Cosmetic Potential of Marine Fish Skin Collagen
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Extraction and Purification of Collagen
2.3. Amino Acid Analysis
2.4. Sodium Dodecyl Sulphate-Polyacrylamide Gel Electrophoresis (SDS-PAGE)
2.5. Fourier Transformation Infrared (FTIR) Spectroscopy
2.6. Rheology
2.7. Circular Dichroism
2.8. X-ray Diffraction
2.9. Humidity Regain
2.10. Biological Assessment
2.10.1. Skin Test Irritation
2.10.2. Cytokine Analysis
2.11. Statistical Analysis
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Collagen Extraction: Salmon and Codfish Skins
3.2. Chemical and Physical Characterization of the Extracted Collagen
3.2.1. Amino acid Content of Collagen Extracts
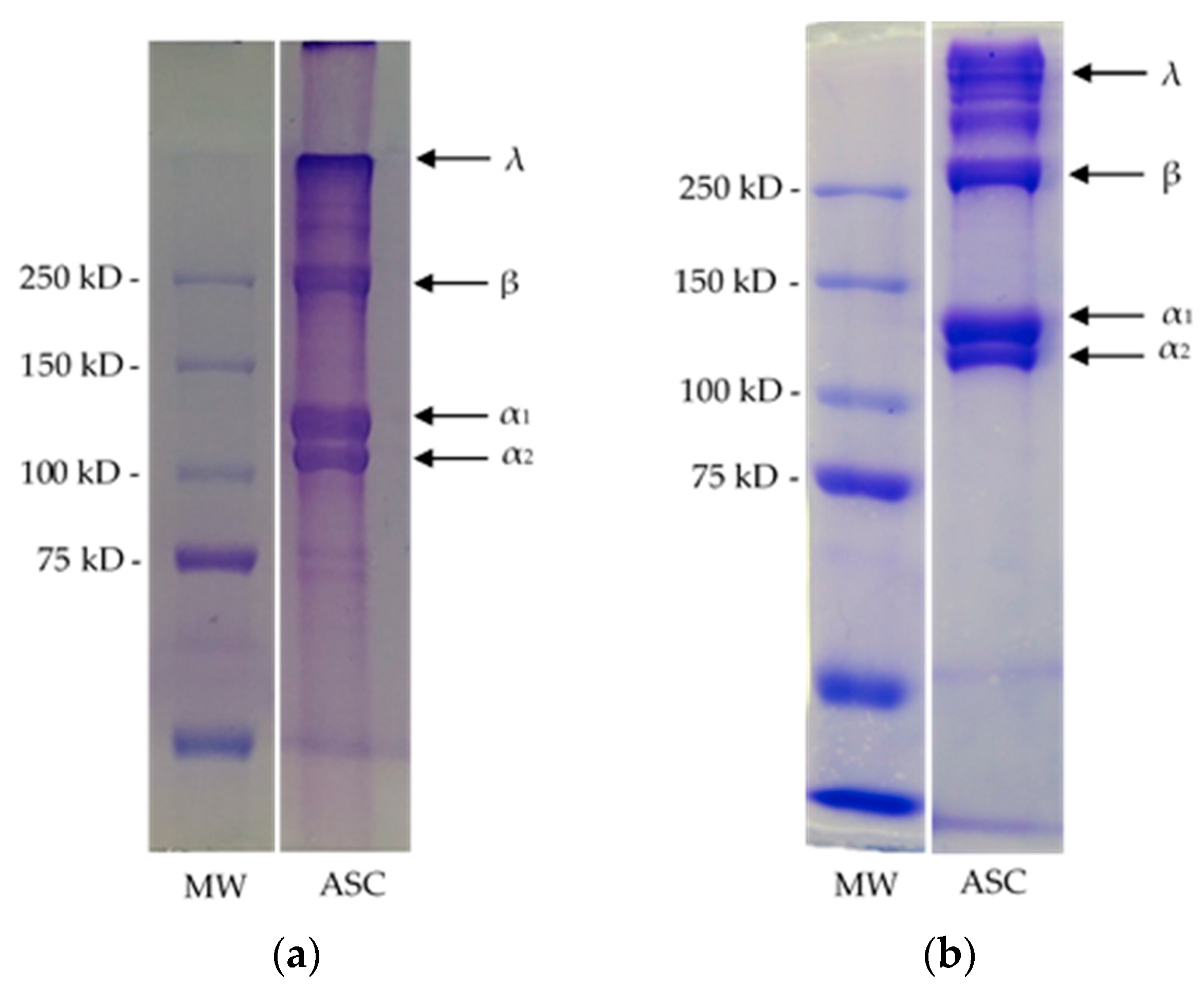
3.2.2. SDS-PAGE Analysis
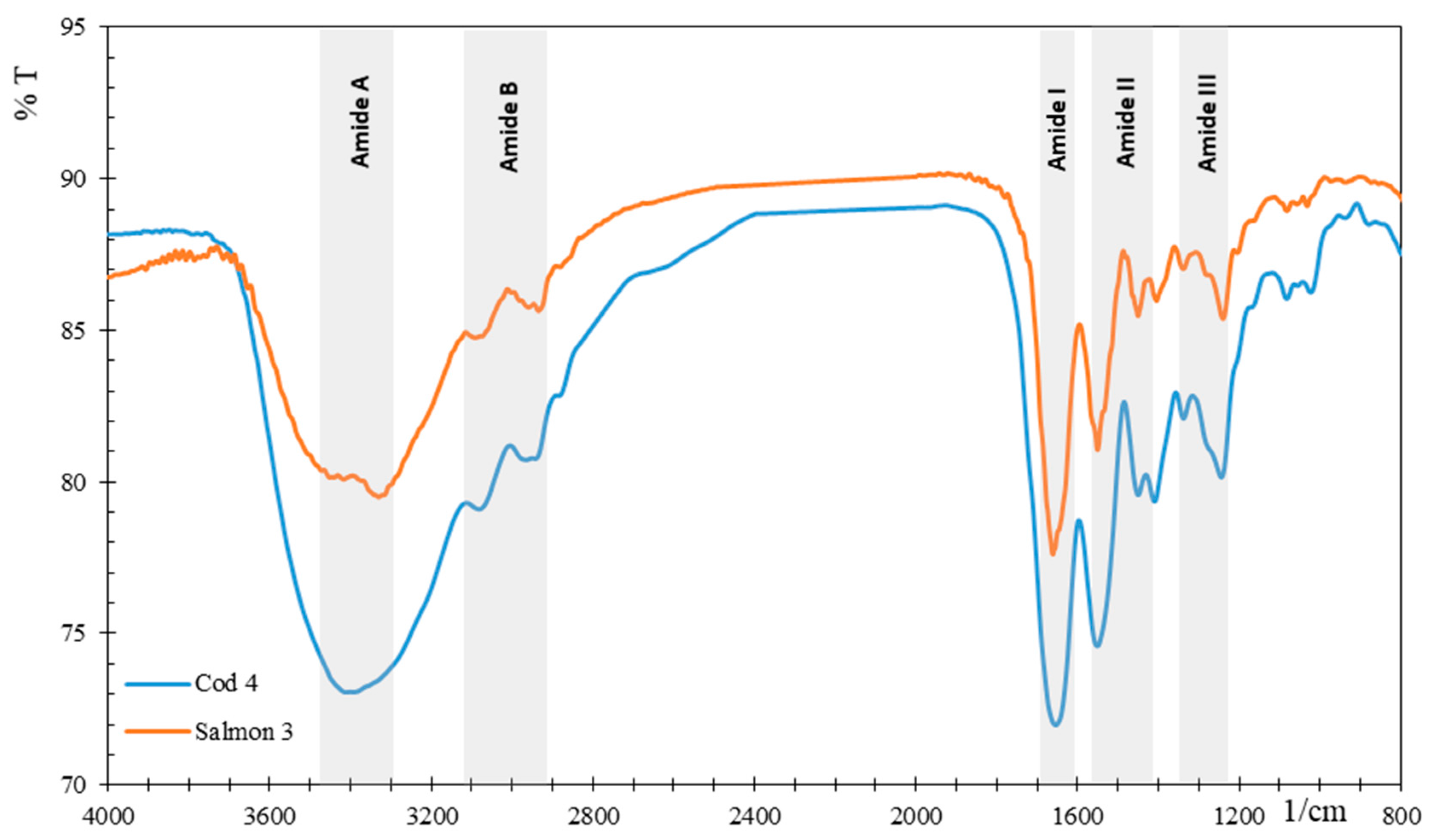
3.2.3. FTIR Analysis
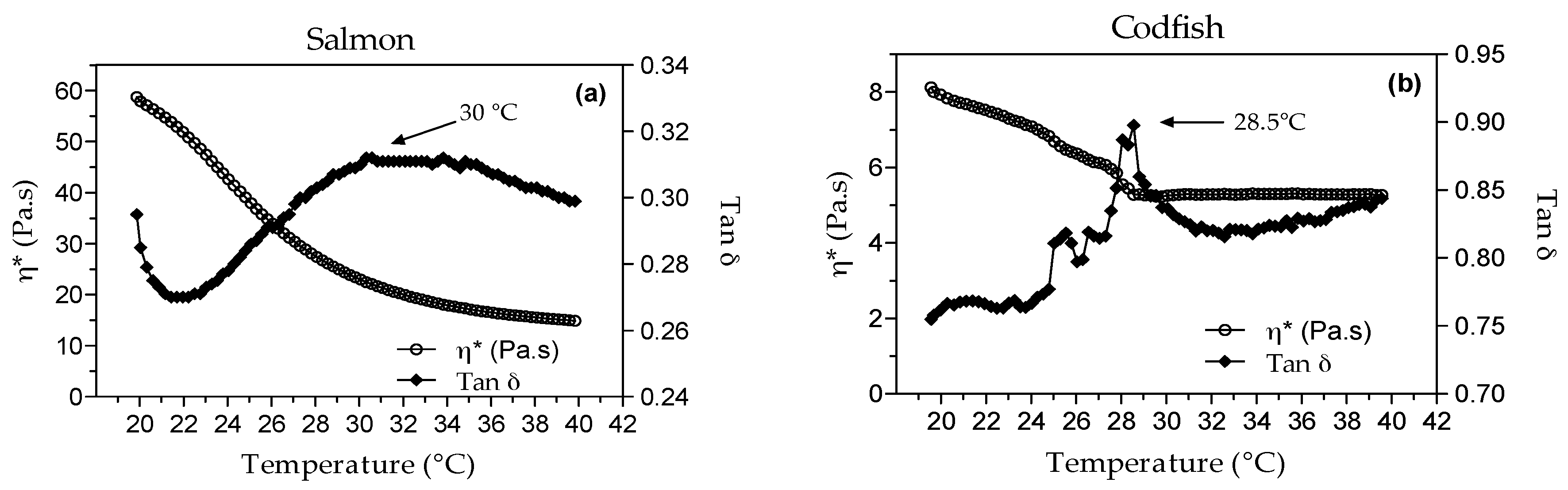
3.2.4. Rheology
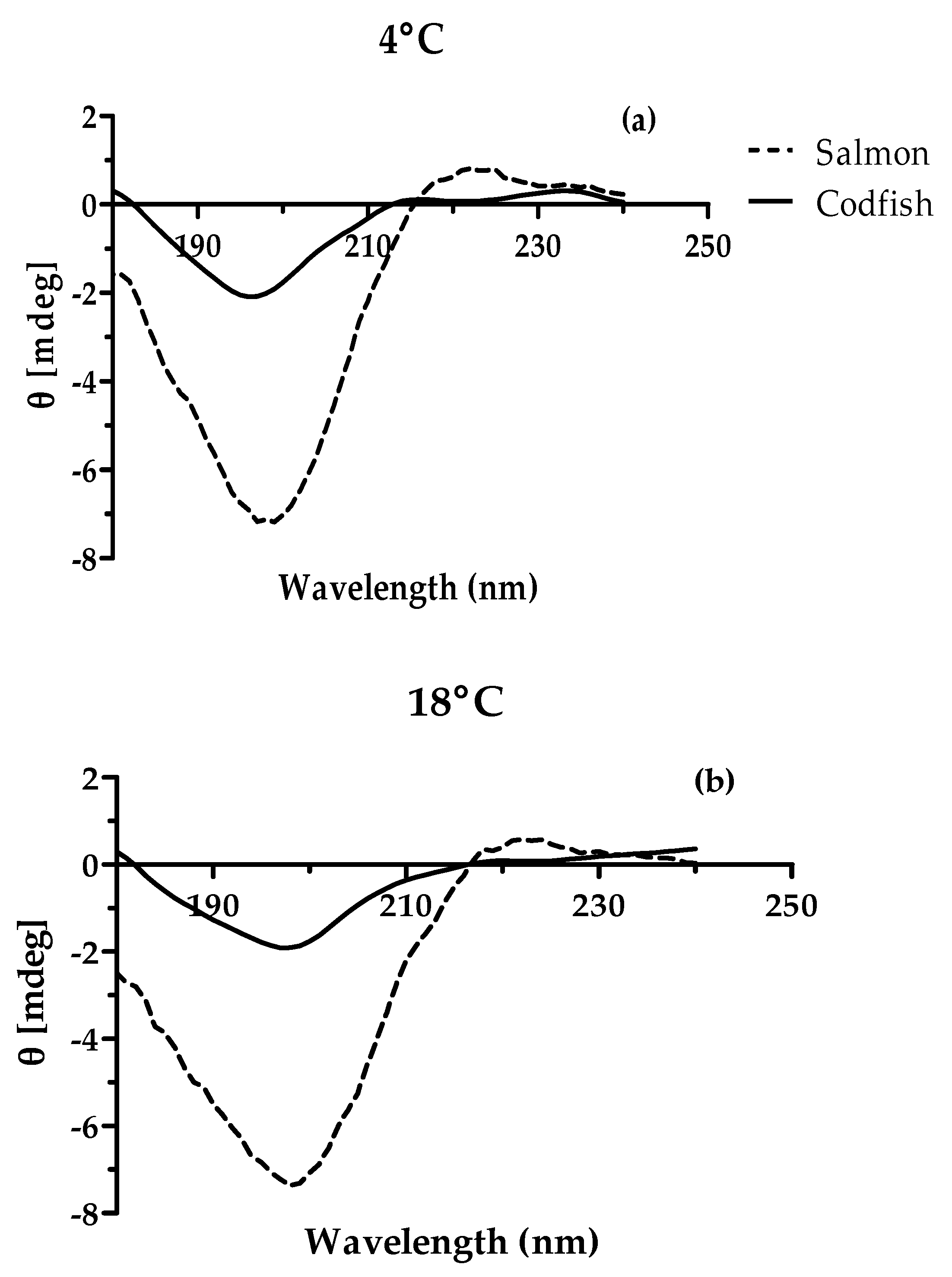
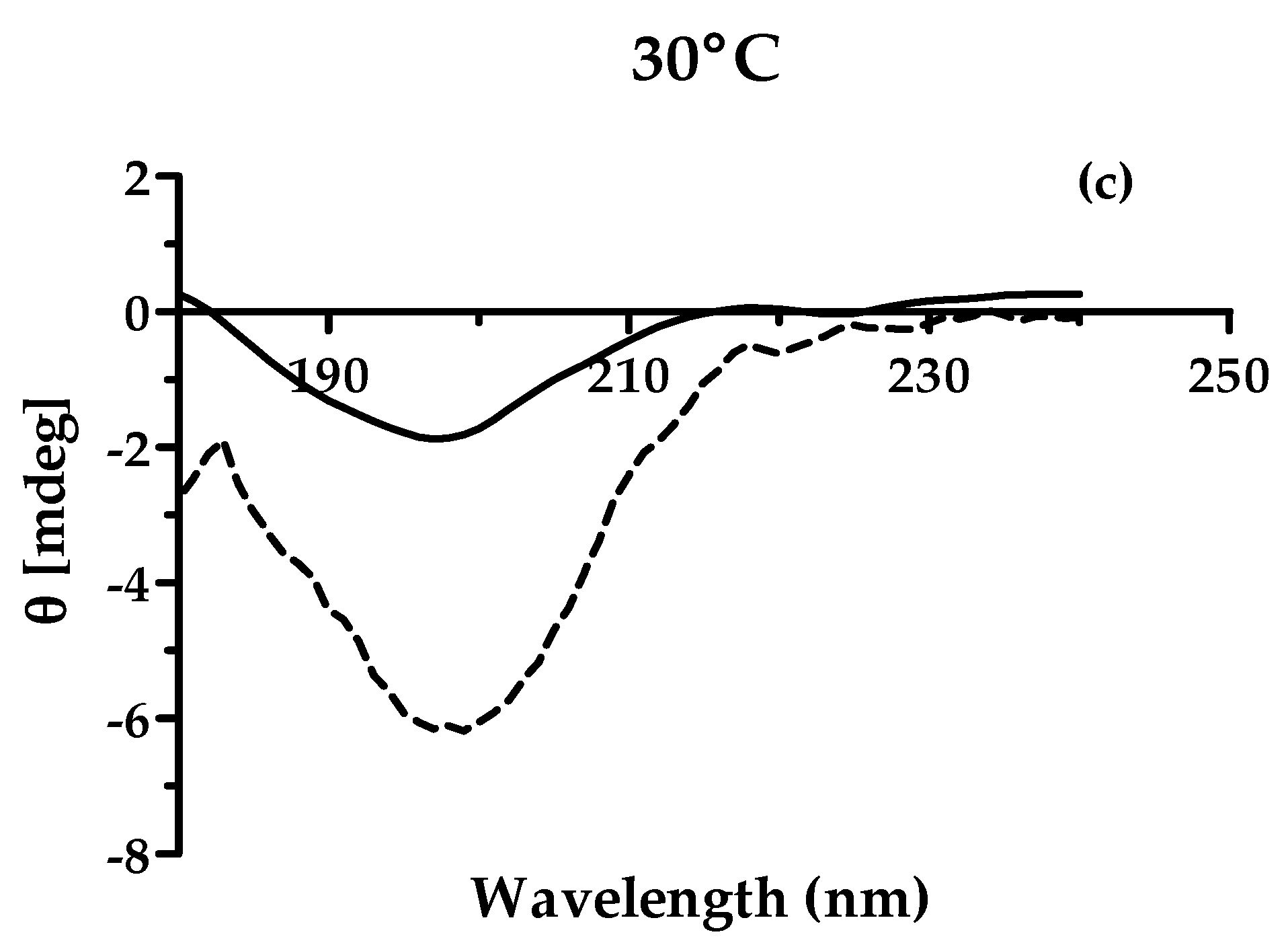
3.2.5. Circular Dichroism
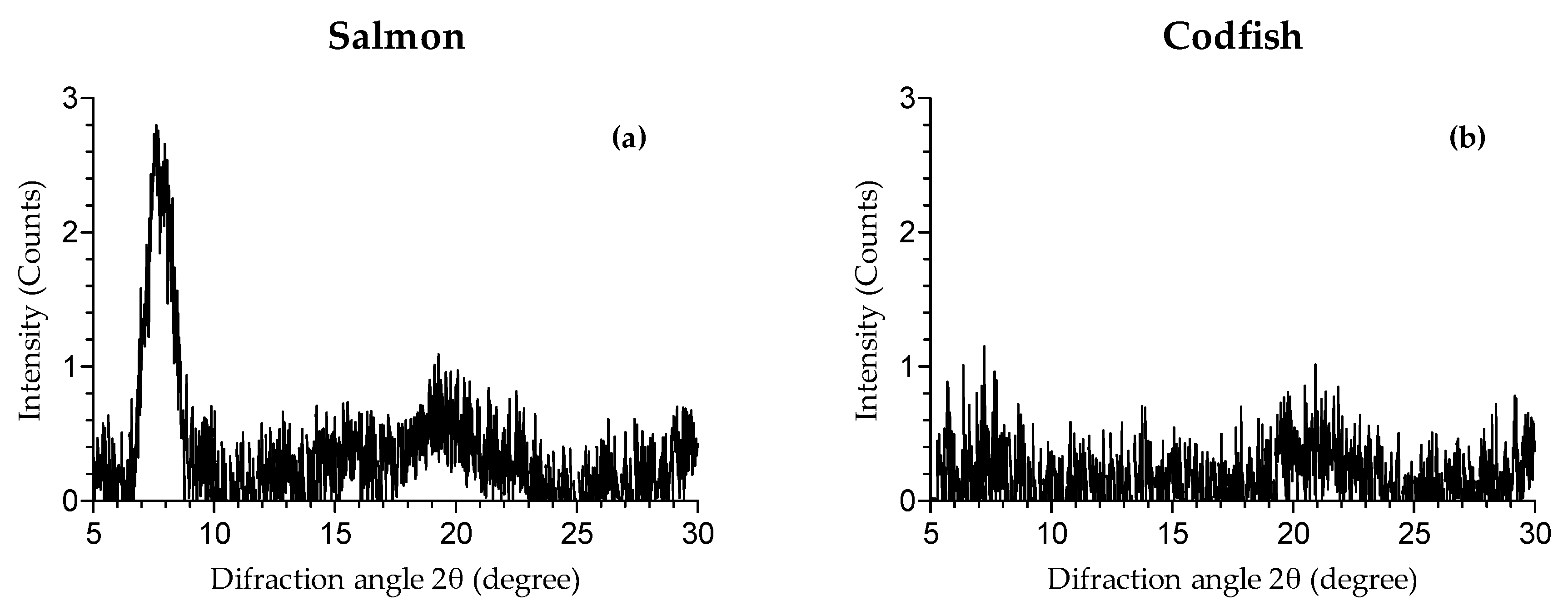
3.2.6. X-ray Diffraction
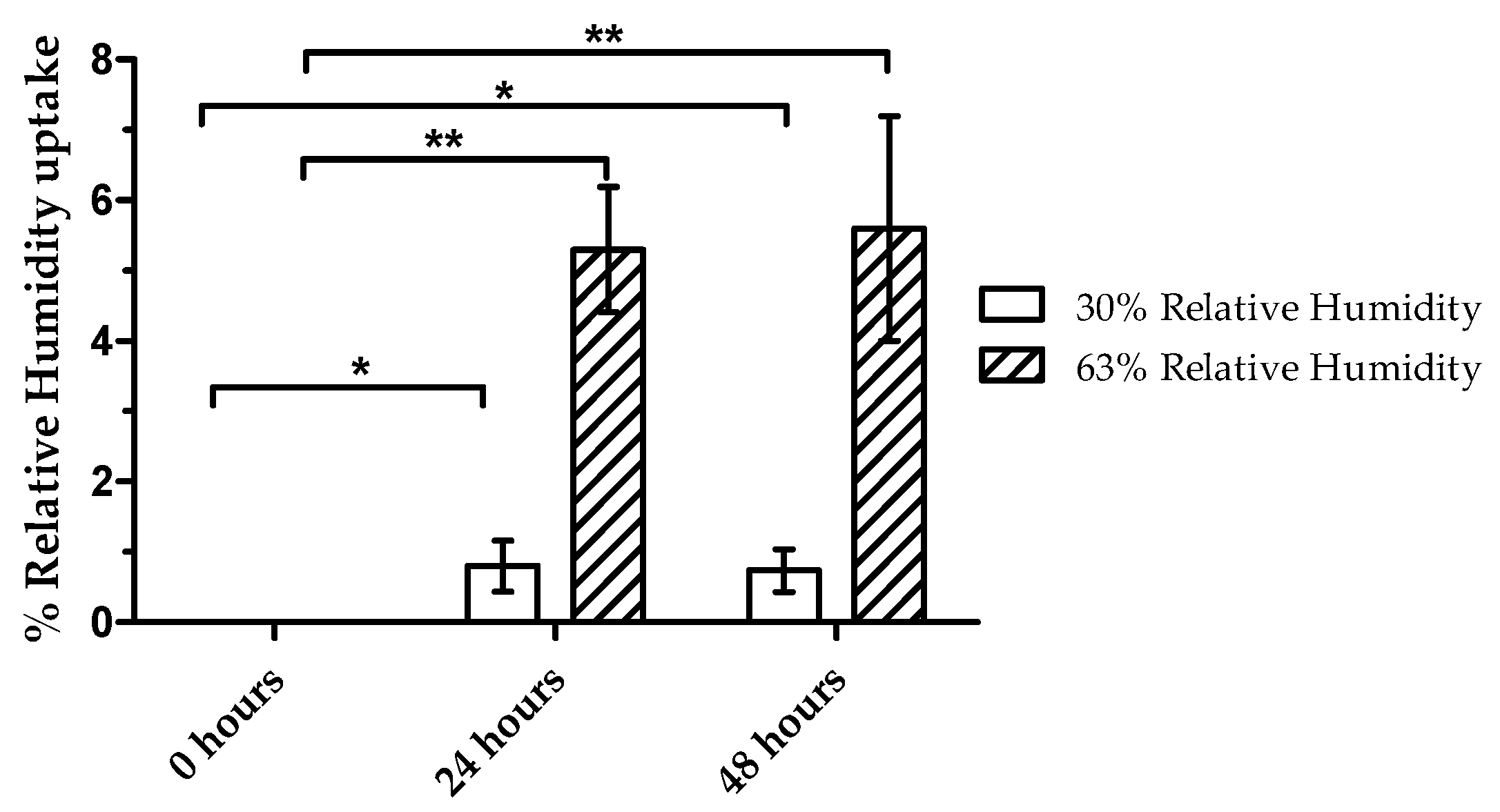
3.3. Humidity Regain Analysis
3.4. Evaluation of Skin Irritation Potential
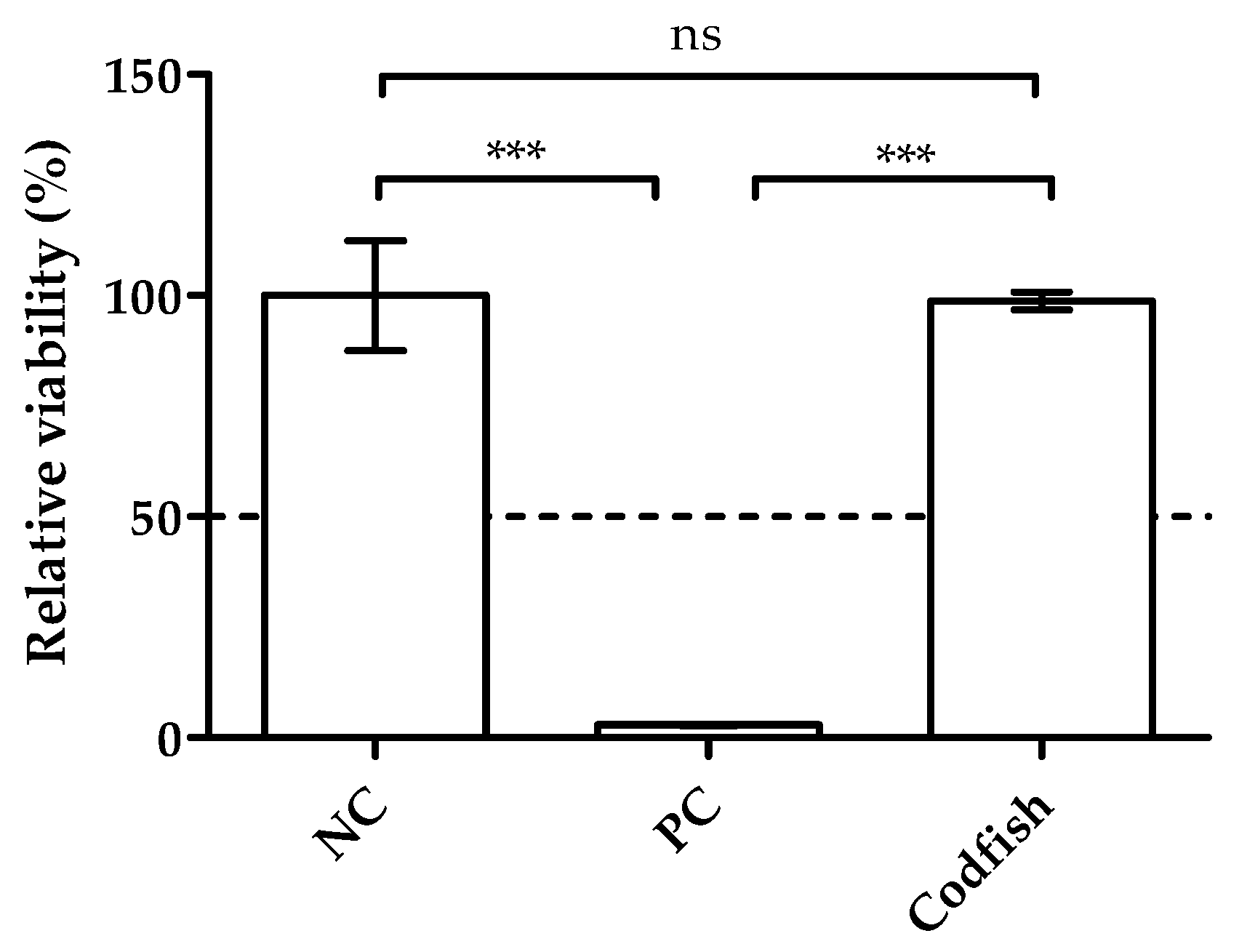
3.4.1. Effect over Viability of Keratinocytes on Reconstructed Skin Model
3.4.2. Cytokine Analysis
4. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shoulders, M.D.; Raines, R.T. Collagen structure and stability. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2009, 78, 929–958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bailey, A. The nature of collagen. Compr. Biochem. 1968, 26, 297–423. [Google Scholar]
- Prockop, D.J.; Kivirikko, K.I. Collagens: Molecular biology, diseases, and potentials for therapy. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 1995, 64, 403–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramshaw, J.A.; Shah, N.K.; Brodsky, B. Gly-xy tripeptide frequencies in collagen: A context for host–guest triple-helical peptides. J. Struct. Biol. 1998, 122, 86–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, J.C.; Barros, A.A.; Aroso, I.M.; Fassini, D.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L.; Duarte, A.R.C. Extraction of collagen/gelatin from the marine demosponge chondrosia reniformis (nardo, 1847) using water acidified with carbon dioxide–process optimization. Ind. Eng. Chem. Res. 2016, 55, 6922–6930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tziveleka, L.