Abstract
Recent data suggest that dandruff might be associated with dysbiosis of the scalp microbiome. This mini review summarizes the microbiome changes seen with the dandruff condition, as well as different solutions for dandruff control and their effects on the scalp microbiome in relation to in vivo efficacy. Since zinc pyrithione has been banned from cosmetics in the EU, the medium-chain fatty acid ester propanediol caprylate is a new option, in addition to the remaining conventional ingredients: piroctone olamine, climbazole, and salicylic acid. The ester is rapidly cleaved by Malassezia hydrolases in the external milieu, thereby releasing active caprylic acid. In addition to its auto-regulatory effects on Malassezia, propanediol caprylate is also able to influence the bacterial microbiota towards a healthier scalp microbiome. In vivo data have shown an efficacy comparable to climbazole and piroctone olamine. In vivo additive and synergistic effects in different combinations allow reductions in the concentration of conventional agents. Surprisingly, a new effect of a lasting healthier scalp has been identified in connection with ester use, in contrast to the usual return of dandruff experienced upon the discontinuation of anti-dandruff shampoo with conventional actives. We also report on new data from an unpublished comparative study on two propanediol monoesters confirming the long-lasting effect.
1. Introduction
Dandruff, a common scalp condition affecting around approximately 50% of the global population, is characterized by itchy, flaky skin with white or yellowish scales [1]. Both dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis (SD) are considered as a continuous spectrum of the same disease, differing only in locality and severity. Although their exact cause is not fully understood, they are suspected to result from various intrinsic and environmental factors, including individual susceptibility, sebaceous secretion, immune response, and the activity of microorganisms [1,2,3].
Lipophilic Malassezia yeasts have long been regarded as a key causative factor. However, recent advancements in sequencing and computational technology have enabled a more comprehensive evaluation of the scalp microbiome, with indications that the overall relative composition, as well as the interactions between individual components, may be of importance in dandruff development. This article summarizes current interventions and treatments, with a particular focus on medium-chain fatty acid esters as a novel option for dandruff control. It is worth noting that many commercially available anti-dandruff products combine multiple active ingredients to address the multifaceted nature of the condition, often targeting both fungal activity and scalp inflammation [4,5,6,7,8,9,10,11].
2. Dandruff—A Fungal Skin Condition?
A connection between fungi and SD/dandruff was first proposed by Louis-Charles Malassez in 1874 [12]. Lipophilic yeasts of the genus Malassezia (previously Pityrosporum) are commensals of the microbiota found on normal skin of 75% to 98% of healthy adults. They are obligatory lipid-dependent, and metabolize fatty compounds in sebum, giving them a special ecological niche in lipid-rich anatomical regions [13].
Several lines of evidence suggest a pathogenic role for yeasts of the genus Malassezia in SD and dandruff [13,14,15,16]. A direct causal link has been proposed based on the distribution of Malassezia species on the skin in seborrheic locations, such as the face, scalp, and trunk; on the presence of Malassezia on affected skin, often in high numbers [17]; and on the therapeutic response seen to antimycotics [18]. Among the multiple chemical entities that are effective in treating SD and dandruff, such as azoles, hydroxypyridones, allylamines, selenium disulfide, and zinc pyrithione, the common mechanism of action is their antifungal activity. Improvements are usually accompanied by a reduction in the yeast’s population on the scalp, whereas recolonization leads to disease recurrence. Recent observations suggest that SD and dandruff-associated Malassezia species belong mainly to the species M. globosa and M. restricta, although M. sympodialis, M. furfur, and M. slooffiae have also been isolated from patients [14,15,16,19].
However, not all patients, particularly those with HIV-related SD, respond to antifungal drugs. Likewise, there is no evidence that fungal numbers on the skin´s surface are correlated with disease severity, even though higher numbers have been detected on the scalps of those with very low helper T-cell counts [20].
Malassezia on human scalps produce lipases as well as other enzymes [13,14,15,16]. For instance, an extracellular lipase LIP1 was found to be expressed on human scalps [21]. As shown by the hydrolysis of fatty acid monoesters, these lipases are preformed, acting very rapidly if suitable substrates are available [22].
Lipase/hydrolase activity and the production of free fatty acids have been attributed to a disrupted epidermal barrier function, dehydration of the scalp, and a triggered inflammatory response [1,2,3,13,14,15,16]. Interestingly, the precipitation of free fatty acids generated by Malassezia might be a possible explanation for the positive effects of lithium succinate in SD [23].
