Abstract
Developments in drones have opened new trends and opportunities in different fields, particularly in small drones. Drones provide interlocation services for navigation, and this interlink is provided by the Internet of Things (IoT). However, architectural issues make drone networks vulnerable to privacy and security threats. It is critical to provide a safe and secure network to acquire desired performance. Small drones are finding new paths for progress in the civil and defense industries, but also posing new challenges for security and privacy as well. The basic design of the small drone requires a modification in its data transformation and data privacy mechanisms, and it is not yet fulfilling domain requirements. This paper aims to investigate recent privacy and security trends that are affecting the Internet of Drones (IoD). This study also highlights the need for a safe and secure drone network that is free from interceptions and intrusions. The proposed framework mitigates the cyber security threats by employing intelligent machine learning models in the design of IoT-aided drones by making them secure and adaptable. Finally, the proposed model is evaluated on a benchmark dataset and shows robust results.
1. Introduction
Pervasive environments have become increasingly popular over the last two decades, especially considering the importance of pervasiveness and the smartness of the objects present in an environment such as a building, a town, a playground, a shopping mall, etc. The element of pervasiveness in an environment enables various tasks such as controlling activities with improved efficiency and efficacy, responding to various events, providing better facilities, etc., by connecting many devices and sensors. In recent times, drone technology has led to small-sized drones such as quadcopters, mini-drones, etc. A benefit of these small-sized drones is that they can easily enter a building and can hover inside a building for the sake of monitoring and surveillance in various fields of life, such as the surveillance of industrial areas [1,2,3] and for disaster management, military uses [4], search and rescue [5,6] shipping and delivery [7], precision agriculture [8,9], and many other applications. There are other possible applications of commercial drones, such as aerial photography, weather forecasting, etc.
Unmanned aerial vehicles (UAVs) are air-bound vehicles without human operators. Typically, UAVs are used by aerodynamics forces to provide the forces with the facility of remotely piloting a machine [10]. There are similar commercial applications as well, which have caused a change in the behavior of many industries and have had an impact on day-to-day life. Since drones are typically capable of collecting aerial data and transmitting these to their base station with ease, this feature makes drones a convenient vehicle for surveillance and monitoring purposes [11]. However, the rapid growth in the use of drone technology in our daily life has brought challenges not only in terms of drone safety and security but also privacy, liability, and regulation in particular [12]. There are so many advantages of small-size drones in agriculture, industry, shipping, delivery, etc., that these drones are becoming part of our daily life. However, the security and privacy of these drones are an open challenge [13]. In recent times, another emerging field of research has been the attempt to make drones smart by adding a few sensors that a small drone may be sufficiently capable of carrying. A set of devices such as sensors, transmitters, and cameras for many different and complex applications can make drones more useful and effective [14].
Small drones are opening new avenues for the defense and civil industries. However, small drones are vulnerable to privacy and security threats due to a lack of appropriate architecture. Evolutions in the Internet of Drones (IoD) and Internet of Things (IoT) provide new directions and also pose additional challenges related to data privacy and data security. The basic architecture and design require modification in order to provide a more secure and reliable network. In the recent past, the structure of a typical drone has been based on a layered architecture [1], as shown in Figure 1.
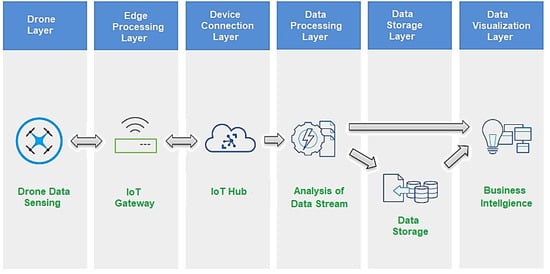
Figure 1.
Layered architecture for industrial drones.
In a typical layered architecture [1] of industrial drones, the drone layer is the first layer, where a quadcopter or other mini drone has a camera attached to it. This drone is attached to an IoT hub through an IoT gateway. Here, IoT gateways play an important role in providing communication; for example, a cloud-based IoT Hub of a base-station. The data received at IoT Hub is further passed to the data processing layer to investigate the data stream of the drone. The results of data analysis are stored in data storage centers at the data storage layer, and data are streamed to the data visualization layer, which visualizes the drone data analytics. This platform can be used in Microsoft’s Azure services for cloud storage and Hub services. However, a problem with such a platform is the lack of support for cybersecurity and data privacy. The Internet of Drone Things (IoDT) [15] is another recent idea that introduces the use of IoT with drones, allowing drones to connect with an IoT network. In this research, the idea of the IoDT is proposed along with security and privacy concerns. The proposed work proposes the use of the IoT with drones to obtain smart drones that have decision-making ability, and we use blockchain technology to make these smart drones secure and private.
The proposed framework consists of seven layers: the drone layer, edge processing layer, security and privacy layer, data connection layer, data processing layer, data storage layer, and data visualization layer. The main goals of this complete IoDT-based architecture are as follows:
- A layered framework is designed to provide security and privacy in the small drone’s network;
- We highlight the design details of the proposed framework, implementation, hardware components, and attack handling methods using ML models;
- The proposed framework utilizes IoT-based sensor data, drone data, and network information to handle security attacks and achieves 99.99% accuracy;
- The experimental results prove the generalizability and robustness of the proposed LRRF model, which is tested on two benchmark datasets—KDD CUP 99 and NSL-KDD.
Section 2 explains the related work regarding the identification of security threats and attacks to drones and IoT systems. A small portion of the literature was found that uses lightweight authentication processes to make drones secure. Section 3 describes the research methodology and the proposed research framework for secure drone systems. Section 4 discusses secure authentication and access control for drones. Section 5 presents the experiments and results, and Section 6 discusses the conclusions and future work.
2. Related Work
The typical usage of drones is for defense and military purposes. The drones range from military usage 200 feet war machines to tiny, inch-wide micro flying particles in the air. The size of drones is also a very important feature for their uses and purposes. The flying range also varies from a few meters around the operators to advanced military drones that fly around 17,000 miles without land controls. The maximum flight time also varies with altitude, surface area, landscape, etc. The height of the flight also varies from a few meters to 65,000 feet [1].
2.1. Security Threats to Drones
Drone security involves several types and layers according to their use, size, and control techniques. In most cases, the drone uses the Wi-Fi communication protocol (IEEE 802.11) [15]. The drone framework includes a Wi-Fi network and respective ground stations, which are vulnerable to cyber security threats. The lack of encryption techniques on their chips can lead to the hijacking of drones [16]. Other attacks, such as man-in-the-middle attacks, normally range up to 2 km and are also a cause of hijackings [4]. The IoD is becoming very popular in the military industry [17]. One main challenge regards privacy and security concerns in its design. Privacy issues involve the protection of data, information leakage, data accessibility, and data encryption and decryption techniques [18]. In the past few years, many researchers have identified security threats. These threats are categorized into four types: jammers, sensor-based and protocol-based threats, and compromised components. A literature review of these four categories is presented in Table 1.

