Abstract
Solar radiation, specifically ultraviolet radiation (UVR), is one of the harmful external factors that affect the integrity of the skin upon sun overexposure. Its detrimental effects include skin aging (photoaging), pigmentation disorders, and skin cancer. Upon UVR exposure, a cascade of different cellular responses is initiated, giving rise to inflammatory processes, oxidative stress, protein misfolding, and DNA lesions, among other effects. Therefore, there is a growing need to explore and characterize new compounds for safeguarding the skin from solar radiation-induced damage. In this work, we analyze the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities of the Mn (II) quinone complex (4QMn) in different cellular models and human skin explants. Importantly, our results suggest that 4QMn is able to ameliorate the oxidative damage produced by protein aggregation by reducing ROS levels, mitochondrial ROS (MitoROS), and DNA oxidative damage (8OH-dG) in a protein accumulation model. These findings suggest that the 4QMn compound could mitigate the deleterious effects of different sources of oxidative damage.
1. Introduction
The skin is the body’s largest organ, protecting the rest of the body from external insults and damage. The epidermis, the outermost layer, is the most exposed structure of our body. It blocks radiation, pollution chemicals, dehydration, and physical damage. It is therefore our first line of defense, which is based on the continuous regeneration of the epidermis through keratinocyte proliferation. As keratinocytes get closer to the surface, they die and generate the stratum corneum, the physical barrier between our internal organs and the external world. Keratinocytes play a pivotal role in the synthesis of keratin and are responsible for establishing the epidermal water barrier through the production and secretion of lipids to construct the stratum corneum [1]. The next layer is the dermis, which is the thickest of the three layers of the skin. In this layer, most of the skin’s specialized cells and structures are found, like blood vessels, hair follicles, sweat glands, and fibroblasts [2]. Fibroblasts are the cells responsible for collagen synthesis and confer the skin its strength and resilience. The last and innermost layer of the skin is the hypodermis, which consists of pads of adipose tissue [3,4]. This intricate structural composition of the skin forms a sophisticated network, functioning as the body’s primary defense against pathogens, ultraviolet (UV) light, chemicals, and mechanical injuries [5]. The protection of the skin is paramount to deterring aging signs and damage to other internal tissues in our body.
Among the external factors that affect the integrity of the skin, solar radiation is one of the major causative factors for age-related changes [6]. It is divided into three wavelength components: ultraviolet (UVR), visible (Vis), and infrared (IR) radiation [7]. Approximately 6% of the spectrum is UVR, 52% is Vis, and 42% is IR. Additionally, UVR is divided into three components: UVC (100–290 nm), UVB (290–320 nm), and UVA (320–400 nm) [8]. UVC is the most energetic radiation, but it is completely absorbed by the ozone layer and does not reach the surface of the Earth. On the other hand, of the total UVR that reaches the Earth, 5% comprises UVB, which penetrates the skin up to the epidermis, and 95% comprises UVA, which can penetrate deeper into the dermis [9].
UV radiation is known to have positive effects apart from the production of vitamin D in the skin, such as heliotherapy (its use to treat a variety of skin diseases, such as psoriasis, atopic dermatitis, or localized scleroderma) and the stimulation of hormones that help the circadian rhythm or improve mood [10,11]. However, this component of solar radiation also poses a significant threat to human skin, leading to a range of detrimental effects. Prolonged exposure to solar radiation can induce a cascade of molecular and cellular events that contribute to skin aging, pigmentation disorders, and, more critically, an increased risk of skin cancer [12,13]. Moreover, UV exposure damage is cumulative, causing premature skin aging (photoaging) [14]. The intricate interaction between UV radiation and the skin has garnered considerable scientific attention due to the rise in skin-related disorders and concerns about long-term health implications.
Upon UVR exposure, oxidative damage begins with the massive production of reactive oxygen species (ROS). These species are able to oxidize cellular molecules like lipids and proteins. Proteins undergoing oxidative modifications exhibit thermodynamic instability and tend to adopt partially unfolded tertiary structures prone to aggregation, which have been implicated in skin disorders such as cutaneous amyloidosis, systemic sclerosis (scleroderma), and dermatitis herpetiformis [15,16,17,18]. Additionally, ROS can also induce different types of oxidative DNA lesions, with the guanine bases being the most susceptible to oxidation [19]. On the other hand, UV radiation also activates the inflammatory cascade in the skin by upregulating the expression of several pro-inflammatory cytokines, such as interleukin-6 (IL6), interleukin-8 (IL8), and TNFα [8]. After extensive and chronic exposure to UV, the accumulation of oxidative molecules and DNA lesions leads to a disruption of control mechanisms that will trigger the detrimental effects mentioned before, like photoaging and skin cancer [20].
In light of these challenges, there is a pressing need to explore innovative approaches to safeguarding the skin from solar radiation-induced damage. Current sunscreens, while effective, often rely on a limited set of active ingredients, and concerns about their potential side effects and environmental impacts have prompted the scientific community to seek alternatives [21].
