Abstract
The growing interest in maintaining a youthful appearance has encouraged an accelerated development of innovative, minimally invasive aesthetic treatments for facial rejuvenation and regeneration. The close correlation between tissue repair, regeneration, and aging has paved the way for the application of regenerative medicine principles in cosmetic dermatology. The theoretical substrates of regenerative medicine applications in dermo-aesthetics are plentiful. However, regenerative dermatology is an emerging field and needs more data and in vivo trials to reach a consensus on the standardization of methods. In this review, we summarize the principles of regenerative medicine and techniques as they apply to cosmetic dermatology, suggesting unexplored fields and future directions.
1. Introduction
The growing interest in maintaining a youthful and rested appearance has prompted an accelerated development of noninvasive and minimally invasive aesthetic approaches for skin rejuvenation and regeneration. The population requiring mini-invasive aesthetic treatments is continuously expanding, extending beyond the traditional limits of the over-45s to also millennials (born ~1981 to 1996) and even Generation Z (born ~from 1997), in the context of pre-rejuvenation [1,2,3]. The term “pre-juvenation” refers to a preventive approach of anti-aging procedures that emerged in the early 2000s between millennials and Generation Z (Gen Z) [2]. Since then, it has become a trending topic across all media platforms and serves as a driving force behind the growing demand of noninvasive treatments in aesthetics [4]. This innovative field sprouts regenerative dermatology as a combination of the principles of regenerative medicine in the context of skin regeneration and rejuvenation. The close correlation between tissue repair, regeneration, and aging [5,6,7] underlies the rationale for the application of regenerative medicine in aesthetic dermatology. Regenerative medicine aims to replace lost or damaged tissues, while regenerative aesthetics focuses on regenerating soft tissues lost or damaged due to aging processes [8].
2. Principles of Regenerative Medicine
The skin shows its regenerative ability mostly during the complex process of wound healing. Following skin trauma, a network of events is launched that involves three steps: the early coagulation and hemostasis phase, inflammatory phase, and growth phase [9]. (Figure 1) The initial response to a wound is the constriction of injured blood vessels and activation of platelets to form a fibrin clot. Platelets are anucleate cells derived from megakaryocytes [10]. They contain secretory granules; among them, α-granules are the most abundant [11,12] and are released immediately after the platelets’ activation. With α-granules, numerous active factors are secreted: platelet-derived growth factor (PDGF), transforming growth factor (TGF), platelet factor interleukin (IL), platelet-derived angiogenesis factor (PDAF), vascular endothelial growth factor (VEGF), epidermal growth factor (EGF), insulin-like growth factor IGF, adhesive proteins (vWF, TSP1, and vitronectin), coagulation factors (factors V, VII, XI, and XIII), protease inhibitors (protein C, PAI-1, and TFPI), and fibronectin [13,14,15]. Growth factors account for various functions, including promoting mitogenesis and the differentiation of stem cells, fibroblasts, keratinocytes, and endothelial cells. They induce cell proliferation, chemotaxis, and angiogenesis, promoting cell differentiation, proliferation, and regeneration [16]. The fibrin clot made by platelets interrupts blood flow and provides a structure for incoming inflammatory cells, including neutrophils, monocytes, Langerhans cells, dermal dendritic cells, and T lymphocytes. When inflammation ends, the growth phase begins with angiogenesis, which involves the proliferation, migration, and branching of endothelial cells [17]. The formation of new blood vessels is a key step in wound healing. The activation of endothelial cells requires growth factors from contiguous cells (from platelets, keratinocytes, macrophages, and subcutaneous adipose tissue) [18]. Endothelial cells branch out to form new capillaries in response to pro-angiogenic, hypoxia-responsive signals, such as VEGF, FGF, PDGF-B, TGF-β, and angiopoietins [17,18,19]. Activated endothelial cells express the surface markers’ intercellular adhesion molecule (ICAM)-1, vascular cell adhesion molecule (VCAM)-1, E-selectin, and P-selectin, which contribute to intercellular and leukocyte interactions. Pro-angiogenic macrophages release growth factors for endothelial cell proliferation while fusing newly formed capillaries [17]. A major hallmark of the proliferative phase of wound healing is wound contraction, in which collagen fibrils are organized to increase the strength of the tissue. Fibroblasts infiltrate and degrade the fibrin clot producing various matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) and replace it with extracellular matrix (ECM) components, such as collagen I–IV and XVIII, glycoproteins, proteoglycans, laminin, thrombospondin, glycosaminoglycans (GAGs), hyaluronic acid (HA), and heparan sulfate [20,21]. Fibroblasts exhibit great heterogeneity based on tissue origin and activation state, leading to different functions in the wound healing process. Studies on fibroblast subpopulations reveal that fibroblasts comprise distinct lineages and return different signals to nearby cells in the skin; this affects dermo-epidermal interactions during wound healing. Dermal papilla fibroblasts play a key role in Wnt/β-catenin signaling in hair follicle development [22]. The inhibition of β-catenin by fibroblasts promotes hair follicle regeneration, while its activation diminishes it [23]. Conversely, epidermal stem cells of the follicular bulge are capable of inducing differentiation into myofibroblasts and smooth muscle cells by sending signals to dermal papilla fibroblasts [24,25]. Myofibroblasts are α-SMA-positive transient cells that derive from activated fibroblasts and play a pivotal role in wound contraction. During mechanical stress, fibroblasts from the dermis and subcutaneous tissue initially transition to proto-myofibroblasts, expressing β- and γ-cytoplasmic actin [20,26]. The interaction of proto-myofibroblasts with fibronectin and stimulation by TGF-β induce differentiation into myofibroblasts that synthesize α-Smooth Cell Actin (α-SMA), [15,27] and produce ECM proteins, including collagen types I and III [28]. Myofibroblasts deposit ECM and show characteristics of contractile smooth muscle cells. Plikus M.V. et al. demonstrated that in murine prototypes, myofibroblasts of early formed hair follicles can form dermal adipocytes following injury and that this transition reduces scar formation [29,30]. Additional ECM components, such as hyaluronic acid, osteopontin, periostin, vitronectin, endothelin, angiotensin, CCN2, and Cx43, are associated with differentiation to myofibroblasts [31,32,33,34]. PDGF is linked to proto-myofibroblast motility [35] and matrix metalloproteinases (MMPs) show that they mediate myofibroblast differentiation, but the exact mechanism remains unknown [36]. Some inflammatory mediators, including TNF-α, can also inhibit differentiation [37]. Shook et al., among others, revealed that myofibroblast transition and dermal adipocytes lipolysis are necessary to initiate inflammation after injury and promote wound repair [38]. Sun et al. studied the interactions between the IL-1 and WNT pathways in the regulation of dermal adipocyte lineage cells during skin development and wound regeneration. They defined the various characteristics of dermal adipocytes in developing or injured mouse skin and revealed that dermal adipogenesis and lipolysis are regulated by an antagonistic interaction between the IL-1-pCREB and WNT-β catenin pathways [39]. During the wound healing, adipocytes cleave triglycerides to promptly release fatty acids to support the metabolism of the surrounding tissues. Adipocyte lipolysis begins with the activation of adipose triglyceride lipase (ATGL), which releases free fatty acid (FFA) and diacylglycerol [40,41]. Subsequent lipases catalyze the hydrolysis of the remaining fatty acids. Shook et al. found that before macrophage infiltration, mature adipocytes undergo lipolysis, releasing FAs into skin wounds [38]. Chang et al. analyzed the function of the long non-coding lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 in ASCs-exos to find if highly expressed lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 in ASCs-derived exosomes affects immortal aneuploid keratinocytes (HaCaT) cells via regulating the miR-185-5p/ROCK2 axis. The study revealed that upregulation of the lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 in exosomes derived from ASCs could enhance the migration and proliferation of HaCaT cells by regulating the miR-185-5p/ROCK2 axis [42]. This evidence makes adipocytes, fibroblasts, and platelets the key cells in the skin regeneration process [14,20,21,38].
