Abstract
Cosmeceutical, a new term in the cosmetic industry, refers to cosmetic products that contain active ingredients and have medicinal benefits. Cosmeceuticals have attracted increased attention because of their beneficial effects on human health. Sea cucumbers, belonging to the class Holothuroidea, marine invertebrates, are rich in bioactive compounds, including saponin, chondroitin sulphate, collagen, amino acids, and phenols. These bioactive compounds have diverse functional roles as a secondary metabolite and these properties can be applied to the developments of novel cosmeceuticals. This review provides an overview the application of sea cucumber derivatives for cosmeceuticals. Further, prospects and trends of sea cucumber in cosmeceuticals industry were also discussed. The proper development of sea cucumber bioactive compounds will be helpful in cosmeceutical product development and industry.
1. Introduction
Marine environment, due to its incredible biodiversity, is an excellent reservoir of bioactive compounds with numerous health benefit effects. In recent years, extensive studies have been conducted to explore biological activities, nutritional value, and potential health benefits of marine-based bioactive substances. To date, a series of promising marine-derived substances have been widely applied in food and pharmaceutical industry. Following the same trend, the search of novel bioactive substances from marine resources as ingredients in cosmetics has gained attention. Cosmetics are defined as articles intended to be applied to the human body for cleansing, beautifying, promoting attractiveness, or altering the appearance without affecting body structure or functions [1]. Nowadays greater attention has been paid to cosmeceuticals. It is a combination of cosmetics and pharmaceuticals, containing active ingredients in creams, lotions, and ointments [2]. These products are formulated with ingredients that can promote healthy skin, hair, and nails at cellular levels. Interestingly, a great deal of interest has been developed by consumers toward marine derivatives as cosmeceutical ingredients, due to the unique structures and pharmaceutical properties.
Sea cucumbers, also known as holothurians, are marine invertebrates which have been used as a culinary delicacy, particularly in some parts of Asia [3]. The consumption of sea cucumbers is thought to boost the immune system and to have aphrodisiac properties. They are soft and cylindrical-bodied echinoderms that feed on microscopic algae, absorbing nutrients from the organic matter [4]. Sea cucumbers contain high protein levels, low sugar and fat content, and no cholesterol [5]. They are also rich in bioactive compounds which exhibit numerous medicinal benefits and health functions, especially the triterpene glycosides (saponins) [6,7,8], chondroitin sulphates [9,10], glycosaminoglycan [11,12], sulphated polysaccharides [13,14,15,16], sterols (glycosides and sulphates) [17], phenolics [18], peptides [19], cereberosides [20], and lectins [21,22,23] (Figure 1). Therefore, sea cucumbers have been well recognized as a tonic and traditional remedy in East and South East Asia literature for various diseases.
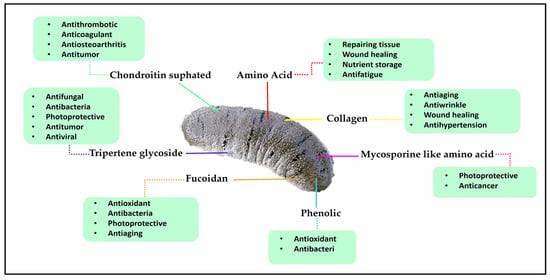
Figure 1.
Bioactive compounds of sea cucumber and their benefit actions on human health.
Like many other commercially-important marine organisms, sea cucumbers continue to be widely exploited because of their perceived unique biological and pharmaceutical properties. More recently, in spite of using them as ingredients in food and medicine, there is also an emerging market for the use of sea cucumbers in cosmetic industries. Investigations conducted on Red Sea Cucumber (S. japonicus) showed remarkable inhibition of melanogenesis [24,25]. It has been reported that S. Japonicus extract inhibited the expression of tyrosinase and tyrosinase-related proteins (TRP-1 and TRP-2). These investigations mean that bioactives of sea cucumbers exhibit a potent skin whitening to be applied in cosmeceutical products. Recently, comprehensive studies have been conducted on the general aspects of the chemical structures, and the physical and biological properties derived from sea cucumbers, and their application as food and drug ingredients. However, previously no comprehensive review of their great potential as cosmeceutical ingredients has been published. This work provides a comprehensive overview covering the description of high-value compounds of sea cucumbers and their bioactivities in cosmetic application.
2. Potential Cosmetic Ingredients from Sea Cucumbers
2.1. Polysaccharides
Polysaccharides from marine organisms have received much attention and have been extensively studied by many researchers. It has been known that marine polysaccharides have displayed a wide range of important biological activities with applications in the food, pharmaceutical, and cosmetic industries. Marine organisms are very rich in carbohydrates, mostly in the form of sulphated and non-sulphated polysaccharides [26]. Sea cucumbers contain a considerable amount of novel sulphated polysaccharides, used in the cosmeceutical and pharmaceutical industry. The sulphated polysaccharides isolated from the body wall of sea cucumbers, named fucosylated chondroitin sulphate (FuCS), are structurally different from sulphated polysaccharides isolated from other invertebrates, vertebrates, and algae. The investigation showed that the body wall of sea cucumbers contain unusual high amounts of sulphated glycans which can be separated into three fractions. The first fraction has a high amount of fucose, whereas the second fraction contains primarily fucoidan. The last fraction has a high proportion of amino sugars and glucuronic acid [10,14]. Sulphated polysaccharides isolated from sea cucumbers are gaining attention, due to their biological activities [5,16,27,28,29,30,31]. Therefore, more complex sulphated polysaccharides of sea cucumbers are continuously isolated and investigated.
Novel FuCS represents the major polysaccharide found in sea cucumbers [14]. FuCS is a unique glucosaminoglycans (GAGs) regarding its structure and medical properties. FuCS has been isolated from a few species of sea cucumber, including Ludwigothurea grisea, Pearsonothuria graeffei, Holothuria vagabunda, Stichopus tremulus, Isostichopus badionotus, Thelenata ananas, Stichopus japonicus, Holothuria edulis, Apostichopus japonicas, Holothuria nobilis, Acaudina molpadioidea, and Athyonidium chilensis [14,15,32,33,34,35,36,37,38,39,40]. The backbone of FuCS is made up of repeating disaccharide units of alternating β-d-glucuronic acid and N-acetyl-β-d-glucosamine [32]. Both glucosamine and its derivative N-acetyl-β-d-glucosamine have an excellent safety profile and has been found to provide benefits in several clinical disorders [41].
