Forecasting of Tomato Yields Using Attention-Based LSTM Network and ARMA Model
Abstract
:1. Introduction
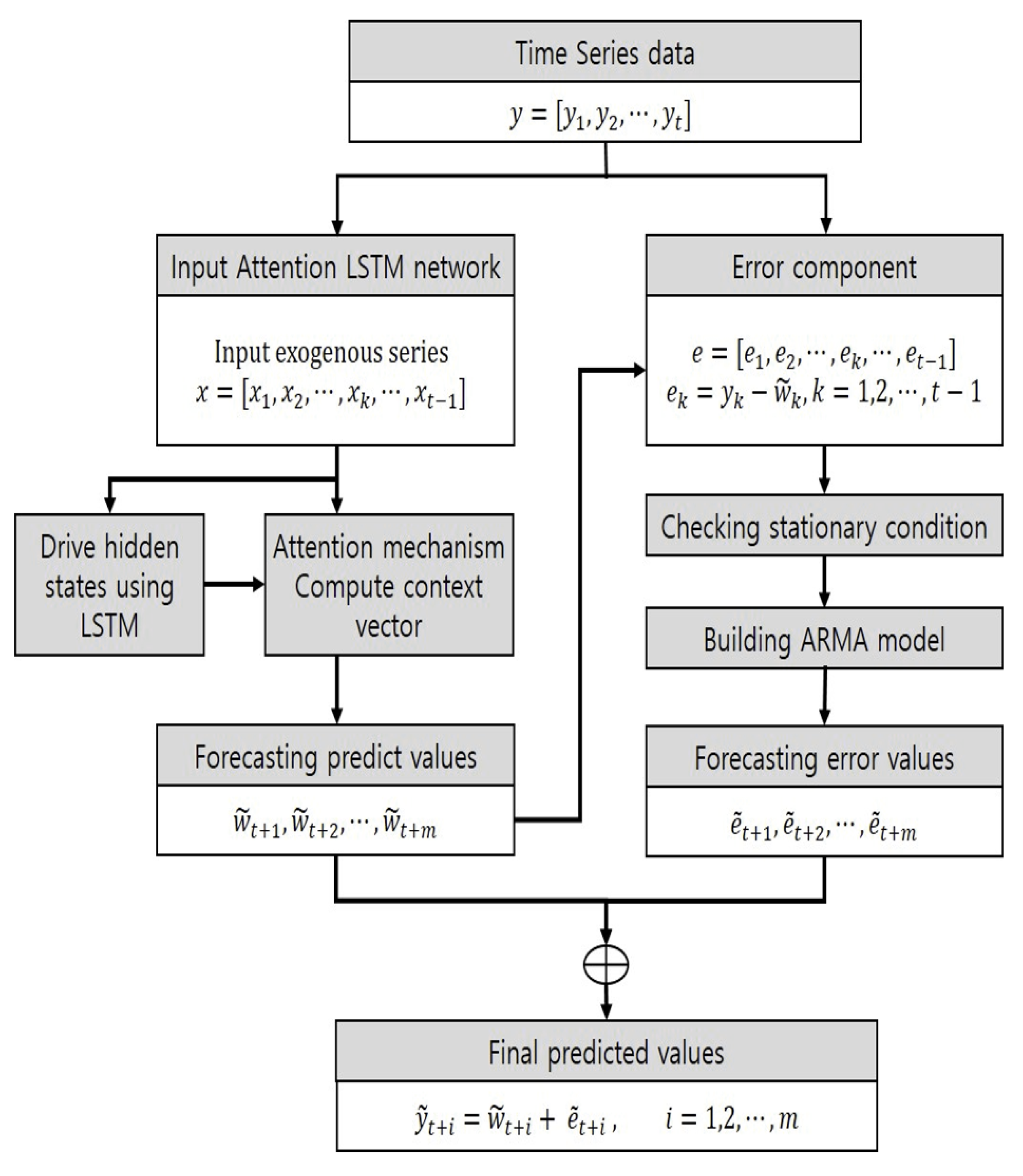
2. Forecasting System using Attention-Based LSTM Network and ARMA Model
2.1. Attention-Based LSTM Network
2.2. Autoregressive Moving Average (ARMA)
2.3. Hybrid Forecasting System using Attention-Based LSTM Network and ARMA Model
- Step 1:
- We train an attention-based LMTM network using learning data including several exogenous factors and yields collected.