3. Studies on the Scalp Microbiome
In 1975, a quantitative scalp microbiome study in normal individuals and in subjects with dandruff and SD was published [24]. Three organisms were repeatedly found: Pityrosporum spp. (today Malassezia), aerobic cocci, and Corynebacterium acnes (today Cutibacterium acnes). Malassezia made up for 46% of the total microbiota in normal individuals, 74% in individuals with dandruff, and 83% in individuals with SD. The geometric mean number of organisms per cm2 in non-dandruff subjects was 5.04 × 105, 9.22 × 105 in dandruff subjects, and 6.45 × 105 in those with SD. C. acnes comprised 26% of the flora on normal subjects, 6% in dandruff subjects, and only 1% in SD subjects. These data were confirmed and extended by recent studies using new tools such as genomic and proteomic analyses [25,26,27]. They all have shown a shift in the scalp microbiome composition in people with dandruff/SD, with an increased abundance of Malassezia (esp. M. restricta) and Staphylococcus genera and a decreased abundance of Cutibacterium acnes [28,29,30,31,32,33] (Table 1). The impact of dysbiosis on altered epidermal barrier function, as well as on triggering inflammation in dandruff, is still not fully elucidated [27,34]. Staphylococcus is associated with epidermal barrier damage, including elevated levels of trans-epidermal water loss and pH [27]. Alterations in skin pH by Malassezia spp. might favor the growth of S. aureus and promote its adhesion to keratinocytes [16,35,36,37]. On the contrary, M. globosa can secrete aspartyl protease, which attenuates the biofilm formation of S. aureus [38]. Like Malassezia spp., Cutibacterium lives in seborrheic areas and produces enzymes to gain nutrients from sebum [37]. Previous studies have shown that Cutibacterium could suppress the overgrowth of Staphylococcus through the secretion of bacteriocin, while Staphylococcus owns an arsenal of different mechanisms to inhibit Cutibacterium acnes, such as the fermentation of glycerol [39,40,41]. Co-colonization of C. acnes and M. restricta can decrease damage to the skin barrier compared to single colonization by M. restricta [35]. The beneficial role of Cutibacterium in the maintenance of a healthy skin barrier was also demonstrated by a positive correlation between Cutibacterium and water content [39]. Investigation of enriched functional pathways in dandruff by shotgun metagenome sequencing has shown that commensal microorganisms such as Cutibacterium spp. carry genes for the synthesis of biotin and other vitamins, which are important to maintain a healthy scalp state [31]. Thus, the restoration of skin microbial composition by increasing the amounts of protective microbes and reducing the amounts of potential pathogens can help to rebuild the skin barrier [27].

Table 1.
Scalp microbiome of healthy and dandruff scalp.
4. Dandruff Control: Effects on Scalp Microbiome in Relation to In Vivo Efficacy
The above-mentioned data imply that SD/dandruff may be a dysbiosis-related skin condition rather than an infectious one. Achieving scalp microbiome homeostasis has therefore been a target in interventional studies. Saxena et al. investigated the effects of topical coconut oil applications on the scalp microbiome (bacterial and fungal) at the taxonomic and functional levels and their correlation with scalp physiological parameters [42]. A 16-week-long time-course study was performed, including a 12-week treatment phase and a 4-week relapse phase, on a cohort of 140 (70 healthy/ 70 dandruff) Indian women. After the treatment phase, an increase in the abundance of Cutibacterium acnes and Malassezia globosa in dandruff scalp was observed, which was negatively correlated to dandruff parameters. At the functional level, an enrichment of healthy scalp-related bacterial pathways, such as biotin metabolism and a decrease in fungal pathogenesis pathways, was observed. Hu et al. analyzed the microbiome of the scalps of 100 dandruff sufferers before and after 3 weeks of treatment with either control or an anti-dandruff shampoo containing 0.5% piroctone olamine (PO) [43]. A higher relative abundance of Malassezia restricta and Staphylococcus capitis along with a lower abundance of Cutibacterium acnes were associated with the dandruff scalps in comparison to the non-dandruff scalps. A 3-week PO shampoo treatment reduced the relative abundance of Malassezia species and Staphylococcus capitis and increased the relative abundance of Cutibacterium acnes. These changes in the composition of the scalp microbiome were consistent with a return to a healthy non-dandruff microbiome and improved clinical signs and symptoms compared with the control shampoo.
In addition to the three conventional ingredients—zinc pyrithione, climbazole, and piroctone olamine—with propanediol caprylate (Crinipan® PMC green), a new concept for dandruff control was launched in 2020. Short- to medium-chain fatty acids possess anti-microbial activities, but their practical use in cosmetics is limited due to their intense smell and other technical disadvantages [22]. Propanediol caprylate is an odorless, colorless and liquid ester, easy to incorporate into shampoo formulations and can be derived from natural materials like palm or palm kernel oil. The ester is rapidly cleaved by Malassezia hydrolases in the external milieu, thereby releasing the free fatty acid, caprylic acid, as an active agent. In detail, ester cleavage of propanediol caprylate and its undecylenic acid derivative, propanediol undecylenate, were investigated for the human-associated species M. globosa and M. restricta [44]. A cell count of 0.5–2.5 × 105 CFU/μL was transferred to an agar plate, overlaid by propanediol caprylate or propanediol undecylenate, respectively and incubated at 32 °C. After defined incubation times of 0, 3, 6, 12, 24, 48, and 72 h, the supernatant was removed and the concentrations of propanediol monoester and caprylic acid/undecylenic acid were determined by gas chromatography. A significant decrease in concentration of propanediol monoester was measured within hours depending on the inoculum of the fungus, with simultaneous increase in the concentration of free caprylic/undecylenic acid (Figure 1). In vivo, this might result in an autoregulation of the Malassezia population dependent on yeasts density. If the ester is not hydrolyzed, it acts as a conditioner and refatting agent [22,44]. In an agar dilution test with 500–1000 ppm for the dandruff-associated species M. globosa and M. restricta, the MIC values of the ester are in a similar range as for caprylic acid [44]. Propanediol caprylate is even effective in the case of azole resistance as shown in azole-resistant strains of M. pachydermatis [45].
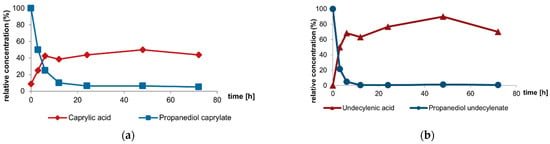
Figure 1.
Ester cleavage by Malassezia hydrolases: The two propanediol monoesters—propanediol caprylate (a); and propanediol undecylenate (b)—are cleaved by M. globosa (CBS 7705) in the medium, releasing propanediol and the respective carboxylic acid [44].
To prove the concept, propanediol caprylate and propanediol undecylenate were tested in several in vivo studies in various cosmetic applications (Table 2).

Table 2.
