Antimonotonicity, Hysteresis and Coexisting Attractors in a Shinriki Circuit with a Physical Memristor as a Nonlinear Resistor
Abstract
1. Introduction
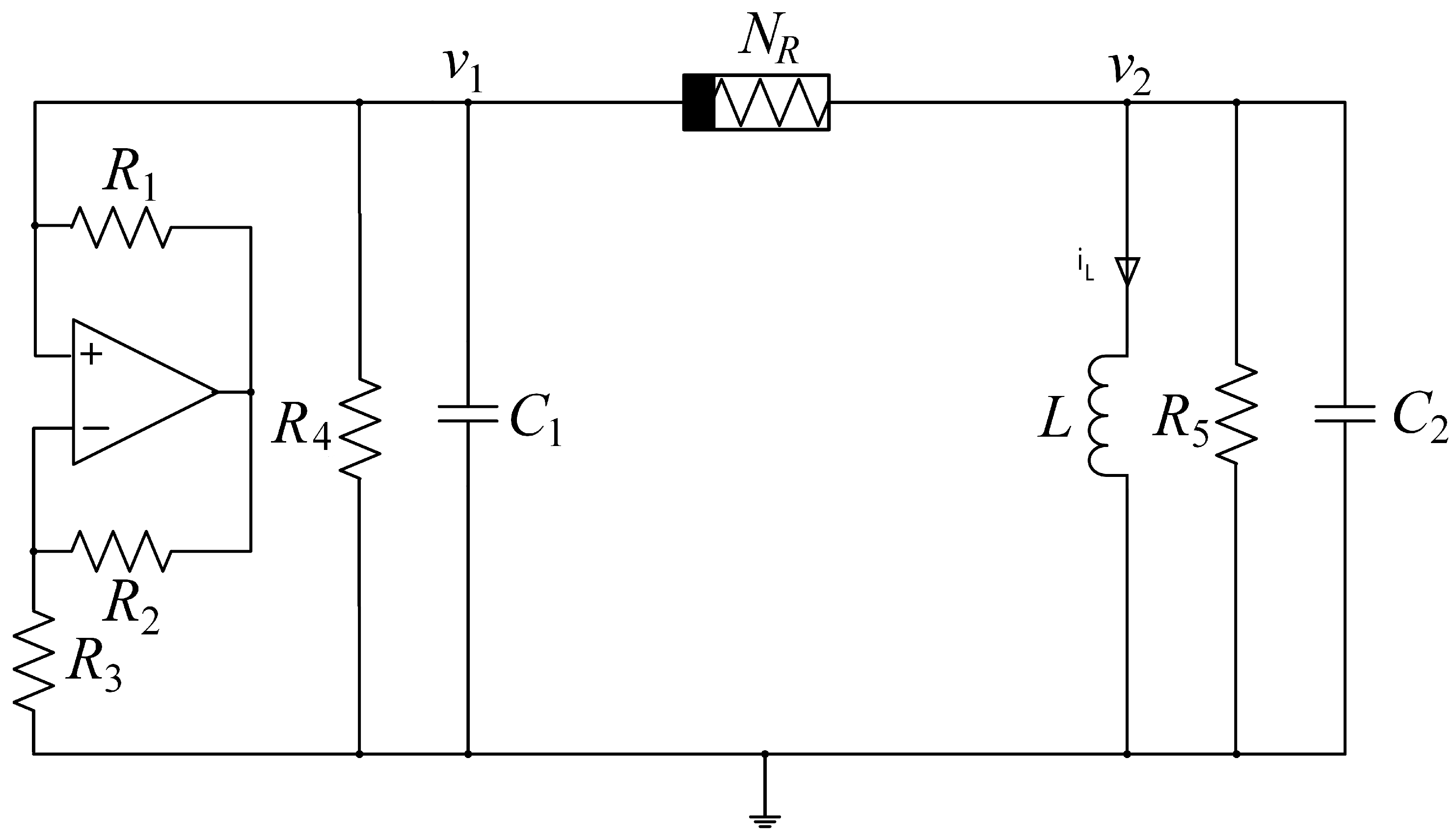
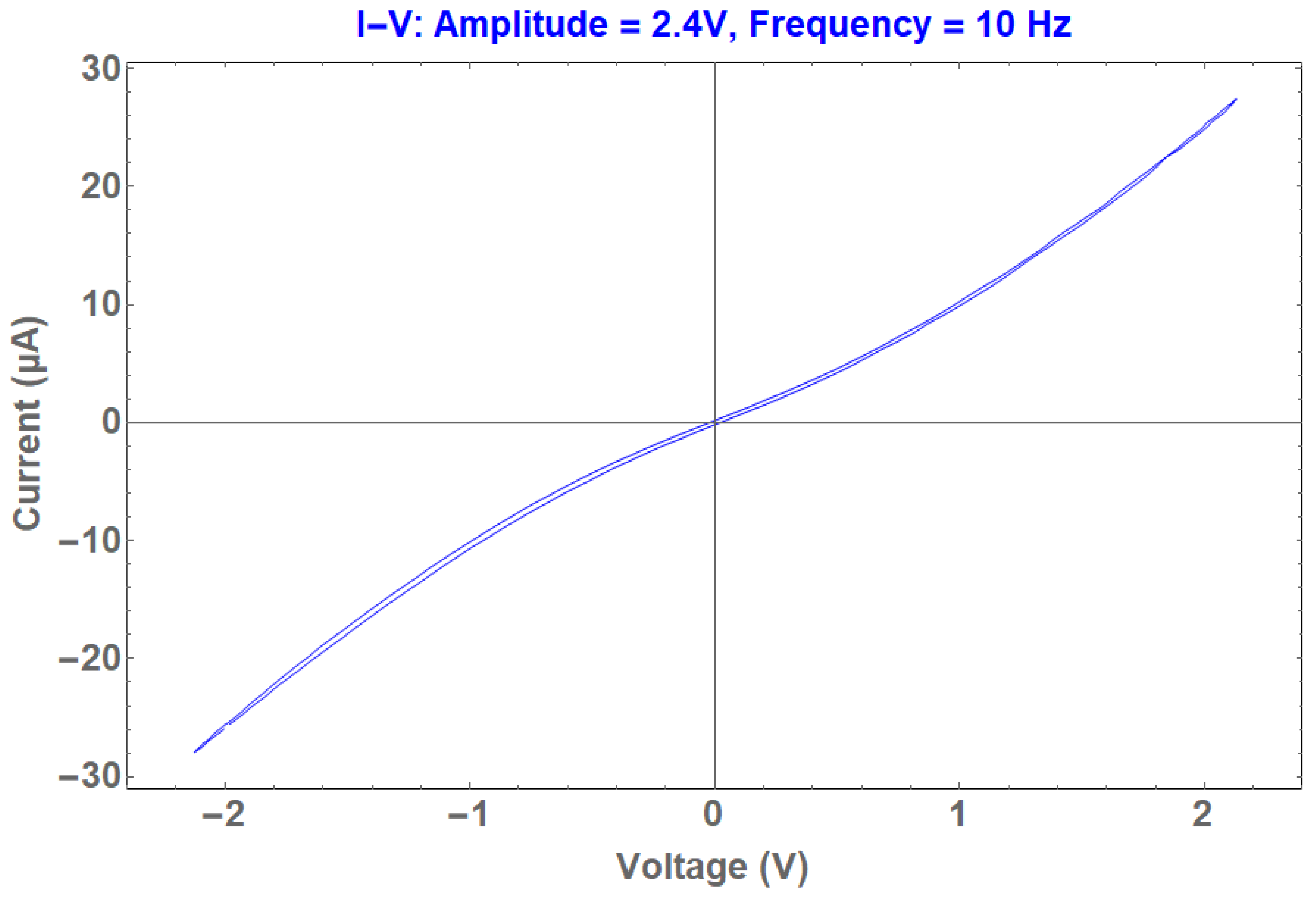
2. Mathematical Model of the Chaotic Circuit
3. Numerical Results
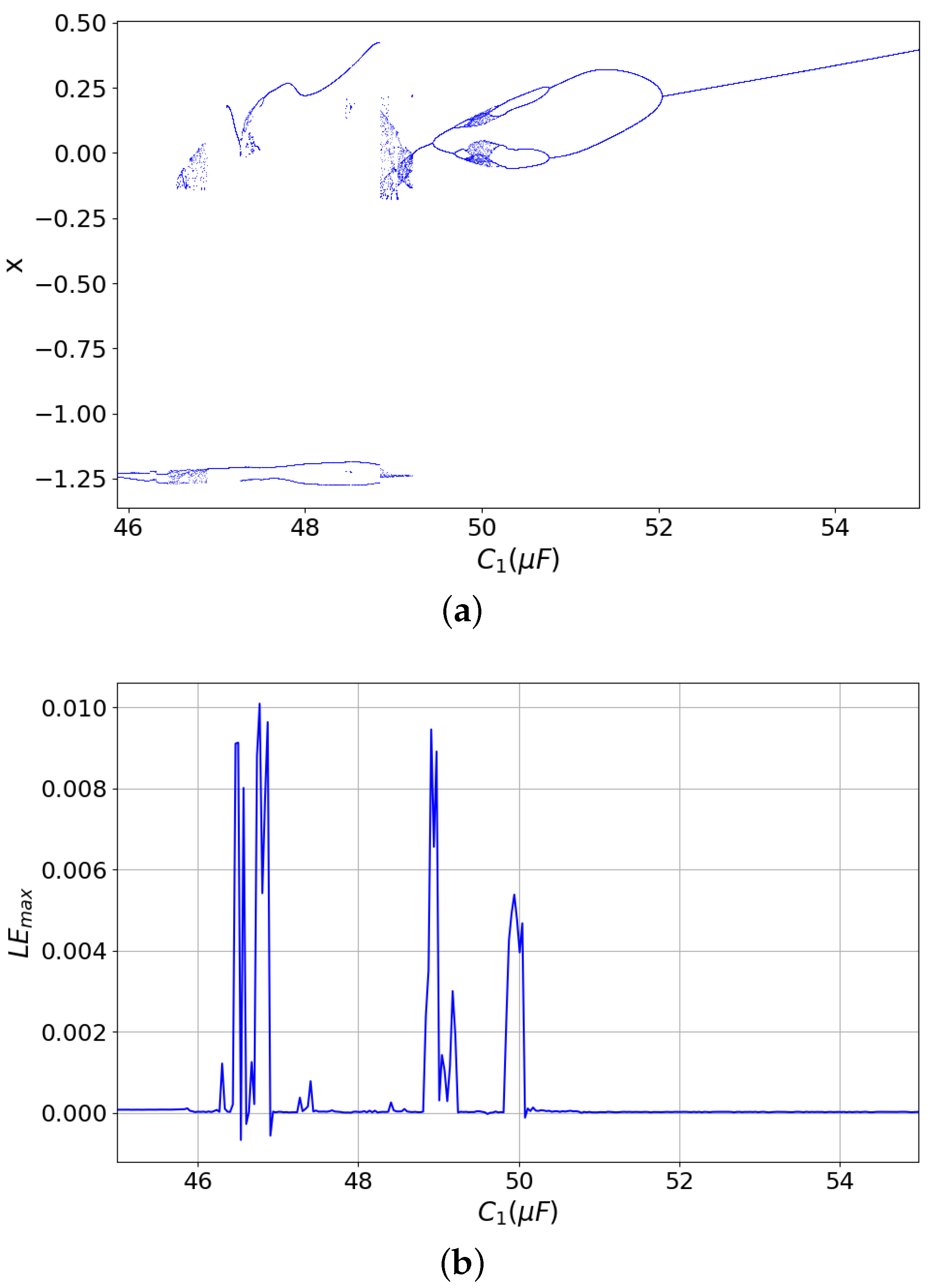
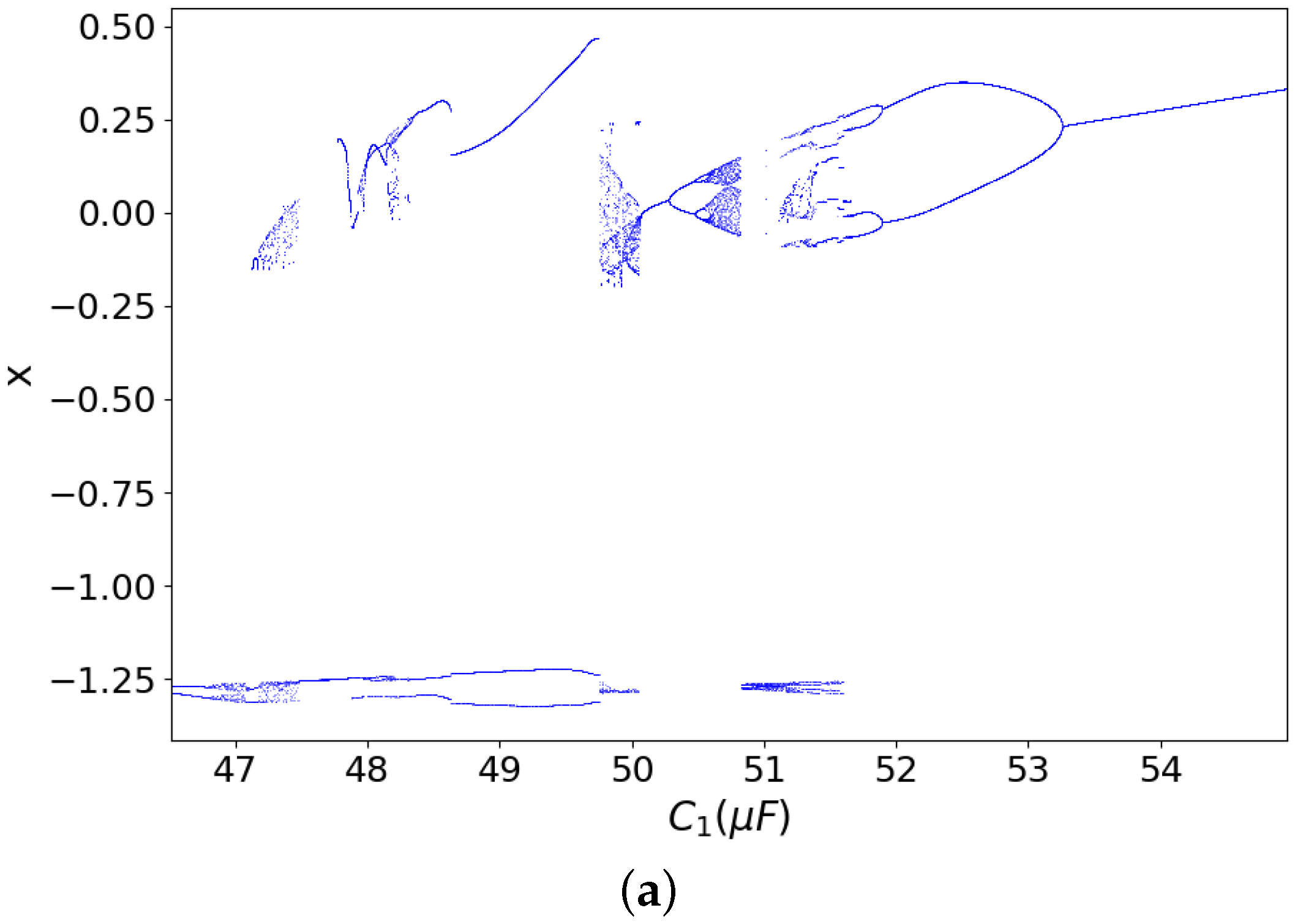
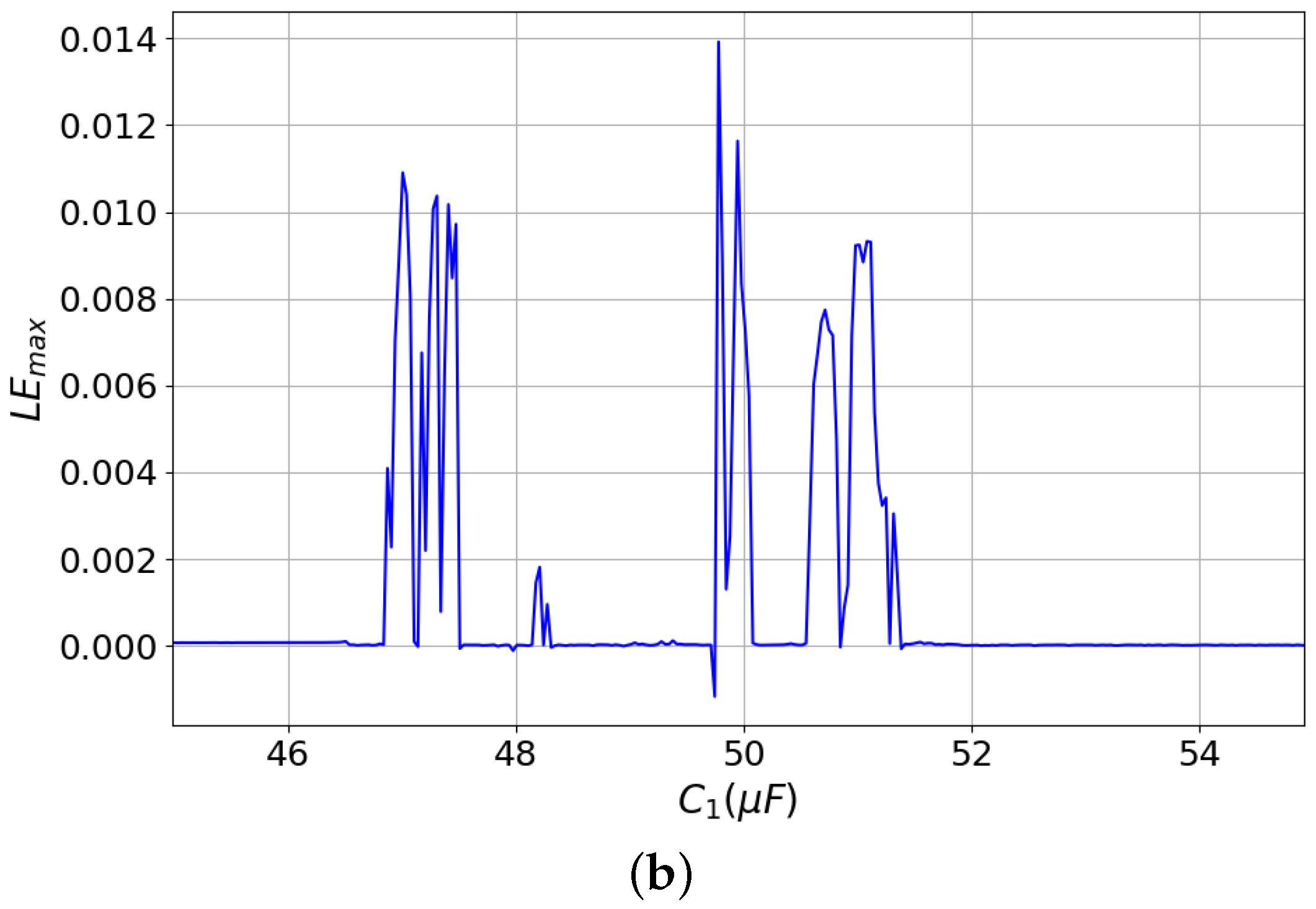
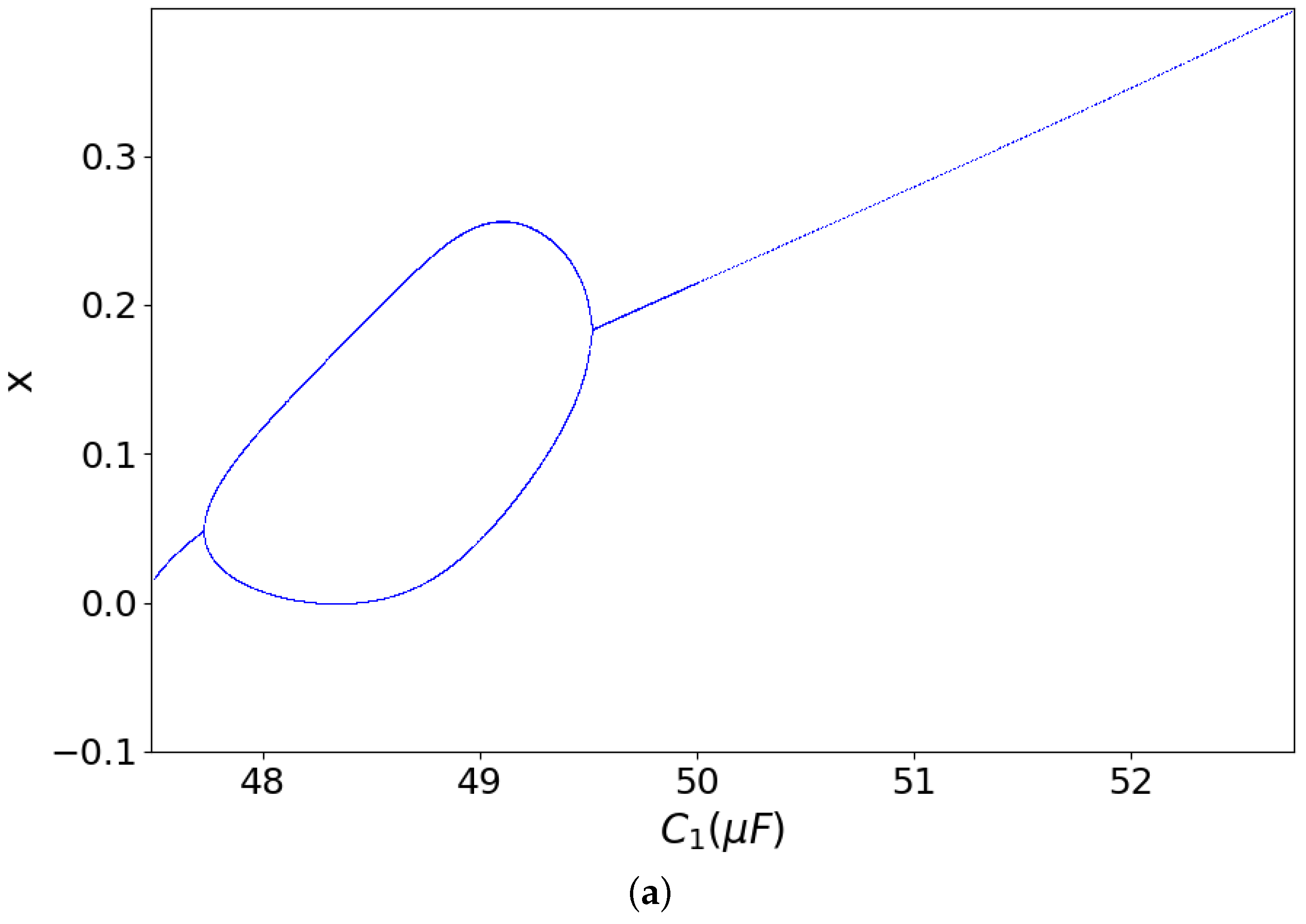
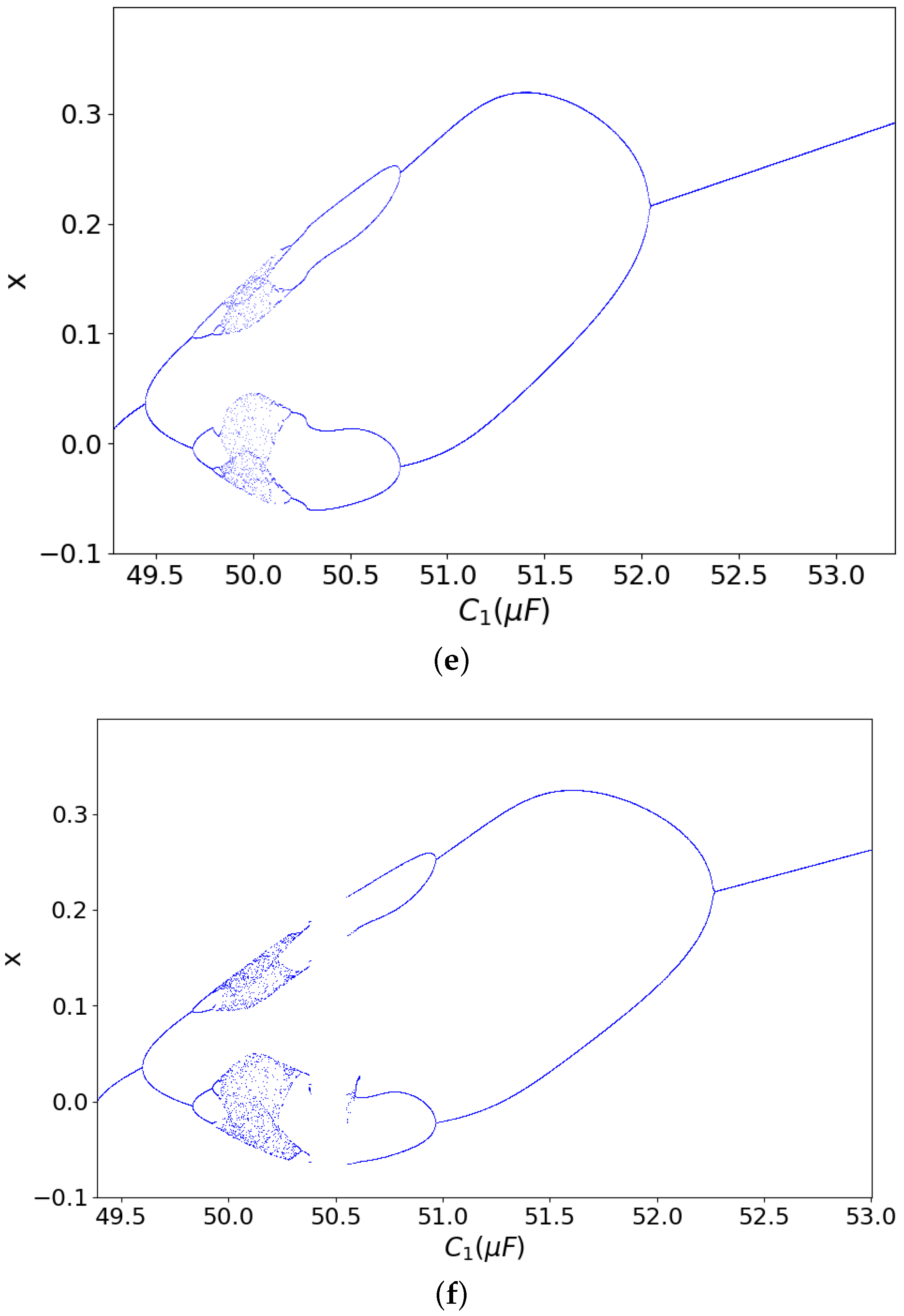
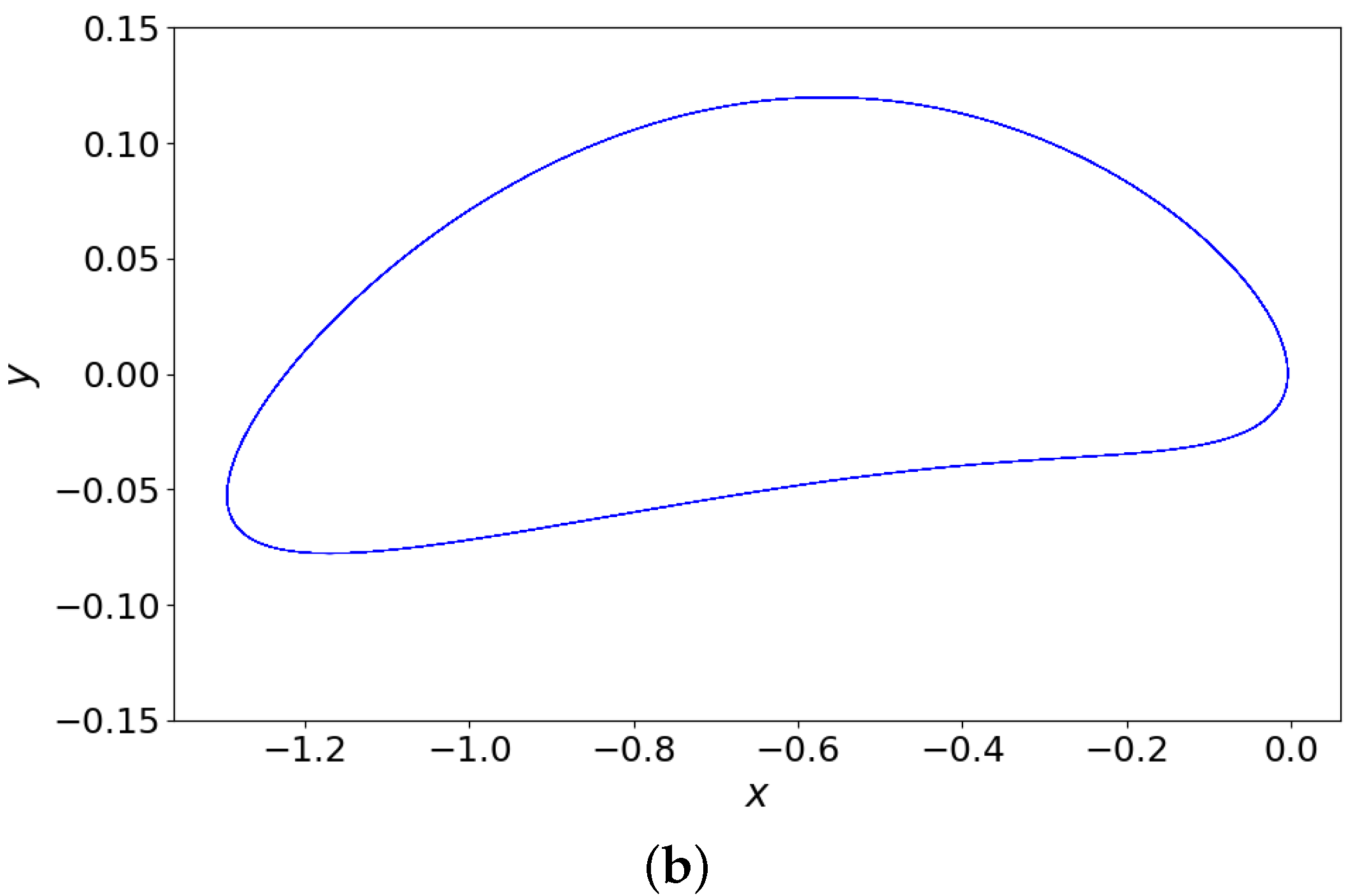
3.1. Dynamics Related to the Capacitor
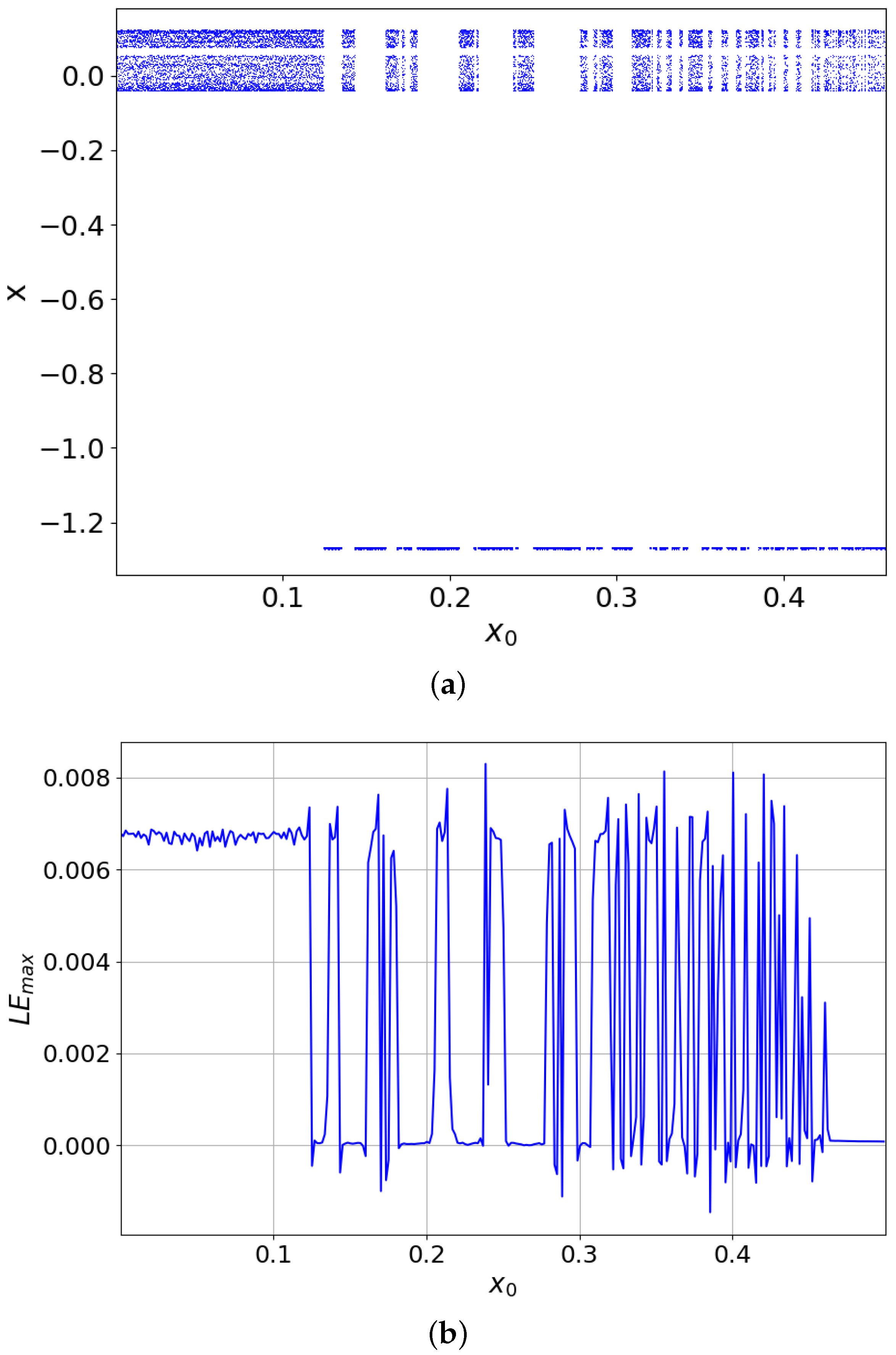
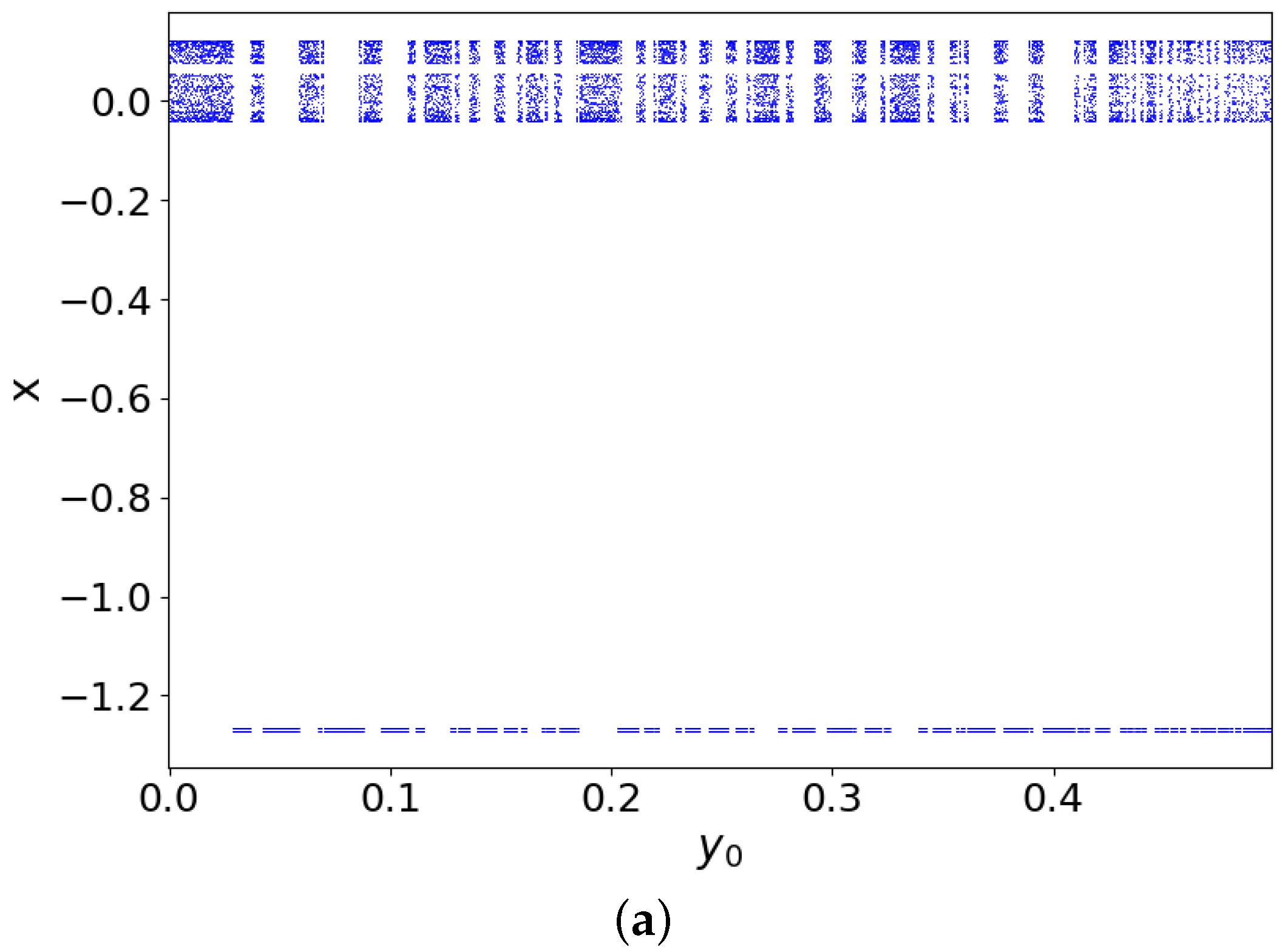
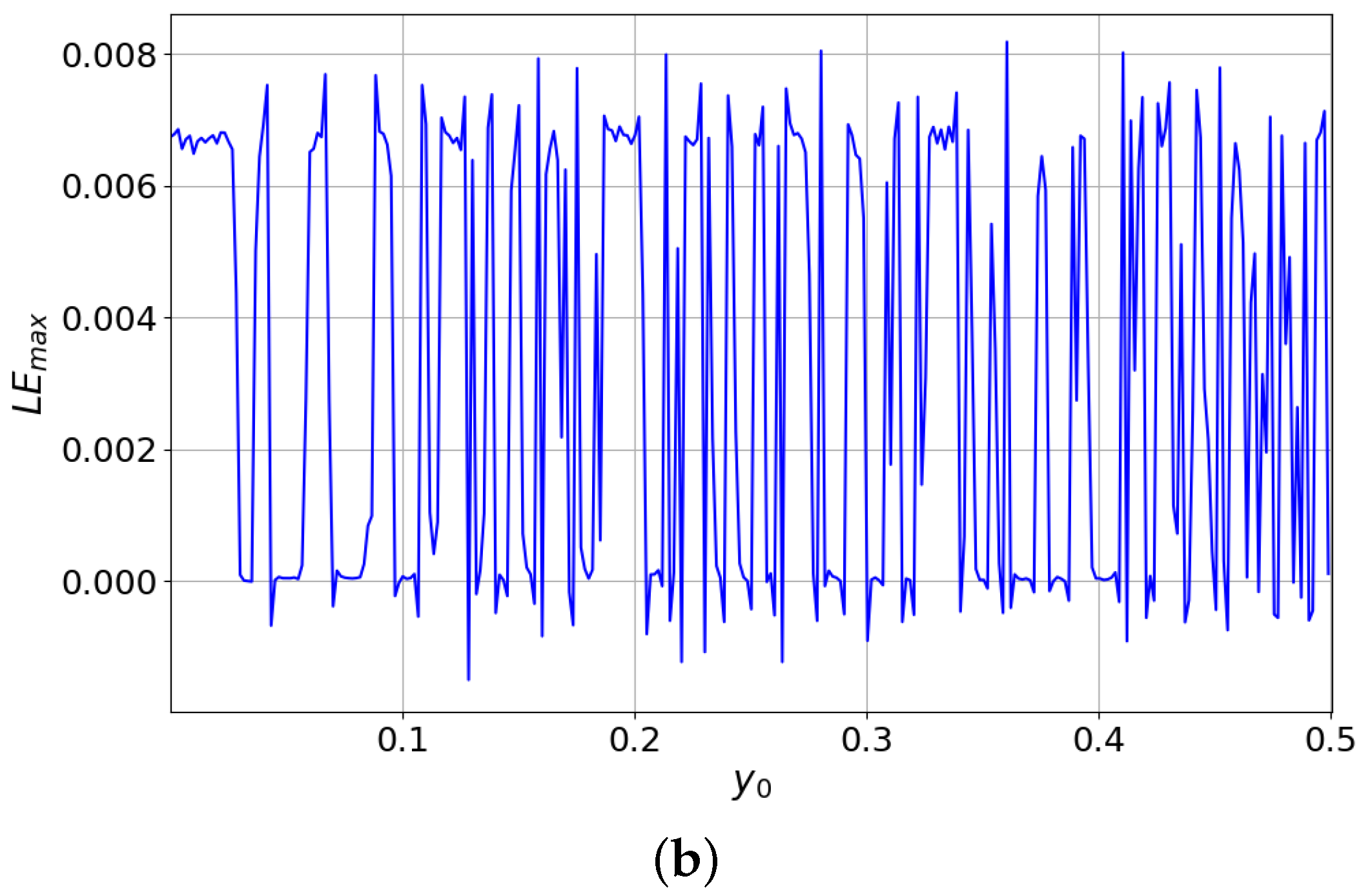
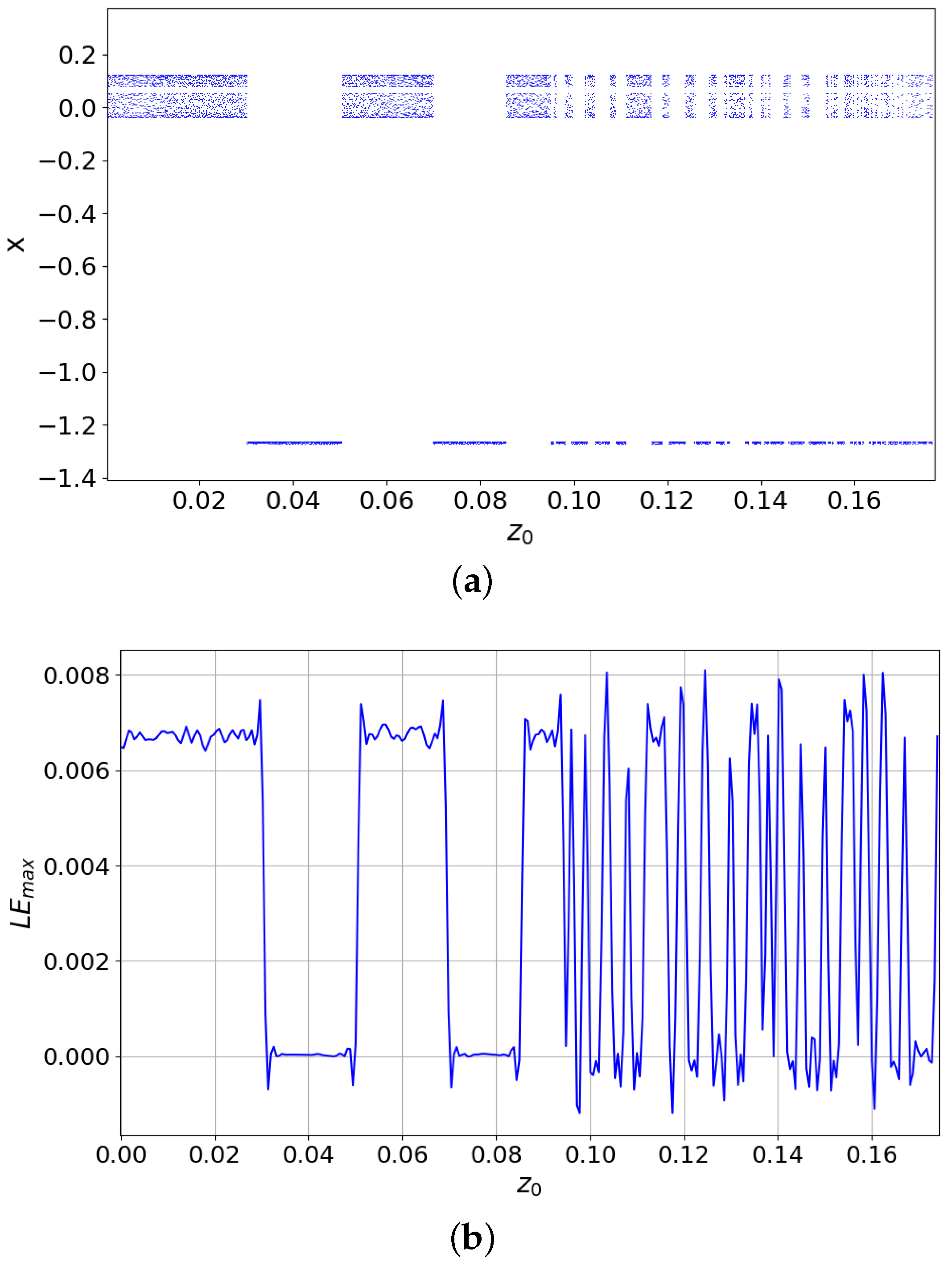
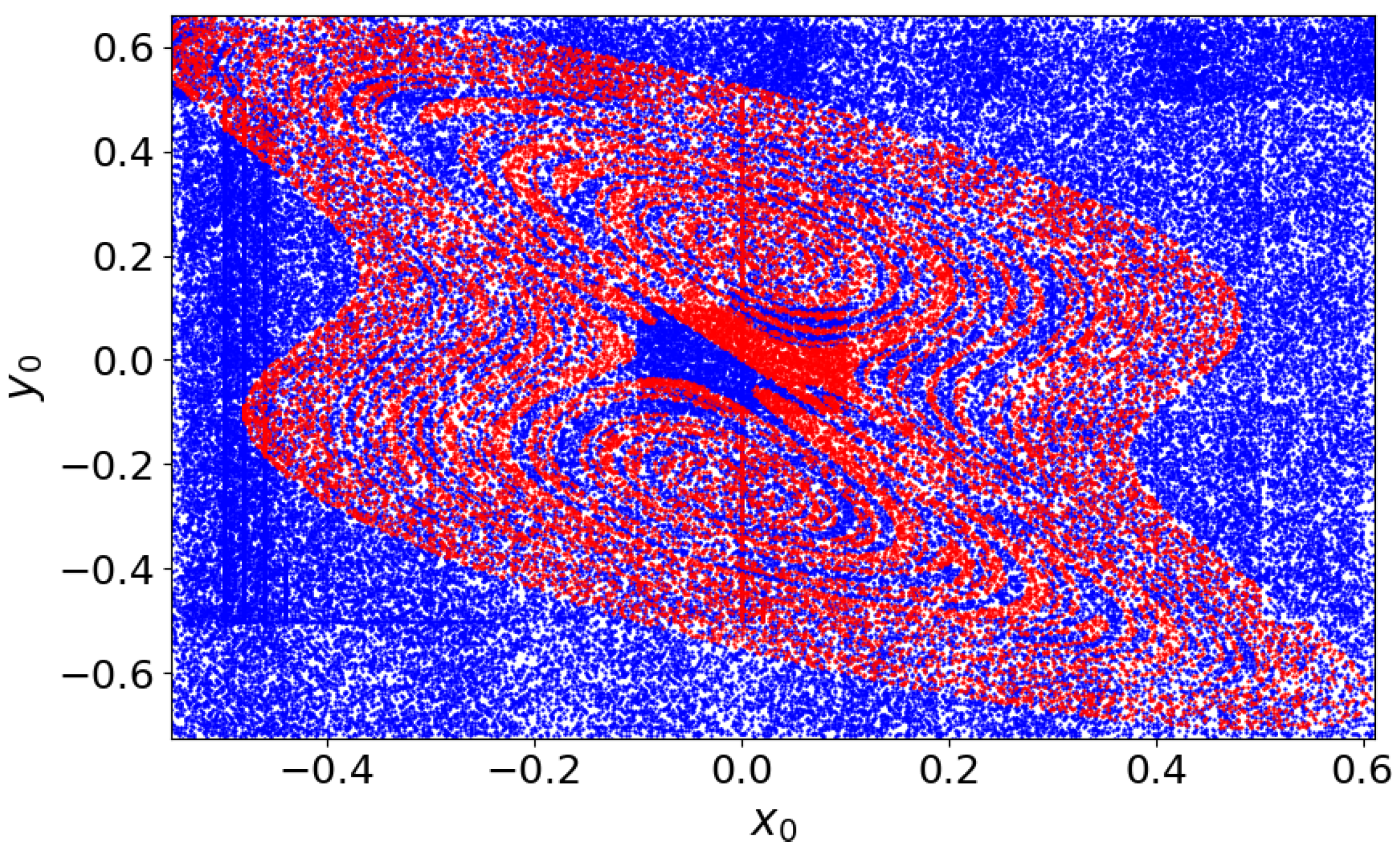
3.2. Dynamics Related to the Initial Conditions
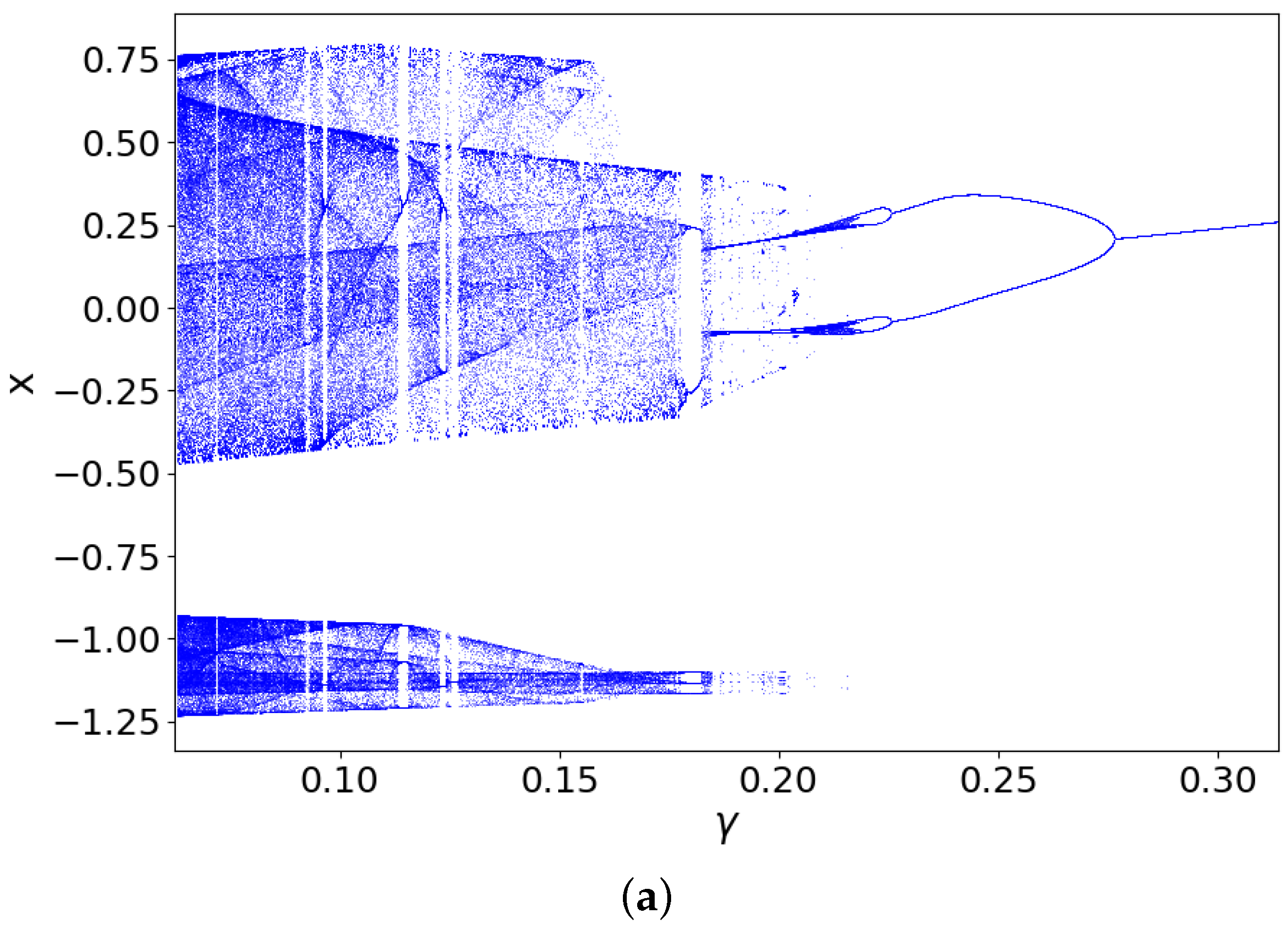
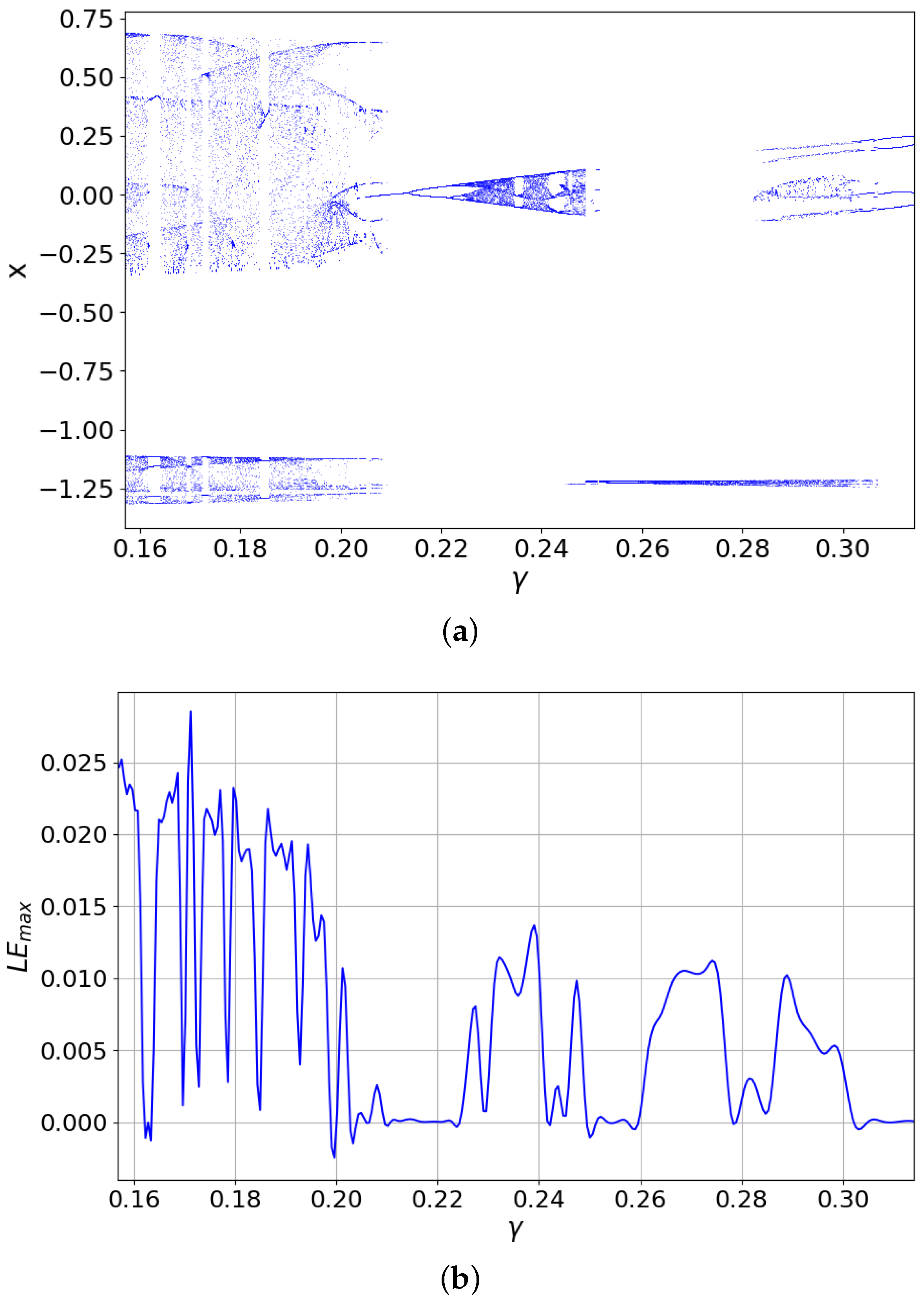
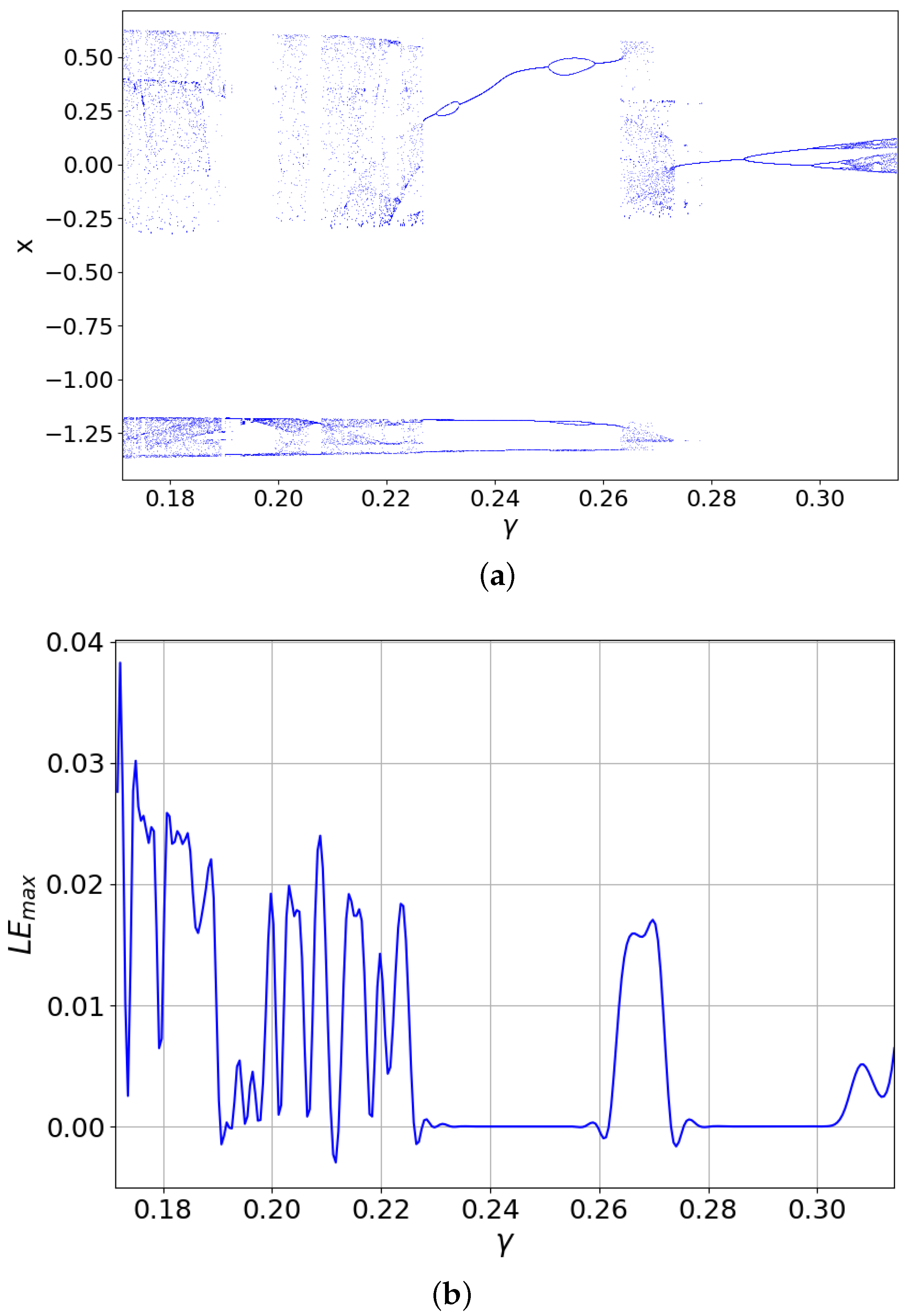
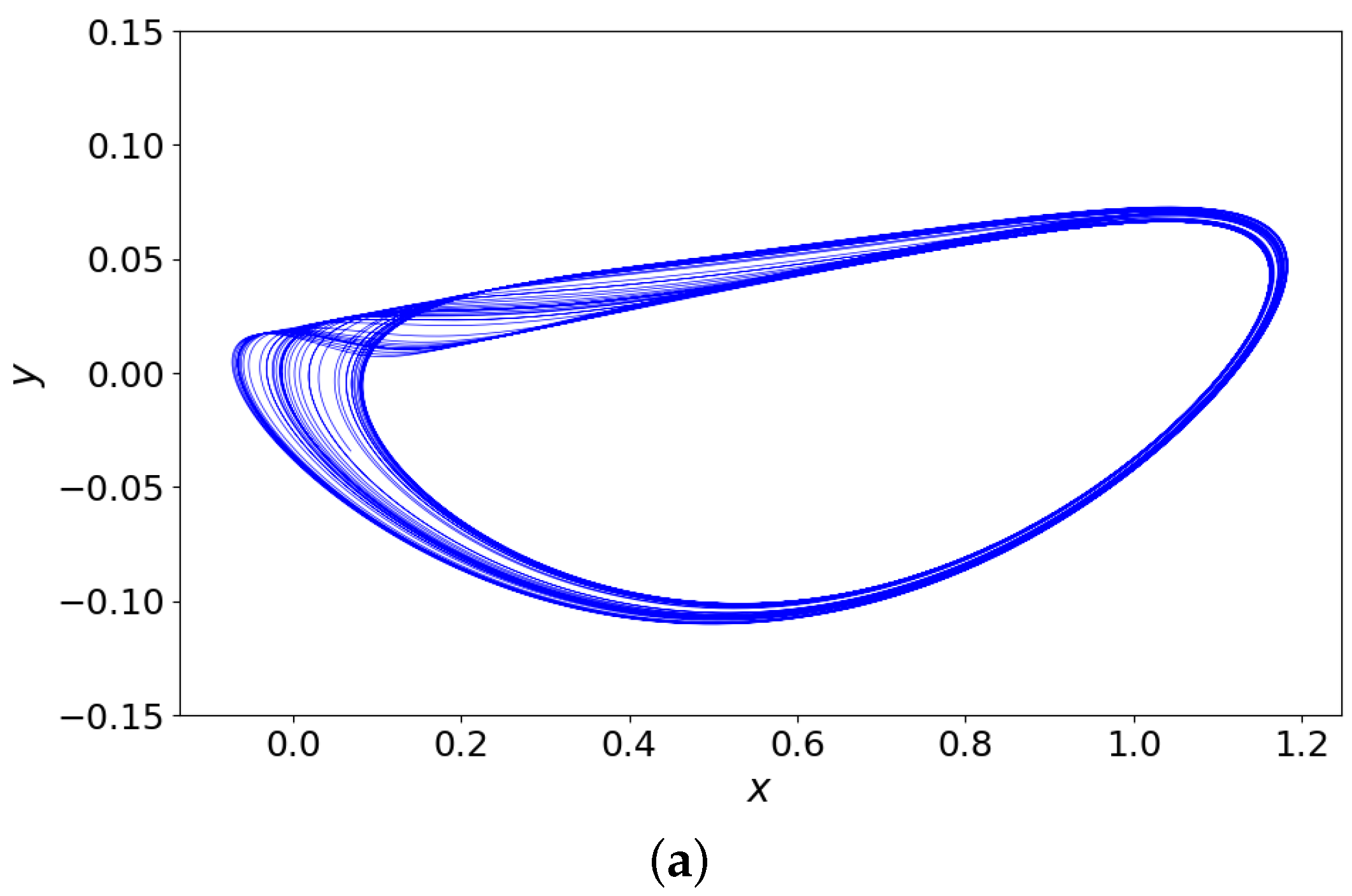
3.3. Dynamics Related to the Parameter (Linear Resistance )
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Chua, L. Memristor-the missing circuit element. IEEE Trans. Circuit Theory 1971, 18, 507–519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tetzlaff, R. Memristors