Skin Barrier Enhancing Alternative Preservation Strategy of O/W Emulsions by Water Activity Reduction with Natural Multifunctional Ingredients
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Raw Materials
2.2. Formulations
2.3. Water Activity Measurement
2.4. Challenge Test
2.5. Study Design
2.6. Evaluation of Skin Paramaters
2.7. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Impact of Solute Combinations on aw of o/w Emulsions
3.2. Effect of aw on Microbial Stability of o/w Emulsions
3.3. Effect of an aw-Reduced o/w Emulsion on Skin Physiological Parameters
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wilson, L.A.; Ahearn, D.G. Pseudomonas-Induced Corneal Ulcers Associated with Contaminated Eye Mascaras. Am. J. Ophthalmol. 1977, 84, 112–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madani, T.A.; Alsaedi, S.; James, L.; Eldeek, B.S.; Jiman-Fatani, A.A.; Alawi, M.M.; Marwan, D.; Cudal, M.; Macapagal, M.; Bahlas, R.; et al. Serratia Marcescens-Contaminated Baby Shampoo Causing an Outbreak among Newborns at King Abdulaziz University Hospital, Jeddah, Saudi Arabia. J. Hosp. Infect. 2011, 78, 16–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carvalho, R.; Maio, P.; Amaro, C.; Santos, R.; Cardoso, J. Hydrogel Allergic Contact Dermatitis and Imidazolidinyl Urea/Diazolidinyl Urea. Cutan. Ocul. Toxicol. 2011, 30, 331–332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Groot, A.C.; White, I.R.; Flyvholm, M.-A.; Lensen, G.; Coenraads, P.-J. Formaldehyde-Releasers in Cosmetics: Relationship to Formaldehyde Contact Allergy. Contact Dermat. 2010, 62, 2–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Gavín, J.; González-Vilas, D.; Fernández-Redondo, V.; Toribo, J. Allergic Contact Dermatitis in a Girl Due to Several Cosmetics Containing Diazolidinyl-Urea or Imidazolidinyl-Urea. Contact Dermat. 2010, 63, 49–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinhard, E.; Waeber, R.; Niederer, M.; Maurer, T.; Maly, P.; Scherer, S. Preservation of Products with MCI/MI in Switzerland. Contact Dermat. 2001, 45, 257–264. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Darbre, P.D.; Aljarrah, A.; Miller, W.R.; Coldham, N.G.; Sauer, M.J.; Pope, G.S. Concentrations of Parabens in Human Breast Tumours. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2004, 24, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varvaresou, A.; Papageorgiou, S.; Tsirivas, E.; Protopapa, E.; Kintziou, H.; Kefala, V.; Demetzos, C. Self-Preserving Cosmetics. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2009, 31, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ballamwar, K.; Sahasrabuddhe, S.; Chafle, K. A Review: The Hurdle Technology- Self-Preservation Technology in Cosmetics. Int. J. Sci. Res. Publ. IJSRP 2020, 10, 820–827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leistner, L. Basic Aspects of Food Preservation by Hurdle Technology. Int. J. Food Microbiol. 2000, 55, 181–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbosa-Cánovas, G.V.; Fontana, A.J.; Schmidt, S.J.; Labuza, T.P. Effects of Water Activity (Aw) on Microbial Stability as a Hurdle in Food Preservation. In Water Activity in Foods: Fundamentals and Applications, 2nd ed.; Tapia, M.S., Alzamora, S.M., Chirife, J., Eds.; Wiley-Blackwell: Chicago, IL, USA, 2020; pp. 323–355. [Google Scholar]
- Pushpalatha, H.B.; Pramod, K.; Sundaram, R.; Shyam, R. Design and Development of Self-Preserving and Preservative-Free Herbal Liquid Oral Formulation. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 054–060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosmetic Ingredient Review. Safety Assessment of Alkane Diols as Used in Cosmetics. Final Report. Available online: https://www.cir-safety.org/ingredients (accessed on 21 March 2022).