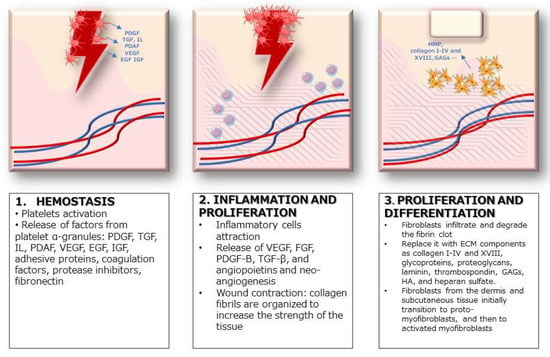
Figure 1.
Stages of wound healing.
3. Regenerative Approaches in Aesthetic Dermatology
Regenerative medicine and even more its application in aesthetic dermatology are recent findings in medical practice. Misha et al. defined three pillars of regenerative medicine, translated into the field of dermo-aesthetics: cells and cell derivatives, Biochemical Cues (Bio-Cues), and scaffolds [43]. (Table 1)The use of stem cells and tissue fractions, first established in the surgical field, is also making its way into the dermo-aesthetic field with nanofat grafting [44,45]. The Bio-Cues represent therapeutic approaches that improve the tissue microenvironment through cell signaling. They include growth factors and derivatives (e.g., platelet-rich plasma and platelet-rich fibrin [13,46]), small bioactive molecules, and extracellular vesicles (EVs) [47,48,49]. The ease of execution and the supporting evidence in the literature made them increasingly more popular [47]. The Aesthetic Regenerative Scaffolds (ARSs) are injectable biomaterials that inhibit a chronic inflammatory response, reverting fibrosis and enhancing physiological tissue regeneration [50,51]. They include Calcium Hydroxyapatite (CaHA), Hyaluronic Acid (HA), and Poli-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA) dermal fillers [50,52,53,54].

Table 1.
Pillars of regenerative medicine in dermo-aesthetics.
3.1. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ASCs) and Nanofat Grafting
Adipose tissue represents a rich deposit of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells (ASCs), which compose a heterogenic population of multipotent progenitors [55,58]. ASCs reside in “stem cell niches” of adipose tissue, where they are closely interconnected with the ECM and other supporting cells [59,60]. Several studies have proven that the niche acts as a modulator of the biological properties and the ability of ASCs to proliferate, differentiate, and migrate in the context of cellular regeneration and wound healing [61,62,63]. ASCs’ secretome represents a topic of great interest in regenerative medicine, because ASCs produce several molecules involved in cell-to-cell signaling, such as inflammatory, immuno-modulatory, and angiogenic cytokines (IL-6 IL-7, IL-8, IL-11, and TNFa) [64,65,66], growth factors (HGF and VEGF) [64,67], and chemokines [64]. In the context of skin regeneration, ASCs act as paracrine actors, [68,69] playing a pivotal role in maintaining the dermo-epidermal structure, as a physiological response to local damage [70]. It has been shown that ASCs can differentiate into keratinocytes, dermal fibroblasts (DFs), and other skin components [70,71]. Autologous fat grafting is considered the filler par excellence because it possesses unique characteristics: biocompatibility, versatility, long-lasting effects, and natural appearance [72]. Since the dawn of its use for soft tissue augmentation by Neuber in 1893, the potential of lipofilling has been recognized, and today it emerges as a key technique in several areas of plastic surgery, such as facelift surgery, breast augmentation, and reconstructive surgery in wound healing [73,74,75,76,77]. Within the area of non-invasive cosmetic procedures comes nanofat grafting, first described in 2013 by Tonnard and colleagues, [44,72], that has gained popularity in cosmetic surgery in recent years [78]. It involves the injection of a highly concentrated solution of autologous progenitor cells, without viable adipocytes [72]. The protocol consists of emulsifying and filtering the microfat harvested by liposuction [79]. A whitish fluid rich in mesenchymal stem cells is obtained, with 25% adipocytes and a 75% stromal vascular fraction (SVF), containing ASCs, ECs, monocytes and macrophages, granulocytes, and lymphocytes [72]. Nanofat is injected intradermally using a retrograde, fan-shaped technique. Nanofat is approximately 400 to 600 μm [80]. Typically, 1 mL of nanofat can cover an area of 1 cm by 1 cm. It can also be delivered by microneedling [44,72]. (Figure 2) Nanofat shows few-to-any filling characteristics, so its field of action includes skin rejuvenation and skin quality by injecting regenerative cells and ECM elements [72]. Menkes et al. evaluate the regenerative and face-lifting effects of nanofat grafting, enrolling 50 patients and treating them with subcutaneous injections of 18 mL of nanofat-PRP. Improved skin quality and a lifting effect were observed at 2–4 weeks, with maintenance of the results up to 6 months after treatment. Biopsies showed an increase in dermal cellularity, vascular density, elastic fiber, and collagen density [81]. Kadry et al. compared the efficacy of PRP versus combined fat transfer and nanofat by treating 30 patients with infraorbital dark circles. Autologous fat transfer with nanofat was shown to be significantly superior to PRP in improvement and satisfaction. In total, 73.7% of patients treated with combined fat transfer and nanofat and 33% of the PRP group showed an excellent and a moderate response in terms of improvement and patients’ satisfaction. Non-responders were significantly higher in the PRP group (53.3% vs. 6.5%) [82]. Nilforoushzadehet al. conducted a study on nine adult patients with atrophic acne scars on the face to investigate the effectiveness of a combined treatment with autologous fat transplantation, SVF cells, and PRP as the cell therapy techniques on atrophic acne scars. The study showed significant improvement in skin pores, blemishes, skin brightness and melanin content, skin elasticity, and TEWL (transepidermal water loss) after 6 months of treatment. In addition, denser skin layers were observed in both the epidermis and dermis. In total, 66.6% of patients showed good satisfaction after treatment [83]. Nanofat grafting is a promising and theoretically attractive option because it looks more “natural” to the patient than other injectables and can produce long-term results. ASCs’ secretome also showed the ability to modulate multiple targets simultaneously, becoming the subject of clinical and preclinical studies on the management of dermatological conditions, such as atopic dermatitis (AD), vitiligo, psoriasis, acne, lichen sclerosus (LS), chronic wounds, and alopecia [84]. However, when considering potential disadvantages, the following should be mentioned: donor site morbidity, unpredictability of graft survival, [85,86] graft hypertrophy, and exposure to local or general anesthesia [87].
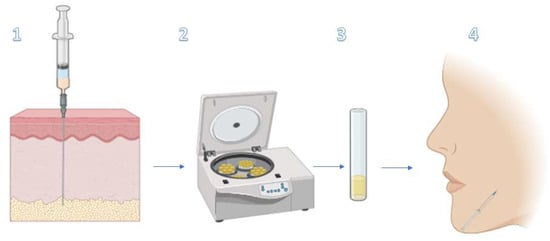
Figure 2.
Nanofat grafting process. 1. Harvest microfat by liposuction 2. Emulsify and filter it. 3. Fluid rich in mesenchymal stem cells is obtained, with 25% adipocytes and 75% SVF (ASCs, ECs, monocytes and macrophages, granulocytes, and lymphocytes). 4. Intradermic injection of nanofat [88].
