Abstract
Winograd’s algorithms are an effective tool for calculating the discrete Fourier transform (DFT). These algorithms described in well-known articles are traditionally represented either with the help of sets of recurrent relations or with the help of products of sparse matrices obtained on the basis of various methods of the DFT matrix factorization. Unfortunately, in the mentioned papers, it is not shown how the described relations were obtained or how the presented factorizations were found. In this paper, we use a simple, understandable and fairly unified approach to the derivation of the Winograd-type DFT algorithms for the cases N = 8, N = 16 and N = 32. It is easy to verify that algorithms for other lengths of sequences that are powers of two can be synthesized in a similar way.
1. Introduction
Winograd’s method for the realization of the discrete Fourier transform (DFT) for several decades has been discussed in a number of publications [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12]. In comparison with the Cooley–Tukey fast Fourier transform (FFT) algorithms, the Winograd DFT algorithm requires substantially fewer multiplications at the cost of a few extra additions. In the known papers, the cases of the Winograd FFTs for small sequences of odd length are mainly considered. Moreover, the algorithms were presented in the form of algebraic relations or in the form of DFT matrix factorizations. However, none of the publications known to us has written on how these relations were obtained or how, on the basis of any considerations, the matrices that make up the corresponding computational procedures were constructed.
In this paper, we want to show a simple, understandable and fairly unified approach to the derivation of Winograd-type FFT algorithms for the cases N = 8, N = 16 and N = 32. It is easy to verify that algorithms for other lengths of sequences that are powers of two can be synthesized similarly.
2. Preliminary Remarks
The discrete Fourier transform (DFT) is one of the most important tools in digital signal and image processing. The DFT can be defined as follows:
where is a uniformly sampled sequence, is the k-th DFT coefficient, and is an imaginary unit.
Implementation of calculations in accordance with expression (2), especially for large N, requires performing a large number of arithmetic operations, which in turn leads to an increase in computation time.
In 1965, J. Cooley and J. Tukey proposed the fast algorithm to compute discrete Fourier transform with a drastically reduced number of arithmetical operations. Mathematically, the fast Fourier transform algorithms are based on factorization of the Fourier matrix into a product of sparse matrices, meaning matrices with many zero entries. However, this factorization can be implemented in different ways. In the case of the Cooley–Tukey algorithm, we are dealing with the representation of the original matrix as a product of sparse structured matrices. As is well known, the complexity of this algorithm is approximately multiplications and the same number of additions of complex numbers.
Another effective algorithm for calculating the DFT is the Winograd FFT algorithm. In comparison with the Cooley–Tukey FFT algorithm, the Winograd FFT algorithm requires substantially fewer multiplications at the cost of a few extra additions. Winograd proved that the multiplicative complexity of FFT algorithms can be significantly reduced by some increase in additive complexity. The Winograd Fourier transform algorithm (WFTA) is an FFT algorithm which achieves a reduction on the number of multiplications from order in the DFT to order N. In the literature known to the authors [1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11,12,13,14,15], the Winograd FFT algorithms that implement DFT transform for a limited set of small-length sequences are mainly considered. As a rule, these algorithms are represented as a set of algebraic relations [1,2,3,4,5,8], although the matrix interpretation of Winograd FFT algorithms are available too [6,9]. In the case of the matrix formulation of the Winograd FFT algorithms, the factorization of the DFT matrix differs from the factorization of the DFT matrix in the Cooley–Tukey FFT algorithms. Moreover, the mechanism for deriving such algorithms for each specific case is unique. In addition, methods for the deriving of recurrent relations are not published anywhere. Additionally, the ways for deriving factorized representations of DFT matrices have never been explained. In this paper, we show a simple, understandable and fairly unified approach to the derivation of the Winograd-like FFT algorithms for the case when the input sequence length is a power of two.
3. Short Background
The main idea of the proposed approach is to use a new method for factorizing the DFT matrix, which is different from Winograd factorization. In contrast to Winograd factorization, we propose the following unified method of DFT matrix decomposition:
where
is k × k DFT matrix; is some “prefix” matrix containing a constellation of twiddle factors specific for each N; is an identity k × k matrix; is the order 2 Hadamard matrix; is the matrix obtained from the k × k identity matrix by shifting its columns by one position to the right; and signs “⊗”, “⊕” denote the tensor product and direct sum of two matrices, respectively [16,17].
Then, the generalized scheme for the synthesis of Winograd-type DFT algorithms for N equal to the power of two can be described as follows:
The methods for factorizing the matrices and are different, but both lead to a factorization of the BCD type [18] similar to the Winograd factorization. Moreover, as follows from expression (1), the expansions for small N are part of the expansions for larger lengths of input sequences. When synthesizing algorithms for separate and , we will use the templates of matrix structures and identities presented in [19,20].
