The Efficacy of Shape Radiomics and Deep Features for Glioblastoma Survival Prediction by Deep Learning †
Abstract
:1. Introduction
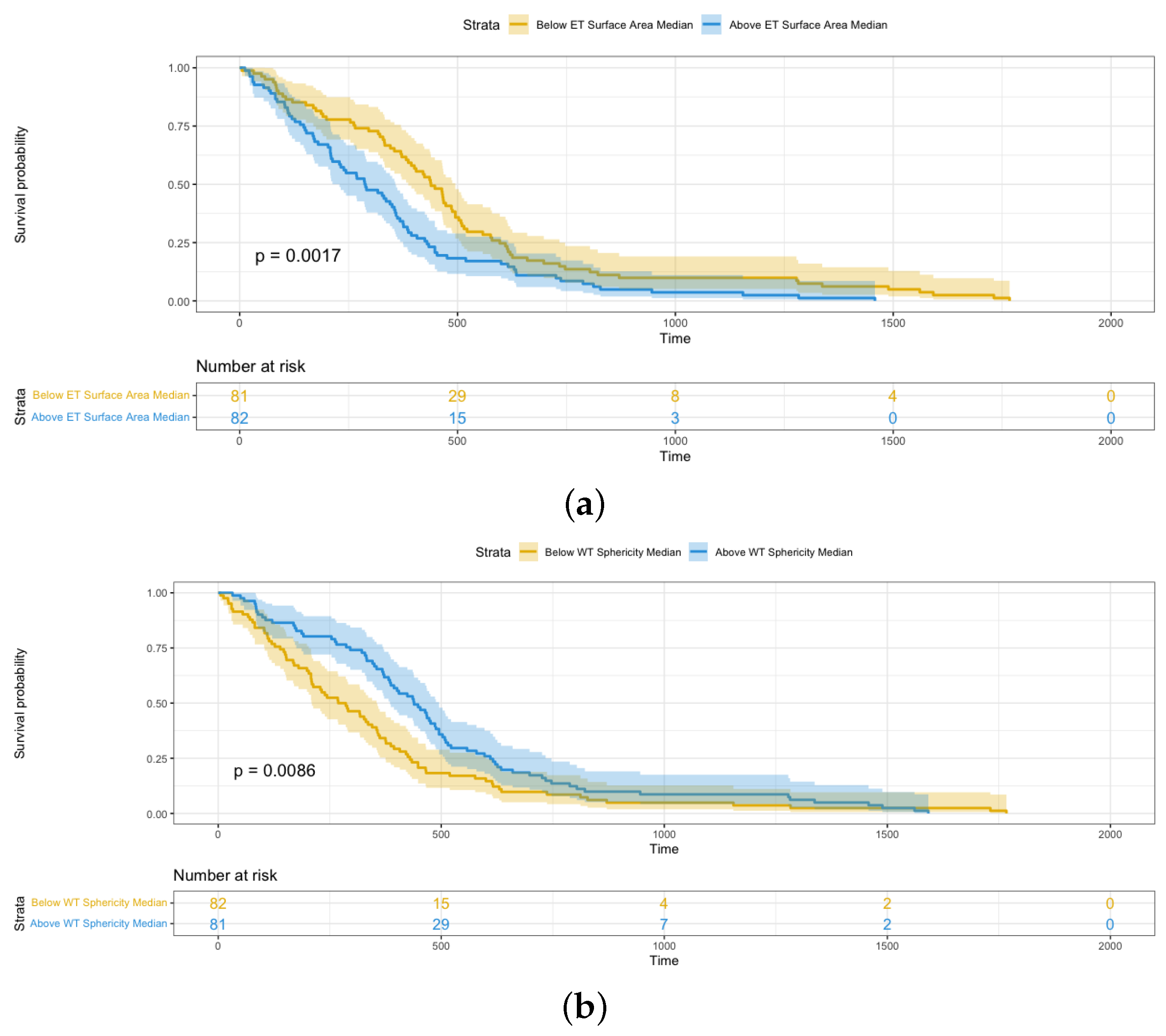
- Sphericity, 3D maximum diameter, and surface area are three significant shape features relevant to the survival analysis of glioblastoma patients. Furthermore, these features from the enhancing tumor have more effect on patients’ survival time than those from the whole tumor based on hazard ratio.