-A.; Ioannou, E.; Tsiourvas, D.; Berillis, P.; Foufa, E.; Roussis, V. Collagen from the marine sponges axinella cannabina and suberites carnosus: Isolation and morphological, biochemical, and biophysical characterization. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jankangram, W.; Chooluck, S.; Pomthong, B. Comparison of the properties of collagen extracted from dried jellyfish and dried squid. Afr. J. Biotechnol. 2016, 15, 642–648. [Google Scholar]
- Cheng, X.; Shao, Z.; Li, C.; Yu, L.; Raja, M.A.; Liu, C. Isolation, characterization and evaluation of collagen from jellyfish rhopilema esculentum kishinouye for use in hemostatic applications. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0169731. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cozza, N.; Bonani, W.; Motta, A.; Migliaresi, C. Evaluation of alternative sources of collagen fractions from loligo vulgaris squid mantle. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2016, 87, 504–513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coelho, R.C.; Marques, A.L.; Oliveira, S.M.; Diogo, G.S.; Pirraco, R.P.; Moreira-Silva, J.; Xavier, J.C.; Reis, R.L.; Silva, T.H.; Mano, J.F. Extraction and characterization of collagen from antarctic and sub-antarctic squid and its potential application in hybrid scaffolds for tissue engineering. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2017, 78, 787–795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, C.-Y.; Kuo, J.-M.; Wu, S.-J.; Tsai, H.-T. Isolation and characterization of fish scale collagen from tilapia (oreochromis sp.) by a novel extrusion–hydro-extraction process. Food Chem. 2016, 190, 997–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.; Chen, H.; Xie, Q.; Hong, B.; Chen, J.; Hua, F.; Bai, K.; He, J.; Yi, R.; Wu, H. Rapid isolation of high purity pepsin-soluble type i collagen from scales of red drum fish (Sciaenops ocellatus). Food Hydrocoll. 2016, 52, 468–477. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silvipriya, K.; Kumar, K.K.; Kumar, B.D.; John, A.; Lakshmanan, P. Fish processing waste: A promising source of type-i collagen. Curr. Trends Biotechnol. Pharm. 2016, 10, 374–383. [Google Scholar]
