Ensemble Prediction Model for Dust Collection Efficiency of Wet Electrostatic Precipitator
Abstract
1. Introduction
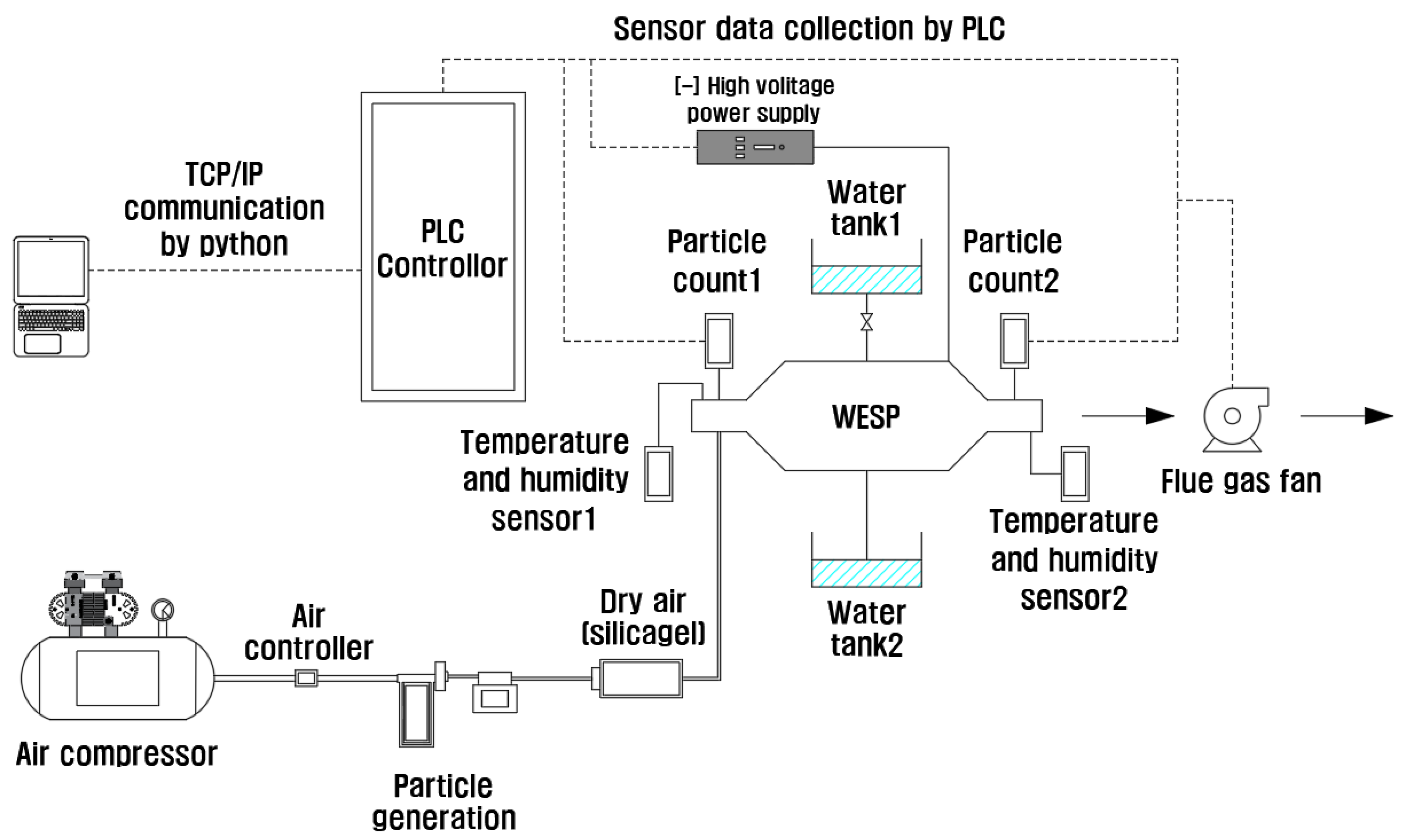
- We collected various sensor data, such as OPC, temperature, humidity, ozone, and applied voltage, in a laboratory-scale WESP in real time on a PC server through a programmable logic controller (PLC).
- A novel method for forecasting the PM collection effectiveness of WESP, which involves utilizing an ensemble model that integrates multiple nonlinear data obtained during the WESP PM collection, proposes a new approach.
- The model proposed in this paper was intended to contribute to efficient WESP design and operation by predicting the PM dust collection efficiency of WESP.