- Step 2:
- We use the validation data as input to the learned attention-based LSTM to generate predicted values for yields.,
- Step 3:
- We use the actual time series dataof the yields and the predicted time series datapredicted by the model to create the residual time series data as follows..
- Step 4:
- We construct an ARMA model for the generated error time series data and generate a predicted value of the error for the future point in time.
- Step 5:
- We add the predicted time series value () by the attention-based LSTM model in step 2 and the error value () predicted by the ARMA model in step 4 to get the time series predicted value at time t + 1 as follows..
3. Experimental Results
3.1. Datasets
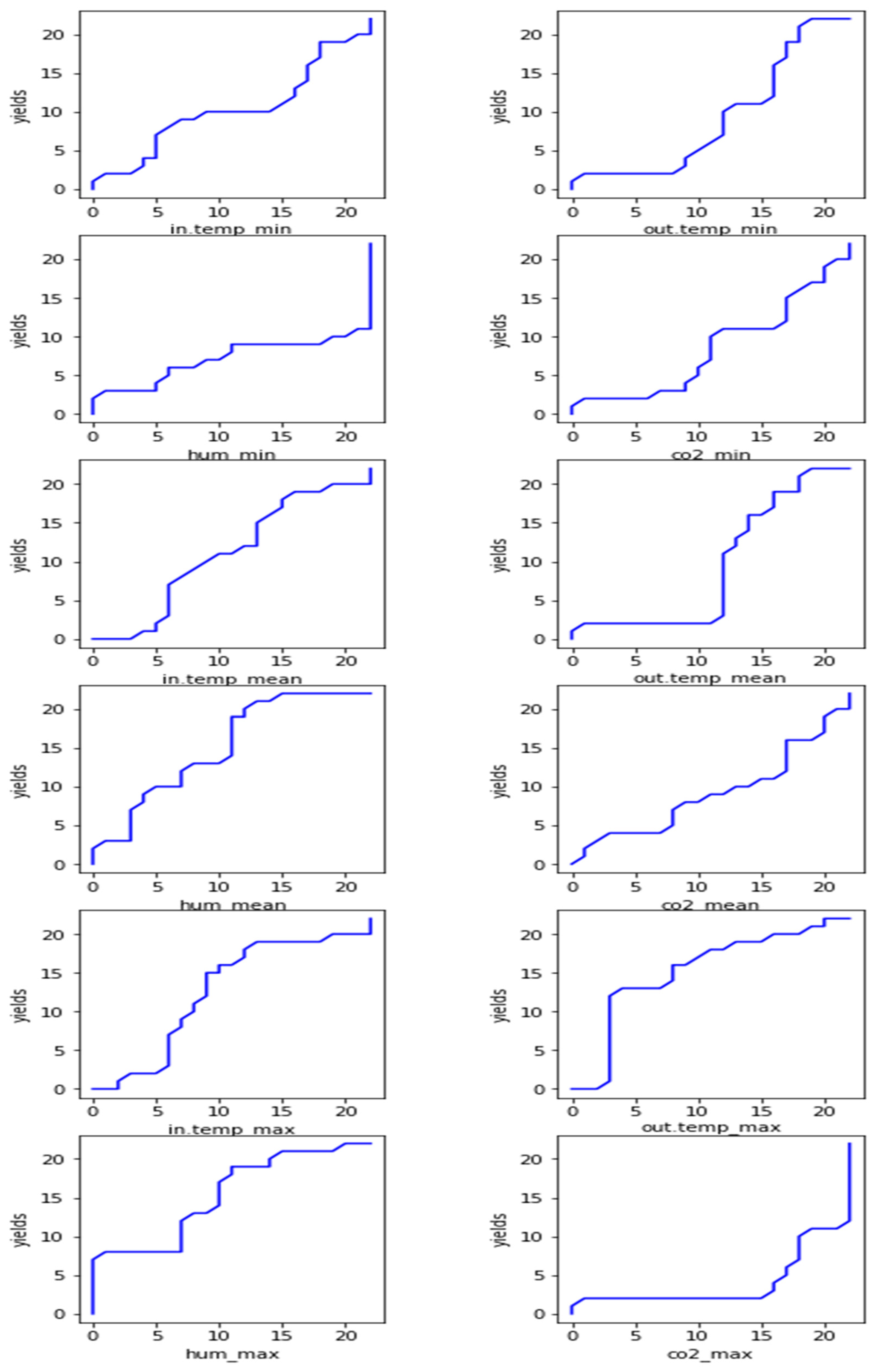
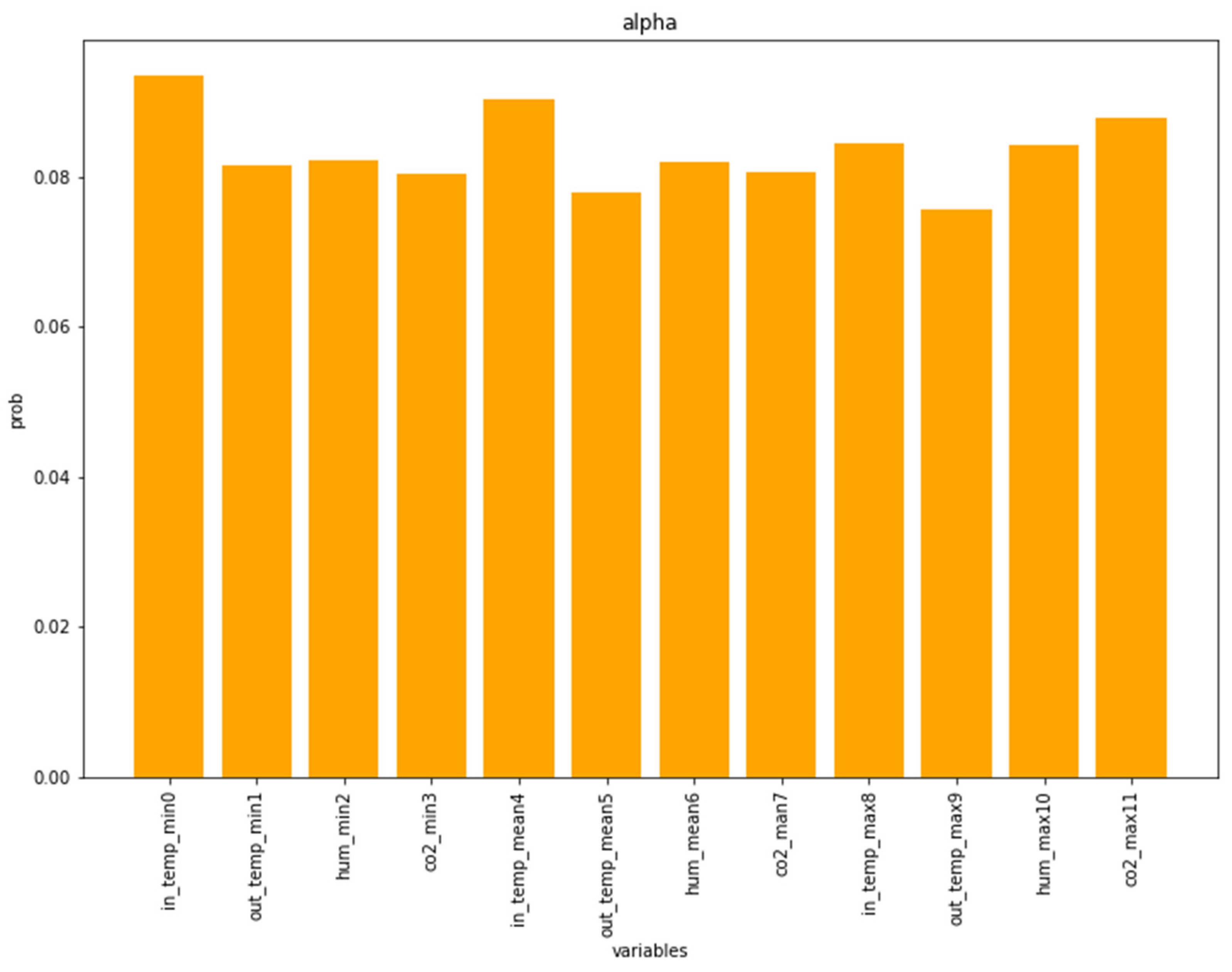
3.2. Association Analysis
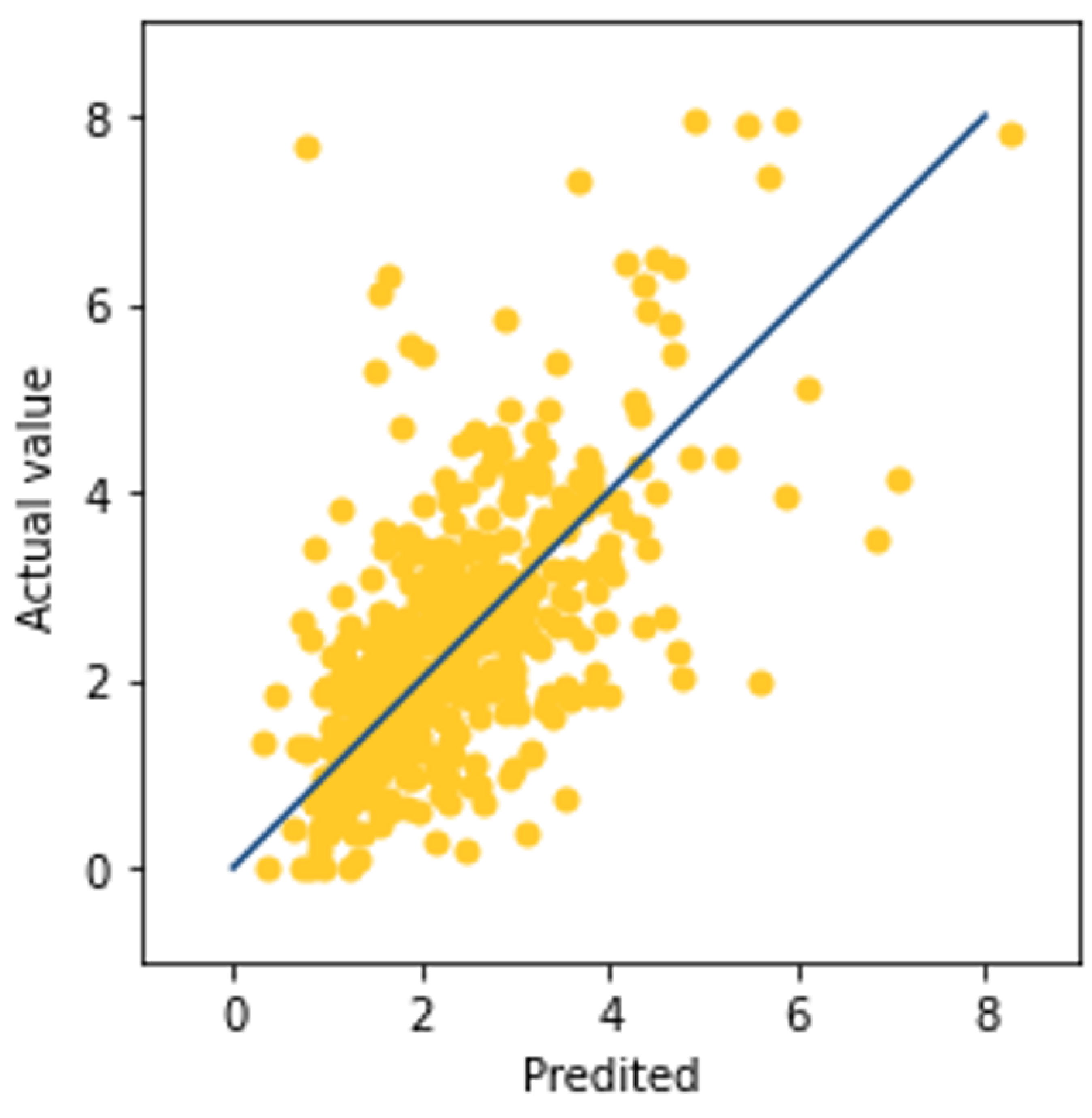
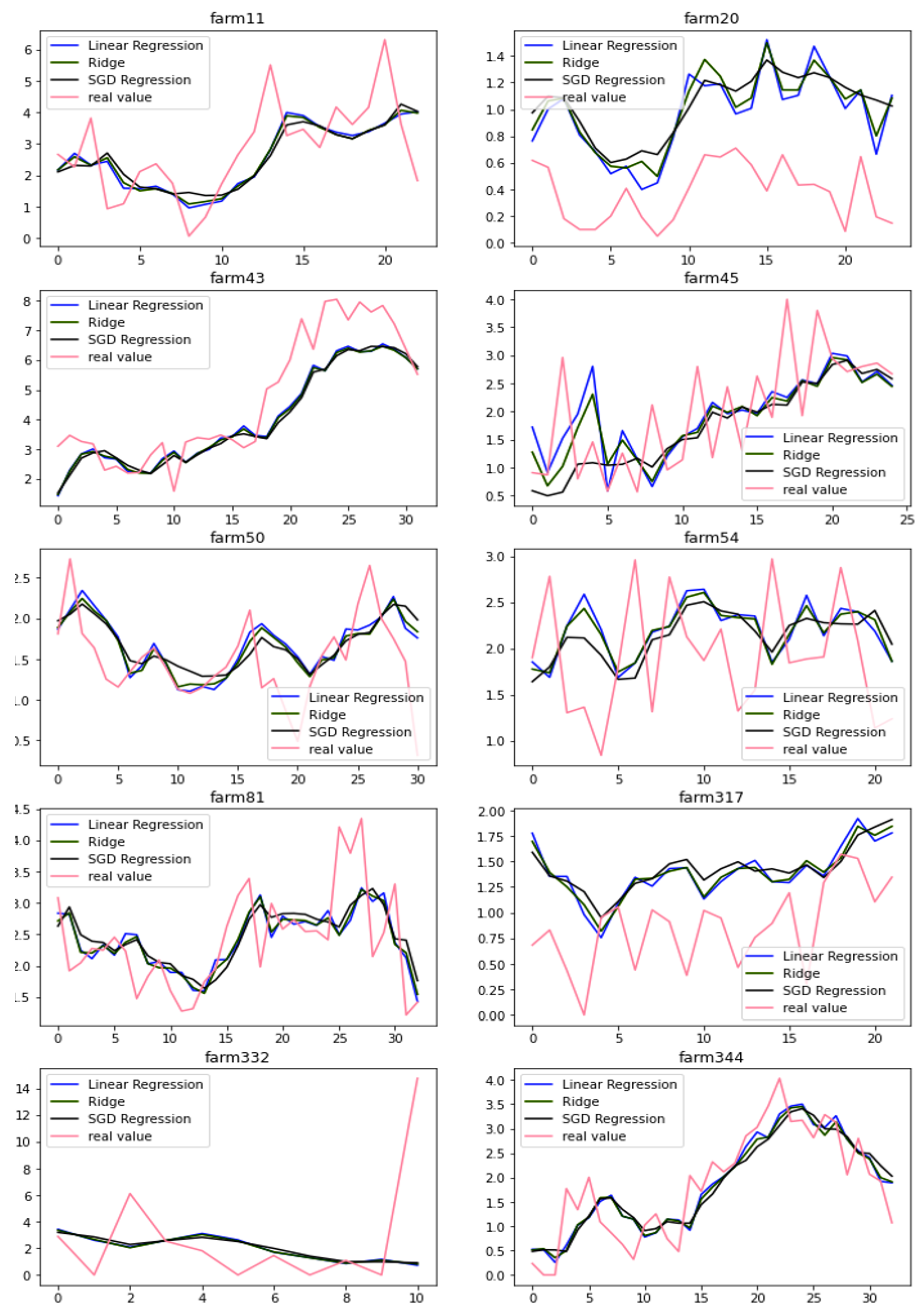
3.3. Prediction by Attention-Based LSTM
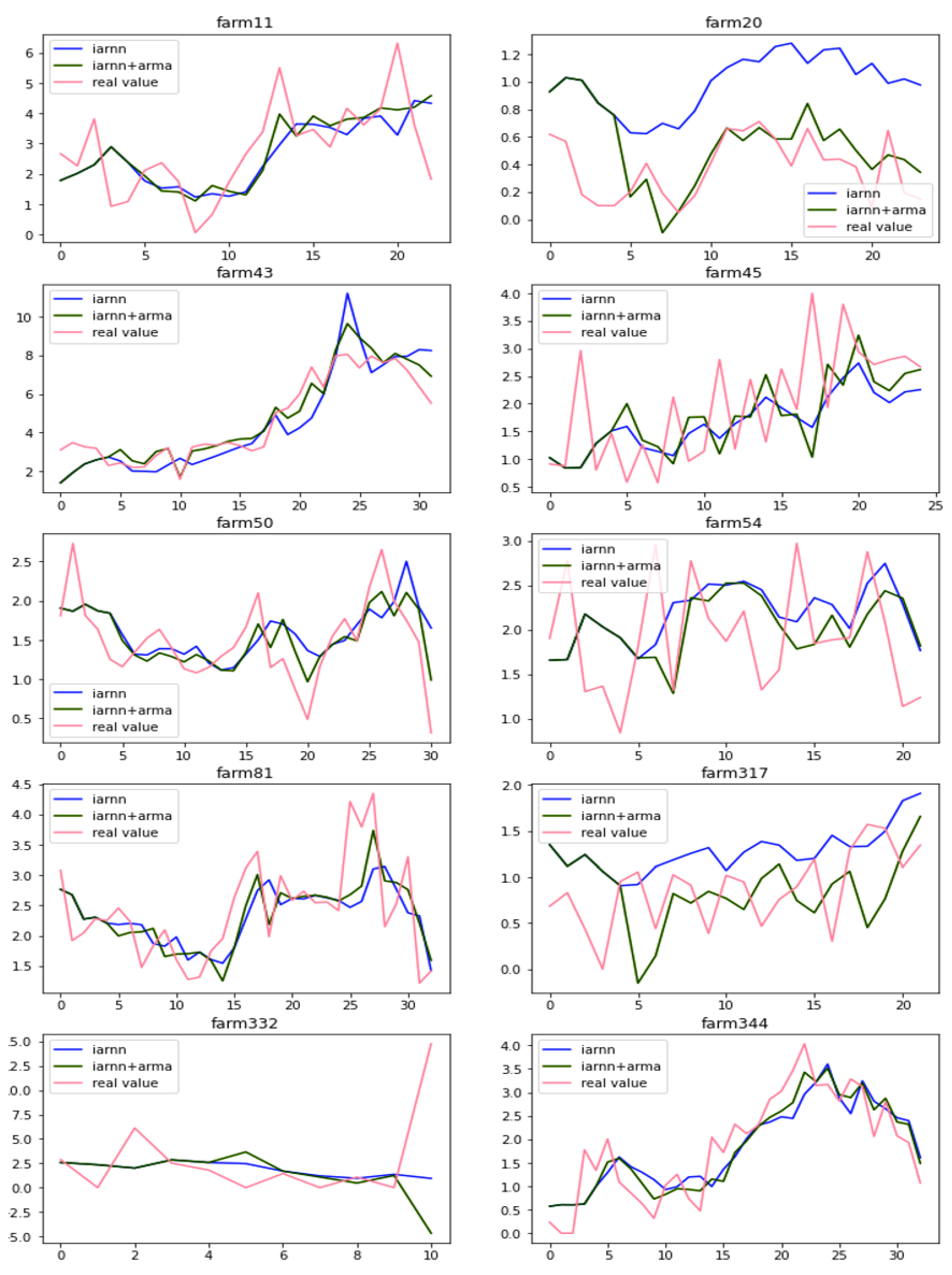
3.4. Prediction by Hybrid Methods
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Box, G.E.P.; Jenkins, G.M.; Reinsel, G.C.; Ljung, G.M. Time series analysis: Forecasting and Control, 5th ed.; Wiley: San