In this work, we have assessed the antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities of the 4QMn compound, a scorpion-type polyamine compound mimetic of the superoxide dismutase enzyme (SOD) that has a structure similar to the active center of the enzyme [22]. This activity was tested in several models widely used to study the harmful effects of sunlight exposure, including monolayer cell cultures of human keratinocytes (HNEKs) and fibroblasts (NHDFs), as well as a more complex model involving human skin explants. These three models were subjected to UVA radiation, which induced the generation of ROS and a pro-inflammatory response. Most importantly, 4QMn presented antioxidant and anti-inflammatory potential, evidenced by the analysis of the cellular oxidative stress and the gene expression analysis of selected biomarkers. In addition, our results showed that 4QMn was able to reduce several biomarkers of oxidative damage resulting from the accumulation and misfolding of proteins, a common feature during biological aging, by using a Huntington’s disease (HD) cell model that courses with protein aggregation. Hence, this compound exhibits potential as a promising candidate to be used in cosmetic formulations for slowing down the aging process by protecting the skin from solar radiation injuries and the loss of proteostasis.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. 4QMn Compound
The metal ligand 4QMn (also named L1) was synthesized as reported previously [22]. Its simplified nomenclature refers to the molecule 6-[(4-(4-quinolil)-3-azabutil)]-3,6,9-triaza-1-(2,6)-piridinciclodecafane, with the chemical structure shown in Figure 1A,B. It was designed to coordinate a metal ion within its structure in a similar manner to how SOD enzymes coordinate metal ions to catalyze electron transfer between radicals and these metal ions. Different studies have been carried out in which it has been determined that the presence of benzimidazole units in this type of molecule allows the coordination sphere to be completed for metals such as manganese (Figure 1B), copper, or iron, which confers greater thermodynamic stability and kinetics to the corresponding complexes of manganese. Additionally, the different substituent groups provide a hydrophobic environment for the metal, which presents lower toxicity and greater functional efficiency both in vitro and in vivo [23,24].

Figure 1.
Ball–and–stick representation of chemical structure of 4Q compound (A) and 4Q coordinated with manganese, 4QMn (B).
2.2. Cell Culture
Human Normal Epidermal Keratinocytes (HNEKs) were cultured in a specific supplemented growth medium (Promocell, Heidelberg, Germany). Normal Human Dermal Fibroblasts (NHDFs) were cultured in high-glucose Gibco DMEM medium (Fisher Scientific, Madrid, Spain) supplemented with L-Glutamine (Sigma Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany), penicillin–streptomycin (Gibco, Fisher Scientific, Madrid, Spain), and Fetal Bovine Serum (FBS) (Gibco, Fisher Scientific, Madrid, Spain). Human Embryonic Kidney 293T cells (HEK293T) were cultured in low-glucose Gibco DMEM medium (Fisher Scientific, Madrid, Spain), also supplemented with L-Glutamine, penicillin–streptomycin, and FBS. Cultures were maintained at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere. To examine the antioxidant effects of the 4QMn compound, prior to UVA radiation, HNEK and NHDF cells were incubated for 24 hours (h) in a medium containing 5–10 µM 4QMn under standard conditions. The selected non-cytotoxic concentrations were determined previously by the MTT assay.
2.3. Cell Transfection
For the Huntington disease cell model generation, HEK293T cells were used. The transient expression of mHtt was induced, as described elsewhere [25], by using a plasmid containing huntingtin exon 1 with a polyQ stretch of 121 glutamines and the CMV promoter. After the transfection process, cells were treated with the 4QMn compound at 20 µM to evaluate its antioxidant efficacy in subsequent studies.
2.4. Human Skin Explants
Human skin explants were received and evaluated for good condition. They were obtained from abdominal plastic surgery surplus from voluntary donors after signing an informed consent document. Skin explants comprising the epidermis and dermis were used to perform these experiments. After the selection of healthy tissues, human skin explants were cut and divided in a 24-well plate with low-glucose DMEM medium (Fisher Scientific, Madrid, Spain). They were maintained at 37 °C in a 5% CO2 humidified atmosphere, and the medium was replaced every day until the end of the experiment. After 24 h of acclimatization, human explants were treated with 10 µM or 5 µM of the 4QMn compound for another 24 h. After the incubation period, human explants were irradiated with UVA to induce oxidative stress. After irradiation, samples were processed for subsequent assays. The human skin explants used in this study were obtained from donors who signed an informed consent form and allowed the use of these explants for R&D and empirical purposes.
2.5. MTT Assay
For cell viability evaluation, 3-(4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-diphenyltetrazolium bromide (Sigma Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) was used. HNEK, NHDF, and HEK293T cells treated with different compounds were incubated with the MTT reagent for 3 h. After the incubation time, dimethyl sulfoxide (Sigma Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) was used to dissolve the formazan crystals, and the color intensity was measured at 550 nm in a spectrophotometer Halo LED 96 (Dynamica Scientific, Livingston, UK).
2.6. UVA Irradiation
The light source was supplied by a Luzchem Exposure Panel EXPO-01 (Luzchem, ON, Canada) that holds five 8-Watt fluorescent lamps. UVA lamps are centered at approximately 300 nm with a radiation peak at 368 nm (Fluorimport, Peschiera Borromeo, Italy). The dosage used for UVA radiation was 6.5 J/cm2. HNEK and NHDF cells were irradiated in the culture medium, and the irradiation panel was located at the bottom of the plate. On the other hand, human skin explants were irradiated from the top, with a distance from the irradiator panel of 10 cm. Parallel HNEK, NHDF, and human skin explants were maintained without irradiation (non-irradiated controls).
2.7. ROS Quantification
The quantification of intracellular ROS was performed with the Fluorometric Intracellular ROS kit (Sigma Aldrich, Darmstadt, Germany) following the manufacturer’s instructions. The ROS probe was added to the cells immediately before irradiation, and fluorescence was measured in a GloMax Microplate Reader (Promega, Madrid, Spain). For HEK293T cells expressing mHtt, the ROS probe was added to the cells and incubated for 2 h. After the incubation period, fluorescence was read at λex = 490/λem = 525.