- Iswariya, S.; Velswamy, P.; Uma, T. Isolation and characterization of biocompatible collagen from the skin of puffer fish (Lagocephalus inermis). J. Polym. Environ. 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, T.H.; Alves, A.; Ferreira, B.; Oliveira, J.M.; Reys, L.; Ferreira, R.; Sousa, R.; Silva, S.; Mano, J.; Reis, R. Materials of marine origin: A review on polymers and ceramics of biomedical interest. Int. Mater. Rev. 2012, 57, 276–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K. Marine Proteins and Peptides: Biological Activities and Applications; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Cheung, R.C.F.; Ng, T.B.; Wong, J.H. Marine peptides: Bioactivities and applications. Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 4006–4043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mao, X.; Liu, Z.; Sun, J.; Lee, S.Y. Metabolic engineering for the microbial production of marine bioactive compounds. Biotechnol. Adv. 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silvipriya, K.; Kumar, K.K.; Bhat, A.; Kumar, B.D.; John, A. Collagen: Animal Sources and Biomedical Application. J. Appl. Pharm. Sci. 2015, 5, 123–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hadzik, J.; Kubasiewicz-Ross, P.; Kunert-Keil, C.; Jurczyszyn, K.; Nawrot-Hadzik, I.; Dominiak, M.; Gedrange, T. A silver carp skin derived collagen in bone defect treatment—A histological study in a rat model. Ann. Anat. 2016, 208, 123–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira-Silva, J.; Diogo, G.S.; Marques, A.L.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Marine collagen isolation and processing envisaging biomedical applications. Biomater. Nat. Adv. Devices Ther. 2016, 16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z.; Yang, P.; Zhou, C.; Li, S.; Hong, P. Marine collagen peptides from the skin of nile tilapia (oreochromis niloticus): Characterization and wound healing evaluation. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guillerme, J.-B.; Couteau, C.; Coiffard, L. Applications for marine resources in cosmetics. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siahaan, E.A.; Pangestuti, R.; Munandar, H.; Kim, S.-K. Cosmeceuticals properties of sea cucumbers: Prospects and trends. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xhauflaire-Uhoda, E.; Fontaine, K.; Pierard, G. Kinetics of moisturizing and firming effects of cosmetic formulations. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2008, 30, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hayashi, Y.; Yamada, S.; Ikeda, T.; Yanagiguchi, K. 11 fish collagen and tissue repair. In Marine Cosmeceuticals: Trends and Prospects; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Morgantii, P.; Randazz, S.; Cardillo, A. Role of insoluhle and soluhle collagen as skin moisturizer. J. Appl. Cosmetol. 1986, 4, 141–152. [Google Scholar]