Francisco, CA, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, B.K. Time Series Analysis Using Autoregressive Integrated Moving Average (ARIMA) Models. Acad. Emerg. Med. 1998, 5, 739–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Engle, R.F. Autoregressive Conditional Heteroskedasticity with Estimates of The Variance of United Kindom Inflation. Econometrika 1982, 50, 987–1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pham, H.T.; Tran, V.T.; Yang, B.S. A Hybrid of Nonlinear Autoregressive Model with Exogenous Input and Autoregressive Moving Average Model for Long-Term Machine State Forecasting. Expert Syst. Appl. 2010, 37, 3310–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Men, Z.; Yee, E.; Lien, F.S.; Yang, Z.; Liu, Y. Ensemble Nonlinear Autoregressive Exogenous Artificial Neural Networks for Short-Term Wind Speed and Power Forecasting. Int. Sch. Res. Not. 2014, 2014, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Boussaada, Z.; Curea, O.; Remaci, A.; Camblong, H.; Bellaaj, N.M. A Nonlinear Autoregressive Exogenous (NARX) Neural Network Model for the Prediction of the Daily Direct Solar Radiation. Energies 2018, 11, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Huo, F.; Poo, A.N. Nonlinear autoregressive network with exogenous imputs based contour error reduction in CNC machines. Int. J. Mach. Tools Manuf. 