Real-Time sEMG Pattern Recognition of Multiple-Mode Movements for Artificial Limbs Based on CNN-RNN Algorithm
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Signal Acquisition
2.1.1. Offline Experiment
2.1.2. Online Experiment
2.2. Data Processing
2.2.1. Preprocessing
2.2.2. Segmentation
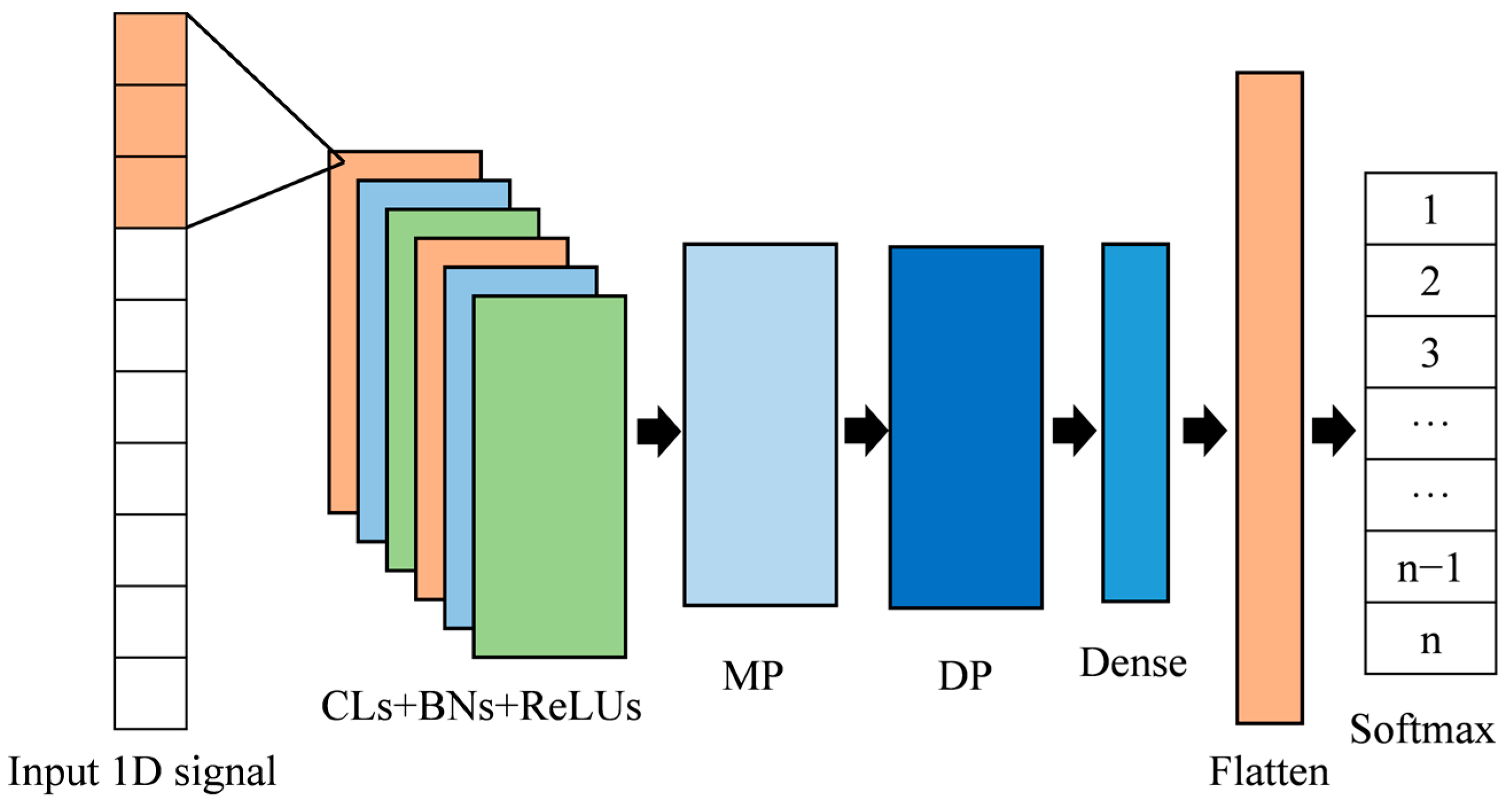
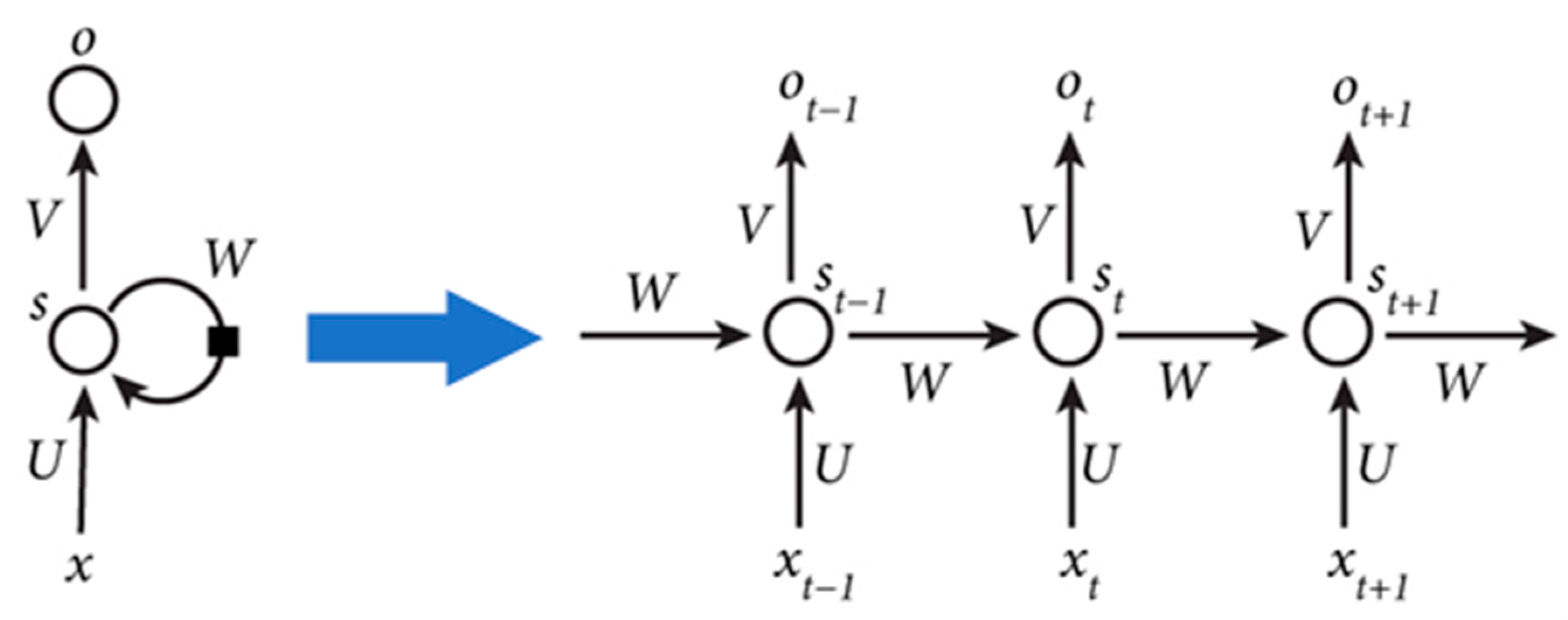
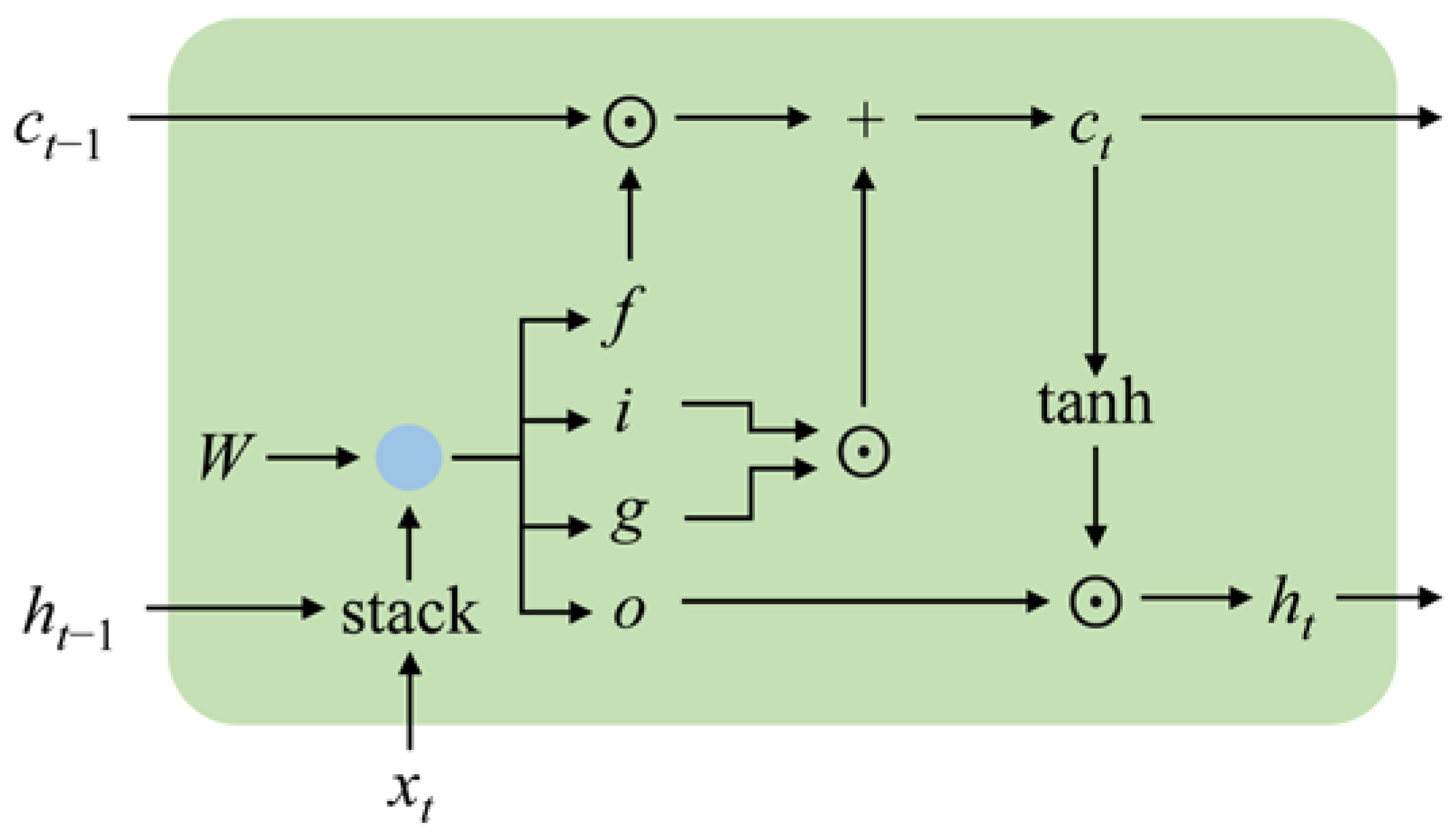
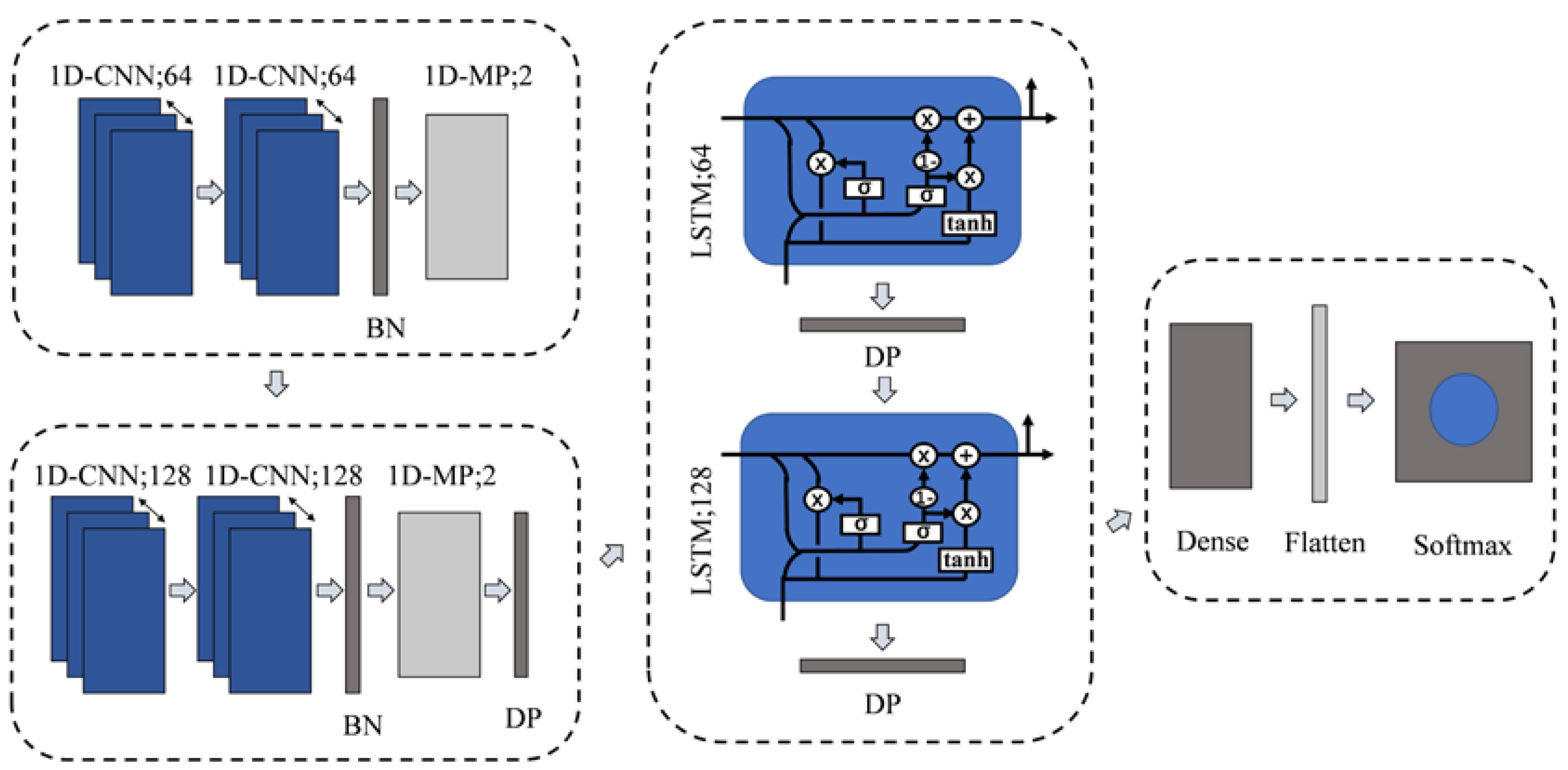
2.3. One-Dimensional CNN-RNN
2.4. Evaluation Metrics
3. Results and Analysis
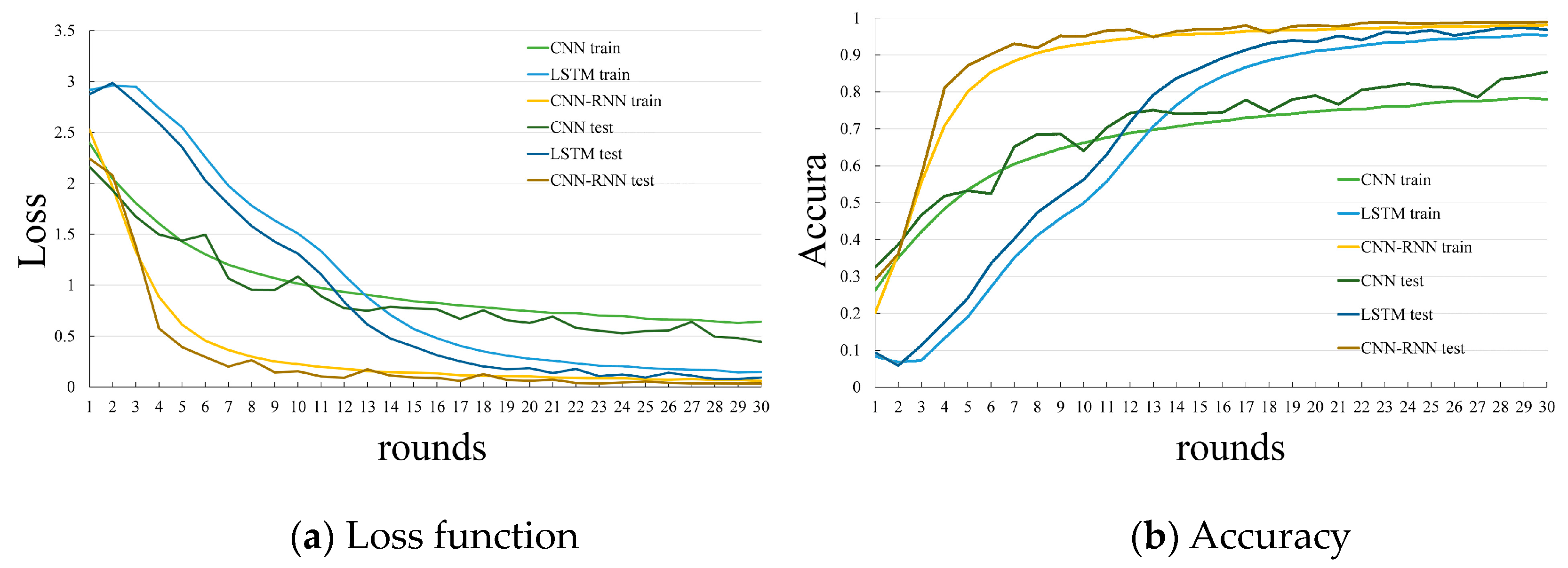
3.1. Offline Result Analysis
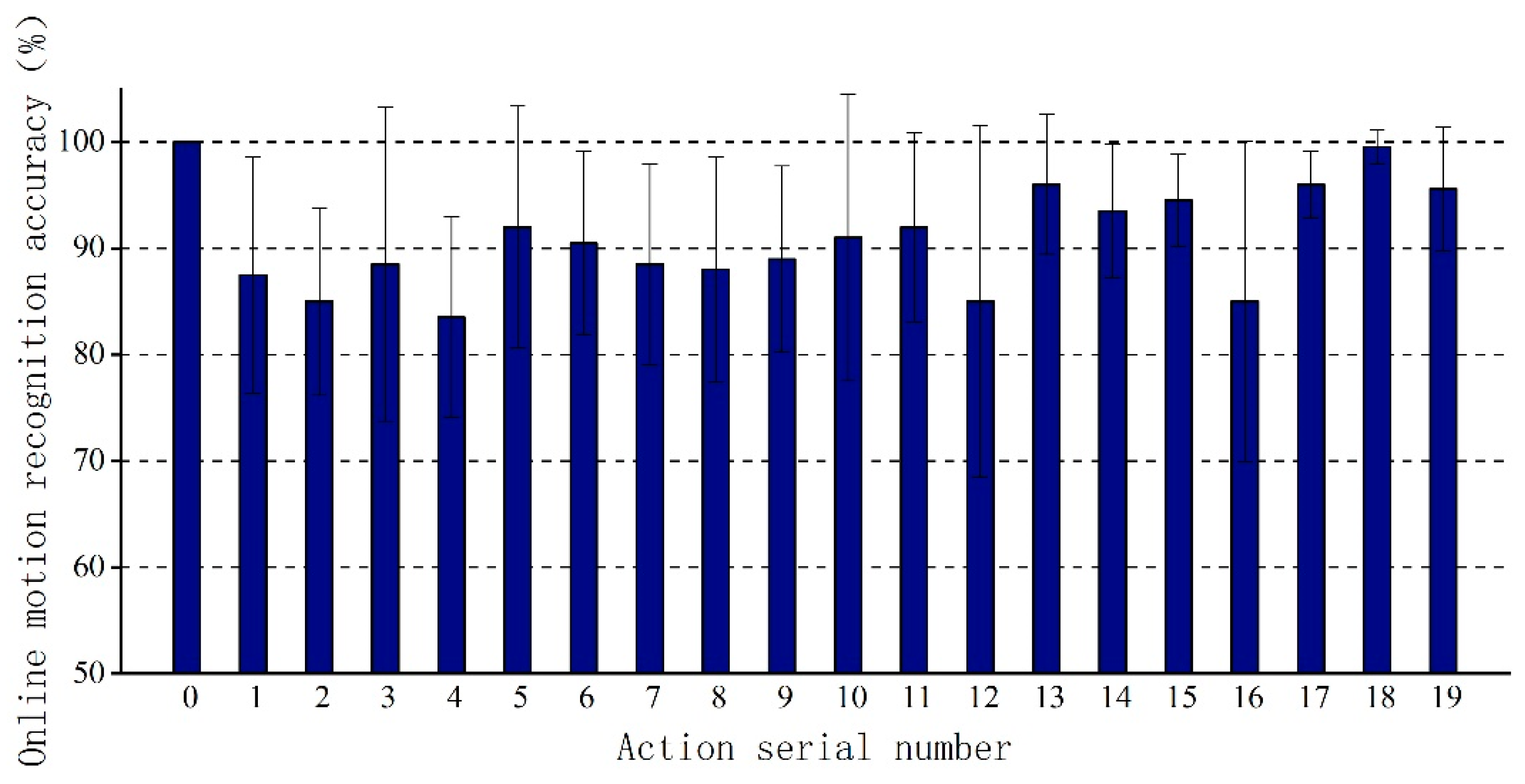
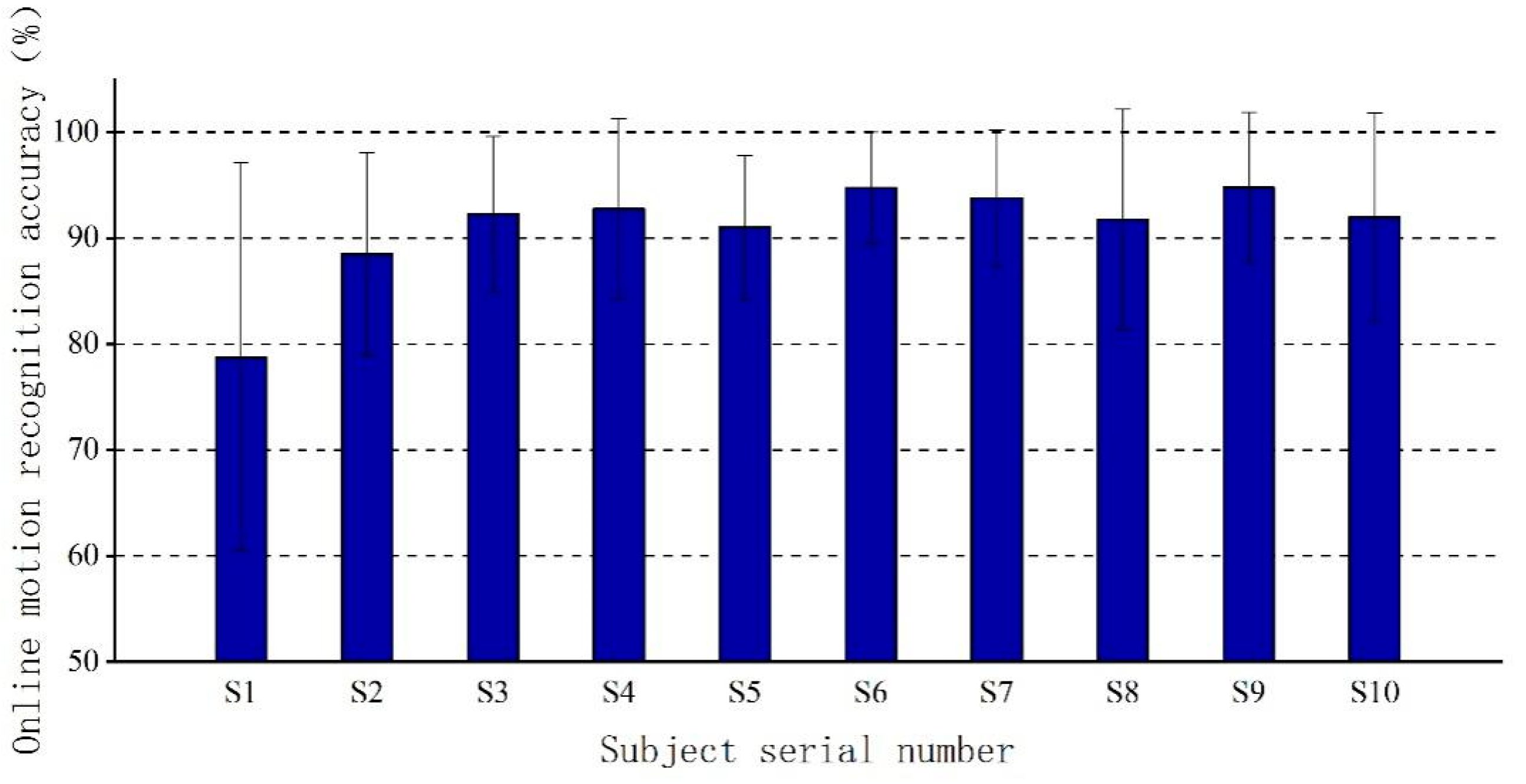
3.2. Online Result Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Scheme, E.; Eenglehart, K. Electromyogram Pattern Recognition for Control of Powered Upper-limb Prostheses: State of the Art and Challenges for Clinical Use. J. Rehabil. Res. Dev. 2011, 48, 643–659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farina, D.; Jiang, N.; Rehbaum, H.; Holobar, A.; Graimann, B.; Dietl, H.; Aszmann, O.C. The Extraction of Neural Information from the Surface EMG for the Control of Upper-Limb Prostheses: Emerging Avenues and Challenges. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2014, 22, 797–809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englehart, K.; Hudgins, B.; Parker, P.A.; Stevenson, M. Classification of the Myoelectric Signal Using Time-frequency Based Representations. Med. Eng. Phys. 1999, 21, 431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Finley, F.R.; Wirta, R.W. Myocoder Studies of Multiple Myopotential Response. Arch. Phys. Med. Rehabil. 