Edge Intelligence Empowered Dynamic Offloading and Resource Management of MEC for Smart City Internet of Things
Abstract
:1. Introduction
- (1)
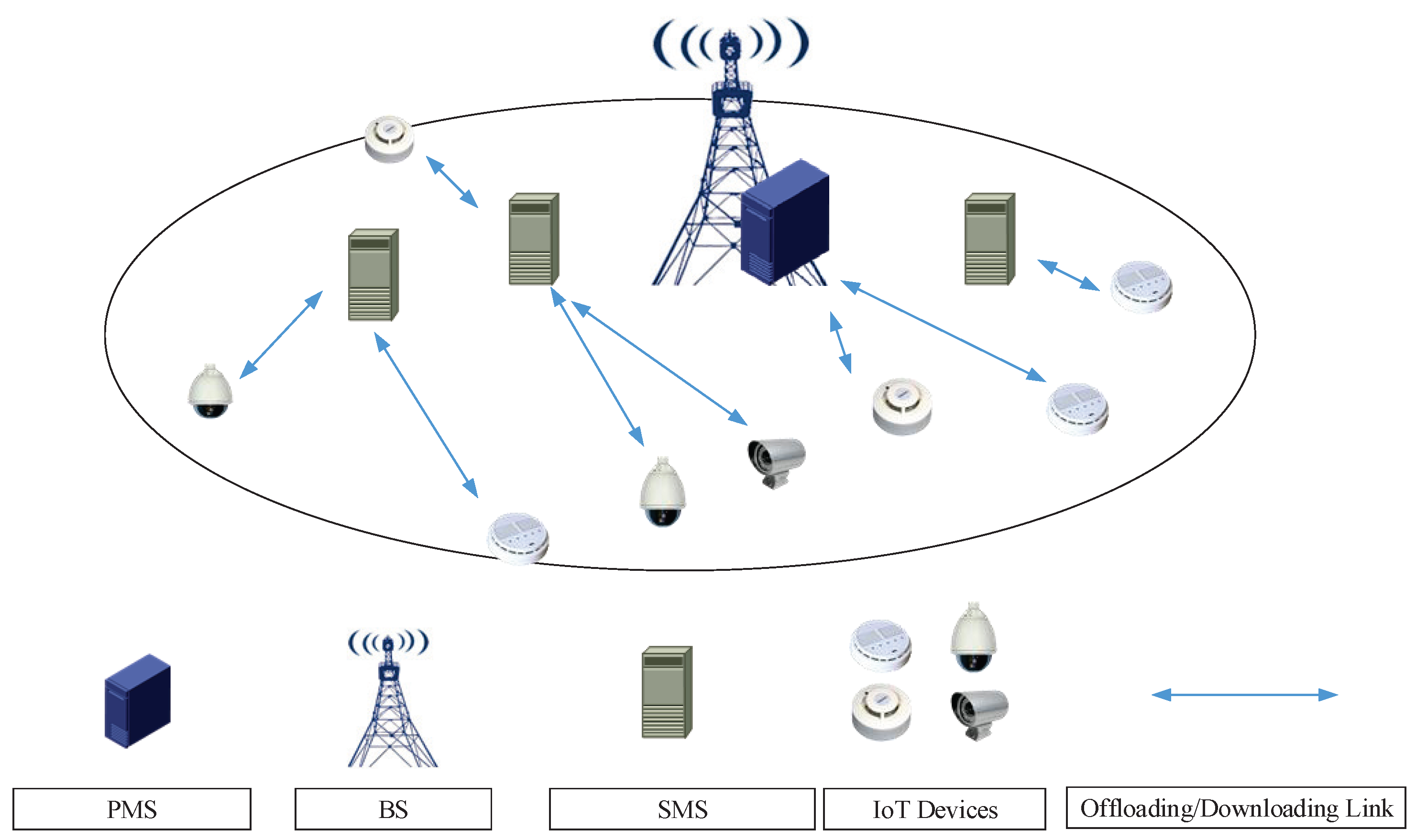
- A multi-MEC server and multi-IoT device cellular network structure is proposed. A high-cost and high-performance primary MEC server (PMS) with relative strong computing power is deployed in the BS, and multiple low-cost secondary MEC servers (SMSs) with relative weak computing powers are deployed within the coverage area of the BS.
