4, 34–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arif, M.; Wang, G.; Balas, V.E.; Geman, O.; Castiglione, A.; Chen, J. SDN based communications privacy-preserving architecture for VANETs using fog computing. Veh. Commun. 2020, 26, 100265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senouci, O.; Aliouat, Z.; Harous, S. MCA-V2I: A multi-hop clustering approach over vehicle-to-internet communication for improving VANETs performances. Future Gener. Comput. Syst. 2019, 96, 309–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, J.; Ahn, K.; Farag, M.; Rakha, H. Impacts of vehicle-to-everything enabled applications: Literature review of existing studies. Comput. Netw. Commun. 2023, 1, 116–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, G.; Mikkili, S. Critical review of vehicle-to-everything (V2X) topologies: Communication, power flow characteristics, challenges, and opportunities. CPSS Trans. Power Electron. Appl. 2023, 9, 10–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalil, R.A.; Safelnasr, Z.; Yemane, N.; Kedir, M.; Shafiqurrahman, A.; Saeed, N. Advanced Learning Technologies for Intelligent Transportation Systems: Prospects and Challenges. IEEE Open J. Veh. Technol. 2024, 5, 397–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalfin, M.; Volgren, J.; LeGoullon, L.; Franz, B.; Shah, S.; Forgach, T.; Jones, M. Vehicle-to-Everything Communication Using a Roadside Unit for Over-the-Horizon Object Awareness. In Proceedings of the IEOM International Conference on Smart Mobility and Vehicle Electrification, Southfield, MI, USA, 10 October 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Pandey, P.K.; Kansal, V.; Swaroop, A. Vehicular Ad Hoc Networks (VANETs): Architecture, Challenges, and Applications. In Handling Priority Inversion in Time-Constrained Distributed Databases; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2020; pp. 224–239. [Google Scholar]
- Qiu, M.; Liu, D.; Wang, H.; Yu, W.; Baldi, S. A cooperative implementation of mesh stability in vehicular platoons. IEEE Trans. Netw. Sci. Eng. 2022, 10, 1537–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohseni, N.A.; Bayati, N.; Ebel, T. Energy management strategies of hybrid electric vehicles: A comparative review. IET Smart Grid 2023, 7, 191–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.-L.; Hwang, R.-H.; Lin, P.-C.; Vyas, A.; Nguyen, V.-T. Towards the age of intelligent vehicular networks for connected and autonomous vehicles in 6G. IEEE Netw. 2022, 37, 44–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, S.; Kaul, A.; Ahmed, S.; Sharma, S. A detailed tutorial survey on VANETs: Emerging architectures, applications, security issues, and solutions. Int. J. Commun. Syst. 2021, 34, e4905. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deng, X.; Wang, L.; Gui, J.; Jiang, P.; Chen, X.; Zeng, F.; Wan, S. A review of 6G autonomous intelligent transportation systems: Mechanisms, applications and challenges. J. Syst. Archit. 2023, 142, 102929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Lawrence, T.; Li, F. An efficient identity-based signature scheme without bilinear pairing for vehicle-to-vehicle communication in VANETs. J. Syst. Archit. 2020, 103, 101692. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-shareeda, M.A.; Alazzawi, M.A.; Anbar, M.; Manickam, S.; Al-Ani, A.K. A comprehensive survey on vehicular ad hoc networks (vanets). In Proceedings of the 2021 International Conference on Advanced Computer Applications (ACA), Maysan, Iraq, 25–26 July 2021; pp. 156–160. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, L.; Han, D.; Long, J. Telematics Communication Based on Blockchain Technology. In Proceedings of the 2023 IEEE 8th International Conference on Smart Cloud (SmartCloud), Tokyo, Japan, 16–18 September 2023; pp. 136–141. [Google Scholar]
