Design Topologies of a CMOS Charge Pump Circuit for Low Power Applications
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Topologies for CP Circuits
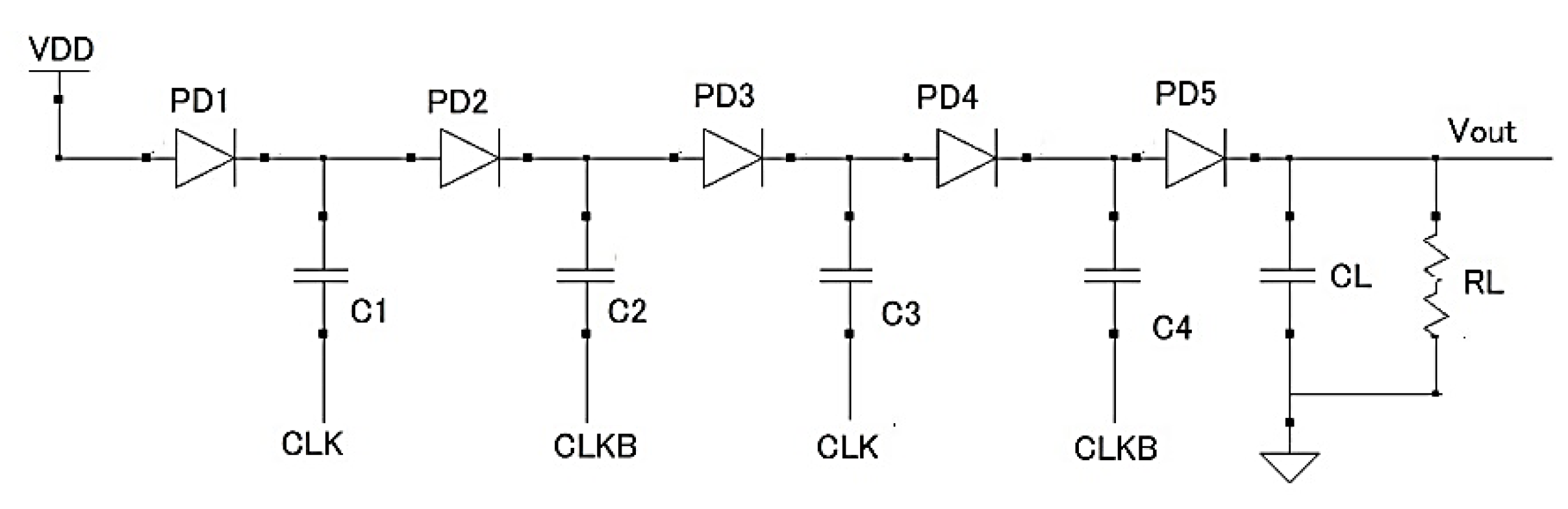
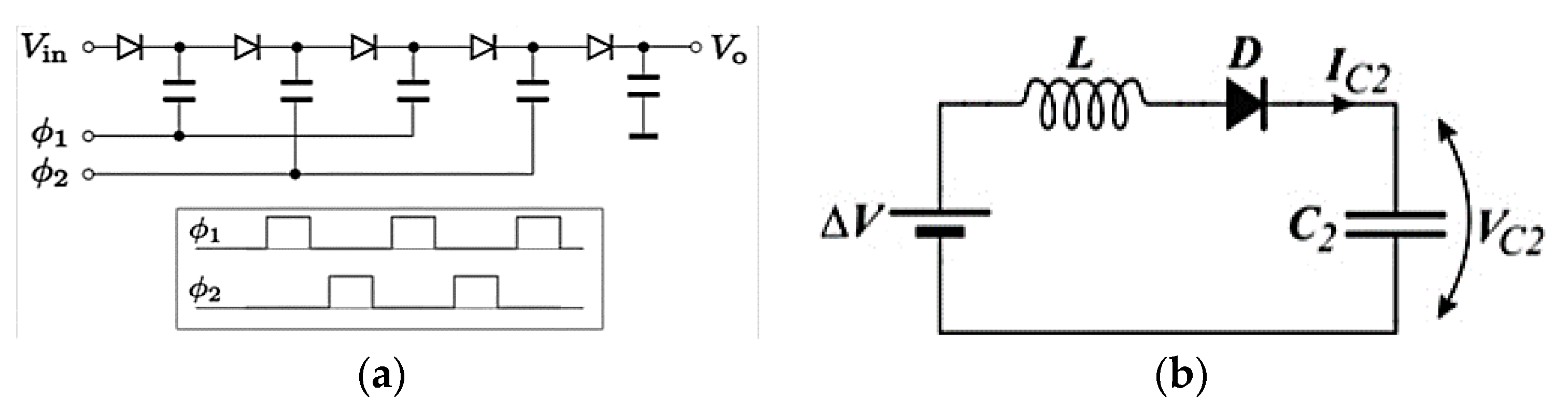
2.1. Basic CP Circuits
2.2. CP for Memory Application
2.3. CP for DC–DC Converter
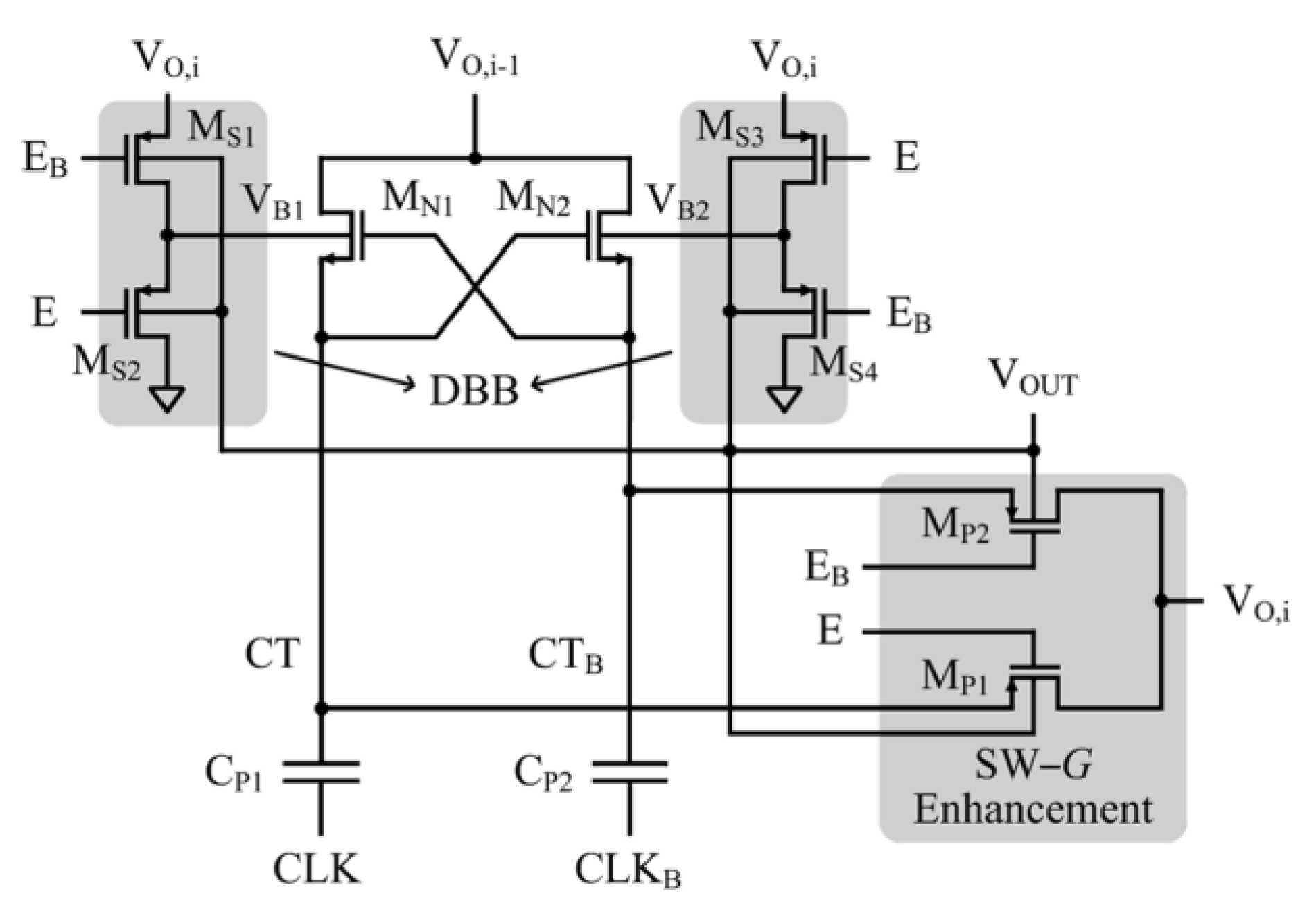
2.4. CP for Energy Harvesting
3. Discussion
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Rahman, L.F.; Marufuzzaman, M.; Alam, L.; Sidek, L.M.; Reaz, M.B.I. A low power and low ripple CMOS high voltage generator for RFID transponder EEPROM. PLoS ONE 2020, 15, e0225408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rahman, L.F.; Alam, L.; Marufuzzaman, M. Design of a Low Power and High-Efficiency Charge Pump Circuit for RFID Transponder EEPROM. Info. MIDEM 2021, 50, 255–262. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, L.F.; Ariffin, N.B.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Marufuzzaman, M. High Performance CMOS Charge Pumps for Phase-locked Loop. Trans. Electr. Electron. Mater. 2015, 16, 241–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dagan, H.; Shapira, A.; Teman, A.; Mordakhay, A.; Jameson, S.; Pikhay, E.; Fish, A. A low-power low-cost 24 GHz RFID tag with a C-flash based embedded memory. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2014, 49, 1942–1957. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Navidi, M.M. Integrated Circuits for Programming Flash Memories in Portable Applications. Ph.D. Thesis, Statler College of Engineering and Mineral Resources, Morgantown, WV, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Rahman, L.F.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Yin, C.C.; Ali, M.A.M.; Marufuzzaman, M. Design of high speed and low offset dynamic latch comparator in 0.18 µm CMOS Process. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e108634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rahman, L.F.; Reaz, M.B.I.; Marufuzzaman, M. Design of Low Power and Low Phase Noise Current Starved Oscillator for RFID Tag EEPROM. Info. MIDEM 2019, 49, 19–24. [Google Scholar]
- Tanzawa, T.; Tanaka, T.; Takeuchi, K.; Nakamura, H. Circuit techniques for a 1.8-V-only NAND flash memory. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2002, 37, 84–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, T.; Kobayashi, T.; Jyouno, Y.; Saeki, S.I.; Miyamoto, N.; Adachi, T.; Kimura, K. Bit-line clamped sensing multiplex and accurate high voltage generator for quarter-micron flash memories. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1996, 31, 1590–1600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.; Ki, W.H.; Yue, C.P. An NMOS-LDO regulated switched-capacitor DC–DC converter with fast-response adaptive-phase digital control. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 2015, 31, 1294–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, B.; Bose, S.; Johnston, M.L. A 1.2 V–20 V closed-loop charge pump for high dynamic range photodetector array biasing. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. Express Briefs 2018, 66, 327–331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballo, A.; Bottaro, M.; Grasso, A.D.; Palumbo, G. Regulated charge pumps: A comparative study by means of Verilog-AMS. Electronics 2020, 9, 998. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, G.; Pappalardo, D.; Gaibotti, M. Charge pump circuits: Power consumption optimization-a summary. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2004, 4, 26–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, G.; Pappalardo, D. Charge pump circuits: An overview on design strategies and topologies. IEEE Circuits Syst. Mag. 2010, 10, 31–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- File: Cockcroft Walton Voltage Multiplier Circuit.svg. Available online: https://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Cockcroft_Walton_voltage_multiplier_circuit.svg (accessed on 12 April 2015).