2013, 67, 45–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L. Application of Nonlinear Autoregressive with Exogenous Input (NARX) neural network in macroeconomic forecasting, national goal setting and global competitiveness assessment. arXiv 2020, arXiv:2005.08735v1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.A.; Yuen, R.K.K.; Lee, E.W.M. Energy Modeling with Nonlinear-Autoregressive Exogenous Neural Network. In E3S Web of Conferences; EDP Sciences: Ulis, France, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Wibowo, A.; Pujianto, H.; Saputro, D.R.S. Nonlinear Autoregressive Exogenous Model (NARX) in Stock Price Index’s Prediction. In Proceedings of the 2017 2nd International Conferences on Information Technology, Information Systems and Electrical Engineering (ICITISEE), Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 1–3 November 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Mohammadi, K.; Eslami, H.R.; Kahawita, R. Parameter estimation of an ARMA model for river flow forecasting using goal programming. J. Hydrol. 2006, 331, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, Y.; Song, D.; Chen, H.; Jiang, G.; Cottrell, G.W. A Dual-Stage Attention-Based Recurrent Neural Network for Time Series Prediction. arXiv 2007, arXiv:1704-02971. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, T.; Lin, T.; Lu, Y. An Interpretable LSTM Neural Network for Autoregressive Exogenous Model. In Proceedings of the Workshop track of ICLR 2018, Vancouver, Canada, 30 April–3 May 2018; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, H. Bidirectional Encoder-Decoder with Dual-Stage Attention for Multivariate Time-Series Prediction. Master’s Thesis, Seoul National University, Seoul, Korea, 2019. (In Korean). [Google Scholar]
- Na, I.S.; Tran, C.; Nguyen, D.; Dinh, S. Facial UV map completion for pose-invariant face recognition: A novel adversarial approach based on coupled attention residual UNets. Hum. Cent. Comput. Inf. Sci. 2020, 10, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, T.X.; Oh, A.R.; Na, I.S.; Kim, S.H. The Role of Attention Mechanism and Multi-Feature in Image Captioning. ICMLSC 2019, 2019, 170–174. [Google Scholar]