Table 1.
Typical cybersecurity and data privacy threats to smart drones.
Table 1 shows that the previous literature has mostly focused on the identification of cyber security threats in drones. The solution to these threats is not discussed in many cases. A research avenue for researchers was the use of encrypted data during the transmission of drone data to its base station by using an encryption algorithm for safe and secure data transmission [17]. Small drones have been in the public eye in the past decade due to their small size, low weight, and wingspan. The small drone is also a threat to public and government data privacy [30]. Many other pieces of research have discussed security threats and challenges faced by drones [29,31,32,33,34,35]. Tian discussed an effective and intelligent authentication model for the edge-assisted IoD that ensured the security of the drone data network [36]. Likewise, Hell presented a monitoring system for the drone data security of a factory area [2]. In 2019, authors proposed a drone for sensing gas in a factory [3]. Drones are mostly being used for monitoring purposes in the agriculture and security fields.
Investigating cyber security threats related to drones has been a widely discussed research area in the last decade. Drone applications of a smart city and their related privacy issues are discussed in [5]. Some important issues are also discussed in Table 1. Researchers have also discussed the cybersecurity threats of drone networks and their limitations and future directions [37]. Other similar studies [6,38,39] presented applications and challenges in business. Some proposed the use of blockchain for safe data transmission using 5G and IoT-based drones [39]. However, this system identified types of threats and their intensity manually. An efficient, intelligent and secure system of drones that can investigate cyberattacks and enact preventive measures to ensure drone data security is required. Some other studies [7,40,41,42] identified challenges and their relevant solutions to security issues related to drones used in industrial and commercial areas. A few studies tried to solve the problem of the authentication of devices by using key agreement [40] and key-enabling data [7] for secure drone data delivery. The application of IoT-based drones in agriculture is discussed in [8,9]. The hijacking of drones, drone data, and UAVs is a common problem faced by commercial drones, as discussed in [20,21,22,23]. The countermeasures and solutions of these problems are proposed in [22] and [23]. GPS spoofing is another common problem related to drones [24] and UAV machines and needs a safe, secure, and authentic solution. Some other studies on drone hijacking and the control intercepting of a drone are also detailed in [25,26,27,28].
2.2. Machine Learning for Drone Security
The basic types of machine learning techniques include supervised, unsupervised, and semi-supervised learning. A literature review revealed that machine learning models have been utilized by many researchers to deal with cyberattacks in mobile-based networks [43], sensor-based wireless networks [44], cloud-computing [45], and IoT-based systems [44]. Vedula et al. combined a supervised learning model with a self-learning model through RF and LSTM (autoencoder) to detect DDoS attacks using two features [46]. Researchers proposed an approach to detect and control an actuation attack in a constrained cyber-physical system using a probabilistic approach in [47]. No work has been found dealing with cyberattacks using machine learning models in drone networks. We have also proposed an access control system in drone security. Our previous work showing the use of machine learning for wireless network security systems is presented in Table 2.

Table 2.
Typical cybersecurity and data privacy threats to smart drones.
An extensive literature review ranging from 2010 to 2020 concerning privacy and safety concerns of drone data security shows a large number of research works have been published. Most of the studies discuss challenges, applications, and issues related to cyber security, data privacy concerns, spoofing, hijacking drones, and other threats. However, many researchers have highlighted the problem domain but have not provided a potential solution to resolve these problems. In [39], a solution based on blockchain is devised for data safety during transmission using 5G and IoT-enabled drones. This system is based on the identification of threats manually. An authentication system based on keys for devices was proposed that was not suitable in an IoT-based network of drones. There is a clear research gap in the area of developing a safe and secure drone network by proposing a solution that deals with cybersecurity threats and makes drones adaptable in industry and the commercial sector.
A smart and intelligent system is required for the security of drones that can investigate data of attacks and ensure the security of drones by taking proactive measures. In the past, machine learning models were proposed in the field of cybersecurity for wireless sensor-based networks and mobile-based networks but not for drone-based security. A machine learning-based solution is proposed in this study for drone security authentication and control access methods.
3. Proposed Architecture: Layers and Hardware Components
The proposed research primarily focuses on improving the cybersecurity of drones and IoT devices. This research assists in enhancing the basic framework of drones—particularly, small drones—to ensure reliability and security against common cybersecurity threats, interception threats, and privacy threats. The proposed framework is presented as a layered approach that deals with the security issues and analysis methods in each layer. This layered approach provides data security and analysis techniques in addition to the traditional operations of drones. Moreover, the layered architecture facilitates the implementation and future enhancement and improvement of our method. In the proposed approach, the use of machine intelligence by utilizing machine learning models improves drone data security. The proposed framework is shown in Figure 2.
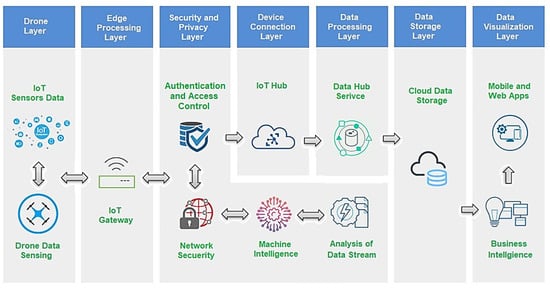
Figure 2.
Proposed architecture for smart drone security.
Small drones are opening new possibilities in the defense and civil industries. However, small drones are vulnerable to privacy and security threats due to a lack of appropriate architecture. Evolutions in the IoD and IoT provide new directions and also pose additional challenges related to data privacy and data security. The available framework is not yet secure and reliable in terms of data privacy concerns.
3.1. Layers
A layered architecture [1], as shown in Figure 2, that is typically used for smart drones is updated by adding a security and privacy layer and updating the data processing layer with machine intelligence components.
3.1.1. Drone Layer
In the proposed layered architecture of industrial drones, the first layer is the drone layer, where a quadcopter or other mini drone has a camera attached to it. This layer is updated by IoT sensor data. Smart sensors are used, including a GPS sensor, altitude sensor, radar, and camera. This is the first step in the proposed architecture. This layer can perform sensing, recording, and sending the information recorded by drones to the next layer. In this layer, an unmanned aircraft system (UAS) drone is involved, which is responsible for drone flight operations, information recording by sensors, etc. The UAS consists of two parts: a ground controller and a communication connection. In the proposed architecture, a DJI phantom 3 drone is used, which consists of a custom remote controller and communication link. In the proposed architecture, sensors are attached to the drone.
