Abstract
In this paper, in order to improve the control performance of a high-power electrically excited synchronous motor (EESM) under low switching frequency, and to improve the poor dynamic response of the traditional selective harmonic elimination pulse width modulation (SHEPWM) strategy, an optimized pulse width modulation (PWM) pulse mode with specific harmonic elimination and good dynamic performance is studied. Based on the fast response characteristics of predictive control, it combines the rolling time domain optimization theory with SHEPWM strategy. Firstly, the stator flux linkage of EESM is taken as the tracking target, and the real-time tracking error value of flux linkage is transformed into a voltage-second product; then, the predictive rolling time domain is established, the above error voltage-second product value is optimized in this time domain and the switching angle of SHEPWM is dynamically adjusted to minimize the stator tracking error so as to realize the dynamic adjustment of EESM at low switching frequency. Through MATLAB simulation and a 50 kW experimental platform, the optimized modulation strategy proposed in this paper has been verified to have good dynamic regulation performance at low switching frequency (≈500 Hz).
1. Introduction
Electrically excited synchronous motors (EESM) have been widely used in high-power industrial fields, such as metal rolling, mine hoisting, ship propulsion, locomotive traction, and so on, because of their high efficiency, high power factor and adjustable and high overload capacity [,,,,]. Low-switching-frequency operation of power electronic devices is one of the main means to solve the device loss of a high-power frequency converter, and at the same time, it can further improve the output power of a frequency converter [,,,,,,]. Usually, the switching frequencies of an insulated-gate bipolar transistor (IGBT), integrated-gate commutated thyristor (IGCT) and other power devices in three-level medium- and high-voltage frequency conversion occasions are generally within 500 Hz [,], but low-switching-frequency operation will lead to the aggravation of motor stator current harmonic, the lag of pulse response and even lead to malfunction of the device in serious cases [,].
At present, the modulation strategy for low switching frequency mainly focuses on optimized pulse width modulation (PWM) strategies. One of them is selective harmonic elimination (SHE). Zhao et al. (2019) have studied the key parameter design technology of cascaded H-bridge (CHB) of SHE in a single-phase system, and have proposed a method based on a harmonic envelope to determine the optimal design parameters []; Wu et al. (2021) have mainly discussed the calculation method of switch angles of selective harmonic elimination PWM (SHEPWM) and have proposed a fast convergent homotopy perturbation method (HPM), which can quickly obtain the switching angle of a multilevel inverter []; Ahmad et al. (2021) have proposed a multilevel converter (MLC) to suppress common mode voltage (CMV) by adjusting the low-order dominant zero-sequence harmonics (ZSH) of three-phase SHEPWM waveforms []; Jiang et al. (2022) have used the improved particle swarm optimization method to solve the disadvantages that the traditional SHEPWM, which is easy to fall into the local optimal solution and cannot balance the neutral point voltage of the three-level inverter under the condition of low-voltage ride through (LVRT), cannot []; based on specific application scenarios, Çelik et al. (2022) have proposed a virtual impedance control scheme based on SHE for the harmonic compensation of inverters connecting electric vehicles and distribution networks []. Another strategy is called selective harmonic mitigation (SHM); Moeini et al. (2019) have proposed a low-switching-frequency selective harmonic current suppression PWM (SHCM-PWM) technology for a grid-connected cascaded H-bridge multilevel rectifier []; Moeini et al. (2019) have proposed an asymmetric selective harmonic current suppression PWM (ASHCM-PWM) technology to eliminate grid voltage harmonics, which is used to improve the power quality standard of grid-connected cascaded H-bridge converters []; Sharifzadeh et al. (2019) have proposed an improved selective harmonic suppression pulse amplitude modulation (SHM-PAM) that can eliminate all third harmonics, which can be applied to all kinds of multilevel voltage waveforms []; Moeini et al. (2020) have proposed a low-frequency hybrid modulation technology of cascaded multilevel converters that meets the harmonic limit conditions specified in IEEE 519 2014 by using asymmetric selective harmonic current suppression []; and Schettino et al. (2021) have proposed a harmonic suppression algorithm for cascaded H-bridge multilevel inverters, which takes saturation, cross coupling, spatial harmonic and iron loss effects into consideration at the same time []. Moreover, the strategy of current harmonic optimization (CHO) has also been studied; Tripathi et al. (2017) have proposed a space-vector-based analysis method, which provides a new method for determining the optimal switching angle of high-power and high-speed motor drivers []; Lago et al. (2018) have proposed an optimized modulation mode of multilevel converters based on CHO []; in order to improve the harmonic characteristics under a low modulation index, Zhou (2018) has proposed the optimal PWM method of carrier dynamic overlapping switching frequency []; Birda (2020) has studied the control performance of synchronous optimal PWM for automotive low-voltage electrical transmission systems composed of a two-level voltage source inverter and a built-in permanent magnet synchronous motor []; and Sun (2021) has proposed a theoretical derivation method to reduce the current stress of three-phase dual active bridge (3P DAB) converters in the whole load range, improve the efficiency of the converter and obtain the best synchronous PWM control scheme [].