Design and results of in vivo studies with propanediol caprylate and propanediol undecylenate on dandruff.
Efficacy was first tested in a randomized, double-blind, three-armed in vivo study with 82 subjects, assessing the reduction in dandruff [46] (Figure 2). Propanediol caprylate at a dosage of 0.5% was compared to control, and to an identical formulation with 0.5% climbazole (positive control).
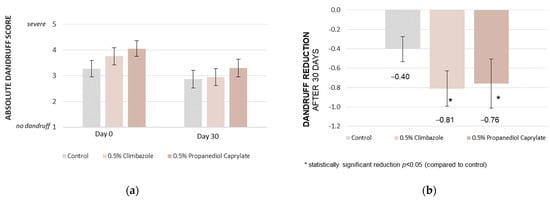
Figure 2.
Propanediol monoester vs. control vs. climbazole: In vivo rinse-off shampoo study, Brazil; 0.5% of propanediol caprylate reduces dandruff significantly in 30 days vs. control, and achieves comparable results to the established anti-dandruff benchmark, climbazole, used at the identical dosage; dandruff scoring (a), and dandruff reduction (b) [46].
The participants were instructed to discontinue using any cosmetic products on their scalp and hair for 48 h before the study commenced. They were also provided with a standard shampoo from the laboratory and instructed to wash their hair with it twice a week for two weeks prior to the study.
Upon entering the study, the subjects were randomly assigned to one of three groups: a control group; a group receiving shampoo with 0.5% climbazole; and a group receiving shampoo with 0.5% propanediol caprylate. The test shampoo was applied three times per week for 30 days, each time adhering to 3 min of incubation time on the scalp (rinse-off study). The in vivo evaluation of dandruff flaking was performed by dermatologists on a 1 (no dandruff) to 5 (severe dandruff) scale, directly after the conditioning phase (Day 0, baseline) and after 30 days of use (Day 30). Additionally, an olfactory evaluation was completed by the subjects to investigate a potential odor from caprylic acid formation.
The statistical comparison was performed by applying the method of Student’s t-test, unpaired, considering a 95% confidence interval. A statistically significant reduction in the absolute dandruff score versus control was found for the two actives, propanediol caprylate (p = 0.0216), and its positive control climbazole (p = 0.0012) (Figure 2).
Interestingly, the shampoo containing propanediol caprylate was rated better than the control for sensory aspects. Almost 30% of the study subjects indicated no inherent smell when applied, compared to only 8% for the control shampoo.
In the next in vivo study, the effects of propanediol caprylate on the scalp microbiome, esp. on Cutibacterium and Staphylococcus spp., were tested [47]. Nine volunteers, with moderate dandruff, participated. All participants had not used topical or systemic antibiotics or antifungals within three months prior to the study, and had not used any anti-dandruff products within 14 days prior to the start of the study. After a conditioning period of 14 days, using a neutral shampoo, they applied a leave-on formulation once daily containing 0.5% propanediol caprylate (5 subjects) or the control (4 subjects) by systematically spraying it onto the scalp (approximately 0.03 μL propanediol caprylate/cm2 skin). The efficacy of the product was rated by subjects via a questionnaire, and a dandruff score was given by a trained technician on a scale of 0 (no scaling) to 10 (heavy, large, thick white or yellow flakes adhering to the scalp) before, and after 4 weeks of application. Microbiome analysis was performed before the first product application, and after 4 weeks of application by bacterial 16S rRNA sequencing. After four weeks of product application, the mean dandruff score decreased from 4.81 to 4.53 in the control group, and from 4.95 to 4.45 in the propanediol caprylate group. Microbiome analysis showed no notable effects on the number of genera present or the identity of genera (Figure 3). However, when comparing the individual numbers of the most abundant genera, Staphylococcus and Cutibacterium, a difference was observed (Table 3). In the propanediol caprylate group, the relative abundance of Cutibacterium increased from 19.3% to 33.3%, while it decreased from 30.4% to 25.9% in the control group. Contrarily, the relative abundance of Staphylococcus decreased in the propanediol caprylate group from 64.0% to 61.9%, but increased in the control group from 59.9% to 68.8%.
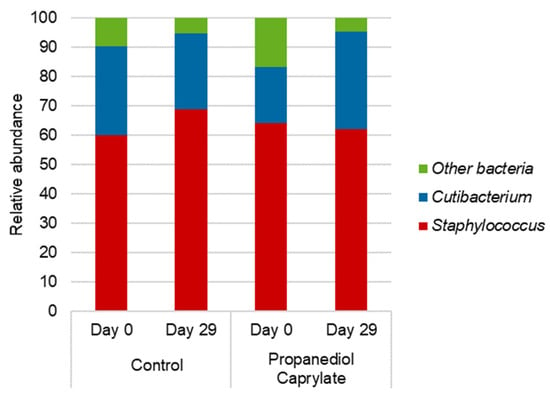
Figure 3.
Propanediol caprylate vs. control: In vivo leave-on study, Germany: Microbiome analysis. Propanediol caprylate supports a favorable shift of the balance of Staphylococcus/Cutibacterium, supporting a healthy scalp microbiome [47].

Table 3.
Propanediol caprylate vs. control: Scalp microbiome composition based on 16S rRNA gene analysis before and after product application for four weeks [47].
