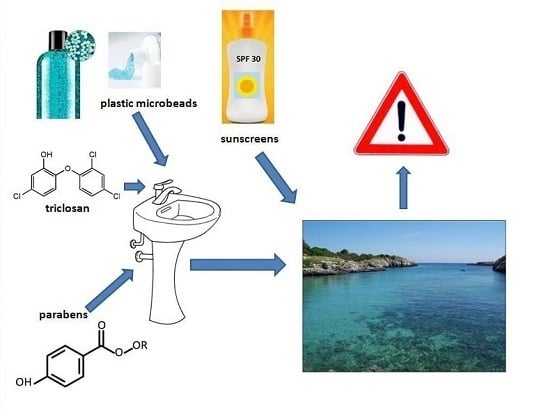
Cosmetic Ingredients as Emerging Pollutants of Environmental and Health Concern. A Mini-Review
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. UV Filters
2.1. Organic Filters
2.2. Inorganic Filters
3. Parabens
4. Triclosan
5. Plastic Microbeads
6. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on cosmetic products. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/LexUriServ/LexUriServ.do?uri=OJ:L:2009:342:0059:0209:en:PDF (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Brausch, J.M.; Rand, G.M. A review of personal care products in the aquatic environment: Environmental concentrations and toxicity. Chemosphere 2011, 82, 1518–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carballa, M.; Omil, F.; Lema, J.M.; Llompart, M.; García-Jares, C.; Rodríguez, I.; Gómez, M.; Ternes, T. Behavior of pharmaceuticals, cosmetics and hormones in a sewage treatment plant. Water Res. 2004, 38, 2918–2926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, N.; Shi, Y.; Li, W.; Xu, L.; Cai, Y. Concentrations and distribution of synthetic musks and siloxanes in sewage sludge of wastewater treatment plants in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 476–477, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campo, J.; Masiá, A.; Picó, Y.; Farré, M.; Barceló, D. Distribution and fate of perfluoroalkyl substances in Mediterranean Spanish sewage treatment plants. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 472, 912–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramos, S.; Homem, V.; Alves, A.; Santos, L. A review of organic UV-filters in wastewater treatment plants. Environ. Int. 2016, 86, 24–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Galloway, T.; Thompson, R. Microplastics—An emerging contaminant of potential concern? Integr. Environ. Assess. Manag. 2009, 3, 559–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; García-Galán, M.J.; Guerra, P.; Jelic, A.; Postigo, C.; Eljarrat, E.; Farré, M.; López de Alda, M.J.; Petrovic, M.; Barceló, D. Analysis of selected emerging contaminants in sewage sludge. Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 1263–1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ternes, T.A.; Joss, A.; Siegrist, H. Scrutinizing pharmaceuticals and personal care products in wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 392A–399A. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jardak, K.; Drogui, P.; Daghrir, R. Surfactants in aquatic and terrestrial environment: Occurrence, behavior, and treatment processes. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2016, 23, 3195–3216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Serpone, N.; Dondi, D.; Albini, A. Inorganic and organic UV filters: their role and efficacy in sunscreens and suncare products. Inorganica Chim. Acta 2007, 360, 794–802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Volkova, K.; Bilanicova, D.; Bartonova, A.; Letašová, S.; Dusinska, M. Association between environmental factors and incidence of cutaneous melanoma. Review. Environ. Health 2012, 11, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chisvert, A.; Salvador, A. UV filters in sunscreen and other cosmetics. Regulatory aspects and analytical methods. In Analysis of Cosmetic Products; Chisvert, A., Salvador, A., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2007; pp. 83–120. [Google Scholar]
- Giokas, D.L.; Salvador, A.; Chisvert, A. UV filters: From sunscreens to human body and the environment. Trends Anal. Chem. 2007, 26, 360–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsui, M.M.P.; Leung, H.W.; Wai, T.-C.; Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Liu, W.; Lam, P.K.S.; Murphy, M.B. Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk assessment of multiple classes of UV filters in surface waters from different countries. Water Res. 2014, 67, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jiang, J.-J.; Lee, C.-L.; Fang, M.-D. Emerging organic contaminants in coastal waters: anthropogenic impact, environmental release and ecological risk. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2014, 85, 391–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez Rodríguez, A.; Rodrigo Sanz, M.; Betancort Rodríguez, J.R. Occurrence of eight UV filters in beaches of Gran Canaria (Canary Islands). An approach to environmental risk assessment. Chemosphere 2015, 131, 85–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ekpeghere, K.I.; Kim, U.-J.; O, S.-H.; Kim, H.-Y.; Oh, J.-E. Distribution and seasonal occurrence of UV filters in rivers and wastewater treatment plants in Korea. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 542, 121–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poiger, T.; Buser, H.R.; Balmer, M.E.; Bergqvist, P.A.; Müller, M.D. Occurrence of UV filter compounds from sunscreens in surface waters: regional mass balance in two Swiss lakes. Chemosphere 2004, 55, 951–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmer, M.E.; Buser, H.R.; Muller, M.D.; Poiger, T. Occurrence of some organic UV filters in wastewater, in surface waters, and in fish from Swiss lakes. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2005, 39, 953–962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amine, H.; Gomez, E.; Halwani, J.; Casella, C.; Fenet, H. UV filters, ethylhexyl methoxycinnamate, octocrylene and ethylhexyl dimethyl PABA from untreated wastewater in sediment from Eastern Mediterranean river transition and coastal zones. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2012, 64, 2435–2442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barón, E.; Gago-Ferrero, P.; Gorga, M.; Rudolph, I.; Mendoza, G.; Zapata, A.M.; Díaz-Cruz, S.; Barra, R.; Ocampo-Duque, W.; Páez, M.; et al. Occurrence of hydrophobic organic pollutants (BFRs and UV-filters) in sediments from South America. Chemosphere 2013, 92, 309–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kameda, Y.; Kimura, K.; Miyazak, M. Occurrence and profiles of organic sun-blocking agents in surface waters and sediments in Japanese rivers and lakes. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1570–1576. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langford, K.H.; Reid, M.J.; Fjeld, E.; Øxnevad, S.; Thomas, K.V. Environmental occurrence and risk of organic UV filters and stabilizers in multiple matrices in Norway. Environ. Int. 2015, 80, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Quiles, D.; Tovar-Sánchez, A. Are sunscreens a new environmental risk associated with coastal tourism? Environ. Int. 2015, 83, 158–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago-Ferrero, P.; Alonso, M.B.; Bertozzi, C.P.; Marigo, J.; Barbosa, L.; Cremer, M.; Secchi, E.R.; Azevedo, A.; Lailson-Brito, J., Jr.; Torres, J.P.M.; et al. First determination of UV filters in marine mammals. Octocrylene levels in Franciscana dolphins. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 5619–5625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachelot, M.; Munaron, D.; Le Gall, P.; Casellas, C.; Fenet, H.; Gomez, E. Organic UV filter concentrations in marine mussels from French coastal regions. Sci. Tot. Environ. 2012, 420, 273–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fent, K.; Zenker, A.; Rapp, M. Widespread occurrence of estrogenic UV-filters in aquatic ecosystems in Switzerland. Environ. Pollut. 2010, 158, 1817–1824. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago-Ferrero, P.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. UV filters bioaccumulation in fish from Iberian river basins. Sci. Total Environ. 2015, 518–519, 518–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, X.; Li, Z.; Chen, W.; Qiang, L.; Xia, J.; Chen, M.; Zhu, L.; Alvarez, P.J.J. Fate of TiO2 nanoparticles entering sewage treatment plants and bioaccumulation in fish in the receiving streams. NanoImpact 2016, 3–4, 96–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sánchez-Quiles, D.; Tovar-Sánchez, A. Sunscreens as a source of hydrogen peroxide production in coastal waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2014, 48, 9037–9042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aziza, I.H.H.; Ingrid, B.; Khémary, U.; Aghleb, B.; Gonzalez, C. Estrogenic activity and parabens occurrence in three Tunisian wastewater treatment plants. Eur. J. Water Qual. 2011, 42, 91–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Yu, Y.; Tang, C.; Tan, J.; Huang, Q.; Wang, Z. Occurrence of steroid estrogens, endocrine-disrupting phenols, and acid pharmaceutical residues in urban riverine water of the Pearl River Delta, South China. Sci. Total Environ. 2008, 397, 158–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kasprzyk-Hordern, B.; Dinsdale, R.M.; Guwy, A.J. The occurrence of pharmaceuticals, personal care products, endocrine disruptors and illicit drugs in surface water in South Wales, UK. Water Res. 2008, 42, 3498–3518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yamamoto, H.; Tamura, I.; Hirata, Y.; Kato, J.; Kagota, K.; Katsuki, S.; Yamamoto, A.; Kagami, Y.; Tatarazako, N. Aquatic toxicity and ecological risk assessment of seven parabens: Individual and additive approach. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 410–411, 102–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kimura, K.; Kameda, Y.; Yamamoto, H.; Nakada, N.; Tamura, I.; Miyazaki, M.; Masunaga, S. Occurrence of preservatives and antimicrobials in Japanese rivers. Chemosphere 2014, 107, 393–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.-W.; Ramaswamy, B.R.; Chang, K.-H.; Isobe, T.; Tanabe, S. Multiresidue analytical method for the determination of antimicrobials, preservatives, benzotriazole UV stabilizers, flame retardants and plasticizers in fish using ultra high performance liquid chromatography coupled with tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. A 2011, 1218, 3511–3520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ramaswamy, B.R.; Kim, J.-W.; Isobe, T.; Chang, K.-H.; Amano, A.; Miller, T.W.; Siringan, F.P.; Tanabe, S. Determination of preservative and antimicrobial compounds in fish from Manila Bay, Philippines using ultra high performance liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry, and assessment of human dietary exposure. J. Hazard. Mater. 2011, 192, 1739–1745. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Kannan, K. Accumulation profiles of parabens and their metabolites in fish, black bear, and birds, including bald eagles and albatrosses. Environ. Int. 2016, 94, 546–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, J.; Sasaki, N.; Elangovan, M.; Diamond, G.; Kannan, K. Elevated accumulation of parabens and their metabolites in marine mammals from the United States coastal waters. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2015, 49, 12071–12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carmona, E.; Andreu, V.; Picó, Y. Occurrence of acidic pharmaceuticals and personal care products in Turia River Basin: from waste to drinking water. Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 484, 53–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gasperi, J.; Geara, D.; Lorgeoux, C.; Bressy, A.; Zedek, S.; Rocher, V.; El Samrani, A.; Chebbo, G.; Moilleron, R. First assessment of triclosan, triclocarban and paraben mass loads at a very large regional scale: Case of Paris conurbation (France). Sci. Total Environ. 2014, 493, 854–861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, Z.-F.; Ying, G.-G.; Liu, Y.-S.; Zhang, Q.-Q.; Zhao, J.-L.; Liu, S.-S.; Chen, J.; Peng, F.-J.; Lai, H.-J.; Pan, C.-G. Triclosan as a surrogate for household biocides: An investigation into biocides in aquatic environments of a highly urbanized region. Water Res. 2014, 58, 269–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yueh, M.-F.; Tukey, R.H. Triclosan: a widespread environmental toxicant with many biological effects. Annu. Rev. Pharmacol. Toxicol. 2016, 56, 251–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roberts, J.; Kumar, A.; Du, J.; Hepplewhite, C.; Ellis, D.J.; Christy, A.G.; Beavis, S.G. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in Australia’s largest inland sewage treatment plant, and its contribution to a major Australian river during high and low flow. Sci. Total Environ. 2016, 541, 1625–1637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kolpin, D.W.; Skopec, M.; Meyer, M.T.; Furlong, E.T.; Zaugg, S.D. Urban contamination of pharmaceuticals and other organic wastewater contaminants to streams during differing flow conditions. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 328, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Benotti, M.J.; Trenholm, R.A.; Vanderford, B.J.; Holady, J.C.; Stanford, B.D.; Snyder, S.A. Pharmaceuticals and endocrine disrupting compounds in US drinking water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2009, 43, 597–603. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dougherty, J.A.; Swarzenski, P.W.; Pinicola, R.S.; Reinhard, M. Occurrence of herbicides and pharmaceuticals and personal care products in surface water and groundwater around Liberty Bay, Puget Sound, Washington. J. Environ. Qual. 2010, 39, 1173–1180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, J.W.; Jang, H.-S.; Kim, J.-G.; Ishibashi, H.; Hirano, M.; Nasu, K.; Ichikawa, N.; Takao, Y.; Shinohara, R.; Arizono, K. Occurrence of pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in surface water from Mankyung River, South Korea. J. Health Sci. 2009, 55, 249–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Coogan, M.A.; Edziyie, R.E.; La Point, T.W.; Venables, B.J. Algal bioaccumulation of triclocarban, triclosan, and methyl-triclosan in a North Texas wastewater treatment plant receiving stream. Chemosphere 2007, 67, 1911–1918. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kookana, R.S.; Shareef, A.; Fernandes, M.B.; Hoare, S.; Gaylard, S.; Kumar, A. Bioconcentration of triclosan and methyl-triclosan in marine mussels (Mytilus galloprovincialis) under laboratory conditions and in metropolitan waters of Gulf St Vincent, South Australia. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2013, 15, 66–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Browne, M.A.; Dissanayake, A.; Galloway, T.S.; Lowe, D.M. Ingested microscopic plastic translocates to the circulatory system of the mussel, Mytilus edulis. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2008, 42, 5026–5031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carr, S.A.; Liu, J.; Tesoro, A.G. Transport and fate of microplastic particles in wastewater treatment plants. Water Res. 2016, 91, 174–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vandermeersch, G.; Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Janssen, C.R.; Marques, A.; Granby, K.; Fait, G.; Kotterman, M.J.J.; Diogène, J.; Bekaert, K.; Robbens, J.; Devriese, L. A critical view on microplastic quantification in aquatic organisms. Environ. Res. 2015, 143, 46–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Isobe, A.; Uchiyama-Matsumoto, K.; Uchida, K.; Tokai, T. Microplastics in the Southern Ocean. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2017, 14, 623–626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davison, P.; Asch, R.G. Plastic ingestion by mesopelagic fishes in the North Pacific Subtropical Gyre. Mar. Ecol. Prog. Ser. 2011, 432, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Franeker, J.A.; Blaize, C.; Danielsen, J.; Fairclough, K.; Gollan, J.; Guse, N.; Hansen, P.-L.; Heubeck, M.; Jensen, J.-K.; Le Guillou, G.; et al. Monitoring plastic ingestion by the northern fulmar Fulmarus glacialis in the North Sea. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 2609–2615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, P.-P.; Shi, Z.-G.; Yu, Q.-W.; Feng, Y.