2.8. Gene Expression Analysis (qRT-PCR)
Total RNA was extracted using the RNeasy mini kit (Qiagen, Madrid, Spain) and treated with DNAse-I (Qiagen, Madrid, Spain) to remove any contamination from genomic DNA. RNA quality and quantity were checked in a Nano-Drop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Madrid, Spain), and 500 ng of total RNA was used to synthesize cDNA using the PrimerScript RT reagent kit (Takara, Saint-Germain-en-Laye, France). qRT-PCR was performed in a QuantStudio 5 thermocycler (Applied Biosystem, Madrid, Spain) using TaqMan probes for CAT, GPX1, NFE2L2, SOD1, IL6, IL8, and TNFα (IDT, Iowa, USA). ACT was used as a housekeeping gene.
2.9. MitoROS Quantification
For the quantification of mitochondrial superoxide radicals, the Mitochondrial Superoxide Detection kit (Fluorimetric) ab219943 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) was used following the manufacturer’s instructions. For HEK293T cells expressing mHtt (121Q), MitoROS 580 dye was added to the cells and incubated for 2 h. After the incubation period, fluorescence was measured at λex = 490/λem = 525 in a GloMax Microplate Reader (Promega, Madrid, Spain).
2.10. 8-Hydroxy-2′-deoxyguanosine (8-OHdG) Quantification
To quantify 8-OHdG, the 8-OHdG ELISA kit ab285254 (Abcam, Cambridge, UK) was used following the manufacturer’s instructions. First, samples were processed for genomic DNA extraction using the PureLink Genomic DNA mini kit (Invitrogen, Thermo Fisher, Madrid, Spain). DNA quality and quantity were analyzed in a Nano-Drop 2000 spectrophotometer (Thermo Scientific, Madrid, Spain), and 1 µg of total DNA was digested with Nuclease P1 (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA). After that, samples were treated with Alkaline Phosphatase (New England Biolabs, Ipswich, MA, USA) and directly used for 8-OHdG quantification by ELISA.
2.11. Statistical Analysis
GraphPad Prism software, version 8 (GraphPad, San Diego, CA, USA), was used to perform the statistical analysis. Data are represented as mean ± SEM, and the ordinary one-way ANOVA test with Dunnet’s post hoc test was applied for the analysis. Data outliers were identified with the ROUT method (Q = 5%) and excluded from the analysis if found. Statistical significance was set at p < 0.05 with 95% confidence. Bars in the charts represent the mean value for each condition, and error bars indicate the standard error of the mean (SEM) for each group of values.
3. Results
3.1. Evaluation of 4QMn Antioxidant Capacity by Quantification of UVA-Induced ROS in Human Skin Cells and Skin Explants
UVA radiation induces ROS in human epidermal cells and skin explants. We exposed HNEK cells, NHDF cells, and human skin explants to a UVA dose of 6.5 J/cm2 to induce an increase in ROS levels (Figure 2A–C; 6500 ± 406.9 Arbitrary Units (A.U.), 1374 ± 145.8 A.U., and 911.2 ± 91.8 A.U., respectively). As described previously [14], a monoculture comprising a single cell is inherently more susceptible to irradiation compared to a multi-dimensional system composed of diverse cell types and layers, which enables the activation of various mechanisms to address oxidative stress and facilitate the repair of the generated damage. To determine the potential of the 4QMn molecule to protect cells from ROS, we first performed an MTT assay on each cell type to determine the working non-toxic concentrations. HNEKs, NHDFs, or skin explants were treated with 5 or 10 µM of the 4QMn compound for 24 h before UVA radiation. Treatment with 5 µM of 4QMn did not show a protective effect against oxidative stress in either of the three models (Figure 2A–C). However, when the concentration was increased to 10 µM, 4QMn treatment significantly reduced UVA-increased ROS levels in HNEK cells (by 227.8 ± 406.9 A.U.), NHDF cells (by 709.6 ± 145.8 A.U.), and human skin explants (by 154.9 ± 91.8 A.U). These results showed the antioxidant efficacy of the 4QMn compound in cellular systems and human skin explants.
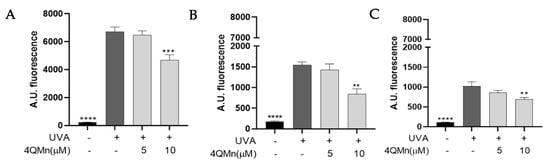
Figure 2.
Bar graph showing ROS levels generated in (A) HNEK cells, (B) NHDF cells, and (C) human skin explants after UVA radiation. Statistical analysis refers to UVA-irradiated cells or skin. ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001 and **** p < 0.0001.
