A New PSO Technique Used for the Optimization of Multiobjective Economic Emission Dispatch
Abstract
1. Introduction
- In classical PSO, the velocity needs to be updated after every iteration in order to update the particle positions. In this PSO, if some particles move away from the search area, they cannot come back and do not participate in the search for a global solution, but they continuously move their position away from the search area. Therefore, it is possible in classical PSO for particles to be used for local solutions. In the new PSO, the focus is to update the particle positions in such a way that they cannot stop before obtaining the neither solution nor move away from the search area.
- In classical PSO, constriction factors C1 and C2 are taken as constant values (C1 = C2 = 2.1), as shown in Equations (10) and (11). Therefore, a constant value is not very effective, and hence it cannot help the particles to come back if they move away from the search area. In the new PSO, the values of C1 and C2 are defined in such a way that they help to move the particles into the search area towards the global solution of the problem and cannot allow them to move away from the search area. The values of C1 and C2 are shown in Equations (12) and (13).
- In classical PSO, the weight of inertia is considered, which depends on the number of iterations and the minimum and maximum values of the inertia weight. In the new PSO, inertia weight is defined between the particle position mean and minimum value; this helps particles move continuously until they obtain the global solution to the problem.
2. PSO in the Literature
3. Economic Emission Load Dispatch Model
3.1. Real Power Balance
3.2. Generation Capacity Limits
3.3. Combined Economic Emission Dispatch (CEED)
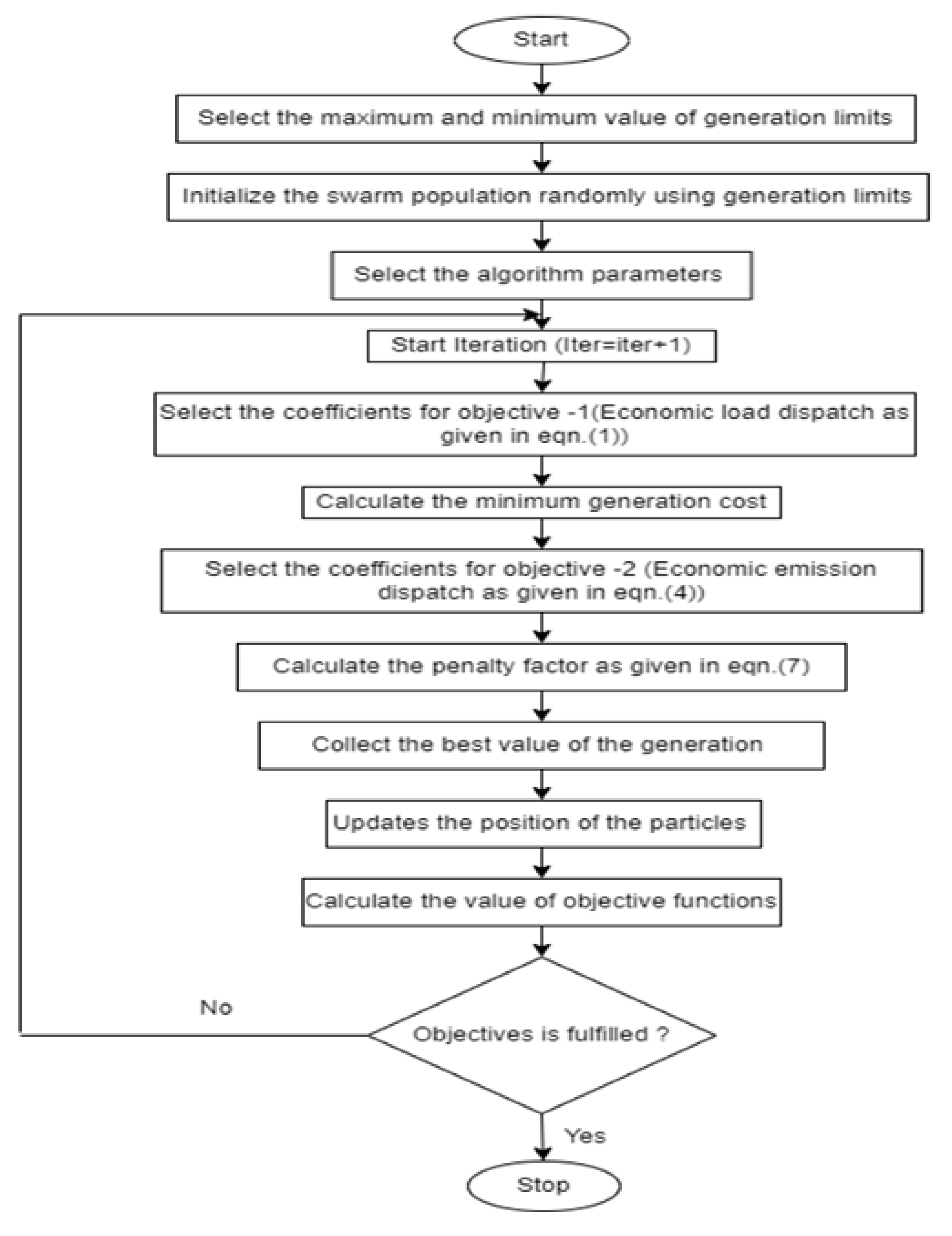
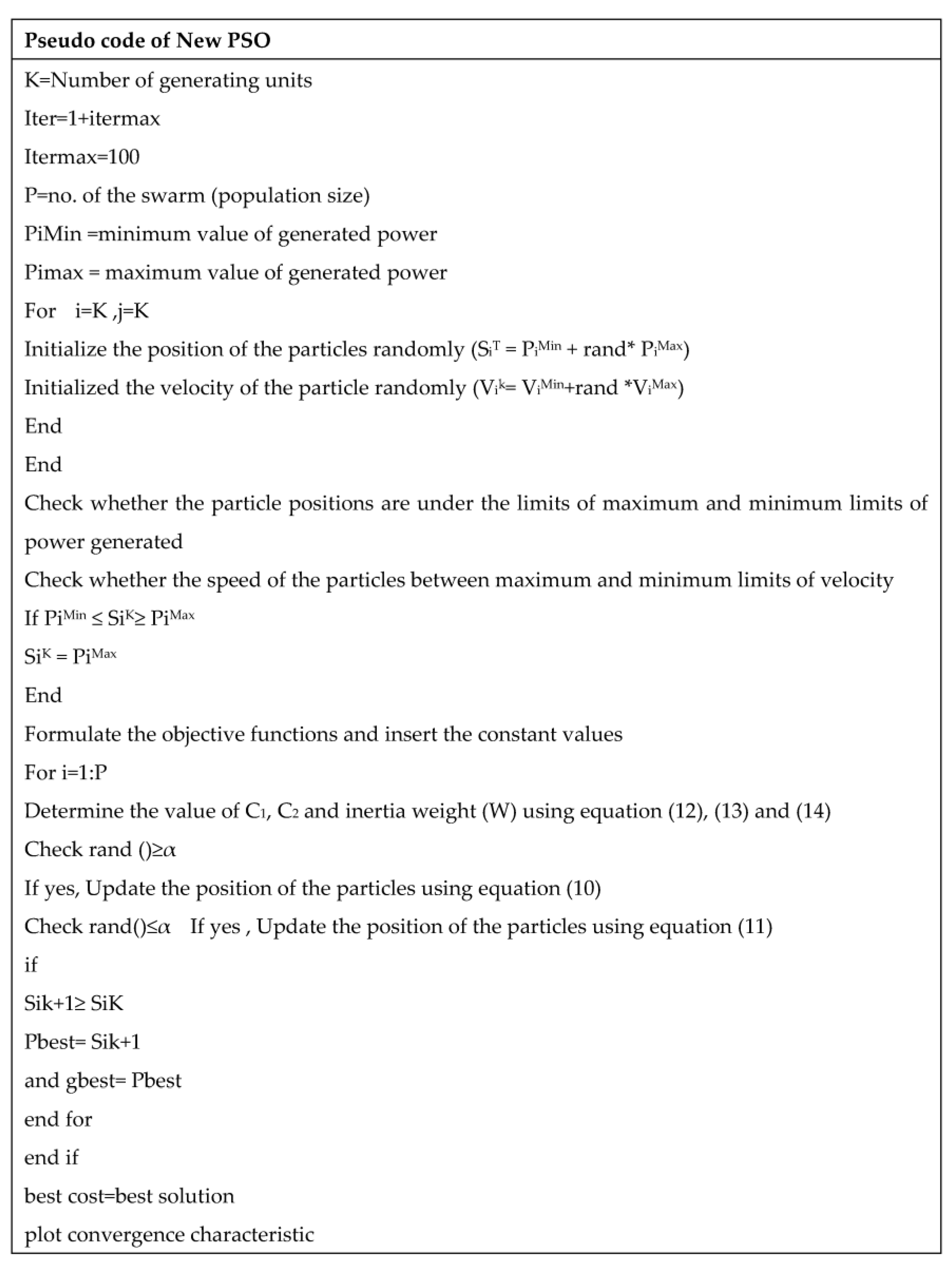
4. Modified PSO (Modified Particle Swarm Optimization)
- First, initiate the particle positions with the help of the maximum and minimum limits of generated power, as given in Equation (8).