From the literature review above, it can be seen that the strategies proposed by scholars can effectively reduce low-order harmonics and optimize inverter output current; however, they have the defects that they can only be operated off-line and have poor dynamic performance. Even if the literature [,,] has given some control strategies suitable for a high-power transmission system, such as optimal time control, direct current (DC) control and model predictive control, the main objects being controlled are asynchronous motors and permanent magnet motors, and there is a lack of discussion on EESM at low switching frequency. Therefore, in this paper, the EESM operating at low switching frequency was the research object. Firstly, its convex rotor effect is considered, and the complex matrix mathematical model isestablished; then, aiming at the poor dynamic performance of traditional optimized PWM modulation, an improved optimized PWM pulse mode combining the predictive control rolling time domain optimization theory and the selective harmonic elimination PWM (SHEPWM) strategy is proposed to realize the dynamic regulation of EESM at low switching frequency by dynamically adjusting the flux linkage tracking error in the rolling time domain.
2. Complex Matrix Model of EESM
If the damping winding is ignored, the voltage equation of EESM in a rotating coordinate system can be written as:
where usd and usq are the d-axis and q-axis components of the three-phase stator voltage; isd and isq are the d-axis and q-axis components of the three-phase stator current; uf is the excitation voltage; if is the excitation current; Ψsd and Ψsq are the d-axis and q-axis components of stator flux linkage, Ψf is the excitation flux linkage; Rs and Rf are stator resistance and excitation resistance; p is the differential operator, ωr is the rotor angular velocity.
If uf is defined as uf = uf + j0, and if is defined as if = if + j0, then:
where us and ud are stator voltage vector and excitation voltage vector, respectively; Ψs and Ψf are stator flux linkage vector and excitation flux linkage vector, respectively; ls is the inductance coefficient of the stator side, lm is the mutual inductance coefficient between stator and rotor, Lf is the excitation inductance coefficient, and
Ld and Lq are the synchronous inductance coefficients of d-axis and q-axis, respectively, and Lmd and Lmq are the armature reaction coefficients of d-axis and q-axis, respectively.
If Equation (2) is simplified, the following equation:
can be obtained, where τ′s = σls/Rs, τ′f = σLf/Rf; σ = 1 − lm2/lsLf is the total leakage inductance factor, kf = lm/Lf is the rotor-coupling coefficient, ks = lm/ls is the stator-coupling coefficient. The model block diagram of EESM is shown in Figure 1, where τm is the mechanical time constant, Te is the electromagnetic torque, TL is the load torque and kr is the calculation constant.
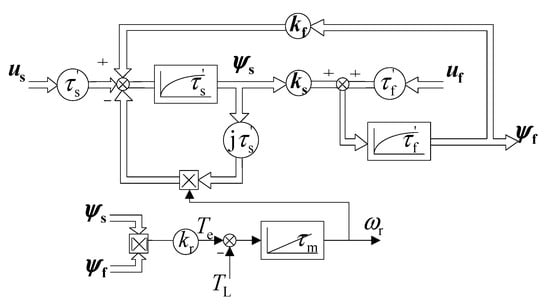
Figure 1.
Complex matrix model of an electrically excited motor.
3. Predictive Optimized PWM Pulse Mode
3.1. Specific Harmonic Elimination Method
When the diode-clamped three-level topology shown in Figure 2 is used to drive the EESM, the corresponding unipolar SHEPWM modulation contains the a-phase voltage waveform of N switching angles, as shown in Figure 3.