In particular, propanediol caprylate shifted the microbiome to a healthier balance between Cutibacterium and Staphylococcus, while at the same time reducing dandruff. Antimicrobial effects of free caprylic acid, as well as effects on skin surface pH might be of importance [22,44]. Next to caprylic acid´s antifungal effects, also the uncleaved propanediol monoester shows certain antibacterial activity, including effects against Gram-positives of the Staphylococcus genus. Despite the fact that reports on most known anti-dandruff actives have often focused on anti-Malassezia effects, according to Symrise data, anti-dandruff actives are commonly also active against Staphylococcus aureus, which may be an additional explanation for supporting a decrease in Staphylococcus in favor of Cutibacterium. In an agar dilution assay, the following minimum inhibitory concentrations for S. aureus have been detected: piroctone olamine 64 ppm, climbazole 250 ppm, propanediol caprylate 500 ppm, propanediol undecylenate 500 ppm.
Since the European ban on zinc pyrithione in cosmetics [50], piroctone olamine and climbazole remain the primary conventional antifungal ingredients for anti-dandruff shampoo manufacturers within the EU market. Previous studies have investigated the efficacy of propanediol caprylate as an alternative anti-dandruff agent, initially comparing it to climbazole and control. To further assess its potential, propanediol caprylate was subsequently evaluated against piroctone olamine in a randomized, double-blind study, involving subjects with greasy scalps and dandruff [48].
The study enrolled 21 participants, with dandruff, all of whom were healthy individuals aged 18 years and above. Individuals with recent use of topical or systemic treatments likely to interfere with the study were excluded. The study used a 0.5% concentration of both propanediol caprylate and piroctone olamine in separate test shampoos. After a conditioning phase, twelve subjects used the propanediol caprylate shampoo, while nine subjects used the piroctone olamine shampoo as a positive control. Both shampoos were applied three times weekly with a three-minute incubation period before rinsing. A dermatologist assessed dandruff severity using a visual scale ranging from 0 to 5 for both adherent and non-adherent flakes. The total dandruff score was derived by summing these individual scores, resulting in a scale from 0 to 10. To be included in this study, subjects had to score at least 4 on the 0 to 10 total dandruff scale.
To assess the change from the baseline value, a paired t-test was performed on the outcome (D28−D0) for each product. The normality assumption was checked using the Shapiro–Wilk test (α = 0.01); where in case rejected, the Wilcoxon signed- rank test was carried out instead. Significant reductions in both adherent and non-adherent dandruff scores were observed at the end of the 28-day application phase (D28) compared to baseline (D0) for both treatment groups (propanediol caprylate: adherent p = 0.0004, non-adherent p = 0.0050; piroctone olamine: adherent p = 0.0056, non-adherent p = 0.0028). No statistically significant difference between the two products was observed, resulting in a decrease in total dandruff from 5.33 to 3.71 (p = 0.0002) for propanediol caprylate, and from 5.64 to 3.64 (p = 0.0032) for piroctone olamine (Figure 4).
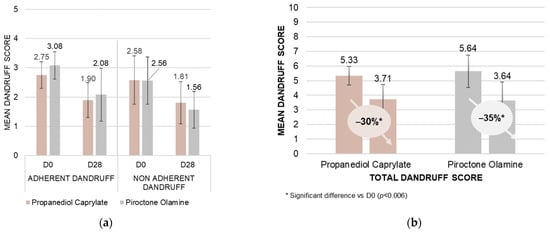
Figure 4.
Propanediol caprylate vs. piroctone olamine: In vivo rinse-off shampoo study; mean visual dandruff scores determined by professional evaluators in Poland on a scale from 0 to 5 adherent/non-adherent dandruff (a), and from 0 to 10 for total dandruff (b) (as a sum of adherent and non-adherent dandruff) with 21 subjects. No significant difference between the two actives was observed [48].
To explore potential synergistic effects, a subsequent randomized, double-blind study was conducted [48], comparing a standard shampoo containing 0.75% piroctone olamine as a positive control [51], against a second shampoo incorporating 0.5% propanediol caprylate with 0.25% piroctone olamine. Twenty subjects with dandruff (10 with greasy scalps/10 with dry scalps), and who had not recently made use of topical or systemic treatments likely to interfere with the study, were randomly assigned to each treatment group. Both shampoos were applied at least three times a week, and dandruff severity was visually assessed at baseline (D0), and after 14 (D14), 28 (D28), 42 (D42) and 63 (D63) days. The 63-day assessment was performed after a 3-week washout period, where subjects reverted to a neutral shampoo.
Both treatment groups demonstrated an anti-dandruff effect, signifying a reduction in dandruff, compared to baseline. The groups were compared using either a paired Student’s t-test, or the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, depending on the normality of the data as assessed by the Shapiro–Wilk test (α = 0.01). While the piroctone olamine positive control shampoo exhibited a slightly faster reduction in scalp flaking, no statistically significant difference was observed between the two treatments. Notably, the combination shampoo demonstrated a prolonged anti-dandruff effect, with the mean dandruff score continuing to decrease even during the wash-out phase (D63 vs. D42). Conversely, the positive control shampoo showed an increase in mean dandruff score from D42 to D63, trending towards the initial value. These findings suggest a particularly long-lasting effect associated with the combination of propanediol caprylate and piroctone olamine (Figure 5).
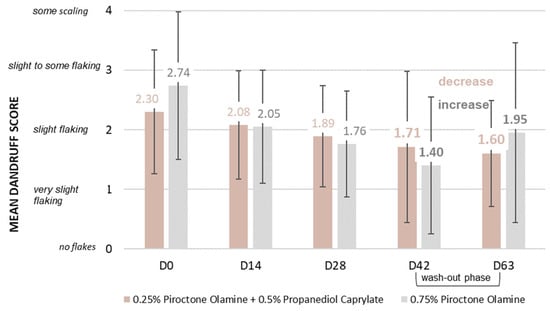
Figure 5.