Fucoidan, a sulphated polysaccharide, is one of the major bioactive substances of sea cucumbers which consists of L-fucose and sulphate ester groups. They are linear polysaccharides consisting of the regular tandem repeat with diverse glycosidic linkages and sulfation patterns. It has been reported that sea cucumber fucoidan exhibits several biological activities [42,43,44]. The structure clarification of a fucoidan would be beneficial to explain its biological activity. However, to date only few studies have focused on clarification of fucoidan structures derived from sea cucumbers.
2.2. Collagen
Collagen is an abundant protein in animal tissue and mainly distributed in the extracellular matrix and basement membrane of the dermis, bone, tendon, ligament, cartilage, and other connective tissues, with forms microfibrillar and fibrillar networks. Collagen fibres contain the specific biochemical properties which can endow the tissues [45]. Collagen has been widely used in industrial applications, especially in food, pharmaceuticals, and cosmetics. Most of the industrial collagen is produced from land animal origin. However, the application of collagen and gelatin, derived from land animal origin, has been declining because of animal disease transmission and religious restrictions. At present, the use of collagen derived from marine sources has become a new trend, since marine biotics are free from such criticism.
Sea cucumbers, marine echinoderms, have been reported to have high amounts of collagen and mucopolysaccharides [46,47]. The total protein of its body wall contains approximately 70% of insoluble collagen fibers [48], which can be converted into gelatin after being hydrolized [49]. Collagen fibers are hardly soluble, due to the intermolecular cross-links formed by non-helical telopeptides of adjacent collagen. Gelatin is a soluble protein obtained by partial hydrolysis of collagen, mainly from animal skin, bone, tendon, and cartilage [50]. So far, studies on sea cucumber collagen have been mainly focused on functions of hydrolytic bioactive peptides, including damaged tissue repairing [51], antitumor [52], antioxidant [53], and angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory activity [54,55]. Due to their antioxidant properties, collagen fibres have been used in skin care products [56,57].
2.3. Saponin
Saponins are secondary metabolites produced by sea cucumbers. Saponins are reported as the major bioactive compound in many effective traditional Chinese and Indian herbal medicines [58]. They play an important role in chemical defence and possess a wide spectrum of pharmacological activities [59,60,61,62,63,64,65,66,67,68]. The majority of sea cucumber saponins, generally known as Holothurins, are usually triterpene glycosides, belonging to the holostane type group rather than non-holostane [62]. The structural features of these compounds are quite comparable to those of the bioactives from ganoderma, ginseng, and other medicinally-popular tonic herbs [63]. Additionally, one recent study revealed that sea cucumber dietary saponins have shown a preventive effect in alleviating the orotic acid-induced fatty liver in rats [69].
2.4. Mycosporine-Like Amino Acids
One of the adaptations whereby marine organisms can prevent UVR-induced damaged is the synthesis of photoprotective compounds such as mycosporine-like amino acids (MAAs) and scytonemin [70,71]. MAAs are polar with low molecular weight (>400 Da) and have a chemical structure based on either a cyclohexenone or cyclohexenimine ring structure with amino acid substituents [72]. MAAs are favoured as photoprotective compounds because they have maximum UV absorption between 310 and 362 nm, high molar extinction coefficients (e = 28,100–50,000 M−1 cm−1), the capability to dissipate absorbed radiation efficiently as heat without producing reactive oxygen species (ROS), and photostability and resistance to several abiotic stressors [47,73,74]. MAAs provide protection from UV radiation not only in their producers, but also in primary and secondary consumers. MAAs have also been shown to be highly-resistant to abiotic stressors, such as temperature, UV radiation, various solvents, and pH [74]. It was found that the examined MAAs protected cells from UV-induced cell death and had a protective effect on human cells. It is further expected that these compounds may have potential applications in cosmetics as antiphotoaging/photoprotective agents [46]. The presence of MAAs has also been reported in the black sea cucumber Holothuria atra (Jaeger) and their probable role in photoprotection has been hypothesized. It is believed that MAAs could probably function as broad-spectrum UV absorbers [49].
2.5. Vitamins and Minerals
Nutritionally, sea cucumber extracts have an impressive profile of valuable nutrients, such as vitamin A, vitamin B1 (thiamine), vitamin B2 (riboflavin), vitamin B3 (niacin), minerals, especially calcium, magnesium, iron, zinc, selenium, germanium, strontium, copper, manganese, molybdenum, and other microelements beneficial to human health [75]. Since sea cucumber extract is rich in vitamins and minerals, it can be used in cosmetic formula. As we know that vitamin and mineral contents are easy to absorb and present a richly-hydrating and skin-fostering treatment. Sea cucumber extracts can rouse the renewal of damaged skin cells. It can detoxify and cleanse, tone the skin, and moisturize it.
3. Biological Activities of Sea Cucumber Cosmetic Ingredients
3.1. Anti-Aging Activities
Human organs undergoes chronological aging; however, unlike other organs, skin, which acts as important fence, is in direct contact with the environment [45,46]. Ultraviolet (UV) irradiation from the sun is the main detrimental environmental factor to the skin. This UV irradiation will induce skin photoaging. In addition, over the past few decades, there has been a substantial loss in the stratospheric ozone layer which has aroused concern on the effect of increased solar UV [47,48]. Therefore, it is important to provide skin with adequate photoprotection.