2. Principles and Structure of Electrostatic Spray-Based WESP
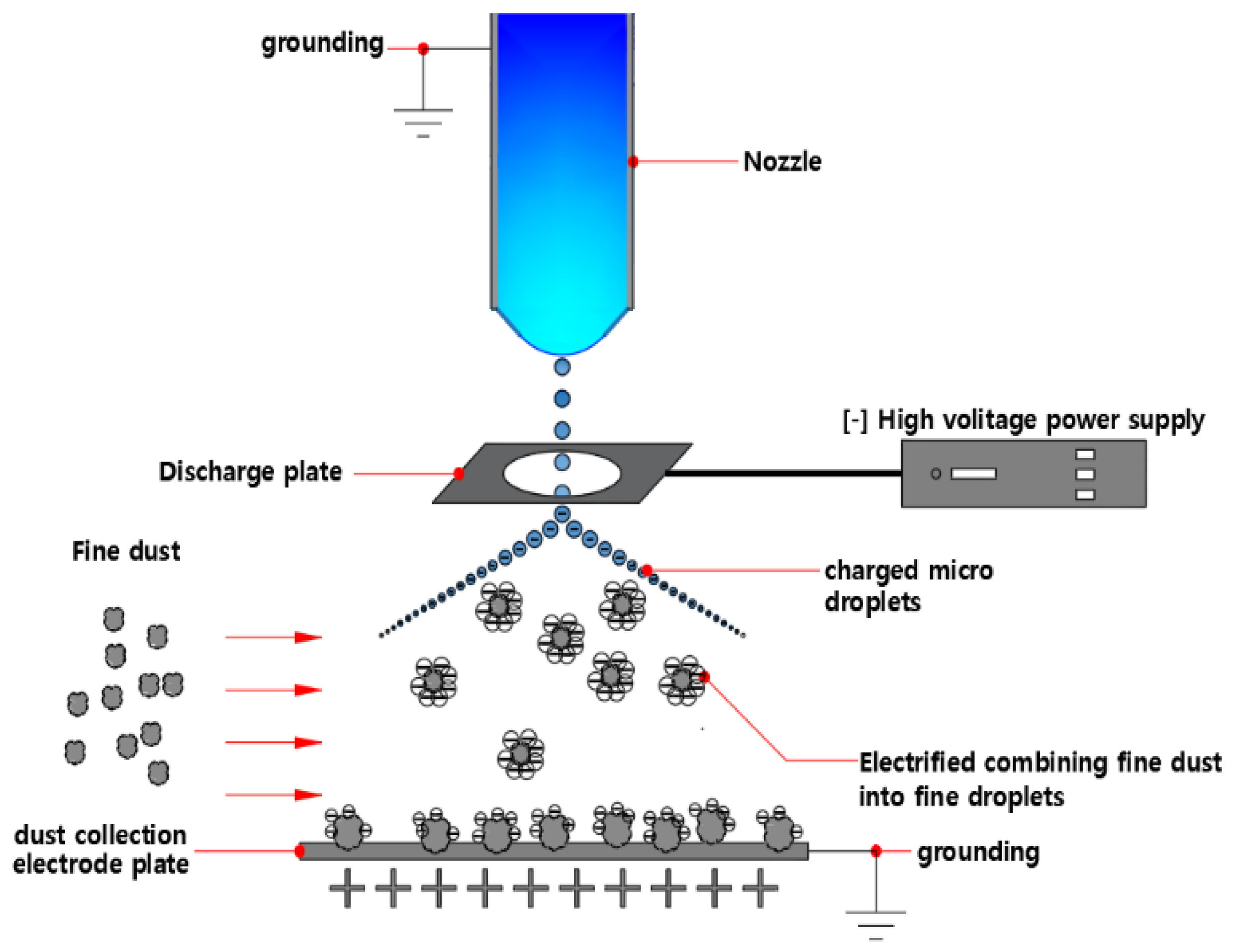
2.1. Direct-Charging Electrostatic Spray ESP
2.2. Electrostatic Spray-Based WESP System
2.3. PM Generation Device
2.4. Electrostatic Spray-Based WESP Device
3. Principles of the Predictive Analysis Technique Based on the Ensemble Model
3.1. kNN (K-Nearest Neighbor)
3.2. DT(Decision Tree)
3.3. RF(Random Forest)
3.4. K-Fold Cross-Validation
3.5. Model Performance Evaluation Metrics
3.5.1. R2 Score
3.5.2. MSE
3.5.3. MAE
4. Experiments and Results
4.1. PLC-Based Dust Collection System Control Device and Real-Time Data Collection and Preprocessing
4.2. Dust Collector Experimental Results
4.3. Experimental Results of Dust Collection Efficiency Prediction Models
4.3.1. kNN Model Prediction Results
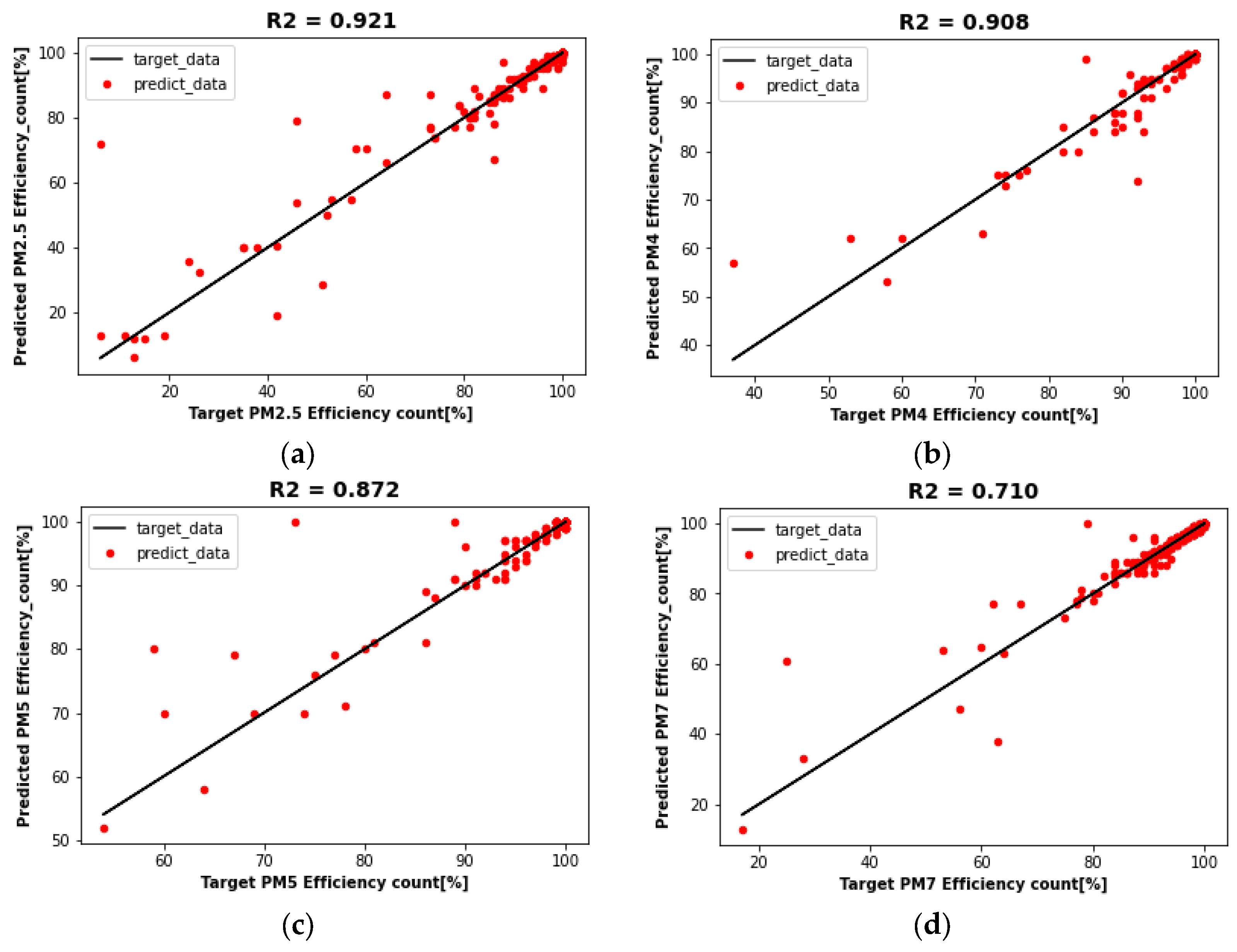
4.3.2. DT Model Prediction Results
4.3.3. RF Model Prediction Results
5. Discussion and Comparison with Similar Works
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Santibáñez-Andrade, M.; Chirino, Y.I.; González-Ramírez, I.; Sánchez-Pérez, Y.; García-Cuellar, C.M. Deciphering the code between air pollution and disease: The effect of particulate matter on cancer hallmarks. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 21, 136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carotenuto, C.; Di Natale, F.; Lancia, A. Wet electrostatic scrubbers for the abatement of submicronic particulate. Chem. Eng. J. 2010, 165, 35–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ritz, B.; Hoffmann, B.; Peters, A. The effects of fine dust, ozone, and nitrogen dioxide on health. Dtsch. Ärztebl. Int. 2019, 51–52, 881–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, Y.; Gao, M.; Chen, M.; Shi, J.; Shangguan, W. Numerical simulation of capture process of fine particles in electrostatic precipitators under consideration of electrohydrodynamics flow. Powder Technol. 2019, 354, 653–675. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, X.; Zheng, C.; Yan, P.; Zhu, W.; Wang, Y.; Gao, X.; Luo, Z.; Ni, M.; Cen, K.; Ni, M.; et al. Effect of electrode configuration on particle collection in a high-temperature electrostatic precipitator. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2016, 166, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaworek, A.; Sobczyk, A.T.; Krupa, A.; Marchewicz, A.; Czech, T.; Śliwiński, L. Hybrid electrostatic filtration systems for fly ash particles emission control. A review. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2019, 213, 283–302. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.F.; Kang, Y.M.; Zhong, K. Effects of geometric parameters and electric indexes on the performance of laboratory-scale electrostatic precipitators. J. Hazard. Mater. 