3.1.2. Edge Processing Layer
In the second layer—the edge processing layer—the drone and IoT raw data are forwarded to the security and privacy layer, where it is verified that the data originate from authenticated devices. This layer deals with the communication and transmission of data to the next station; i.e., the cloud layer. Several gateway device mechanisms are available which provide wireless communication. Wi-Fi communication transmits information at a fast speed. The edge processing layer provides device to cloud communication efficiently. This layer is responsible for data protection, cashing, and flooding. The proposed research uses the Azure IoT gateway for cloud communication. The architecture of the IoT gateway is shown in Figure 3.
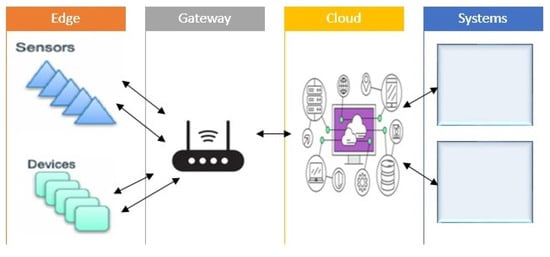
Figure 3.
IoT gateway model.
3.1.3. Security and Privacy Layer
This layer plays an important role in providing device authentication and secure access control by using machine learning models. At this level, the safety and security of data are implemented, which is the key element of this IoT framework. There are several types of privacy threats that can occur at this stage. These are as follows:
- Physical privacy threat;
- Behavior privacy threat;
- Location privacy threat.
Physical privacy is related to capturing someone’s property. If a third party is secretly monitoring the drone information, then the private information of someone’s property can be compromised. A location privacy threat refers to someone’s location being captured by an unauthorized person. A behavior privacy threat is related to the monitoring of someone’s activities and behavior by an unauthorized person. Such types of security risks must be tackled by using authentication schemes and protocols. Several types of security breaches are used by unauthorized persons to make such security threats. Intrusion, spoofing, jamming, and DoS attacks are the most common kinds of threat. In the proposed architecture, device authentication is maintained using a machine learning algorithm to detect and alert users of such security attacks.
3.1.4. Device Connection Layer
IoT gateways play an important role in providing a link for communication to a cloud-based IoT Hub at a base station. Here, an extra module is added for security orchestration and automation to ensure connectivity for only authenticated devices. The IoT Hub works by providing a message medium between IoT applications and IoT devices. The IoT hub allows message passing between IoT devices and cloud systems in an IoT network. This communication is bidirectional. In this layer, security arrangements for only authenticated devices are made. Figure 4 shows the registration and encryption process of devices that are attached to the network. Sensor data, along with drone and network information, is forwarded to the blockchain client, which performs data integrity protection and stores the information in a database on a cloud server. A basic blockchain mechanism provides devices and the IoT security in real-time.
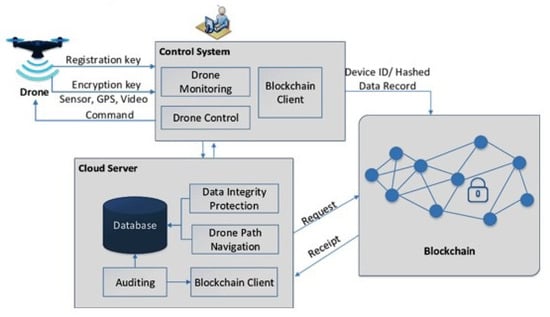
Figure 4.
Blockchain-based communication for a drone.
3.1.5. Data Processing Layer
The data received at the IoT Hub are then passed to the data processing layer to analyze the data stream of the drone. Here, two new modules are implemented: a machine intelligence module that performs intelligent data analysis and a data hub service that assists in smooth and simple cloud storage. Several machine learning algorithms are available that are suitable according to the situations and requirements of data. This research focuses on device authentication using an intelligent machine learning approach. This layer consists of an authentication scheme based on the Naïve Bayes model, an intelligent machine learning algorithm. The IoT hub layer works by authenticating devices using the timestamp data of drones for a fixed interval of time. Drone flight data are used for the training and testing of the model. Firstly, training of the model is performed, and then testing is carried out to check if the model is intelligent enough to detect malicious drone activities. If drone information is miscellaneous, the model will alert the system and stop the device from connecting to the cloud. If a drone’s behavior is not suitable, it is detected immediately, and unauthorized access is denied using machine intelligence. Several security threats are associated with flight operations. A man in the middle attack is the most common kind of threat, which occurs when a third person hijacks the drone and takes it over. The spreading of false information can also occur when an unauthorized person tries to take control of the drone. In the proposed architecture, a model is trained using the Naïve Bayes classifier, and this trained model is used to authenticate newly engendered aircraft paths. We have used the KDD’99 dataset and real-time dataset to determine accuracy, precision, and recall. Precision is the rate of correct predictions that are truly correct, and recall is the rate of correct predictions that are incorrect in reality.
3.1.6. Data Storage Layer
The results of the data analysis generated by the data processing layer are stored in the data storage centers at the data storage layer. A cloud-based NoSQL database is used for the storage of results generated by drones in the drone layer. The data consist of IoT sensor data along with network and drone information. The NoSQL database provides the schema-less storage of information, making it easy to access and retrieve data quickly. A large volume of data can be stored with this technique. A NoSQL databse is a self-referential database, which makes it more useful than SQL databases. Figure 5 shows the common storage structures that are used in such databases. A document structure, graph structure, key–value structure, and column structure are shown, which are the most used structures.
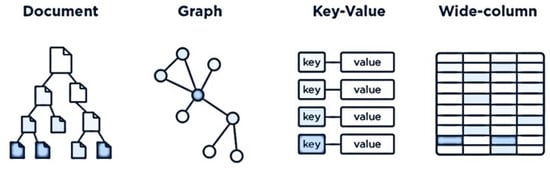
Figure 5.
Storage structures used in NoSQL databases.
3.1.7. Data Visualization Layer
The data visualization layer allows data monitoring using several tools and services. Microsoft Azure services for storage services and hub services are used in this platform. A mobile app is used to view the results generated by the visualization layer, showing the predictions made by our intelligent model about the security level of a drone. Drone attacks are identified using the intelligent Naïve Bayes model. Figure 6 shows the architecture of how business intelligence works using stream analytics results, which are stored in a storage center. These results are used by Power BI, which is a platform for business intelligence modeling and result visualization.