- Elsner, P.; Berardesca, E.; Maibach, H.I. Bioengineering of the Skin: Water and the Stratum Corneum; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 1994; Volume 1. [Google Scholar]
- Peng, Y.; Glattauer, V.; Werkmeister, J.A.; Ramshaw, J.A. Evaluation for collagen products for cosmetic application. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2004, 26, 313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swatschek, D.; Schatton, W.; Kellermann, J.; Müller, W.E.; Kreuter, J. Marine sponge collagen: Isolation, characterization and effects on the skin parameters surface-ph, moisture and sebum. Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2002, 53, 107–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Ngo, D.-H.; Vo, T.-S.; Ryu, B. Industry perspectives of marine-derived proteins as biomaterials. In Marine Biomaterials; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2013; pp. 737–746. [Google Scholar]
- Senaratne, L.; Park, P.-J.; Kim, S.-K. Isolation and characterization of collagen from brown backed toadfish (lagocephalus gloveri) skin. Bioresour. Technol. 2006, 97, 191–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, M.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Du, Z. Rheological properties of fish skin collagen solution: Effects of temperature and concentration. Korea-Aust. Rheol. J. 2010, 22, 119–127. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, F.; Wang, A.; Li, Z.; He, S.; Shao, L. Preparation and characterisation of collagen from freshwater fish scales. Food Nutr. Sci. 2011, 2, 818–823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kandárová, H.; Hayden, P.; Klausner, M.; Kubilus, J.; Sheasgreen, J. An in vitro skin irritation test (sit) using the epiderm reconstructed human epidermal (rhe) model. J. Vis. Exp. 2009, 1366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venkatesan, J.; Anil, S.; Kim, S.-K.; Shim, M.S. Marine fish proteins and peptides for cosmeceuticals: A review. Mar. Drugs 2017, 15, 143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Silva, T.H.; Moreira-Silva, J.; Marques, A.L.; Domingues, A.; Bayon, Y.; Reis, R.L. Marine origin collagens and its potential applications. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 5881–5901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed] [Green Version]