2009, 169, 941–947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sobczyk, A.T.; Marchewicz, A.; Krupa, A.; Jaworek, A.; Czech, T.; Kluk, D.; Charchalis, A. Enhancement of collection efficiency for fly ash particles (PM 2.5) by unipolar agglomerator in two-stage electrostatic precipitator. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2017, 187, 91–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, C.; Fan, X.; Li, J. Effect of charged water drop atomization on particle removal performance in plate type wet electrostatic precipitator. J. Electrostat. 2020, 104, 103426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; You, C. Effects of thermophoresis, vapor, and water film on particle removal of electrostatic precipitator. J. Aerosol. Sci. 2013, 63, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Wei, Z.; Yang, X.; Tao, S.; Zhang, Y.; Shangguan, W. Comprehensive control of PM 2.5 capture and ozone emission in two-stage electrostatic precipitators. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 858, 159900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Du, Q.; Wang, Y.; Dong, H.; Gao, J.; Wang, M.; Dong, P. Purification characteristics of fine particulate matter treated by a self-flushing wet electrostatic precipitator equipped with a flexible electrode. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2018, 68, 725–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, H.; Pan, D.; Jiang, Y.; Huang, R.; Hong, G.; Yang, B.; Peng, Z.; Yang, L.; Yang, L. Improving the removal of fine particles from desulfurized flue gas by adding humid air. Fuel 2016, 184, 153–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, C.; Chang, J.; Meng, Z.; Wang, X.; Zhang, J.; Cui, L.; Ma, C. Wetting properties and performance test of modified rigid collector in wet electrostatic precipitators. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2016, 66, 1019–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Gu, C.; Zhang, D.; Zeng, F. Removal characteristics of sulfuric acid aerosols in the wet electrostatic precipitator system. Energy Fuels 2019, 33, 7813–7818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, T.; Xie, Y.; Su, S.; Wang, L.; Song, Y.; Chen, Y.; Xiang, J. Synergistic Removal Effects of Ultralow Emission Air Pollution Control Devices on Trace Elements in a Coal-Fired Power Plant. Energy Fuels 2022, 36, 2474–2487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bozdağ, A.; Dokuz, Y.; Gökçek, Ö.B. Spatial prediction of PM10 concentration using machine learning algorithms in Ankara, Turkey. Environ. Pollut. 2020, 263, 114635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, B.Y.; Lim, Y.K.; Cha, J.W. Short-term prediction of particulate matter. In Seoul, South Korea using tree-based machine learning algorithms. Atmos. Pollut. Res. 2022, 13, 101547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iskandaryan, D.; Ramos, F.; Trilles, S. Air quality prediction in smart cities using machine learning technologies based on sensor data: A review. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 2401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, G.; Lee, H.; Lee, G. A hybrid deep learning model to forecast particulate matter concentration levels in Seoul, South Korea. Atmosphere. 2020, 11, 348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waseem, K.H.; Mushtaq, H.; Abid, F.; Abu-Mahfouz, A.M.; Shaikh, A.; Turan, M.; Rasheed, J. Forecasting of air quality using an optimized recurrent neural network. Processes 2022, 10, 2117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Zheng, C.; Xu, Z.; Yang, Z.; Weng, W.; Wang, Y.; Lu, J.; Gao, X.; Gao, X. Hybrid modeling scheme for PM concentration prediction of electrostatic precipitators. Powder Technol. 2018, 340, 163–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wu, X.; Jiao, W.; Qi, G.; Liu, Y. Modelling of dust removal in rotating packed bed using artificial neural networks (ANN). Appl. Therm. Eng. 2017, 112, 208–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Cai, Y.; Li, Q.; Li, H.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, R.; Zheng, C.; Sun, D.; Gao, X.; Sun, D.; et al. Predicting particle collection performance of a wet electrostatic precipitator under varied conditions with artificial neural networks. Powder Technol. 2021, 377, 632–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, J.; Jeong, K.; Jung, H. Examining microdroplet characteristics of electrospray electric precipitation for direct and indirect voltage application methods. Int. J. Fire Sci. Eng. 2022, 36, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, J.R.; Ali, R.S. Personal computer/programmable logic controller based variable frequency drive training platform using wxPython and PyModbus. Int. J. Electr. Comput. Eng. 2022, 12, 2088–8708. [Google Scholar]
- Teng, C.; Li, J. Experimental study on particle removal of a wet electrostatic precipitator with atomization of charged water drops. Energy Fuels 2020, 34, 7257–7268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Jung, M.; Choi, S.; Lee, J.; Lim, J.; Kim, M. Discharge current of water electrospray with electrical conductivity under high-voltage and high-flow-rate conditions. Exp. Therm. Fluid Sci. 2020, 118, 110151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hackeling, G. Mastering Machine Learning with Scikit-Learn; Packt Publishing Ltd.: Birmingham, UK, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Aldrich, C.; Auret, L. Fault detection and diagnosis with random forest feature extraction and variable importance methods. IFAC Proc. Vol. 2010, 43, 79–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathabadi, A.; Seyedian, S.M.; Malekian, A. Comparison of Bayesian, k-Nearest Neighbor and Gaussian process regression methods for quantifying uncertainty of suspended sediment concentration prediction. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 818, 151760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jong-wook, L.; Kim Young-Ho, B.B.-H.; Doo-seong, H. Obesity and metabolic syndrome data classification and feature importance analysis based on decision trees. Korean Inf. Process. Soc. Conf. Proc. 2021, 28, 880–883. [Google Scholar]
