Numerical Analysis on the Effects of Saline Injection and Deformation for Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
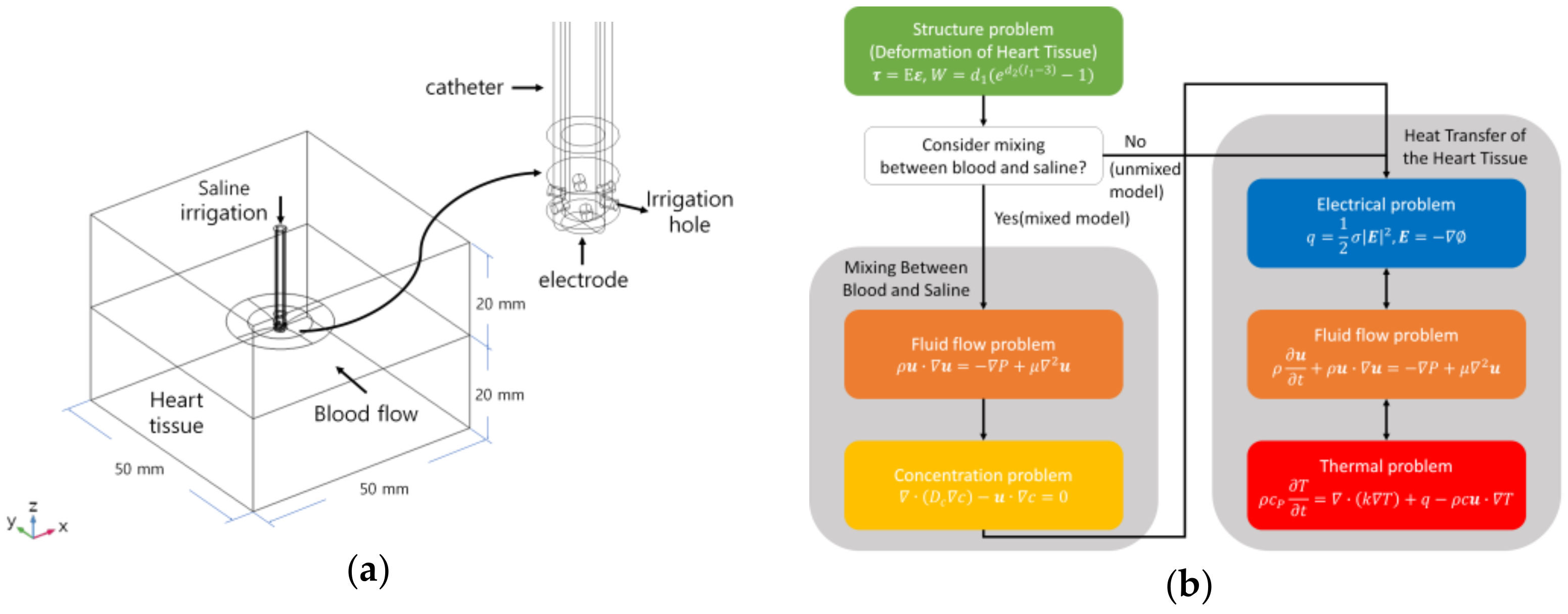
2.1. Model Geometry
2.2. Governing Equation
2.2.1. Deformation of Heart Tissue
2.2.2. Mixing Between Blood and Saline
2.2.3. Heat Transfer of the Heart Tissue
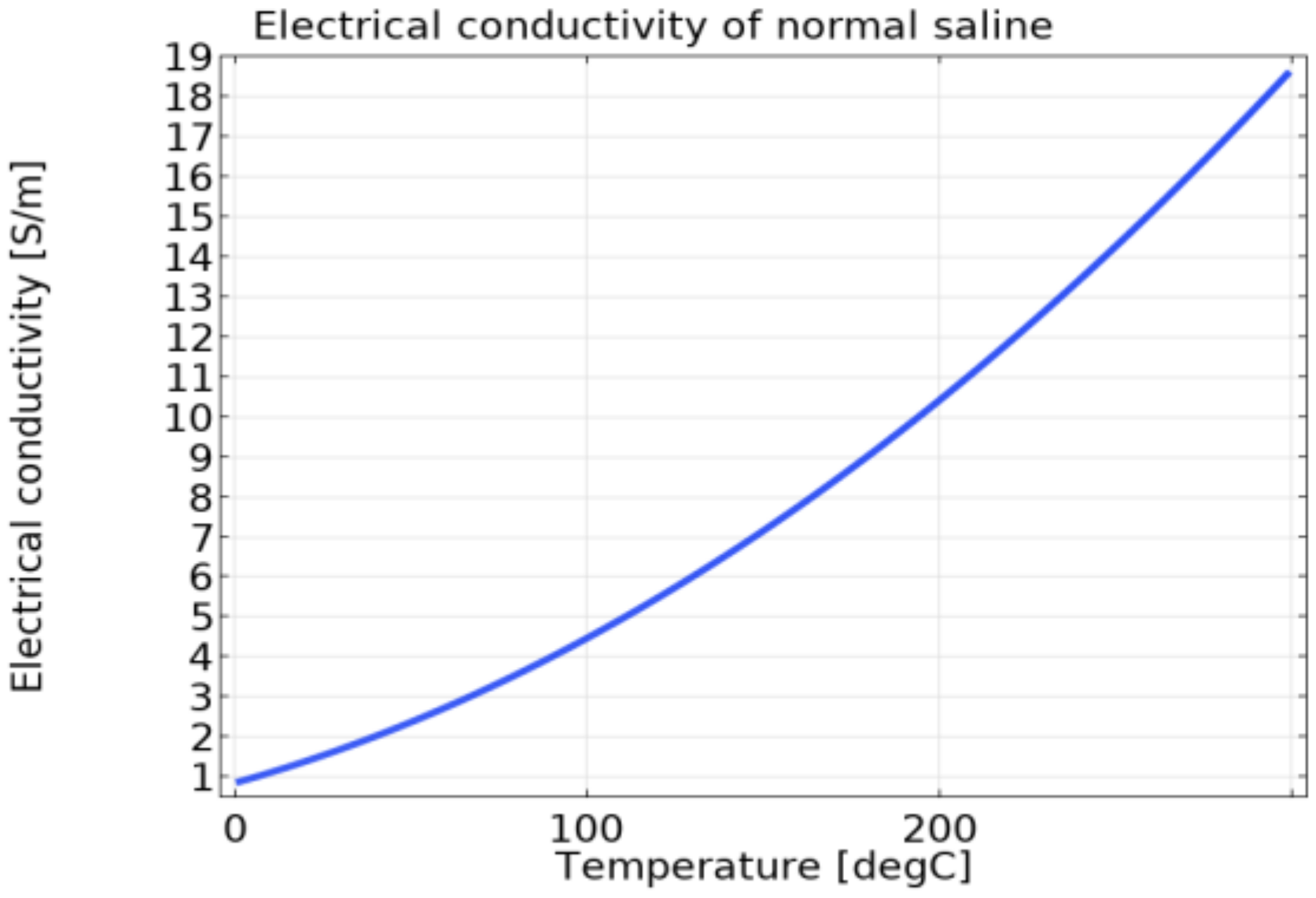
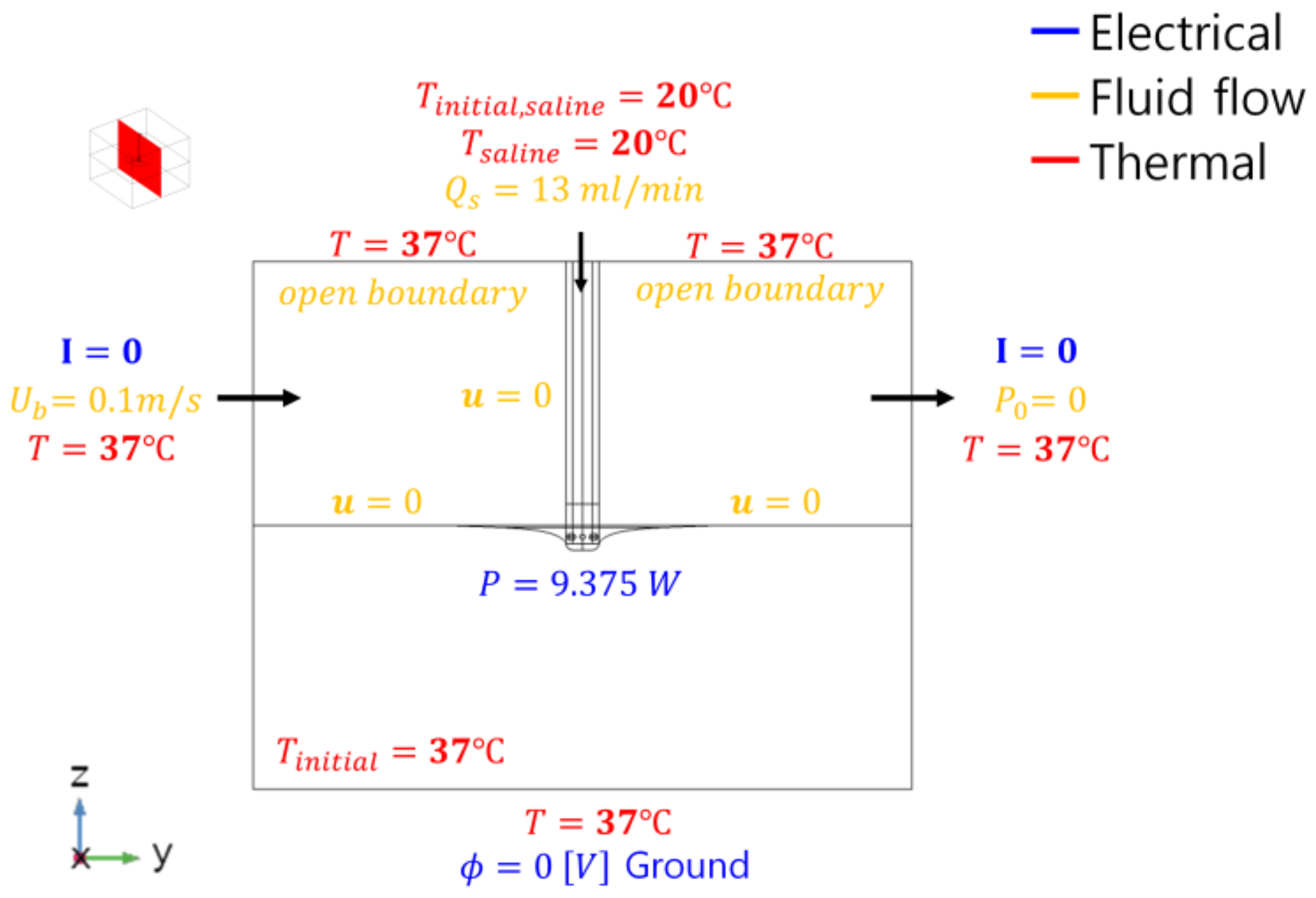
2.3. Material Property and Boundary Conditions
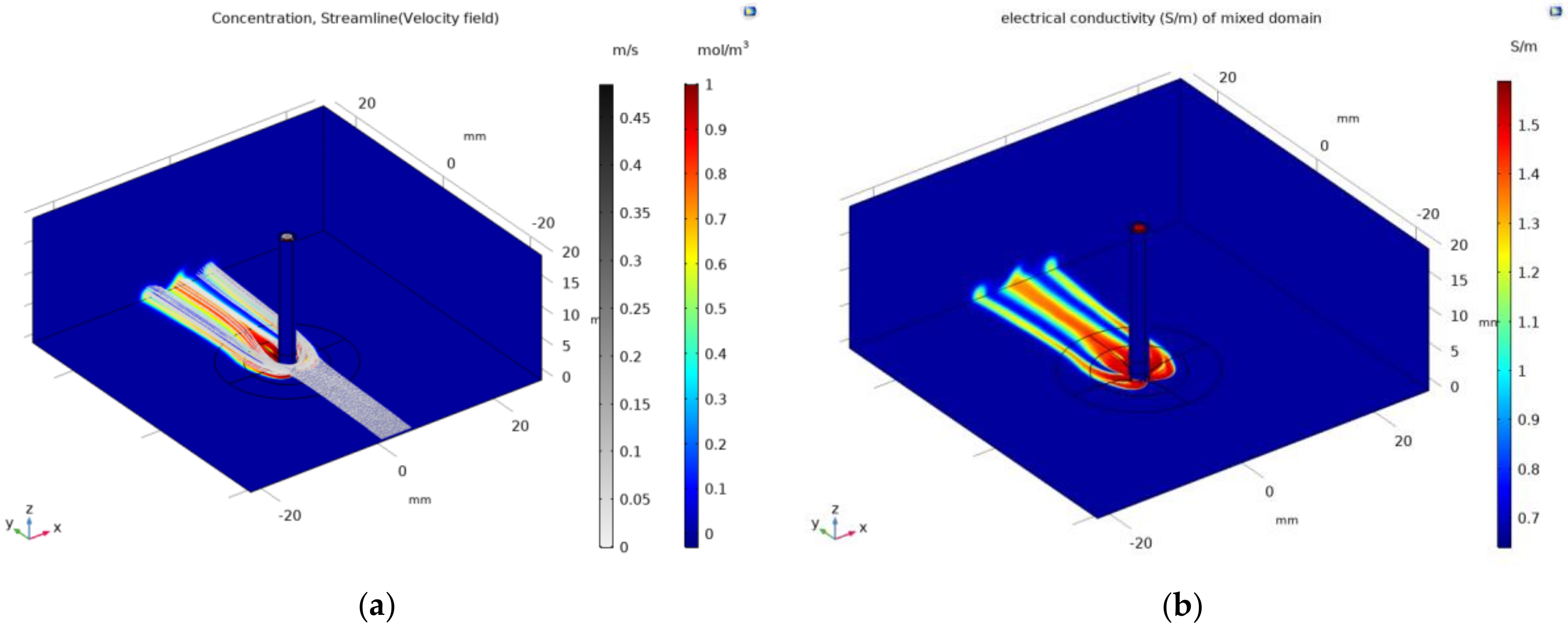
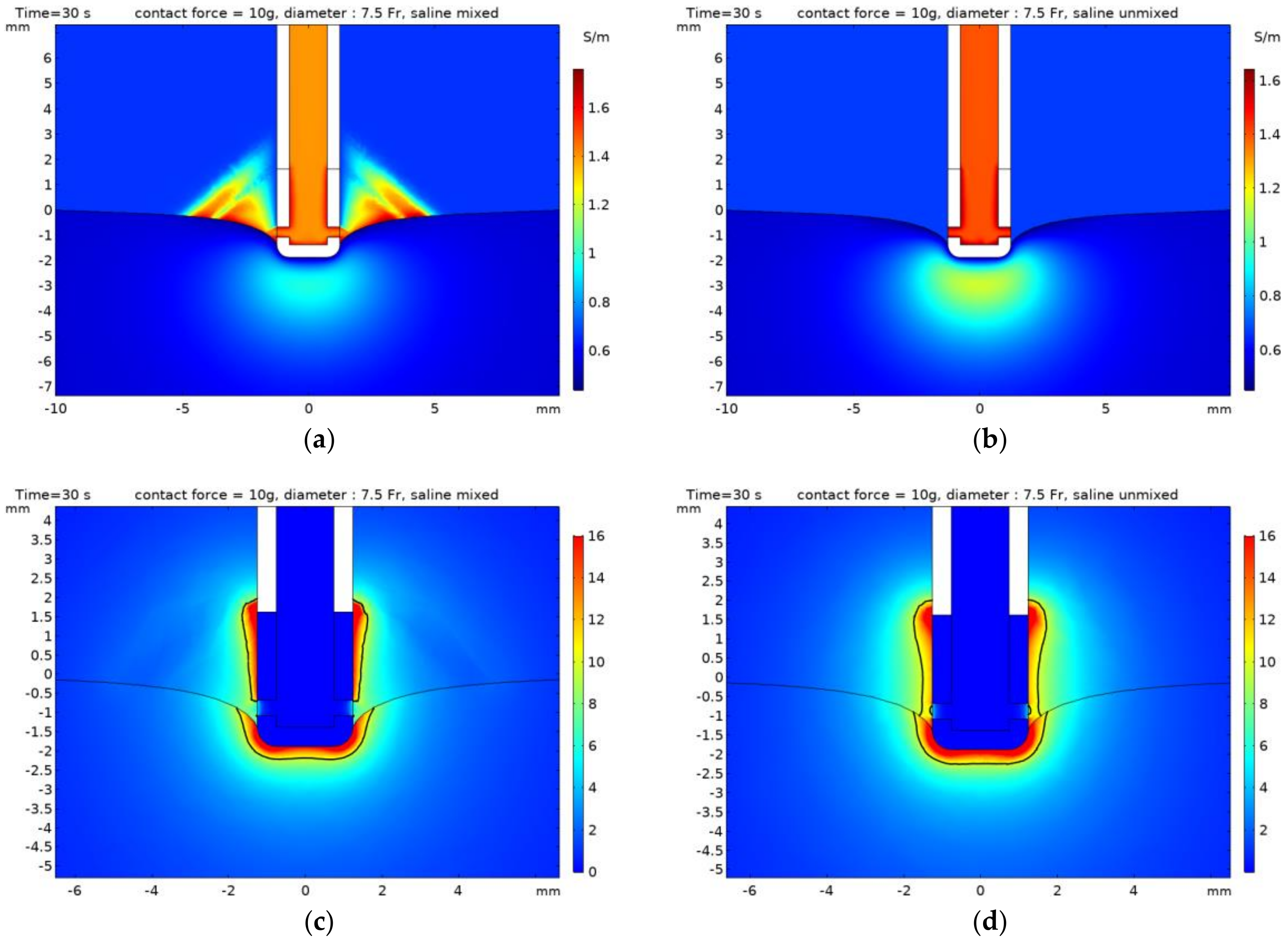
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- McRury, I.D.; Haines, D.E. Ablation for the treatment of arrhythmias. Proc. IEEE 1996, 84, 404–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, D.E. The biophysics of radiofrequency catheter ablation in the heart: The importance of temperature monitoring. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1993, 16, 586–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jain, M.K.; Wolf, P.D. Temperature-controlled and constant-power radio-frequency ablation: What affects lesion growth? IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 1999, 46, 1405–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guerra, J.M.; Jorge, E.; Raga, S.; Galvez-Monton, C.; Alonso-Martin, C.; Rodriguez-Font, E.; Cinca, J.; Vinolas, X. Effects of open-irrigated radiofrequency ablation catheter design on lesion formation and complications: In vitro comparison of 6 different devices. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2004, 24, 1157–1162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, M.A.; Goldberg, S.M.; Parvez, B.; Pathak, V.; Holland, K.; Ellenbogen, A.L.; Han, F.T.; Alexander, D.; Lau, M.; Reshko, L.; et al. Effect of electrode orientation on lesion sizes produced by irrigated radiofrequency ablation catheters. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2009, 20, 1262–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everett, T.H., IV; Lee, K.W.; Wilson, E.E.; Guerra, J.M.; Varosy, P.D.; Olgin, J.E. Safety profiles and lesion size of different radiofrequency ablation technologies: A comparison of large tip, open and closed irrigation catheters. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2009, 20, 325–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demazumder, D.; Mirotznik, M.S.; Schwartzman, D. Biophysics of radiofrequency ablation using an irrigated electrode. J. Interv. Card. Electrophysiol. 2001, 5, 377–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yokoyama, K.; Nakagawa, H.; Wittkampf, F.H.; Pitha, J.V.; Lazzara, R.; Jackman, W.M. Comparison of electrode cooling between internal and open irrigation in radiofrequency ablation lesion depth and incidence of thrombus and steam pop. Circulation 2006, 113, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weiss, C.; Antz, M.; Eick, O.; Eshagzaiy, K.; Meinertz, T.; Willems, S. Radiofrequency catheter ablation using cooled electrodes: Impact of irrigation flow rate and catheter contact pressure on lesion dimensions. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 2002, 25, 463–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Suárez, A.; Berjano, E.; Guerra, J.M.; Gerardo-Giorda, L. Computational modelling of open-irrigated electrodes for radiofrequency cardiac ablation including blood motion-saline flow interaction. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0150356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Pérez, J.J.; D’avila, A.; Aryana, A.; Berjano, E. Electrical and thermal effects of esophageal temperature probes on radiofrequency catheter ablation of atrial fibrillation: Results from a computational modelling study. J. Cardiovasc. Electrophysiol. 2015, 26, 556–564. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jain, M.K.; Wolf, P.D. A three-dimensional finite element model of radiofrequency ablation with blood flow and its experimental validation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2000, 28, 1075–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gopalakrishnan, J. A mathematical model for irrigated epicardial radiofrequency ablation. Ann. Biomed. Eng. 2002, 30, 884–893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gallagher, N.; Fear, E.C.; Byrd, I.A.; Vigmond, E.J. Contact geometry affects lesion formation in radio-frequency cardiac catheter ablation. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e73242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Tungjitkusolmun, S.; Woo, E.J.; Cao, H.; Tsai, J.Z.; Vorperian, V.R.; Webster, J.G. Thermal—electrical finite element modelling for radio frequency cardiac ablation: Effects of changes in myocardial properties. Medic. Biol. Eng. Comput. 2000, 38, 562–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González-Suarez, A.; Berjano, E. Comparative analysis of different methods of modelling the thermal effect of circulating blood flow during RF cardiac ablation. IEEE Trans. Biomed. Eng. 2016, 63, 250–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Yan, S.; Gu, K.; Wu, X.; Wang, W. Computer simulation study on the effect of electrode–tissue contact force on thermal lesion size in cardiac radiofrequency ablation. Int. J. Hyperth. 2020, 37, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petras, A.; Leoni, M.; Guerra, J.M.; Jansson, J.; Gerardo-Giorda, L. A computational model of open-irrigated radiofrequency catheter ablation accounting for mechanical properties of the cardiac tissue. Int J. Numer. Methods Biomed. Eng. 2019, 35, e3232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Gonzalez-Suarez, A.; Perez, J.J.; Enrique, B. Should fluid dynamics be included in computer models of RF cardiac ablation by irrigated-tip electrodes? Biomed. Eng. Online 2018, 17, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Humphrey, J.D.; Halperin, H.R.; Yin, F.C.P. Small indentation superimposed on a finite equibiaxial stretch. Implications for cardiac mechanics. J. Appl. Phys. Trans. ASME 1991, 58, 1108–1111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zisis, T.; Zafiropoulou, V.I.; Giannakopoulos, A.E. Evaluation of material properties of incompressible hyperelastic materials based on instrumented indentation of an equal-biaxial prestretched substrate. Int. J. Solids Struct. 2015, 64, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, H.W.; Jansen, B.; Birrer, D.; Kassab, G.S. Effect of saline injection mixing on accuracy of conductance lumen sizing of peripheral vessels. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e74622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, H.W.; Farren, N.D.; Zhang, Z.D.; Huo, Y.; Kassab, G.S. Conductance catheter measurements of lumen area of stenotic coronary arteries: Theory and experiment. J. Appl. Physiol. 2011, 111, 758–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pennes, H.H. Analysis of tissue and arterial blood temperatures in the resting human forearm. J. Appl. Physiol. 1948, 1, 93–122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Obradović, M.; Avilla, A.; Thiagalingam, A.; Filipović, N. Finite element modeling of the endocardial radiofrequency ablation, J. Serb. Soc. Comput. Mech. 2010, 4, 43–53. [Google Scholar]
- Haines, D.E.; Watson, D.D. Tissue heating during radiofrequency catheter ablation: A thermodynamic model and observations in isolated perfused and superfused canine right ventricular free wall. Pacing Clin. Electrophysiol. 1989, 12, 962–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doss, J.D. Calculation of electric fields in conductive media. Med. Phys. 1982, 9, 566–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plonsey, R.; Heppner, D.B. Considerations of quasi-stationarity in electrophysiological systems. Bull. Math. Biol. 1967, 29, 657–664. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stogryn, A. Equations for calculating the dielectric constant of saline water (correspondence). IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Techn. 1971, 19, 733–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berjano, E.; d’Avila, A. Lumped element electrical model based on three resistors for electrical impedance in radiofrequency cardiac ablation: Estimations from analytical calculations and clinical data. Open Biomed. Eng. J. 2013, 7, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nakagawa, H.; Wittkampf, F.H.M.; Yamanashi, W.S.; Pitha, J.V.; Imai, S.; Campbell, B.; Arruda, M.; Lazzara, R.; Jackman, W.M. Inverse relationship between electrode size and lesion size during radiofrequency ablation with active electrode cooling. Circulation 1998, 98, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]





| Properties of the Model Elements | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model element | σ [S/m] | k [W/m/K] | cp [J/kg/K] | ρ [kg/m3] |
| Electrode | 4.6 × 106 | 71 | 132 | 21500 |
| Heart tissue | σ0: 0.54 | k0: 0.531 | 3111 | 1060 |
| PU (catheter) | N/A | 0.026 | 1045 | 70 |
| Blood | 0.667 | 0.54 | 4180 | 1000 |
| Saline | 0.59 | 4186 | 1000 | |
| Displacement of Catheter (mm) | ||
|---|---|---|
| Diameter of Catheter (Fr) | Contact Force = 10 g | Contact Force = 20 g |
| 7 | 1.9402 | 3.0352 |
| 7.5 | 1.8762 | 2.9634 |
| 8 | 1.8145 | 2.8932 |
| Time, CF | Model Mixed Saline | Model Unmixed | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 7 Fr | 7.5 Fr | 8 Fr | 7 Fr | 7.5 Fr | 8 Fr | ||
| D (Depth, mm) | 30 s, 10 g | 5.36 | 5.29 | 5.27 | 5.93 | 5.84 | 5.77 |
| 60 s, 10 g | 6.99 | 6.91 | 6.84 | 7.63 | 7.50 | 7.47 | |
| 30 s, 20 g | 6.34 | 6.16 | 6.09 | 6.76 | 6.63 | 6.55 | |
| 60 s, 20 g | 8.06 | 7.96 | 7.80 | 8.56 | 8.45 | 8.36 | |
| MW (Maximum width, mm) | 30 s, 10 g | 8.29 | 8.20 | 8.15 | 9.05 | 8.98 | 8.97 |
| 60 s, 10 g | 10.09 | 10.07 | 10.04 | 10.95 | 10.86 | 10.78 | |
| 30 s, 20 g | 9.31 | 9.27 | 9.22 | 9.99 | 9.94 | 9.92 | |
