Abstract
The Causse of El Hajeb belongs to the Tabular Middle Atlas (TMA), in which thousands of karst landforms have been identified. Among them, collapse dolines and dissolution sinkholes have been highlighted as a source of environmental risks and geo-hazards. In particular, such sinkholes have been linked to the degradation of water quality in water springs located in the junction of the TMA and Saïss basin. Furthermore, the developments of collapse dolines in agricultural and inhabited areas enhance the risk of life loss, injury, and property damage. Here, the lack of research on newly formed cavities has exacerbated the situation. The limited studies using remote sensing or geophysical methods to determine the degree of karstification and vulnerability of this environment fail to provide the spatial extent and depth location of individual karst cavities. In order to contribute to the effort of sinkhole risk reduction in TMA, we employed remote sensing and geophysical surveys to integrate electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and self-potential (SP) for subsurface characterization of four sinkholes identified in the Causse of El Hajeb. The results revealed the existence of sinkholes, both visible and non-accessible at the surface, in carbonate rocks. The sinkholes exhibited distinct morphologies, with depths reaching 35 m. Topography, geographic coordinates and land cover information extracted on remote sensing data demonstrated that these cavities were developed in depressions in which agricultural activities are regularly performed. The fusion of these methods benefits from remote sensing in geophysical surveys, particularly in acquisition, georeferencing, processing and interpretation of geophysical data. Furthermore, our proposed method allows identification of the protection perimeter required to minimize the risks posed by sinkholes.
1. Introduction
Introduced by Fairbridge [1] as subcircular surface depressions or collapse structures created by the collapse of small subterranean karst cavities [2], sinkholes are fascinating structures in karst landscapes. There are also known as dolines [3], or in general, as karst cavities. However, the use of these two terms is not interchangeable and can be differentiated via their development and their evolution aspects. More specifically, sinkholes are defined as cavities resulting from the collapse or cover dolines developed in carbonate or dissolution rocks, while dolines are cavities defined by their morphogenetical mechanisms and hydrological structures [4]. For carbonate rocks with a fluctuating water table, as the level of water in the aquifer drops, unsupported cover-cavities become instable. Furthermore, continuous decreases in the water table and a diminishing roof thickness by gradual erosion consequently result in the inability of some areas to support heavy charges at the surface. This results in the eventual collapse of the roof. Such a phenomenon can occur in both urban areas due to the presence of new infrastructures or buildings, and in rural areas due to the movement of agricultural trucks. The development of sinkholes (or collapse dolines) enhances the risk of injury and life loss, property damage [2] and groundwater pollution.
The Causse of El Hajeb forms part of the large area of Tabular Middle Atlas (TMA), where thousands of karst landforms developed in Lower Liassic dolomite and Middle Liassic Limestone have been identified [5]. These carbonate rocks are highly fractured and are generally affected by two fracture systems (NE-SW and NW-SE) in which snow and rainwater precipitation gradually dissolved and created karst landforms. The development of karst landforms in this region is driven by the tectono-karstification process [6]. Among these karst landforms, collapse and cover-subsidence dolines and dissolution sinkholes have been identified as a source of environmental and geo-hazards risks. Chemical analysis performed on water springs located in the junction of the TMA and Saïs Basin [7,8,9,10] revealed that, during periods of high precipitation, the degradation of water quality is linked to superficial pollutants infiltrated into reservoirs through sinkholes located in agricultural areas, thus resulting in the internal gradual erosion of karst systems. The pesticides, herbicides and chemical fertilizers used in farming and agricultural production percolate into the groundwater aquifer and consequently change the composition, color and the taste of water springs. Long periods of drought [11], as well as the extraction of groundwater resources for agricultural activities, have reduced the level of water, enhanced the instability of subterranean karst cavities and ultimately increased the sinkhole development frequency in this region. In addition, newly formed cavities are rarely reported, thus further heightening the vulnerabilities in this environment [12]. Previous studies have applied remote sensing [8,13] and traditional geological surveying [14] in the TMA area, providing the degree of karstification of superficial karstic forms developed in carbonate, marno-calcareous rocks, and clays. However, these studies failed to identify their exact subsurface extent and depth location. Furthermore, a large number of sinkholes have previously been identified within a NE-SW fracture system, which has structured the area into graben and plays a big role in surface water infiltration [5].