- Shoar, S.; Chileshe, N.; Edwards, J.D. Machine learning-aided engineering services’ cost overruns prediction in high-rise residential building projects: Application of random forest regression. J. Build. Eng. 2022, 50, 104102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwak, S.; Kim, J.; Ding, H.; Xu, X.; Chen, R.; Guo, J.; Fu, H. Machine learning prediction of the mechanical properties of γ-TiAl alloys produced using random forest regression model. J. Mater. Res. Technol. 2022, 18, 520–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plocoste, T.; Laventure, S. Forecasting PM10 concentrations in the Caribbean area using machine learning models. Atmosphere 2023, 14, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, M.A.; Khan, R.; Algarni, F.; Kumar, I.; Choudhary, A.; Srivastava, A. Performance evaluation of regression models for COVID-19: A statistical and predictive perspective. Ain Shams Eng. J. 2022, 13, 101574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pattana-Anake, V.; Joseph, F.J.J. Hyper parameter optimization of stack LSTM based regression for PM 2.5 data in Bangkok. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Business and Industrial Research (ICBIR), Bangkok, Thailand, 19–20 May 2022; IEEE Publications: New York, NY, USA, 2022; Volume 2022, pp. 13–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Xia, T.; Wang, D.; Fang, X.; Xi, L. Adversarial regressive domain adaptation approach for infrared thermography-based unsupervised remaining useful life prediction. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 7219–7229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiaochuan, L.; Mingrui, Z.; Yefeng, J.; Li, W.; Xinli, Z.; Xi, C.; Haoyu, B.; Xianming, D.; Xianming, D. Air curtain dust-collecting technology: Investigation of factors affecting dust control performance of air curtains in the developed transshipment system for soybean clearance based on numerical simulation. Powder Technol. 2022, 396, 59–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]












| ML Algorithms | Setting Value | Dataset | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|
| kNN | k = 3 (Euclidean distance) | PM 10 (Caribbean Area) | Plocoste et al. [35]. |
| DT | Tree number ~100 Max depth | PM 10 (Caribbean Area) | Plocoste et al. [35]. |
| RF | num. trees = 390, mtry = 16, min. node size = 4 | PM 10, PM 2.5 (Atmosphere data) | Kim et al. [17]. |
| Input Data | Target Data | |
|---|---|---|
| Inlet Temperature | Outlet Temperature | PM collection efficiency |
| Inlet Humidity | Outlet Humidity | |
| Inlet PM 2.5 | Outlet PM 2.5 | |
| Inlet PM 4 | Outlet PM 4 | |
| Inlet PM 5 | Outlet PM 5 | |