3.2. Biochemical Cues (Bio-Cues)—Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP), Platelet-Rich Fibrin (FRP), and Extracellular Vescicles (EVs)
Platelet concentrates are processed blood extracts obtained mostly by centrifugation [89]. Depending on the content of leukocytes and fibrin, they are classified into four groups: pure platelet-rich plasma (PRP), leukocyte-rich and platelet-rich plasma (LPRP), pure platelet-rich fibrin (PRF), and leukocyte-rich and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF) [90,91]. Platelet-rich plasma (PRP) is defined as the concentration and collection of autologous platelet-rich plasma by centrifugation (Figure 3). Platelet-rich fibrin (PRF) represents a new-generation platelet concentrate with simplified preparation without the biochemical manipulation of blood [8,46]. Both preparations contain significant concentrations of VEGF, EGF, PDGF, TGF-B, and adhesive proteins, such as fibrin and fibronectin [13,46,92]. The exact mechanism of action of PRP in rejuvenation is still unclear, but it is thought that an injection of PRP can induce tissue repair, through the release of biologically active factors and adhesion proteins, with the initiation of tissue regeneration: hemostatic cascade, synthesis of new connective tissue, and angiogenesis [92,93]. It has been hypothesized that locally released growth factors and cytokines contribute to tissue repair through paracrine and autocrine mechanisms at all stages of the tissue repair process [94]. Su et al. suggested the negative regulation of JAK/STAT activation by PRP, pre-treating a skin flap ischemia–reperfusion injury murine model with PRP. PRP was found to protect against flap injury by improving survival, blood perfusion, and angiogenesis; reducing oxidative stress and inflammation; and attenuating apoptosis, in part through the inactivation of the JAK/STAT signaling pathway [95]. PRP is currently used both topically and intradermally. Despite the availability of different procedures for PRP extraction and on the large-scale use of PRP in aesthetics, there is no consensus regarding either the mode of extraction or the administration of the product [93,96,97]. Even the terminology itself is lacking standardization, leading to confusion [98]. The lack of consensus and standardization has not stopped the use of PRP from growing in popularity and widespread use in various medical fields. Xiao et al.’s systematic review of 44 studies on the use of PRP for facial rejuvenation showed beneficial effects both in monotherapy and in combination (e.g., laser, fat grafting, subcision, growth factors, and thread lifting), revealing the high regenerative potential of PRP [93]. Trink et al. conducted a randomized, double-blind study on 45 patients to evaluate the effects of PRP on alopecia areata (AA). PRP achieved better results to Triamcinolone and Placebo in terms of an increase in hair regrowth, a decrease in dystrophic hair number, and a reduction in burning or itching sensation. The Ki-67 levels were significantly higher with PRP, indicating increased cell proliferation [99]. Mahmoodabadi et al. injected the PRF matrix into the subcutis in the periorbital areas of 15 patients over the age of 30. The results showed significant improvement in deep, fine, and small wrinkles; periocular hyperpigmentation; and overall skin appearance in the treated area [100]. PRF is widely used in dental and bone grafting procedures, but it is rapidly gaining ground in the fields of cosmetic dermatology and wound healing. Shashank et al. reported four representative cases in which injectable PRF (iPRF) has proven to be useful in the treatment of androgenetic alopecia, rejuvenation of the under-eye area, temporary correction of facial skin folds, and healing of difficult-to-treat wounds and ulcers [101]. Extracellular vesicles (EVs) are defined as membrane structures released by cells and include two main types, exosomes and microvesicles (MVs) [56]. EVs are fundamental components of cell–cell communication, carrying transport proteins, nucleic acids, and lipids. They have been reported to mediate many cellular processes, such as proliferation, differentiation, and cell migration [102,103]. The regenerative properties of EVs have been demonstrated on a large variety of degenerative diseases, such as osteoarthritis (OA), Diabetes Mellitus (DM), stroke, and heart failure [104,105,106,107,108]. Flemming et al. conducted a review analyzing the role of EVs as biomarkers and therapeutic tools in dermatologic conditions. They considered EVs to be central in immune modulation and inflammation signaling, particularly in psoriasis and AD, and hypothesized that they may alter T-cell polarization to reduce clinical symptom scores. Similarly, they analyzed the role of EVs in the polarization of M2 macrophages, an important immune cell phenotype in wound healing. They highlighted the use of EVs in wound healing, psoriasis, and AD, and they appear to modulate a wide variety of biological functions [109]. Exosomes are nanoscale EVs that offer several size advantages: they can easily penetrate organs and skin due to their size; they do not undergo the bystander effect, retaining their properties even in an immunosuppressive environment; and they can be stored long term [56]. Research in regenerative aesthetics has focused in recent years on stem cell-derived exosomes, referring mainly to exosomes secreted by adipose stem cells (ASC-exos), mesenchymal stem cells (MSC-exos), and pluripotent stem cells [110]. MSC-exos and exosomes in body fluid have been found to participate and improve wound healing [111]. Studies conducted on murine umbilical cord-derived MSC-exos have been shown to optimize fibroblast characteristics, thus inducing wound healing in the skin [112]. Their use has been postulated also in AD, psoriasis, SLE, and cutaneous systemic sclerosis [112,113,114,115]. Exos have also been shown to improve Collagen Type I production and decrease MMPs [116] and to revert senescence-induced alterations in dermal fibroblasts [117]. Park et al. evaluated the clinical efficacy of combining ASC-exos and microneedling on 28 subjects. The results showed improvement in the GAIS and clinical improvements in skin wrinkles, elasticity, hydration, and pigmentation [118]. Tang et al. showed that ADSC-Exos promote healthy hair growth and counteracted the inhibitory effects of DHT on hair growth, using human hair follicle organs, in vitro dermal papilla cells, and in vivo animal models. They found that ADSC-Exos increased the levels of glycogen synthase kinase-3β-phosphorylated Ser9 and facilitated the nuclear translocation of β-catenin, which could be blocked by the specific inhibitor of the Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway, the Dickkopf-binding protein [119].
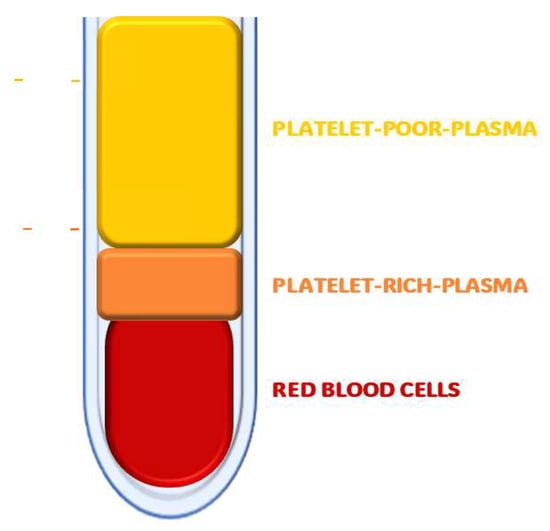
Figure 3.
Platelet-rich plasma (PRP): Concentration and collection of autologous platelet-rich plasma by centrifugation.