- Gohar, A.; Nencioni, G. The role of 5G technologies in a smart city: The case for intelligent transportation system. Sustainability 2021, 13, 5188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, M.M.; Thill, J.-C. Impacts of connected and autonomous vehicles on urban transportation and environment: A comprehensive review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 96, 104649. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeong, H.H.; Shen, Y.C.; Jeong, J.P.; Oh, T.T. A comprehensive survey on vehicular networking for safe and efficient driving in smart transportation: A focus on systems, protocols, and applications. Veh. Commun. 2021, 31, 100349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muslam, M.M.A. Enhancing Security in Vehicle-to-Vehicle Communication: A Comprehensive Review of Protocols and Techniques. Vehicles 2024, 6, 450–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatterjee, T.; Karmakar, R.; Kaddoum, G.; Chattopadhyay, S.; Chakraborty, S. A survey of VANET/V2X routing from the perspective of non-learning-and learning-based approaches. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 23022–23050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ameur, A.I.; Lakas, A.; Yagoubi, M.B.; Oubbati, O.S. Peer-to-peer overlay techniques for vehicular ad hoc networks: Survey and challenges. Veh. Commun. 2022, 34, 100455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, P.S.; Joice, C.S. Vehicle-to-vehicle (V2V) communication using routing protocols: A review. In Proceedings of the 2019 International Conference on Smart Structures and Systems (ICSSS), Chennai, India, 14–15 March 2019; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Storck, C.R.; Duarte-Figueiredo, F. A survey of 5G technology evolution, standards, and infrastructure associated with vehicle-to-everything communications by internet of vehicles. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 117593–117614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malik, R.Q.; Ramli, K.N.; Kareem, Z.H.; Habelalmatee, M.I.; Abbas, A.H.; Alamoody, A. An overview on V2P communication system: Architecture and application. In Proceedings of the 2020 3rd International Conference on Engineering Technology and its Applications (IICETA), Najaf, Iraq, 6–7 September 2020; pp. 174–178. [Google Scholar]
- Ding, R.; Wang, T.; Song, L.; Han, Z.; Wu, J. Roadside-unit caching in vehicular ad hoc networks for efficient popular content delivery. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Wireless Communications and Networking Conference (WCNC), New Orleans, LA, USA, 9–12 March 2015; pp. 1207–1212. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, J. Internet of Vehicles over VANETs: Smart and secure communication using IoT. Scalable Comput. Pract. Exp. 2020, 21, 425–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, S.; Gong, S.; Li, X. A Comparative Study of IEEE 802.11 bd and IEEE 802.11 p on the Data Dissemination Properties in Dynamic Traffic Scenarios. Appl. Sci. 2024, 14, 2099. [Google Scholar]
- Santa, J.; Fernandez, P.J.; Pereñíguez, F. Deployment of vehicular networks in highways using 802.11 p and IPv6 technologies. Int. J. Ad Hoc Ubiquitous Comput. 2017, 24, 33–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansari, K. Joint use of DSRC and C-V2X for V2X communications in the 5.9 GHz ITS band. IET Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 15, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masini, B.M.; Bazzi, A.; Zanella, A. A survey on the roadmap to mandate on board connectivity and enable V2V-based vehicular sensor networks. Sensors 2018, 18, 2207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Klapez, M.; Grazia, C.A.; Casoni, M. Application-level performance of IEEE 802.11 p in safety-related V2X field trials. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 3850–3860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Absi, M.A.; Al-Absi, A.A.; Lee, H.J. Comparison between DSRC and other short range wireless communication technologies. In Proceedings of the 2020 22nd International Conference on Advanced Communication Technology (ICACT), Phoenix Park, Republic of Korea, 16–19 February 2020; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Azzaoui, N.; Korichi, A.; Brik, B.; Fekair, M.e.a.; Kerrache, C.A. Wireless communication in internet of vehicles networks: DSRC-based Vs cellular-based. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Smart City Applications, Casablanca, Morocco, 2–4 October 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ernst, J.; Wang, Z.D.; Abraham, S.; Lyotier, J.; Jensen, C.; Quinn, M.; Harvey, D. A Decentralized Mobile Mesh Networking Platform Powered by Blockchain Technology and Tokenization. RightMesh AG, White Paper. 2019. Available online: https://www.rightmesh.io/docs/RightMesh_WP6.pdf (accessed on 4 July 2024).