Photoprotective compounds, such as carotenoids, mycosporine-like amino acids (MAA) have been identified in the epidermial tissues of black sea cucumbers (Holothuria atra) [76]. The epidermal tissue of H. atra contains varied amounts of mycosporine-gly, palythine, asterina-330, shinorine, porphyra-334, and palythinol. In addition, the ripe ovaries and brooded juveniles of Cucumaria ferrari contain moderate amounts of mycosporine-gly, shinorine, porphyra-334, mycosporine-gly-val, and palythine [76]. It has been suggested that food diet might be responsible for the presence of MAA in holothurians. The role of MAA in photoprotection has been reported. It is believed that MAA functions as a broad-spectrum UV absorber. As an example, porphyra-334 was encapsulated in liposomes and used as sunscreen on UVA-induced skin aging. Comparing skin lipid oxidation and skin aging parameters, such as elasticity, wrinkle depth, and roughness, porphyra-334 liposomes performed as well as a cream with a synthetic UVA sunscreen. Upon irradiation, reactive intermediates were not produced by porphyra-334 MAAs, suggesting that porphyra-334 were able to transform absorbed UV into harmless thermal energy [77,78]. The high efficacy of MAA as photoprotective compounds suggests potential commercial application in the cosmetic industry. However, to fulfil the sunscreen demands, the amino acid or the amino alcohol functions in the MAA must be replaced by alkyl amino groups to reduce their hydrophilic nature. There has been accumulating reports that MAA play additional roles as antioxidants. Some MAAs may protect the skin against UV radiation not only by absorbing high-energy photons and dissipating the energy as heat, but also by scavenging reactive oxygen species (ROS). As an example, mycosporine-gly, porphyra-334, and palythine showed potent antioxidant activity [79,80].
Antioxidant activities of Holothuria leucospiota, H. atra extract, and their bioactive compounds have been demonstrated [81]. Antioxidant activity of H. leucospilota-derived carotenoids have been determined by various methods, such as 1,1-diphenyl-2-picrylhydrazyl (DPPH), linoleic acid free radical scavenging, as well as β-carotene bleaching assays [82,83]. In addition, fucoidan from Thelenota ananas , was proven to possess a significant superoxide radical scavenging activity with an IC50 value of 17.46 ± 0.14 μg/mL [84]. The radical scavenging effect of fucoidan on superoxide radicals improved along with the increasing sulphate content. However, additional 2-O-sulphation in a specific residue increase the radical scavenging effect; suggesting that antioxidant activity of fucoidan derived from T. ananas depends on the sulphation pattern not simply on sulphate content. Combinations of photoprotective and antioxidant activities may be used in order to improve the efficacy of topical sunscreens.
Fucoidan isolated from Stichopus japonicus, Isostichopus badionotus, and Ludwigothurea grisea showed potent biological activities in cosmetics [42,38]. The sulphation content and structure of fucoidan have a profound relationship with its biological application [42,43]. Fucoidan could increase the metalloproteinase-1 enzyme activity in human skin [44]. This means that fucoidan can be used as an anti-aging agent to prevent skin photo aging in cosmetic production.
3.2. Skin Whitening Activities
Skin whitening has been in practice worldwide and continues to be the best-selling skin care product in Asia. Skin whitening can be achieved by several mechanisms of action, such as microphthalmia-associated transcription factor inhibition, downregulation of melanocortin receptor 1 activity, interference with melanosome maturation and transfer, melanocyte loss, and tyrosinase inhibition [45,46,47,48,49,82]. Tyrosinase (EC 1.14.18.1), is a copper-containing glycoprotein of approximately 60–70 kDa that is considered as the rate-limiting enzyme of the melanogenic pathways [85]. Tyrosinase catalyzes two oxidative reactions: the hydroxylation of l-tyrosine to l-dihydroxyphenylalanine (DOPA), which is followed by the oxidation of DOPA to DOPA quinone (EC 1.10.3.1, catechol oxidase). Quinones, highly-reactive compounds, can polymerize spontaneously to form high-molecular-weight compounds or brown pigments (i.e., eumelanin or pheomelanin) or react with amino acids and proteins that enhance the brown colour produced [48,85]. Hence, tyrosinase inhibition has become the most common and is increasingly important in skin-whitening cosmetics.
Despite the enormous amount of research conducted thus far into the development of skin whitening cosmetics, the use of synthetic tyrosinase inhibitors is rather limited, owing to high toxicity, low stability, poor skin penetration, and insufficient activity [86]. Hence, development of novel tyrosinase inhibitors from natural resources continues to arouse great attention. Even though studies of tyrosinase inhibitory activities of sea cucumbers are still in their infancy, a number of studies have reported tyrosinase inhibitory activity of sea cucumbers.
In vitro mechanisms of the skin whitening effect from several sea cucumber extracts have been well demonstrated. Lee et al. [87] evaluated the skin whitening effects of Sanguisorba officinalis and S. japonicus extracts on the clone M-3 cell meloanocyte. The mixture of S. officinalis extract and S. japonicus extract showed 59.14% inhibition of tyrisinase activity [87]. A similar study on melanoma inhibition using S. japonicus extract has been reported by Sik et al. [24]. The extract of S. japonicus showed 61.78% inhibition of tyrosinase activity [24]. Yoon et al. [25] partitioned S. japonicus extract and demonstrated MTT assay for measuring the melanogenesis inhibition. The investigation showed that ethyl acetate fractions of S. japonicus was effectively inhibited melanogenesis in murine B16F10 melanoma cells and downregulated the protein level of melanocyte-specific isoform of tyrosinase-related genes [25]. Notably, sea cucumber extracts were not irritable in ocular irritation test. Moreover, tyrosinase inhibition by ethanol extract of S. japonicus was higher than the water extract [88]. More recently, glycoprotein fraction of boiled S. japonicus have been demonstrated to enhance tyrosinase inhibitory activities by 50.84% [89].
Collectively, this tyrosinase inhibitory activity of S. japonicus suggests that sea cucumber have promising potential to be used as skin whitening agents in the cosmetics industry. There are numerous advantages over other classes of skin whitening cosmetics, such as relatively low production costs, broad spectrum of skin whitening properties, low cytotoxicity, safety, wide acceptability, and novel modes of action, suggesting sea cucumbers as promising skin-whitening candidates in the near future. Further studies are needed with clinical trials for these skin-whitening effects.