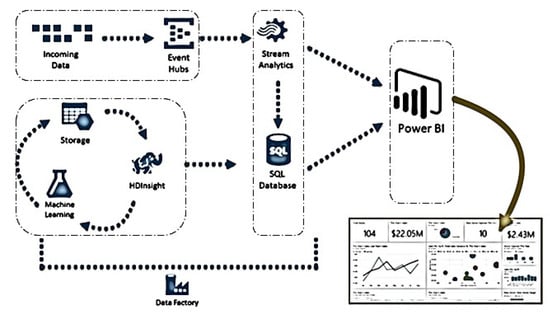
Figure 6.
Microsoft Azure working and hub services.
3.2. Hardware Components
The hardware components used in this experiment are cheap and easily available in the market. As the microcontroller, an Arduino mega 2560 with a built-in WiFi module ESP8266 was used as a processing device to receive data from sensors. Figure 7 shows the hardware components used in the proposed methodology.
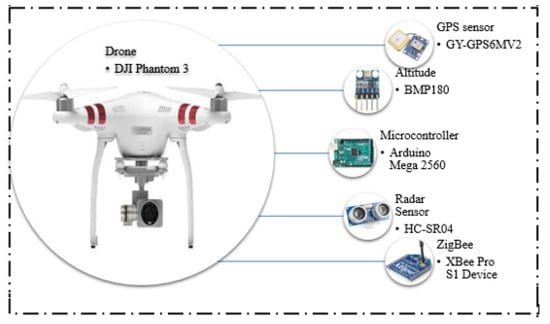
Figure 7.
Hardware components of the proposed system.
3.2.1. DJI Phantom 3 Drone
Drones are now available in different shapes and sizes. These shapes also define the working of a drone concerning its working style and size. The drone used in the proposed framework is a powerful Phantom 3 standard flying vehicle produced and distributed under the banner of DJI. It is controlled by a custom controller that can be connected wirelessly from distant areas. Table 3 shows the specifications of this unmanned aerial vehicle.

Table 3.
Detail of classes in the dataset.
3.2.2. Radar Sensor
A radar sensor is used to track, locate, and identify items from distant locations. These sensors work by transmitting electromagnetic energy toward the objects and target areas. These sensors can precisely detect objects, as compared to optical sensors. Accelerometers can be used in place of a radar sensor. In the proposed system, an HC-SR04 ultrasonic proximity sensor is used for this purpose. This sensor calculates object patterns. Table 4 shows the sensor specifications.

Table 4.
Performance measures used for evaluation in this study.
3.2.3. GPS Sensor
The GY-GPS6MV2 is a global positioning system receiver device that consists of an NEO-6M crumb combined on an electric board. It consists of batteries and an LED light. The light is turned on when it sends or receives GPS data to/from satellites. This sensor module also provides a sensitivity of around −161 dBm. Table 5 shows the GY-GPS6MV2 specifications. Figure 8 shows the GPS sensor.

Table 5.
Result comparison of classifiers.
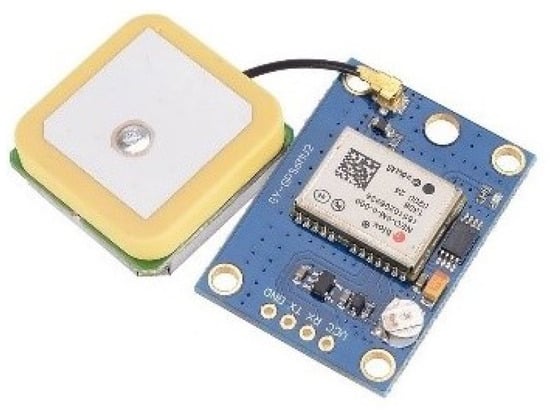

Figure 8.
GY-GPS6MV2.
3.2.4. Pressure Sensor
BMP180 provides altitude and pressure values of a specified location with low battery consumption. It is small in size and provides high accuracy. This module is factory calibrated, which makes it more accurate than other altitude measurement sensors. Table 6 shows the specifications of this altitude measurement sensor. Figure 9 shows the hardware of the pressure sensor.

Table 6.
Performance comparison of proposed model with state-of-the-art models.
Figure 9.
BMP180.
3.2.5. ZigBee Wireless Transmission
ZigBee wireless transmission technology is currently widely used because of its feature and analogy as well as digital data communication capabilities. XBee Pro S1 is used here, which can send and receive data over long distances. Figure 10 shows the hardware of this module.
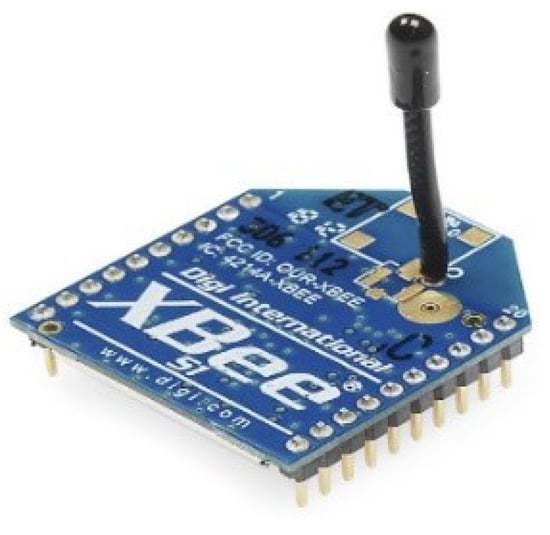

Figure 10.
XBee pro S1.
4. Securing Drones
A smart and intelligent system is needed for the security of drones that can investigate the data of attacks and ensure the security of drones by taking proactive measures. A secure IoD relies on security, reliability, and consistency to develop a trustworthy system. In past, machine learning models have been proposed in the field of cyber-security for wireless sensor-based networks and mobile-based networks but not for drone-based security. A machine learning-based solution is proposed in this study for drone security authentication and control access methods.
Various metrics are used for the evaluation of cyber-security systems. The purpose of using these metrics is that they are better for handling various performance indices in the cyber-security of a system. In this research, we propose the use of the following cyber-security metrics to evaluate the performance of the proposed system [63].
- Drone cyber-security threat exposure;
- Denial of service attacks;
- Malicious attacks;
- Jamming;
- Spoofing.
The machine-learning-based research solution for secure authentication and access control for drones and IoT devices is a key contribution of this research. This work aims to fill the research gap by making drones safe and reliable against major cyber-security issues and making them a useful monitoring tool, both commercially and for the industry. As explained in Section 3, the proposed architecture of the drone security system consists of seven layers. Data from the drone layer and edge processing layer are passed through the security and privacy layer before being forwarded to the device connection layer. At the security and privacy layer, data are protected from security threats by deploying machine learning models, where a mobile alert is sent when an attack is identified. Figure 11 shows the mobile alert of an identified attack.