3.2. Gene Expression Analysis after 4QMn Treatment in Human Skin Cells and Skin Explants following UVA Radiation
One of the key mechanisms involved in UVA radiation protection is the activation of the transcription factor NRF2, which regulates the expression of antioxidant genes such as catalase (CAT) and superoxide dismutase 1 (SOD1) [26]. CAT plays a crucial role in scavenging hydrogen peroxide, while SOD1 acts as a major antioxidant enzyme involved in the detoxification of superoxide radicals [27]. Hence, the antioxidant efficacy of 4QMn treatment was evaluated by investigating the regulation of these genes. When HNEK cells were exposed to UVA radiation, CAT, NRF2, and SOD1 gene expression levels were increased by 31.9 ± 9.6%, 52.0 ± 3.4%, and 30.7 ± 5.3%, respectively (Figure 3A–C). 4QMn treatment of HNEKs prior to UVA radiation did not change the responses of these genes to UVA radiation. On the other hand, NHDF cells exhibited a higher response to UVA radiation than HNEKs, resulting in a significant upregulation of CAT, NRF2, and SOD1 gene expression levels by 80.6 ± 13.1%, 63.8 ± 6.8%, and 21.3 ± 9.0%, respectively (Figure 3D–F). Remarkably, the treatment of NHDF cells with 4QMn at 5 µM significantly reduced the UVA-induced CAT, NRF2, and SOD1 gene expression levels by 81.7 ± 12.9%, 72.5 ± 6.7%, and 63.7 ± 9.0%, respectively (Figure 3D–F). Furthermore, sustained antioxidant effects were observed when NHDF cells were treated with 10 µM of 4QMn, leading to a further reduction in CAT, NRF2, and SOD1 gene expression levels by 61.3 ± 12.9%, 58.9 ± 6.7%, and 56.3 ± 8.9%, respectively (Figure 3D–F). Finally, in human skin explants, UVA radiation increased CAT, NRF2, and SOD1 gene expression levels by 64.8 ± 8.6%, 60.9 ± 21.8%, and 63.2 ± 13.0%, respectively (Figure 3G–I). In this model, the higher antioxidant effect of 4QMn treatment was reached when used at 10 µM, significantly reducing UVA-induced CAT, NRF2, and SOD1 gene expression levels by 51.1 ± 8.6%, 53.5 ± 21.8%, and 50.1 ± 13.0%, respectively (Figure 3G–I). These results confirm the antioxidant capacity of the 4QMn compound in epidermal cells and human skin explants and validate its effectiveness in both unicellular models and more complex systems like human skin.
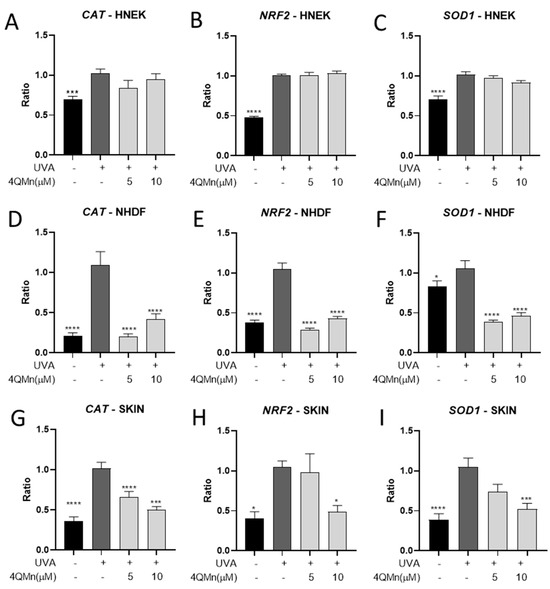
Figure 3.
Bar graph showing CAT, NRF2, and SOD1 gene expression levels generated for (A–C) HNEK cells, (D–F) NHDF cells, and (G–I) human skin explants after UVA radiation. Statistical analysis referred to UVA-irradiated cells or skin. * p < 0.05, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.
Furthermore, UVA exposure and the induction of ROS also trigger an inflammatory process characterized by the activation of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, such as interleukin-6 (IL6), interleukin-8 (IL8), and tumor necrosis factor-alpha (TNFα) [28,29,30]. These cytokines play pivotal roles in orchestrating the inflammatory response by recruiting immune cells, promoting vasodilation, and activating downstream signaling pathways. Elevated levels of IL-6, IL-8, and TNF-α have been observed in UVA-exposed skin and are associated with various skin disorders and inflammatory conditions [31,32,33]. Understanding the intricate relationship between UVA radiation, inflammation, and the dysregulation of these cytokines is essential for devising effective therapeutic interventions to mitigate UVA-induced inflammation and its detrimental effects on the skin. To address this objective, the potential anti-inflammatory response of 4QMn upon UVA exposure was also assessed. After the UVA radiation of HNEK cells, IL6 and TNFα gene expression levels were increased by 92.8 ± 8.9% and 20.9 ± 6.3%, respectively, and treatment with 4QMn at 10 µM was able to reduce TNFα gene levels by 17.9 ± 6.8% (Figure 4A–C). In the case of NHDF cells, UVA radiation induced an inflammatory response, activating IL6, IL8, and TNFα gene expression by 53.5 ± 15.8%, 94.8 ± 11.9%, and 40.9 ± 15.0%, respectively, compared to the non-irradiated control (Figure 4D–F). Interestingly, treatment with 4QMn at 5 µM reduced UVA-induced IL8 and TNFα gene expression levels by 34.2 ± 11.9% and 72.8 ± 14.7%, respectively (Figure 4D–F). Additionally, when 4QMn was used at 10 µM, reductions in IL6 and TNFα gene expression levels of 65.8 ± 15.8% and 62.2 ± 15.0%, respectively, were also observed (Figure 4D–F). Finally, when human skin explants were exposed to UVA radiation, IL6, IL8, and TNFα gene expression levels were increased by 94.0 ± 18.6%, 94.4 ± 9.5%, and 66.0 ± 12.3%, respectively. Most importantly, treatment with 4QMn at 5 µM reduced IL8 gene expression levels by 50.3 ± 9.5%, and, when used at 10 µM, it decreased IL6 and IL8 gene levels by 65.5 ± 18.6% and 63.4 ± 9.5%, respectively (Figure 4G–I). These results demonstrate that the 4QMn compound reduces the activation of pro-inflammatory interleukins induced by UVA radiation in epidermal cells and human skin explants.
