Research on the Use of an Ocean Turbulence Bubble Simulation Model to Analyze Wireless Optical Transmission Characteristics
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Basic Principles of the Bubble Simulation Model Used for Ocean Turbulence Channels
2.1. Seawater Refractive Index Model
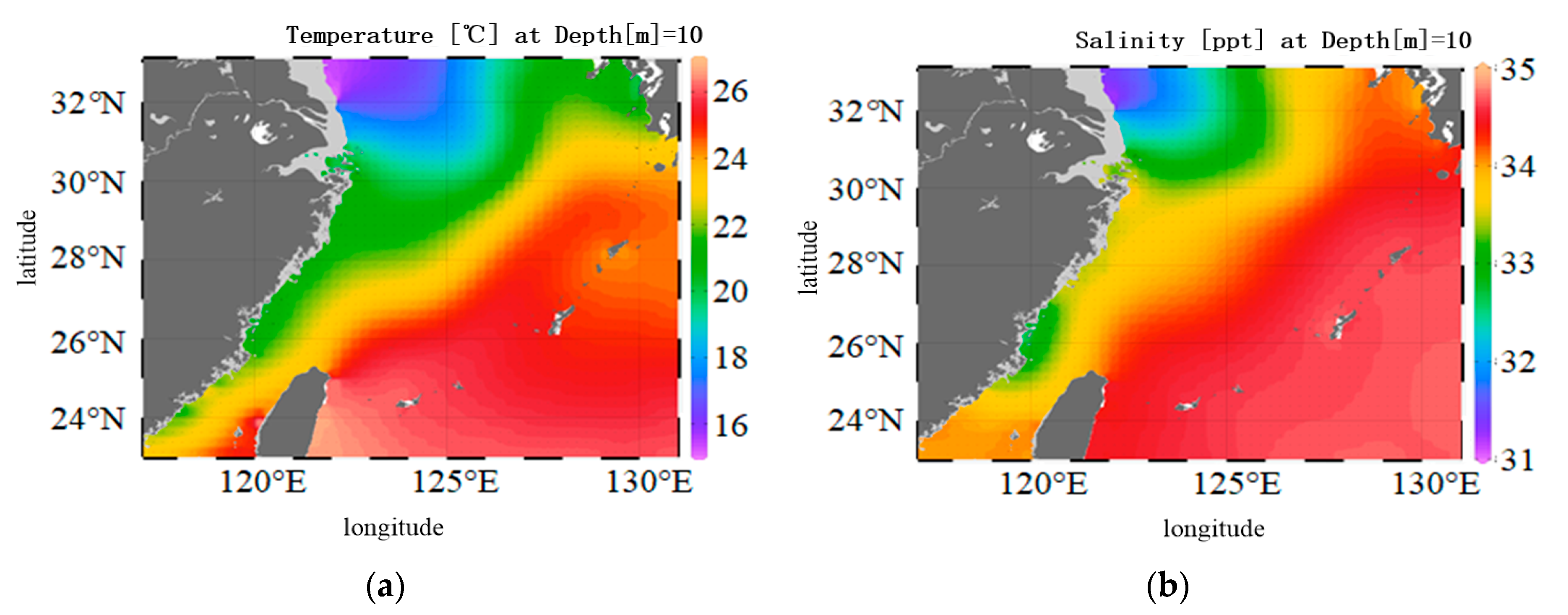
2.2. Hydrological Data of the East China Sea Area
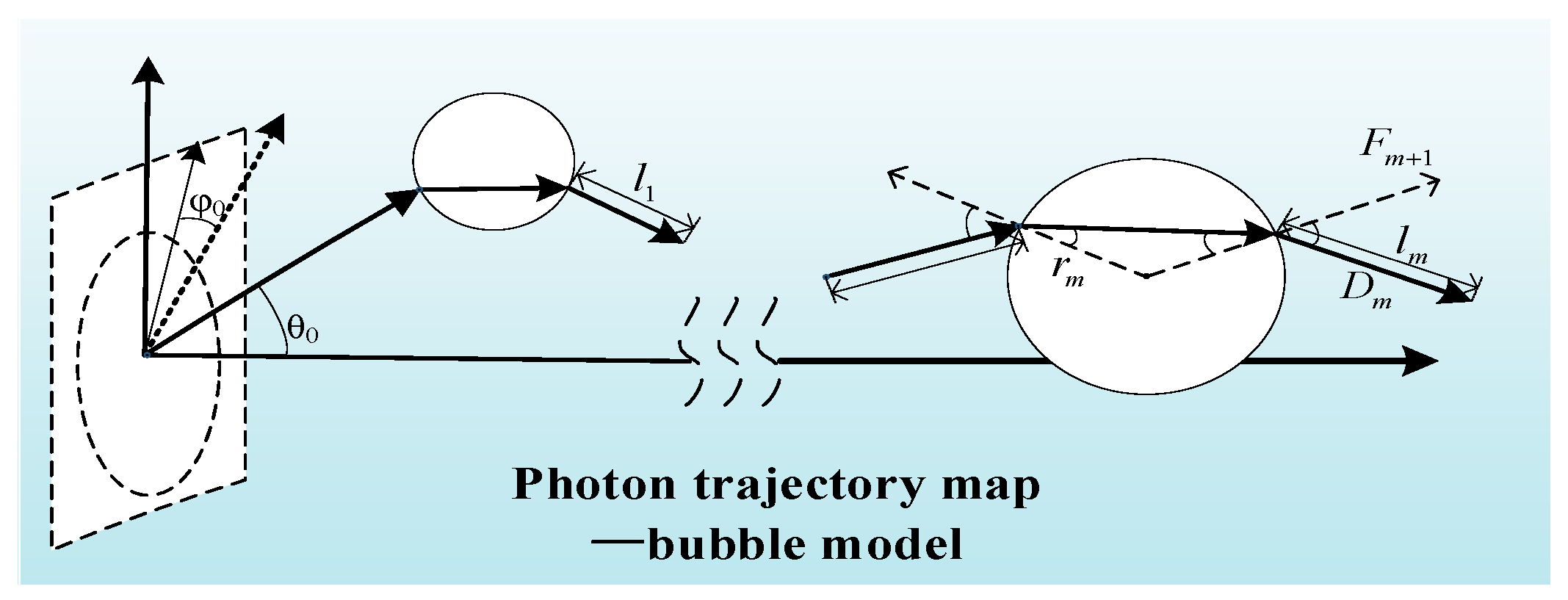
2.3. Establishment of a Bubble Simulation Model for the Ocean Turbulence Channels
3. Simulation Analysis of the Bubble Simulation Model for Turbulent Ocean Channels
3.1. Distribution of the Light Intensity Probability Density Function
3.2. The Influence of the Turbulent Bubble Parameters on Fluctuations on the Light Intensity
3.3. The Models of Logarithmic Intensity Variance with Turbulent Bubble Parameters
3.4. The Relationship between Logarithmic Intensity Variance and Equivalent Structure Constants
3.5. Comparison between Simulation Results and Theoretical Values of Transmission Characteristics in Bubble Models
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Saeed, N.; Celik, A.; Al-Naffouri, T.Y.; Alouini, M.S. Underwater optical wireless communications, networking, and localization: A survey. Ad Hoc Netw. 2019, 94, 101935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anous, N.; Abdallah, M.; Uysal, M.; Qaraqe, K. Performance evaluation of LOS and NLOS vertical inhomogeneous links in underwater visible light communications. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 22408–22420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayakumari, P.; Chanthirasekaran, K.; Jayamani, K.; Nirmala, P.; ThandaiahPrabu, R. BIT Error Rate Analysis of Various Water Samples in Underwater Wireless Optical Communication System. In Proceedings of the 2022 International Conference on Advances in Computing, Communication and Applied Informatics (ACCAI), Chennai, India, 28–29 January 2022; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Ye, Z.; Huang, N.; Li, S.; Xu, Z. Multilevel polarization shift keying modulation for turbulence-robust underwater optical wireless communication. Opt. Express 2023, 31, 8400–8413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Xu, G.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Z. Average symbol error probability and channel capacity of the underwater wireless optical communication systems over oceanic turbulence with pointing error impairments. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 15327–15343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ji, X.; Yin, H.; Jing, L.; Liang, Y.; Wang, J. Modeling and performance analysis of oblique underwater optical communication links considering turbulence effects based on seawater depth layering. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 18874–18888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hill, R. Optical propagation in turbulent water. JOSA 1978, 68, 1067–1072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, G.; Yan, Q.; Yu, L.; Hu, L.; Zhang, Y. Spatial coherence length and wave structure function for plane waves transmitted in anisotropic turbulent oceans. JOSA A 2023, 40, 1602–1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Xu, G.; Wang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Song, Z. Scintillation index for the optical wave in the vertical oceanic link with anisotropic tilt angle. Opt. Express 2022, 30, 38804–38820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, R.; Zhang, M.; Dai, D.; Shi, Y.; Gao, S. Analysis of the Underwater Wireless Optical Communication Channel Based on a Comprehensive Multiparameter Model. Appl. Sci. 2021, 11, 6051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, Y.; Wang, P.; Wang, W.; Li, S.; Cheng, M.; Guo, L. Statistical model for the weak turbulence-induced attenuation and crosstalk in free space communication systems with orbital angular momentum. Opt. Express 2021, 29, 12644–12662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xie, Y.; Li, B. Probability of orbital angular momentum for square Hermite–Gaussian vortex pulsed beam in oceanic turbulence channel. Results Phys. 2021, 28, 104590. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niu, C.; Wang, X.; Lu, F.; Han, X. Validity of beam propagation characteristics through oceanic turbulence simulated by phase screen method. Infrared Laser Eng. 2020, 49, 243–249. [Google Scholar]
- Baykal, Y. Expressing oceanic turbulence parameters by atmospheric turbulence structure constant. Appl. Opt. 2016, 55, 1228–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuksel, H.; Atia, W.; Davis, C.C. A geometrical optics approach for modeling atmospheric turbulence. In Atmospheric Optical Modeling, Measurement, and Simulation; Yuksel, H., Atia, W., Davis, C.C., Eds.; SPIE: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2005; Volume 5891, pp. 77–88. [Google Scholar]
- Xue, Y.; Ma, L.; Shi, L.; Luo, J. Performance analysis of free space quantum key distribution based on refraction of turbulence bubble. Acta Photonica Sin. 2017, 46, 36–41. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Yang, H.; Feng, X.; Fan, J.; Wang, H.; Han, C.; Ding, Y. Monte Carlo simulation of beam wander in atmospheric turbulence based on spherical bubble model. J. Chang. Univ. Sci. Technol. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2008, 31, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Quan, X.; Fry, E.S. Empirical equation for the index of refraction of seawater. Appl. Opt. 1995, 34, 3477–3480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yao, J.R.; Elamassie, M.; Korotkova, O. Spatial power spectrum of natural water turbulence with any average temperature, salinity concentration, and light wavelength. J. Opt. Soc. Am. A Opt. Image Sci. Vis. 2020, 37, 1614–1621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, N.; Zhang, B.; Luo, N. Simultaneous inversion of seawater temperature and salinity based on stimulated brillouin scattering. Acta Opt. Sin. 2022, 42, 2429001. [Google Scholar]
