AI Ekphrasis: Multi-Modal Learning with Foundation Models for Fine-Grained Poetry Retrieval
Abstract
:1. Introduction
Contributions
- 1.
- The developed solution provides multi-modal representation learning about fine-grained poetry for matching images with poetry.
- 2.
- We combine the advantages of CLIP’s [8] strong pre-training and the shared attention parameters learning for multi-modal image–poem data. This improves the context awareness of our model by liaising among feature representations of image and poem sequences.
- 3.
- Our proposed model leverages the state-of-the-art pre-trained CLIP model and outperforms its zero-shot, few-shot, and fully supervised poetry retrieval performance for the image–poetry retrieval task.
- 4.
- The proposed solution considers fine-grained attribute recognition for matching the most relevant poems to a query image, contemplating the mutual association of scenes, sentiments, and objects under ekphrasis considerations of symbolism and metaphors. This enables automatic poetry retrieval for the visual artwork appreciation of people with visual impairments.
2. Related Studies
2.1. Multi-Sensory Artwork Poetry Exploration for People with Visual Impairments
2.2. Transformers for Natural Language Processing
2.3. Multi-Modal Image-Inspired Poetry Generation with Neural Networks
2.4. Deep Neural Networks for Visual and Textual Data Matching
3. Approach
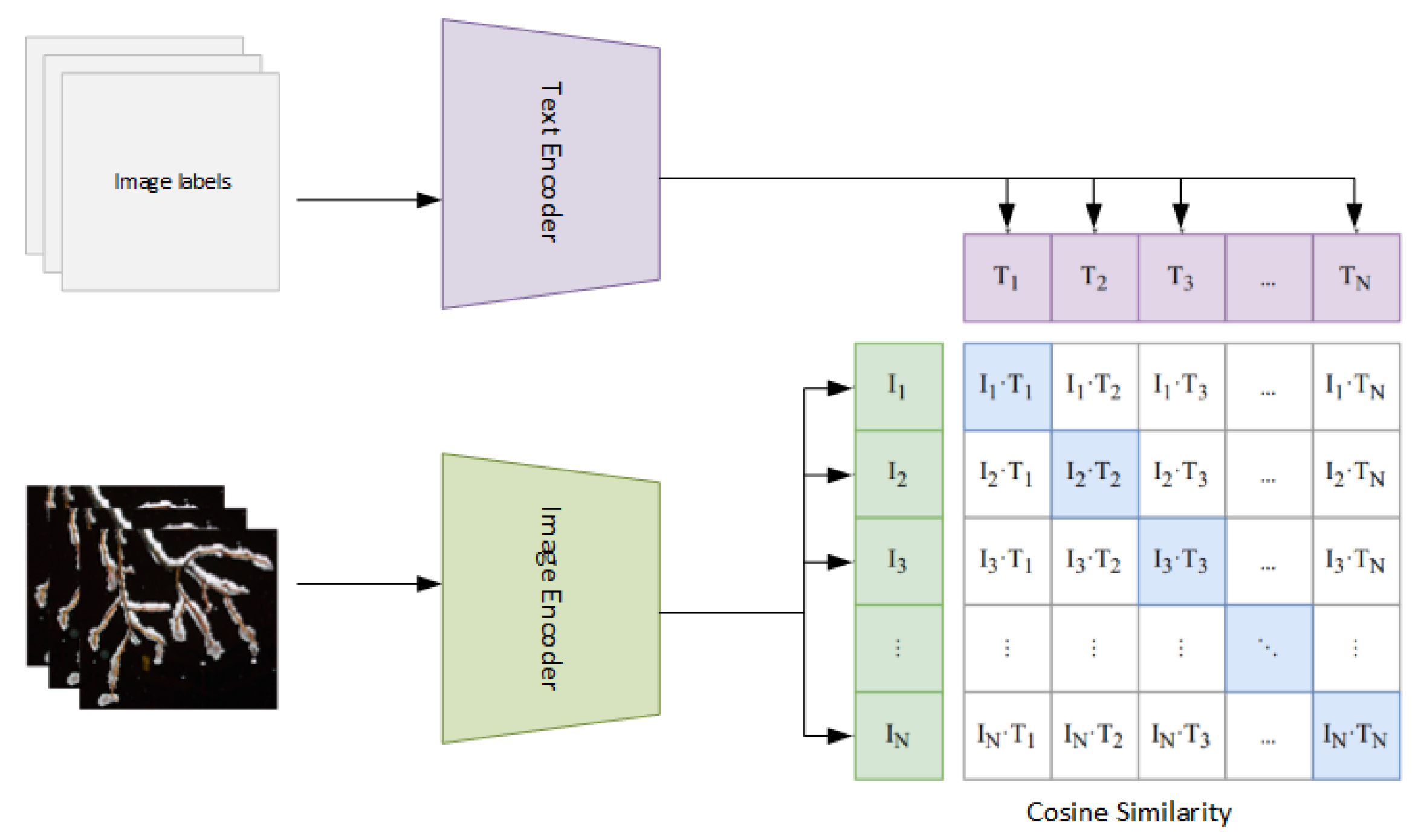
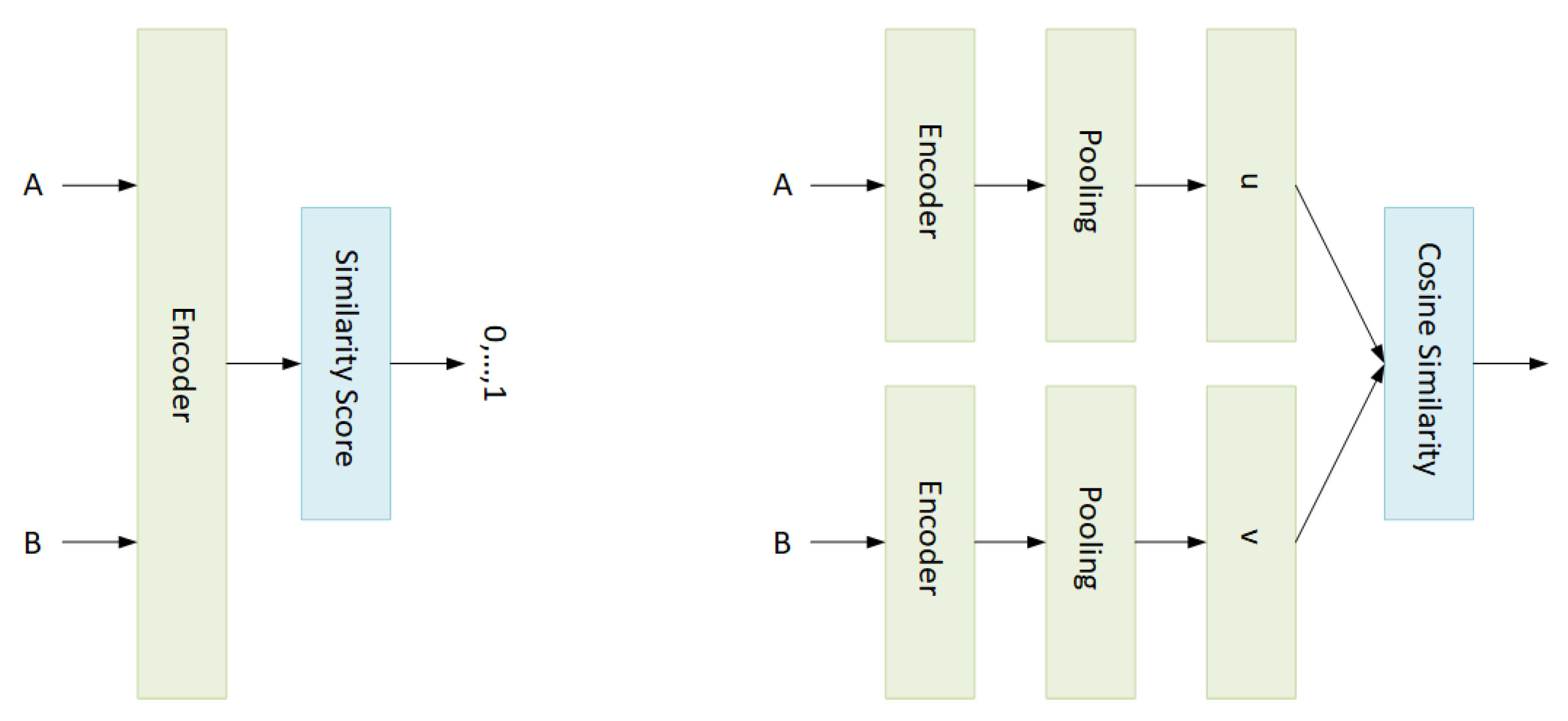
3.1. Baseline Model: Contrastive Language-Image Pre-Training (CLIP)
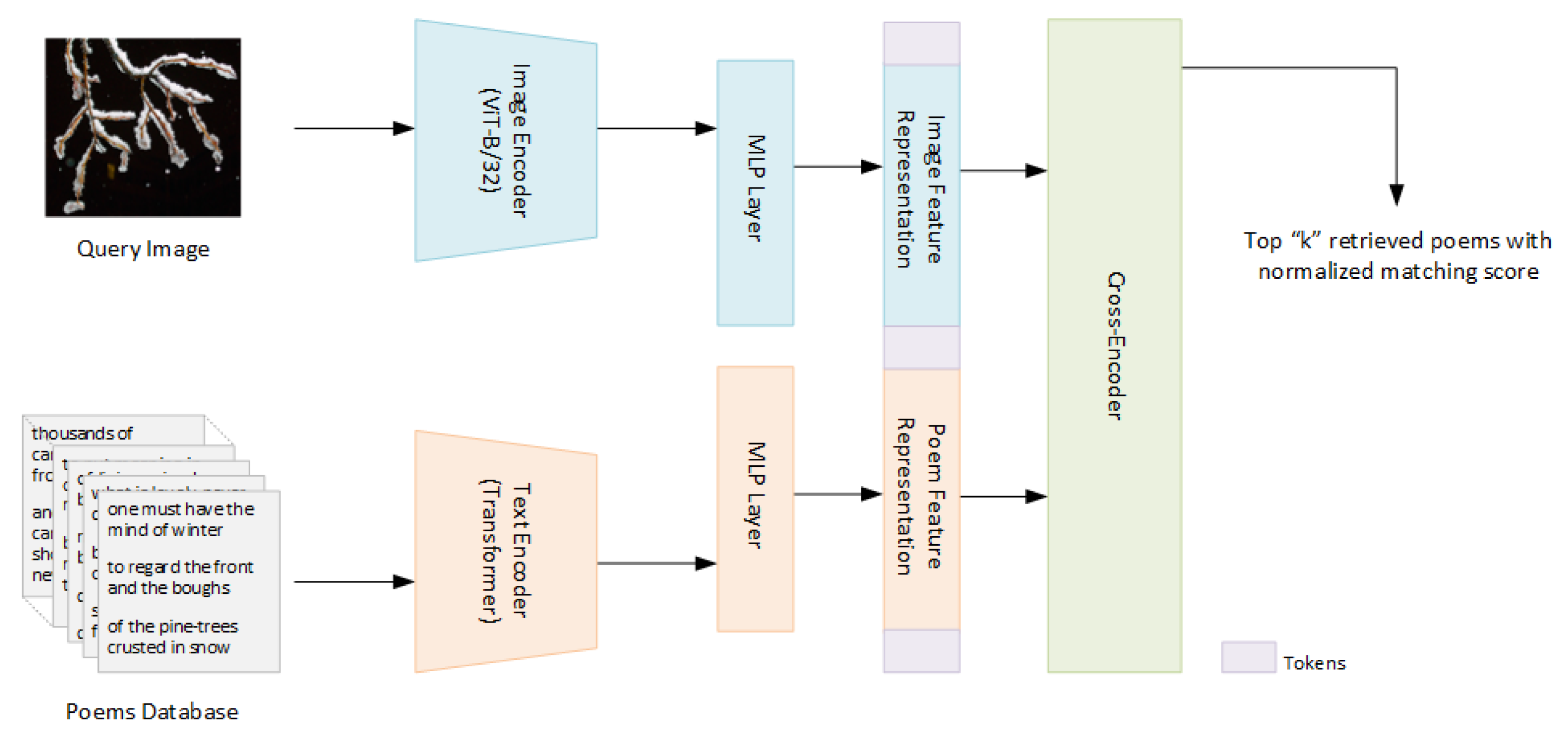
3.2. Cross-Encoder CLIP
| Algorithm 1 Training Process of Proposed Method. |
Input: image–poem pairs (Ii, Pj), and their Labels (L = 1 if j = i, else 0)
|
4. Experiments
4.1. Dataset
4.2. CE-CLIP Training Objective
4.3. Implementation Details
4.4. Evaluation Metrics
5. Results and Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Papineni, K.; Roukos, S.; Ward, T.; Zhu, W.J. Bleu: A method for automatic evaluation of machine translation. In Proceedings of the 40th Annual Meeting of the Association for Computational Linguistics, Philadelphia, PA, USA, 7–12 July 2002; pp. 311–318. [Google Scholar]