1967, 48, 598. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Hudgins, B.; Parker, P. A New Strategy for Multifunction Myoelectric Control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 40, 82–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Englehart, K.; Hudgins, B. A Robust, Real-time Control Scheme for Multifunction Myoelectric Control. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2003, 50, 848–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; He, J.; Sheng, X.; Zhang, D.; Zhu, X. A New Feature Extraction Method Based on Autoregressive Power Spectrum for Improving sEMG Classification. Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2013, 2013, 5746–5749. [Google Scholar]
- Futamata, M.; Nagata, K.; Magatani, K. The Evaluation of The Discriminant Ability of Multiclass SVM in a Study of Hand Motion Recognition by Using SEMG. Int. Conf. IEEE Eng. Med. Biol. Soc. 2012, 2012, 5246–5249. [Google Scholar]
- Purushothaman, G.; Vikas, R. Identification of a Feature Selection Based Pattern Recognition Scheme for Finger Movement Recognition from Multichannel EMG Signals. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2018, 41, 549–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geethanjali, P. A Mechatronics Platform to Study Prosthetic Hand Control Using EMG Signals. Australas. Phys. Eng. Sci. Med. 2016, 39, 765–771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amirabdollahian, F.; Walters, M.L. Application of Support Vector Machines to Detect Hand and Wrist Gestures Using a Myoelectric Armband. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Rehabilitation Robotics, London, UK, 20 February 2017; pp. 111–115. [Google Scholar]