and Memristive Systems; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2013; pp. 1–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parajuli, S.; Budhathoki, R.K.; Kim, H. Nonvolatile Memory Cell Based on Memristor Emulator. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1905.04864. [Google Scholar]
- Chua, L.O.; Kang, S.M. Memristive devices and systems. Proc. IEEE 1976, 64, 209–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.J.; Strukov, D.B.; Stewart, D.R. Memristive devices for computing. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2013, 8, 13–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.; Pershin, Y.V.; Yin, M.; Datta, T.; Di Ventra, M. An Experimental Proof that Resistance-Switching Memory Cells are not Memristors. Adv. Electron. Mater. 2020, 6, 2000010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strukov, D.B.; Snider, G.S.; Stewart, D.R.; Williams, R.S. The missing memristor found. Nature 2008, 453, 80–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prodromakis, T.; Toumazou, C. A review on memristive devices and applications. In Proceedings of the 2010 17th IEEE International Conference on Electronics, Circuits and Systems, Athens, Greece, 12–15 December 2010; pp. 934–937. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Y.; Mathew, J.; Pradhan, D.K. Matching in memristor based auto-associative memory with application to pattern recognition. In Proceedings of the 2014 12th International Conference on Signal Processing (ICSP), Hangzhou, China, 19–23 October 2014; pp. 1463–1468. [Google Scholar]
- Shin, S.; Kim, K.; Kang, S.M. Memristor applications for programmable analog ICs. IEEE Trans. Nanotechnol. 2010, 10, 266–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, G.S. Architecture and Methods for Computing with Reconfigurable Resistor Crossbars. U.S. Patent 7,203,789, 24 November 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Li, C.; Hu, M.; Li, Y.; Jiang, H.; Ge, N.; Montgomery, E.; Zhang, J.; Song, W.; Dávila, N.; Graves, C.E.; et al. Analogue signal and image processing with large memristor crossbars. Nat. Electron. 2018, 1, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Z.; Lai, C.S.; He, Y.; Qi, D.; Duan, S. Hybrid dual-complementary metal–oxide–semiconductor/memristor synapse-based neural network with its applications in image super-resolution. IET Circuits Devices Syst. 2019, 13, 1241–1248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, G. Molecular-Junction-Nanowire-Crossbar-Based Neural Networ. U.S. Patent 7,359,888, 