Computer-Assisted Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Thyroid Using Two-Stage Refined Convolutional Neural Network
Abstract
1. Introduction
- To better migrate and apply it to clinical programs, we built a thyroid cytopathology dataset generated from 360 FNAB specimens in practical medical institutions. This dataset is well-annotated for both detection and classification tasks.
- Mimicking the diagnostic experiences of pathologists, we utilized an object detection algorithm to search suspected target areas in WSI and then leverage another network to refine the classification result. To the best of our knowledge, this is the first work to apply an object detection algorithm for the automatic discovery of ROIs in thyroid cytology screening.
- Extensive experiments with promising results on the built thyroid cytopathology dataset validated the effectiveness of the proposed method for thyroid cancer diagnosis. The proposed refined two-stage network provides a novel solution for automatic CAD systems in practical thyroid cancer screening.
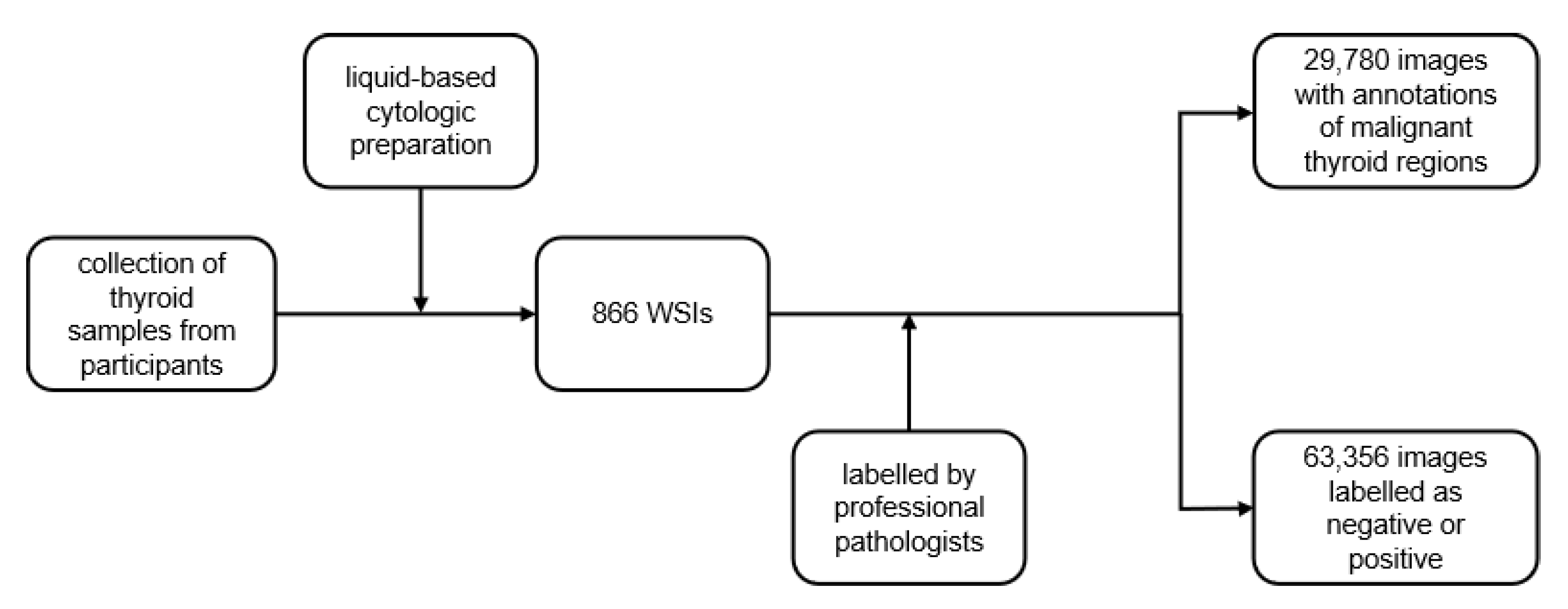
2. Dataset Generation
2.1. Overview
2.2. WSI Collection
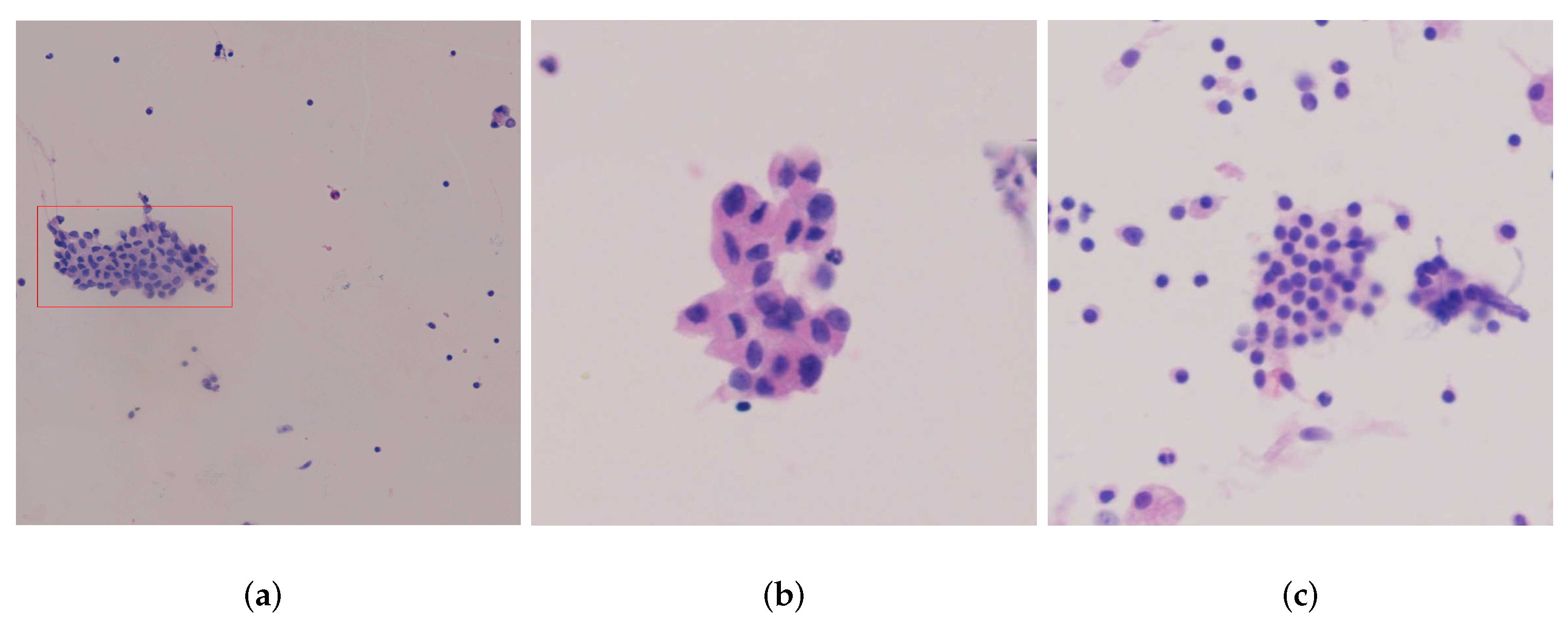
2.3. Image Labeling
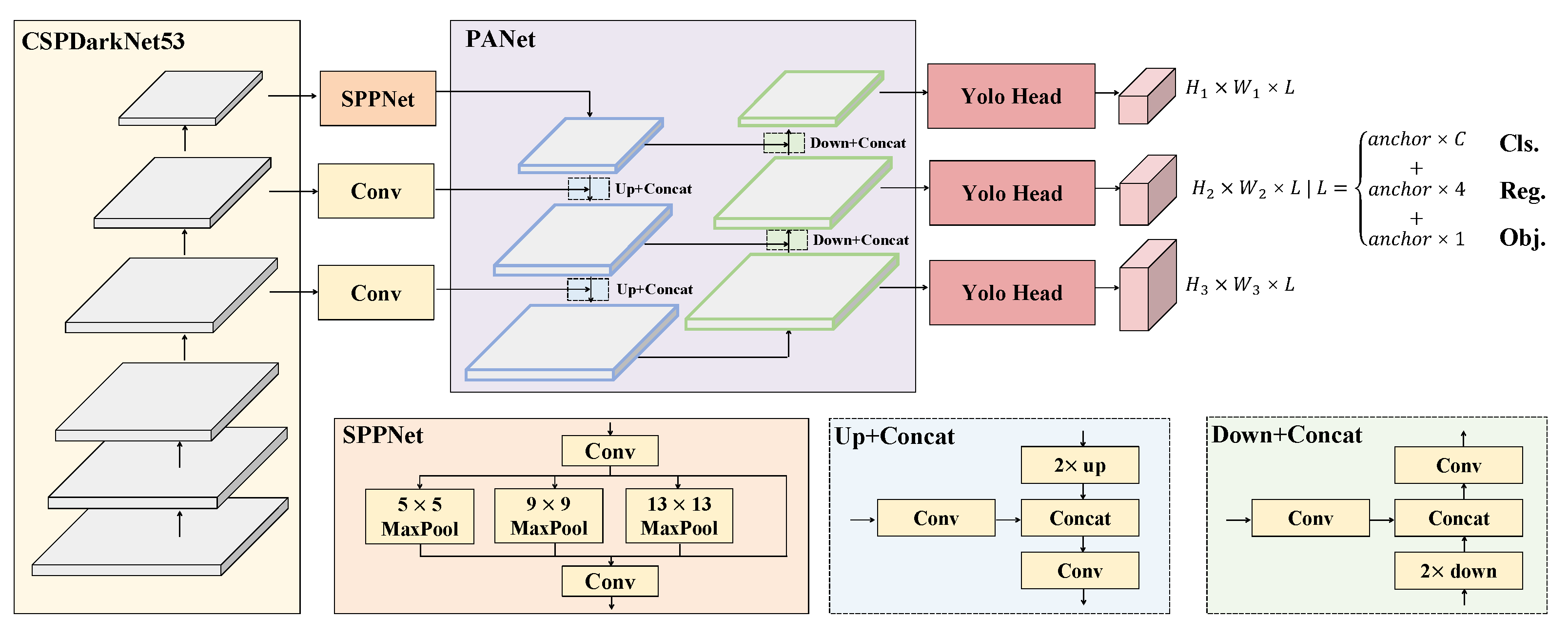
3. System Architecture
3.1. Suspicious Area Detection
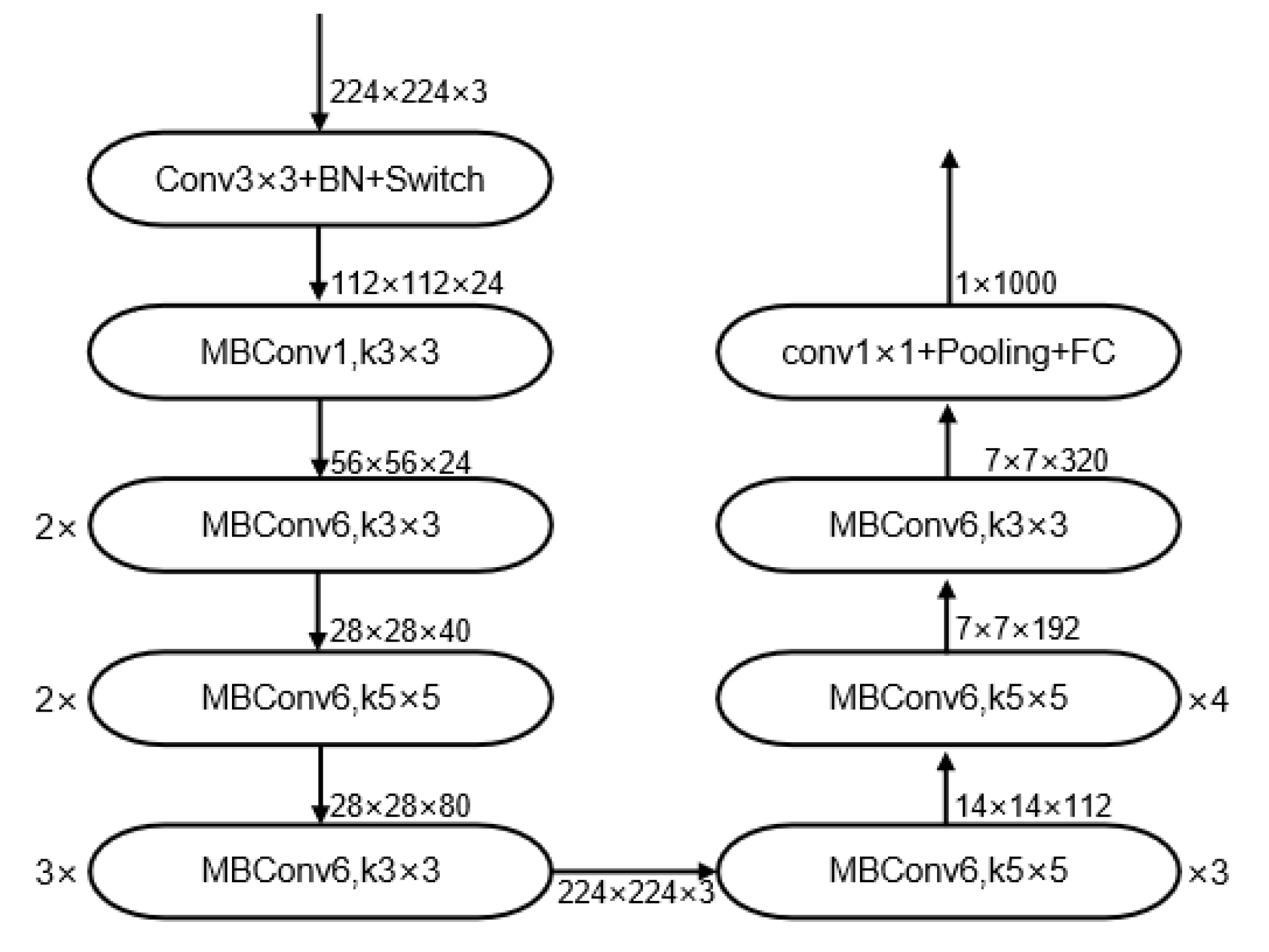
3.2. Lesion Classification
4. Experiment
4.1. Experimental Setup and Evaluation Measures
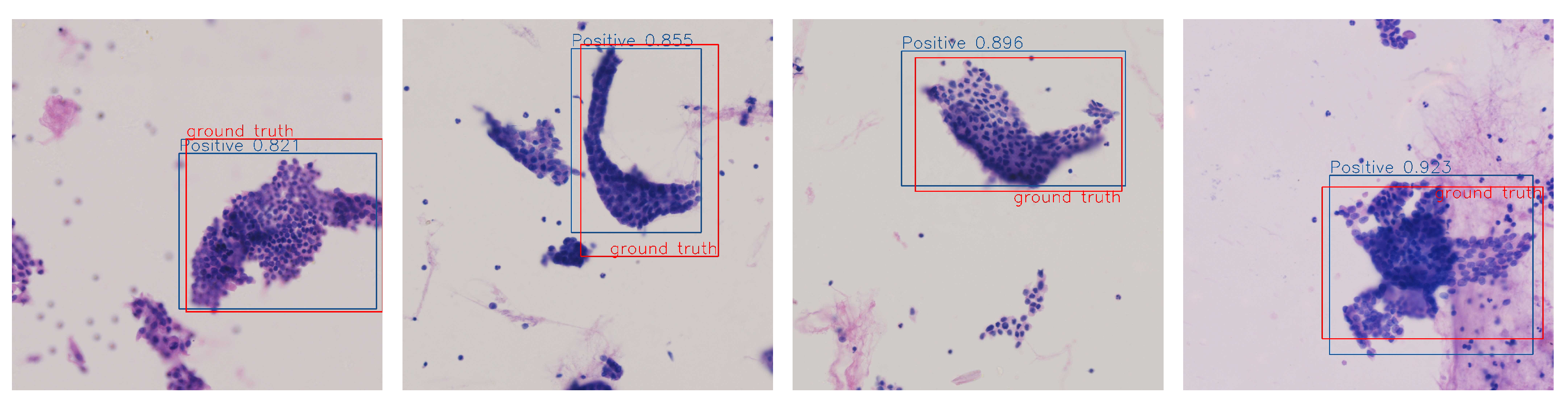
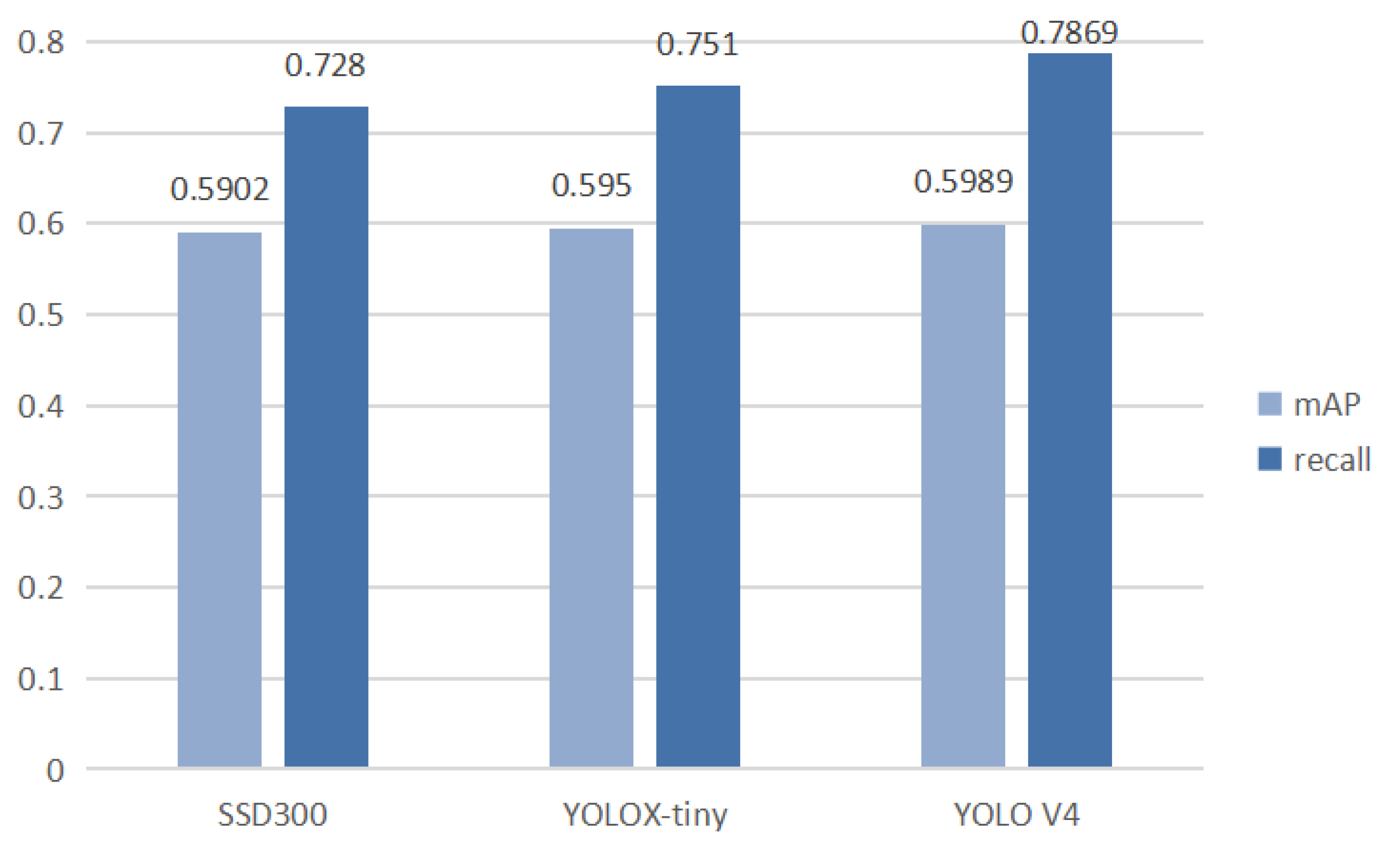
4.2. Lesion Detection Performance
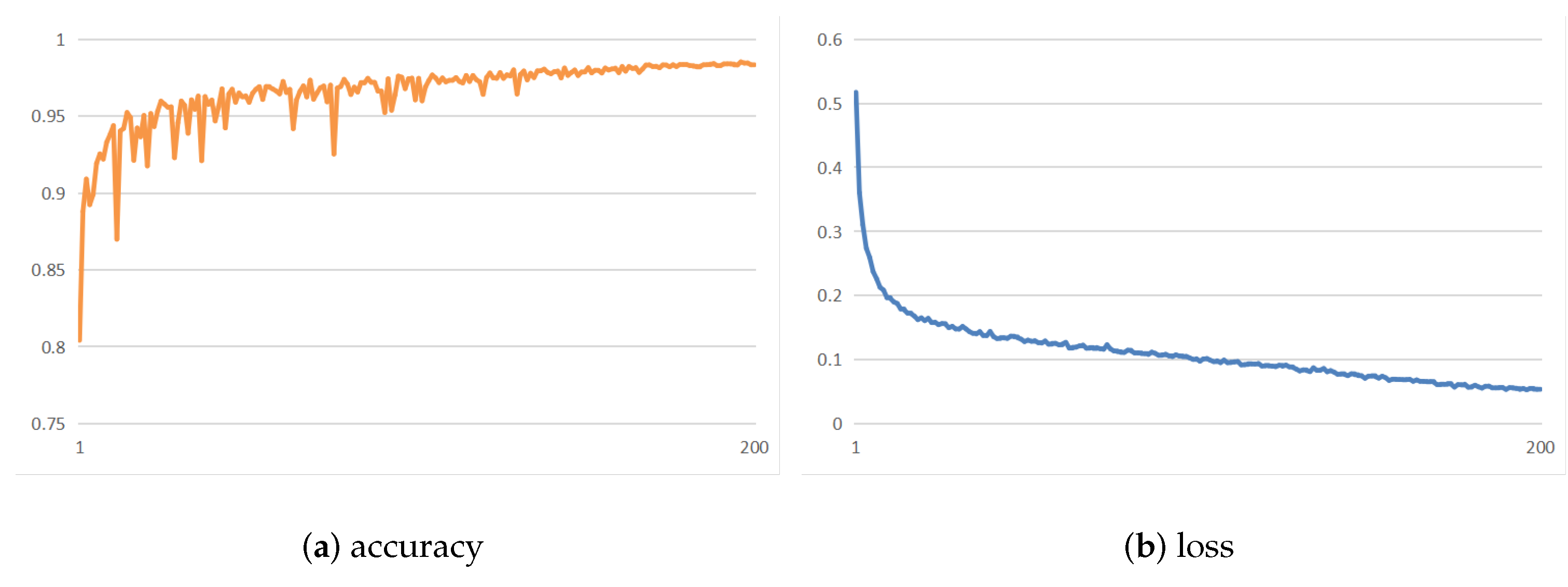
4.3. Lesion Classification Performance
4.4. Two-Stage Network Performance