- Fiume, M.M.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.v.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W.; et al. Safety Assessment of PCA (2-Pyrrolidone-5-Carboxylic Acid) and Its Salts as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2019, 38, 5S–11S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fiume, M.M. Alpha Hydroxy Acids. Int. J. Toxicol. 2017, 36, 15S–21S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burnett, C.L.; Bergfeld, W.F.; Belsito, D.v.; Hill, R.A.; Klaassen, C.D.; Liebler, D.C.; Marks, J.G.; Shank, R.C.; Slaga, T.J.; Snyder, P.W.; et al. Safety Assessment of Alkyl Betaines as Used in Cosmetics. Int. J. Toxicol. 2018, 37, 28S–46S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO 11930:2019; Cosmetics—Microbiology—Evaluation of the Antimicrobial Protection of a Cosmetic Product. Beuth Verlag GmbH: Berlin, Germany, 2019.
- Kerdudo, A.; Fontaine-Vive, F.; Dingas, A.; Faure, C.; Fernandez, X. Optimization of Cosmetic Preservation: Water Activity Reduction. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2015, 37, 31–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabara, J.J.; Orth, D.S. Preservative-Free and Self-Preserving Cosmetics and Drugs-Principles and Practices, 1st ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1997. [Google Scholar]
- European Pharmacopeia. Ph. Eur. 7.0, 50103 (01/2011) Efficacy of Antimicrobial Preservation, Council of Europe; European Directorate for the Quality of Medicines and Healthcare: Strasbourg, France, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Vilhelmsson, O.; Miller, K.J. Humectant Permeability Influences Growth and Compatible Solute Uptake by Staphylococcus Aureus Subjected to Osmotic Stress. J. Food Prot. 2002, 65, 1008–1015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Schwan, W.R.; Wetzel, K.J. Osmolyte Transport in Staphylococcus Aureus and the Role in Pathogenesis. World J. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2016, 6, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Graham, J.E.; Wilkinson, B.J. Staphylococcus Aureus Osmoregulation: Roles for Choline, Glycine Betaine, Proline, and Taurine. J. Bacteriol. 1992, 174, 2711–2716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Miller, K.J.; Zelt, S.C.; Bae, J.-H. Glycine Betaine and Proline Are the Principal Compatible Solutes of Staphylococcus Aureus. Curr. Microbiol. 1991, 23, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grant, W.D.; Danson, M.J.; Scott, D.J.; Halling, P.J.; Engberts, J.B.F.N.; Ho, M.W.; Berendsen, H.J.C. Life at Low Water Activity. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. B Biol. Sci. 2004, 359, 1249–1267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Berthele, H.; Sella, O.; Lavarde, M.; Mielcarek, C.; Pense-Lheritier, A.M.; Pirnay, S. Determination of the Influence of Factors (Ethanol, PH and Aw) on the Preservation of Cosmetics Using Experimental Design. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2014, 36, 54–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kabara, J.J.; Vrable, R.; Lie Ken Jie, M.S.F. Antimicrobial Lipids: Natural and Synthetic Fatty Acids and Monoglycerides. Lipids 1977, 12, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyldgaard, M.; Sutherland, D.S.; Sundh, M.; Mygind, T.; Meyer, R.L. Antimicrobial Mechanism of Monocaprylate. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2012, 78, 2957–2965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Hu, Y.; Qiao, J.; Zhang, X.; Ge, C. Antimicrobial Effect of Magnolia Officinalis Extract against Staphylococcus Aureus. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1050–1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Wit, J.C.; Rombouts, F.M. Antimicrobial Activity of Sodium Lactate. Food Microbiol. 1990, 7, 113–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du Plessis, J.; Stefaniak, A.; Eloff, F.; John, S.; Agner, T.; Chou, T.C.; Nixon, R.; Steiner, M.; Franken, A.; Kudla, I.; et al. International Guidelines for the in Vivo Assessment of Skin Properties in Non-Clinical Settings: Part 2. Transepidermal Water Loss and Skin Hydration. Ski. Res. Technol. 2013, 19, 265–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Loden, M.; Maibach, H.I. Glycerol—Just a Moisturizer? Biological and Biophysical Effects. In Dry Skin and Moisturizers; Fluhr, J.W., Bornkessel, A., Berardesca, E., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 227–243. [Google Scholar]
- Albèr, C.; Buraczewska-Norin, I.; Kocherbitov, V.; Saleem, S.; Lodén, M.; Engblom, J. Effects of Water Activity and Low Molecular Weight Humectants on Skin Permeability and Hydration Dynamics—A Double-Blind, Randomized and Controlled Study. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2014, 36, 412–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piquero-Casals, J.; Morgado-Carrasco, D.; Granger, C.; Trullàs, C.; Jesús-Silva, A.; Krutmann, J. Urea in Dermatology: A Review of Its Emollient, Moisturizing, Keratolytic, Skin Barrier Enhancing and Antimicrobial Properties. Dermatol. Ther. 2021, 11, 1905–1915. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Loden, M.; Maibach, H.I. Effects of Natural Moisturizing Factor and Lactic Acid Isomers on Skin Function. In Dry Skin and Moisturizers; Harding, C.R., Rawlings, A.V., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2006; pp. 187–209. [Google Scholar]
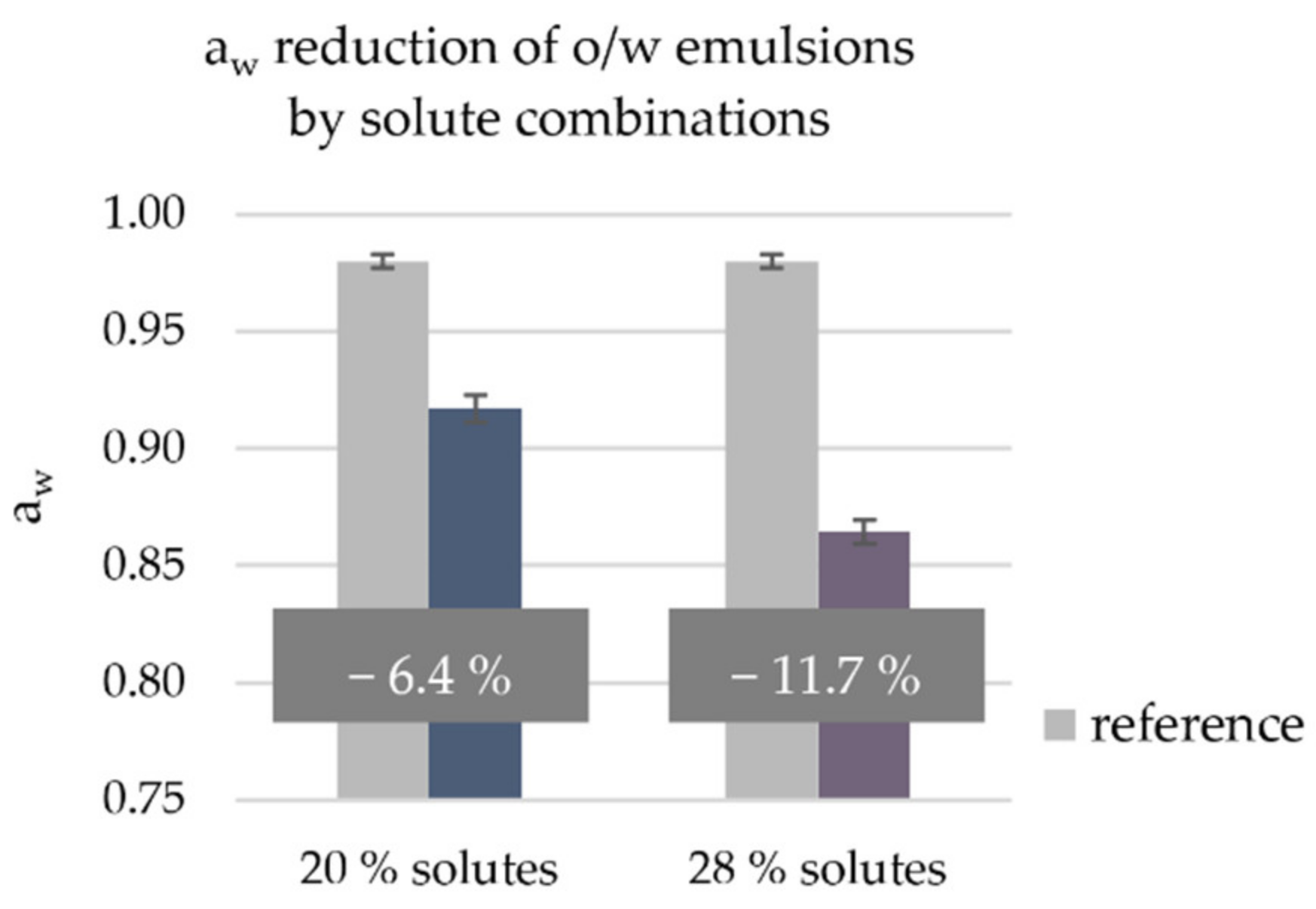

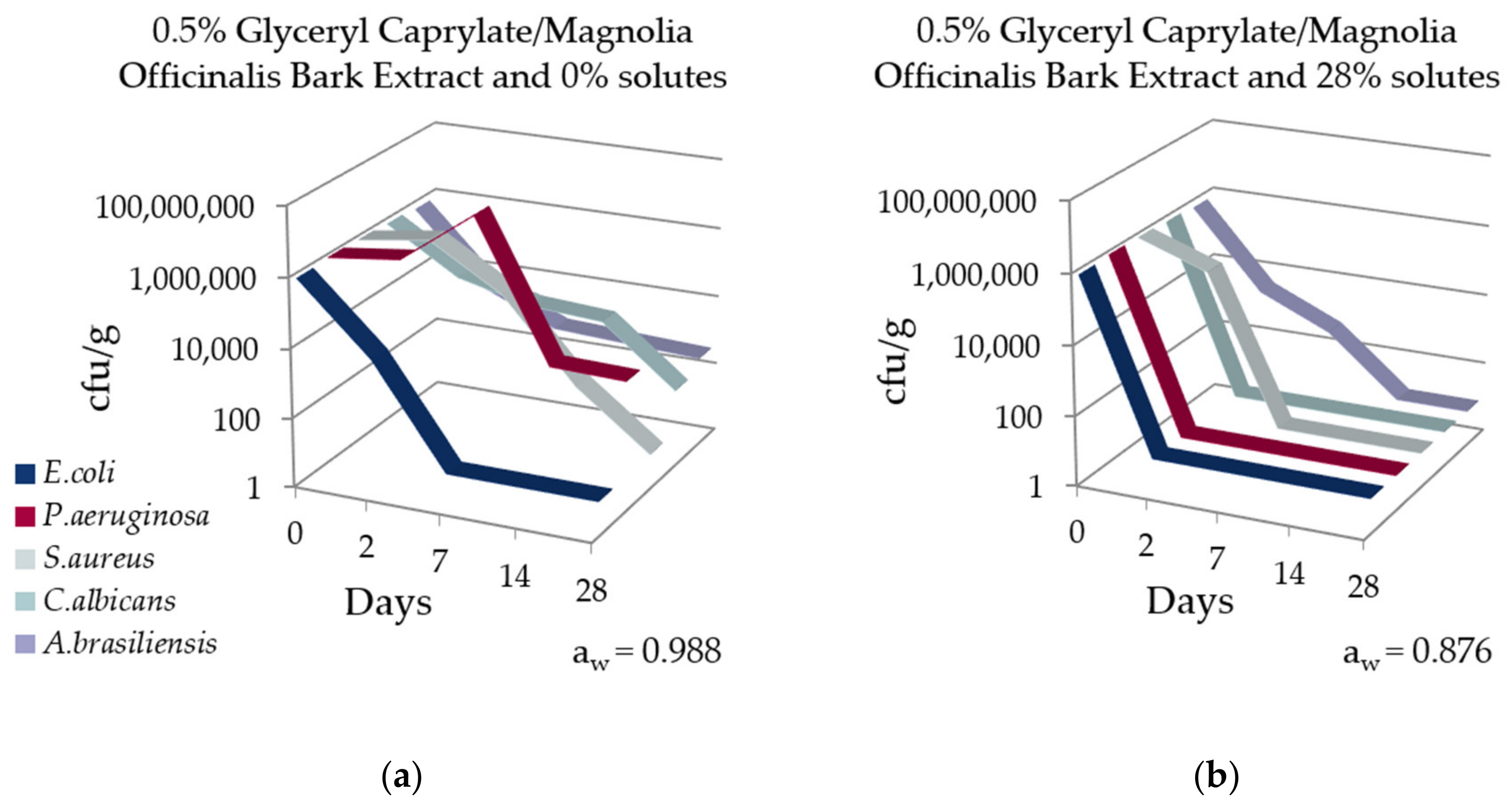
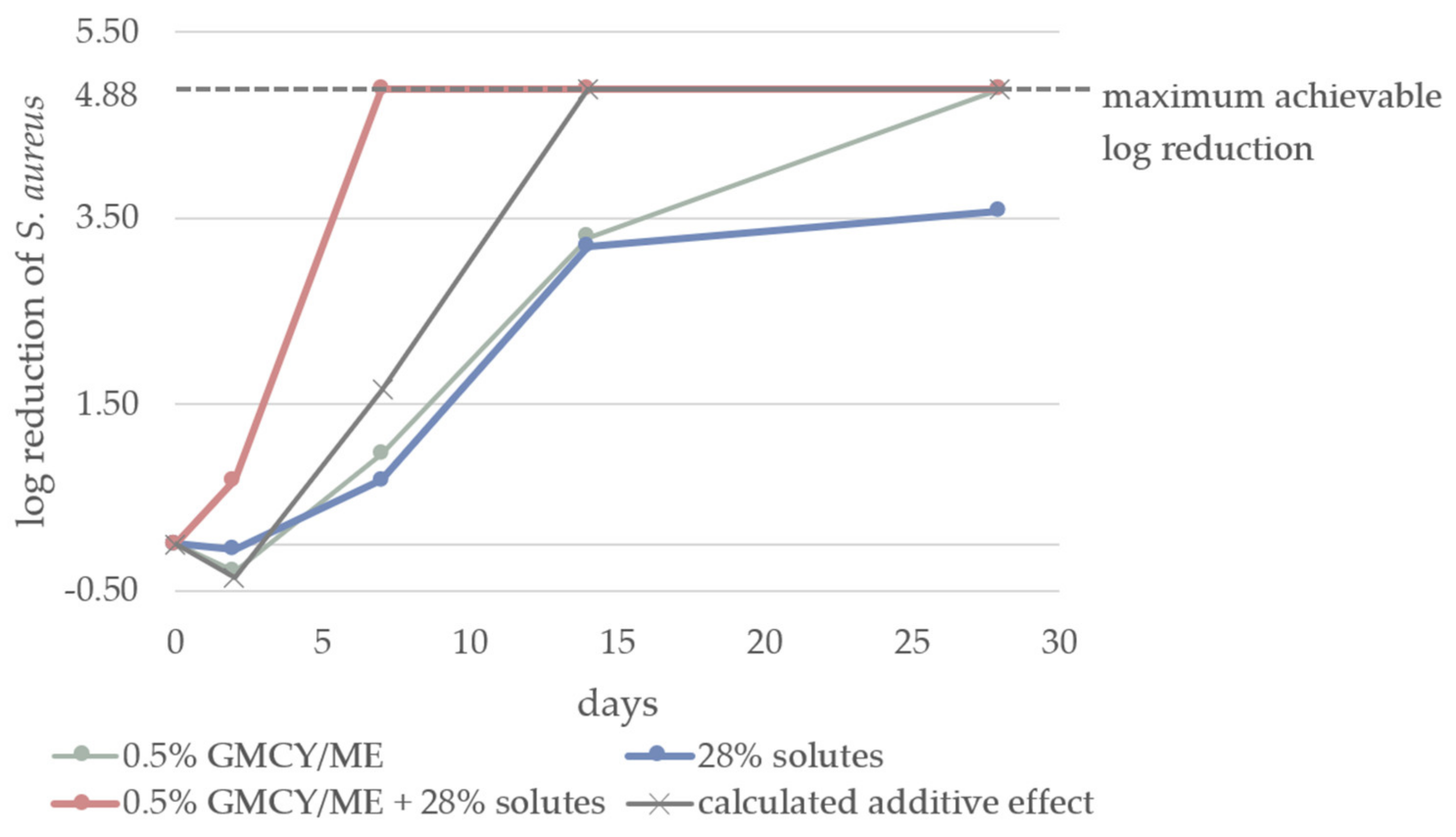
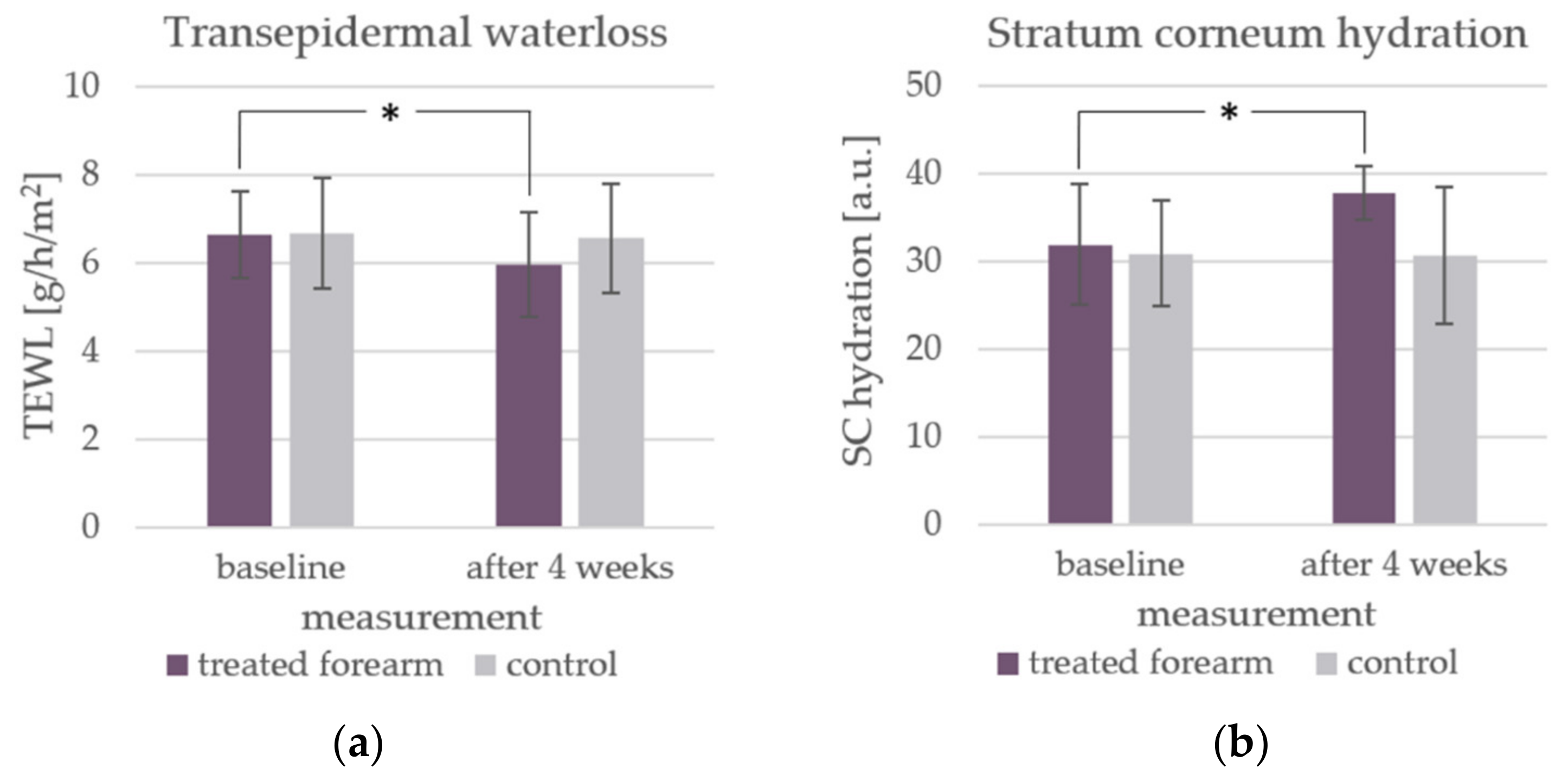
| Solute | INCI | Composition of Combination [%] | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 20% | 28% | ||