- Caesarendra, W.; Tjahjowidodo, T.; Nico, Y.; Wahyudati, S.; Nurhasanah, L. EMG Finger Movement Classification Based on ANFIS. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Mechanical, Electronics, Computer, and Industrial Technology, Prima, Indonesia, 6–8 December 2018; Volume 1007. [Google Scholar]
- Paul, Y.; Goyal, V.; Jaswal, R.A. Comparative Analysis Between SVM & KNN Classifier for EMG Signal Classification on Elementary Time Domain Features. In Proceedings of the 2017 4th International Conference on Signal Processing, Computing and Control (ISPCC), Solan, India, 21–23 September 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Chan, F.H.Y.; Yang, Y.S. Fuzzy EMG Classification for Prosthesis Control. IEEE Trans. Rehabil. Eng. 2000, 8, 305–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ajiboye, A.B.; Weir, R.F. A Heuristic Fuzzy Logic Approach to EMG Pattern Recognition for Multifunctional Prosthesis Control. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2005, 13, 280–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Li, Y.; Liang, W. CNN-RNN Based Intelligent Recommendation for Online Medical Pre-Diagnosis Support. IEEE-ACM Trans. Comput. Biol. Bioinf. 2021, 18, 912–921. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manfredo, A.; Matteo, C.; Henning, M. Deep Learning with Convolutional Neural Networks Applied to Electromyography Data: A Resource for the Classification of Movements for Prosthetic Hands. Front. Neurorobot. 2016, 10, 9. [Google Scholar]