Propanediol monoester in combination with piroctone olamine: In vivo rinse-off shampoo study; mean visual dandruff rating on a scale from 0 to 10 by experts in Germany with 40 subjects: a combination of piroctone olamine and propanediol caprylate vs. piroctone olamine used alone. No significant difference in dandruff reduction was observed between the two groups, but the shampoo using propanediol caprylate showed a continued reduction in dandruff during the wash-out phase [48].
While conventional anti-dandruff actives (zinc pyrithione, climbazole, piroctone olamine) primarily target an overgrowth of Malassezia on the scalp, a fourth ingredient, salicylic acid, is frequently used for keratolytic effects, aiming for an enhanced removal of dead skin flakes. In a further randomized, double-blind, in vivo rinse-off shampoo study, two identical base formulations, one containing salicylic acid at its maximum dose of 3% (acc. US FDA anti-dandruff monograph), versus the second formulation featuring a reduced salicylic acid dose of 2% in combination with 0.5% propanediol caprylate, were explored [49]. The study included 22 participants, all of whom were healthy. An expert rating of dandruff was performed on a 0 to 10 visual scale. The subjects were required to have a total dandruff score of ≥4, as well as oily scalps. Participants had to be accustomed to washing their hair minimum 3 times a week, and had to be willing to avoid other hair treatments, including anti-dandruff products, for the duration of the study. They were also required to refrain from hair dyeing, bleaching, perms, and straightening during the study. After a pre-conditioning phase of 14 days, the subjects each applied, at least 3 times per week, either the salicylic acid (positive control) shampoo, or the test shampoo with the combination of salicylic acid/propanediol caprylate. Rating of the visual dandruff score was performed before the first application (D0), and at the end of the study after 28 days (D28) of application. The groups were compared using either a paired Student’s t-test or the Wilcoxon signed-rank test, depending on the normality of the data, as assessed by the Shapiro–Wilk test (α = 0.01). The actives combination reduced adherent dandruff by 32%, while the positive control only showed a reduction of 21%. This led to a better reduction in the total dandruff score for the group that used the shampoo containing both salicylic acid and propanediol caprylate. Nonetheless, both treatments showed an anti-dandruff effect with a significant (Wilcoxon signed-rank test) reduction in dandruff, D28 vs. D0 (Figure 6). The erythema score (Wilcoxon signed-rank test) and the irritation score (Student’s t-test) also showed significant reductions after 28 days for both shampoos. The shampoo with the reduced level of salicylic acid combined with propanediol caprylate showed again a stronger decrease of 57% (vs. 33–39%) in both scores (Figure 7). In summary, by the addition of propanediol caprylate, it is possible to reduce the dose of salicylic acid, while observing a stronger reduction in dandruff and an enhanced preservation efficacy. Furthermore, an improved overall sensorial performance of the product was observed for the shampoo containing this ingredient combination.
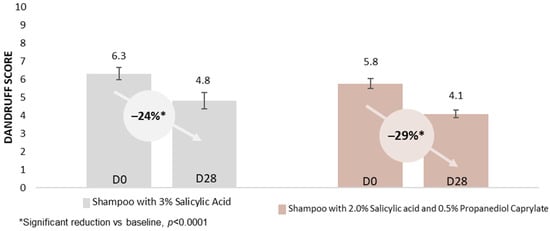
Figure 6.
Propanediol monoester in combination with salicylic acid: In vivo rinse-off shampoo study; mean visual dandruff rating on a scale from 0 to 10 by experts in Poland with 44 subjects: a combination of salicylic acid and propanediol caprylate vs. salicylic acid used alone [49].
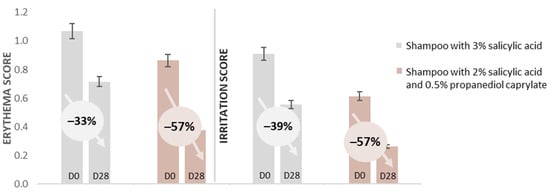
Figure 7.
Propanediol monoester in combination with salicylic acid: In vivo rinse-off shampoo study; mean erythema score and mean irritation score with 44 subjects: salicylic acid vs. a combination of salicylic acid and propanediol caprylate [49].
In order to further investigate the long-lasting effect observed for propanediol caprylate, combined with piroctone olamine (Figure 5), and to explore the anti-dandruff efficacy for propanediol esters used as single actives, an additional randomized, double-blind, in vivo shampoo study was designed. Propanediol caprylate and propanediol undecylenate were investigated at a dose of 0.5% each, used in a transparent simple sodium laureth sulfate shampoo base, also looking for a comparison between the two monoesters.
The study included 39 participants, all of whom were healthy. They were required to have dry or oily scalps with slight to moderate dandruff. Participants had to be willing to avoid other hair treatments, including anti-dandruff products, for the duration of the study. After a conditioning period, 20 subjects used the test shampoo with propanediol undecylenate, and 19 subjects used the identical base formulation with propanediol caprylate instead. The test shampoos were applied once daily for a period of 28 days, adhering to a period of three minutes before rinsing. Visual rating of dandruff was performed by a dermatologist shortly before the first shampoo application after finishing the conditioning phase (D0), at the end of the application period (D28), and at an additional time point (D42) after a final wash-out phase without anti-dandruff shampoo use. Dandruff scoring was performed on a 0 (no scaling) to 10 (very dense dandruff) visual scale. A statistically significant decrease (p < 0.02, Wilcoxon signed-rank test) in the dandruff score was observed at the end of the application phase (D28) versus baseline (D0) for both products equally. The dandruff score was reduced from 3.38 to 2.38 in the propanediol undecylenate group, and from 3.50 to 2.00 in the propanediol caprylate group, observing no significant difference between the two groups. In line with previous observations, long-lasting effects were observed for both propanediol monoesters used as single actives, indicating that this effect is not linked to a combination with piroctone olamine but to the ester. The dandruff score was further reduced during the wash-out phase for both shampoos applied. A reduction from 2.38 to 1.00 was observed for propanediol undecylenate, and from 2.00 to 1.25 for propanediol caprylate (Figure 8). As part of this study, subject ratings for various sensory parameters were recorded, indicating good consumer acceptance for both esters equally (Figure 9).