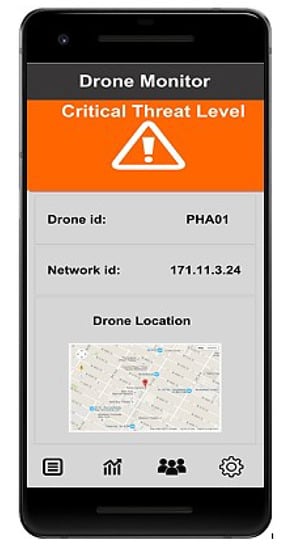
Figure 11.
Result visualization.
4.1. Approach
In the previous section, the architecture and complete design details of the proposed system are explained. In this section, we discuss the implementation of the proposed system along with machine learning.
4.1.1. Dataset
This experiment was performed on real-time data of drones. This drone dataset comprised geo-location-based features (latitude, longitude, and altitude), drone OBD data, and KDD intrusion detection features [64]. The proposed model was trained and tested with the drone dataset as well as with two other benchmark datasets for intrusion detection and cyber security attacks prediction. Table 3 presents the classes of the dataset.
4.1.2. Machine and Deep Learning Models
Machine learning has contributed considerably to improving the results of rating prediction based on reviews. There are many rich variants of machine learning classifiers that exist for performing rating classification. A large number of machine learning classifiers can be found in the Python Scikit-learn library. It is an open-source library with a large user support base. In this study, the Scikit-Learn library was used for all the classifiers, including Random Forest, the Gradient Boosting model, Extra Tree classifier, Naïve Bayes, Logistic Regression, and Stochastic Gradient Classifier.
Random Forest is an ensemble learning classifier that works with the decision trees—also called estimators—for classification. Results of various trees are aggregated by voting to produce improved results [65]. Bootstrap samples are used to train trees using the bagging technique. All trees are built in the same way to test the performance of the model on test data. A higher weight is assigned to the decision tree with a low error rate resulting in smaller chances of an incorrect prediction.
Decision Tree [66] is a commonly used machine learning model for text classification and is based on multiple variables. This algorithm is applied to predict a target variable. It classifies data features into branch-like segments that are used to build an inverted tree including a root node, internal nodes, and leaf nodes. The algorithm is non-parametric and can handle large-sized and complex datasets efficiently without imposing a complicated parametric structure.
Logistic Regression is based on a statistical approach that analyzes the data and works on multiple variables to predict the results [67]. It is a simple yet efficient algorithm with low variance and is mostly used in classification. Features can also be extracted using this model. It is easy to update with new data by using Stochastic Gradient Descent.
Bayes’ theorem is the foundation of the Naïve Bayesian classifier [68], in which independent assumptions are made between predictors. It is very convenient to construct, with simple iterative parameters estimation. Therefore, it is considered very suitable for large datasets. In spite of being simple in nature, it gives extremely good results and performs better than other sophisticated classifiers.
The Support Vector Machine (SVM) is very common in text classification. It draw hyperplanes that separate classes by maximizing the marginal distance. The SVM hyperplane divides the text into two (non-overlapping) classes in the case of binary classification [69]. It is simpler and less complex than deep learning methods and provides simple interpretability [70]. SVM has also been widely used for intrusion detection [71,72].
Multilayer Perceptron (MLP) is a simple deep learning model and has a reasonable classification ability. It is a layered model, where input layer neurons indicate the number of features and hidden layers work on the basis of weights to process input data and feed them to the output layer where neurons represent the output value. To obtain optimal results, numbers of neurons and numbers of hidden layers are selected according to requirements. To improve training efficiency for classification, the model is trained with the appropriate values of hyperparameters. To deal with the weights of MLP layers, backpropagation is generally used, which is based on Gradient Descent.
In hidden layers, the Rectified Linear Unit (ReLU) is used, and the sigmoid is used as an activation function f(x) in the last layer.
In voting classifiers, the results of various classifiers are combined and the final decision is made based on voting. Voting classifiers are generally classified into hard voting and soft voting. The hard voting type considers the results predicted by the majority of the classifiers. On the other hand, the soft voting category computes the percentage weight of each classifier. For every record, the model predicts class probability, multiplies it with the classifier weight, and averages it to determine the final outcome. This study utilizes a voting classifier by combining Logistic Regression and Random Forest, which outperformed other approaches at intrusion detection individually. Algorithm 1 describes the working of the proposed voting classifier, which can be presented as follows:
where and both show the prediction result based on probability against each test sample. After that, the probabilities for each instance by both Logistic Regression and Random Forest pass through the soft voting criteria as shown in Algorithm 1.
| Algorithm 1 Ensembling of Logistic Regression and Random Forest Classifier (LRRF). |
| Input: input data = Trained_ LR = Trained_ RF
|
This is also shown in Figure 12.
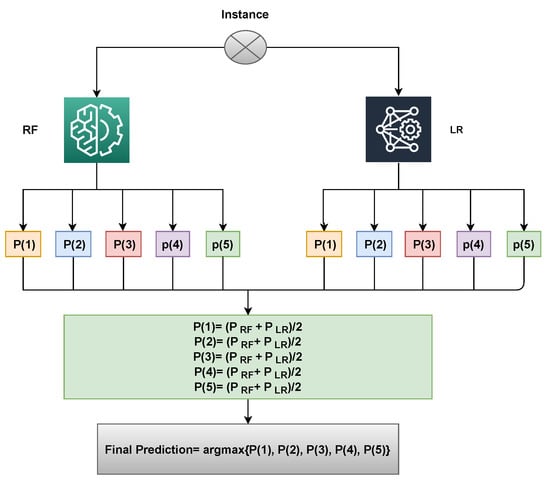
Figure 12.
Proposed voting classifier architecture (LRRF).
5. Experiments and Results
In the previous section, the list of proposed sensors and algorithms is explained and the experimentation is explained in detail. In this section, the results produced by the model as well as the experiment are explained. The results are displayed for the mobile system consisting of the security status of the drones and the IoT network identified using machine learning. This study utilizes four evaluation measures to compare the performance of the models. The confusion matrix help to calculate these measures. The elements of the confusion matrix are the True Positive (TP), True Negative (TN), False Positive (FP), and False Negative (FN). The measures of the performance are given in Table 4.
5.1. Comparison of the Results of the Proposed Model with Baseline Classifiers
In this section, the results obtained from the experiments are discussed. Results of the proposed model are evaluated and compared with the other state-of-the-art machine learning models employed on the drone dataset. The classifiers employed in this study are Random Forest, Decision Tree, Naïve Bayes, Logistic Regression, MLP, and LRRF (voting ensemble of Logistic Regression and Random Forest). All experiments were performed in Python using sklearn, keras and Tensorflow.