- Baykal, Y. Intensity fluctuations of multimode laser beams in underwater medium. JOSA A 2015, 32, 593–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, D.M.; Ellis, A.D.; Li, Y.; Hu, Z. Emulating atmospheric turbulence effects on a micro-mirror array: Assessing the DMD for use with free-space-to-fibre optical connections. Eng. Res. Express 2022, 4, 045004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, F.; Du, Y.; Zhang, J. Bit error rate of pulse position modulation wireless optical communication in gamma-gamma oceanic anisotropic turbulence. Acta Phys. Sin. 2019, 68, 236–244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]











| Parameter | Parameter Definition |
|---|---|
| n | refractive index under average T and S in the East China Sea |
| the standard deviation of the refractive index fluctuations | |
| the minimum ocean turbulence vortex scale | |
| the largest ocean turbulence vortex scale | |
| the mean free path of turbulent transmission | |
| the standard deviation of the free path | |
| N | the total number of simulated photons |
| L | transmission distance |
| Change (L = 40 m) | Scintillation Index | L Change = 5 m) | Scintillation Index |
|---|---|---|---|
| 3 m | 0.1307 | 20 m | 0.0083 |
| 5 m | 0.1098 | 30 m | 0.0401 |
| 7 m | 0.0881 | 40 m | 0.1098 |
| Parameter | Value | Parameter Definition | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Theoretical Calculation | dissipation rate of Kinetic Energy | ||
| −2 | Thermohaline diffusion ratio | ||
| dissipation rate of temperature variance | |||
| 0.001 m | the minimum ocean turbulence vortex scale | ||
| 5 m | the largest ocean turbulence vortex scale | ||
| 5 m | the spacing between phase screens | ||
| Turbulent Bubble Simulation Model | n | 1.341 | refractive index under average T and S |
| 0.00093 | standard deviation of refractive index fluctuations | ||
| 5/3 m | the standard deviation of the free path | ||
| 0.001 m | the minimum ocean turbulence vortex scale | ||
| 5 m | the largest ocean turbulence vortex scale | ||
| 5 m | the mean free path of turbulent transmission |
| Transmission Characteristics | Theoretical Calculation | Bubble Model |
|---|---|---|
| Beam expansion (cm) | 1.0569 | 1.0523 |
| Centroid drift (cm) | 0.1280 | 0.1245 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhu, Y.; Nie, H.; Liu, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, J. Research on the Use of an Ocean Turbulence Bubble Simulation Model to Analyze Wireless Optical Transmission Characteristics. Electronics 2024, 13, 2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132626
Zhu Y, Nie H, Liu Q, Yang Y, Zhang J. Research on the Use of an Ocean Turbulence Bubble Simulation Model to Analyze Wireless Optical Transmission Characteristics. Electronics. 2024; 13(13):2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132626
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhu, Yunzhou, Huan Nie, Qian Liu, Yi Yang, and Jianlei Zhang. 2024. "Research on the Use of an Ocean Turbulence Bubble Simulation Model to Analyze Wireless Optical Transmission Characteristics" Electronics 13, no. 13: 2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132626
APA StyleZhu, Y., Nie, H., Liu, Q., Yang, Y., & Zhang, J. (2024). Research on the Use of an Ocean Turbulence Bubble Simulation Model to Analyze Wireless Optical Transmission Characteristics. Electronics, 13(13), 2626. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics13132626