3.3. Anti-Microbial Activities
Microbial contamination in cosmetics may cause spoilage of cosmetic product and, when pathogenic, they represent a serious health risk and harmful for consumers worldwide. Moreover, microbial contamination is still one of the major causes for cosmetic product recalls in the world, in particular in developing tropical countries [90]. Therefore, it is important to improve the preservative systems that provide good protection of cosmetic products against microbial contamination [91].
Sea cucumber species such as Stichopus hermanni (Figure 2), Holothuria fuscogilva, Actinopyga mauritiana, A. crassa, Bohadschia vitiensis, Bohadschia tenuissima, Pearonothuria graeffei, Bohadschia cousteaui, Holothuria atra, Holothuria leucospilota, and Holothuria nobilis possess potent antibacterial activities [92,93,94]. In addition, xanthophyll, β-crptoxanthin, and β-carotene were isolated from the Egyptian sea cucumber Holothuria scabra by the bioactivity-directed isolation method, and it showed strong anti-bacterial activity against Staphylococcus aureus (ATCC 6538) [93].

Figure 2.
Sea cucumbers. (A) Stichopus hermannii; and (B) Holothuria atra.
3.4. Wound Healing Activities
Wound dressings are applied for the treatment of different wounds without tissue loss, such as burns, trauma, and diabetic ulcers. The wound healing process consists of three phases. The initial inflammatory phase is characterized by platelet activation and the release of growth factors and cytokines, followed by the proliferative phase, where growth factors are secreted and cell proliferation is enhanced. The last phase is the remodelling phase, where collagen production and organization take place, leading to the mature scar [94]. The use of natural products as cosmetics for wound healing and skin regeneration has gained more importance recently.
In Asian countries, sea cucumber has long been used as a traditional remedy for healing of various internal and external wounds. Sea cucumber bioactive metabolites have been characterized to induce tissue repair and wound healing process. It has been reported that glycosaminoglycan from integumental tissue of Stichopus vastus and Stichopus hermanni exert wound healing properties in rats [95]. Masre et al. (2012) reported that integument part of sea cucumber showed the highest content of total O-sulphated glycosaminoglycan, followed by the internal organs and coelomic fluid [96]. Recently, Stichopus hermannii was incorporated into hydrogel formulation by using an electron beam irradiation technique and was introduced as novel cross-linked Gamat Hydrogel dressing. Gamat Hydrogel possess wound healing properties that have been demonstrated to treat burn wounds in rats. The result showed that Gamat Hydrogel markedly enhanced wound contraction and improved tissue regeneration. Gamat Hydrogel dressing also modulated the inflammatory responses, stimulated the activation and proliferation of fibroblasts, and enhanced rapid production of collagen fibre network with a consequently shorter healing time [96]. Accelerated wound closure in a rat burn model is attributed in part due to sea cucumber being released from the hydrogel matrix which acts in synergy with the moist environment provided by the hydrogel system. Hence, sea cucumbers may provide a new and effective alternative treatment for wound healing in clinical practice.
4. Prospects and Trends of Sea Cucumber in Cosmetic Industry
Sea cucumber-derived proteins such as gelatin and collagen have great potential as functional ingredients in cosmetics such as cream, lotions, lipstick, and gel. Previously, collagen and gelatin were mostly produced from terrestrial animal, such as pig skin, and cattle hides and bones. However, collagen and gelatin from cattle and pig have been declining due to the animal diseases and some ethnic or religious barriers. For collagen and gelatin manufacturers, yield from a particular raw material is also important. Recent experimental studies have shown that these quality parameters vary greatly depending on the biochemical characteristics of the raw materials, the manufacturing processes applied, and the experimental settings used for quality control tests [97]. Sea cucumber, from a nutritional point of view, is an ideal source of collagen and gelatin, as it contains a higher level of proteins and a lower level of lipids than most other foods. The main part of the described sea cucumber presents a high collagen and gelatin contents. The body wall of sea cucumber, which consists of insoluble collagen, has been used as a nutrient supplement of hematogenesis. The use of commercial enzymes to produce collagen from sea cucumbers appears to be a feasible process to convert an under-utilized species to a more useful product that contains bioactive compounds for the cosmetics industry. However, further studies are needed to isolate and identify the specific peptides and/or amino acid sequences in sea cucumber collagen hydrolysates with functional activity for potential utilization in cosmetics production. Gelatin from sea cucumber is considered to be more valuable than gelatins from others organisms because of its characteristic amino acid composition, especially the essential amino acids.
In addition, with the invention of photoprotective compounds, anti-wrinkling agents, and anti-aging compounds in cosmetic industry, new trends has focused on the manufacture of anti-aging creams/lotions, sunscreen lotions, skin whitening creams/lotions, and other cosmetics. In this regard sea cucumbers are promising sources of bioactive compounds for novel cosmetics with various health benefits.
Sea cucumbers are susceptible to overexploitation due to their late maturity, density-dependent reproduction, and low rates of recruitment. Furthermore, the high value of some species, the ease with which such shallow water forms can be harvested, and their vulnerable nature due to their biology, population dynamics and habitat preferences, all contribute to the overexploitation in several areas. Further, to support the usage of sea cucumber in cosmetics, aquaculture technology of sea cucumber needs to be developed.
5. Conclusions
Natural cosmetics that incorporate marine-based extracts are being increasingly sought after in the industry, with more and more consumers demanding products that are of natural origin. Sea cucumbers show great potential as functional ingredients in the cosmetic industry. However, understanding the specific structures and bioactivities of sea cucumber bioactive compounds is still a significant challenge. In addition, adequate clinical trials are needed in the development of cosmetics derived from sea cucumber bioactive materials. More importantly, once their biological activities in cosmetics are demonstrated and further commercialized, new aspects need to be addressed, such as the culture of sea cucumbers.
Acknowledgments
This study is supported by Thematic Research Program Research Center for Oceanography, Indonesian Institute of Sciences. The authors would like to thank Ucu Yanu Arbi for providing sea cucumber photographs.