- Cho, J.D. A Study of Multi-Sensory Experience and Color Recognition in Visual Arts Appreciation of People with Visual Impairment. Electronics 2021, 10, 470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.D.; Jeong, J.; Kim, J.H.; Lee, H. Sound Coding Color to Improve Artwork Appreciation by People with Visual Impairments. Electronics 2020, 9, 1981. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, A.N.; Martin, R.; Kemp, S.E. Cross-modal correspondence between vision and olfaction: The color of smells. Am. J. Psychol. 1996, 109, 335–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iranzo Bartolomé, J.; Cho, J.D.; Cavazos Quero, L.; Jo, S.; Cho, G. Thermal Interaction for Improving Tactile Artwork Depth and Color-Depth Appreciation for Visually Impaired People. Electronics 2020, 9, 1939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lawrence, M.A.; Kitada, R.; Klatzky, R.L.; Lederman, S.J. Haptic roughness perception of linear gratings via bare finger or rigid probe. Perception 2007, 36, 547–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cho, J.D.; Lee, Y. ColorPoetry: Multi-Sensory Experience of Color with Poetry in Visual Arts Appreciation of Persons with Visual Impairment. Electronics 2021, 10, 1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radford, A.; Kim, J.W.; Hallacy, C.; Ramesh, A.; Goh, G.; Agarwal, S.; Sastry, G.; Askell, A.; Mishkin, P.; Clark, J.; et al. Learning transferable visual models from natural language supervision. In Proceedings of the 38th International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Online, 18–24 July 2021; pp. 8748–8763. [Google Scholar]
- Maric, Y.; Jacquot, M. Contribution to understanding odour–colour associations. Food Qual. Prefer. 2013, 27, 191–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slobodenyuk, N.; Jraissati, Y.; Kanso, A.; Ghanem, L.; Elhajj, I. Cross-modal associations between color and haptics. Atten. Percept. Psychophys. 2015, 77, 1379–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jabbar, M.S.; Lee, C.H.; Cho, J.D. ColorWatch: Color Perceptual Spatial Tactile Interface for People with Visual Impairments. Electronics 2021, 10, 596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, Y.; Jeong, H.; Cho, J.D.; Shin, J. Construction of a soundscape-based media art exhibition to improve user appreciation experience by using deep neural networks. Electronics 2021, 10, 1170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vaswani, A.; Shazeer, N.; Parmar, N.; Uszkoreit, J.; Jones, L.; Gomez, A.N.; Kaiser, L.; Polosukhin, I. Attention is all you need. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017, 30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, T.; Debut, L.; Sanh, V.; Chaumond, J.; Delangue, C.; Moi, A.; Cistac, P.; Rault, T.; Louf, R.; Funtowicz, M.; et al. Transformers: State-of-the-art natural language processing. In Proceedings of the 2020 Conference on Empirical Methods in Natural Language Processing: System Demonstrations, Online, 16–20 November 2020; pp. 38–45. [Google Scholar]
- Bommasani, R.; Hudson, D.A.; Adeli, E.; Altman, R.; Arora, S.; von Arx, S.; Bernstein, M.S.; Bohg, J.; Bosselut, A.; Brunskill, E.; et al. On the opportunities and risks of foundation models. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2108.07258. [Google Scholar]
- Devlin, J.; Chang, M.W.; Lee, K.; Toutanova, K. Bert: Pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1810.04805. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Z.; Dai, Z.; Yang, Y.; Carbonell, J.; Salakhutdinov, R.R.; Le, Q.V. Xlnet: Generalized autoregressive pretraining for language understanding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2019, 32, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Song, K.; Tan, X.; Qin, T.; Lu, J.; Liu, T.Y. Mpnet: Masked and permuted pre-training for language understanding. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2020, 33, 16857–16867. [Google Scholar]
- Medsker, L.; Jain, L.C. Recurrent Neural Networks: Design and Applications; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1999. [Google Scholar]
- Tschannen, M.; Bachem, O.; Lucic, M. Recent advances in autoencoder-based representation learning. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1812.05069. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Guo, Q.; Li, W.; Lv, J. A multi-modal chinese poetry generation model. In Proceedings of the 2018 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 8–13 July 2018; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Lv, J.; Sang, Y. Generating Chinese Poetry from Images via Concrete and Abstract Information. In Proceedings of the 2020 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks (IJCNN), Glasgow, UK, 19–24 July 2020; pp. 1–8. [Google Scholar]