- Salama, A.; Stergioulis, A.; Hayajneh, A.M.; Zaidi, S.A.R.; McLernon, D.; Robertson, I. Decentralized federated learning over slotted aloha wireless mesh networking. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 18326–18342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salama, A.; Stergioulis, A.; Zaidi, S.A.; McLernon, D. Decentralized Federated Learning on the Edge Over Wireless Mesh Networks. IEEE Access 2023, 11, 124709–124724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chitanvis, R.; Ravi, N.; Zantye, T.; El-Sharkawy, M. Collision avoidance and Drone surveillance using Thread protocol in V2V and V2I communications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE National Aerospace and Electronics Conference (NAECON), Dayton, OH, USA, 15–19 July 2019; pp. 406–411. [Google Scholar]
- Marzal, S.; González-Medina, R.; Salas-Puente, R.; Figueres, E.; Garcerá, G. A novel locality algorithm and peer-to-peer communication infrastructure for optimizing network performance in smart microgrids. Energies 2017, 10, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahlawat, C.; Krishnamurthi, R. Towards smart technologies with integration of the internet of things, cloud computing, and fog computing. Int. J. Netw. Virtual Organ. 2023, 29, 73–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, B.; Fong, A.C.; Hong, G.Y. Sustainable micromobility management in Smart Cities. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 15890–15896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, J.; Chen, B.; Wang, S. Smart Manufacturing Factory: Artificial-Intelligence-Driven Customized Manufacturing; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Silva, L.; Magaia, N.; Sousa, B.; Kobusińska, A.; Casimiro, A.; Mavromoustakis, C.X.; Mastorakis, G.; De Albuquerque, V.H.C. Computing paradigms in emerging vehicular environments: A review. IEEE/CAA J. Autom. Sin. 2021, 8, 491–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naeem, M.A.; Zikria, Y.B.; Ali, R.; Tariq, U.; Meng, Y.; Bashir, A.K. Cache in fog computing design, concepts, contributions, and security issues in machine learning prospective. Digit. Commun. Netw. 2023, 9, 1033–1052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meng, Y.; Naeem, M.A.; Almagrabi, A.O.; Ali, R.; Kim, H.S. Advancing the State of the Fog Computing to Enable 5G Network Technologies. Sensors 2020, 20, 1754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, W.; Su, Y.; Liu, J.; Li, S.; Huang, W.; Wu, F.; Liu, Y.a. Joint task offloading and resource allocation for vehicular edge computing based on V2I and V2V modes. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 24, 4277–4292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Liu, T.; Kim, B.; Lin, C.-W.; Shiraishi, S.; Xie, J.; Han, Z. Architectural design alternatives based on cloud/edge/fog computing for connected vehicles. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2020, 22, 2349–2377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fraga-Lamas, P.; Fernández-Caramés, T.M. A review on blockchain technologies for an advanced and cyber-resilient automotive industry. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 17578–17598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, J.; Du, J.; Shen, Y.; Wang, J.; Yuan, J.; Han, Z. DRL-based V2V computation offloading for blockchain-enabled vehicular networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2022, 22, 3882–3897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, I.; Gervais, M.; Ahene, E.; Li, F. A blockchain-based certificateless public key signature scheme for vehicle-to-infrastructure communication in VANETs. J. Syst. Archit. 2019, 99, 101636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.S.; Balan, K.; Javed, Y.; Tarmizi, S.; Abdullah, J. Secure trust-based blockchain architecture to prevent attacks in VANET. Sensors 2019, 19, 4954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mollah, M.B.; Zhao, J.; Niyato, D.; Guan, Y.L.; Yuen, C.; Sun, S.; Lam, K.-Y.; Koh, L.H. Blockchain for the internet of vehicles towards intelligent transportation systems: A survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 8, 4157–4185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oham, C.; Michelin, R.A.; Jurdak, R.; Kanhere, S.S.; Jha, S. B-FERL: Blockchain based framework for securing smart vehicles. Inf. Process. Manag. 2021, 58, 102426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, M.; Das, D.; Banerjee, S.; Mukherjee, A.; AL-Numay, W.; Biswas, U.; Zhang, Y. Blockchain-enabled communication framework for secure and trustworthy internet of vehicles. Sustainability 2023, 15, 9399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Ghosh, S.; Busari, S.A.; Huq, K.M.S.; Dagiuklas, T.; Mumtaz, S.; Iqbal, M.; Rodriguez, J. Robust, resilient and reliable architecture for v2x communications. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 22, 4414–4430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdel Hakeem, S.A.; Hady, A.A.; Kim, H. 5G-V2X: Standardization, architecture, use cases, network-slicing, and edge-computing. Wirel. Netw. 2020, 26, 6015–6041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alaba, F.A.; Oluwadare, A.; Sani, U.; Oriyomi, A.A.; Lucy, A.O.; Najeem, O. Enabling Sustainable Transportation Through IoT and AIoT Innovations. In Artificial Intelligence of Things for Achieving Sustainable Development Goals; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2024; pp. 273–291. [Google Scholar]