- Soottawat Benjakul, S.N. Fereidoon Shahidi. Fish collagen. In Food Biochemistry and food Processing; Simpson, B.K., Ed.; John Wiley & Sons, Inc.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2012; pp. 365–387. [Google Scholar]
- Regenstein, J.; Zhou, P. Collagen and gelatin from marine by-products. In Maximising the Value of Marine by-Products; Woodhead Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2007; pp. 279–303. [Google Scholar]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.C.; Turnay, J.; Fernández-Dı́az, M.D.; Ulmo, N.; Lizarbe, M.A.; Montero, P. Structural and physical properties of gelatin extracted from different marine species: A comparative study. Food Hydrocoll. 2002, 16, 25–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tylingo, R.; Mania, S.; Panek, A.; Piątek, R.; Pawłowicz, R. Isolation and characterization of acid soluble collagen from the skin of african catfish (Clarias gariepinus), salmon (Salmo salar) and baltic cod (Gadus morhua). J. Biotechnol. Biomater. 2016, 6, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duan, R.; Zhang, J.; Du, X.; Yao, X.; Konno, K. Properties of collagen from skin, scale and bone of carp (Cyprinus carpio). Food Chem. 2009, 112, 702–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenbloom, J.; Harsch, M.; Jimenez, S. Hydroxyproline content determines the denaturation temperature of chick tendon collagen. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 1973, 158, 478–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jenkins, C.L.; Bretscher, L.E.; Guzei, I.A.; Raines, R.T. Effect of 3-hydroxyproline residues on collagen stability. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2003, 125, 6422–6427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamada, S.; Yamamoto, K.; Ikeda, T.; Yanagiguchi, K.; Hayashi, Y. Potency of fish collagen as a scaffold for regenerative medicine. BioMed Res. Int. 2014, 2014, 302932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Deyl, Z.; Mikšık, I.; Eckhardt, A. Preparative procedures and purity assessment of collagen proteins. J. Chromatogr. B 2003, 790, 245–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skierka, E.; Sadowska, M. The