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabanillas, M.E.; McFadden, D.G.; Durante, C. Thyroid cancer. Lancet 2016, 388, 2783–2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global cancer statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN estimates of incidence and mortality worldwide for 36 cancers in 185 countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haugen, B.R.; Alexander, E.K.; Bible, K.C.; Doherty, G.M.; Mandel, S.J.; Nikiforov, Y.E.; Pacini, F.; Randolph, G.W.; Sawka, A.M.; Schlumberger, M.; et al. 2015 American Thyroid Association management guidelines for adult patients with thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer: The American Thyroid Association guidelines task force on thyroid nodules and differentiated thyroid cancer. Thyroid 2016, 26, 1–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cibas, E.S.; Ali, S.Z. The 2017 Bethesda system for reporting thyroid cytopathology. Thyroid 2017, 27, 1341–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, N.; Gupta, R.; Gupta, S. Whole slide imaging (WSI) in pathology: Current perspectives and future directions. J. Digit. Imaging 2020, 33, 1034–1040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chain, K.; Legesse, T.; Heath, J.E.; Staats, P.N. Digital image-assisted quantitative nuclear analysis improves diagnostic accuracy of thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology. Cancer Cytopathol. 2019, 127, 501–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gadekallu, T.R.; Rajput, D.S.; Reddy, M.; Lakshmanna, K.; Bhattacharya, S.; Singh, S.; Jolfaei, A.; Alazab, M. A novel PCA—Whale optimization-based deep neural network model for classification of tomato plant diseases using GPU. J. Real-Time Image Process. 2021, 18, 1383–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagaraj, P.; Deepalakshmi, P.; Mansour, R.F.; Almazroa, A. Artificial flora algorithm-based feature selection with gradient boosted tree model for diabetes classification. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Obes. Targets Ther. 2021, 14, 2789. [Google Scholar]