- Ran, X.; Shan, Z.; Fang, Y.; Lin, C. An LSTM-Based Method with Attention Mechanism for Travel Time Prediction. Sensors 2019, 19, 861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Jędrszczyk, E.; Skowera, B.; Gawęda, M.; Libik, M. The effect of temperature and precipitation conditions on the growth and development dynamics of five cultivars of processing tomato. Hortic. Sci. 2016, 24, 63–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Greco, A.; De Luca, D.L.; Avolio, E. Heavy Precipitation Systems in Calabria Region (Southern Italy): High-Resolution Observed Rainfall and Large-Scale Atmospheric Pattern Analysis. Water 2020, 12, 1468. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Role of Variable | Name of Variable | Measure Unit |
|---|---|---|
| Response Variable | Yields of Tomatoes | Kg/m2 |
| Explanatory Variable | Internal Temperature Min, Avg, Max | °C |
| External Temperature Min, Avg, Max | °C | |
| Internal Humidity Min, Avg, Max | % | |
| CO2 Level Min, Avg, Max | ppm | |
| Measure of Interval | No. of Time Lag | No. of Observation |
| 2017~2018, and 2018~2019 | 30 Weeks | 83 Farms |
| No. | Variables | Distance |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Internal Temperature Min | 4.70 |
| 2 | External Temperature Min | 5.78 |