| Cosphaderm® Propanediol natural | Propanediol | 5.7 | 8.0 |
| Sodium Lactate | Sodium Lactate | 5.7 | 8.0 |
| ERYLITE® | Erythritol | 3.6 | 5.0 |
| Natural Betaine | Betaine | 3.6 | 5.0 |
| Sodium PCA | Sodium PCA | 1.4 | 2.0 |
| Antimicrobial Substances | INCI | Ratio | Use Concentration [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cosphaderm® GMCY (GMCY)/Cosphaderm® Magnolia Extract 98 (ME) | Glyceryl Caprylate, Magnolia Officinalis Bark Extract | 60:40 | 0.5 |
| Phase | Ingredient | INCI | Quantity [%] |
|---|---|---|---|
| A | Demineralized Water | Aqua | ad. 100% |
| Solutes 1 | - | varying | |
| Antimicrobial agents 2 X 34 | - Xanthan Gum | varying 0.50 | |
| B | Feel Imwitor 372 P MCT Oil Softisan 154 Cetyl Alcohol | Triheptanoin Glyceryl Stearate Citrate Caprylic/Capric Triglyceride Hydrogenated Palm Oil Cetyl Alcohol | 5.00 2.50 5.00 1.00 2.00 |
| Shea Butter | Butyrosperum Parkii Butter | 5.00 | |
| C 3 | Solute 4 | - | varying |
| Demineralized Water | Aqua | varying |
| Log Reduction | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Microorganisms | Criteria | Day 7 | Day 14 | Day 28 |
| Bacteria | A | ≥3 | ≥3 + NI | ≥3 + NI |
| B | - | ≥3 | ≥3 + NI | |
| C. albicans | A | ≥1 | ≥1 + NI | ≥1 + NI |
| B | - | ≥1 | ≥1 + NI | |
| A. brasiliensis | A | - | ≥0 | ≥1 + NI |
| B | - | ≥0 | ≥0 + NI | |
| Microorganisms | Minimum aw |
|---|---|