influence of different acids and pepsin on the extractability of collagen from the skin of baltic cod (Gadus morhua). Food Chem. 2007, 105, 1302–1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagai, T.; Suzuki, N. Isolation of collagen from fish waste material—Skin, bone and fins. Food Chem. 2000, 68, 277–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; An, X.; Xin, Z.; Zhao, L.; Hu, Q. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the skin of deep-sea redfish (Sebastes mentella). J. Food Sci. 2007, 72, E450–E455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, P.; Benjakul, S.; Maqsood, S.; Kishimura, H. Isolation and characterisation of collagen extracted from the skin of striped catfish (Pangasianodon hypophthalmus). Food Chem. 2011, 124, 97–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahboob, S. Isolation and characterization of collagen from fish waste material-skin, scales and fins of catla catla and cirrhinus mrigala. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2015, 52, 4296–4305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muralidharan, N.; Shakila, R.J.; Sukumar, D.; Jeyasekaran, G. Skin, bone and muscle collagen extraction from the trash fish, leather jacket (Odonus niger) and their characterization. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2013, 50, 1106–1113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guzzi Plepis, A.M.D.; Goissis, G.; Das-Gupta, D.K. Dielectric and pyroelectric characterization of anionic and native collagen. Polym. Eng. Sci. 1996, 36, 2932–2938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kittiphattanabawon, P.; Benjakul, S.; Visessanguan, W.; Shahidi, F. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the cartilages of brownbanded bamboo shark (Chiloscyllium punctatum) and blacktip shark (Carcharhinus limbatus). LWT-Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 43, 792–800. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, Q.; Wang, L.; Sun, W.; Wang, Z.; Xu, J.; Ma, H. Isolation and characterization of collagen from the cartilage of amur sturgeon (Acipenser schrenckii). Process Biochem. 