3.3. Aesthetic Regenerative Scaffolds (ARS)—Calcium Hydroxyapatite (CaHA), Hyaluronic Acid (HA), and Poli-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA)
Since the beginning, aesthetic medicine has used biomaterials-based injectables for anti-aging and rejuvenation purposes. An inflammatory response occurs at the injection sites, causing a range of outcomes, from tissue regeneration to fibrosis. This is the basis for the concept of Aesthetic Regenerative Scaffolds (ARSs): the injection biomaterial can predetermine the inflammatory response. The ARSs are defined as biomaterials that inhibit a chronic inflammatory response, reverting fibrosis and enhancing physiological tissue regeneration. They include Calcium Hydroxyapatite (CaHA), Hyaluronic Acid (HA), and Poli-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA) dermal fillers [50,52,53,54]. ARSs have historically been considered as space supports and barriers, typically inert and non-bioactive, lacking regulatory properties of tissue regeneration [45]. However, several in vitro and in vivo studies have shown local modulation by the ARSs of collagenogenesis, fibrosis, and immune activity [53,54,120,121]. Courderot-Masuyer et al. conducted a study performing biopsies on the wrinkled and normal aged skin of three patients. The results showed that a mixture composed of CaHa tends to restore the contractile properties of aged fibroblasts to the same level as normal fibroblasts [121]. Gonzalez et al. evaluated 15 patients with changes in the presence of elastic fibers, proteoglycans, and elastin in photodamaged skin after injections with CaHa. An evaluation at 6 months showed that CaHa can increase proteoglycans (76%), influencing also elastin, and induces the remodeling of ECM [53]. HA has always been a major player in aesthetic medicine, as it is the most common dermal filler in use [122]. HA participates in several skin biochemical processes. First known for its face-filling characteristics, it has also been used in skin rejuvenation for years [57]. It is a non-sulfated glycosaminoglycan (GAG) that has the rheological property of holding ≈ 1000 times its weight of water [123]. At the skin level, HA associates with CD44. Interactions between CD44 and HA mediate the binding of Langerhans cells to HA in the ECM. The receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility (RHAMM) is also expressed in human skin and mediates the TGF-β1-induced stimulation of fibroblast motility [122,124,125]. Seok et al. injected six middle-aged male subjects with 2 mL of HA filler to evaluate its efficacy in terms of transepidermal water loss (TEWL), hydration level (corneometer), patient satisfaction, and the GAIS [126]. Williams et al. injected 15 healthy subjects with microdroplet placement of hyaluronic acid in aging hands [127]. Both studies showed improvement in clinical appearance, patient satisfaction, and skin parameters [126,127]. Yutskovskaya et al. conducted a randomized, comparative, clinical study and an immunohistochemical analysis on eight adult females to assess the efficacy of the combined use of CaHa and HA fillers in terms of skin quality improvement. A comparative analysis of histological changes in skin tissue revealed that the simultaneous or consequential injection of HA and CaHa results in skin remodeling and that the combined use of HA and CaHA has a considerable impact on aging and skin remodeling due to the ECM accumulation of elastic fibers [128]. PLLA is an alpha hydroxy acid polymer of the L-Lactic Acid that has been used in regenerative medicine for more than 30 years [54,129,130]. The most known property of PLLA is volume restoration [54,131], but its ability to induce collagen synthesis has also positioned it as a tool in regenerative medicine [132,133]. In the field of rejuvenation, PLLA has been used for years, in numerous clinical trials in different areas and indications (Table 2), not only for volume enhancement but also for contouring and wrinkle correction [131,134,135]. A study was conducted by Zhu et al. on PLLA-inducted collagen synthesis in a cultured dermal fibroblast. Increased PLLA concentrations resulted in the production of procollagen, elastin, COL1A1, COL1A2, TIMP-1, TIMP-2, and tGF-β and attenuated the expression of MMP-1. The results confirmed that PLLA promotes the collagen gene expression and synthesis by the TGF-β/Smad signaling pathway [136]. This results clinically in cross-sectional use for skin rejuvenation of the face and body, including edematous fibrosclerotic panniculopathy (EFP). Swearingen et al. enrolled 31 healthy women with EFP, administering PLLA (treatment group) or saline (control group) injections combined with subcision into each of the glutes or thighs. After 3 and 6 months, significant changes in the global aesthetic improvement scale (GAIS) and the cellulite severity scale (CSS) were reported [137]. In the field of regenerative scaffolds, it is also worth mentioning bacterial cellulose (BC), which has been studied as a biomaterial for cartilage regeneration and wound healing [138,139]. However, its use in the field of cosmetic dermatology remains unexplored.

Table 2.
Relevant studies on the use of PLLA for aesthetic regenerative purposes.
4. Conclusions and Future Directions
Aesthetic dermatology represents a thriving field of application of regenerative medicine, gaining attention and popularity across different generations. While previously reserved for the over-50 population, it now represents a field with a large and expanding target population. The regenerative treatments analyzed in our review focus on the punctual compensation of factors (Bio-Cues) or cells (ASCs and nanofat) and on the induction of regenerative effects by injection of biomaterials (ARSs). Although the theoretical substrate is favorable for the application of regenerative techniques on an aesthetic–dermatological level, the method is not yet standardized and lacks consensus, so the evidence in the literature is variable and often unsatisfactory. Our hypothesis regarding the weaknesses of the abovementioned techniques relates to their punctual nature. The pathophysiology of skin regeneration is not a punctual process but rather a sequential one. The initiation of the skin’s regenerative potential occurs as a result of a triggering cause, with the launching of a chain of events, starting with platelets and the derived activity and extending to stem cell differentiation and fibroblastic activation. In the context of regenerative dermatology, the ensemble of consequential processes should be considered as building blocks in the restoration and enhancement of skin regenerative capacity. This perspective may suggest why the theoretical substrate of the three mentioned pillars (cells and cell derivatives, Bio-Cues, and ARSs) struggles with the clinical evidence, which is, in some cases, unsatisfactory. In our vision, the use of schemes involving the activation, via physio-mimetics, and proliferation of quiescent stem cells through growth factors (e.g., VEGF, FGF, PDGF-B, and TGF-β), with the subsequent stabilization of results over time with components of the ECM (e.g., amino acids, collagen, and choline), could represent a therapeutic strategy that mimics the pathophysiology of skin regeneration. The clinical application of regenerative medicine methods in dermo-aesthetics cannot exclude the physiological mechanisms of stem cell action, so the treatment scheme cannot be monotherapeutic and punctual but multi-target and sequential, including steps of activation, stimulation/enhancement, and maintenance. We believe that understanding the pathophysiology of skin regeneration has paved new paths toward a new era of cosmetic dermatology, comprising therapeutic schemes that mimic physiological pathways.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, H.I.G., G.P., F.T. and S.C.; validation, H.I.G., G.P., F.T. and S.C.; formal analysis, H.I.G., S.G., G.V., L.C. and S.M.; investigation, F.T.; resources, F.T. and S.M.; data curation, F.T.; writing—original draft preparation, F.T.; writing—review and editing, F.T., S.P.N. and S.M.; visualization, F.T.; supervision, S.G., S.C., H.I.G., S.P.N. and G.P.; project administration, G.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Kurtti, A.; Charles, C.; Jagdeo, J.; Nguyen, J. Combination Facial Aesthetic Treatment in Millennials. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2022, 21, 37–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haykal, D.; Nahai, F.; Cartier, H. Prejuvenation: The Global New Anti-Aging Trend. Aesthetic Surg. J. Open Forum 2023, 5, ojad061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hogan, S.R.; Zachary, C.B.; Arndt, K.A. Prejuvenation: Definition of the Term and Evolution of the Concept. Dermatol. Surg. 2021, 47, 871–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.V.; Akintilo, L.; Geronemus, R.G. Growth of cosmetic procedures in millennials: A 4.5-year clinical review. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2020, 19, 3210–3212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Allan, G.J.; Beattie, J.; Flint, D.J. Epithelial injury induces an innate repair mechanism linked to cellular senescence and fibrosis involving IGF-binding protein-5. J. Endocrinol. 2008, 199, 155–164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sameri, S.; Samadi, P.; Dehghan, R.; Salem, E.; Fayazi, N.; Amini, R. Stem Cell Aging in Lifespan and Disease: A State-of-the-Art Review. Curr. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2020, 15, 362–378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coffman, J.A.; Rieger, S.; Rogers, A.N.; Updike, D.L.; Yin, V.P. Comparative biology of tissue repair, regeneration and aging. npj Regen. Med. 2016, 1, 16003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldie, K. The evolving field of regenerative aesthetics. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeo, M.; Lee, W.; Ito, M. Wound healing and skin regeneration. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Med. 2015, 5, a023267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thon, J.N.; Italiano, J.E. Platelets: Production, morphology and ultrastructure. Handb. Exp. Pharmacol. 2012, 210, 3–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irmak, G.; Demirtaş, T.T.; Gümüşderelioğlu, M. Sustained release of growth factors from photoactivated platelet rich plasma (PRP). Eur. J. Pharm. Biopharm. 2020, 148, 67–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blair, P.; Flaumenhaft, R. Platelet alpha-granules: Basic biology and clinical correlates. Blood Rev. 2009, 23, 177–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lubkowska, A.; Dolegowska, B.; Banfi, G. Growth factor content in PRP and their applicability in medicine. J. Biol. Regul. Homeost. Agents. 2012, 26 (Suppl. S1), 3S–22S. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Jurk, K.; Kehrel, B.E. Platelets: Physiology and biochemistry. Semin. Thromb. Hemost. 2005, 31, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Briggs, S.L. The role of fibronectin in fibroblast migration during tissue repair. J. Wound Care 2005, 14, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pixley, J.N.; Cook, M.K.; Singh, R.; Larrondo, J.; McMichael, A.J. A comprehensive review of platelet-rich plasma for the treatment of dermatologic disorders. J. Dermatolog. Treat. 2023, 34, 2142035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodrigues, M.; Kosaric, N.; Bonham, C.A.; Gurtner, G.C. Wound Healing: A Cellular Perspective. Physiol. Rev. 2019, 99, 665–706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eilken, H.M.; Adams, R.H. Dynamics of endothelial cell behavior in sprouting angiogenesis. Curr. Opin. Cell Biol. 2010, 22, 617–625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonnesen, M.G.; Feng, X.; Clark, R.A. Angiogenesis in wound healing. J. Investig. Dermatol. Symp. Proc. 2000, 5, 40–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Wang, J.H.C. Fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in wound healing: Force generation and measurement. J. Tissue Viability 2011, 20, 108–120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bainbridge, P. Wound healing and the role of fibroblasts. J. Wound Care 2013, 22, 407–408, 410–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, J.; Tumbar, T. Hairy tale of signaling in hair follicle development and cycling. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2012, 23, 906–916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rognoni, E.; Gomez, C.; Pisco, A.O.; Rawlins, E.L.; Simons, B.D.; Watt, F.M.; Driskell, R.R. Inhibition of β-catenin signalling in dermal fibroblasts enhances hair follicle regeneration during wound healing. Development 2016, 143, 2522–2535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fujiwara, H.; Ferreira, M.; Donati, G.; Marciano, D.K.; Linton, J.M.; Sato, Y.; Hartner, A.; Sekiguchi, K.; Reichardt, L.F.; Watt, F.M. The basement membrane of hair follicle stem cells is a muscle cell niche. Cell 2011, 144, 577–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amoh, Y.; Hoffman, R.M. Hair follicle-associated-pluripotent (HAP) stem cells. Cell Cycle. 2017, 16, 2169–2175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Darby, I.A.; Laverdet, B.; Bonté, F.; Desmoulière, A. Fibroblasts and myofibroblasts in wound healing. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2014, 7, 301–311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shinde, A.V.; Humeres, C.; Frangogiannis, N.G. The role of α-smooth muscle actin in fibroblast-mediated matrix contraction and remodeling. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Mol. Basis Dis. 2017, 1863, 298–309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tomasek, J.J.; Gabbiani, G.; Hinz, B.; Chaponnier, C.; Brown, R.A. Myofibroblasts and mechano-regulation of connective tissue remodelling. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 3, 349–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Plikus, M.V. Aged Skin Cells Nurture Stem Cells toward Regeneration. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2023, 144, 11–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Plikus, M.V.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Ito, M.; Li, Y.R.; Dedhia, P.H.; Zheng, Y.; Shao, M.; Gay, D.L.; Ramos, R.; Hsi, T.C.; et al. Regeneration of fat cells from myofibroblasts during wound healing. Science 2017, 355, 748–752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Asazuma-Nakamura, Y.; Dai, P.; Harada, Y.; Jiang, Y.; Hamaoka, K.; Takamatsu, T. Cx43 contributes to TGF-β signaling to regulate differentiation of cardiac fibroblasts into myofibroblasts. Exp. Cell Res. 2009, 315, 1190–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, H.; Li, P.; Liu, M.; Liu, C.; Sun, Z.; Guo, X.; Zhang, Y. CCN2 and CCN5 exerts opposing effect on fibroblast proliferation and transdifferentiation induced by TGF-β. Clin. Exp. Pharmacol. Physiol. 2015, 42, 1207–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leask, A. Potential therapeutic targets for cardiac fibrosis: TGFbeta, angiotensin, endothelin, CCN2, and PDGF, partners in fibroblast activation. Circ. Res. 2010, 106, 1675–1680. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Simpson, R.M.L.; Meran, S.; Thomas, D.; Stephens, P.; Bowen, T.; Steadman, R.; Phillips, A. Age-related changes in pericellular hyaluronan organization leads to impaired dermal fibroblast to myofibroblast differentiation. Am. J. Pathol. 2009, 175, 1915–1928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.; Moon, A.; Kim, H.R. Both platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR)-alpha and PDGFR-beta promote murine fibroblast cell migration. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2001, 282, 697–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zigrino, P.; Brinckmann, J.; Niehoff, A.; Lu, Y.; Giebeler, N.; Eckes, B.; Kadler, K.E.; Mauch, C. Fibroblast-Derived MMP-14 Regulates Collagen Homeostasis in Adult Skin. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2016, 136, 1575–1583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- TNF-Alpha Suppresses Alpha-Smooth Muscle Actin Expression in Human Dermal Fibroblasts: An Implication for Abnormal Wound Healing. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/17554369/ (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Shook, B.A.; Wasko, R.R.; Mano, O.; Rutenberg-Schoenberg, M.; Rudolph, M.C.; Zirak, B.; Horsley, V. Dermal adipocyte lipolysis and myofibroblast conversion are required for efficient skin repair. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 880–895.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Zhang, X.; Wu, S.; Liu, Y.; Guerrero-Juarez, C.F.; Liu, W.; Huang, J.; Yao, Q.; Yin, M.; Li, J.; et al. Dynamic interplay between IL-1 and WNT pathways in regulating dermal adipocyte lineage cells during skin development and wound regeneration. Cell Rep. 2023, 42, 112647. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zechner, R.; Zimmermann, R.; Eichmann, T.O.; Kohlwein, S.D.; Haemmerle, G.; Lass, A.; Madeo, F. FAT SIGNALS—Lipases and Lipolysis in Lipid Metabolism and Signaling. Cell Metab. 2012, 15, 279–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frühbeck, G.; Méndez-Giménez, L.; Fernández-Formoso, J.A.; Fernández, S.; Rodríguez, A. Regulation of adipocyte lipolysis. Nutr. Res. Rev. 2014, 27, 63–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, H.; Chen, J.; Ding, K.; Cheng, T.; Tang, S. Highly-expressed lncRNA FOXD2-AS1 in adipose mesenchymal stem cell derived exosomes affects HaCaT cells via regulating miR-185-5p/ROCK2 axis. Adipocyte 2023, 12, 2173513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarbafian, M.; Fabi, S.G.; Dayan, S.; Goldie, K. The Emerging Field of Regenerative Aesthetics—Where We Are Now. Dermatol. Surg. 2022, 48, 101–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonnard, P.; Verpaele, A.; Peeters, G.; Hamdi, M.; Cornelissen, R.; Declercq, H. Nanofat Grafting: Basic Research and Clinical Applications. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2013, 132, 1017–1026. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moioli, E.K.; Bolotin, D.; Alam, M. Regenerative Medicine and Stem Cells in Dermatology. Dermatol. Surg. 2017, 43, 625–634. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF): A Second-Generation Platelet Concentrate. Part I: Technological Concepts and Evolution. Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/16504849/ (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Li, J.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Yao, B.; Enhejirigala; Li, Z.; Song, W.; Wang, Y.; Duan, X.; Yuan, X.; et al. Biophysical and Biochemical Cues of Biomaterials Guide Mesenchymal Stem Cell Behaviors. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 640388. Available online: https://www.frontiersin.org/articles/10.3389/fcell.2021.640388 (accessed on 1 December 2023). [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quinlan, D.J.; Ghanem, A.M.; Hassan, H. Topical growth factors and home-based microneedling for facial skin rejuvenation. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 3469–3478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kose, O.; Botsali, A.; Caliskan, E. Role of exosomes in skin diseases. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 3219–3225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Corduff, N. Introducing aesthetic regenerative scaffolds: An immunological perspective. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22 (Suppl. S1), 8–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Collins, K.L.; Gates, E.M.; Gilchrist, C.L.; Hoffman, B.D. Chapter 1—Bio-Instructive Cues in Scaffolds for Musculoskeletal Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine. In Bio-Instructive Scaffolds for Musculoskeletal Tissue Engineering and Regenerative Medicine; Brown, J.L., Kumbar, S.G., Banik, B.L., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2017; pp. 3–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, S.; Galadari, H.; Patil, A.; Goldust, M.; Al Salam, S.; Guida, S. Evaluation of the biostimulatory effects and the level of neocollagenesis of dermal fillers: A review. Int. J. Dermatol. 2022, 61, 1284–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- González, N.; Goldberg, D.J. Evaluating the Effects of Injected Calcium Hydroxylapatite on Changes in Human Skin Elastin and Proteoglycan Formation. Dermatol. Surg. 2019, 45, 547–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fitzgerald, R.; Bass, L.M.; Goldberg, D.J.; Graivier, M.H.; Lorenc, Z.P. Physiochemical Characteristics of Poly-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA). Aesthet Surg. J. 2018, 38 (Suppl. S1), S13–S17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bunnell, B.A. Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Cells. 2021, 10, 3433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thakur, A.; Wei, Z.; Chen, H.J. Editorial: Extracellular vesicles and cell-cell communication in normal cellular processes and cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2023, 10, 1172797. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bukhari, S.N.A.; Roswandi, N.L.; Waqas, M.; Habib, H.; Hussain, F.; Khan, S.; Sohail, M.; Ramli, N.A.; Thu, H.E.; Hussain, Z. Hyaluronic acid, a promising skin rejuvenating biomedicine: A review of recent updates and pre-clinical and clinical investigations on cosmetic and nutricosmetic effects. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2018, 120, 1682–1695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nahmgoong, H.; Jeon, Y.G.; Park, E.S.; Choi, Y.H.; Han, S.M.; Park, J.; Ji, Y.; Sohn, J.H.; Han, J.S.; Kim, Y.Y.; et al. Distinct properties of adipose stem cell subpopulations determine fat depot-specific characteristics. Cell Metab. 2022, 34, 458–472.e6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Voog, J.; Jones, D.L. Stem cells and the niche: A dynamic duo. Cell Stem Cell 2010, 6, 103–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gonzales, K.A.U.; Fuchs, E. Skin and Its Regenerative Powers: An Alliance between Stem Cells and Their Niche. Dev. Cell 2017, 43, 387–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blanpain, C.; Horsley, V.; Fuchs, E. Epithelial stem cells: Turning over new leaves. Cell 2007, 128, 445–458. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanpain, C.; Fuchs, E. Epidermal stem cells of the skin. Annu. Rev. Cell Dev. Biol. 2006, 22, 339–373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanpain, C.; Fuchs, E. Epidermal homeostasis: A balancing act of stem cells in the skin. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2009, 10, 207–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kilroy, G.E.; Foster, S.J.; Wu, X.; Ruiz, J.; Sherwood, S.; Heifetz, A.; Ludlow, J.W.; Stricker, D.M.; Potiny, S.; Green, P.; et al. Cytokine profile of human adipose-derived stem cells: Expression of angiogenic, hematopoietic, and pro-inflammatory factors. J. Cell. Physiol. 2007, 212, 702–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Blaber, S.P.; Webster, R.A.; Hill, C.J.; Breen, E.J.; Kuah, D.; Vesey, G.; Herbert, B.R. Analysis of in vitro secretion profiles from adipose-derived cell populations. J. Transl. Med. 2012, 10, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coppack, S.W. Pro-inflammatory cytokines and adipose tissue. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 2001, 60, 349–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Growth Factors Profile in Conditioned Medium Human Adipose Tissue-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells (CM-hATMSCs)—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S2352939318300113 (accessed on 30 November 2023).
- Trzyna, A.; Banaś-Ząbczyk, A. Adipose-Derived Stem Cells Secretome and Its Potential Application in “Stem Cell-Free Therapy”. Biomolecules 2021, 11, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mitchell, R.; Mellows, B.; Sheard, J.; Antonioli, M.; Kretz, O.; Chambers, D.; Zeuner, M.-T.; Tomkins, J.E.; Denecke, B.; Musante, L.; et al. Secretome of adipose-derived mesenchymal stem cells promotes skeletal muscle regeneration through synergistic action of extracellular vesicle cargo and soluble proteins. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2019, 10, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mazini, L.; Rochette, L.; Admou, B.; Amal, S.; Malka, G. Hopes and Limits of Adipose-Derived Stem Cells (ADSCs) and Mesenchymal Stem Cells (MSCs) in Wound Healing. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, M.; Abe, R.; Fujita, Y.; Ando, S.; Inokuma, D.; Shimizu, H. Mesenchymal stem cells are recruited into wounded skin and contribute to wound repair by transdifferentiation into multiple skin cell type. J. Immunol. 2008, 180, 2581–2587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tonnard, P.; Verpaele, A.; Carvas, M. Fat Grafting for Facial Rejuvenation with Nanofat Grafts. Clin. Plast. Surg. 2020, 47, 53–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Illouz, Y.G. The fat cell “graft”: A new technique to fill depressions. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 1986, 78, 122–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanson, S.E. The Future of Fat Grafting. Aesthetic Surg. J. 2021, 41 (Suppl. S1), S69–S74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, S.; Sekigami, Y.; Schwartz, T.; Losken, A.; Margenthaler, J.; Chatterjee, A. Lipofilling after breast conserving surgery: A comprehensive literature review investigating its oncologic safety. Gland. Surg. 2019, 8, 569–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gkagkaris, L.; Papadakis, M.; Lytsikas-Sarlis, P. The Revolutionary Gustav Adolf Neuber: A Tribute to the Father of Aseptic Surgery. Surg. Innov. 2022, 29, 817–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chkadua, T.Z.; Visaitova, Z.Y.; Strukova, O.O.; Krechina, E.K.; Hodyachij, A.E.; Belkov, P.A. The feasibility of combined lipofilling methods in the treatment of patients with facial hemiatrophy. Stomatologiia 2019, 98, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- La Padula, S.; Ponzo, M.; Lombardi, M.; Iazzetta, V.; Errico, C.; Polverino, G.; Russo, F.; D’andrea, L.; Hersant, B.; Meningaud, J.P.; et al. Nanofat in Plastic Reconstructive, Regenerative, and Aesthetic Surgery: A Review of Advancements in Face-Focused Applications. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12, 4351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, P.; Lu, E.; Li, G.; Sun, Y.; Yang, W.; Zhao, Z. Research Progress on Preparation, Mechanism, and Clinical Application of Nanofat. J. Burn. Care Res. 2022, 43, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeyaraman, M.; Muthu, S.; Sharma, S.; Ganta, C.; Ranjan, R.; Jha, S.K. Nanofat: A therapeutic paradigm in regenerative medicine. World J. Stem Cells 2021, 13, 1733–1746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menkes, S.; Luca, M.; Soldati, G.; Polla, L. Subcutaneous Injections of Nanofat Adipose-derived Stem Cell Grafting in Facial Rejuvenation. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. Glob. Open. 2020, 8, e2550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadry, A.; Gamal, A.; Alkhalifah, A.; Ibrahim, S.M.A. Efficacy of Platelet-Rich Plasma Versus Autologous Fat Transfer with Nanofat in the Treatment of Infraorbital Dark Circles: A Single-Blinded Randomized Comparative Clinical Trial. Dermatol. Surg. 2023, 49, 247–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nilforoushzadeh, M.A.; Heidari-Kharaji, M.; Alavi, S.; Nouri, M.; Nikkhah, N.; Jahangiri, F.; Mahmoudbeyk, M.; Peyrovan, A.; Tork, B.B.; Torkamaniha, E.; et al. Transplantation of autologous fat, stromal vascular fraction (SVF) cell, and platelet-rich plasma (PRP) for cell therapy of atrophic acne scars: Clinical evaluation and biometric assessment. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2022, 21, 2089–2098. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bellei, B.; Migliano, E.; Picardo, M. Therapeutic potential of adipose tissue-derivatives in modern dermatology. Exp. Dermatol. 2022, 31, 1837–1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Canizares, O.J.; Thomson, J.E.; Allen, R.J.J.; Davidson, E.H.; Tutela, J.P.; Saadeh, P.B.; Warren, S.M.; Hazen, A. The Effect of Processing Technique on Fat Graft Survival. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2017, 140, 933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pinski, K.S.; Roenigk, H.H. Autologous fat transplantation. Long-term follow-up. J. Dermatol. Surg. Oncol. 1992, 18, 179–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rihani, J. Microfat and Nanofat: When and Where These Treatments Work. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2019, 27, 321–330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Created with Biorender.com. Available online: https://www.biorender.com/ (accessed on 10 March 2023).