4. Synthesis of the Fast Winograd-Type DFT Algorithms
Let us show, based on specific examples, how it works.
4.1. Fast DFT Algorithm for N = 4
Let us now define the permutation and write it as a matrix in this way:
Permute the columns of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
where
According to the concept, Expression (4) for a given transform size can be rewritten as follows:
where
As you can see, after rearranging the columns of the DFT matrix , it can be decomposed, as follows from the proposed technique, into the order 2 DFT matrix and the order 2 prefix matrix .
For matrices and , we can offer the following factorization schemes leading to a reduction in computational complexity:
Taking into account the above factorization schemes, we can finally write
where
Figure 1 shows a data flow graph of synthesized algorithm for 4 point DFT. As can be seen, in this case, the algorithm takes only eight additions.
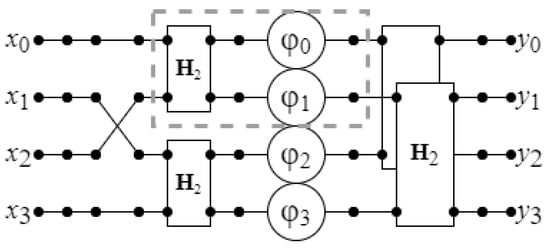
Figure 1.
The data flow graph of the proposed algorithm for computation of 4-point DFT.
4.2. Fast DFT Algorithm for N = 8
Let us now define the permutation in the following form:
Permutation can be written as a matrix in this way:
Permute columns of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
where
According to the concept, Expression (4) for a given transform size can be rewritten as follows:
Such a structure of the matrix allows to apply a divide and conquer algorithm that recursively breaks down a matrix–vector product of order eight into two smaller matrix–vector products of order 4 [19]. If we write the matrix as a product , the Equation (8) will take the form:
where
Permute columns of the matrix and rows of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such permutations, we obtain the matrices
where
Such structures of the matrices and allow to apply the same schemes of factorization. Therefore, we can write
where
For matrices , , , we can offer the following factorization schemes leading to a reduction in computational complexity:
Taking into account the above factorization schemes, we can finally write
where
Expression (12) describes the Winograd-type fast Fourier transform algorithm for N = 8. Figure 2 shows a data flow graph of synthesized algorithm for 8 point DFT. As can be seen, in this case the algorithm takes 2 multiplications and 26 additions.
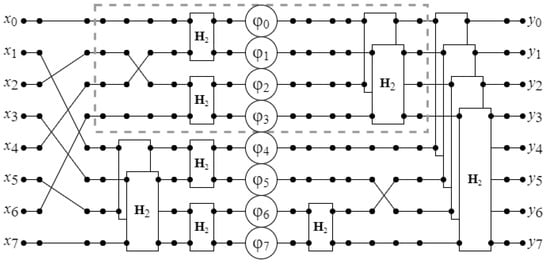
Figure 2.
The data flow graph of the proposed algorithm for computation of 8-point DFT.
4.3. Fast DFT Algorithm for N = 16
Now let us consider the synthesis of a similar algorithm for N = 16. In matrix–vector notation, we can rewrite the DFT in the following form:
where
where
where
Let us define the permutation in the following form:
Permute columns of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such permutation, we obtain the matrix
where
According to the concept, expression (4) for a given transform size can be rewritten as follows:
Such a matrix structure allows for the factorization of the matrix ; similarly, as was done in the case of the matrix of order N = 8 [19].
If we write the matrix as a product , Equation (13) takes the form
where the corresponding permutation matrix takes the following form:
Now let us permute columns of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
where
Then the matrix can be represented as a product . Next, we permute rows of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
where
Then the matrix can be represented as a product . Taking into account the above factorization schemes, we can finally write
where
We now consider the matrices , , , and . Permute columns of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
Next, we permute rows of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
Now, we permute rows of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
Next, we define the permutation in the following way:
Permute rows and columns of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix .
where
Then
where
Taking into account the matrix transformations performed above, we can write
where
In turn, the matrices , , , , , , and also have structures that provide effective factorization, which leads to a decrease in the multiplicative complexity of calculations:
where
where
Combining the above partial decompositions in a single procedure, we can rewrite (13) as follows:
where
Figure 3 shows a data flow graph of synthesized algorithm for 16 point DFT. As can be seen, in this case the algorithm takes 10 multiplications and 74 additions.