- (2)
- An optimization problem is formulated. The problem considers the weighted sum of multiple optimization objectives, including the minimization of the weighted sum of the computing pressure on the PMS, the sum of energy consumption of the network, and the task dropping cost. The formulated problem is a nonconvex mixed integer nonlinear program (MINLP) problem, which is solved by our proposed DRL-based optimization algorithm.
- (3)
- Simulation results are presented to evaluate the performance of the proposed algorithm. The correctness and effectiveness of the proposed algorithm are demonstrated by the simulation results.
2. System Model
2.1. Network and Channel Model
2.2. Computation Task Model
2.3. Problem Formulation
3. Proposed DRL-Based Optimization Algorithm
| : A Bisection Algorithm for Solving |
| 1: Initialization: |
| 2: The bisection algorithm iteration index , maximum number |
| of iterations , , , the tolerance errors . |
| 3: for: : |
| 4: Update . |
| 5: if then |
| 6: The optimal value of is ; |
| 7: break; |
| 8: end if |
| 9: if then |
| 10: Update ; |
| 11: end if |
| 12: if then |
| 13: Update ; |
| 14: end if |
| 15: if or then |
| 16: The optimal value of is ; |
| 17: end if |
| 18: end for |
| : The proposed DRL-based algorithm. |
| 1: Initialization: |
| 2: , , target policy , behavior policy |
| maximal number of iterations , discount factor , the learning |
| rate of policy , the learning rate of the baseline ; |
| 3: for : |
| 4: Using and Algorithm 1 to generate trajectory |
| , |
| by action policy ; |
| 5: for : |
| 6: Update G: ; |
| 7: Update : ; |
| 8: Update by (18) with ; |
| 9: end for |
| 10: end for |
4. Complexity and Convergence Analysis
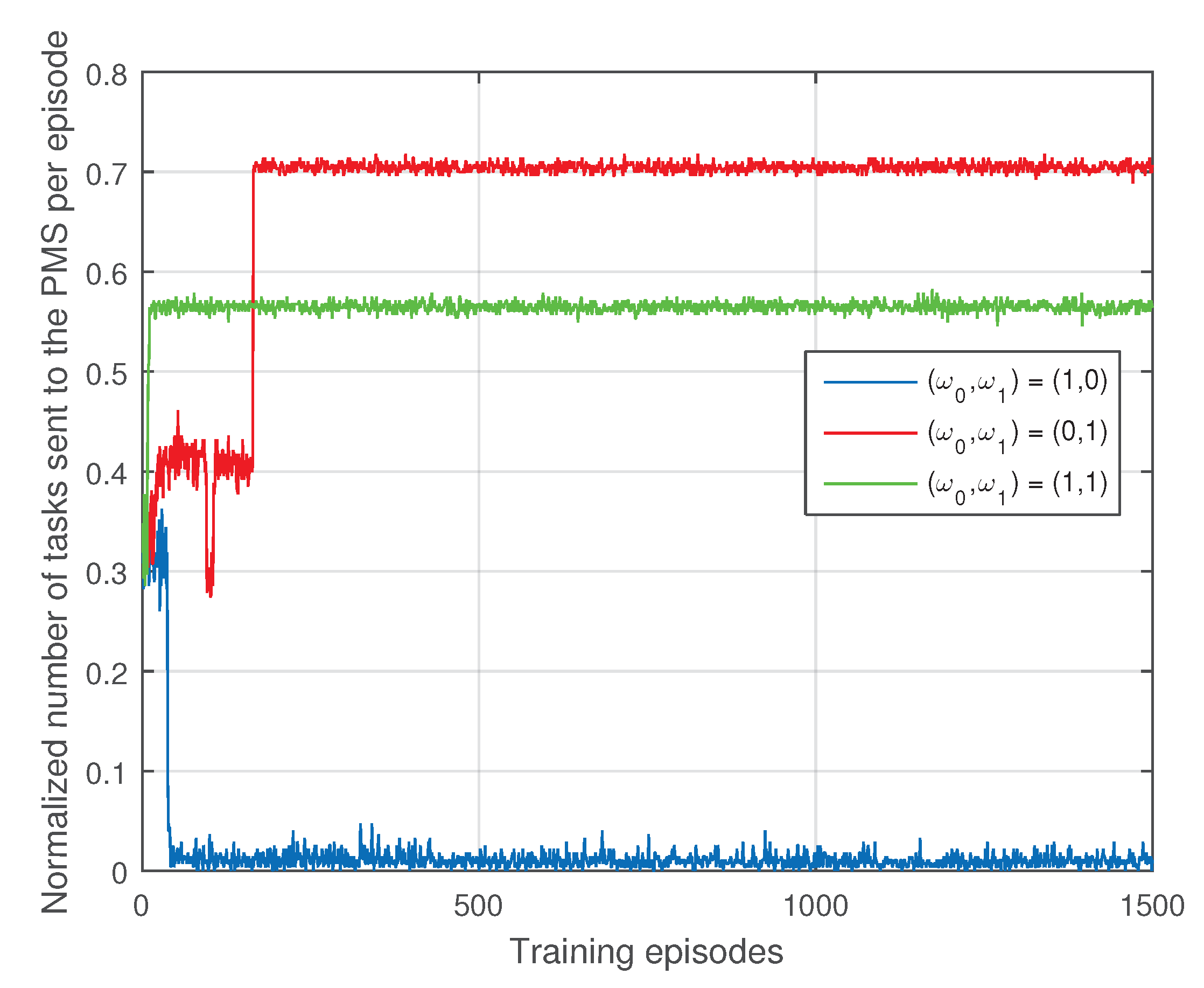
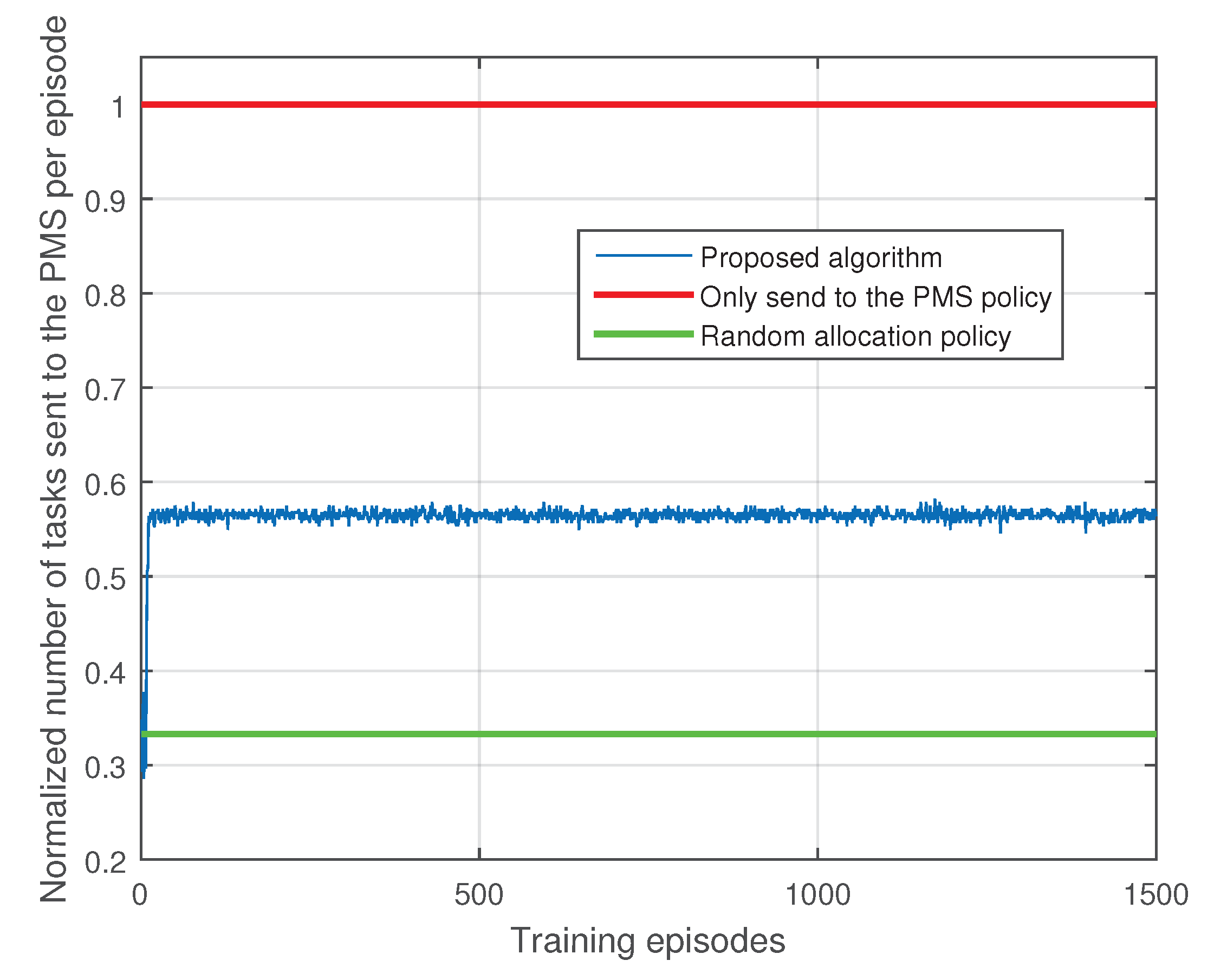
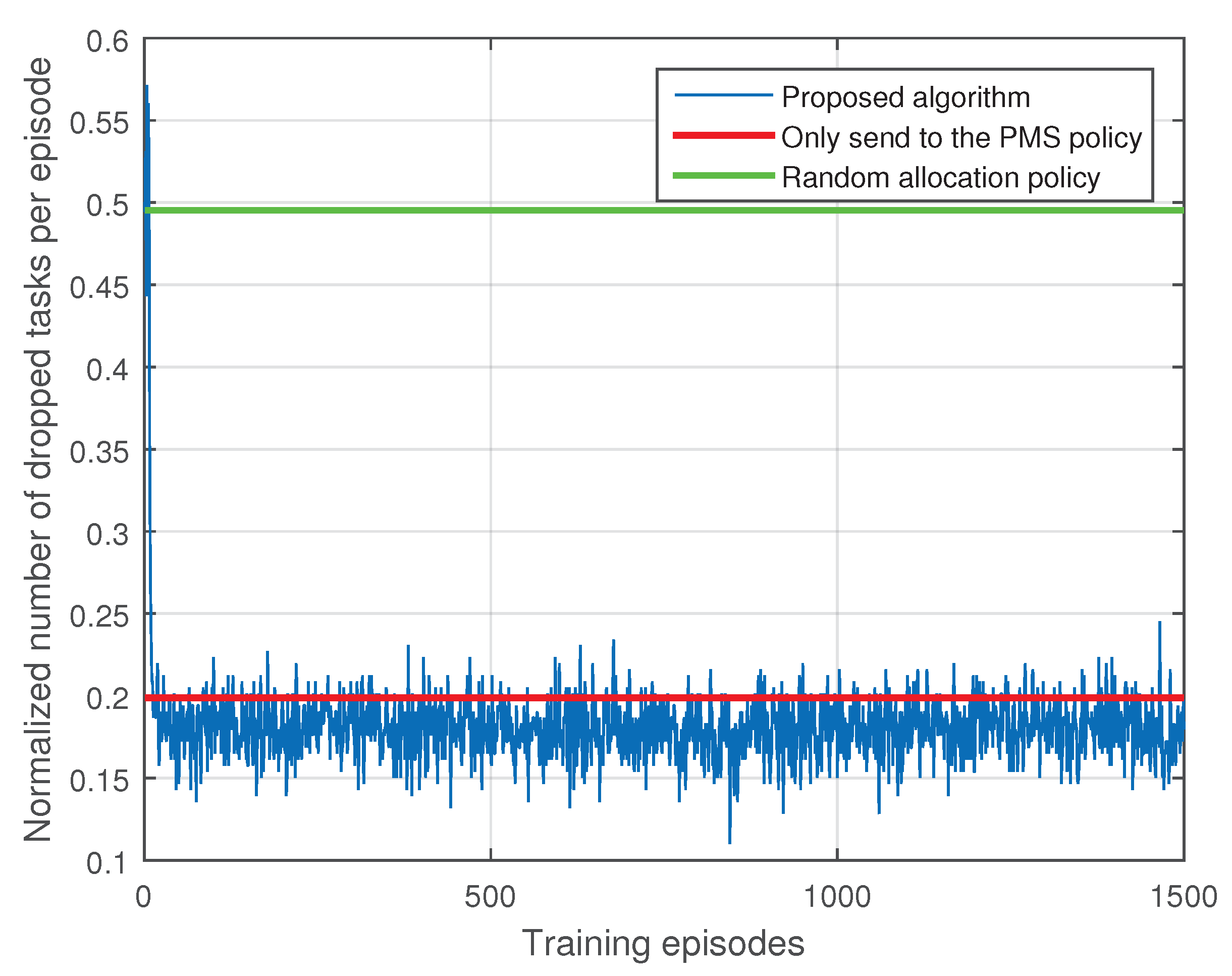
5. Simulation Results
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
References
- Zhao, Y.; Xu, K.; Wang, H.; Li, B.; Qiao, M.; Shi, H. MEC-enabled hierarchical emotion recognition and perturbation-aware defense in smart cities. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 16933–16945. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, L.U.; Yaqoob, I.; Tran, N.H.; Kazmi, S.M.A.; Dang, T.N.; Hong, C.S. Edge-computing-enabled smart cities: A comprehensive survey. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 10200–10232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wu, H.; Zhang, Z.; Guan, C.; Wolter, K.; Xu, M. Collaborate edge and cloud computing with distributed deep learning for smart city internet of things. IEEE Internet Things J. 2020, 7, 8099–8110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; You, C.; Zhang, J.; Huang, K.; Letaief, K.B. A survey on mobile edge computing: The communication perspective. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2017, 1, 2322–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ryu, J.W.; Pham, Q.V.; Luan, H.N.T.; Hwang, W.J.; Kim, J.D.; Lee, J.T. Multi-access edge computing empowered heterogeneous networks: A novel architecture and potential works. Symmetry 2019, 11, 842. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Bi, S.; Zhang, Y.J. Computation rate maximization for wireless powered mobile-edge computing with binary computation offloading. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 4177–4190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Wang, F.; Xu, J.; Wang, X.; Cui, S. Joint offloading and computing optimization in wireless powered mobile-edge computing systems. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2018, 17, 1784–1797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Ren, J.; Yu, G.; Cai, Y. D2D communications meet mobile edge computing for enhanced computation capacity in cellular networks. IEEE Trans. Wirel. Commun. 2019, 18, 1750–1763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El Haber, E.; Nguyen, T.M.; Assi, C.; Ajib, W. Macro-cell assisted task offloading in mec-based heterogeneous networks with wireless backhaul. IEEE Trans. Netw. Serv. Manag. 2019, 16, 1754–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Shen, C.; Zhou, P.; Xu, J. Collaborative service placement for edge computing in dense small cell networks. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2021, 20, 377–390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zarandi, S.; Tabassum, H. Delay minimization in sliced multi-cell mobile edge computing (mec) systems. IEEE Commun. lett. 2021, 25, 1964–1968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.Y.B.; Ng, J.S.; Xiong, Z.; Jin, J.; Zhang, Y.; Niyato, D.; Leung, C.S.; Miao, C. Decentralized Edge Intelligence: A Dynamic Resource Allocation Framework for Hierarchical Federated Learning. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2022, 33, 536–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, W.Y.B.; Ng, J.S.; Xiong, Z.; Niyato, D.; Miao, C.; Kim, D.I. Dynamic Edge Association and Resource Allocation in Self-Organizing Hierarchical Federated Learning Networks. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 3640–3653. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, H.; Zhao, J.; Xiong, Z.; Lam, K.-Y.; Sun, S.; Xiao, L. Privacy-Preserving Federated Learning for UAV-Enabled Networks: Learning-Based Joint Scheduling and Resource Management. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2021, 39, 3144–3159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Liu, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, Y.; Chen, X.; Zhao, L. Deep reinforcement learning-based dynamic resource management for mobile edge computing in industrial internet of things. IEEE Trans. Ind. Informat. 2021, 17, 4925–4934. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, C.; Gursoy, M. C.; Velipasalar, S. Deep reinforcement learning-based edge caching in wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2020, 6, 48–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Tang, F.; Hu, Y.; Li, K.; Tang, Z.; Li, K. Distributed task migration optimization in mec by extending multi-agent deep reinforcement learning approach. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2021, 32, 1603–1614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, A.; Zhang, K.; Maharjan, S.; Zhang, Y. Edge intelligence for energy-efficient computation offloading and resource allocation in 5G beyond. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 12175–12186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Wang, Q.; Hu, R. Q.; Zhu, H. Mobility-Aware Offloading and Resource Allocation in a MEC-Enabled IoT Network With Energy Harvesting. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021, 8, 17541–17556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ale, L.; Zhang, N.; Fang, X.; Chen, X.; Wu, S.; Li, L. Delay-aware and energy-efficient computation offloading in mobile-edge computing using deep reinforcement learning. IEEE Trans. Cogn. Commun. Netw. 2021, 7, 881–892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Temesgene, D.A.; Miozzo, M.; Gündüz, D.; Dini, P. Distributed deep reinforcement learning for functional split control in energy harvesting virtualized small cells. IEEE Trans. Sustain. Comput. 2021, 6, 626–640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Fang, L.; Lu, W.; Zhai, W.; Li, Y.; Zhao, J. A GCICA Grant-Free Random Access Scheme for M2M Communications in Crowded Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Internet Things J. 2021. early access. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, H.; Fang, L.; Lu, W.; Chi, K.; Zhai, W.; Zhao, J. A Novel Grant-Based Pilot Access Scheme for Crowded Massive MIMO Systems. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 11111–11115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.; Zhang, J.; Letaief, K.B. Dynamic Computation offloading for mobile-edge computing with energy harvesting devices. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2016, 34, 3590–3605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Liu, Y.; Xie, S.; Zhang, Y. Cooperative offloading and resource management for uav-enabled mobile edge computing in power iot system. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 12229–12239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Yu, F.R.; Zhu, L.; Tang, T.; Ning, B. Finite-state markov modeling for wireless channels in tunnel communication-based train control systems. IEEE Trans. Intell. Transp. Syst. 2014, 15, 1083–1090. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, M.; Wong, V.W.S. Deep reinforcement learning for task offloading in mobile edge computing systems. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2020, in press. [CrossRef]
- Sutton, R.S.; Barto, A.G. Reinforcement Learning: An Introduction, 2nd ed.; The MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Palomar, D.P.; Chiang, M. A tutorial on decomposition methods for network utility maximization. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2006, 24, 1439–1451. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Boyd, S.; Vandenberghe, L. Convex Optimization; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2004. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Xia, J.; Liu, F.; Li, D.; Fan, L.; Karagiannidis, G.K.; Nallanathan, A. Dynamic Offloading for Multiuser Muti-CAP MEC Networks: A Deep Reinforcement Learning Approach. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2021, 70, 2922–2927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Work | Objective | Method | Environments |
|---|---|---|---|
| Our work | Weighted sum of computing pressure on the PMS, energy consumption, and task dropping cost | DRL | Dynamic |
| [6] | Computation rate of the wireless devices | Convex optimization | Static |
| [7] | Energy consumption of the AP | Convex optimization | Static |
| [8] | Number of serviced devices | Convex optimization | Static |
| [9] | Total energy consumption of the devices | Convex optimization | Static |
| [10] | System utility | Game theory | Static |
| [11] | Latency | Convex optimization | Static |
| [15] | Long-term average delay of the tasks | DRL | Dynamic |
| [16] | Cache bit rate | DRL | Dynamic |
| [17] | Average completion time of tasks | DRL | Dynamic |
| [18] | Energy consumption of the system | DRL | Dynamic |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tian, K.; Chai, H.; Liu, Y.; Liu, B. Edge Intelligence Empowered Dynamic Offloading and Resource Management of MEC for Smart City Internet of Things. Electronics 2022, 11, 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11060879
Tian K, Chai H, Liu Y, Liu B. Edge Intelligence Empowered Dynamic Offloading and Resource Management of MEC for Smart City Internet of Things. Electronics. 2022; 11(6):879. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11060879
Chicago/Turabian StyleTian, Kang, Haojun Chai, Yameng Liu, and Boyang Liu. 2022. "Edge Intelligence Empowered Dynamic Offloading and Resource Management of MEC for Smart City Internet of Things" Electronics 11, no. 6: 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11060879
APA StyleTian, K., Chai, H., Liu, Y., & Liu, B. (2022). Edge Intelligence Empowered Dynamic Offloading and Resource Management of MEC for Smart City Internet of Things. Electronics, 11(6), 879. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11060879