- Chung, J.; Gulcehre, C.; Cho, K.; Bengio, Y. Empirical evaluation of gated recurrent neural networks on sequence modeling. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1412.3555. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, L.; Xu, M.; Qian, S.; Cui, J. Image to modern chinese poetry creation via a constrained topic-aware model. ACM Trans. Multimed. Comput. Commun. Appl. (TOMM) 2020, 16, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Wan, X.; Guo, Z. Images2poem: Generating chinese poetry from image streams. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM international conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 1967–1975. [Google Scholar]
- Hochreiter, S.; Schmidhuber, J. Long short-term memory. Neural Comput. 1997, 9, 1735–1780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.; Fu, J.; Kato, M.P.; Yoshikawa, M. Beyond narrative description: Generating poetry from images by multi-adversarial training. In Proceedings of the 26th ACM International Conference on Multimedia, Seoul, Korea, 22–26 October 2018; pp. 783–791. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, C.; Wang, J.; Yuan, S.; Wang, L.; Zhang, W. Generate classical Chinese poems with theme-style from images. Pattern Recognit. Lett. 2021, 149, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.; Liu, D.; Lv, J. Deep poetry: A chinese classical poetry generation system. Proc. AAAI Conf. Artif. Intell. 2020, 34, 13626–13627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, D.; Ni, B.; Zhi, Q.; Plummer, T.; Li, Q.; Zheng, H.; Zeng, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D. Through the eyes of a poet: Classical poetry recommendation with visual input on social media. In Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM International Conference on Advances in Social Networks Analysis and Mining (ASONAM), Vancouver, BC, Canada, 27–30 August 2019; pp. 333–340. [Google Scholar]
- Nam, H.; Ha, J.W.; Kim, J. Dual attention networks for multimodal reasoning and matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 299–307. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, K.H.; Chen, X.; Hua, G.; Hu, H.; He, X. Stacked cross attention for image–text matching. In Proceedings of the European Conference on Computer Vision (ECCV), Munich, Germany, 8–14 September 2018; pp. 201–216. [Google Scholar]
- Li, K.; Zhang, Y.; Li, K.; Li, Y.; Fu, Y. Visual semantic reasoning for image–text matching. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27–28 October 2019; pp. 4654–4662. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, S.; He, K.; Girshick, R.; Sun, J. Faster r-cnn: Towards real-time object detection with region proposal networks. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2015, 28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Conde, M.V.; Turgutlu, K. CLIP-Art: Contrastive Pre-Training for Fine-Grained Art Classification. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Nashville, TN, USA, 20–25 June 2021; pp. 3956–3960. [Google Scholar]