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Andia, I.; Zumstein, M.A.; Zhang, C.Q.; Pinto, N.R.; Bielecki, T. Classification of platelet concentrates (Platelet-Rich Plasma-PRP, Platelet-Rich Fibrin-PRF) for topical and infiltrative use in orthopedic and sports medicine: Current consensus, clinical implications and perspectives. Muscles Ligaments Tendons J. 2014, 4, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dohan Ehrenfest, D.M.; Rasmusson, L.; Albrektsson, T. Classification of platelet concentrates: From pure platelet-rich plasma (P-PRP) to leucocyte- and platelet-rich fibrin (L-PRF). Trends Biotechnol. 2009, 27, 158–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Napit, I.B.; Shrestha, D.; Neupane, K.; Adhikari, A.; Dhital, R.; Koirala, R.; Gopali, L.; Ilozumba, O.; Gill, P.; I Watson, S.; et al. Autologous blood products: Leucocyte and Platelets Rich Fibrin (L-PRF) and Platelets Rich Plasma (PRP) gel to promote cutaneous ulcer healing—A systematic review. BMJ Open 2023, 13, e073209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Growth Factor and Pro-Inflammatory Cytokine Contents in Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP), Plasma Rich in Growth Factors (PRGF), Advanced Platelet-Rich Fibrin (A-PRF), and Concentrated Growth Factors (CGF). Available online: https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/27747711/ (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Xiao, H.; Xu, D.; Mao, R.; Xiao, M.; Fang, Y.; Liu, Y. Platelet-Rich Plasma in Facial Rejuvenation: A Systematic Appraisal of the Available Clinical Evidence. Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2021, 14, 1697–1724. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Everts, P.; Onishi, K.; Jayaram, P.; Lana, J.F.; Mautner, K. Platelet-Rich Plasma: New Performance Understandings and Therapeutic Considerations in 2020. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 7794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Xie, S.; Li, T.; Jia, Y.; Wang, Y. Pretreatment with platelet-rich plasma protects against ischemia–reperfusion induced flap injury by deactivating the JAK/STAT pathway in mice. Mol. Med. 2024, 30, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emer, J. Platelet-Rich Plasma (PRP): Current Applications in Dermatology. Skin Ther. Lett. 2019, 24, 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, W.; Yang, L.; Li, J.; Chen, Y.; Yao, B. A bibliometric analysis of trends in the application of platelet-rich plasma in cosmetics research between 2001 and 2022. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 23, 780–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Everts, P.A.M.; van Zundert, A.; Schönberger, J.P.A.M.; Devilee, R.J.J.; Knape, J.T.A. What do we use: Platelet-rich plasma or platelet-leukocyte gel? J. Biomed. Mater. Res. A 2008, 85, 1135–1136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Trink, A.; Sorbellini, E.; Bezzola, P.; Rodella, L.; Rezzani, R.; Ramot, Y.; Rinaldi, F. A randomized, double-blind, placebo- and active-controlled, half-head study to evaluate the effects of platelet-rich plasma on alopecia areata. Br. J. Dermatol. 2013, 169, 690–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoodabadi, R.A.; Golafshan, H.A.; Pezeshkian, F.; Shahriarirad, R.; Namazi, M.R. Evaluation of the Effect of Platelet-Rich Fibrin Matrix in the Correction of Periorbital Wrinkles: An Experimental Clinical Trial. Dermatol. Pract. Concept. 2023, 13, e2023050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shashank, B.; Bhushan, M. Injectable Platelet-Rich Fibrin (PRF): The newest biomaterial and its use in various dermatological conditions in our practice: A case series. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 1421–1426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, L.; Thakur, A.; Li, W.K.; Qiu, G.; Yang, T.; He, B.; Lee, Y.; Wu, C.-M.L. Site specific biotinylated antibody functionalized Ag@AuNIs LSPR biosensor for the ultrasensitive detection of exosomal MCT4, a glioblastoma progression biomarker. Chem. Eng. J. 2022, 446, 137383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thakur, A.; Qiu, G.; Ng, S.P.; Wu, C.M.L.; Lee, Y. Detection of membrane antigens of extracellular vesicles by surface plasmon resonance. J. Lab. Precis. Med. 2017, 2, 98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suzman, R.; Beard, J.R.; Boerma, T.; Chatterji, S. Health in an ageing world—What do we know? Lancet 2015, 385, 484–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bian, S.; Zhang, L.; Duan, L.; Wang, X.; Min, Y.; Yu, H. Extracellular vesicles derived from human bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells promote angiogenesis in a rat myocardial infarction model. J. Mol. Med. 2014, 92, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cosenza, S.; Ruiz, M.; Toupet, K.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal stem cells derived exosomes and microparticles protect cartilage and bone from degradation in osteoarthritis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 16214. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- D’Arrigo, D.; Roffi, A.; Cucchiarini, M.; Moretti, M.; Candrian, C.; Filardo, G. Secretome and Extracellular Vesicles as New Biological Therapies for Knee Osteoarthritis: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Med. 2019, 8, 1867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boulestreau, J.; Maumus, M.; Rozier, P.; Jorgensen, C.; Noël, D. Mesenchymal Stem Cell Derived Extracellular Vesicles in Aging. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2020, 8, 107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flemming, J.P.; Wermuth, P.J.; Mahoney, M.G. Extracellular Vesicles in the Skin Microenvironment: Emerging Roles as Biomarkers and Therapeutic Tools in Dermatologic Health and Disease. J. Investig. Dermatol. 2024, 144, 225–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, X.; Song, S.; Chen, N.; Liao, J.; Zeng, L. Stem cell-derived exosomes: A supernova in cosmetic dermatology. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2021, 20, 3812–3817. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiong, M.; Zhang, Q.; Hu, W.; Zhao, C.; Lv, W.; Yi, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tang, H.; Wu, M.; Wu, Y. The novel mechanisms and applications of exosomes in dermatology and cutaneous medical aesthetics. Pharmacol. Res. 2021, 166, 105490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cho, B.S.; Kim, J.O.; Ha, D.H.; Yi, Y.W. Exosomes derived from human adipose tissue-derived mesenchymal stem cells alleviate atopic dermatitis. Stem Cell Res. Ther. 2018, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wermuth, P.J.; Piera-Velazquez, S.; Jimenez, S.A. Exosomes isolated from serum of systemic sclerosis patients display alterations in their content of profibrotic and antifibrotic microRNA and induce a profibrotic phenotype in cultured normal dermal fibroblasts. Clin. Exp. Rheumatol. 2017, 35, S21–S30. [Google Scholar]
- Jiang, M.; Fang, H.; Shao, S.; Dang, E.; Zhang, J.; Qiao, P.; Yang, A.; Wang, G. Keratinocyte exosomes activate neutrophils and enhance skin inflammation in psoriasis. FASEB J. 2019, 33, 13241–13253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Circulating Exosomes Derived-miR-146a from Systemic Lupus Erythematosus Patients Regulates Senescence of Mesenchymal Stem Cells. Available online: https://www.hindawi.com/journals/bmri/2019/6071308/ (accessed on 3 December 2023).