Author Contributions
E.A.S. and R.P. performed the search of the literature and wrote the review. H.M. searched the literature and commented. S.K.K. revised and proofread the paper. All authors agreed with the final submitted version.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Nelson, F.P.; Rumsfield, J. Cosmetics: Content and function. Int. J. Dermatol. 1988, 27, 665–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-K.; Wijesakara, I. Cosmeceuticals from marine resources. In Marine Cosmeceuticals: Trends and Prospects; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; CRC Press, Taylor & Francis Group: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Taiyeb-Ali, T.B.; Zainuddin, S.L.A.; Swaminathan, D.; Yaacob, H. Efficacy of “Gamadent” toothpaste on the healing of gingival tissues: A preliminary report. J. Oral Sci. 2003, 45, 153–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Conand, C. The Fishery Resources of Pacific Island Countries. Part 2: Holothurians, FAO Fisheries Technical Paper 272.2; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations: Rome, Italy, 1990; p. 143. [Google Scholar]
- Lu, Y.; Wang, B.L. The research progress of antitumorous effectiveness of Stichopus japonicus acid mucopolysaccharide in north of China. Am. J. Med. Sci. 2009, 337, 195–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, R.; Chen, Z. In vivo and in vitro biosynthesis of saponins in sea cucumbers (Holothuroidea). J. Nat. Prod. 1995, 58, 172–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miyamoto, T.; Togawa, K.; Higuchi, R.; Komori, T.; Sasaki, T. Constituents of Holothuroidea, II. Six newly identified biologically active triterpenoid glycoside sulfates from the sea cucumber Cucumaria echinata. Eur. J. Org. Chem. 1990, 1990, 453–460. [Google Scholar]
- Aminin, D.L.; Chaykina, E.L.; Agafonova, I.G.; Avilov, S.A.; Kalinin, V.I.; Stonik, V.A. Antitumor activity of the immunomodulatory lead Cumaside. Int. Immunopharmacol. 2010, 10, 648–654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vieira, R.P.; Mulloy, B.; Mourão, P.A. Structure of a fucose-branched chondroitin sulphate from sea cucumber. Evidence for the presence of 3-O-sulfo-β-d-glucuronosyl residues. J. Biol. Chem. 1991, 266, 13530–13536. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Vieira, R.P.; Pedrosa, C.; Mourao, P.A. Extensive heterogeneity of proteo glycans bearing fucose-branched chondroitin sulfate extracted from the connective tissue of sea cucumber. Biochemistry 1993, 32, 2254–2262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nagase, H.; Enjyoji, K.; Minamiguchi, K.; Kitazato, K.T.; Kitazato, K.; Saito, H.; Kato, H. Depolymerized holothurian glycosaminoglycan with novel anticoagulant actions: Antithrombin III and heparin cofactor II-independent inhibition of factor X activation by factor IXa-factor VIIIa complex and heparin cofactor II-dependent inhibition of thrombin. Blood 1995, 85, 1527–1534. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pacheco, R.G.; Vicente, C.P.; Zancan, P.; Mourão, P.A.S. Different antithrombotic mechanisms among glycosaminoglycans revealed with a new fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from an echinoderm. Blood Coagul. Fibrinolysis 2000, 11, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourao, P.A.S.; Pereira, M.S. Searching for alternatives to heparin: Sulfated fucans from marine invertebrates. Trends Cardiovasc. Med. 1999, 9, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mourao, P.A.; Bastos, I.G. Highly acidic glycans from sea cucumbers. Isolation and fractionation of fucose-rich sulfated polysaccharides from the body wall of Ludwigothurea grisea. Eur. J. Biochem. 1987, 166, 639–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourao, P.A.; Pereira, M.S.; Pavao, M.S.; Mulloy, B.; Tollefsen, D.M.; Mowinckel, M.C.; Abildgaard, U. Structure and anticoagulant activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate frome chinoderm. Sulfated fucose branches on the polysaccharide account for its high anticoagulant action. J. Biol. Chem. 1996, 271, 23973–23984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mourao, P.A.; Boisson-Vidal, C.; Tapon-Bretaudiere, J.; Drouet, B.; Bros, A.; Fischer, A. Inactivation of thrombin by a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from echinoderm. Thromb. Res. 2001, 102, 167–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goad, L.J.; Garneau, F.X.; Simard, J.L.; ApSimon, J.W.; Girard, M. Isolation of Δ9 (11)-sterols from the sea cucumber. Implications for holothurin biosynthesis. Tetrahedron Lett. 1985, 26, 3513–3516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mamelona, J.; Pelletier, E.M.; Lalancette, K.G.; Legault, J.; Karboune, S.; Kermasha, S. Quantification of phenolic contents and antioxidant capacity of Atlantic sea cucumber Cucumaria frondosa. Food Chem. 2007, 104, 1040–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafiuddin, A.M.; Venkateshwarlu, U.; Jayakumar, R. Multilayered peptide incorporated collagen tubules for peripheral nerve repair. Biomaterials 2004, 25, 85–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sugawara, T.; Zaima, N.; Yamamoto, A.; Sakai, S.; Noguchi, R.; Hirata, T. Isolation of sphingoid bases of sea cucumber cerberosides and their cytotoxicity against human colon cancer cells. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2006, 70, 2906–2912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mojica, E.R.E.; Merca, F.E. Lectin from the body walls of black sea cucumber (Holothuria atra Jäger). Philipp. J. Sci. 2004, 133, 77–85. [Google Scholar]
- Mojica, E.R.E.; Merca, F.E. Biological properties of lectin from sea cucumber (Holothuria scabra Jäger). J. Biol. Sci. 2005, 5, 472–477. [Google Scholar]
- Mojica, E.R.E.; Merca, F.E. Isolation and partial characterization of a lectin from the internal organs of the sea cucumber (Holothuria scabra Jäger). Int. J. Zool. Res. 2005, 1, 59–65. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, G.-S.; Park, S.-H.; Kang, Y.-G. Skin Whitening Effects of Stichopus japonicus extracts. J. Int. Wonkwang Cult. 2012, 2, 115–120. [Google Scholar]