-Q. A new device for magnetic stirring-assisted dispersive liquid–liquid microextraction of UV filters in environmental water samples. Talanta 2011, 83, 1711–1715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jurado, A.; Gago-Ferrero, P.; Vàzquez-Suñé, E.; Carrera, J.; Pujades, E.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Urban groundwater contamination by residues of UV filters. J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 271, 141–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsui, M.M.P.; Leung, H.W.; Kwan, B.K.Y.; Ng, K.-Y.; Yamashita, N.; Taniyasu, S.; Lam, P.K.S.; Murphy, M.B. Occurrence, distribution and ecological risk assessment of multiple classes of UV filters in marine sediments in Hong Kong and Japan. J. Hazard. Mater. 2015, 292, 180–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gago-Ferrero, P.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Fast pressurized liquid extraction with in-cell purification analysis by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry for the determination of UV filters and their degradation products in sediments. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2011, 400, 2195–2204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kaiser, D.; Wappelhorst, O.; Oekten, M.; Oehlmann, M. Occurrence of widely used organic UV filters in lake and river sediments. Environ. Chem. 2012, 9, 139–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Choi, K. Occurrences, toxicities, and ecological risks of benzophenone-3, a common component of organic sunscreen products: a mini-review. Environ. Int. 2014, 70, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oie, C.S.I.; Albaugh, C.E.; Peyton, B.M. Benzoate and salicylate degradation by Halomonas campisalis, an alkaliphilic and moderately halophilic microorganism. Water Res. 2007, 41, 1235–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teo, T.L.L.; Coleman, H.M.; Khan, S.J. Chemical contaminants in swimming pools: Occurrence, implications and control. Environ. Int. 2015, 76, 16–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zwiener, C.; Richardson, S.D.; DeMarini, D.; Frimmel, F.H. Drowning in disinfection byproducts? Assessing swimming pool water. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2007, 41, 363–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Díaz-Cruz, M.S.; Barceló, D. Chemical analysis and ecotoxicological effects of organic UV-absorbing compounds in aquatic ecosystems. Trends Anal. Chem. 2009, 28, 708–717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lakind, J.S.; Richardson, S.D.; Blount, B.C. The good, the bad, and the volatile: can we have both healthy pools and healthy people? Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 3205–3210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kockler, J.; Oelgemöller, M.; Robertson, S.; Glass, B.D. Photostability of sunscreens. J. Photoch. Photobio. C 2012, 13, 91–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, A.J.M.; Miranda, M.S.; Esteves da Silva, J.C.G. The degradation products of UV filters in aqueous and chlorinated aqueous solutions. Water Res. 2012, 46, 3167–3176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Danovaro, R.; Bongiorni, L.; Corinaldesi, C.; Giovannelli, D.; Damiani, E.; Astolfi, P.; Greci, L.; Pusceddu, A. Sunscreens cause coral bleaching by promoting viral infections. Environ. Health Perspect. 2008, 116, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kunz, P.Y.; Galicia, H.F.; Fent, K. Comparison of in vitro and in vivo estrogenic activity of UV filters in fish. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 90, 349–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Faass, O.; Schlumpf, M.; Reolon, S.; Henseler, M.; Maerkel, K.; Durrer, S.; Lichtensteiger, W. Female sexual behavior, estrous cycle and gene expression in sexually dimorphic brain regions after pre- and postnatal exposure to endocrine active UV filter. Neurotoxicology 2009, 30, 249–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schlumpf, M.; Kypke, K.; Vökt, C.C.; Birchler, M.; Durrer, S.; Faass, O.; Ehnes, C.; Fuetsch, M.; Gaille, C.; Henseler, M.; et al. Endocrine active UV filters: developmental toxicity and exposure through breast milk. Chimia 2008, 62, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2016/1143 of 13 July 2016 amending Annex VI to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council on cosmetic products. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32016R1143&from=EN (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Commission Regulation (EU) 2016/621 of 21 April 2016, amending Annex VI to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council on cosmetic products. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32016R0621&from=EN (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Botta, C.; Labille, J.; Auffan, M.; Borschneck, D.; Miche, H.; Cabié, M.; Masion, A.; Rose, J.; Bottero, J.-Y. TiO2-based nanoparticles released in water from commercialized sunscreens in a life-cycle perspective: Structures and quantities. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1543–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lewicka, Z.A.; Yu, W.W.; Oliva, B.L.; Contreras, E.Q.; Colvin, V.L. Photochemical behavior of nanoscale TiO2 and ZnO sunscreen ingredients. J. Photoch. Photobio. A 2013, 263, 24–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buchalska, M.; Kras, G.; Oszajca, M.; Łasocha, W.; Macyk, W. Singlet oxygen generation in the presence of titanium dioxide materials used as sunscreens in suntan lotions. J. Photoch. Photobio. A 2010, 213, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barker, P.J.; Branch, A. The interaction of modern sunscreen formulations with surface coatings. Prog. Org. Coat. 2008, 62, 313–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Auffan, M.; Pedeutour, M.; Rose, J.; Masion, A.; Ziarelli, F.; Borschneck, D.; Chaneac, C.; Botta, C.; Chaurand, P.; Labille, J.; et al. Structural degradation at the surface of a TiO2-based nanomaterial used in cosmetics. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2010, 44, 2689–2694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menard, A.; Drobne, D.; Jemec, A. Ecotoxicity of nanosized TiO2. Review of in vivo data. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 677–684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, D.; Fang, T.; Yu, L.; Sima, X.; Zhu, W. Effects of nano-scale TiO2, ZnO and their bulk counterparts on zebrafish: Acute toxicity, oxidative stress and oxidative damage. Sci. Total Environ. 2011, 409, 1444–1452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaise, C.; Gagne, F.; Ferard, J.F.; Eullaffoy, P. Ecotoxicity of selected nano-materials to aquatic organisms. Environ. Toxicol. 2008, 23, 591–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Brennan, A.; Diamond, S.A. Phototoxicity of TiO2 nanoparticles under solar radiation to two aquatic species: Daphnia magna and Japanese medaka. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 1621–1629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, Z.; Castro, V.L.; Feitosa, L.O.; Lima, R.; Jonsson, C.M.; Maia, A.H.; Fraceto, L.F. Fish exposure to nano-TiO2 under different experimental conditions: Methodological aspects for nanoecotoxicology investigations. Sci. Total Environ. 2013, 463–464, 647–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hund-Rinke, K.; Simon, M. Ecotoxic effect of photocatalytic active nanoparticles (TiO2) on algae and daphnids. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2006, 13, 225–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wages, M.; Cox, S.B.; Maul, J.D.; Li, Y.; Barnes, M.; Hope-Weeks, L.; Cobb, G.P. Effect of titanium dioxide nanomaterials and ultraviolet light coexposure on African clawed frogs (Xenopus laevis). Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2012, 31, 176–183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Clemente, Z.; Castro, V.L.; Moura, M.A.M.; Jonsson, C.M.; Fraceto, L.F. Toxicity assessment of TiO2 nanoparticles in zebrafish embryos under different exposure conditions. Aquat. Toxicol. 2014, 147, 129–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, X.; Wang, S.; Wu, Y.; You, H.; Lv, L. Acute ZnO nanoparticles exposure induces developmental toxicity, oxidative stress and DNA damage in embryo-larval zebrafish. Aquat. Toxicol. 2013, 136–137, 49–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, T.-H.; Lin, C.-C.; Meng, P.-J. Zinc oxide nanoparticles alter hatching and larval locomotor activity in zebrafish (Danio rerio). J. Hazard. Mater. 2014, 277, 134–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Suman, T.Y.; Radhika Rajasree, S.R.; Kirubagaran, R. Evaluation of zinc oxide nanoparticles toxicity on marine algae Chlorella vulgaris through flow cytometric, cytotoxicity and oxidative stress analysis. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2015, 113, 23–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, J.; Tan, L.; Chen, X. Toxic effects of nano-ZnO on marine microalgae Skeletonema costatum: Attention to the accumulation of intracellular Zn. Aquat. Toxicol. 2016, 178, 158–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Manzo, S.; Miglietta, M.L.; Rametta, G.; Buono, S.; Di Francia, G. Embryotoxicity and spermiotoxicity of nanosized ZnO for Mediterranean sea urchin Paracentrotus lividus. J. Hazard. Mater. 2013, 254–255, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahru, A.; Dubourguier, H.-C. From ecotoxicology to nanoecotoxicology. Toxicology 2010, 269, 105–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ma, H.; Kabengi, N.J.; Bertsch, P.M.; Unrine, J.M.; Glenn, T.C.; Williams, P.L. Comparative phototoxicity of nanoparticulate and bulk ZnO to a free-living nematode Caenorhabditis elegans: The importance of illumination mode and primary particle size. Environ. Pollut. 2011, 159, 1473–1480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Chang, Y.; Chen, Y. The impact of ZnO nanoparticle aggregates on the embryonic development of zebrafish (Danio rerio). Nanotechnology 2009, 20, 195103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeon, S.; Kim, E.; Lee, J.; Lee, S. Potential risks of TiO2 and ZnO nanoparticles released from sunscreens into outdoor swimming pools. J. Hazard. Mater. 2016, 317, 312–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Błędzka, D.; Gromadzińska, J.; Wąsowicz, W. Parabens. From environmental studies to human health. Environ. Int. 2014, 67, 27–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baardseth, P.; Russwurm, H., Jr. Content of some organic acids in cloudberry (Rubus chamaemorus L.). Food Chem. 1978, 3, 43–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, X.; Adachi, K.; Chen, C.; Kasai, H.; Kanoh, K.; Shizuri, Y.; Misawa, N. Discovery of a marine bacterium producing 4-hydroxybenzoate and its alkyl esters, parabens. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2006, 72, 5556–5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Regulation (EU) No 358/2014 amending Annexes II and V to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on cosmetic products. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32014R0358&from=EN (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Regulation (EU) No 1004/2014 amending Annex V to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 30 November 2009 on cosmetic products. Available online: http://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32014R1004&from=EN (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Haman, C.; Dauchy, X.; Rosin, C.; Munoz, J.-F. Occurrence, fate and behavior of parabens in aquatic environments: A review. Water Res. 2015, 68, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Mariño, I.; Quintana, J.B.; Rodríguez, I.; Cela, R. Evaluation of the occurrence and biodegradation of parabens and halogenated by-products in wastewater by accurate mass liquid chromatography-quadrupole-time-of-flight-mass spectrometry (LC-QTOF-MS). Water Res. 2011, 45, 6770–6780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Canosa, P.; Rodríguez, I.; Rubí, E.; Negreira, N.; Cela, R. Formation of halogenated by-products of parabens in chlorinated water. Anal. Chim. Acta 2006, 575, 106–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, K.W.; Braun, J.M.; Williams, P.L.; Ehrlich, S.; Correia, K.F.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Ford, J.; Keller, M.; Meeker, J.D.; et al. Predictors and variability of urinary paraben concentrations in men and women, including before and during pregnancy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2012, 120, 1538–1543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philippat, C.; Wolff, M.S.; Calafat, A.M.; Ye, X.; Bausell, R.; Meadows, M.; Stone, J.; Slama, R.; Engel, S.M. Prenatal exposure to environmental phenols: concentrations in amniotic fluid and variability in urinary concentrations during pregnancy. Environ. Health Perspect. 2013, 121, 1225–1231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hines, E.P.; Mendola, P.; von Ehrenstein, O.S.; Ye, X.; Calafat, A.M.; Fenton, S.E. Concentrations of environmental phenols and parabens in milk, urine and serum of lactating North Carolina women. Reprod. Toxicol. 2015, 54, 120–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moos, K.; Koch, H.M.; Angerer, J.; Apel, P.; Schröter-Kermani, C.; Brüning, T.; Kolossa-Gehring, M. Parabens in 24 h urine samples of the German Environmental Specimen Bank from 1995 to 2012. Int. J. Hyg. Environ. Health 2015, 218, 666–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.; Asimakopoulos, A.G.; Kannan, K. Accumulation of 19 environmental phenolic and xenobiotic heterocyclic aromatic compounds in human adipose tissue. Environ. Int. 2015, 78, 45–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valle-Sistac, J.; Molins-Delgado, D.; Díaz, M.; Ibáñez, L.; Barceló, D.; Díaz-Cruz, M.S. Determination of parabens and benzophenone-type UV filters in human placenta. First description of the existence of benzyl paraben and benzophenone-4. Environ. Int. 2016, 88, 243–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Wu, C.; Lu, D.; Jiang, S.; Liang, W.; Chang, X.; Xu, H.; Wang, G.; Zhou, Z. Urinary paraben concentrations and their associations with anthropometric measures of children aged 3 years. Environ. Pollut. 2017, 222, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbre, P.D.; Aljarrah, A.; Miller, W.R.; Coldham, N.G.; Sauer, M.J.; Pope, G.S. Concentrations of parabens in human breast tumours. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2004, 24, 5–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barr, L.; Metaxas, G.; Harbach, C.A.J.; Savoy, L.A.; Darbre, P.D. Measurement of paraben concentrations in human breast tissue at serial locations across the breast from axilla to sternum. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2012, 32, 219–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbre, P.D.; Harvey, P.W. Paraben esters: review of recent studies of endocrine toxicity, absorption, esterase and human exposure, and discussion of potential human health risks. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2008, 28, 561–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Routledge, E.J.; Parker, J.; Odum, J.; Ashby, J.; Sumpter, J.P. Some alkyl hydroxy benzoate preservatives (parabens) are estrogenic. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 1998, 153, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darbre, P.D. Environmental oestrogens, cosmetics and breast cancer. Best Pract. Res. Clin. Endocrinol. Metab. 2006, 20, 121–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- National Cancer Institute Fact Sheets. Antiperspirants/Deodorants and Breast Cancer. 2008. Available online: http://www.cancer.gov/about-cancer/causes-prevention/risk/myths/antiperspirants-fact-sheet (accessed on 9 August 2016).