2014, 49, 318–323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skopinska-Wisniewska, J.; Olszewski, K.; Bajek, A.; Rynkiewicz, A.; Sionkowska, A. Dialysis as a method of obtaining neutral collagen gels. Mater. Sci. Eng. C 2014, 40, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muyonga, J.; Cole, C.; Duodu, K. Characterisation of acid soluble collagen from skins of young and adult nile perch (Lates niloticus). Food Chem. 2004, 85, 81–89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barros, A.A.; Aroso, I.M.; Silva, T.H.; Mano, J.o.F.; Duarte, A.R.C.; Reis, R.L. Water and carbon dioxide: Green solvents for the extraction of collagen/gelatin from marine sponges. ACS Sustain. Chem. Eng. 2015, 3, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [Green Version]
- Lee, J.K.; Kang, S.I.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, M.J.; Heu, M.S.; Choi, B.D.; Kim, J.-S. Comparison of collagen characteristics of sea-and freshwater-rainbow trout skin. Food Sci. Biotechnol. 2016, 25, 131–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lai, G.; Li, Y.; Li, G. Effect of concentration and temperature on the rheological behavior of collagen solution. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2008, 42, 285–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kelly, S.M.; Jess, T.J.; Price, N.C. How to study proteins by circular dichroism. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2005, 1751, 119–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Greenfield, N.J. Using circular dichroism spectra to estimate protein secondary structure. Nat. Protoc. 2006, 1, 2876. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Li, Y.; Du, Z.; Li, G. Comparison of dynamic denaturation temperature of collagen with its static denaturation temperature and the configuration characteristics in collagen denaturation processes. Thermochim. Acta 2008, 469, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bigi, A.; Burghammer, M.; Falconi, R.; Koch, M.H.; Panzavolta, S.; Riekel, C. Twisted plywood pattern of collagen fibrils in teleost scales: An X-ray diffraction investigation. J. Struct. Biol. 2001, 136, 137–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faller, C.; Bracher, M.; Dami, N.; Roguet, R. Predictive ability of reconstructed human epidermis equivalents for the assessment of skin irritation of cosmetics. Toxicol. In Vitro 2002, 16, 557–572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.K.; Cohen, C.; de Fraissinette, A.D.B.; Ponec, M.; Whittle, E.; Fentem, J.H. Non-animal testing strategies for assessment of the skin corrosion and skin irritation potential of ingredients and finished products. Food Chem. Toxicol. 2002, 40, 573–592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- OECD. Test No. 439: In Vitro Skin Irritation—Reconstructed Human Epidermis Test Method; OECD Publishing: Paris, France, 2013. [Google Scholar]