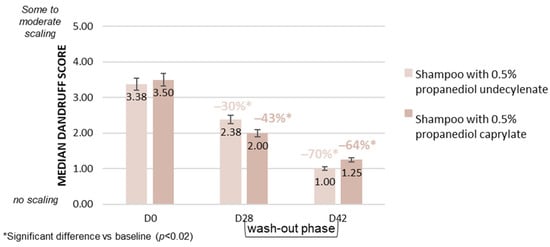
Figure 8.
Lasting reduction in dandruff by propanediol monoesters: In vivo rinse-off shampoo study; mean visual dandruff scores on a scale from 0 to 10 by expert rating in Poland with 39 subjects: propanediol undecylenate vs. propanediol caprylate. A reduction in dandruff is also recorded in the final wash-out phase using a neutral shampoo for both esters.
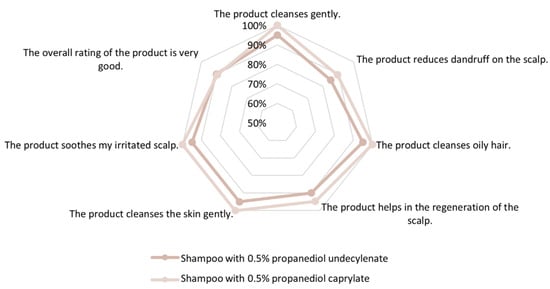
Figure 9.
Propanediol monoesters, sensory analysis: In vivo rinse-off shampoo study; sensory self-analysis by 39 subjects: propanediol undecylenate vs. propanediol caprylate. Both esters support consumer acceptance when used in anti-dandruff shampoo.
5. Conclusions
Propanediol caprylate or propanediol undecylenate were tested in six in vivo studies in various cosmetic applications (Table 2). In addition to their effects on Malassezia spp., which are based on an auto-activation by Malassezia’s external lipases and hydrolases, these ingredients are also able to influence the bacterial flora towards a healthier scalp microbiome. While zinc pyrithione has been banned from European cosmetics, propanediol caprylate is a new option—already found in the final consumer product market – in addition to the remaining conventional agents piroctone olamine, climbazole, and salicylic acid. Considering the common practice of combining various anti-dandruff actives, it is worth noting that in vivo additive and synergistic effects using propanediol caprylate in different combinations allow reduction in the concentration of conventional anti-dandruff agents and preservatives.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, methodology, investigation, writing—original draft preparation, and validation, P.M. and F.G.; data curation and visualization, L.M.; resources and validation, S.N. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Informed Consent Statement
Written informed consent was obtained from all participants for all studies including voluntary participation. Studies were conducted either in accordance with protocols approved by an Ethics Committee or were non-invasive, cosmetic anti-dandruff studies.
Conflicts of Interest
Florian Genrich, Laura Meunier and Steffen Nordzieke are employees of Symrise AG. Peter Mayser states no conflicts of interest. For the use of fatty acid esters for Malassezia-associated skin conditions, respective patent applications by Justus-Liebig-Universität Gießen (Deutsche Patentanmeldung 102,013 009616.2) and Symrise AG exist (WO2020160741A1 Fatty acid esters as anti-Malassezia agents). Symrise AG owns additional patent applications including but not limited to WO2020160904A1 (Active agents for skin and hair care with physicochemical modifying properties), WO2020160742A1 (Active agents for skin and hair care with sensory modifying properties), WO2020160905A1 (Antimicrobial activity of fatty acid esters and combinations thereof), WO2023025399A1 (Antimicrobial esters for skin and scalp care), and WO2021224509A2 (Antimicrobial combinations).