- Cochand-Priollet, B.; Koutroumbas, K.; Megalopoulou, T.M.; Pouliakis, A.; Sivolapenko, G.; Karakitsos, P. Discriminating benign from malignant thyroid lesions using artificial intelligence and statistical selection of morphometric features. Oncol. Rep. 2006, 15, 1023–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopinath, B.; Shanthi, N. Development of an automated medical diagnosis system for classifying thyroid tumor cells using multiple classifier fusion. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2015, 14, 653–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M.; Wu, Y.H.; Chen, P.Y.; Hsieh, J.W.; Yeh, I.H. CSPNet: A new backbone that can enhance learning capability of CNN. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 390–391. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, T.; Huang, L.; You, S.; Wang, F.; Qian, C.; Xu, C. LightViT: Towards Light-Weight Convolution-Free Vision Transformers. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2207.05557. [Google Scholar]
- Li, T.; Bo, W.; Hu, C.; Kang, H.; Liu, H.; Wang, K.; Fu, H. Applications of deep learning in fundus images: A review. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 69, 101971. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kezlarian, B.; Lin, O. Artificial intelligence in thyroid fine needle aspiration biopsies. Acta Cytol. 2021, 65, 324–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanyal, P.; Mukherjee, T.; Barui, S.; Das, A.; Gangopadhyay, P. Artificial intelligence in cytopathology: A neural network to identify papillary carcinoma on thyroid fine-needle aspiration cytology smears. J. Pathol. Inform. 2018, 9, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, Q.; Wang, Y.; Ping, B.; Li, D.; Du, J.; Qin, Y.; Lu, H.; Wan, X.; Xiang, J. Deep convolutional neural network VGG-16 model for differential diagnosing of papillary thyroid carcinomas in cytological images: A pilot study. J. Cancer 2019, 10, 4876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simonyan, K.; Zisserman, A. Very deep convolutional networks for large-scale image recognition. arXiv 2014, arXiv:1409.1556. [Google Scholar]