Data were classified into three classes: spoofing, jamming and DOS attack. In this task, 99.99% accuracy was obtained, which is the best accuracy score for the cybersecurity controlling process.
A comparative analysis of classifiers was performed on the drone dataset. Table 5 presents the evaluation results of classifiers. The analysis of the results reveals that the machine learning models as well as a simple deep learning model have shown considerable results for intrusion detection on the drone dataset. It can be seen in Table 5 that Naïve Bayes shows the lowest results in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-Score. However, MLP shows a slightly better accuracy at 98.46%. Furthermore, Random Forest, Decision Tree, and SVM achieve a value greater than 99% in terms of all evaluation measures. Our proposed LRRF method achieves robust results with 99.99% values in terms of accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-Score in classifying attacks into DoS, Prob, R2L, and U2R on thedrone dataset.
From Table 5, it can be observed clearly that the voting ensemble of the two best-performing models can accurately classify attacks into four categories—DoS, Prob, R2L, and U2R—with 99.99% accuracy. The graph shows the comparison of the drone dataset performance along with system data. The drone data are given to the machine learning model for the identification of cyber-attacks and to generate alerts.
5.2. Comparison with Other State-of-the-Art Approaches
Table 6 shows the accuracy comparison of the proposed voting classifier with state-of-the-art models from the previous literature. It can be observed that researchers have applied various approaches such as SVM-ANN, PCA + MCA, and DT-RFE to enhance the performance of the models for intrusion detection, and some have employed the latest deep learning approaches such as the Deep Hierarchical model. However, the proposed approach outperformed all approaches with 99.99% accuracy for intrusion detection.
To show the robustness and generalizability of the proposed approach, we have also experimented on KDD Cup 99 [73] and NSL-KDD [74] datasets as shown in Table 6. The proposed LRRF model is superior over all state-of-the-art models from the literature and is suitable for intrusion detection.
6. Conclusions
This paper proposes IoT-aided cyber-security for drone-based networks using a voting ensemble of machine learning algorithms. This framework utilizes IoT-based data from sensors, drones, and network information to achieve security-level patterns and identify the security attacks using these patterns. With this framework, the model can identify attacks in the network data. The proposed framework is tested with the drone dataset and shows robust results in real-time cyber attack identification. The accuracy achieved by the model is 99.99%, which is greater than previous approaches. The accuracy, precision, recall, and F1-score are calculated to estimate the performance. The proposed LRRF model works by identifying attack types accurately and proves its generalizability and robustness. In the future, the proposed framework will be tested on other domains for intrusion detection.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.M.; Funding acquisition, M.N.; Investigation, N.A.A. and R.M.; Methodology, M.U. and M.F.M.; Project administration, M.F.M. and N.A.A.; Supervision, M.N. and N.A.A.; Writing—original draft, R.M. and M.F.M.; Writing—review and editing, M.U. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript
Data Availability Statement
The datasets generated during and/or analyzed during the current study are not publicly available due to a research privacy policy. The dataset is available from the corresponding authors on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
This work is supported by Directorate of Information Technology, The Islamia University of Bahawalpur, Bahawalpur, Pakistan.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funding agency had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript, or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Fujimoto, K. DroneWorks Teams Up with Microsoft to Build a Safety Flight Platform for Industrial Drones by Using Azure IoT Hub. Available online: https://microsoft.github.io/techcasestudies/iot/2017/05/19/DroneWorks.html (accessed on 8 April 2020).
- Hell, P.M.; Varga, P.J. Drone systems for factory security and surveillance. Interdiscip. Descr. Complex Syst. INDECS 2019, 17, 458–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tosato, P.; Facinelli, D.; Prada, M.; Gemma, L.; Rossi, M.; Brunelli, D. An autonomous swarm of drones for industrial gas sensing applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE 20th International Symposium on “A World of Wireless, Mobile and Multimedia Networks” (WoWMoM), Washington, DC, USA, 10–12 June 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Koslowski, R.; Schulzke, M. Drones along borders: Border security UAVs in the United States and the European Union. Int. Stud. Perspect. 2018, 19, 305–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vattapparamban, E.; Güvenç, I.; Yurekli, A.I.; Akkaya, K.; Uluağaç, S. Drones for smart cities: Issues in cybersecurity, privacy, and public safety. In Proceedings of the 2016 international wireless communications and mobile computing conference (IWCMC), Paphos, Cyprus, 5–9 September 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 216–221. [Google Scholar]
- Alsamhi, S.H.; Ma, O.; Ansari, M.S.; Almalki, F.A. Survey on collaborative smart drones and internet of things for improving smartness of smart cities. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 128125–128152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nouacer, R.; Ortiz, H.E.; Ouhammou, Y.; González, R.C. Framework of Key Enabling Technologies for Safe and Autonomous Drones’ Applications. In Proceedings of the 2019 22nd Euromicro Conference on Digital System Design (DSD), Kallithea, Greece, 28–30 August 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 420–427. [Google Scholar]
- Saha, H.N.; Roy, R.; Chakraborty, M.; Sarkar, C. IoT-Enabled Agricultural System Application, Challenges and Security Issues. In Agricultural Informatics: Automation Using the IoT and Machine Learning; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2021; pp. 223–247. [Google Scholar]
- Ferrag, M.A.; Shu, L.; Yang, X.; Derhab, A.; Maglaras, L. Security and privacy for green IoT-based agriculture: Review, blockchain solutions, and challenges. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 32031–32053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, C.; He, D.; Kumar, N.; Choo, K.K.R.; Vinel, A.; Huang, X. Security and privacy for the internet of drones: Challenges and solutions. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2018, 56, 64–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, J. Small States and Armed Drones; Small States and the New Security Environment; University of Iceland: Reykjavik, Iceland, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Chang, V.; Chundury, P.; Chetty, M. Spiders in the sky: User perceptions of drones, privacy, and security. In Proceedings of the 2017 CHI Conference on Human Factors in Computing Systems, Denver, CO, USA, 6–11 May 2017; pp. 6765–6776. [Google Scholar]