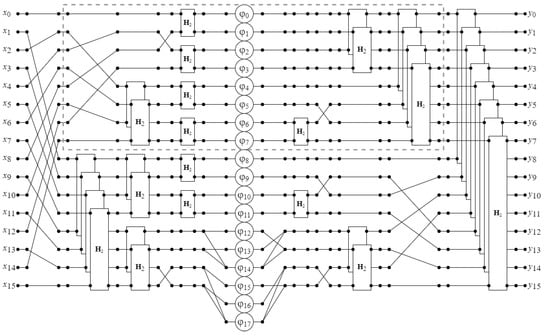
Figure 3.
The data flow graph of the proposed algorithm for computation of 16-point DFT.
4.4. Fast DFT Algorithm for N = 32
Now let us consider the synthesis of a similar algorithm for N = 32. In matrix–vector notation, we can rewrite the DFT in the following form:
where
Let us define the permutation in the following form:
Permute columns of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such permutation, we obtain the matrix
According to the concept, expression (4) for a given transform size can be rewritten as follows:
where
is the same as in the algorithm for N = 16, so we will skip this part.
is a new matrix. Permute rows of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
where
and
where
Taking into account the above factorization scheme, we can finally write
where
and are the same as in the algorithm for N = 16, so we will skip this part.
and are a new matrix from the bottom half of the algorithm for N = 32. Permute rows of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
where
Let us now define the permutation in the following form:
Permutation can be written as a matrix in this way:
Then, we permute rows and columns of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
where
To reduce the computational complexity for matrix , we need to perform the following calculations:
where
and
Taking into account the above factorization scheme, we can finally write
where
where
, , and are the same as in the algorithm for N = 16, so we will skip this part. , , and are a new matrix from the bottom half of the algorithm for N = 32. Permute rows of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
where
Permute rows and columns of the matrix according to permutation . As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
where
To reduce the computational complexity for matrix , we need to perform the following calculations:
where
and
Let us define the permutations and in the following form:
Permutations and can be written as matrices in this way:
Permute rows and columns of the matrix according to permutation for rows and for columns. As a result of such a permutation, we obtain the matrix
where
To reduce the computational complexity for matrix , we need to perform the following calculations:
where
The same permutations as on matrix are applied to matrix . As a result of such permutations, we obtain the matrix
where
To reduce the computational complexity for matrix , we need to perform the following calculations:
Taking into account the above factorization scheme, we can finally write
where
In turn, the matrices , , , , , , and are the same as in the algorithm for N = 16, so we will skip this part. The matrices , , , , , , , , and also have structures that provide effective factorization, which leads to a decrease in the multiplicative complexity of calculations:
Taking into account the above factorization scheme, we can finally write
where
and finally
where
Figure 4 shows a data flow graph of a synthesized algorithm for the 32-point DFT. As can be seen, in this case, the algorithm takes 36 multiplications and 244 additions.
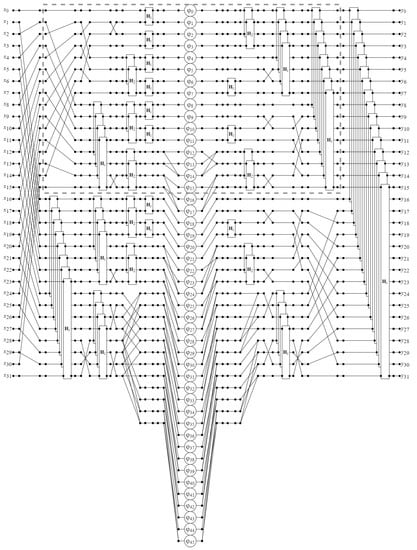
Figure 4.
The data flow graph of the proposed algorithm for computation of 32-point DFT.
5. Conclusions
In this article, we show for the first time a simple, clear and unified approach to the derivation of fast Winograd-like DFT algorithms. The idea of constructing algorithms is based on the application of the method of synthesis of fast algorithms for calculating matrix–vector products described in [19]. The mathematical background for the construction of the described algorithms is the original method of hierarchical factorization of the DFT matrix, which differs from the factorization of this matrix in the case of the Cooley–Tukey FFT. The method of synthesis of algorithms is shown by the examples of the construction of these algorithms for two typical lengths of the initial data sequences: N = 4, N = 8, N = 16 and N = 32. As follows from Figure 1, the upper part of the data flow graph for N = 4, outlined by the dotted line, corresponds to the algorithm for N = 2. In turn, the upper part of the data flow graph for N = 8 (see Figure 2), circled with a dotted line, corresponds to the algorithm for N = 4. The upper part of the data flow graph for N = 16 (Figure 3), circled by a dotted line, corresponds to the algorithm for N = 8. Finally, the upper part of the data flow graph for N = 32 (Figure 4), circled with a dotted line, corresponds to the algorithm for N = 16. It is easy to verify that algorithms for other lengths of sequences that are powers of two can be synthesized in a similar way. Therefore, the described method can be considered as universal.