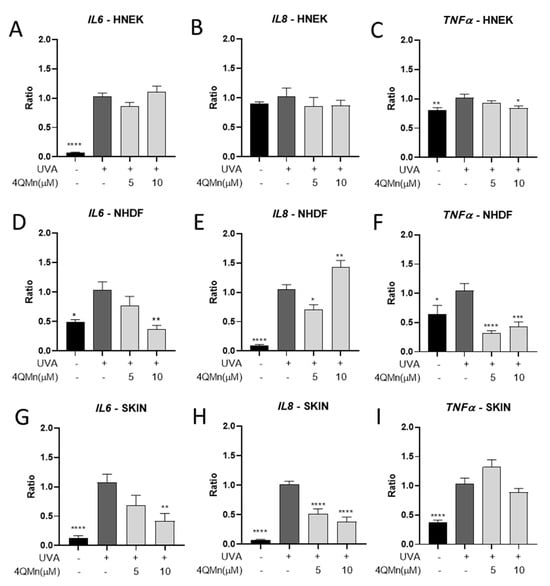
Figure 4.
Bar graph showing IL6, IL8, and TNFα gene expression levels generated for (A–C) HNEK cells, (D–F) NHDF cells, and (G–I) human skin explants after UVA radiation. Statistical analysis referred to UVA-irradiated cells or skin. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.
3.3. Oxidative Damage Assessment after 4QMn Treatment in an In Vitro Model of Protein Aggregation
The overproduction of ROS and mitochondrial dysfunction play a prominent role when protein repair and degradative systems are unable to act upon oxidized proteins and restore cellular function during biological aging [34]. Age-dependent increments in the rate of ROS generation or the diminishing efficiency of cellular repair and degradation mechanisms will increase the oxidative burden on the cell. This, in turn, leads to proportional elevations in the concentrations of oxidized proteins and the subsequent formation of abnormal protein aggregates [15]. Therefore, the effect of the compound 4QMn in ameliorating oxidative damage in a protein aggregation model, like the HD cell model used in our previous studies, was analyzed [25]. First, attention was focused on measuring ROS, the most common oxidants produced in cells when there is an imbalance between oxidants and antioxidants, resulting in cell damage [35]. As observed in Figure 5A, the aggregation of proteins (121Q, cells expressing huntingtin protein aggregates) led to significantly increased ROS levels (by 68.2 ± 8.2%) as compared to control cells. This observation substantiates the phenomenon of ROS overproduction inherent to skin diseases characterized by protein aggregation and misfolding. Notably, the 4QMn treatment of cells accumulating proteins resulted in a reduction in ROS levels of 41.1 ± 8.2% (Figure 5A), underscoring 4QMn’s antioxidant efficacy. On the other hand, as mitochondria are one of the main sources of ROS, the specific accumulation of ROS in mitochondria was measured through MitoROS quantification [36]. The results indicated that protein misfolding and accumulation led to a MitoROS increase of 38.9 ± 4.8% (Figure 5B). Interestingly, 4QMn treatment decreased MitoROS levels by 19.6 ± 4.8% compared to the 121Q-untreated condition (Figure 5B). Finally, the assessment of 8-hydroxydeoxyguanosine (8OH-dG), a well-established biomarker of DNA oxidative damage, was performed. Increased levels of 8OH-dG were quantified (59.9 ± 10.6%) as a consequence of protein aggregation (121Q) (Figure 5C). Moreover, following treatment with 4QMn, 8OH-dG levels were reduced by 27.7 ± 10.6% (Figure 5C). These findings provide evidence for the antioxidant capacity of the 4QMn compound in mitigating oxidative damage resulting from the accumulation of misfolded proteins and suggest its potential as a promising compound for ameliorating aging symptoms.
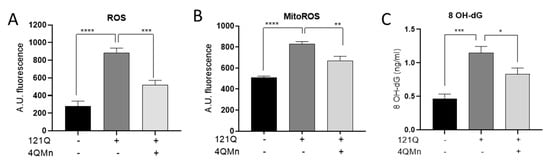
Figure 5.
Bar graph showing (A) ROS, (B) MitoROS, and (C) 8 OH-dG levels in HEK293T cells. 121Q—transfected cells producing protein aggregation; 4QMn—cells treated with 4QMn compound. Statistical analysis referred to non-treated transfected cells (121Q). * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, *** p < 0.001, **** p < 0.0001.
4. Discussion
The present study aimed to investigate the potential protective effects of the 4QMn compound from UV-induced ROS generation and inflammatory IL secretion in human skin cells. Our results indicated that UVA radiation significantly increased ROS levels in HNEK cells, NHDF cells, and human skin explants. HNEK cells showed the highest ROS accumulation, followed by NHDF cells and human skin explants. This could be explained by the higher susceptibility of fibroblasts to UV radiation in comparison to keratinocytes. Fibroblasts and keratinocytes possess distinct DNA repair capabilities, and keratinocytes exhibit a superior ability to recover from the deleterious effects of UVA radiation and restore cellular homeostasis [26,37,38]. Additionally, this finding suggests that monoculture cells are more susceptible to UVA radiation-induced oxidative stress compared to multi-dimensional systems like human skin explants, which can activate various mechanisms to counteract oxidative damage [14]. Treatment with 5 µM of the 4QMn compound did not show any protective effect against UVA-induced oxidative stress in any of the three models. However, when used at 10 µM, 4QMn treatment significantly reduced ROS levels in all models, demonstrating the protective antioxidant efficacy of the compound. These results are in agreement with previous studies where the antioxidant capabilities of manganese complexes were described and also evaluated in prokaryotic and eukaryotic organisms [22,23]. Using different SOD-deficient E. coli strains, it was demonstrated that the 4QMn (Mn-L1) complex improved their aerobic growth in restricted culture media due to the SOD mimetic activity. On the other side, Saccharomyces cerevisiae strains defective in the cytoplasmatic copper-dependent SOD were used to evaluate the SOD-like activity of the 4QMn (Mn-L1) complex. In this case, S. cerevisiae’s poor growth in glycerol was almost completely rescued by 4QMn activity [23].