In order to improve the qualitative interpretation of aeromagnetic data in the Middle Atlas mountain range, Mhiyaoui et al. [15] reinterpreted maps of the digitized magnetic field determined from aeromagnetic surveys over the Middle Atlas and High Moulouya. Results revealed the relationship between fractures affecting carbonate rocks and the development of karstic landforms in the regions of Azrou, Sefrou, El Hajeb and Boulemane. In particular, a major accident oriented NE-SW and second degree accidents oriented NNW-SSE and ENE-WSW, were identified to merge with karst depression alignments developed in Liassic limestone. Moreover, Quaternary volcanism activity increased the development of cryptokarsts, sinkholes and karst cavities in Jurassic fractured carbonate rocks in the direction of major faults.
Recent geophysical research in the Causse of El Hajeb [16] characterized the hydrogeological connection between the TMA and the Saiss basin, with a focus on the mapping of fracture networks involved in the hydrogeological system of Bittit water springs. In particular, complex water flow behavior involving probable water drains composed by fractures, karst cavities and stratification joints was detected via electrical tomography, suggesting the direct connection between identified karst cavities and the groundwater aquifer in this region.
Despite the accurate results produced from studies on karst cavities conducted using either geophysical [17,18,19,20] or remote sensing [21,22,23,24] methods, the fusion of the two techniques results in advantages in the acquisition, processing, and interpretation of geophysical data. Collecting spatial information on electrodes and surveyed points can particularly enhance sinkhole research. Billi et al. [25] combined calibrated electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and dynamic penetration measurements with well logs to investigate hidden sinkholes and Karst cavities in the highly-populated geothermal seismic territory of the Travertine plateau. The study identified the presence of sinkholes and caves that failed to be detected by previous studies using digital elevation models (DEMs), aerial photography and field surveys. Youssef et al. [26] used remote sensing images with geophysical data in predicting the susceptible areas for sinkholes that may collapse in the future. The study analyzed low resolution Landsat data to identify surface features related to subsurface sinkholes which were ultimately investigated using fieldwork and geophysical explorations.
However, remote sensing measurements are not always precise enough to provide the exact coordinates of every point surveyed on the regional scale. This is attributed to the specific geographic coordinate system used for the measurements or the inadequate spatial resolution of the measurements.
In order to contribute to the effort of determining a flexible and cost-effective methodology for sinkhole research and as an attempt to overcome the aforementioned problems of the current methods, we propose a method that integrates geo-electrical and remote sensing techniques. Optical satellite imagery (Sentinel-2 and Google images), GPS coordinate and DEM data were re-projected to the local datum (Merchich Degree) by transforming the 1984 World Geodetic System UTM zone 30N into Lambert Conic Conform based on information from Moroccan cartographic zonation (Morocco Z1). We employ the ERT and Self-Potential (SP) methods adapted to areas dominated by clay, basalts and carbonate rocks, along with well log data provided by local authorities. The equipment used for the geo-electrical surveying is capable of providing resistivity ranges for each of these geological formations [27]. SP instrumentation is suitable for hazardous areas due to its simple manipulation and the limited required manpower during the data acquisition. Furthermore, we investigate the local population with a living radius of 1 km from each sinkhole, with a particular focus on how they can behave and live with these sinkholes in terms of adaptation and mitigation to danger.