- Szegedy, C.; Vanhoucke, V.; Ioffe, S.; Shlens, J.; Wojna, Z. Rethinking the inception architecture for computer vision. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 2818–2826. [Google Scholar]
- Dov, D.; Kovalsky, S.Z.; Assaad, S.; Cohen, J.; Range, D.E.; Pendse, A.A.; Henao, R.; Carin, L. Weakly supervised instance learning for thyroid malignancy prediction from whole slide cytopathology images. Med. Image Anal. 2021, 67, 101814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duc, N.T.; Lee, Y.M.; Park, J.H.; Lee, B. An ensemble deep learning for automatic prediction of papillary thyroid carcinoma using fine needle aspiration cytology. Expert Syst. Appl. 2022, 188, 115927. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bochkovskiy, A.; Wang, C.Y.; Liao, H.Y.M. Yolov4: Optimal speed and accuracy of object detection. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2004.10934. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, M.; Le, Q. Efficientnet: Rethinking model scaling for convolutional neural networks. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Machine Learning, PMLR, Long Beach, CA, USA, 9–15 June 2019; pp. 6105–6114. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Divvala, S.; Girshick, R.; Farhadi, A. You only look once: Unified, real-time object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Las Vegas, NV, USA, 27–30 June 2016; pp. 779–788. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. YOLO9000: Better, faster, stronger. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 7263–7271. [Google Scholar]
- Redmon, J.; Farhadi, A. Yolov3: An incremental improvement. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1804.02767. [Google Scholar]