This study also investigated how 4QMn regulates the gene expression of key antioxidant genes, including CAT, NRF2, and SOD1, and the potential anti-inflammatory effects of 4QMn by measuring the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines (IL6, IL8, and TNFα) after UVA exposure. The results exposed, once again, the differences between fibroblast and keratinocyte responses to UV radiation. As explained before, keratinocytes possess a higher capacity to recover from the deleterious effects of UVA radiation, showing low activation of antioxidant and anti-inflammatory genes and reduced protective effects with 4QMn treatment. On the other hand, fibroblasts had higher gene expression activation and, in consequence, presented the highest protective effect of the 4QMn compound, supporting the antioxidant capacity of 4QMn and its potential as an anti-inflammatory compound, as evidenced by the reduction in cytokine expression across all three models. In this regard, a previous study showed that after LPS inflammation induction in THP1 cells, 4QMn (Mn-L1) treatment was able to attenuate the LPS-induced mRNA expression of all tested pro-inflammatory genes, such as TNFα, IL6, IL8, IL1β, and PTGS2 [24]. Additionally, this anti-inflammatory potential was also evaluated in an LPS mouse model of sepsis, resulting in a reduction in TNFα and IL6 serum protein levels after 4QMn exposure [24]. This consistency with previous findings reinforces the effectiveness of 4QMn in human cells and tissues to control ROS and mitigate irritation in the skin. Therefore, the 4QMn molecule could be used as an effective treatment to ameliorate oxidative stress in the skin and reduce irritation outbreaks due to ROS induction.
Finally, we examined the compound’s ability to mitigate oxidative damage in a protein aggregation cellular model as an aging-related process that occurs in the skin [39,40]. It was observed that 4QMn treatment reduced ROS levels, mitochondrial ROS (MitoROS) levels, and DNA oxidative damage (8OH-dG) in cells with misfolded protein accumulation. These findings suggest that 4QMn may have the potential to treat conditions characterized by oxidative stress and inflammation, including skin disorders that are characterized by protein aggregation, like cutaneous amyloidosis. Numerous research studies have demonstrated that oxidative stress plays a central role in the amyloid formation process [41]. Free radical damage is involved in either the process of amyloid formation or post-fibrillar modification in various forms of amyloidosis, suggesting radical scavenger treatments as the possible solution [42,43]. Another skin disease characterized by predominant oxidative stress and inflammation is atopic dermatitis (AD). This chronic skin inflammation is correlated with the overproduction of ROS, and treatments with antioxidants such as vitamin E or beta carotene have been under consideration [44].
Hence, for a treatment to be truly effective in maintaining skin health, it is important not only to demonstrate antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects but also to enhance and improve the mechanisms responsible for abnormal protein degradation to maintain proteostasis. Proteostasis is a crucial requirement for skin health, given that the elimination of these abnormal proteins constitutes a crucial intracellular function, and it is essential for the antioxidant defense system in the cell. In recent studies, we showed that the compound 4QMn enhanced ubiquitin–proteasome and autophagy activity, reducing the number of protein aggregates of mHTT in the cellular model of HD used in this study, as well as in worm and mouse models [25,45].
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, antioxidant compounds are used not only as active ingredients in cosmetic formulations but also in therapeutic approaches to skin conditions, showing promising results in slowing down the progression of diseases. Our findings underscore the promising future of the 4QMn compound. It is a water-soluble molecule with low toxicity, mimics the superoxide dismutase enzyme, displays high antioxidant and anti-inflammatory capacities, and helps with protein degradation by enhancing autophagy. Further research and clinical studies are warranted to explore its clinical applications and safety profile, and research should continue to explore the multifaceted interplay between oxidative stress and skin health, with the aim of developing effective treatments for slowing down the skin aging process.
6. Patents
The 4QMn compound is the subject of several patents: “Metallic complexes mimetic of SOD” (Spain 2355784B1, WO WO2011/033163, United States 9,145,386, Europe 2492270); “Use of SOD mimetic metal complexes as food agents and as cosmetic, patent addition” (Spain 2543850B1, WO WO2015/124824, United States US9.570.677); and “New European 4Q application and autophagy for neurodegenerative diseases” (Europe PCT-07877, WO PCT/EP2018/068010).
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.M. and J.L.M.; methodology, M.M., S.G. and J.L.M.; formal analysis, M.M. and J.L.M.; investigation, M.M. and J.L.M.; resources, M.P.C., E.G.-E. and J.L.M.; data curation, M.M. and J.L.M.; writing—original draft preparation, M.M.; writing—review and editing, M.M. and J.L.M.; supervision, J.L.M.; funding acquisition, E.G.-E. and J.L.M. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
M.M. used an Innodocto grant (INNTA3/2021/26) funded by the Valencian Agency of Innovation (AVI). Funds from the NEOTEC Project were also used. Additionally, this work was supported partly by the Conselleria de Innovación, Universidades, Ciencia y Sociedad Digital, Generalitat Valenciana (PROMETEO Grant CIPROM/2021/030).