15 April 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Mouttet, B.L. Crossbar Control Circuit. U.S. Patent 7,609,086, 27 October 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Pino, R.E. Reconfigurable Electronic Circuit. U.S. Patent 7,902,857, 8 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Mouttet, B.L. Memristor crossbar neural interface. US Patent 7,902,867, 8 March 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kang, H.B. RFID Device with Memory Unit Having Memristor Characteristics. U.S. Patent 8,113,437, 14 February 2012. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, L.; Dong, Z.; Duan, S.; Lai, C.S. Memristor-based stateful logic gates for multi-functional logic circuit. IET Circuits Dev. Syst. 2020, 14, 811–818. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lehtonen, E.; Poikonen, J.; Laiho, M. Two memristors suffice to compute all Boolean functions. Electron. Lett. 2010, 46, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chattopadhyay, A.; Rakosi, Z. Combinational logic synthesis for material implication. In Proceedings of the 2011 IEEE/IFIP 19th International Conference on VLSI and System-on-Chip, Hong Kong, China, 3–5 October 2011; pp. 200–203. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, H.; Sah, M.P.; Yang, C.; Cho, S.; Chua, L.O. Memristor emulator for memristor circuit applications. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2012, 59, 2422–2431. [Google Scholar]
- Sánchez-López, C.; Mendoza-Lopez, J.; Carrasco-Aguilar, M.; Muñiz-Montero, C. A floating analog memristor emulator circuit. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. II Express Briefs 2014, 61, 309–313. [Google Scholar]
- Minati, L.; Gambuzza, L.; Thio, W.; Sprott, J.; Frasca, M. A chaotic circuit based on a physical memristor. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 138, 109990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Strachan, J.P.; Williams, R.S. Chaotic dynamics in nanoscale NbO2 Mott memristors for analogue computing. Nature 2017, 548, 318–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buscarino, A.; Fortuna, L.; Frasca, M.; Valentina Gambuzza, L. A chaotic circuit based on Hewlett-Packard memristor. Chaos Interdiscip. J. Nonlinear Sci. 2012, 22, 023136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volos, C.K.; Pham, V.T.; Nistazakis, H.E.; Stouboulos, I.N. A dream that has come true: Chaos from a nonlinear circuit with a real memristor. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 2020, 30, 2030036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volos, C.; Nistazakis, H.; Pham, V.T.; Stouboulos, I. The first experimental evidence of chaos from a nonlinear circuit with a real memristor. In Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Conference on Modern Circuits and Systems Technologies (MOCAST), Bremen, Germany, 7–9 September 2020; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Campbell, K.A. Self-directed channel memristor for high temperature operation. Microelectronics 2017, 59, 10–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wolf, A.; Swift, J.B.; Swinney, H.L.; Vastano, J.A. Determining Lyapunov exponents from a time series. Phys. Nonlinear Phenom. 1985, 16, 285–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dingwell, J.B. Lyapunov exponents. In Wiley Encyclopedia of Biomedical Engineering; John Wiley and Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Sandri, M. Numerical calculation of Lyapunov exponents. Math. J. 1996, 6, 78–84. [Google Scholar]
- Maaita, J.; Kyprianidis, I.; Volos, C.K.; Meletlidou, E. The study of a nonlinear duffing–type oscillator driven by two voltage sources. J. Eng. Sci. Technol. Rev. 2013, 6, 74–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Luo, A.; Reyes, Z.; Reyes, A.; Goonesekere, R. On experimental periodic motions in a Duffing oscillatory circuit. J. Vibr. Test. Syst. Dyn. 2019, 3, 55–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volos, C.K.; Moysis, L.; Roumelas, G.D.; Giakoumis, A.; Nistazakis, H.E.; Tombras, G.S. Circuit Implementation of a Modified Chaotic System with Hyperbolic Sine Nonlinearities Using Bi-Color LED. Technologies 2021, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinriki, M.; Yamamoto, M.; Mori, S. Multimode oscillations in a modified van der Pol oscillator containing a positive nonlinear conductance. Proc. IEEE 1982, 69, 394–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawson, S.P.; Grebogi, C.; Yorke, J.A.; Kan, I.; Koçak, H. Antimonotonicity: Inevitable reversals of period-doubling cascades. Phys. Lett. A 1992, 162, 249–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kengne, J.; Negou, A.N.; Tchiotsop, D. Antimonotonicity, chaos and multiple attractors in a novel autonomous memristor-based jerk circuit. Nonlinear Dyn. 2017, 88, 2589–2608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kan, I.; Yorke, J. Antimonotonicity: Concurrent creation and annihilation of periodic orbits. Bull. Am. Math. Soc. 1990, 23, 469–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Kocarev, L.; Halle, K.S.; Eckert, K.; Chua, L.O. Experimental observation of antimonotonicity in Chua’s circuit. Int. J. Bifurc. Chaos 1993, 3, 1051–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Laskaridis, L.; Volos, C.; Stouboulos, I. Antimonotonicity, Hysteresis and Coexisting Attractors in a Shinriki Circuit with a Physical Memristor as a Nonlinear Resistor. Electronics 2022, 11, 1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11121920
Laskaridis L, Volos C, Stouboulos I. Antimonotonicity, Hysteresis and Coexisting Attractors in a Shinriki Circuit with a Physical Memristor as a Nonlinear Resistor. Electronics. 2022; 11(12):1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11121920
Chicago/Turabian StyleLaskaridis, Lazaros, Christos Volos, and Ioannis Stouboulos. 2022. "Antimonotonicity, Hysteresis and Coexisting Attractors in a Shinriki Circuit with a Physical Memristor as a Nonlinear Resistor" Electronics 11, no. 12: 1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11121920
APA StyleLaskaridis, L., Volos, C., & Stouboulos, I. (2022). Antimonotonicity, Hysteresis and Coexisting Attractors in a Shinriki Circuit with a Physical Memristor as a Nonlinear Resistor. Electronics, 11(12), 1920. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics11121920