- 2
- Take the set of data cost coefficients (a, b, and c) and emission coefficients (c, d, e, and f) from Table 1.
- 3
- Then, initiate the velocity of the particles using the particle positions, as given by Equation (9).
- 4.
- Set the number of iterations (iteration = 1 + maximum iteration).
- 5.
- Define the initial particle best and global best values.
- 6.
- After completion of iterations, select the Pbest and Gbest from the swarm. Then, the updating of the position of the particle is given as in Equation (11) when rand () ≥ α:
- 7.
- Select the weight of inertia, which helps the movement of particles until they reach the solution. In this new PSO, a modified inertia weight is used, as given in Equation (14). Here, the inertia weight does not depend on the number of iterations, and its value always follows the position of the particles. Therefore, it always tries to move the particles in such a way that they can reach the solution as soon as possible and cannot move away from the search space.
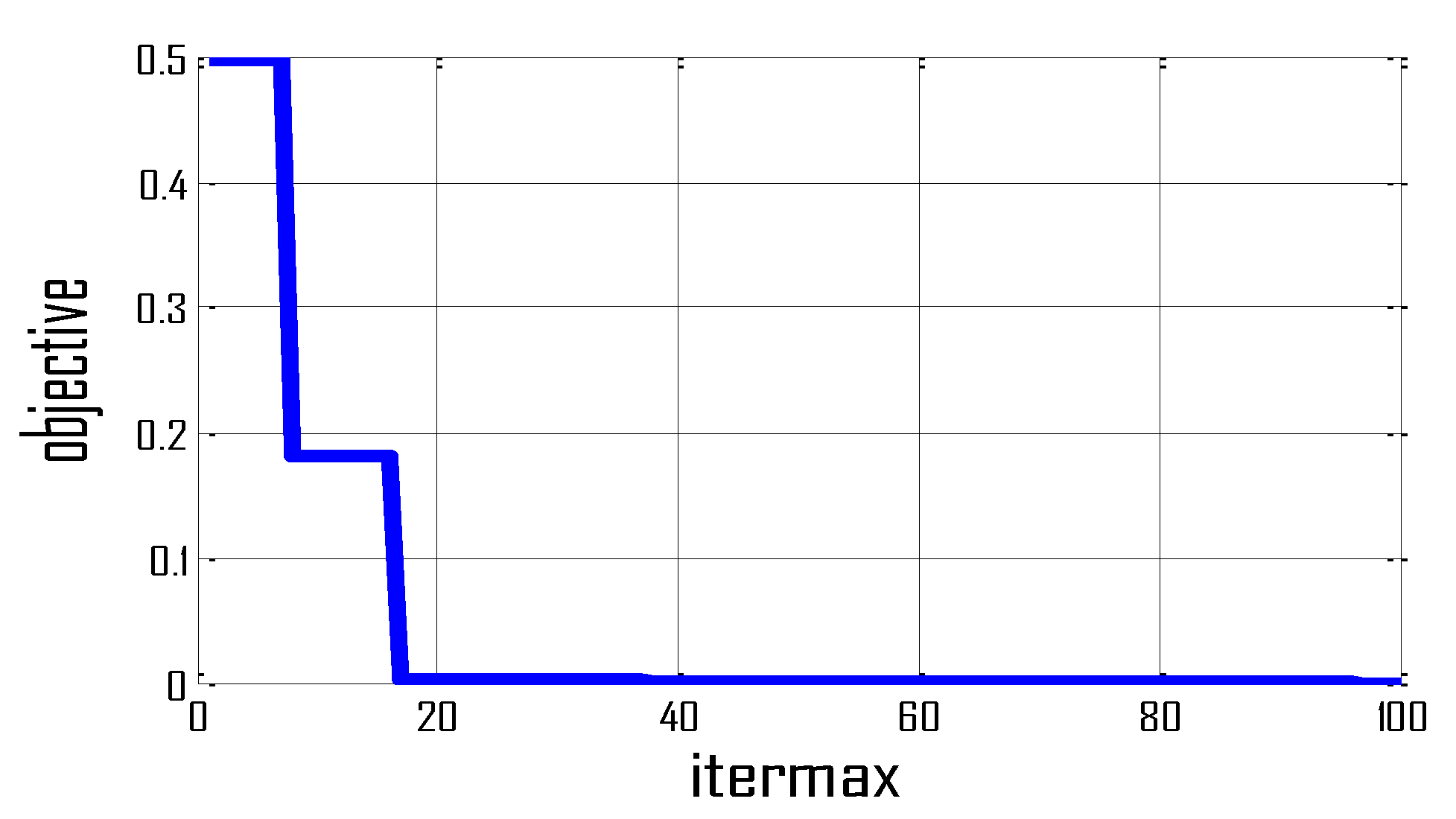
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Case 1
5.2. Case 2
5.3. Case 3
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Singh, N.; Chakrabarti, T.; Chakrabarti, P.; Margala, M.; Gupta, A.; Praveen, S.P.; Krishnan, S.B.; Unhelkar, B. Novel Heuristic Optimization Technique to Solve Economic Load Dispatch and Economic Emission Load Dispatch Problems. Electronics 2023, 12, 2921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajarathinam, V.; Radhakrishnan, A. Water Evaporation algorithm to solve combined Economic and Emission dispatch problems. Glob. J. Pure Appl. Math. 2017, 13, 1049–1067. [Google Scholar]
- Nagarajan, K.; Rajagopalan, A.; Angalaeswari, S.; Natrayan, L.; Mammo, W.D. Combined Economic Emission Dispatch of Microgrid with the Incorporation of Renewable Energy Sources Using Improved Mayfly Optimization Algorithm. Comput. Intell. Neurosci. 2022, 2022, 6461690. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nanda, J.; Hari, L.; Kothari, M. Economic emission load dispatch with line flow constraints using a classical technique. IEE Proc.-Gener. Transm. Distrib. 1994, 141, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Singh, C. Stochastic economic emission load dispatch through a modified particle swarm optimization algorithm. Electr. Power Syst. Res. 2008, 78, 1466–1476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Freitas, C.A.O.; de Oliveira, R.C.L.; Da Silva, D.J.A.; Leite, J.C.; Junior, J.D.A.B. Solution to Economic–Emission Load Dispatch by Cultural Algorithm Combined with Local Search: Case Study. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 64023–64040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ellahi, M.; Abbas, G.; Satrya, G.B.; Usman, M.R.; Gu, J. A Modified Hybrid Particle Swarm Optimization with Bat Algorithm Parameter Inspired Acceleration Coefficients for Solving Eco-Friendly and Economic Dispatch Problems. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 82169–82187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Xu, W. A New Particle Swarm Algorithm and Its Globally Convergent Modifications. IEEE Trans. Syst. Man Cybern. Part B (Cybernetics) 2011, 41, 1334–1351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Satish, K.K. Economic load dispatch with emission constraints using various PSO algorithms. WSEAS Trans. Power Syst. 2008, 9, 598–608. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, X.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S. Multi-objective optimal dispatch of microgrid containing electric vehicles. J. Clean. Prod. 2017, 165, 1572–1581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivedi, I.N.; Jangir, P.; Bhoye, M.; Jangir, N. An economic load dispatch and multiple environmental dispatch problem solution with microgrids using interior search algorithm. Neural Comput. Appl. 2016, 30, 2173–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Y.; Li, B.; Wang, H.; Wang, X.; Negnevitsky, M. Multi-objective optimal scheduling of microgrid with electric vehicles. Energy Rep. 2022, 8, 4512–4524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, N.; Kumar, Y. Multiobjective Economic Load Dispatch Problem Solved by New PSO. Adv. Electr. Eng. 2015, 2015, 536040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Ma, X.; Xu, M.; Bian, X. Research on scheduling optimization of grid-connected micro-grid based on improved brid swarm algorithm. Adv. Technol. Electr. Eng. Energy 2018, 37, 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, X.G.; Zhang, Z.Q.; Xie, Y.M.; Meng, J. Economic-environmental dispatch of microgrid based on improved quantum particle swarm optimization. Energy 2020, 195, 32–39. [Google Scholar]
- Mohsenizadeh, M.; Tural, M.K.; Kentel, E. Municipal solid waste management with cost minimization and emission control objectives: A case study of Ankara. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 52, 101807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoroa, K.O.; Daramola, M.O. CO2 emission sources, greenhouse gases, and the global warming effect. In Advances in Carbon Capture; Woodhead Publishing: Sawston, UK, 2020; pp. 1–26. [Google Scholar]
- Gherbi, Y.A.; Bouzeboudja, H.; Gherbi, F.Z. The combined economic environmental dispatch using new hybrid metaheuristic. Energy 2016, 115, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basetti, V.; Rangarajan, S.S.; Shiva, C.K.; Pulluri, H.; Kumar, R.; Collins, R.E.; Senjyu, T. Economic Emission Load Dispatch Problem with Valve-Point Loading Using a Novel Quasi-Oppositional-Based Political Optimizer. Electronics 2021, 10, 2596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, D.; Jain, N.; Nangia, U. Multi area Economic Emission load dispatch using perfectly convergent Particle swarm optimization. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE Delhi Section Conference (DELCON), New Delhi, India, 11–13 February 2022; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.-F.; Li, L.-L.; Liu, Y.-W.; Liu, J.-Q.; Li, H.