- Dickson, J.F. On-chip high-voltage generation in MNOS integrated circuits using an improved voltage multiplier technique. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1976, 11, 374–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Witters, J.S.; Groeseneken, G.; Maes, H.E. Analysis and modeling of on-chip high-voltage generator circuits for use in EEPROM circuits. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1989, 24, 1372–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cataldo, G.D.; Palumbo, G. Optimized design of an Nth order Dickson voltage multiplier. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Fundam. Theory Appl. 1996, 43, 414–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, G.; Barniol, N.; Bethaoui, M. Improved behavioral and design model of an Nth-order charge pump. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Fundam. Theory Appl. 2000, 47, 264–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanzawa, T.; Tanaka, T. A dynamic analysis of the Dickson charge pump circuit. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1997, 32, 1231–1240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.C.; Wu, J.C. Efficiency improvement in charge pump circuits. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1997, 32, 852–860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.T.; Chang, K.L. MOS charge pumps for low-voltage operation. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1998, 33, 592–597. [Google Scholar]
- Favrat, P.; Deval, P.; Declercq, M.J. A high-efficiency CMOS voltage doubler. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1998, 33, 410–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lauterbach, C.; Weber, W.; Romer, D. Charge sharing concept and new clocking scheme for power efficiency and electromagnetic emission improvement of boosted charge pumps. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2000, 35, 719–723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palumbo, G.; Pappalardo, D.; Gaibotti, M. Charge-pump circuits: Power-consumption optimization. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. Fundam. Theory Appl. 2002, 49, 1535–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canet, P.; Lalande, F.; Razafindramora, J.; Bouquet, V.; Postel-Pellerin, J.; Bouchakour, R.; Mirabel, J.M. Integrated reliability in EEPROM nonvolatile memory cell design. In Proceedings of the IEEE Computational Systems Bioinformatics Conference, Stanford, CA, USA, 17 November 2004; pp. 66–69. [Google Scholar]
- Bowen, M.; Pepper, P.; McPhie, R.; Winter, M. Evaluation of a remote drafting system for regulating sheep access to supplement. Anim. Prod. Sci. 2009, 49, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cockcroft, J.D.; Walton, E.T. Experiments with high velocity positive ions. (I) Further developments in the method of obtaining high velocity positive ions. Proc. R. Soc. Lond. 1932, 136, 619–630. [Google Scholar]
- Pylarinos, L.; Roger, E. Charge Pumps: An Overview; Department of Electrical and Computer Engineering University of Toronto: Toronto, ON, Canada, 2003; p. 7. [Google Scholar]
- Umezawa, A.; Atsumi, S.; Kuriyama, M.; Banba, H.; Imamiya, K.I.; Naruke, K.; Tanaka, S. A 5-V-only operation 0.6-mu m flash EEPROM with row decoder scheme in triple-well structure. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 1992, 27, 1540–1546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Atsumi, S.; Kuriyama, M.; Umezawa, A.; Banba, H.; Naruke, K.; Yamada, S.; Yoshikawa, K. A 16-Mb flash EEPROM with a new self-data-refresh scheme for a sector erase operation. IEICE Trans. Electron. 1994, 77, 791–799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, S.Y.; Wang, J.S. A high-efficiency CMOS charge pump circuit. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems Cat. No. 01CH37196, Sydney, NSW, Australia, 6–9 May 2001; Volume 4, pp. 406–409. [Google Scholar]
- Pelliconi, R.; Iezzi, D.; Baroni, A.; Pasotti, M.; Rolandi, P.L. Power Efficient Charge Pump in Deep Submicron Standard CMOS Technology. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2003, 38, 1068–1071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, N.; Min, H. A high efficiency all-PMOS charge pump for low-voltage operations. In Proceedings of the 2005 IEEE Asian Solid-State Circuits Conference, Hsinchu, Taiwan, 1–3 November 2005; pp. 361–364. [Google Scholar]