- Weidong, G.; Yu, D.; Wenguang, J.; Wei, W.; Hu, Y.; Li, J. Gesture Recognition by Instantaneous Surface EMG Images. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 36571–36579. [Google Scholar]
- Zhai, X.; Beth, J.; Chan, R.H.M.; Tin, C. Self-Recalibrating Surface EMG Pattern Recognition for Neuroprosthesis Control Based on Convolutional Neural Network. Front. Neurosci. 2017, 11, 379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W.; Wong, Y.; Du, Y.; Hu, Y.; Kankanhalli, M.; Geng, W. A Multi-stream Convolutional Neural Network for sEMG-based Gesture Recognition in Muscle-Computer Interface. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2017, 119, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Zhang, Y.; Li, G.; Fang, Y.; Liu, H. Surface Electromyography Feature Extraction via Convolutional Neural Network. Int. J. Mach. Learn. Cybern. 2020, 11, 185–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husken, M.; Stagge, P. Recurrent Neural Networks for Time Series Classification. Neurocomputing 2003, 50, 223–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barron, O.; Raison, M.; Gaudet, G.; Achiche, S. Recurrent Neural Network for electromyographic gesture recognition in transhumeral amputees. Appl. Soft Comput. 2020, 96, 106616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teban, T.A.; Precup, R.E.; Voisan, E.L.; de Oliveira, T.E.A.; Petriu, E.M. Recurrent Dynamic Neural Network Model for Myoelectric-based Control of a Prosthetic Hand. In Proceedings of the 2016 Annual IEEE Systems Conference (SysCon), Orlando, FL, USA, 18–21 April 2016; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Koch, P.; Phan, H.; Maass, M.; Katzberg, F.; Mertins, A. Recurrent Neural Network Based Early Prediction of Future Hand Movements. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 4710–4713. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long Short-Term Memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quivira, F.; Koike-Akino, T.; Ye, W.; Erdogmus, D. Translating sEMG Signals to Continuous Hand Poses using Recurrent Neural Networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Biomedical and Health Informatics, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 4–7 March 2018; pp. 166–169. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, Y.; Wong, Y.; Wei, W.; Du, Y.; Kankanhalli, M.; Geng, W. A Novel Attention-based Hybrid CNN-RNN Architecture for sEMG-based Gesture Recognition. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0206049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xia, P.; Hu, J.; Peng, Y. EMG-Based Estimation of Limb Movement Using Deep Learning With Recurrent Convolutional Neural Networks. Artif. Organs 2017, 42, E67–E77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Song, L.; Zhang, J.; Song, Y.; Yan, M. Multi-Category Gesture Recognition Modeling Based on sEMG and IMU Signals. Sensors 2022, 22, 5855. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Dai, C.; Chen, W. Cross-Comparison of EMG-to-Force Methods for Multi-DoF Finger Force Prediction Using One-DoF Training; IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2020; Volume 8, pp. 13958–13968. [Google Scholar]
- Azizjon, M.; Jumabek, A.; Kim, W. 1D CNN Based Network Intrusion Detection with Normalization on Imbalanced Data. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Conference on Artificial Intelligence in Information and Communication (ICAIIC), Fukuoka, Japan, 19–21 February 2020; pp. 218–224. [Google Scholar]
- Nasri, N.; Orts-Escolano, S.; Gomez-Donoso, F.; Cazorla, M. Inferring Static Hand Poses from a Low-Cost Non-Intrusive sEMG Sensor. Sensors 2019, 19, 371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- He, Y.; Fukuda, O.; Bu, N.; Okumura, H.; Yamaguchi, N. Surface EMG Pattern Recognition Using Long Short-Term Memory Combined with Multilayer Perceptron. In Proceedings of the 2018 40th Annual International Conference of the IEEE Engineering in Medicine and Biology Society (EMBC), Honolulu, HI, USA, 18–21 July 2018; pp. 5636–5639. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, Z.; He, C.; Yang, K. A Novel Surface Electromyographic Signal-Based Hand Gesture Prediction Using a Recurrent Neural Network. Sensors 2020, 20, 3994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, L.H.; Hargrove, L.J.; Lock, B.A.; Kuiken, T.A. Determining the Optimal Window Length for Pattern Recognition-based Myoelectric Control: Balancing the Competing Effects of Classification Error and Controller Delay. IEEE Trans. Neural Syst. Rehabil. Eng. 2011, 19, 186–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simo, M.; Neto, P.; Gibaru, O. EMG-based Online Classification of Gestures with Recurrent Neural Networks. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2019, 128, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botros, F.S.; Phinyomark, A.; Scheme, E.J. Electromyography-Based Gesture Recognition: Is It Time to Change Focus from the Forearm to the Wrist? IEEE Trans. Ind. Inf. 2022, 18, 174–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Zhang, Q.; Zhang, M.; Shahnewaz, S.; Wei, S.; Ruan, J.