- Saad, M.M.; Khan, M.T.R.; Srivastava, G.; Jhaveri, R.H.; Islam, M.; Kim, D. Cooperative vehicular networks: An optimal and machine learning approach. Comput. Electr. Eng. 2022, 103, 108348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Deng, Y.; Ding, H.; Qu, G.; Zhang, H.; Li, P.; Fang, Y. Vehicle as a service (VaaS): Leverage vehicles to build service networks and capabilities for smart cities. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kanellopoulos, D.; Sharma, V.K.; Panagiotakopoulos, T.; Kameas, A. Networking architectures and protocols for IoT applications in smart cities: Recent developments and perspectives. Electronics 2023, 12, 2490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Javed, A.R.; Shahzad, F.; ur Rehman, S.; Zikria, Y.B.; Razzak, I.; Jalil, Z.; Xu, G. Future smart cities: Requirements, emerging technologies, applications, challenges, and future aspects. Cities 2022, 129, 103794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raza, S.; Wang, S.; Ahmed, M.; Anwar, M.R. A survey on vehicular edge computing: Architecture, applications, technical issues, and future directions. Wirel. Commun. Mob. Comput. 2019, 2019, 3159762:1–3159762:19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendiboure, L.; Chalouf, M.-A.; Krief, F. Edge computing based applications in vehicular environments: Comparative study and main issues. J. Comput. Sci. Technol. 2019, 34, 869–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, A.; Iqbal, M.M.; Jabbar, S.; Asghar, M.N.; Raza, U.; Al-Turjman, F. VABLOCK: A blockchain-based secure communication in V2V network using icn network support technology. Microprocess. Microsyst. 2022, 93, 104569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sellami, B. Investigation of Deep Learning and Blockchain Applicability for Software-Defined Internet of Things; Faculty of Sciences of Tunis: Tunis, Tunisia, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Sharif, A.; Li, J.P.; Saleem, M.A. Internet of things enabled vehicular and ad hoc networks for smart city traffic monitoring and controlling: A review. Int. J. Adv. Netw. Appl. 2018, 10, 3833–3842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermesan, O.; John, R.; Pype, P.; Daalderop, G.; Kriegel, K.; Mitic, G.; Lorentz, V.; Bahr, R.; Sand, H.E.; Bockrath, S. Automotive intelligence embedded in electric connected autonomous and shared vehicles technology for sustainable green mobility. Front. Future Transp. 2021, 2, 688482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, C.; Song, J.; Xu, Y.; Fan, H.; Wu, X.; Sun, T. Vehicle-based machine vision approaches in intelligent connected system. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2023, 25, 2827–2836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elbamby, M.S.; Perfecto, C.; Liu, C.-F.; Park, J.; Samarakoon, S.; Chen, X.; Bennis, M. Wireless edge computing with latency and reliability guarantees. Proc. IEEE 2019, 107, 1717–1737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arthurs, P.; Gillam, L.; Krause, P.; Wang, N.; Halder, K.; Mouzakitis, A. A taxonomy and survey of edge cloud computing for intelligent transportation systems and connected vehicles. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2021, 23, 6206–6221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahir, M.N.; Katz, M. Performance evaluation of IEEE 802.11 p, LTE and 5G in connected vehicles for cooperative awareness. Eng. Rep. 2022, 4, e12467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Aspects | DMS | CI-V2V Hub | V2V-EC | V2V BEN | V2V HCAN | V2V AI-DN |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Latency | Low | Moderate | Low | Moderate | Moderate | Low |
| Reliability | High | Moderate | High | High | High | High |
| Data Processing | Decentralized | Centralized | Decentralized | Decentralized | Hybrid | AI-driven |
| Scalability | High | High | High | Moderate | High | High |
| Implementation Cost | Low | High | Moderate | High | Moderate | Moderate |
| Interoperability | Moderate | High | High | Moderate | High | High |
| Infrastructure Dependency | Low | High | Moderate | Moderate | High | Low |
| Use Case Suitability | Ideal for rural and sparse urban areas | Suitable for urban areas | Ideal for latency-sensitive applications | Suitable for high-security applications | Suitable for mixed urban and rural environments | Ideal for complex and dynamic urban environments |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Naeem, M.A.; Chaudhary, S.; Meng, Y. Road to Efficiency: V2V Enabled Intelligent Transportation System. Electronics 2024, 13, 2673. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132673
Naeem MA, Chaudhary S, Meng Y. Road to Efficiency: V2V Enabled Intelligent Transportation System. Electronics. 2024; 13(13):2673. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132673
Chicago/Turabian StyleNaeem, Muhammad Ali, Sushank Chaudhary, and Yahui Meng. 2024. "Road to Efficiency: V2V Enabled Intelligent Transportation System" Electronics 13, no. 13: 2673. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132673
APA StyleNaeem, M. A., Chaudhary, S., & Meng, Y. (2024). Road to Efficiency: V2V Enabled Intelligent Transportation System. Electronics, 13(13), 2673. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132673