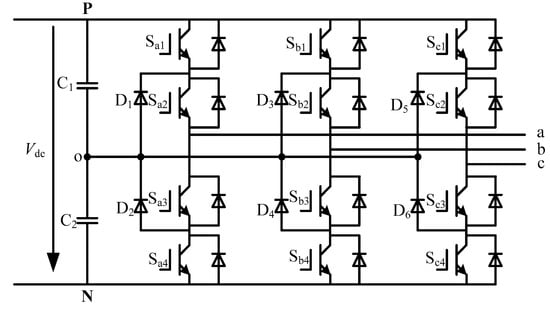
Figure 2.
Topology of diode-clamped three-level converter.
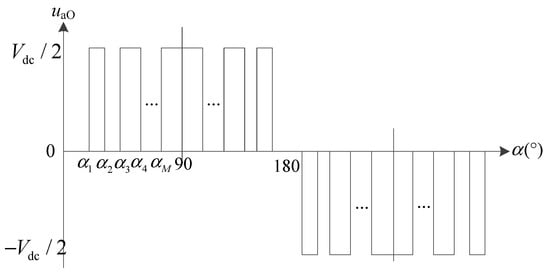
Figure 3.
a-phase voltage uaO based on the unipolar SHEPWM.
Generally speaking, the switching angle of SHEPWM can be solved with the help of the fsolve function in the MATLAB optimization toolbox, which is realized based on FPGA after piecewise linear fitting. Taking the switching angle N = 7 as an example, the off-line calculation shows that the seven switching angles of the bridge arm switching on a-phase in a quarter cycle are 28.54°, 31.24°, 41.15°, 45.34°, 52.61°, 60.84° and 64.24°, respectively. Then, according to the phase difference relationship of a, b and c three-phase and the π mirror symmetry and π/2 even symmetry characteristics of SHEPWM modulation itself, the theoretical pulse waveform of three-phase output phase voltage (relative to neutral point O) of the three-level inverter at this time can be obtained, as shown in Figure 4.
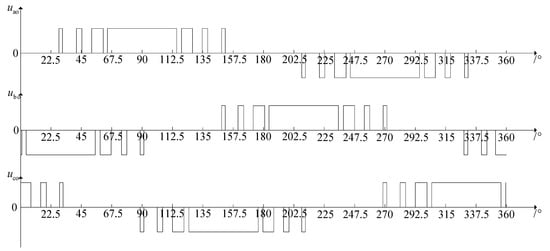
Figure 4.
Three-phase output phase voltage waveform when switching angle N = 7.
3.2. Optimized PWM Pulse Mode
The essence of high-performance control for motors lies in torque and flux linkage control; that is, the PWM pulse mode needs to ensure the error between the desired flux linkage ψp (obtained by integrating the desired PWM output voltage vector) in the dynamic process and the actual flux linkage ψobs (obtained by flux observer) is minimized, and the dynamic performance of torque regulation should be met. Based on the steady-state SHEPWM pulse mode as the basis of dynamic regulation, by calculating the flux tracking error, the tracking error can be transformed into the width change of PWM output pulse based on the principle of voltage-second balance, as shown in Equation (4).
Using the characteristics of model predictive control, such as multi-step prediction, rolling optimization and feedback correction, the original pulse width is adjusted in rolling time domain period Tp; if the sampling time is small enough, the dynamic adjustment of the pulse mode can be realized, and Equation (4) can be transformed into discrete state:
where Na, Nb and Nc are the adjustment times of three-phase pulses in rolling time domain cycle Tp, respectively, Vdc is the voltage value at DC side, Δti (i = a, b, c), Δsi is the switching action amplitude (for diode-clamped three-level topology, si has only three possible values: +1, −1 and 0). In order to ensure the loss to be controlled during switching of switching state, jump switching is not considered in this paper, which means that |Δsi| = 1 can be ensured. Taking the quarter cycle of a-phase output voltage shown in Figure 3 as an example, the corresponding Ts = 0.1 ms, Tp = 1 ms and pulse adjustment diagram are shown in Figure 5 (the corresponding pulse adjustment can be different if different Ts and Tp value are selected).
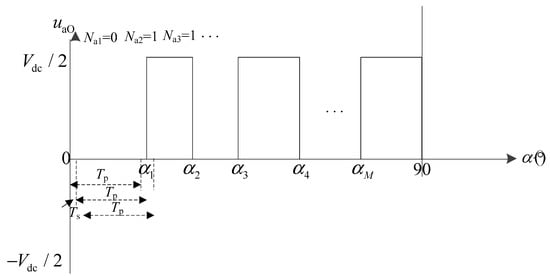
Figure 5.