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, L. Toward Hand Pattern Recognition in Assistive and Rehabilitation Robotics Using EMG and Kinematics. Front. Neurorobot. 2021, 15, 659876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Model | Data Set | Loss Value | Recall | Accuracy | Precision | F1 Score | Training Time |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CNN | Training | 0.6431 | 73.14% | 77.99% | 83.34% | 0.7791 | 493 min |
| CNN | Test | 0.4446 | 79.93% | 85.43% | 90.55% | 0.8491 | / |
| LSTM | Training | 0.1497 | 94.75% | 95.39% | 96.17% | 0.9545 | 1642 min |
| LSTM | Test | 0.0952 | 96.58% | 96.88% | 93.77% | 0.9695 | / |
| 1D-CNN-RNN | Training | 0.0607 | 98.01% | 98.19% | 98.42% | 0.9821 | 672 min |
| 1D-CNN-RNN | Test | 0.0340 | 98.88% | 98.96% | 99.04% | 0.9896 | / |
| Serial Number | Loss | Recall | Accuracy | Precision | F1 Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0.0065 | 99.80% | 99.82% | 99.85% | 0.9983 |
| 2 | 0.0274 | 99.28% | 99.34% | 99.39% | 0.9934 |
| 3 | 0.0407 | 98.60% | 98.73% | 98.81% | 0.9870 |
| 4 | 0.0328 | 98.98% | 99.04% | 99.20% | 0.9909 |
| 5 | 0.0580 | 97.98% | 98.15% | 98.34% | 0.9816 |
| 6 | 0.0303 | 99.06% | 99.15% | 99.25% | 0.9915 |
| 7 | 0.0539 | 97.98% | 98.18% | 98.42% | 0.9820 |
| 8 | 0.0265 | 99.31% | 99.33% | 99.43% | 0.9937 |
| 9 | 0.0547 | 98.19% | 98.30% | 98.35% | 0.9827 |
| 10 | 0.0259 | 99.20% | 99.27% | 99.35% | 0.9928 |
| Mean | 0.0357 ± 0.0162 | 98.84 ± 0.62% | 98.93 ± 0.57% | 98.84 ± 0.62% | 0.9894 ± 0.0057 |