References
- Borda, L.J.; Wikramanayake, T.C. Seborrheic Dermatitis and Dandruff: A Comprehensive Review. J. Clin. Investig. Dermatol. 2015, 3, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.R.; Messenger, A.G.; Tosti, A.; Todd, G.; Hordinsky, M.; Hay, R.J.; Wang, X.; Zachariae, C.; Kerr, K.M.; Henry, J.P.; et al. A comprehensive pathophysiology of dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis—Towards a more precise definition of scalp health. Acta Derm. Venereol. 2013, 93, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dessinioti, C.; Katsambas, A. Seborrheic dermatitis: Etiology, risk factors, and treatments: Facts and controversies. Clin. Dermatol. 2013, 31, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Turner, G.A.; Matheson, J.R.; Li, G.-Z.; Fei, X.-Q.; Zhu, D.; Baines, F.L. Enhanced efficacy and sensory properties of an anti-dandruff shampoo containing zinc pyrithione and climbazole. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 78–83. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmidt-Rose, T.; Braren, S.; Fölster, H.; Hillemann, T.; Oltrogge, B.; Philipp, P.; Weets, G.; Fey, S. Efficacy of a piroctone olamine/climbazol shampoo in comparison with a zinc pyrithione shampoo in subjects with moderate to severe dandruff. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2011, 33, 276–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schwartz, J.R.; Bacon, R.A.; Shah, R.; Mizoguchi, H.; Tosti, A. Therapeutic efficacy of anti-dandruff shampoos: A randomized clinical trial comparing products based on potentiated zinc pyrithione and zinc pyrithione/climbazole. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2013, 35, 381–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Market Example for the Combination of Climbazole and Salicylic acid: Henkel/Schwarzkopf Seborin Dual Effect Shampoo Anticaspa, Chile, 2011. Mintel GNPD Database. Record ID 1562280. Available online: https://www.mintel.com/products/gnpd/ (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Market Example for the Combination of Zinc Pyrithione and Climbazole: Unilever CLEAR Men Antiforfora Shampoo Purificante, Italy, 2013. Mintel GNPD Database. Record ID 2261277. Available online: https://www.mintel.com/products/gnpd (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Market Example for the Combination of Piroctone Olamine and Climbazole: Beiersdorf NIVEA for Men Anti-Schuppen Pure Shampoo, Germany, 2010. Mintel GNPD Database. Record ID 1403922. Available online: https://www.mintel.com/products/gnpd/ (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Market Example for the Combination of Zinc Pyrithione and Piroctone Olamine: Wella Professionals Invigo Balance Shampoo, UK, 2018. Mintel GNPD Database. Record ID 5854667. Available online: https://www.mintel.com/products/gnpd/ (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Market Example for the Combination of Piroctone Olamine and Sodium Salicylate: Procter & Gamble Head & Shoulders Sensitive Duschgel & Shampoo, Germany, 2022. Mintel GNPD Database. Record ID 9397368. Available online: https://www.mintel.com/products/gnpd/ (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Malassez, L.C. Note sur le champignon de la pelade. Arch. Physiol. 1874, 11, 203–212. [Google Scholar]
- Gaitanis, G.; Magiatis, P.; Hantschke, M.; Bassukas, I.D.; Velegraki, A. The Malassezia genus in skin and systemic diseases. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2012, 25, 106–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hay, R.J. Malassezia dandruff and seborrhoeic dermatitis: An overview. Br. J. Dermatol. 2011, 165 (Suppl. 2), 2–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rudramurthy, S.M.; Honnavar, P.; Dogra, S.; Yegneswaran, P.P.; Handa, S.; Chakrabarti, A. Association of Malassezia species with dandruff. Indian J. Med. Res. 2014, 139, 431–437. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Meray, Y.; Gençalp, D.; Güran, M. Putting it all together to understand the role of Malassezia spp. in dandruff etiology. Mycopathologia 2018, 183, 893–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heng, M.C.; Henderson, C.L.; Barker, D.C.; Haberfelde, G. Correlation of Pityosporum ovale density with clinical severity of seborrheic dermatitis as assessed by a simplified technique. J. Am. Acad. Dermatol. 1990, 23, 82–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuster, S. The aetiology of dandruff and the mode of action of therapeutic agents. Br. J. Dermatol. 1984, 111, 235–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tajima, M.; Sugita, T.; Nishokawa, A.; Tsuboi, R. Molecular analysis of Malassezia in seborrheic dermatitis patients: Comparison with other diseases and healthy subjects. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2008, 128, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schechtman, R.C.; Midgley, G.; Hay, R.J. HIV disease and Malassezia yeasts: A quantitative study of patients presenting with seborrhoeic dermatitis. Br. J. Dermatol. 1995, 133, 694–698. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeAngelis, Y.M.; Saunders, C.W.; Johnstone, K.R.; Reeder, N.L.; Coleman, C.G.; Kaczvinsky, J.R.; Gale, C.; Walter, R.; Mekel, M.; Lacey, M.P.; et al. Isolation and expression of a Malassezia globosa lipase gene, LIP1. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2007, 127, 2138–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayser, P. Medium chain fatty acid ethyl esters—Activation of antimicrobial effects by Malassezia enzymes. Mycoses 2015, 58, 215–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayser, P.; Schulz, S. Precipitation of free fatty acids generated by Malassezia—A possible explanation for the positive effects of lithium succinate in seborrhoeic dermatitis. J. Eur. Acad. Dermatol. Venereol. 2016, 30, 1384–1389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGinley, K.J.; Leyden, J.J.; Marples, R.R.; Kligman, A.M. Quantitative microbiology of the scalp in non-dandruff, dandruff, and seborrheic dermatitis. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1975, 64, 401–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wikramanayake, T.C.; Borda, L.J.; Miteva, M.; Paus, R. Seborrheic dermatitis-Looking beyond Malassezia. Exp. Dermatol. 2019, 28, 991–1001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paulino, L.C. New perspectives on dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis: Lessons we learned from bacterial and fungal skin microbiota. Eur. J. Dermatol. 2017, 27, 4–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, R.; Li, R.; Wang, R. Skin microbiome alterations in seborrheic dermatitis and dandruff: A systematic review. Exp. Dermatol. 