Schematic diagram of Ts, Tp and the number of pulse adjustment.
It can be seen from Figure 5 that: (1) multiple rolling time domain optimization can be carried out in one stator fundamental frequency cycle; (2) the switching adjustment times Ni of each phase in each rolling time domain cycle Tp are not fixed; (3) based on the rolling optimization theory, no matter what the value Ni is, only the first adjustment is selected and put into the actual system to realize multi-step prediction and feedback correction.
3.3. Relization Design
The system control block diagram of EESM at low switching frequency is shown in Figure 6. It includes speed measurement, speed closed-loop, flux linkage closed-loop (including weak magnetic field adjusting), current closed-loop, SHEPWM steady-state optimization and its dynamic correction link.
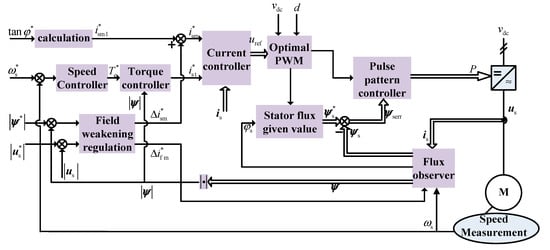
Figure 6.
System control block diagram of EESM at low switching frequency.
The module of “Stator flux given value” in Figure 6 is used to integrate the output voltage during steady-state optimized SHEPWM modulation, so as to obtain the given value of stator flux linkage; the input of the module “Pulse pattern controller” is the flux linkage tracking error and the steady-state switching angle of SHEPWM, and the output signal is the change value of the output pulse width of SHEPWM after dynamic adjustment.
Based on the concept of model prediction rolling time domain adjustment, the goal of this pulse dynamic adjustment can be described as:
where ψs,corr is the stator flux linkage tracking adjustment value, q is the weight factor, and qΔtTΔt is introduced to reduce the number of switching actions in the process of dynamic adjustment.
In Equation (6), ∆t is the dynamic adjustment point of the switching angle, which can be expressed as
and
where , and are the first original switching angle time of each phase outside the rolling time domain cycle Tp, respectively.
Taking a-phase as an example, the adjustment width of the i-th switching angle in the rolling time domain cycle Tp is ∆tai = tai − t*ai, where t*ai is the original switching angle action time and tai is the adjusted switching angle action time; the corresponding voltage-second product value is ∆Sai. According to the above analysis, the tracking adjustment value of stator flux linkage can be obtained as
The adjustment times Ni (i = a, b, c) of the three-phase pulses in the rolling time domain cycle Tp can be calculated in advance through the off-line-calculated SHEPWM switching angle and the actual Tsample and Tp values. Take 0~22.5° in Figure 4 as an example, after amplification, the position of the three-phase switching angle is shown in Figure 7. Since there is no switching angle in this section, the adjustable times Na of a-phase is 0; in this section, b-phase has two switching angles, so its adjustable times Nb = 2; similarly, the adjustable times of c-phase is Nc = 2.
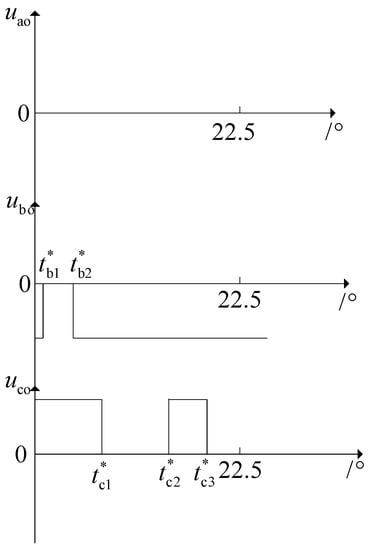
Figure 7.
Principle of the calculation for Ni.
Taking the original SHEPWM switching angle shown in Figure 4 as an example, the switching angle after one dynamic adjustment is shown in Figure 8, in which the pulse adjustment times of each phase are Na = 3, Nb = 0 and Nc = 2, respectively, and the adjusted switching angle is shown in the dotted line.
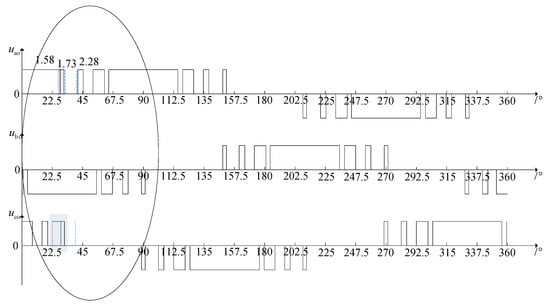
Figure 8.