Institutional Review Board Statement
The protocol for obtaining human skin explants was approved by the Ethics Committee of Instituto de Investigación Sanitaria La Fe (protocol code BIONOS_2021, registry number 2021-356-1, and date of approval 7 July 2021).
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from the voluntary donors of the skin explants used in the study.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be available upon request.
Acknowledgments
We wish to thank Rafael P. Vázquez Manrique for sharing the plasmid.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors Marián Merino, Sonia González, and José L. Mullor are employees of Bionos Biotech SL. The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as potential conflicts of interest.
References
- Prost-Squarcioni, C. Histology of skin and hair follicle. Med. Sci. 2006, 22, 131–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arda, O.; Göksügür, N.; Tüzün, Y. Basic histological structure and functions of facial skin. Clin. Dermatol. 2014, 32, 3–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopez-Ojeda, W.; Pandey, A.; Alhajj, M.; Oakley, A.M. Anatomy, Skin (Integument). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. Available online: http://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK441980/ (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Graham, H.K.; Eckersley, A.; Ozols, M.; Mellody, K.T.; Sherratt, M.J. Human Skin: Composition, Structure and Visualisation Methods. In Skin Biophysics: From Experimental Characterisation to Advanced Modelling; Limbert, G., Ed.; Studies in Mechanobiology, Tissue Engineering and Biomaterials; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 1–18. ISBN 978-3-030-13279-8. [Google Scholar]
- Yousef, H.; Alhajj, M.; Sharma, S. Anatomy, Skin (Integument), Epidermis. In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2023. [Google Scholar]
- Amaro-Ortiz, A.; Yan, B.; D’Orazio, J.A. Ultraviolet Radiation, Aging and the Skin: Prevention of Damage by Topical cAMP Manipulation. Molecules 2014, 19, 6202–6219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Polefka, T.G.; Meyer, T.A.; Agin, P.P.; Bianchini, R.J. Effects of solar radiation on the skin. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2012, 11, 134–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ichihashi, M.; Ando, H.; Yoshida, M.; Niki, Y.; Matsui, M. Photoaging of the skin. Anti-Aging Med. 2009, 6, 46–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diffey, B.L. Human exposure to solar ultraviolet radiation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2002, 1, 124–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Juzeniene, A.; Moan, J. Beneficial effects of UV radiation other than via vitamin D production. Dermato-Endocrinology 2012, 4, 109–117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shin, D.W. Various biological effects of solar radiation on skin and their mechanisms: Implications for phototherapy. Anim. Cells Syst. 2020, 24, 181–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vierkötter, A.; Krutmann, J. Environmental influences on skin aging and ethnic-specific manifestations. Dermato-Endocrinology 2012, 4, 227–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neale, R.E.; Lucas, R.M.; Byrne, S.N.; Hollestein, L.; Rhodes, L.E.; Yazar, S.; Young, A.R.; Berwick, M.; Ireland, R.A.; Olsen, C.M. The effects of exposure to solar radiation on human health. Photochem. Photobiol. Sci. 2023, 22, 1011–1047. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merino, M.; Mullor, J.L.; Sánchez-Sánchez, A.V. Medaka (Oryzias latipes) Embryo as a Model for the Screening of Compounds That Counteract the Damage Induced by Ultraviolet and High-Energy Visible Light. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 5769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Squier, T.C. Oxidative stress and protein aggregation during biological aging. Exp. Gerontol. 2001, 36, 1539–1550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrotra, K.; Dewan, R.; Kumar, J.V.; Dewan, A. Primary Cutaneous Amyloidosis: A Clinical, Histopathological and Immunofluorescence Study. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2017, 11, WC01–WC05. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kowalska-Kępczyńska, A. Systemic Scleroderma—Definition, Clinical Picture and Laboratory Diagnostics. J. Clin. Med. 2022, 11, 2299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nguyen, C.N.; Kim, S.-J. Dermatitis Herpetiformis: An Update on Diagnosis, Disease Monitoring, and Management. Medicina 2021, 57, 843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Svobodová, A.; Vostálová, J. Solar radiation induced skin damage: Review of protective and preventive options. Int. J. Radiat. Biol. 2010, 86, 999–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biskanaki, F.; Kefala, V.; Lazaris, A.C.; Rallis, E. Aging and the Impact of Solar Ultraviolet Radiation on the Expression of Type I and Type VI Collagen. Cosmetics 2023, 10, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garnacho Saucedo, G.M.; Salido Vallejo, R.; Moreno Giménez, J.C. Effects of solar radiation and an update on photoprotection. An. Pediatría 2020, 92, 377.e1–377.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clares, M.P.; Blasco, S.; Inclán, M.; del Castillo Agudo, L.; Verdejo, B.; Soriano, C.; Doménech, A.; Latorre, J.; García-España, E. Manganese(II) complexes of scorpiand-like azamacrocycles as MnSOD mimics. Chem. Commun. 