- Witorsch, R.J.; Thomas, J.A. Personal care products and endocrine disruption: A critical review of the literature. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2010, 3, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scientific Committee on Consumer Safety. Opinion on Parabens. 2011 SCCS/1348/10. Available online: https://ec.europa.eu/health/scientific_committees/consumer_safety/docs/sccs_o_069.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Nohynek, G.J.; Borgert, C.J.; Dietrich, D.; Rozman, K.K. Endocrine disruption: Fact or urban legend? Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 223, 295–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pan, S.; Yuan, C.; Tagmount, A.; Rude, R.A.; Ackerman, J.M.; Yaswen, P.; Vulpe, C.D.; Leitman, D.C. Parabens and human epidermal growth factor receptor ligand cross-talk in breast cancer cells. Environ. Health Perspect. 2016, 124, 563–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, L.; Yu, T.; Guo, J.; Zhang, Z.; Hu, Y.; Xiao, X.; Sun, Y.; Xiao, H.; Li, J.; Zhu, D.; et al. The estrogenicity of methylparaben and ethylparaben at doses close to the acceptable daily intake in immature Sprague-Dawley rats. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 25173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dann, A.B.; Hontela, A. Triclosan: environmental exposure, toxicity and mechanisms of action. J. Appl. Toxicol. 2011, 31, 285–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, J.-L.; Ying, G.-G.; Liu, Y.-S.; Chen, F.; Yang, J.-F.; Wang, L. Occurrence and risks of triclosan and triclocarban in the Pearl River system, South China: from source to the receiving environment. J. Hazard. Mater. 2010, 179, 215–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.-L.; Wong, M.-H. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs): A review on environmental contamination in China. Environ. Int. 2013, 59, 208–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chalew, T.E.; Halden, R.U. Environmental exposure of aquatic and terrestrial biota to triclosan and triclocarban. J. Am. Water Works Assoc. 2009, 45, 4–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Prosser, R.S.; Lissemore, L.; Topp, E.; Sibley, P.K. Bioaccumulation of triclosan and triclocarban in plants grown in soils amended with municipal dewatered biosolids. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2014, 33, 975–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Higgins, C.P.; Paesani, Z.J.; Chalew, T.E.; Halden, R.U.; Hundal, L.S. Persistence of triclocarban and triclosan in soils after land application of biosolids and bioaccumulation in Eisenia foetida. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2011, 30, 556–563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coogan, M.A.; La Point, T.W. Snail bioaccumulation of triclocarban, triclosan, and methyltriclosan in a North Texas, USA, stream affected by wastewater treatment plant runoff. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1788–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Palenske, N.M.; Nallani, G.C.; Dzialowski, E.M. Physiological effects and bioconcentration of triclosan on amphibian larvae. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. C 2010, 152, 232–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Houtman, C.J.; Van Oostveen, A.M.; Brouwer, A.; Lamoree, M.H.; Legler, J. Identification of estrogenic compounds in fish bile using bioassay-directed fractionation. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 6415–6423. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fair, P.A.; Lee, H.B.; Adams, J.; Darling, C.; Pacepavicius, G.; Alaee, M.; Bossart, G.D.; Henry, N.; Muir, D. Occurrence of triclosan in plasma of wild Atlantic bottlenose dolphins (Tursiops truncatus) and in their environment. Environ. Pollut. 2009, 157, 2248–2254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balmer, M.E.; Poiger, T.; Droz, C.; Romanin, K.; Bergqvist, P.-A.; Müller, M.D.; Buser, H.-R. Occurrence of methyl triclosan, a transformation product of the bactericide triclosan, in fish from various lakes in Switzerland. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2004, 38, 390–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, L.-H.; Ying, G.-G.; Su, H.-C.; Stauber, J.; Adams, M.S.; Binet, M.T. Growth-inhibiting effects of 12 antibacterial agents and their mixtures on the freshwater microalga Pseudokirchneriella subcapitata. Environ. Toxicol. Chem. 2008, 27, 1201–1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Drury, B.; Scott, J.; Rosi-Marshall, E.J.; Kelly, J.J. Triclosan exposure increases triclosan resistance and influences taxonomic composition of benthic bacterial communities. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 8923–8930. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, R.; Domingues, I.; Koppe, G.C.; Soares, A.M. Effects of triclosan on zebrafish early-life stages and adults. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2009, 16, 679–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crofton, K.M.; Paul, K.B.; DeVito, M.J.; Hedge, J.M. Short-term in vivo exposure to the water contaminant triclosan: evidence for disruption of thyroxine. Environ. Toxicol. Pharmacol. 2007, 24, 194–197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allmyr, M.; Adolfsson-Erici, M.; McLachlan, M.S.; Sandborgh-Englund, G. Triclosan in plasma and milk from Swedish nursing mothers and their exposure via personal care products. Sci. Total Environ. 2006, 372, 87–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boyd, G.R.; Reemtsma, H.; Grimm, D.A.; Mitra, S. Pharmaceuticals and personal care products (PPCPs) in surface and treated waters of Louisiana, USA and Canada. Sci. Total Environ. 2003, 311, 135–149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stackelberg, P.E.; Furlong, E.T.; Meyer, M.T.; Zaugg, S.D.; Hendersen, A.K.; Reissman, D.B. Persistence of pharmaceutical and other organic wastewater contaminants in a conventional drinking-water-treatment plant. Sci. Total Environ. 2004, 329, 99–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dhillon, G.S.; Kaur, S.; Pulicharla, R.; Brar, S.K.; Cledón, M.; Verma, M.; Surampalli, R.Y. Triclosan: current status, occurrence, environmental risks and bioaccumulation potential. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2015, 12, 5657–5684. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moore, C.J. Synthetic polymers in the marine environment: A rapidly increasing, long term threat. Environ. Res. 2008, 108, 131–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fendall, L.S.; Sewell, M.A. Contributing to marine pollution by washing your face: Microplastics in facial cleanser. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2009, 58, 1225–1228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Halsband, C.; Galloway, T. Microplastics as contaminants in the marine environment: A review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 2588–2597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouin, T.; Avalos, J.; Brunning, I.; Brzuska, K.; de Graaf, J.; Kaumanns, J.; Konong, T.; Meyberg, M.; Rettinger, K.; Schlatter, H.; et al. Use of micro-plastic beads in cosmetic products in Europe and their estimated emissions to the North Sea environment. SOFW J. 2015, 3, 1–33. [Google Scholar]
- Napper, I.E.; Bakir, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C. Characterisation, quantity and sorptive properties of microplastics extracted from cosmetics. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2015, 99, 178–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Derraik, J.G.B. The pollution of the marine environment by plastic debris: a review. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2002, 44, 842–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Devriese, L.; Galgani, F.; Robbens, J.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics in sediments: A review of techniques, occurrence and effects. Mar. Environ. Res. 2015, 111, 5–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gouin, T.; Roche, N.; Lohmann, R.; Hodges, G. A thermodynamic approach for assessing the environmental exposure of chemical absorbed to microplastic. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2011, 45, 1466–1472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mato, Y.; Isobe, T.; Takada, H.; Kanehiro, H.; Ohtake, C.; Kaminuma, T. Plastic resin pellets as a transport medium for toxic chemicals in the marine environment. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2001, 35, 318–324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teuten, E.L.; Saquing, J.M.; Knappe, D.R.U.; Morton, A.M.A.; Jonsson, S.; Björn, A.; Rowland, S.J.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S.; Yamashita, R.; et al. Transport and release of chemicals from plastics to the environment and to wildlife. Philos. Trans. R. Soc. Lond. B Biol. Sci. 2009, 364, 2027–2045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Von Moos, N.; Burkhardt-Holm, P.; Koehler, A. Uptake and effects of micro-plastics on cells and tissues of the blue mussel Mytilus edulis L. after experimental exposure. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2012, 46, 11327–11335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Cauwenberghe, L.; Janssen, C.R. Microplastics in bivalves cultured for human consumption. Environ. Pollut. 2014, 193, 65–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boerger, C.M.; Lattin, G.L.; Moore, S.L.; Moore, C.J. Plastic ingestion by planktivorous fishes in the North Pacific Central Gyre. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2010, 60, 2275–2278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cole, M.; Lindeque, P.; Fileman, E.; Halsband, C.; Goodhead, R.; Moger, J.; Galloway, T.S. Microplastic ingestion by zooplankton. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2013, 47, 6646–6655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wright, S.L.; Thompson, R.C.; Galloway, T.S. The physical impacts of microplastics on marine organisms: A review. Environ. Pollut. 2013, 178, 483–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sussarellu, R.; Suquet, M.; Thomas, Y.; Lambert, C.; Fabioux, C.; Pernet, M.E.J.; Le Goïc, N.; Quillien, V.; Mingant, C.; Epelboin, Y.; et al. Oyster reproduction is affected by exposure to polystyrene microplastics. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2016, 113, 2430–2435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eriksson, C.; Burton, H. Origins and biological accumulation of small plastic particles in fur seals from Macquarie Islands. Ambio 2003, 32, 380–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Andrady, A.L. Microplastics in the marine environment. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2011, 62, 1596–1605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wardrop, P.; Shimeta, J.; Nugegoda, D.; Morrison, P.D.; Miranda, A.; Tang, M.; Clarke, B.O. Chemical pollutants sorbed to ingested microbeads from personal care products accumulate in fish. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2016, 50, 4037–4044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Council of European Union 2014. Note 16263/14. Elimination of micro-plastics in products – an urgent need. Available online: http://register.consilium.europa.eu/doc/srv?l=EN&f=ST%2016263%202014%20INIT (accessed on 10 March 2017).
- Cosmetics Europe 2015. Available online: https://www.cosmeticseurope.eu/news-a-events/news/822-cosmetics-europe-issues-a-recommendation-on-solid-plastic-particles-plastic-micro-particles.html (accessed on 3 April 2017).
- Congress of the United States of America 2015. Microbead-Free Waters Act of 2015. Available online: https://www.congress.gov/114/plaws/publ114/PLAW-114publ114.pdf (accessed on 10 March 2017).
© 2017 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Juliano, C.; Magrini, G.A. Cosmetic Ingredients as Emerging Pollutants of Environmental and Health Concern. A Mini-Review. Cosmetics 2017, 4, 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4020011
Juliano C, Magrini GA. Cosmetic Ingredients as Emerging Pollutants of Environmental and Health Concern. A Mini-Review. Cosmetics. 2017; 4(2):11. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4020011
Chicago/Turabian StyleJuliano, Claudia, and Giovanni Antonio Magrini. 2017. "Cosmetic Ingredients as Emerging Pollutants of Environmental and Health Concern. A Mini-Review" Cosmetics 4, no. 2: 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4020011
APA StyleJuliano, C., & Magrini, G. A. (2017). Cosmetic Ingredients as Emerging Pollutants of Environmental and Health Concern. A Mini-Review. Cosmetics, 4(2), 11. https://doi.org/10.3390/cosmetics4020011