Regulated switching angles with SHEPWM.
4. Performance Analysis
Due to the power limitation of an experimental motor, simulation and experimental verification are only carried out on a 380 V, 50 kW motor. The experimental parameters are shown in Table 1.

Table 1.
The average tour length, gap percentage and average solution time of TSP.
4.1. Simulation Analysis
Firstly, the simulation analysis is carried out based on MATLAB simulation software. In the simulation, start at the rated speed with the rated load at the maximum allowable current when t = 0.2 s, then reduce the load suddenly to half of the rated load when t = 2 s, and increase the load suddenly to the rated load when t = 3 s. At this point in time, record the motor speed, stator current, load and torque waveform, a-phase current waveform and the dynamic trajectory of the corresponding a-phase switching pulse and stator current, respectively; the corresponding results are seen in Figure 9, Figure 10, Figure 11, Figure 12, Figure 13.
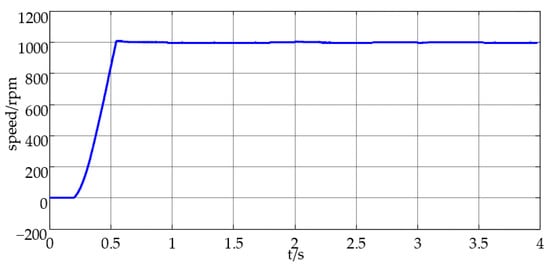
Figure 9.
Dynamic speed waveform.
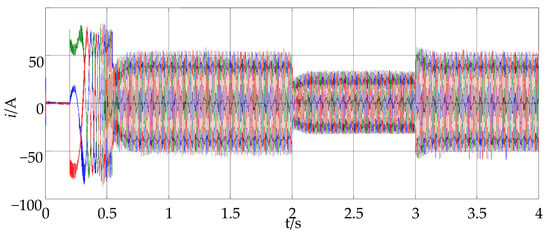
Figure 10.
Three-phase stator current waveform.
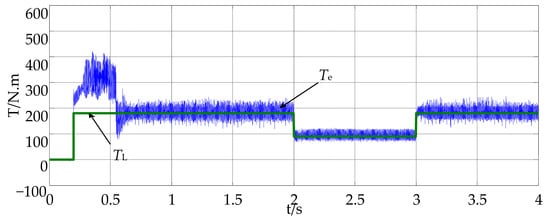
Figure 11.
Load and torque waveform.
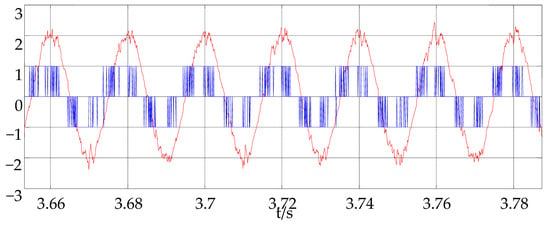
Figure 12.
a-phase stator current (reduced) waveform and corresponding pulse waveform.
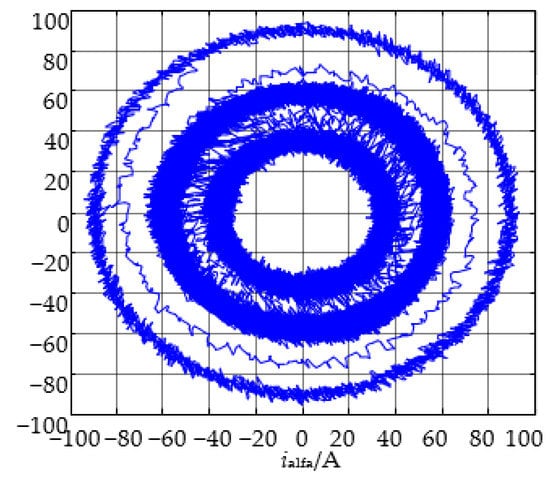
Figure 13.
Dynamic trace diagram of stator current.
4.2. Experimental Verification
According to the discussion at the beginning of this section, the experimental system is set up, and the experimental devices can be seen in Figure 14.