| Research | Channel Number | Number of Moves | Number of Repetitions | Number of Subjects | Classifier | Accuracy | Time Delay |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [37] | 16 | 8 | / | / | LSTM | 95.0% | / |
| [33] | 8 | 6 | 195 | 35 | RNN | 99.8% | 940 ms |
| [35] | 8 | 21 | 30 | 13 | RNN | 89.6% | 200 ms |
| [34] | 12 | 52 | 10 | 27 | LSTM | 75.5% | 400 ms |
| This research | 8 | 20 | 20 | 10 | CNN-RNN | 91.0% | 153 ms |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Li, S.; Zhang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Li, W.; Sun, W.; Yu, H. Real-Time sEMG Pattern Recognition of Multiple-Mode Movements for Artificial Limbs Based on CNN-RNN Algorithm. Electronics 2023, 12, 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12112444
Li S, Zhang Y, Tang Y, Li W, Sun W, Yu H. Real-Time sEMG Pattern Recognition of Multiple-Mode Movements for Artificial Limbs Based on CNN-RNN Algorithm. Electronics. 2023; 12(11):2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12112444
Chicago/Turabian StyleLi, Sujiao, Yue Zhang, Yuanmin Tang, Wei Li, Wanjing Sun, and Hongliu Yu. 2023. "Real-Time sEMG Pattern Recognition of Multiple-Mode Movements for Artificial Limbs Based on CNN-RNN Algorithm" Electronics 12, no. 11: 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12112444
APA StyleLi, S., Zhang, Y., Tang, Y., Li, W., Sun, W., & Yu, H. (2023). Real-Time sEMG Pattern Recognition of Multiple-Mode Movements for Artificial Limbs Based on CNN-RNN Algorithm. Electronics, 12(11), 2444. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics12112444