-Y.; Shen, Q. Dynamic economic emission dispatch considering renewable energy generation: A novel multi-objective optimization approach. Energy 2021, 235, 121407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balamurugan, R.; Subramanian, S. A Simplified Recursive Approach to Combined Economic Emission Dispatch. Electr. Power Compon. Syst. 2007, 36, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karthikeyan, R. Combined economic emission dispatch using grasshopper optimization algorithm. Mater. Today Proc. 2020, 33, 3378–3382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, L.; Ouyang, H.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Mohamed, A.W. A constrained cooperative adaptive multi-population differential evolutionary algorithm for economic load dispatch problems. Appl. Soft Comput. 2022, 121, 108719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Li, H.; Zhou, K.; Yang, S. Optimal load dispatch of energy hub considering uncertainties of renewable energy and demand response. Energy 2023, 262, 285–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Xu, T.; Xu, H.; Gao, G.; Zhang, Y.; Zhu, K. Robust multi-objective load dispatch in microgrid involving unstable renewable generation. Int. J. Electr. Power Energy Syst. 2023, 148, 137–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.-Y.; Hao, W.-K.; Wang, J.-S.; Zhu, J.-H.; Zhao, X.-R.; Zheng, Y. Manta ray foraging optimization algorithm with mathematical spiral foraging strategies for solving economic load dispatching problems in power systems. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 70, 613–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tai, T.-C.; Lee, C.-C.; Kuo, C.-C. A Hybrid Grey Wolf Optimization Algorithm Using Robust Learning Mechanism for Large Scale Economic Load Dispatch with Vale-Point Effect. Appl. Sci. 2023, 13, 2727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassan, M.H.; Kamel, S.; Eid, A.; Nasrat, L.; Jurado, F.; Elnaggar, M.F. A developed eagle-strategy supply-demand optimizer for solving economic load dispatch problems. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2023, 14, 32–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srivastava, A.; Das, D.K. A New Aggrandized Class Topper Optimization Algorithm to Solve Economic Load Dispatch Problem in a Power System. IEEE Trans. Cybern. 2020, 52, 4187–4197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholamghasemi, M.; Akbari, E.; Asadpoor, M.B.; Ghasemi, M. A new solution to the non-convex economic load dispatch problems using phasor particle swarm optimization. Appl. Soft Comput. 2019, 79, 111–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reddy, M.S.; Subramanyam, P.S. A Meta-Heuristic Approach of Bat Algorithm to Evaluate the Combined EED Problem. Int. J. Eng. Res.Technol. 2014, 3, 35–44. [Google Scholar]