- Aside from shape features, the extracted features (known as deep features) from enhancing tumor and whole tumor are essential for survival prediction compared to those from the whole tumor only; therefore, enhancing tumor’s characteristics affects the survival prediction for GBM patients.
2. Related Work
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Overview
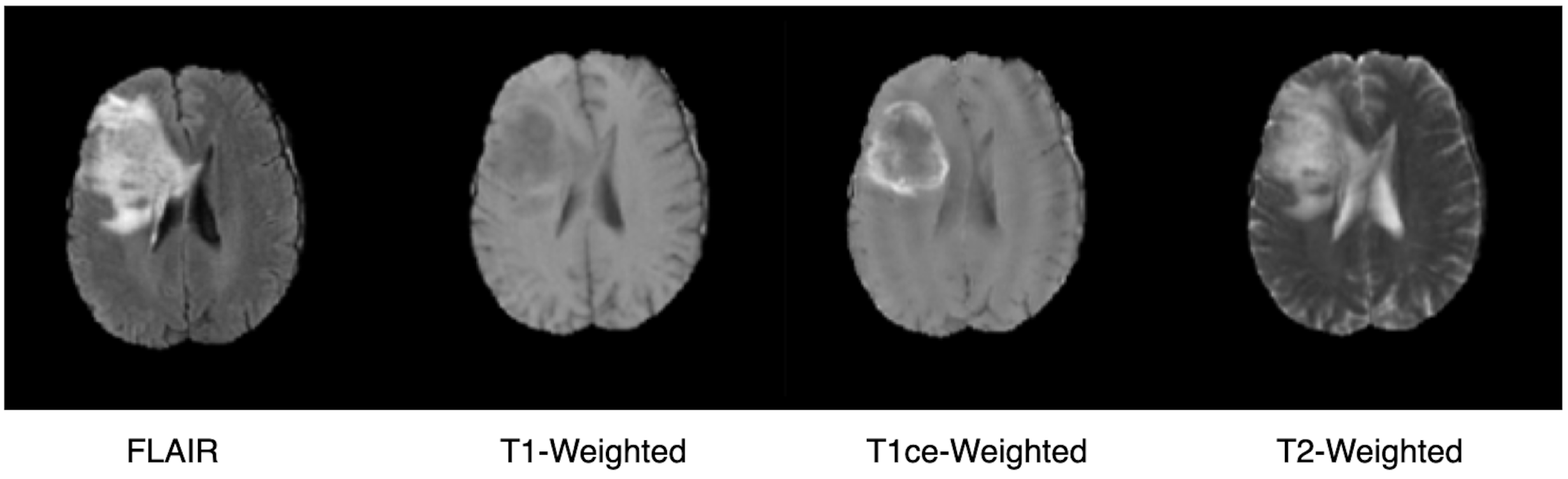
3.2. Dataset
3.3. Segmentation
3.4. Tumor Shape Radiomics Features Analysis
- is the time point at least one patient dead.
- is number of patients dead at .
- is number of patients surviving until time .
- h(t|z): hazard function determined by given vector of several predictors z.
- : is an unspecific function of time.
- : hazard ratio (HR). HR = 1: predictors does not have effect on survival time, HR < 1: associated with improved survival time, HR > 1: associated with increased risk or decreased survival time [21].