- Yoon, W.; Kim, M.; Koh, H.; Lee, W.; Lee, N.; Hyun, C. Effect of Korean red sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus) on melanogenic protein expression in murine B16 melanoma. Int. J. Pharmocol. 2010, 6, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruocco, N.; Costantini, S.; Guariniello, S.; Costantini, M. Polysaccharides from the marine environment with pharmacological, cosmeceutical and nutraceutical potential. Molecules 2016, 21, 551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, X.; Sun, Z.; Zhang, M.; Meng, X.; Xia, X.; Yuan, W.; Xue, F.; Liu, C. Antioxidant and antihyperlipidemic activities of polysaccharides from sea cucumber Apostichopus japonicus. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 90, 1664–1670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsig, L.; Wang, L.; Cavalcante, M.C.; Cardilo-Reis, L.; Ferreira, P.L.; Mourao, P.A. Select in blocking activity of a fucosylated chondroitin sulfate glycosaminoglycan from sea cucumber. Effect on tumor metastasis and neutrophil recruitment. J. Biol. Chem. 2007, 282, 14984–14991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tapon-Bretaudiere, J.; Chabut, D.; Zierer, M.; Matou, S.; Helley, D.; Bros, A.; Mourão, P.A.; Fischer, A.M. A fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from echinoderm modulates in vitro fibroblast growth factor2- dependent angiogenesis. Mol. Cancer Res. 2002, 1, 96–102. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- San Miguel-Ruiz, J.E.; Garcia-Arraras, J.E. Common cellular events occur during wound healing andorgan regeneration in the sea cucumber Holothuria glaberrima. BMC Dev. Biol. 2007, 7, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kariya, Y.; Mulloy, B.; Imai, K.; Tominaga, A.; Kaneko, T.; Asari, A. Isolation and partial characterization of fucan sulfates from the body wall of sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus and their ability to inhibit osteoclastogenesis. Carbohydr. Res. 2004, 339, 1339–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, S.G.; Xue, C.H.; Yin, L.A.; Tang, Q.J.; Yu, G.L.; Chai, W.G. Comparison of structures and anticoagulant activities of fucosylated chondroitin sulfates from different sea cucumbers. Carbohydr. Polym. 2011, 83, 688–696. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoshida, H.-I.; Minami, Y. Structure of DHG, a depolymerized holothurian glycosaminoglycan from sea cucumber, Stichopus japonicus. Tetrahedron Lett. 1992, 33, 4959–4962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Wu, M.; Xu, L.; Lian, W.; Xiang, J.; Lu, F.; Gao, N.; Xiao, C.; Wang, S.; Zhao, J. Comparison of physicochemical characteristics and anticoagulant activities of polysaccharides from three sea cucumbers. Mar. Drugs 2013, 11, 399–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, L.; Xu, L.; Li, J. Preparation and anticoagulant activity of a fucosylated polysaccharide sulfate from a sea cucumber Acaudina molpadioidea. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 2052–2057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuhiro, B.; Osorio-Roman, I.O.; Torres, R. Vibrational spectroscopy characterization and anticoagulant activity of a sulfated polysaccharide from sea cucumber Athyonidium chilensis. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 88, 959–965. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kariya, Y.; Watabe, S.; Hashimoto, K.; Yoshida, K. Occurance of chondroitin sulfate-E in glycosaminoglycan isolated from the body wall of sea-cucumber Stichopus japonicus. J. Biol. Chem. 1990, 265, 5081–5085. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Mulloy, B.; Ribeiro, A.C.; Alves, A.P.; Vieira, R.P.; Mourao, P.A. Sulfated fucans from echinoderms have a regular tetrasaccharide repeating unit defined by specific patterns of sulfation at the 0-2 and 0-4 positions. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 22113–22123. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.C.; Su, W.; Zhang, C.Y.; Xue, C.H.; Chang, Y.G.; Wu, X.L.; Tang, Q.; Wang, J. Protective effect of sea cucumber (Acaudina molpadioides) fucoidan against ethanol-induced gastric damage. Food Chem. 2012, 133, 1414–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, M.; Huang, R.; Wen, D.; Gao, N.; He, J.; Li, Z.; Zhao, J. Structure and effect of sulfated fucose branches on anticoagulant activity of the fucosylated chondroitin sulfate from sea cucumber Thelenata ananas. Carbohydr. Polym. 2012, 87, 862–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.-K.; Ravichandran, Y.D.; Khan, S.B.; Kim, Y.T. Prospective of the cosmeceuticals derived from marine organisms. Biotechnol. Bioprocess Eng. 2008, 13, 511–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Li, G.; Wu, N.; Guo, X.; Liao, N.; Ye, X.; Liu, D.; Xue, C.; Chai, W. Sulfation pattern of the fucose branch is important for the anticoagulant and antithrombotic activities of fucosylated chondroitin sulfates. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1830, 3054–3066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pomin, V.H. Structure-function relationship of anticoagulant and antithrombotic well-defined sulfated polysaccharides from marine invertebrates. Adv. Food Nutr. Res. 2012, 65, 195–209. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Moon, I.S.; Cho, S.J.; Lee, H.; Seog, D.H.; Jung, Y.W.; Jin, I.; Walikonis, R. Up regulation by KCl treatment of eukaryotic translation elongation factor 1A (eEF1A) mRNA in the dendrites of cultured rat hippocampal neurons. Mol. Cells 2008, 25, 538–544. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Fisher, G.J.; Kang, S.; Varani, J.; Bata-Csorgo, Z.; Wan, Y.; Datta, S.; Voorhees, J.J. Mechanisms of photoaging and chronological skin aging. Arch. Dermatol. 2002, 138, 1462–1470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pallela, R.; Na-Young, Y.; Kim, S.-K. Anti-photoaging and photoprotective compounds derived from marine organisms. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 1189–1202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rastogi, R.P.; Sinha, R.P.; Singh, S.P.; Häder, D.-P. Photoprotective compounds from marine organisms. J. Ind. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2010, 37, 537–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.-K.; Pangestuti, R. Biological Properties of Cosmeceuticals Derived from Marine Algae; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 191–200. [Google Scholar]