| Inlet PM 7 | Outlet PM 7 | |
| Ozone | Voltage | |
| Item | Value |
|---|---|
| Solution | Tap water |
| Solution flow rate | 10 [mL/min] |
| Nozzle inner diameter | 0.55 [mm] |
| Voltage | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7 kV |
| Measurement time by voltage | 150 min |
| Data storage time unit | 6 s |
| Target: Collection Efficiency | Model | R2-Score | MAE | MSE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Train | Test | Train | Test | Train | Test | ||
| PM 2.5 | kNN | 0.955 | 0.905 | 0.383 | 0.710 | 4.834 | 10.772 |
| DT | 0.998 | 0.921 | 0.046 | 0.460 | 0.173 | 8.887 | |
| RF | 0.993 | 0.942 | 0.120 | 0.380 | 0.741 | 6.548 | |
| PM 4 | kNN | 0.855 | 0.763 | 0.270 | 0.353 | 3.077 | 3.958 |
| DT | 1.0 | 0.908 | 0.0 | 0.194 | 0.0 | 1.536 | |
| RF | 0.978 | 0.936 | 0.073 | 0.154 | 0.466 | 1.066 | |
| PM 5 | kNN | 0.661 | 0.705 | 0.508 | 0.618 | 7.529 | 4.266 |
| DT | 1.0 | 0.872 | 0.0 | 0.205 | 0.0 | 1.850 | |
| RF | 0.972 | 0.944 | 0.075 | 0.613 | 0.154 | 0.815 | |
| PM 7 | kNN | 0.611 | 0.173 | 1.506 | 16.073 | 2.370 | 32.848 |
| DT | 1.0 | 0.710 | 0.0 | 0.412 | 0.0 | 11.500 | |
| RF | 0.982 | 0.956 | 0.109 | 0.747 | 0.246 | 1.748 | |
| Algorithms | Model Evaluation Index | Parameter | Result | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Hybrid model | R2 | Inlet temperature[°C] Inlet concentration (g/m3) Rated migration velocity (ω) | 0.933 | Guo, Yishan, et al. [21]. |
| ANN | R2, MSE | Inlet concentration (kg/m3) Gas flow rate (m3/s) Liquid flow rate (104 m3/s) Rotor speed (rpm) Particle size range (lm) | R2 = 0.962 MSE = 2.87 | Li, Weiwei, et al. [22]. |
| ANN | R2, MSE | gas temperature gas humidity gas velocity particle concentration | R2 = 0.9897 MSE = 0.27 | Yang, Zhengda, et al. [23]. |
| Random forest | R2, MSE, MAE | Inlet Temperature Outlet Temperature Inlet Humidity Outlet Humidity Inlet PM 2.5, 4, 5, 7 Outlet PM 2.5, 4, 5, 7 Ozone Voltage Blower | R2 = 0.956 MSE = 1.74 | RF model [Ours] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Choi, S.; Kim, S.; Jung, H. Ensemble Prediction Model for Dust Collection Efficiency of Wet Electrostatic Precipitator. Electronics 2023, 12, 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122579
Choi S, Kim S, Jung H. Ensemble Prediction Model for Dust Collection Efficiency of Wet Electrostatic Precipitator. Electronics. 2023; 12(12):2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122579
Chicago/Turabian StyleChoi, Sugi, Sunghwan Kim, and Haiyoung Jung. 2023. "Ensemble Prediction Model for Dust Collection Efficiency of Wet Electrostatic Precipitator" Electronics 12, no. 12: 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122579
APA StyleChoi, S., Kim, S., & Jung, H. (2023). Ensemble Prediction Model for Dust Collection Efficiency of Wet Electrostatic Precipitator. Electronics, 12(12), 2579. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12122579