- Naik, S.M.; Cannon, G.; Burbach, G.J.; Singh, S.R.; Swerlick, R.A.; Ansel, J.C.; Caughman, S.W.; Wilcox, J.N. Human keratinocytes constitutively express interleukin-18 and secrete biologically active interleukin-18 after treatment with pro-inflammatory mediators and dinitrochlorobenzene. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1999, 113, 766–772. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, D.H.; Park, H.J. Il-18 and cutaneous inflammatory diseases. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2015, 16, 29357–29369. [Google Scholar]
- Scheller, J.; Chalaris, A.; Schmidt-Arras, D.; Rose-John, S. The pro-and anti-inflammatory properties of the cytokine interleukin-6. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2011, 1813, 878–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Amino Acid | Salmon Collagen | Codfish Collagen |
|---|---|---|
| moL % | ||
| Asp | 47 | 51 |
| Thr | 16 | 23 |
| Ser | 56 | 67 |
| Glu | 71 | 71 |
| Gly | 365 | 332 |
| Ala | 121 | 106 |
| Cys | 3 | 5 |
| Val | 18 | 19 |
| Met | 28 | 17 |
| Ile | 6 | 11 |
| Leu | 24 | 21 |
| Nleu | 27 | 22 |
| Tyr | 1 | 4 |
| Phe | 16 | 12 |
| OHLys | 12 | 7 |
| His | 9 | 8 |
| Lys | 25 | 26 |
| Arg | 36 | 51 |
| OHPro | 48 | 55 |
| Pro | 73 | 91 |
| Total | 1000 | 1000 |
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Alves, A.L.; Marques, A.L.P.; Martins, E.; Silva, T.H.; Reis, R.L. Cosmetic Potential of Marine Fish Skin Collagen. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4040039
Alves AL, Marques ALP, Martins E, Silva TH, Reis RL. Cosmetic Potential of Marine Fish Skin Collagen. Cosmetics. 2017; 4(4):39. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4040039
Chicago/Turabian StyleAlves, Ana L., Ana L. P. Marques, Eva Martins, Tiago H. Silva, and Rui L. Reis. 2017. "Cosmetic Potential of Marine Fish Skin Collagen" Cosmetics 4, no. 4: 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4040039
APA StyleAlves, A. L., Marques, A. L. P., Martins, E., Silva, T. H., & Reis, R. L. (2017). Cosmetic Potential of Marine Fish Skin Collagen. Cosmetics, 4(4), 39. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4040039