| P. aeruginosa | 0.97 |
| E. coli | 0.95 |
| S. aureus | 0.86 |
| C. albicans | 0.87 |
| A. brasiliensis | 0.77 |
Publisher’s Note: MDPI stays neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations. |
© 2022 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Nadarzynski, A.; Scholz, J.; Schröder, M.S. Skin Barrier Enhancing Alternative Preservation Strategy of O/W Emulsions by Water Activity Reduction with Natural Multifunctional Ingredients. Cosmetics 2022, 9, 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics9030053
Nadarzynski A, Scholz J, Schröder MS. Skin Barrier Enhancing Alternative Preservation Strategy of O/W Emulsions by Water Activity Reduction with Natural Multifunctional Ingredients. Cosmetics. 2022; 9(3):53. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics9030053
Chicago/Turabian StyleNadarzynski, Alexandra, Jonas Scholz, and Markus S. Schröder. 2022. "Skin Barrier Enhancing Alternative Preservation Strategy of O/W Emulsions by Water Activity Reduction with Natural Multifunctional Ingredients" Cosmetics 9, no. 3: 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics9030053
APA StyleNadarzynski, A., Scholz, J., & Schröder, M. S. (2022). Skin Barrier Enhancing Alternative Preservation Strategy of O/W Emulsions by Water Activity Reduction with Natural Multifunctional Ingredients. Cosmetics, 9(3), 53. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics9030053