- Altawy, R.; Youssef, A.M. Security, privacy, and safety aspects of civilian drones: A survey. ACM Trans. Cyber-Phys. Syst. 2016, 1, 1–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, R.N.; Markantonakis, K.; Mayes, K.; Habachi, O.; Sauveron, D.; Steyven, A.; Chaumette, S. Security, privacy and safety evaluation of dynamic and static fleets of drones. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE/AIAA 36th Digital Avionics Systems Conference (DASC), St. Petersburg, FL, USA, 17–21 September 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–12. [Google Scholar]
- Nayyar, A.; Nguyen, B.L.; Nguyen, N.G. The internet of drone things (IoDT): Future envision of smart drones. In First International Conference on Sustainable Technologies for Computational Intelligence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2020; pp. 563–580. [Google Scholar]
- Yin, Z.; Song, Q.; Han, G.; Zhu, M. Unmanned optical warning system for drones. In Proceedings of the Global Intelligence Industry Conference (GIIC 2018), Beijing, China, 22–24 May 2018; International Society for Optics and Photonics: Bellingham, WA, USA, 2018; Volume 10835, p. 108350Q. [Google Scholar]
- Ozmen, M.O.; Yavuz, A.A. Dronecrypt-an efficient cryptographic framework for small aerial drones. In Proceedings of the MILCOM 2018–2018 IEEE Military Communications Conference (MILCOM), Angeles, CA, USA, 29–31 October 2018; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2018; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Ozmen, M.O.; Behnia, R.; Yavuz, A.A. IoD-crypt: A lightweight cryptographic framework for Internet of drones. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1904.06829. [Google Scholar]
- Bertino, E. Data Security and Privacy in the IoT. In Proceedings of the 19th International Conference on Extending Database Technology (EDBT), Bordeaux, France, 15–18 March 2016; Volume 2016, pp. 1–3. [Google Scholar]
- Rodday, N. Hacking a professional drone. Black Hat Asia 2016, 2016, 1–2. [Google Scholar]
- Highnam, K.; Angstadt, K.; Leach, K.; Weimer, W.; Paulos, A.; Hurley, P. An uncrewed aerial vehicle attack scenario and trustworthy repair architecture. In Proceedings of the 2016 46th Annual IEEE/IFIP International Conference on Dependable Systems and Networks Workshop (DSN-W), Toulouse, France, 28 June–1 July 2016; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2016; pp. 222–225. [Google Scholar]
- Shoufan, A. Continuous authentication of uav flight command data using behaviometrics. In Proceedings of the 2017 IFIP/IEEE International Conference on Very Large Scale Integration (VLSI-SoC), Abu Dhabi, United Arab Emirates, 23–25 October 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, A. Drones Hijacking; Tech. Report; DEF CON: Paris, France, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Kerns, A.J.; Shepard, D.P.; Bhatti, J.A.; Humphreys, T.E. Unmanned aircraft capture and control via GPS spoofing. J. Field Robot. 2014, 31, 617–636. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, Z.; Guan, N.; Lv, M.; Liu, W.; Deng, Q.; Liu, X.; Yi, W. Efficient drone hijacking detection using onboard motion sensors. In Proceedings of the Design, Automation & Test in Europe Conference & Exhibition (DATE), Lausanne, Switzerland, 27–31 March 2017; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 1414–1419. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Guan, N.; Lv, M.; Liu, W.; Deng, Q.; Liu, X.; Yi, W. An efficient uav hijacking detection method using onboard inertial measurement unit. ACM Trans. Embed. Comput. Syst. (TECS) 2018, 17, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Son, Y.; Shin, H.; Kim, D.; Park, Y.; Noh, J.; Choi, K.; Choi, J.; Kim, Y. Rocking drones with intentional sound noise on gyroscopic sensors. In Proceedings of the 24th fUSENIXg Security Symposium (fUSENIXg Security 15), Washington, DC, USA, 12–14 August 2015; pp. 881–896. [Google Scholar]
- Choi, H.; Lee, W.C.; Aafer, Y.; Fei, F.; Tu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Xu, D.; Deng, X. Detecting attacks against robotic vehicles: A control invariant approach. In Proceedings of the 2018 ACM SIGSAC Conference on Computer and Communications Security, Toronto, ON, Canada, 15–19 October 2018; pp. 801–816. [Google Scholar]
- Gallacher, D. Drones to manage the urban environment: Risks, rewards, alternatives. J. Unmanned Veh. Syst. 2016, 4, 115–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lv, Z. The security of Internet of drones. Comput. Commun. 2019, 148, 208–214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, G.; Sharma, V.; Gupta, T.; Kim, J.; You, I. Internet of Drones (IoD): Threats, vulnerability, and security perspectives. arXiv 2018, arXiv:1808.00203. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, J.; Cao, Z.; Dong, X.; Vasilakos, A.V. Security and privacy for cloud-based IoT: Challenges. IEEE Commun. Mag. 2017, 55, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nassi, B.; Shabtai, A.; Masuoka, R.; Elovici, Y. SoK-security and privacy in the age of drones: Threats, challenges, solution mechanisms, and scientific gaps. arXiv 2019, arXiv:1903.05155. [Google Scholar]
- Giraldo, J.; Sarkar, E.; Cardenas, A.A.; Maniatakos, M.; Kantarcioglu, M. Security and privacy in cyber-physical systems: A survey of surveys. IEEE Des. Test 2017, 34, 7–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lagkas, T.; Argyriou, V.; Bibi, S.; Sarigiannidis, P. UAV IoT framework views and challenges: Towards protecting drones as “Things”. Sensors 2018, 18, 4015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tian, Y.; Yuan, J.; Song, H. Efficient privacy-preserving authentication framework for edge-assisted Internet of Drones. J. Inf. Secur. Appl. 2019, 48, 102354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yaacoub, J.P.; Noura, H.; Salman, O.; Chehab, A. Security analysis of drones systems: Attacks, limitations, and recommendations. Internet Things 2020, 11, 100218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Albalawi, M.; Song, H. Data security and privacy issues in swarms of drones. In Proceedings of the 2019 Integrated Communications, Navigation and Surveillance Conference (ICNS), New York, NY, USA, 9–11 April 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2019; pp. 1–11. [Google Scholar]