2011, 47, 5988–5990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clares, M.P.; Serena, C.; Blasco, S.; Nebot, A.; del Castillo, L.; Soriano, C.; Domènech, A.; Sánchez-Sánchez, A.V.; Soler-Calero, L.; Mullor, J.L.; et al. Mn(II) complexes of scorpiand-like ligands. A model for the MnSOD active centre with high in vitro and in vivo activity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2015, 143, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serena, C.; Calvo, E.; Clares, M.P.; Diaz, M.L.; Chicote, J.U.; Beltrán-Debon, R.; Fontova, R.; Rodriguez, A.; García-España, E.; García-España, A. Significant in vivo anti-inflammatory activity of Pytren4Q-Mn a superoxide dismutase 2 (SOD2) mimetic scorpiand-like Mn (II) complex. PLoS ONE 2015, 10, e0119102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, M.; Sequedo, M.D.; Sánchez-Sánchez, A.V.; Clares, M.P.; García-España, E.; Vázquez-Manrique, R.P.; Mullor, J.L. Mn(II) Quinoline Complex (4QMn) Restores Proteostasis and Reduces Toxicity in Experimental Models of Huntington’s Disease. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 8936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ryšavá, A.; Čížková, K.; Franková, J.; Roubalová, L.; Ulrichová, J.; Vostálová, J.; Vrba, J.; Zálešák, B.; Rajnochová Svobodová, A. Effect of UVA radiation on the Nrf2 signalling pathway in human skin cells. J. Photochem. Photobiol. B 2020, 209, 111948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ighodaro, O.M.; Akinloye, O.A. First line defence antioxidants-superoxide dismutase (SOD), catalase (CAT) and glutathione peroxidase (GPX): Their fundamental role in the entire antioxidant defence grid. Alex. J. Med. 2018, 54, 287–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansary, T.M.; Hossain, M.d.R.; Kamiya, K.; Komine, M.; Ohtsuki, M. Inflammatory Molecules Associated with Ultraviolet Radiation-Mediated Skin Aging. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 3974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhao, H.-C.; Xiao, T.; Chen, Y.-J. Ultraviolet Induced Skin Inflammation. Int. J. Dermatol. Venereol. 2021, 4, 229–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hruza, L.L.; Pentland, A.P. Mechanisms of UV-Induced Inflammation. J. Investig. Dermatol. 1993, 100, S35–S41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Willems, E.; Singh, A.; Hafeez, B.B.; Ong, I.M.; Mehta, S.L.; Verma, A.K. Ultraviolet radiation-induced tumor necrosis factor alpha, which is linked to the development of cutaneous SCC, modulates differential epidermal microRNAs expression. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 17945–17956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, S.; Gao, J.; Dinh, Q.T.; Chen, C.; Fimmel, S. IL-8 production and AP-1 transactivation induced by UVA in human keratinocytes: Roles of d-α-tocopherol. Mol. Immunol. 2008, 45, 2288–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schneider, L.A.; Raizner, K.; Wlaschek, M.; Brenneisen, P.; Gethöffer, K.; Scharffetter-Kochanek, K. UVA-1 exposure in vivo leads to an IL-6 surge within the skin. Exp. Dermatol. 2017, 26, 830–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Widmer, R.; Ziaja, I.; Grune, T. Protein oxidation and degradation during aging: Role in skin aging and neurodegeneration. Free Radic. Res. 2006, 40, 1259–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schieber, M.; Chandel, N.S. ROS Function in Redox Signaling and Oxidative Stress. Curr. Biol. 2014, 24, R453–R462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopes, C.; Ferreira, I.L.; Maranga, C.; Beatriz, M.; Mota, S.I.; Sereno, J.; Castelhano, J.; Abrunhosa, A.; Oliveira, F.; Rosa, M.D.; et al. Mitochondrial and redox modifications in early stages of Huntington’s disease. Redox Biol. 2022, 56, 102424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goyeneche, A.A.; Garcia de Alba Graue, P.; Mastromonaco, C.; McDonald, M.; Burnier, J.V.; Burnier, M.N. Distinctive responses of keratinocytes and fibroblasts to sunlight-induced DNA damage. Investig. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2020, 61, 4671. [Google Scholar]
- Izykowska, I.; Cegielski, M.; Gebarowska, E.; Podhorska-Okolow, M.; Piotrowska, A.; Zabel, M.; Dziegiel, P. Effect of Melatonin on Human Keratinocytes and Fibroblasts Subjected to UVA and UVB Radiation In Vitro. In Vivo 2009, 23, 739–745. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tuite, M.F.; Melki, R. Protein Misfolding and Aggregation in Ageing and Disease. Prion 2007, 1, 116–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jones, R. Protein Aggregation Increases with Age. PLOS Biol. 2010, 8, e1000449. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ando, Y.; Nyhlin, N.; Suhr, O.; Holmgren, G.; Uchida, K.; el Sahly, M.; Yamashita, T.; Terasaki, H.; Nakamura, M.; Uchino, M.; et al. Oxidative stress is found in amyloid deposits in systemic amyloidosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1997, 232, 497–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, M.; Ando, Y. Amyloidosis and oxidative stress. Rinsho Byori 2003, 51, 140–145. [Google Scholar]
- Ando, Y.; Suhr, O.; el-Salhy, M. Oxidative stress and amyloidosis. Histol. Histopathol. 1998, 13, 845–850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertino, L.; Guarneri, F.; Cannavò, S.P.; Casciaro, M.; Pioggia, G.; Gangemi, S. Oxidative Stress and Atopic Dermatitis. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merino, M.; González, S.; Tronch, M.C.; Sánchez-Sánchez, A.V.; Clares, M.P.; García-España, A.; García-España, E.; Mullor, J.L. Small Molecule Pytren-4QMn Metal Complex Slows down Huntington’s Disease Progression in Male zQ175 Transgenic Mice. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 15153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).