- Trentini, M.; Zanolla, I.; Zanotti, F.; Tiengo, E.; Licastro, D.; Monego, S.D.; Lovatti, L.; Zavan, B. Apple Derived Exosomes Improve Collagen Type I Production and Decrease MMPs during Aging of the Skin through Downregulation of the NF-κB Pathway as Mode of Action. Cells 2022, 11, 3950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, H.; Cha, H.; Park, J.H. Derivation of Cell-Engineered Nanovesicles from Human Induced Pluripotent Stem Cells and Their Protective Effect on the Senescence of Dermal Fibroblasts. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, G.H.; Kwon, H.H.; Seok, J.; Yang, S.H.; Lee, J.; Park, B.C.; Shin, E.; Park, K.Y. Efficacy of combined treatment with human adipose tissue stem cell-derived exosome-containing solution and microneedling for facial skin aging: A 12-week prospective, randomized, split-face study. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 3418–3426. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, X.; Cao, C.; Liang, Y.; Han, L.; Tu, B.; Yu, M.; Wan, M. Adipose-Derived Stem Cell Exosomes Antagonize the Inhibitory Effect of Dihydrotestosterone on Hair Follicle Growth by Activating Wnt/β-Catenin Pathway. Stem Cells Int. 2023, 2023, 5548112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marmur, E.S.; Phelps, R.; Goldberg, D.J. Clinical, histologic and electron microscopic findings after injection of a calcium hydroxylapatite filler. J. Cosmet. Laser Ther. 2004, 6, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Courderot-Masuyer, C.; Robin, S.; Tauzin, H.; Humbert, P. Evaluation of lifting and antiwrinkle effects of calcium hydroxylapatite filler. In vitro quantification of contractile forces of human wrinkle and normal aged fibroblasts treated with calcium hydroxylapatite. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 260–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, G.T.; Kam, J.; Bloom, J.D. Hyaluronic Acid Basics and Rheology. Facial Plast. Surg. Clin. N. Am. 2022, 30, 301–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hyaluronic Acid: The Scientific and Clinical Evidence—ScienceDirect. Available online: https://www.sciencedirect.com/science/article/pii/S1748681507001805 (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Papakonstantinou, E.; Roth, M.; Karakiulakis, G. Hyaluronic acid: A key molecule in skin aging. Dermatoendocrinol 2012, 4, 253–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nedvetzki, S.; Gonen, E.; Assayag, N.; Reich, R.; Williams, R.O.; Thurmond, R.L.; Huang, J.-F.; Neudecker, B.A.; Wang, F.-S.; Turley, E.A.; et al. RHAMM, a receptor for hyaluronan-mediated motility, compensates for CD44 in inflamed CD44-knockout mice: A different interpretation of redundancy. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2004, 101, 18081–18086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Seok, J.; Hong, J.Y.; Choi, S.Y.; Park, K.Y.; Kim, B.J. A potential relationship between skin hydration and stamp-type microneedle intradermal hyaluronic acid injection in middle-aged male face. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2016, 15, 578–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, S.; Tamburic, S.; Stensvik, H.; Weber, M. Changes in skin physiology and clinical appearance after microdroplet placement of hyaluronic acid in aging hands. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2009, 8, 216–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yutskovskaya, Y.A.; Kogan, E.A.; Koroleva, A.Y.; Galadari, H.I. Comparative Clinical and Histomorphologic Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Combined Use of Calcium Hydroxyapatite and Hyaluronic Acid Fillers for Aesthetic Indications. Dermatol. Clin. 2024, 42, 103–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacombe, V. Sculptra: A stimulatory filler. Facial Plast. Surg. 2009, 25, 95–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Verheyen, C.C.; de Wijn, J.R.; van Blitterswijk, C.A.; de Groot, K. Evaluation of hydroxylapatite/poly(L-lactide) composites: Mechanical behavior. J. Biomed. Mater. Res. 1992, 26, 1277–1296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Christen, M.O. Collagen Stimulators in Body Applications: A Review Focused on Poly-L-Lactic Acid (PLLA). Clin. Cosmet. Investig. Dermatol. 2022, 15, 997–1019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, S.; Xu, W.; Chen, X.; He, R.; Deng, K.; Su, H.; Yin, X.; Su, S.; Liang, T.; et al. Poly-l-lactide-co-ε-caprolactone (PLCL) and poly-l-lactic acid (PLLA)/gelatin electrospun subacromial spacer improves extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition for the potential treatment of irreparable rotator cuff tears. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2023, 245, 125522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, C.; Jiang, S.; Wu, Y.; Liu, L.; Su, S.; Liang, T.; He, R.; Guo, Z.; Zhang, Y.; Lin, Z.; et al. The Regenerative Role of Gelatin in PLLA Electrospun Membranes for the Treatment of Chronic Massive Rotator Cuff Injuries. Macromol. Biosci. 2021, 22, 2100281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rejuvenation of the Aging Chest: A Review and Our Experience: Dermatologic Surgery. Available online: https://journals.lww.com/dermatologicsurgery/abstract/2011/05000/rejuvenation_of_the_aging_chest__a_review_and_our.1.aspx (accessed on 1 December 2023).
- Vleggaar, D. Soft-Tissue Augmentation and the Role of Poly-L-Lactic Acid. Plast. Reconstr. Surg. 2006, 118, 46S–54S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, W.; Dong, C. Poly-L-Lactic acid increases collagen gene expression and synthesis in cultured dermal fibroblast (Hs68) through the TGF-β/Smad pathway. J. Cosmet. Dermatol. 2023, 22, 1213–1219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swearingen, A.; Medrano, K.; Ferzli, G.; Sadick, N.; Arruda, S. Randomized, Double-Blind, Placebo-Controlled Study of Poly-L-Lactic acid for Treatment of Cellulite in the Lower Extremities. J. Drugs Dermatol. 2021, 20, 529–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, A.; Nicklasson, E.; Harrah, T.; Panilaitis, B.; Kaplan, D.; Brittberg, M.; Gatenholm, P. Bacterial cellulose as a potential scaffold for tissue engineering of cartilage. Biomaterials 2005, 26, 419–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, P.; Yadav, H.; Shah, V.G.; Shah, G.; Dhaka, G. Biomedical Biopolymers, their Origin and Evolution in Biomedical Sciences: A Systematic Review. J. Clin. Diagn. Res. 2015, 9, ZE21–ZE25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goldberg, D.; Guana, A.; Volk, A.; Daro-Kaftan, E. Single-arm study for the characterization of human tissue response to injectable poly-L-lactic acid. Dermatol. Surg. 2013, 39, 915–922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).