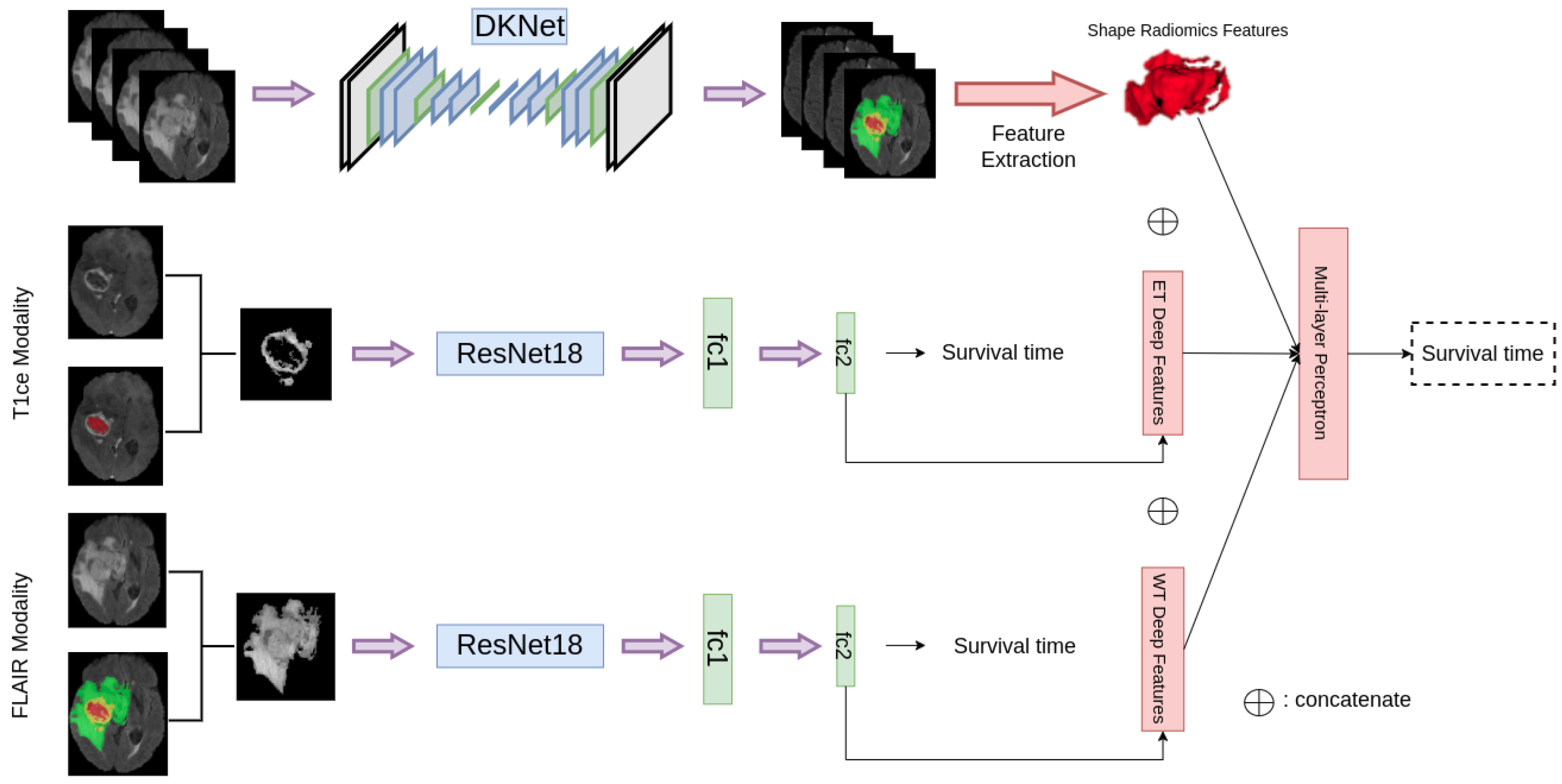
3.5. Deep Feature Extraction
3.6. Overall Survival Prediction
4. Results
4.1. Segmentation
4.2. Evaluation Metrics for Survival Prediction
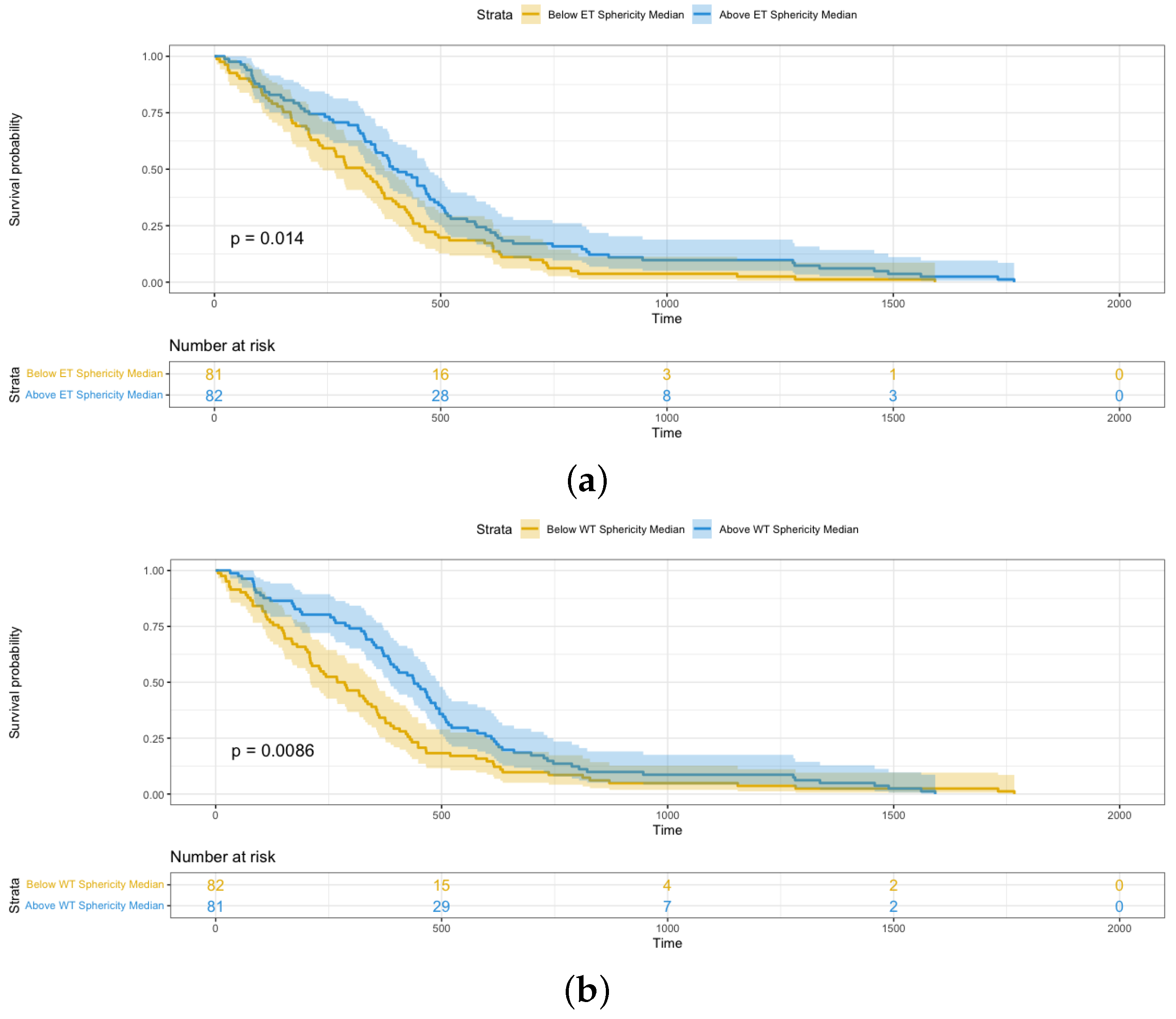
4.3. Shape Radiomics Features Analysis
| HR | 95% CI | p-Value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Enhancing Tumor | |||
| Elongation | 0.779 | 0.284–2.138 | 0.6 |
| Flatness | 0.837 | 0.319–2.195 | 0.7 |
| Least Axis Length | 1.018 | 1.002–1.035 | 0.06 |
| Major Axis Length | 1.013 | 1.004–1.021 | 0.07 |
| Maximum 2D Diameter Column | 1.011 | 0.960–1.022 | 0.06 |
| Maximum 2D Diameter Row | 1.014 | 1.000–1.024 | 0.004 |
| Maximum 2D Diameter Slice | 1.012 | 0.990–1.021 | 0.005 |
| Maximum 3D Diameter | 1.112 | 1.023–1.223 | 0.005 |
| Mesh Volume | 1 | 1–1 | 0.05 |
| Minor Axis Length | 1.019 | 1.004–1.033 | 0.06 |
| Sphericity | 0.184 | 0.049–0.698 | 0.01 |
| Surface Area | 1.231 | 1.139–1.342 | 0.0001 |
| Surface Volume Ratio | 1.054 | 0.642–1.729 | 0.8 |
| Voxel Volume | 1 | 1–1 | 0.04 |
| Whole Tumor | |||
| Elongation | 0.514 | 0.122–2.160 | 0.4 |
| Flatness | 0.315 | 0.068–1.456 | 0.1 |
| Least Axis Length | 1.012 | 0.995–1.028 | 0.2 |
| Major Axis Length | 1.012 | 1.003–1.012 | 0.07 |
| Maximum 2D Diameter Column | 1.008 | 1.000–1.016 | 0.06 |
| Maximum 2D Diameter Row | 1.009 | 0.992–1.017 | 0.04 |
| Maximum 2D Diameter Slice | 1.010 | 1.000–1.017 | 0.03 |
| Maximum 3D Diameter | 1.017 | 1.011–1.028 | 0.03 |
| Mesh Volume | 1 | 1–1 | 0.1 |
| Minor Axis Length | 1.016 | 0.984–1.031 | 0.02 |
| Sphericity | 0.2669 | 0.069–0.762 | 0.02 |
| Surface Area | 1.023 | 1.003–1.127 | 0.02 |
| Surface Volume Ratio | 0.796 | 0.201–3.151 | 0.7 |
| Voxel Volume | 1 | 1–1 | 0.1 |
| Clinical Information | |||
| Age | 1.036 | 1.021–1.051 | 0.000001 |
4.4. Overall Survival Prediction
5. Discussion