| 3 | Humidity Min | 5.88 |
| 4 | CO2 min | 4.01 |
| 5 | Internal Temperature Avg | 4.41 |
| 6 | External Temperature Avg | 6.76 |
| 7 | Humidity Avg | 5.41 |
| 8 | CO2 Avg | 4.52 |
| 9 | Internal Temperature Max | 5.18 |
| 10 | External Temperature Max | 6.22 |
| 11 | Humidity Max | 6.07 |
| 12 | CO2 Max | 7.18 |
| No. | Variables (vs. Tomato Yields) | Correlation |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | Internal Temperature Min | 0.407 |
| 2 | External Temperature Min | −0.052 |
| 3 | Humidity Min | −0.146 |
| 4 | CO2 min | 0.396 |
| 5 | Internal Temperature Avg | 0.418 |
| 6 | External Temperature Avg | 0.064 |
| 7 | Humidity Avg | −0.307 |
| 8 | CO2 Avg | 0.277 |
| 9 | Internal Temperature Max | 0.374 |
| 10 | External Temperature Max | 0.118 |
| 11 | Humidity Max | −0.201 |
| 12 | CO2 Max | 0.314 |
| No. of Farm | Linear Regression | Ridge Regression | SGD Regression | IARNN | Proposed Method |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 11 | 1.394 | 1.438 | 1.588 | 1.676 | 1.359 |
| 20 | 0.419 | 0.446 | 0.473 | 0.418 | 0.103 |
| 43 | 1.186 | 1.226 | 1.279 | 1.550 | 0.609 |
| 45 | 0.706 | 0.703 | 0.704 | 0.828 | 1.110 |
| 50 | 0.260 | 0.260 | 0.279 | 0.243 | 0.126 |