- Said, M.; Houssein, E.H.; Deb, S.; Ghoniem, R.M.; Elsayed, A.G. Economic Load Dispatch Problem Based on Search and Rescue Optimization Algorithm. IEEE Access 2022, 10, 47109–47123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hao, W.-K.; Wang, J.-S.; Li, X.-D.; Wang, M.; Zhang, M. Arithmetic optimization algorithm based on elementary function disturbance for solving economic load dispatch problem in power system. Appl. Intell. 2022, 52, 11846–11872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, B.; Wang, F.; Chang, Y. Multi-objective economic load dispatch method based on data mining technology for large coal-fired power plants. Control. Eng. Pract. 2021, 121, 105018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Betar, M.A.; Awadallah, M.A.; Makhadmeh, S.N.; Abu Doush, I.; Abu Zitar, R.; Alshathri, S.; Elaziz, M.A. A hybrid Harris Hawks optimizer for economic load dispatch problems. Alex. Eng. J. 2023, 64, 365–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Said, M.; El-Rifaie, A.M.; Tolba, M.A.; Houssein, E.H.; Deb, S. An Efficient Chameleon Swarm Algorithm for Economic Load Dispatch Problem. Mathematics 2021, 9, 2770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandi, V.R.; Panigrahi, B.; Mohapatra, A.; Mallick, M.K. Economic load dispatch solution by improved harmony search with wavelet mutation. Int. J. Comput. Sci. Eng. 2011, 6, 122–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Gen. Unit | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.1525 | 38.54 | 756.8 | 0.0042 | 0.33 | 13.86 | 10 | 125 |
| 2 | 0.106 | 46.16 | 451.32 | 0.004 | 0.33 | 13.86 | 10 | 150 |
| 3 | 0.0208 | 40.159 | 1049.99 | 0.00683 | −0.5455 | 40.27 | 35 | 225 |
| 4 | 0.0355 | 38.31 | 1234.5 | 0.0068 | −0.5455 | 40.27 | 35 | 210 |
| 5 | 0.0211 | 36.328 | 1658.6 | 0.0046 | −0.5112 | 42.7 | 130 | 325 |
| 6 | 0.0179 | 38.27 | 1356.7 | 0.0042 | −0.5112 | 42.7 | 125 | 315 |
| Output Power | WEO [2] | FA [18] | BA [18] | DE [22] | GOA [23] | PSO [9] | New PSO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 (MW) | 62.0893 | 62.1127 | 62.1032 | 43.446 | 56.24 | 62.0205 | 41.43 |
| P2 (MW) | 61.6638 | 61.6689 | 61.6698 | 42.426 | 58.57 | 61.62 | 43.65 |
| P3 (MW) | 119.9716 | 119.9746 | 119.9712 | 123.758 | 151.72 | 120.48 | 121.511 |
| P4 (MW) | 119.4758 | 119.4606 | 119.4756 | 117.855 | 136.97 | 119.67 | 119.12 |
| P5 (MW) | 178.1915 | 178.1913 | 178.1929 | 189.36 | 171.50 | 178.16 | 185.73 |
| P6 (MW) | 175.6549 | 175.6480 | 175.6432 | 183.148 | 125.00 | 175.57 | 188.56 |
| Power output (MW) | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 | 700 |
| Fuel cost ($/h) | 37,500.17 | 37,500.93 | 37,500.84 | 36,313.9 | 36,837.05 | 37,500 | 36,144.84 |
| Emission (tons/h) | 439.60 | 439.61 | 439.61 | 434.38 | 443.11 | 439.635 | 424.242 |
| Total EED cost ($/h) | 57,189.11 | 57,190.01 | 57,190.01 | 57,128.3 | 57,127.33 | 57,190 | 56,534.84 |
| Computation time(s) | 11.4 | 7.14 | 4.7 | 2.01 | 5.47 | 1.838 | 1.710 |
| Gen. Units | Price Penalty Factor (h) Using Equation (6) |
|---|---|
| 1 | 65.95 |
| 2 | 61.85 |
| 3 | 42.47 |
| 4 | 47.89 |
| 5 | 43.27 |
| 6 | 44.93 |
| Output Power | WEO [2] | FA [18] | BA [18] | DE [22] | GOA [23] | PSO [22] | New PSO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 (MW) | 76.5712 | 76.5733 | 76.5756 | 55.170 | 55.17 | 55.17 | 52.53 |