- Radford, A.; Wu, J.; Child, R.; Luan, D.; Amodei, D.; Sutskever, I. Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI Blog 2019, 1, 9. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Deep residual learning for image recognition. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 26 June–1 July 2016; pp. 770–778. [Google Scholar]
- Dosovitskiy, A.; Beyer, L.; Kolesnikov, A.; Weissenborn, D.; Zhai, X.; Unterthiner, T.; Dehghani, M.; Minderer, M.; Heigold, G.; Gelly, S.; et al. An image is worth 16x16 words: Transformers for image recognition at scale. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2010.11929. [Google Scholar]
- Krause, J.; Stark, M.; Deng, J.; Fei-Fei, L. 3d object representations for fine-grained categorization. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV) Workshops, Sydney, Australia, 2–8 December 2013; pp. 554–561. [Google Scholar]
- Bossard, L.; Guillaumin, M.; Gool, L.V. Food-101–mining discriminative components with random forests. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 446–461. [Google Scholar]
- Soomro, K.; Zamir, A.R.; Shah, M. UCF101: A dataset of 101 human actions classes from videos in the wild. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1212.0402. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, Z.; Lin, Y.; Cao, Y.; Hu, H.; Wei, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Lin, S.; Guo, B. Swin transformer: Hierarchical vision transformer using shifted windows. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Montreal, QC, Canada, 11–17 October 2021; pp. 10012–10022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, H.; Xu, S.; Fu, J.; Liu, Y.; Xie, N.; Wang, C.C.; Wang, B.; Sun, Y. CMA-CLIP: Cross-Modality Attention CLIP for image–text Classification. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2112.03562. [Google Scholar]
- Researchmm/img2poem: [MM’18] Beyond Narrative Description: Generating Poetry from Images by Multi-Adversarial Training /Data. Available online: https://github.com/researchmm/img2poem/tree/master/data (accessed on 31 March 2022).