2021, 30, 1546–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clavaud, C.; Jourdain, R.; Bar-Hen, A.; Tichit, M.; Bouchier, C.; Pouradier, F.; Rawadi, C.E.; Guillot, J.; Ménard-Szczebara, F.; Breton, L.; et al. Dandruff is associated with disequilibrium in the proportion of the major bacterial and fungal populations colonizing the scalp. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e58203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Clavaud, C.; Bar-Hen, A.; Cui, M.; Gao, J.; Liu, Y.; Liu, C.; Shibagaki, N.; Guéniche, A.; Jourdain, R.; et al. Characterization of the major bacterial-fungal populations colonizing dandruff scalps in Shanghai, China, shows microbial disequilibrium. Exp. Dermatol. 2015, 24, 398–400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, T.; Kim, H.J.; Myeong, N.R.; Lee, H.G.; Kwack, I.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.J.; Sul, W.J.; An, S. Collapse of human scalp microbiome network in dandruff and seborrheic dermatitis. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 835–838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saxena, R.; Mittal, P.; Clavaud, C.; Dhakan, D.B.; Hegde, P.; Veeranagaiah, M.M.; Saha, S.; Souverain, L.; Roy, N.; Breton, L.; et al. Comparison of Healthy and Dandruff Scalp Microbiome Reveals the Role of Commensals in Scalp Health. Front. Cell Infect. Microbiol. 2018, 8, 346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grimshaw, S.G.; Smith, A.M.; Arnold, D.S.; Xu, E.; Hoptroff, M.; Murphy, B. The diversity and abundance of fungi and bacteria on the healthy and dandruff affected human scalp. PLoS ONE 2019, 14, e0225796. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Q.; Panchamukhi, A.; Li, P.; Shan, W.; Zhou, H.; Hou, L.; Chen, W. Malassezia and Staphylococcus dominate scalp microbiome for seborrheic dermatitis. Bioprocess Biosyst. Eng. 2021, 44, 965–975. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shah, R.R.; Larrondo, J.; Dawson, T.; Mcmichael, A. Scalp microbiome: A guide to better understanding scalp diseases and treatments. Arch. Dermatol. Res. 2024, 316, 495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meloni, M.; Balzaretti, S.; Collard, N.; Desaint, S.; Laperdrix, C. Reproducing the scalp microbiota community: Co-colonization of a 3D reconstructed human epidermis with C. acnes and M. restricta. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2021, 43, 235–245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rippke, F.; Schreiner, V.; Doering, T.; Maibach, H.I. Stratum corneum pH in atopic dermatitis: Impact on skin barrier function and colonization with Staphylococcus aureus. Am. J. Clin. Dermatol. 2004, 5, 217–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scharschmidt, T.C.; Fischbach, M.A. What lives on our skin: Ecology, genomics and therapeutic opportunities of the skin microbiome. Drug Discov. Today Dis. Mech. 2013, 10, e83–e89. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, H.; Goh, B.N.; Teh, W.K.; Jiang, Z.; Goh, J.P.Z.; Goh, A.; Wu, G.; Hoon, S.S.; Raida, M.; Camattari, A.; et al. Skin Commensal Malassezia globosa Secreted Protease Attenuates Staphylococcus aureus Biofilm Formation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2018, 138, 1137–1145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, Z.; Wang, Z.; Yuan, C.; Liu, X.; Yang, F.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Manabe, K.; Qin, O.; Wang, X.; et al. Dandruff is associated with the conjoined interactions between host and microorganisms. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 24877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christensen, G.J.; Scholz, C.F.; Enghild, J.; Rohde, H.; Kilian, M.; Thürmer, A.; Brzuszkiewicz, E.; Lomholt, H.B.; Brüggemann, H. Antagonism between Staphylococcus epidermidis and Propionibacterium acnes and its genomicbasis. BMC Genom. 2016, 17, 152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Kuo, S.; Shu, M.; Yu, J.; Huang, S.; Dai, A.; Two, A.; Gallo, R.L.; Huang, C.M. Staphylococcus epidermidis in the human skin microbiome mediates fermentation to inhibit the growth of Propionibacterium acnes: Implications of probiotics in acne vulgaris. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2014, 98, 411–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saxena, R.; Mittal, P.; Clavaud, C.; Dhakan, D.B.; Roy, N.; Breton, L.; Misra, N.; Sharma, V.K. Longitudinal study of the scalp microbiome suggests coconut oil to enrich healthy scalp commensals. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 7220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, P.; Henry, J.; Tiesman, J.P.; Parlov, M.; Bacon, R.; Charbonnea, D.; Venkataraman, A.; Locker, K.C.S.; Krigbaum, H.; Schwartz, J. Scalp microbiome composition changes and pathway evaluations due to effective treatment with Piroctone Olamine shampoo. Int. J. Cosmet. Sci. 2024, 46, 333–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Pesaro, M.; Schmaus, G.; Mayser, P. Medium-chain fatty acid esters-Optimising their efficacy as anti-Malassezia agents. Mycoses 2020, 63, 704–710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koch, C.; Nordzieke, S.; Grieger, J.; Mayser, P. Medium-chain fatty acid esters are effective even in azole-resistant Malassezia pachydermatis. Mycoses 2022, 65, 1188–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Genrich, F.; Koch, C.; Lange, S.; Bugdahn, N.; Schmaus, G. Next Generation dandruff control. SOFW J. 2020, 146, 8–12. [Google Scholar]
- Genrich, F.; Koch, C.; Massironi, M.; Thomaz, F. Propanediol Caprylate: Shifting the Microbiome, Sebum Levels and Classic Approach to Dandruff. Cosmet. Toilet. 2021, 136, 44–51. [Google Scholar]
- Genrich, F.; Meunier, L.; Nordzieke, S. The Green Future of Dandruff Control. Pers. Care Mag. Glob. 2022, 23, 64–68. [Google Scholar]
- Meunier, L.; Genrich, F.; Fontán Yanes, M.T. Advancing salicylic acid-based dandruff control. Euro Cosmet. 2023, 32, 3–6. [Google Scholar]
- COMMISSION REGULATION (EU) 2021/1902 of 29 October 2021 amending Annexes II, III and V to Regulation (EC) No 1223/2009 of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards the use in cosmetic products of certain substances classified as carcinogenic, mutagenic or toxic for reproduction. Off. J. Eur. Union 2021, L387, 120–125. Available online: https://eur-lex.europa.eu/legal-content/EN/TXT/PDF/?uri=CELEX:32021R1902 (accessed on 29 August 2024).
- Kita, K.; Caravieri, F.; Birkel, S. Piroctone Olamine—Advancing Anti-dandruff Care & More. Efficient and safe scalp care for new formats & applications. SOFW J. 2021, 147, 26–31. [Google Scholar]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).