- Bandaranayake, W.M.; Rocher, A.D. Role of secondary metabolites and pigments in the epidermal tissues, ripe ovaries, viscera, gut contents and diet of the sea cucumber Holothuria atra. Mar. Biol. 1999, 133, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gómez-Guillén, M.; Giménez, B.; López-Caballero, M.; Montero, M. Functional and bioactive properties of collagen and gelatin from alternative sources: A review. Food Hydrocoll. 2011, 25, 1813–1827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.Y.; Lim, H.K.; Lee, S.; Hwang, H.C.; Cho, S.K.; Cho, M. Pepsin-solubilised collagen (PSC) from red sea cucumber (Stichopus japonicus) regulates cell cycle and the fibronectin synthesis in HaCaT cell migration. Food Chem. 2012, 132, 487–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.Q.; Wang, C.H.; Jiang, A.L. In vitro antitumor activities of low molecular sea cucumber Stichopus japonicus peptides sequentially hydrolyzed by proteases. Adv. Mater. Res. 2012, 393, 1259–1262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.Q.; Wan, C.H.; Jiang, A.L. Antioxidant peptides isolated from sea cucumber Stichopus Japonicus. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2012, 234, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Li, B.; Dong, S.; Liu, Z.; Zhao, X.; Wang, J.; Zeng, M. A novel ACE inhibitory peptide isolated from Acaudina molpadioidea hydrolysate. Peptides 2009, 30, 1028–1033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forghani, B.; Ebrahimpour, A.; Bakar, J.; Hamid, A.A.; Hassan, Z.; Saari, N. Enzyme hydrolysates from Stichopus horrens as a new source for angiotensin-converting enzyme inhibitory peptides. Evid.-Based Complement. Altern. Med. 2012, 9, 236384. [Google Scholar]
- Xinrong, P.; Ruiyue, Y.; Haifeng, Z.; Qiong, L.; Zhigang, L.; Junbo, W.; Yong, L. Preventive effect of marine collagen peptide on learning and memory impairment in SAMP8 Mice. Food Ferment. Ind. 2009, 7, 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, Y.J.; Han, X.L.; Li, Y. Effect of marine collagen peptides on long bone development in growing rats. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2010, 90, 1485–1491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bahrami, Y.; Zhang, W.; Franco, C. Discovery of novel saponins from the viscera of the sea cucumber Holothuria lesson. Mar. Drugs 2014, 12, 2633–2667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hostettmann, K.; Marston, A. Chemistry and Pharmacology of Natural Products; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 1995. [Google Scholar]
- Dong, P.; Xue, C.; Du, Q. Separation of two main triterpene glycosides from sea cucumber Pearsonothuria graeffei by high-speed countercurrent chromatography. Acta Chromatogr. 2008, 20, 269–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, M.S.; Roccatagliata, A.J.; Kuriss, A.; Chludil, H.; Seldes, A.M.; Pujol, C.A.; Damonte, E.B. Two new cytotoxic and virucidal trisulfated triterpene glycosides from the Antarctic sea cucumber Staurocucumis liouvillei. J. Nat. Prod. 2001, 64, 732–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dang, N.H.; Thanh, N.V.; Kiem, P.V.; Huongle, M.; Minh, C.V.; Kim, Y.H. Two new triterpene glycosides from the Vietnamese sea cucumber Holothuria scabra. Arch. Pharm. Res. 2007, 30, 1387–1391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, J. Overview of sea cucumber farming and sea ranching practices in China. SPC Beche-de-mer Inf. Bull. 2003, 18, 18–23. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, F.; Zhang, X.; Tong, Y.; Yi, Y.; Zhang, S.; Li, L.; Sun, P.; Lin, L.; Ding, J. PE, a new sulfated saponin from sea cucumber, exhibits anti-angiogenic and anti-tumor activities in vitro and in vivo. Cancer Biol. Ther. 2005, 4, 874–882. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaswandi, M.A.; Hing, H.L.; Sahalan, A.Z.; Farah, F.; Ridzwan, B.H.; Samsudin, M.W.; Yasin, M.S.M.; Ali, A.M. Saponin from sea cucumber Stichopus badionotus sluiter as potential cytotoxic agent on CEM-SS T-lymphoblastic cell. J. Microsc. Soc. Thail. 2004, 18, 79–84. [Google Scholar]
- Tian, F.; Zhu, C.; Zhang, X.; Xie, X.; Xin, X.; Yi, Y.; Lin, L.; Geng, M.; Ding, J. Philinopside E, a new sulfated saponin from sea cucumber, blocks the interaction between kinase insert domain-containing receptor (KDR) and αvβ3 integrin via binding to the extracellular domain of KDR. Mol. Pharmacol. 2007, 72, 545–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Dyck, S.; Gerbaux, P.; Flammang, P. Qualitative and quantitative saponin contents in five sea cucumbers from the Indian Ocean. Mar. Drugs 2010, 8, 173–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Caulier, G.; van Dyck, S.; Gerbaux, P.; Eeckhaut, I.; Flammang, P. Review of saponin diversity in sea cucumbers belonging to the family Holothuridae. SPC Beche-de-mer Inf. Bull. 2011, 31, 48–54. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, X.; Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Xue, Y.; Li, Z.; Nagao, K.; Yanagita, T.; Xue, C. Dietary saponins of sea cucumber alleviate orotic acid-induced fatty liver in rats via PPARα and SREBP-1c signalling. Lipids Health Dis. 2010, 9, 25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Karentz, D. Chemical defences of marine organisms against solar radiation exposure: UV-absorbing mycosporine-like amino acids and scytonemin. In Marine Chemical Ecology; Mc-Clintock, J.B., Baker, J., Eds.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2001; pp. 481–520. [Google Scholar]
- Shick, J.M.; Dunlap, W.C. Mycosporine-like amino acids and related gadusols: Biosynthesis, accumulation, and UV-protective functions in aquatic organisms. Annu. Rev. Physiol. 2002, 64, 223–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, B.; Lin, X.; Zhou, X.-F.; Yang, X.-W.; Liu, Y. Chemical and biological aspects of marine cosmeceuticals. In Marine Cosmeceutical: Trends and Prospects; Kim, S.-K., Ed.; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2012; pp. 11–38. [Google Scholar]