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hanif, F.; Muzaffar, K.; Perveen, K.; Malhi, S.M.; Simjee, S.U. Glioblastoma multiforme: A review of its epidemiology and pathogenesis through clinical presentation and treatment. APJCP 2017, 18, 3. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trinh, D.; Kim, S.; Yang, H.; Lee, G. Brain Tumor Survival Prediction using Shape Radiomics Features by Linear Regression. SMA2021 2021, 4. [Google Scholar]
- Menze, B.H.; Andras, J.; Stefan, B.; Jayashree, K.; Keyvan, F.; Justin, K.; Yuliya, B.; Nicole, P.; Johannes, S.; Roland, W.; et al. The multimodal brain tumor image segmentation benchmark (BRATS). IEEE Trans. Med. Imaging 2014, 34, 1993–2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, D.; Tran, M.; Kim, S.; Yang, H.; Lee, G. Multi-task learning for small brain tumor segmentation from MRI. Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 7790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shboul, Z.A.; Vidyaratne, L.; Alam, M.; Iftekharuddin, K.M. Glioblastoma and survival prediction. Int. MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop 2017, 10670, 358–368. [Google Scholar]
- Baid, U.; Talbar, S.; Rane, S.; Gupta, S.; Thakur, M.H.; Moiyadi, A.; Thakur, S.; Mahajan, A. Deep learning radiomics algorithm for gliomas (drag) model: A novel approach using 3d unet based deep convolutional neural network for predicting survival in gliomas. In International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 369–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, X.; Tustison, N.J.; Patel, S.H.; Meyer, C.H. Brain tumor segmentation using an ensemble of 3d u-nets and overall survival prediction using radiomic features. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, S.; Luo, L. Tumor segmentation and survival prediction in glioma with deep learning. In International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 83–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ronneberger, O.; Fischer, P.; Brox, T. U-net: Convolutional networks for biomedical image segmentation. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Munich, Germany, 5–9 October 2015; pp. 234–241. [Google Scholar]