The advantage of the presented algorithms in comparison with the Cooley–Tukey algorithms is that the critical path in the graph of any of the obtained algorithms contains only one multiplication. If there is more than one multiplication in the critical path of the algorithm, then this will create additional problems for the implementation of computations. As a result of multiplying two n-bit operands, a 2n-bit product is obtained. The need for repeated multiplication requires an additional amount of manipulations with the operands and therefore requires more time and effort than when we are dealing with only a single multiplication. In fixed-point devices, this fact can cause overflow–underflow handling. If we want to preserve the accuracy, then double access to the memory is required both when writing and when reading. Using floating-point arithmetic in this case also creates additional problems related to exponent alignment, mantissa addition, etc. This is what we had in mind when we wrote about additional dignity. Another important advantage of these algorithms over the Cooley–Tukey algorithms is that the multiplications here are either purely real or purely imaginary. Multiplying complex numbers requires three multiplications of real numbers, while multiplying a complex number by a real number requires only two real multiplications. It leads to an additional reduction in the multiplicative complexity of computations. These two advantages are typical of all Winograd-type algorithms.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.C.; methodology, A.C. and M.R.; validation, A.C. and M.R.; formal analysis, A.C. and M.R.; investigation, M.R.; writing—original draft, A.C. and M.R.; writing—review and editing, M.R.; supervision, A.C. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Not applicable.
Acknowledgments
We would like to thank Dorota Majorkowska-Mech for advice and guidance on how to improve the manuscript.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- McClellan, J.H.; Rader, C.M. Number Theory in Digital Signal Processing; Prentice-Hall Signal Processing Series; Prentice-Hall: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1979. [Google Scholar]
- Douglas, E.; Rao, K.R. Fast Transforms Algorithms, Analyses, Applications; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Elliott, D.F. (Ed.) Handbook of Digital Signal Processing: Engineering Applications; Academic Press: San Diego, CA, USA, 1987. [Google Scholar]
- Nussbaumer, H.J. Fast Fourier Transform and Convolution Algorithms; Springer Series in Information Sciences; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 1982; Volume 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrus, C.S.; Parks, T.W.; Potts, J.F. DFT/FFT and Convolution Algorithms: Theory and Implementation; Topics in Digital Signal Processing; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1984. [Google Scholar]
- Blahut, R.E. Fast Algorithms for Digital Signal Processing; Addison-Wesley Pub. Co.: Reading, MA, USA, 1985. [Google Scholar]
- Tolimieri, R.; An, M.; Lu, C. Algorithms for Discrete Fourier Transform and Convolution; Signal Processing and Digital Filtering; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 1989. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.W.; Smith, J.M. Handbook of Real-Time Fast Fourier Transforms: Algorithms to Product Testing; IEEE Press: New York, NY, USA, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Parhi, K.K. VLSI Digital Signal Processing Systems: Design and implementation; Wiley: New York, NY, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Moon, T.K.; Stirling, W.C. Mathematical Methods and Algorithms for Signal Processing; Prentice Hall: Upper Saddle River, NJ, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Garg, H.K. Digital Signal Processing Algorithms: Number Theory, Convolution, Fast Fourier Transforms, and Applications; Press Computer Engineering Series; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Bi, G.; Zeng, Y. Transforms and Fast Algorithms for Signal Analysis and Representations; Birkhäuser Boston: Boston, MA, USA, 2004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burrus, C.S.; Selesnick, I. Winograd’s Short DFT Algorithms; OpenStax CNX, Rice University: Houston, TX, USA; Available online: http://cnx.org/content/m16333/latest (accessed on 15 March 2022).
- Winograd, S. On computing the discrete Fourier transform. Math. Comput. 1978, 32, 175–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silverman, H. An introduction to programming the Winograd Fourier transform algorithm (WFTA). IEEE Trans. Acoust. Speech Signal Process. 1977, 25, 152–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regalia, P.A.; Sanjit, M.K. Kronecker Products, Unitary Matrices and Signal Processing Applications. SIAM Rev. 1989, 31, 586–613. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steeb, W.H.; Hardy, Y. Matrix Calculus and Kronecker Product: A Practical Approach to Linear and Multilinear Algebra, 2nd ed.; World Scientific: Singapore, 2011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beck, A.; Tetruashvili, L. On the Convergence of Block Coordinate Descent Type Methods. SIAM J. Optim. 2013, 23, 2037–2060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cariow, A. Strategies for the Synthesis of Fast Algorithms for the Computation of the Matrix-vector Products. J. Signal Process. Theory Appl. 2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreatto, B.; Cariow, A. Automatic generation of fast algorithms for matrix–vector multiplication. Int. J. Comput. Math. 2018, 95, 626–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).