- Conde, F.R.; Churio, M.S.; Previtali, C.M. The photoprotector mechanism of mycosporine-like amino acids. Excited-state properties and photostability of porphyra-334 in aqueous solution. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B—Biol. 2000, 56, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groniger, A.; Hader, D.P. Stability of mycosporine-like amino acids. Recent Res. Dev. Photochem. Photobiol. 2000, 4, 247–252. [Google Scholar]
- Bordbar, S.; Anwar, F.; Saari, N. High-value components and bioactives from sea cucumbers for functional foods—A review. Mar. Drugs 2011, 9, 1761–1805. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McClintock, J.; Karentz, D. Mycosporine-like amino acids in 38 species of subtidal marine organisms from McMurdo Sound, Antarctica. Antarct. Sci. 1997, 9, 392–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daniel, S.; Cornelia, S.; Fred, Z. UV-A sunscreen from red algae for protection against premature skin aging. Cosmet. Toilet Manuf. Worldw. 2004, 2004, 139–143. [Google Scholar]
- Torres, A.; Enk, C.D.; Hochberg, M.; Srebnik, M. Porphyra-334, a potential natural source for UVA protective sunscreens. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2006, 5, 432–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dunlap, W.C.; Yamamoto, Y. Small-molecule antioxidants in marine organisms: Antioxidant activity of mycosporine-glycine. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. B: Biochem. Mol. Biol. 1995, 112, 105–114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De la Coba, F.; Aguilera, J.; Figueroa, F.; De Gálvez, M.; Herrera, E. Antioxidant activity of mycosporine-like amino acids isolated from three red macroalgae and one marine lichen. J. Appl. Phycol. 2009, 21, 161–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dakrory, A.I.; Fahmy, S.R.; Soliman, A.M.; Mohamed, A.S.; Amer, S.A. Protective and curative effects of the sea cucumber Holothuria atra extract against DMBA-induced hepatorenal diseases in rats. BioMed. Res. Int. 2015, 2015, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pangestuti, R.; Murniasih, T.; Putra, M.Y.; Rasyid, A.; Wibowo, J.T.; Ardiansyah, A.; Untari, F. Free radical scavenging activity of selected sea cucumber species from Mataram-Lombok, Indonesia. J. Teknol. 2016, 78, 179–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Althunibat, O.Y.; Hashim, R.B.; Taher, M.; Daud, J.M.; Ikeda, M.-A.; Zali, B. In vitro antioxidant and antiproliferative activities of three Malaysian sea cucumber species. Eur. J. Sci. Res. 2009, 37, 376–387. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, L.; Xue, C.; Chang, Y.; Xu, X.; Ge, L.; Liu, G.; Wang, Y. Structure elucidation of fucoidan composed of a novel tetrafucose repeating unit from sea cucumber Thelenota ananas. Food Chem. 2014, 146, 113–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebanks, J.; Wickett, R.; Boissy, R. Mechanisms regulating skin pigmentation: The rise and fall of complexion coloration. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2009, 10, 4066–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Peng, L.-H.; Liu, S.; Xu, S.-Y.; Chen, L.; Shan, Y.-H.; Wei, W.; Liang, W.-Q.; Gao, J.-Q. Inhibitory effects of salidroside and paeonol on tyrosinase activity and melanin synthesis in mouse B16F10 melanoma cells and ultraviolet B-induced pigmentation in guinea pig skin. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 1082–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, M.-O.; Oh, H.-G.; Park, S.-H.; Lee, H.-A.; Sul, J.-D.; Song, J.; Kim, O. Skin Whitening Effects of Sanguisorba officinalis and Stichopus japonicus. Lab. Anim. Res. 2010, 26, 127–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Husni, A.; Jeon, J.S.; Um, B.H.; Han, N.S.; Cung, D. Tyrosinase inhibition by water and ethanol extracts of far eastern sea cucumber, Stichopus japonicus. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2011, 91, 1541–1547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, S.J.; Park, S.Y.; Hong, S.-M.; Kwon, E.-H.; Lee, T.-K. Skin whitening and anti-corrugation activities of glycoprotein fractions from liquid extracts of boiled sea cucumber. Asian Pac. J. Trop. Med. 2016, 9, 1002–1006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Senevirathne, M.; Kim, S.-K. Brown Algae-Derived Compounds as Potential Cosmeceuticals; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2011; pp. 179–190. [Google Scholar]
- Lawrence, A.; Afifi, R.; Ahmed, M.; Khalifa, S.; Paget, T. Bioactivity as an options value of sea cucumbers in the Egyptian Red Sea. Conserv. Biol. 2010, 24, 217–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ibrahim, H.A.H. Antibacterial carotenoids of three Holothuria species in Hurghada, Egypt. Egypt. J. Aquat. Res. 2012, 38, 185–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarhadizadeh, N.; Afkhami, M.; Ehsanpour, M. Evaluation bioactivity of a sea cucumber, Stichopus hermanni from Persian Gulf. Eur. J. Exp. Biol. 2014, 4, 254–258. [Google Scholar]
- Enoch, S.; Leaper, D.J. Basic science of wound healing. Surgery (Oxf.) 2008, 26, 31–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masre, S.F.; Yip, G.W.; Sirajudeen, K.; Ghazali, F.C. Wound healing activity of total sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) from Stichopus vastus and Stichopus hermanni integumental tissue in rats. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2010, 6, 49–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masre, S.F.; Yip, G.W.; Sirajudeen, K.; Ghazali, F.C. Quantitative analysis of sulphated glycosaminoglycans content of Malaysian sea cucumber Stichopus hermanni and Stichopus vastus. Nat. Prod. Res. 2012, 26, 684–689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campana, R.; Scesa, C.; Patrone, V.; Vittoria, E.; Baffone, W. Microbiological study of cosmetic products during their use by consumers: health risk and efficacy of preservative systems. Lett. Appl. Microbiol. 2006, 43, 301–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).