| P2 (MW) | 79.2635 | 79.2629 | 79.2678 | 56.189 | 56.19 | 56.89 | 55.22 |
| P3 (MW) | 135.2372 | 135.2268 | 135.225 | 139.112 | 139.11 | 139.52 | 142.11 |
| P4 (MW) | 134.1532 | 134.1554 | 134.153 | 131.751 | 131.76 | 131.751 | 131.51 |
| P5 (MW) | 199.7063 | 199.7071 | 199.710 | 212.225 | 212.22 | 212.225 | 210.78 |
| P6 (MW) | 197.2528 | 197.2628 | 197.256 | 205.552 | 205.55 | 205.52 | 207.85 |
| Power output | 800 MW | 800 MW | 800 MW | 800 MW | 800 MW | 800 MW | 800 MW |
| Fuel cost ($/h) | 42,784.22 | 42,784.41 | 42,784.52 | 41,152.6 | 41,147.85 | 41,160.3 | 40,932 |
| Emission (ton/h) | 557.19 | 557.20 | 557.20 | 547.802 | 547.78 | 547.844 | 526.226 |
| Total EED cost ($/h) Equation (7) | 67,739.85 | 67,740.26 | 67,740.26 | 67,064.47 | 67,389.75 | 67,412.23 | 66,773.2 |
| Output Power | WEO [2] | FA [18] | BA [18] | PSO [22] | DE [22] | Grasshopper Optimization Algorithm [23] | New PSO |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P1 (MW) | 107.1622 | 107.1685 | 107.1631 | 78.45 | 78.617 | 82.53 | 81.2 |
| P2 (MW) | 116.5485 | 116.5498 | 116.5483 | 83.97 | 83.716 | 97.40 | 92.93 |
| P3 (MW) | 165.6537 | 165.6550 | 165.6599 | 169.32 | 169.820 | 206.35 | 171.4 |
| P4 (MW) | 163.4009 | 163.4014 | 163.4001 | 159.74 | 159.542 | 181.20 | 161.84 |
| P5 (MW) | 242.0415 | 242.0380 | 242.0355 | 257.744 | 257.944 | 219.08 | 239.26 |
| P6 (MW) | 239.7982 | 239.7979 | 239.8036 | 250.56 | 250.361 | 213.44 | 253.37 |
| Power output | 1000 MW | 1000 MW | 1000 MW | 1000 MW | 1000 MW | 1000 MW | 1000 MW |
| Fuel cost ($/h) | 54,123.83 | 54,124.28 | 54,124.12 | 51,269.6 | 51,264.5 | 51,833.81 | 51,225.22 |
| Emission (tons/h) | 851.52 | 851.53 | 851.53 | 828.863 | 828.715 | 834.79 | 785.136 |
| Total EED cost ($/h) | 94,845.59 | 94,846.36 | 94,846.36 | 91,285.4 | 91,271.05 | 90,934.41 | 90,204.88 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Singh, N.; Chakrabarti, T.; Chakrabarti, P.; Margala, M.; Gupta, A.; Krishnan, S.B.; Unhelkar, B. A New PSO Technique Used for the Optimization of Multiobjective Economic Emission Dispatch. Electronics 2023, 12, 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132960
Singh N, Chakrabarti T, Chakrabarti P, Margala M, Gupta A, Krishnan SB, Unhelkar B. A New PSO Technique Used for the Optimization of Multiobjective Economic Emission Dispatch. Electronics. 2023; 12(13):2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132960
Chicago/Turabian StyleSingh, Nagendra, Tulika Chakrabarti, Prasun Chakrabarti, Martin Margala, Amit Gupta, Sivaneasan Bala Krishnan, and Bhuvan Unhelkar. 2023. "A New PSO Technique Used for the Optimization of Multiobjective Economic Emission Dispatch" Electronics 12, no. 13: 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132960
APA StyleSingh, N., Chakrabarti, T., Chakrabarti, P., Margala, M., Gupta, A., Krishnan, S. B., & Unhelkar, B. (2023). A New PSO Technique Used for the Optimization of Multiobjective Economic Emission Dispatch. Electronics, 12(13), 2960. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12132960