- Isensee, F.; Kickingereder, P.; Wick, W.; Bendszus, M.; Maier-Hein, K.H. Brain tumor segmentation and radiomics survival prediction: Contribution to the brats 2017 challenge. In International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 287–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, G.; Li, W.; Ourselin, S.; Vercauteren, T. Automatic brain tumor segmentation using cascaded anisotropic convolutional neural networks. In International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2017; pp. 178–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Soltani, M.; Bonakdar, A.; Shakourifar, N.; Babaie, R.; Raahemifar, K. Efficacy of Location-Based Features for Survival Prediction of Patients with Glioblastoma Depending on Resection Status. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, H.; Zhang, W.; Fang, Y.; Hong, J.; Su, S.; Lai, X. Overall Survival Prediction for Gliomas Using a Novel Compound Approach. Front. Oncol. 2021, 3150, 724191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hermoza, R.; Maicas, G.; Nascimento, J.C.; Carneiro, G. Post-hoc Overall Survival Time Prediction from Brain MRI. In Proceedings of the 2021 IEEE 18th International Symposium on Biomedical Imaging (ISBI), Nice, France, 13–16 April 2021; pp. 1476–1480. [Google Scholar]
- Pei, L.; Vidyaratne, L.; Rahman, M.M.; Iftekharuddin, K.M. Context aware deep learning for brain tumor segmentation, subtype classification, and survival prediction using radiology images. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakas, S.; Akbari, H.; Sotiras, A.; Bilello, M.; Rozycki, M.; Kirby, J.S.; Freymann, J.B.; Farahani, K.; Davatzikos, C. Advancing the cancer genome atlas glioma MRI collections with expert segmentation labels and radiomic features. Sci. Data 2017, 4, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Bakas, S.; Reyes, M.; Jakab, A.; Bauer, S.; Rempfler, M.; Crimi, A.; Shinohara, R.T.; Berger, C.; Ha, S.M.; Rozycki, M.; et al. Identifying the best machine learning algorithms for brain tumor segmentation, progression assessment, and overall survival prediction in the BRATS challenge. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1811.02629. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.; Liu, X.; Ding, M.; Zheng, J.; Li, J. 3D Dilated Multi-Fiber Network for Real-time Brain Tumor Segmentation in MRI. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Medical Image Computing and Computer-Assisted Intervention, Shenzhen, China, 13–17 October 2019; pp. 184–192. [Google Scholar]
- Radiomic Features. Available online: https://pyradiomics.readthedocs.io/ (accessed on 26 December 2012).
- Goel, M.K.; Khanna, P.; Kishore, J. Understanding survival analysis: Kaplan-Meier estimate. Int. J. Ayurveda Res. 2010, 1, 274. [Google Scholar] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Devarajan, K.; Ebrahimi, N. Testing for covariate effect in the cox proportional hazards regression model. Commun. Stat.-Theory Methods 2009, 14, 2333–2347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baid, U.; Rane, S.U.; Talbar, S.; Gupta, S.; Thakur, M.H.; Moiyadi, A.; Mahajan, A. Overall survival prediction in glioblastoma with radiomic features using machine learning. Front. Comput. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spearman’s Rank-Order Correlation. Available online: https://statistics.laerd.com/ (accessed on 26 December 2021).
- Weninger, L.; Rippel, O.; Koppers, S.; Merhof, D. Segmentation of brain tumors and patient survival prediction: Methods for the brats 2018 challenge. In International MICCAI Brainlesion Workshop; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2018; pp. 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