- Bera, B.; Saha, S.; Das, A.K.; Kumar, N.; Lorenz, P.; Alazab, M. Blockchain-envisioned secure data delivery and collection scheme for 5g-based iot-enabled internet of drones environment. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2020, 69, 9097–9111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; He, D.; Li, L.; Chen, B. A lightweight authentication and key agreement scheme for internet of drones. Comput. Commun. 2020, 154, 455–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chriki, A.; Touati, H.; Snoussi, H.; Kamoun, F. FANET: Communication, mobility models and security issues. Comput. Netw. 2019, 163, 106877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mehta, P.; Gupta, R.; Tanwar, S. Blockchain envisioned UAV networks: Challenges, solutions, and comparisons. Comput. Commun. 2020, 151, 518–538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiao, L.; Xie, C.; Chen, T.; Dai, H.; Poor, H.V. A mobile offloading game against smart attacks. IEEE Access 2016, 4, 2281–2291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kulkarni, R.V.; Venayagamoorthy, G.K. Neural network based secure media access control protocol for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the 2009 International Joint Conference on Neural Networks, Atlanta, GA, USA, 14–19 June 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1680–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Alsheikh, M.A.; Lin, S.; Niyato, D.; Tan, H.P. Machine learning in wireless sensor networks: Algorithms, strategies, and applications. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2014, 16, 1996–2018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Vedula, V.; Lama, P.; Boppana, R.V.; Trejo, L.A. On the Detection of Low-Rate Denial of Service Attacks at Transport and Application Layers. Electronics 2021, 10, 2105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinzadeh, M.; Sinopoli, B. Active Attack Detection and Control in Constrained Cyber-Physical Systems Under Prevented Actuation Attack. arXiv 2021, arXiv:2101.09885. [Google Scholar]
- Han, G.; Xiao, L.; Poor, H.V. Two-dimensional anti-jamming communication based on deep reinforcement learning. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Conference on Acoustics, Speech and Signal Processing (ICASSP), New Orleans, LA, USA, 5–9 March 2019; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2017; pp. 2087–2091. [Google Scholar]
- Tan, Z.; Jamdagni, A.; He, X.; Nanda, P.; Liu, R.P. A system for denial-of-service attack detection based on multivariate correlation analysis. IEEE Trans. Parallel Distrib. Syst. 2013, 25, 447–456. [Google Scholar]
- Li, Y.; Quevedo, D.E.; Dey, S.; Shi, L. SINR-based DoS attack on remote state estimation: A game-theoretic approach. IEEE Trans. Control. Netw. Syst. 2016, 4, 632–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Xiao, L.; Li, Y.; Huang, X.; Du, X. Cloud-based malware detection game for mobile devices with offloading. IEEE Trans. Mob. Comput. 2017, 16, 2742–2750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narudin, F.A.; Feizollah, A.; Anuar, N.B.; Gani, A. Evaluation of machine learning classifiers for mobile malware detection. Soft Comput. 2016, 20, 343–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buczak, A.L.; Guven, E. A survey of data mining and machine learning methods for cyber security intrusion detection. IEEE Commun. Surv. Tutor. 2015, 18, 1153–1176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Branch, J.W.; Giannella, C.; Szymanski, B.; Wolff, R.; Kargupta, H. In-network outlier detection in wireless sensor networks. Knowl. Inf. Syst. 2013, 34, 23–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Ozay, M.; Esnaola, I.; Vural, F.T.Y.; Kulkarni, S.R.; Poor, H.V. Machine learning methods for attack detection in the smart grid. IEEE Trans. Neural Netw. Learn. Syst. 2015, 27, 1773–1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Shi, C.; Liu, J.; Liu, H.; Chen, Y. Smart user authentication through actuation of daily activities leveraging WiFi-enabled IoT. In Proceedings of the 18th ACM International Symposium on Mobile Ad Hoc Networking and Computing, Chennai, India, 10–14 July 2017; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xiao, L.; Li, Y.; Han, G.; Liu, G.; Zhuang, W. PHY-layer spoofing detection with reinforcement learning in wireless networks. IEEE Trans. Veh. Technol. 2016, 65, 10037–10047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, B.; Ma, Y.; Huang, X.; Lin, Z.; Sun, Y. A novel real-time ddos attack detection mechanism based on MDRA algorithm in big data. Math. Probl. Eng. 2016, 2016, 1467051. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Andresini, G.; Appice, A.; Di Mauro, N.; Loglisci, C.; Malerba, D. Multi-channel deep feature learning for intrusion detection. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 53346–53359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lian, W.; Nie, G.; Jia, B.; Shi, D.; Fan, Q.; Liang, Y. An Intrusion Detection Method Based on Decision Tree-Recursive Feature Elimination in Ensemble Learning. Math. Probl. Eng. 2020, 2020, 2835023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, J.; Lalmuanawma, S.; Chhakchhuak, L. A two-stage hybrid classification technique for network intrusion detection system. Int. J. Comput. Intell. Syst. 2016, 9, 863–875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Jiang, K.; Wang, W.; Wang, A.; Wu, H. Network intrusion detection combined hybrid sampling with deep hierarchical network. IEEE Access 2020, 8, 32464–32476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radanliev, P.; De Roure, D.C.; Nicolescu, R.; Huth, M.; Montalvo, R.M.; Cannady, S.; Burnap, P. Future developments in cyber risk assessment for the internet of things. Comput. Ind. 2018, 102, 14–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MUmerSabir. Mumersabir/MDPIELECTRONICS: MDPI Electronics Revision Dataset.
- Svetnik, V.; Liaw, A.; Tong, C.; Culberson, J.C.; Sheridan, R.P.; Feuston, B.P. Random forest: A classification and regression tool for compound classification and QSAR modeling. J. Chem. Inf. Comput. Sci. 2003, 43, 1947–1958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, Y.Y.; Ying, L. Decision tree methods: Applications for classification and prediction. Shanghai Arch. Psychiatry 2015, 27, 130. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Korkmaz, M.; Güney, S.; YİĞİTER, Ş. The importance of logistic regression implementations in the Turkish livestock sector and logistic regression implementations/fields. Harran Tarım ve Gıda Bilimleri Dergisi 2012, 16, 25–36. [Google Scholar]
- Leung, K.M. Naive bayesian classifier. Polytech. Univ. Dep. Comput. Sci. Risk Eng. 2007, 2007, 123–156. [Google Scholar]
- Ribeiro, A.A.; Sachine, M. On the optimal separating hyperplane for arbitrary sets: A generalization of the SVM formulation and a convex hull approach. Optimization 2020, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, B.; Shirani, A.; Lo, D.; Alipour, M.A. Prediction of relatedness in stack overflow: Deep learning vs. SVM: A reproducibility study. In Proceedings of the 12th ACM/IEEE International Symposium on Empirical Software Engineering and Measurement, Oulu, Finland, 11–12 October 2018; pp. 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, H.; Gu, J.; Wang, S. An effective intrusion detection framework based on SVM with feature augmentation. Knowl.-Based Syst. 2017, 136, 130–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, P.; Sun, Z.; Sun, Z. An improved intrusion detection algorithm based on GA and SVM. IEEE Access 2018, 6, 13624–13631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siddique, K.; Akhtar, Z.; Khan, F.A.; Kim, Y. KDD cup 99 data sets: A perspective on the role of data sets in network intrusion detection research. Computer 2019, 52, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavallaee, M.; Bagheri, E.; Lu, W.; Ghorbani, A.A. A detailed analysis of the KDD CUP 99 data set. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE Symposium on Computational Intelligence for Security and Defense Applications, Ottawa, ON, Canada, 8–10 July 2009; IEEE: Piscataway, NJ, USA, 2009; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).