- Ge, Z.; Liu, S.; Wang, F.; Li, Z.; Sun, J. Yolox: Exceeding yolo series in 2021. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2107.08430. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, T.Y.; Dollár, P.; Girshick, R.; He, K.; Hariharan, B.; Belongie, S. Feature pyramid networks for object detection. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Honolulu, HI, USA, 21–26 July 2017; pp. 2117–2125. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, S.; Qi, L.; Qin, H.; Shi, J.; Jia, J. Path aggregation network for instance segmentation. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 8759–8768. [Google Scholar]
- He, K.; Zhang, X.; Ren, S.; Sun, J. Spatial pyramid pooling in deep convolutional networks for visual recognition. IEEE Trans. Pattern Anal. Mach. Intell. 2015, 37, 1904–1916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, M.; Chen, B.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Le, Q.V. Mnasnet: Platform-aware neural architecture search for mobile. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Long Beach, CA, USA, 15–20 June 2019; pp. 2820–2828. [Google Scholar]
- Sandler, M.; Howard, A.; Zhu, M.; Zhmoginov, A.; Chen, L.C. Mobilenetv2: Inverted residuals and linear bottlenecks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 4510–4520. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, J.; Shen, L.; Sun, G. Squeeze-and-excitation networks. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Salt Lake City, UT, USA, 18–23 June 2018; pp. 7132–7141. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, K.; Wang, J.; Pang, J.; Cao, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Li, X.; Sun, S.; Feng, W.; Liu, Z.; Xu, J.; et al. MMDetection: Open MMLab Detection Toolbox and Benchmark. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1906.07155. [Google Scholar]