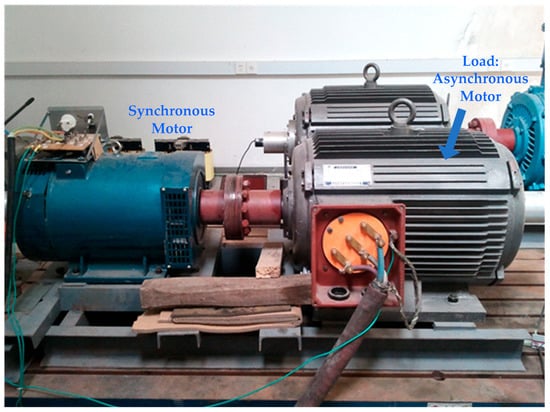
Figure 14.
Photo of experimental devices.
The model predictive control is used to optimize the way to control the PWM mode; the EESM at low switching frequency has been dynamically adjusted. Firstly, when using SHEPWM modulation, the motor starts without load, accelerates to 1000 rpm in forward rotation, accelerates to 1000 rpm in reverse rotation and then decelerates to zero in reverse rotation. The motor speed (CH1), electromagnetic torque (CH3), air gap flux amplitude (CH2) and excitation current waveform (CH4) are shown in Figure 15.
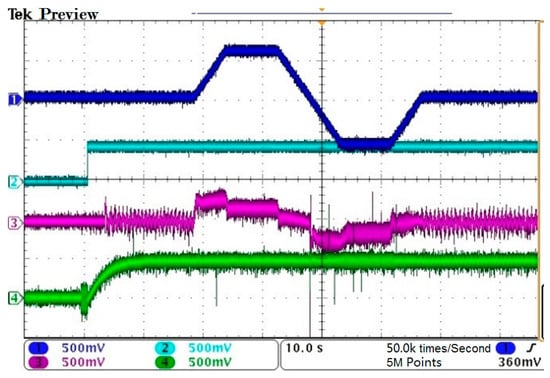
Figure 15.
The starting, forward and reverse rotation and deceleration process of motor.
When the motor is started at 1000 rpm with light load, the a-phase switching pulse output by the PWM inverter and the a-phase stator current of the motor are output to the oscilloscope, as shown in Figure 16.
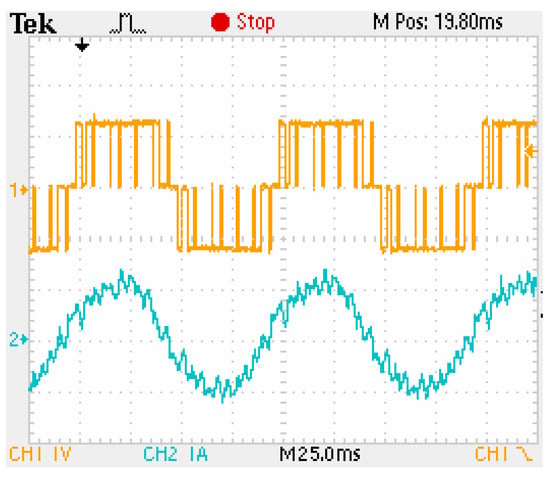
Figure 16.
a-phase switching pulse and stator current waveform of motor in steady state.
As the forward rotation speed of 1000 rpm was maintained, the speed and torque waveforms of EESM during sudden load addition and sudden load reduction are shown in Figure 17. The green-blue line at the top of the figure below is the speed, while the dark blue line at the bottom is the torque. The increase in torque indicates loading and the decrease represents load reduction. The embodiment of the control effect can be clearly seen from the stability of the speed kept during loading and unloading.
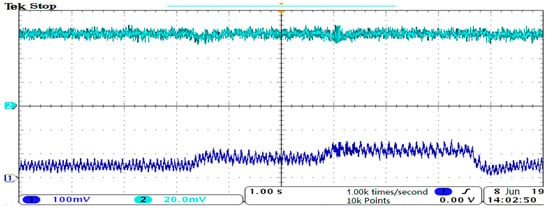
Figure 17.
Dynamic load addition and load reduction process of EESM at low switching frequency, CH1: speed waveform; CH2: torque waveform.