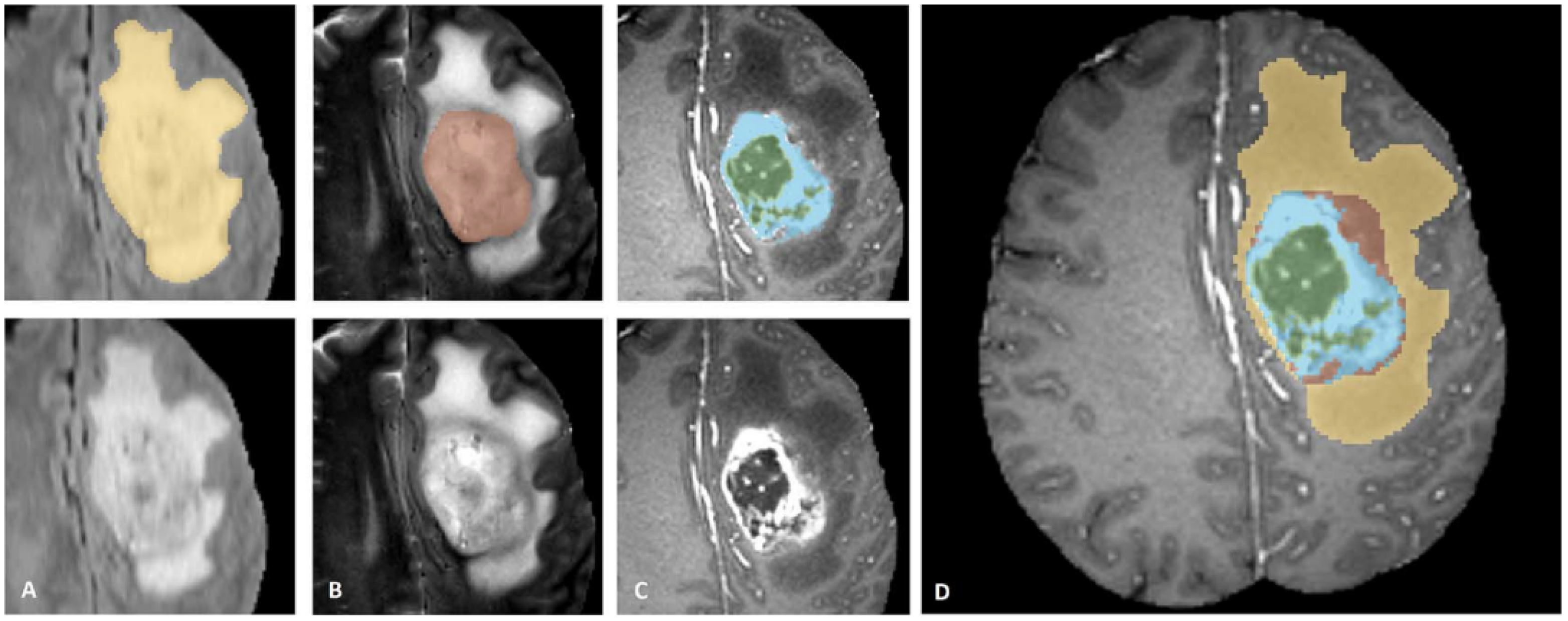


| Method | Dice ET | Dice TC | Dice WT | HD 95 ET | HD 95 TC | HD 95 WT |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| DKNet | 0.8182 | 0.8181 | 0.8876 | 2.6835 | 5.6112 | 4.6000 |
| DFs | Accuracy | MSE |
|---|---|---|
| WT DFs | 0.393 | 244,139.9 |
| ET DFs | 0.321 | 185,454.8 |
| Selected DFs (18 features) | 0.464 | 123,320.8 |
| Features | Linear Regression | LightGBM | MLP | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Acc | MSE | Acc | MSE | Acc | MSE | |
| SFs + Age | 0.536 | 128,839.4 | 0.500 | 108,577.9 | 0.536 | 99,482.7 |
| SFs + DFs + Age | 0.500 | 116,463.9 | 0.464 | 99,577.4 | 0.571 | 97,531.8 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Trinh, D.-L.; Kim, S.-H.; Yang, H.-J.; Lee, G.-S. The Efficacy of Shape Radiomics and Deep Features for Glioblastoma Survival Prediction by Deep Learning. Electronics 2022, 11, 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11071038
Trinh D-L, Kim S-H, Yang H-J, Lee G-S. The Efficacy of Shape Radiomics and Deep Features for Glioblastoma Survival Prediction by Deep Learning. Electronics. 2022; 11(7):1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11071038
Chicago/Turabian StyleTrinh, Dang-Linh, Soo-Hyung Kim, Hyung-Jeong Yang, and Guee-Sang Lee. 2022. "The Efficacy of Shape Radiomics and Deep Features for Glioblastoma Survival Prediction by Deep Learning" Electronics 11, no. 7: 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11071038
APA StyleTrinh, D.-L., Kim, S.-H., Yang, H.-J., & Lee, G.-S. (2022). The Efficacy of Shape Radiomics and Deep Features for Glioblastoma Survival Prediction by Deep Learning. Electronics, 11(7), 1038. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11071038