- Wightman, R. PyTorch Image Models. 2019. Available online: https://github.com/rwightman/pytorch-image-models (accessed on 28 September 2022). [CrossRef]
- Touvron, H.; Cord, M.; Douze, M.; Massa, F.; Sablayrolles, A.; Jégou, H. Training data-efficient image transformers & distillation through attention. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2012.12877v2. [Google Scholar]
- Loshchilov, I.; Hutter, F. Decoupled weight decay regularization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1711.05101. [Google Scholar]
- Yun, S.; Han, D.; Oh, S.J.; Chun, S.; Choe, J.; Yoo, Y. Cutmix: Regularization strategy to train strong classifiers with localizable features. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision, Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019; pp. 6023–6032. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Cisse, M.; Dauphin, Y.N.; Lopez-Paz, D. mixup: Beyond empirical risk minimization. arXiv 2017, arXiv:1710.09412. [Google Scholar]
- Cubuk, E.D.; Zoph, B.; Shlens, J.; Le, Q.V. Randaugment: Practical automated data augmentation with a reduced search space. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 702–703. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, W.; Anguelov, D.; Erhan, D.; Szegedy, C.; Reed, S.; Fu, C.Y.; Berg, A.C. SSD: Single Shot MultiBox Detector. In European Conference on Computer Vision; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Han, K.; Wang, Y.; Tian, Q.; Guo, J.; Xu, C.; Xu, C. Ghostnet: More features from cheap operations. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF Conference on Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition, Seattle, WA, USA, 14–19 June 2020; pp. 1580–1589. [Google Scholar]