| 60 s, 20 g | 11.33 | 11.25 | 11.17 | 12.11 | 12.06 | 12.00 | |
| DW (Depth at maximum width, mm) | 30 s, 10 g | 2.23 | 2.13 | 2.05 | 2.32 | 2.28 | 2.23 |
| 60 s, 10 g | 3.03 | 2.85 | 2.78 | 3.21 | 3.11 | 3.09 | |
| 30 s, 20 g | 2.72 | 2.57 | 2.54 | 2.74 | 2.69 | 2.63 | |
| 60 s, 20 g | 3.47 | 3.32 | 3.26 | 3.53 | 3.48 | 3.37 | |
| Maximum temperature (°C) | 30 s, 10 g | 78.31 | 76.07 | 75.67 | 90.63 | 86.75 | 83.36 |
| 60 s, 10 g | 84.72 | 82.47 | 82.11 | 98.35 | 94.18 | 91.06 | |
| 30 s, 20 g | 82.63 | 79.72 | 76.80 | 91.78 | 88.18 | 84.80 | |
| 60 s, 20 g | 90.20 | 87.13 | 83.83 | 99.90 | 96.62 | 93.10 | |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ahn, J.W.; Kim, Y.-J. Numerical Analysis on the Effects of Saline Injection and Deformation for Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation. Electronics 2021, 10, 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10141674
Ahn JW, Kim Y-J. Numerical Analysis on the Effects of Saline Injection and Deformation for Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation. Electronics. 2021; 10(14):1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10141674
Chicago/Turabian StyleAhn, Jin Woo, and Young-Jin Kim. 2021. "Numerical Analysis on the Effects of Saline Injection and Deformation for Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation" Electronics 10, no. 14: 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10141674
APA StyleAhn, J. W., & Kim, Y.-J. (2021). Numerical Analysis on the Effects of Saline Injection and Deformation for Radiofrequency Catheter Ablation. Electronics, 10(14), 1674. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10141674