- Su, L.; Ma, D. Design and optimization of integrated low-voltage low-power monolithic CMOS charge pumps. In Proceedings of the 2008 International Symposium on Power Electronics, Electrical Drives, Automation and Motion, Ischia, Italy, 11–13 June 2008; pp. 43–48. [Google Scholar]
- Richelli, A.; Colalongo, L.; Tonoli, S.; Kovacs, Z. A 0.2 V–1.2 V converter for power harvesting applications. In Proceedings of the 34th European Solid-State Circuits Conference, Edinburgh, UK, 15–19 September 2008; pp. 406–409. [Google Scholar]
- Richelli, A.; Mensi, L.; Colalongo, L.; Kovacs, Z.; Rolandi, P.L. A 1.2 V–5 V high efficiency CMOS charge pump for non-volatile memories. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Symposium on Circuits and Systems, New Orleans, LA, USA, 27–30 May 2007; pp. 2411–2414. [Google Scholar]
- Richelli, A.; Mensi, L.; Colalongo, L.; Rolandi, P.L.; Kovacs-Vajna, Z.M. A 1.2-to-8 V charge-pump with improved power efficiency for non-volatille memories. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 11–15 February 2007; Digest of Technical Papers. pp. 522–619. [Google Scholar]
- Shiau, M.S.; Hsieh, Z.H.; Hsieh, C.C.; Liu, H.Y.; Liu, D.G. A novel static CTS charge pump with voltage level controller for DC-DC converters. In Proceedings of the 2007 IEEE Conference on Electron Devices and Solid-State Circuits, Tainan, Taiwan, 20–22 December 2007; pp. 481–484. [Google Scholar]
- Huang, M.-H.; Hsieh, C.-Y.; Fan, P.-C.; Chen, K.-H. A dual-phase charge pump circuit with compact size. Analog. Integr. Circuits Signal Process. 2009, 64, 55–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, F.; Yunlong, L.; Nanjian, W. A high efficiency charge pump circuit for low power applications. J. Semicond. 2010, 31, 015009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.T.; Chang, Y.H.; Chang, K.L. 1.2 V CMOS switched-capacitor circuits. In Proceedings of the 1996 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 10 February 1996; Digest of TEchnical Papers. pp. 388–389. [Google Scholar]
- Dong-Sheng, L.; Xue-Cheng, Z.; Fan, Z.; Min, D. Embeded EEPROM memory achieving lower power-new design of EEPROM memory for RFID tag IC. IEEE Circuits Devices Mag. 2006, 22, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yan, L.; Shilin, Z.; Yiqiang, Z. High voltage generator circuit with low power and high efficiency applied in EEPROM. J. Semicond. 2012, 33, 065006. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, K.C.; Amin, M.S.; Reaz, B. Low voltage charge pump circuit using 0.18 µm CMOS technology. Rev. Roum. Sci. Techn. Électrotechn. Énerg. 2013, 58, 83–92. [Google Scholar]
- Zucchelli, M.; Colalongo, L.; Richelli, A.; Kovacs-Vajna, Z.M. Dickson charge pump using integrated inductors in complementary metal–oxide semiconductor technology. IET Power Electron. 2016, 9, 553–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rumberg, B.; Graham, D.W.; Navidi, M.M. A regulated charge pump for tunneling floating-gate transistors. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. Express Briefs 2017, 64, 516–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdi, A.; Kim, H.S.; Cha, H.K. A High-Voltage Generation Charge-Pump IC using Input Voltage Modulated Regulation for Neural Implant Devices. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. Express Briefs 2018, 66, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richelli, A.; Colalongo, L.; Mensi, L.; Cacciatori, A.; Kovacs-Vajna, Z.M. Charge pump architectures based on dynamic gate control of the pass-transistors. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. VLSI Syst. 2009, 17, 964–967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shih, Y.C.; Otis, B.P. An Inductor less DC–DC Converter for Energy Harvesting With a 1.2 µW Bandgap-Referenced Output Controller. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. Express Briefs 2011, 58, 832–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, H.; Tang, N.; Yang, Y.; Heo, D. CMOS start-up charge pump with body bias and backward control for energy harvesting step-up converters. IEEE Trans Circuits Syst. Regul. Pap. 2014, 61, 1618–1628. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ker, M.D.; Chen, S.L. Ultra-high-voltage charge pump circuit in low-voltage bulk CMOS processes with polysilicon diodes. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. Express Briefs 2007, 54, 47–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, J.; Mok, P.K.; Kim, C. A 0.15 V input energy harvesting charge pump with dynamic body biasing and adaptive dead-time for efficiency improvement. IEEE J. Solid State Circuits 2015, 50, 414–425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, S.; Paily, R. An efficient on-chip switched-capacitor-based power converter for a microscale energy transducer. IEEE Trans. Circuit Syst. Express Briefs 2015, 63, 254–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, R.; Ju, C.; Hou, B.; Wei, Q.; Zhou, B.; Zhang, R. A Regulated Temperature-Insensitive High-Voltage Charge Pump in Standard CMOS Process for Micromachined Gyroscopes. Sensors 2019, 19, 4149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



| Source | Design Topology | Process (μm) | Supply Voltage VDD (V) | Frequency fclk (MHz) | Output | Pumping Efficiency (%) | Die Area (mm2) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [1] | CTS | 0.13 | 1.2 ~ 1.8 | 11.3 | 9.6~14.59 | 88~90 | 0.044 | RFID tag EEPROM |
| [2] | enhanced-NCP2CTS | 0.18 | 1.8 | 20 | 5.95 | 66 | 2.4 | RFIDtransponder Memory |
| [8] | intrinsic high-voltage transistors | 0.18 | 1.8 | - | 4–18 | 40 | - | Flash memories |
| [24] | two-step adiabatic switching | 0.25 | 2.5 | - | 9.16 | 57 | - | EEPROM and Flash memories |
| [32] | body bias technique | 0.35 | 3 | 10 | 6 | - | - | NVM |
| [33] | clocking scheme | 0.18 | 1.8 | 100 | 10.1 | 55 | - | Flash memories |
| [34] | all PMOS CP | 0.35 | 2 | 3 | 15.5 | - | - | Memory application |
| [35] | 4-phase complementarycharge pump. | 0.18 | 1.8 | 4 | 1.89 | 92.01 | - | DC–DCconverter |
| [39] | static CTS | 0.35 | 1.5 | 1.5 | 7.5 | - | 20 | DC–DCconverters |
| [40] | switched-capacitor-based | 0.35 | 2.9 | 0.25 | 5.5 | 90 | 2454.8 | DC–DCconverter |
| [41] | dynamically bias the CTS’s | 0.18 | 2 | 0.78 | 9.8 | 54 | 15.75 | NVM |
| [43] | dynamic CTS | 0.35 | 3.3 | 3 | 2.5–5 | - | 0.6 | NVM |
| [44] | improved charge sharing method | 0.35 | 3.3 | 5 | 14 | 83.3 | - | DC–DCconverter |
| [47] | regulated CP | 0.35 | 2.5 | 30 | 16 | 34 | 69 | NVM |
| [48] | frequency modulation | 0.18 | 2.8 | 10 | 12.8 | 80 | 0.6 | DC–DCconverter |
| Source | Design Topology | Process (μm) | Supply Voltage VDD (V) | Frequency fclk (MHz) | Output | Pumping Efficiency (%) | Die Area (mm2) | Applications |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| [50] | boost converter scheme | 0.13 | 0.27 | 0.80 | 1.4 | 58 | 0.42 | energy harvesting with PV cell |
| [51] | cross-coupled body bias | 0.18 | 0.32 | 0.45 | 2.04 | 89 | 1376 | energy harvesting |
| [53] | cross-coupled with DBB | 0.13 | 0.15 | 0.25 | 0.619 | 54 | 66 | low voltage energyharvesting |
| [54] | single-clock tree topology | 0.18 | 0.39 – 0.43 | 17 – 23 | 1 | 70 | 0.48 | microscale solar energy harvesting |
| [55] | closed loop control | 0.18 | 5 | 0.01 | 16.95 | - | 2.53 | sensor based microgyroscope |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Rahman, L.F.; Marufuzzaman, M.; Alam, L.; Mokhtar, M.B. Design Topologies of a CMOS Charge Pump Circuit for Low Power Applications. Electronics 2021, 10, 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10060676
Rahman LF, Marufuzzaman M, Alam L, Mokhtar MB. Design Topologies of a CMOS Charge Pump Circuit for Low Power Applications. Electronics. 2021; 10(6):676. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10060676
Chicago/Turabian StyleRahman, Labonnah Farzana, Mohammad Marufuzzaman, Lubna Alam, and Mazlin Bin Mokhtar. 2021. "Design Topologies of a CMOS Charge Pump Circuit for Low Power Applications" Electronics 10, no. 6: 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10060676
APA StyleRahman, L. F., Marufuzzaman, M., Alam, L., & Mokhtar, M. B. (2021). Design Topologies of a CMOS Charge Pump Circuit for Low Power Applications. Electronics, 10(6), 676. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10060676