- Howard, A.; Sandler, M.; Chu, G.; Chen, L.C.; Chen, B.; Tan, M.; Wang, W.; Zhu, Y.; Pang, R.; Vasudevan, V.; et al. Searching for MobileNetV3. In Proceedings of the IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), Seoul, Korea, 27 October–2 November 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Pan, J.; Bulat, A.; Tan, F.; Zhu, X.; Dudziak, L.; Li, H.; Tzimiropoulos, G.; Martinez, B. EdgeViTs: Competing Light-weight CNNs on Mobile Devices with Vision Transformers. arXiv 2022, arXiv:2205.03436. [Google Scholar]


| Reference | Dataset | Method |
|---|---|---|
| Cochand-Priollet et al. [9] | 157 cases of thyroid FNA | Nuclear features extraction + parametric classifiers |
| Gopinath et al. [10] | 35 cases of thyroid FNA | Textural feature extraction + four traditional classifiers |
| Chain et al. [6] | 35 cases of thyroid FNA | Calculating nuclear area and elongation as classification criteria |
| Sanyal et al. [15] | 370 cases of PTC and non-PTC | Simple five-layer network |
| Guan et al. [16] | 279 cases of PTCs and non-PTCs | VGG-16 [17] and Inception-v3 model [18] |
| Dov et al. [19] | 908 WSIs form 659 patients | Improved two-stage multiple instance learning (MIL) algorithm |
| Duc et al. [20] | 367 hematoxylin–eosin (H&E)-stained images | Utilizing stain normalization and ensemble deep learning methods |
| Class | TBSRTC Diagnostic Category | WSI Image Count | Type |
|---|---|---|---|
| 0 | Nondiagnostic or unsatisfactory | - | - |
| 1 | Benign | 222 | negative |
| 2 | Atypia of undetermined significance or follicular lesion of undetermined significance | 10 | positive |
| 3 | Follicular neoplasm or suspicious for a follicular | 2 | positive |
| 4 | Suspicious for malignancy | 36 | positive |
| 5 | Malignant | 90 | positive |
| Dataset for the Detection Model | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Set of boxing images | positive | ||
| Training set | 26,802 | ||
| Testing set | 2978 | ||
| total | 29,780 | ||
| Dataset for the Classification Model | |||
| Set of labeled images | Positive | Negative | total |
| Training set | 30,726 | 31,085 | 61,811 |
| Testing set | 840 | 705 | 1545 |