| 54 | 0.634 | 0.611 | 0.562 | 0.537 | 0.517 |
| 81 | 0.425 | 0.416 | 0.437 | 0.430 | 0.289 |
| 317 | 0.427 | 0.427 | 0.459 | 0.335 | 0.340 |
| 332 | 21.102 | 20.858 | 20.503 | 20.325 | 37.951 |
| 344 | 0.286 | 0.306 | 0.341 | 0.358 | 0.228 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2021 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Cho, W.; Kim, S.; Na, M.; Na, I. Forecasting of Tomato Yields Using Attention-Based LSTM Network and ARMA Model. Electronics 2021, 10, 1576. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10131576
Cho W, Kim S, Na M, Na I. Forecasting of Tomato Yields Using Attention-Based LSTM Network and ARMA Model. Electronics. 2021; 10(13):1576. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10131576
Chicago/Turabian StyleCho, Wanhyun, Sangkyuoon Kim, Myunghwan Na, and Inseop Na. 2021. "Forecasting of Tomato Yields Using Attention-Based LSTM Network and ARMA Model" Electronics 10, no. 13: 1576. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10131576
APA StyleCho, W., Kim, S., Na, M., & Na, I. (2021). Forecasting of Tomato Yields Using Attention-Based LSTM Network and ARMA Model. Electronics, 10(13), 1576. https://doi.org/10.3390/electronics10131576