5. Conclusions
In order to improve the dynamic speed regulation performance of an EESM at low switching frequency, the following work has been carried out in this paper: (1) the EESM is modeled based on a complex matrix, which simplifies the model and reveals the internal electromagnetic structure of the system; (2) taking the stator flux linkage as the tracking target, the rolling time domain optimization theory is combined with the optimized PWM strategy to realize the dynamic adjustment of the motor through the dynamic adjustment of the switching angle in the rolling time domain; (3) the 50 kW experimental platform verifies the accuracy of rotor initial position angle acquisition and good dynamic regulation performance of the EESM at a low switching frequency (≈500 Hz).
From the simulation as well as the experiment results shown in this paper, it can be seen that the control performance of the high-power electrically excited synchronous motor (EESM) under low switching frequency is improved to a great extent, and the poor dynamic response of the traditional selective harmonic elimination pulse width modulation (SHEPWM) strategy is evidently improved. Limited by the experimental conditions, the experimental verification is not carried out on the real high-power platform, which is one of the future works which are supposed to be carried out.
Author Contributions
K.L. and Q.Y. proposed the idea of an optimized pulse width modulation (PWM) pulse mode combining rolling time domain optimization theory with selective harmonic elimination PWM (SHEPWM) strategy; K.L. conceived and designed the experiments; Q.Y. set up and performed the simulation and experiments; K.L., Q.Y. and W.N. analyzed the simulation and experimental results; W.N. wrote the paper. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was supported in part by the Science and Technology Commission of Shanghai Foundation under Grant No. 19DZ1205804, the Jiaxing Public Welfare Research Project under Grant No. 2020AY10033, No. 2020AY30025 and No. 2021AY10079 and the General Scientific Research Fund of Zhejiang Provincial Education Department under Grant No. Y202147878.
Data Availability Statement
The data used to support the findings of this study are available from the corresponding author upon request.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Zhou, Y.Z.; Hu, Y.W. A novel direct torque control for electrically excited synchronous motor drives with high power factor and low ripples in flux and torque. In Proceedings of the IEEE Power Electronics Specialists Conference, Rhodes, Greece, 15–19 June 2008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pontt, J.A.; Rodrigues, J.R.; Liendo, A.; Newman, P. Network-friendly low-switching-frequency multipulse high-power three-level PWM rectifier. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 1254–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, F.; Jia, G.; Zhao, Y.; Yang, Z.; Cao, W.; Kirtley, J.L. Simulation and experimental analysis of a brushless electrically excited synchronous machine with a hybrid rotor. IEEE Trans. Magn. 2015, 51, 8115007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jeong, I.; Gu, B.-G.; Kim, J.; Nam, K.; Kim, Y. Inductance estimation of electrically excited synchronous motor via polynomial appoximations by least square method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2015, 51, 1526–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, Y.; Wu, X.; He, G.; Hu, Y.; Ni, K. Inductance estimation of electrically excited synchronous motor via polynomial appoximations by least square method. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2020, 35, 11053–11063. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.; Ge, Q.; Yin, Z.; Liu, C.; Li, Y. The optimal control strategy for rectifier side of low switching frequency back-to-back converter. In Proceedings of the 25th Annual IEEE Applied Power Electronics Conference and Exposition (APEC), Palm Springs, CA, USA, 21–25 February 2010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtz, J.; Oikonomou, N. Optimal control of a dual three-level inverter system for medium-voltage drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2010, 46, 1034–1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtz, J.; Oikonomou, N. Fast dynamic control of medium voltage drives operating at very low switching frequency—An overview. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2008, 55, 1005–1013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gnanasambandam, K.; Edpuganti, A.; Rathore, A.K.; Srinivasan, D.; Cecati, C.; Buccela, C. Optimal low switching frequency pulsewidth modulation of current-fed three-level converter for solar power integration. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2016, 63, 6877–6886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, W.; Wang, C.; Wu, X. Coupling analysis on current control at low switching frequency for the three-phase PWM converter based on RGA and a novel output feedback decoupling method. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2016, 63, 6685–6694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasongko, F.; Akagi, H. Low-switching-frequency operation of a modular multilevel DSCC converter with phase-shifted rotating-carrier PWM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2016, 32, 5058–5069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tian, H.; Li, Y.W.; Zhao, Q. Multirate harmonic compensation control for low switching frequency converters: Scheme, modeling, and analysis. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 35, 4143–4156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieckerhoff, S.; Bernet, S.; Krug, D. Power loss-oriented evaluation of high voltage IGBTs and multilevel converters in transformerless traction applications. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2005, 20, 1328–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bose, B.K. Power electronics and motor drives—Technology advances, trends and applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Industrial Technology (ICIT), Hong Kong, China, 14–17 December 2005. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtz, J.; Oikonomou, N. Estimation of the fundamental current in low-switching-frequency high dynamic medium-voltage drives. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 1597–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Franklin, G.F.; Powell, J.D.; Naeini, A.E. Feedback Control of Dynamic Systems, 8th ed.; Pearson Prentice Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2018; pp. 43–55. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, H.; Wang, S.; Moeini, A. Critical parameter design for a caascaded H-bridge with selective harmonic elimination/compensation based on harmonic envelope analysis for single-phase systems. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2019, 64, 2914–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Xue, C.; Li, Y.W.; Yang, K. A generalized selective harmonic elimination PWM formulation with common-mode voltage reduction ability for multilevel converters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 36, 10753–10765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, S.; Iqbal, A.; Ali, M.; Rahman, K.; Ahmed, A.S. A fast convergent homotopy perturbation method for solving selective harmonics elimination PWM problem in multi level inverter. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 113040–113051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, X.; Qin, C.; Xing, X.; Chen, Z. Improved particle swarm optimization based selective harmonic elimination and neutral point balance control for three-level inverter in low-voltage ride-through operation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Inform. 2022, 18, 642–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çelik, D.; Meral, M.E. A coordinated virtual impedance control scheme for three phase four leg inverters of electric vehicle to grid (V2G). Energy 2022, 246, 123354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, A.; Zhao, H.; Wang, S. A current-reference-based selective harmonic current mitigation PWM technique to improve the performance of cascaded H-bridge multilevel active rectifiers. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2018, 65, 727–737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, A.; Wang, S. A DC link sensor-less voltage balancing technique for cascaded H-bridge multilevel converters with asymmetric selective harmonic current mitigation PWM. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 33, 7571–7581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharifzadeh, M.; Vahedi, H.; Portillo, R.; Franquelo, L.G.; Al-Haddad, K. Selective harmonic mitigation based self-elimination of triplen harmonics for single-phase five-level inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2019, 34, 86–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moeini, A.; Wang, S.; Zhang, B.; Yang, L. A hybrid phase shift-pulsewidth modulation and asymmetric selective harmonic current mitigation-pulsewidth modulation technique to reduce harmonics and inductance of single-phase grid-tied cascaded multilevel converters. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 67, 10388–18398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schettino, G.; Nevoloso, C.; Miceli, R.; Di Tommaso, A.O.; Viola, F. Impact evaluation of innovative selective harmonic mitigation algorithm for cascaded H-bridge inverter on IPMSM drive application. IEEE Open J. Ind. Appl. 2021, 2, 347–365. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, A.; Narayanan, G. Investigations on optimal pulse width modulation to minimize total harmonic distortion in the line current. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2017, 53, 212–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lago, J.; Heldwein, M.L. Generalized synchronous optimal pulse width modulation for multilevel inverters. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2017, 32, 6297–6307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, F.; Xu, Q.; Luo, A.; He, Z.; Li, Y.; Xie, N.; Wang, Y. Carrier dynamic overlapping switching frequency optimal pulse width modulation method for modular multilevel converters. J. Mod. Power Syst. Clean Energy 2018, 6, 1306–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Birda, A.; Reuss, J.; Hackl, C.M. Synchronous optimal pulsewidth modulation for synchronous machines with highly operating point dependent magnetic anisotropy. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2020, 68, 3760–3769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Qiu, L.; Liu, X.; Zhang, J.; Ma, J.; Fang, Y. Optimal simultaneous PWM control for three-phase dual-active-bridge converters to minimize current stress in the whole load range. IEEE J. Emerg. Sel. Top. Power Electron. 2021, 9, 5822–5837. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holtz, J.; Oikonomou, N. Closed-loop control of medium-voltage drives operated with synchronous optimal pulsewidth modulation. IEEE Trans. Ind. Appl. 2008, 44, 115–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nemec, M.; Drobnic, K.; Nedeljkovic, D.; Ambrozic, V. Direct current control of a synchronous machine in field coordinates. IEEE Trans. Ind. Electron. 2009, 56, 4052–4061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alnajjar, M.; Gerling, D. Model predictive control of six-phase variable frequency electrically excited starter generator for more electric aircraft. In Proceedings of the IEEE 11th International Conference on Power Electronics and Drive Systems, Sydney, Australia, 9–12 June 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).