| Total | 31,566 | 31,790 | 63,356 |
| Model | Accuracy | F1-Score | Precision | Recall |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ghost50 | 90.16 | 90.04 | 90.30 | 89.88 |
| Ghost130 | 91.59 | 91.50 | 91.62 | 91.41 |
| Mobile50 | 93.07 | 93.04 | 92.97 | 93.21 |
| Mobile100 | 93.40 | 93.34 | 93.37 | 93.32 |
| EdgeVit_xxs | 97.74 | 97.71 | 97.86 | 97.60 |
| EdgeVit_s | 97.02 | 96.98 | 97.31 | 96.78 |
| LightVit | 94.76 | 94.72 | 94.71 | 94.72 |
| EfficientNet | 97.93 | 97.92 | 97.83 | 98.08 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Duan, W.; Gao, L.; Liu, J.; Li, C.; Jiang, P.; Wang, L.; Chen, H.; Sun, X.; Cao, D.; Pang, B.; et al. Computer-Assisted Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Thyroid Using Two-Stage Refined Convolutional Neural Network. Electronics 2022, 11, 4089. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244089
Duan W, Gao L, Liu J, Li C, Jiang P, Wang L, Chen H, Sun X, Cao D, Pang B, et al. Computer-Assisted Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Thyroid Using Two-Stage Refined Convolutional Neural Network. Electronics. 2022; 11(24):4089. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244089
Chicago/Turabian StyleDuan, Wensi, Lili Gao, Juan Liu, Cheng Li, Peng Jiang, Lang Wang, Hua Chen, Xiaorong Sun, Dehua Cao, Baochuan Pang, and et al. 2022. "Computer-Assisted Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Thyroid Using Two-Stage Refined Convolutional Neural Network" Electronics 11, no. 24: 4089. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244089
APA StyleDuan, W., Gao, L., Liu, J., Li, C., Jiang, P., Wang, L., Chen, H., Sun, X., Cao, D., Pang, B., Li, R., & Liu, S. (2022). Computer-Assisted Fine-Needle Aspiration Cytology of Thyroid Using Two-Stage Refined Convolutional Neural Network. Electronics, 11(24), 4089. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11244089