- Henderson, M.; Al-Rfou, R.; Strope, B.; Sung, Y.H.; Lukács, L.; Guo, R.; Kumar, S.; Miklos, B.; Kurzweil, R. Efficient natural language response suggestion for smart reply. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1705.00652. [Google Scholar]
- Openai/CLIP: Contrastive Language-Image Pretraining. Available online: https://github.com/openai/CLIP (accessed on 31 March 2022).
- UKPLab/Sentence-Transformers: Multilingual Sentence & Image Embeddings with BERT. Available online: https://github.com/UKPLab/sentence-transformers/blob/master/docs/pretrained_models.md (accessed on 31 March 2022).
- Plummer, B.A.; Wang, L.; Cervantes, C.M.; Caicedo, J.C.; Hockenmaier, J.; Lazebnik, S. Flickr30k Entities: Collecting region-to-phrase correspondences for richer image-to-sentence models. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision, Washington, DC, USA, 7–13 December 2015; pp. 2641–2649. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Maire, M.; Belongie, S.; Hays, J.; Perona, P.; Ramanan, D.; Dollár, P.; Zitnick, C.L. Microsoft coco: Common objects in context. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2014; pp. 740–755. [Google Scholar]

| Method | Data (%) | Retrieval@K (↑) | Retrieval Ranking (↓) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K = 1 | K = 5 | K = 20 | Mean | Median | ||
| CLIP (Zero Shot) | 0 | 10.9 | 25.1 | 40.5 | 139.9 | 42 |
| CLIP (Few Shot) | 20 | 12.0 | 27.7 | 44.3 | 116.3 | 31 |
| CLIP (Fully Supervised) | 100 | 13.0 | 28.6 | 45.5 | 109.8 | 26 |
| This Work | 100 | 18.4 | 44.7 | 65.1 | 71.4 | 17 |
| Method | Data (%) | Retrieval@K (↑) | Retrieval Ranking (↓) | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| K = 1 | K = 5 | K = 20 | Mean | Median | ||
| CLIP (Zero Shot) | 0 | 31 | 51 | 74 | 15.5 | 5 |
| CLIP (Few Shot) | 20 | 34 | 59 | 81 | 12.1 | 4 |
| CLIP (Fully Supervised) | 100 | 32 | 63 | 84 | 9.3 | 3 |
| This Work | 100 | 53 | 78 | 90 | 8.2 | 1 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Jabbar, M.S.; Shin, J.; Cho, J.-D. AI Ekphrasis: Multi-Modal Learning with Foundation Models for Fine-Grained Poetry Retrieval. Electronics 2022, 11, 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11081275
Jabbar MS, Shin J, Cho J-D. AI Ekphrasis: Multi-Modal Learning with Foundation Models for Fine-Grained Poetry Retrieval. Electronics. 2022; 11(8):1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11081275
Chicago/Turabian StyleJabbar, Muhammad Shahid, Jitae Shin, and Jun-Dong Cho. 2022. "AI Ekphrasis: Multi-Modal Learning with Foundation Models for Fine-Grained Poetry Retrieval" Electronics 11, no. 8: 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11081275
APA StyleJabbar, M. S., Shin, J., & Cho, J.-D. (2022). AI Ekphrasis: Multi-Modal Learning with Foundation Models for Fine-Grained Poetry Retrieval. Electronics, 11(8), 1275. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11081275