The current study forms part of a larger research initiative on the adaptation and mitigation of the effects of climate change on water resources in the Fez/Meknes region. This region is particularly important for the Moroccan economy due to its agricultural production of olive oil, wheat, maize, and onion. However, the water availability and quality in this region is deteriorating due to the presence of substances introduced into the karst aquifer via sinkholes and karst landforms. To reduce the consequences of this geo-hazard cycle, both the scientific community and general public have been working together to implement solutions for the reduction of sinkhole risks. As part of this, we performed geophysical surveys around four sinkholes identified as the most hostile to both the local communities and to the environment. The methodology adopted to mitigate the risks posed by the presence of sinkholes in the Causse of El Hajeb provides information that can improve the management of the relationship between the needs of the communities and the presence of sinkholes. The main objectives of this study are as follows: (1) To determine and characterize horizontal and vertical repartition collapse dolines; (2) to provide the exact coordinates of the studied sinkholes; and (3) to identify a location for the sinkhole protection perimeter in order to reduce environmental and geo-hazards risks.
2. Geological and Geomorphological Overview of the Middle Atlas
During the Triassic period Morocco was subdivided into several basins [28]. The formation of these Triassic basins was initiated during the Permian period and was accentuated during the Triassic by distension. This subsequently led to the formation of the basins, particularly in grabens and half-grabens with fracture networks distributed across the directions N60, N90 and N120. This rhombic aspect constituted a permanent geometrical characteristic in the Triassic and Jurassic evolution [29,30]; during the early stages of the Pangea breakup in the upper Triassic, visible at the outcrops. The individualization of the basins was carried out via two stages. First, the sinistral motion along the N90 and N120 directions occurred, causing NW-SE distension compatible with the formation of the NE-SW grabens. This was followed by the accentuation of the directional movement along N90 and N120, again due to sinistral motion [30,31].
The filling of these formed basins began with variable detrital material composed by conglomerates, sandstones and arkoses developed in the High Atlas of Marrakech and in the Middle Atlas in the North of Midelt. The filling continued by depositing evaporite argillites in the Middle Atlas and in the Mesetian domain, where it is possible to distinguish the lower and upper saliferous argillites separated by the basaltic complex. This basaltic complex is formed by a stack of lava flow with deposited sedimentary levels that indicate that these basalts are typical oceanic and continental tholeites [32]. The effusions of the basaltic flows were either in a shallow marine environment or in the open air under a hot and arid climate. This intrusive (sill and dyke) or effusive basaltic complex, associated with the explosive volcanism common throughout North Africa and the eastern coast of North America, is one of the manifestations of the Hercynian basement disintegration linked to Atlantic rifting [33].
During the Jurassic period, the Atlas domain differentiated and evolved into regions separated by the old massif of the High Atlas. The Saouira-Agadir lies in the western region, while the eastern region is occupied by the Atlas chain domain, stretching from the East of the Hercyanian central massif to Mediterranean Sea. The Liassic carbonate platforms experienced a great extension during the Sinemurian and Carixian, represented by thick carbonate sedimentation in subsiding zones which can be subdivided into two litho-stratigraphic units separated by a sedimentary discontinuity [34]. During the Liassic period, the indices of the synsedimentary tectonics were frequent, namely the slip, synsedimentary faults and progressive discordances. These synsedimentary tectonics led to the dislocation of the Liassic carbonate platform and the differentiation of the intracontinental basins (from the Middle Atlas and the High Atlas separated by carbonate forms).
The middle Liassic–upper Liassic is characterized by a tectonic activity that yielded a major sedimentary discontinuity, condensed stratigraphic deficiency of the Lower Toarcian. This tectonic activity led to the dislocation of the Liassic carbonated platform and the individualization of the basins of the High Atlas and Middle Atlas. Newly formed basins were surrounded by remnant or sub-emerged horst residual platforms (the Highlands and the Causses) which contained subsidence zones with marly sedimentation that evolved into sub-basin depocentres and high zones. The filling of the basins by an essentially carbonated syntectonic sedimentation initiated at the beginning of the lower Toarcian, following sedimentation marly deposits that included carbonate intercalations on the borders of the basins. In the Middle Atlas, these deposits experienced lateral variations in facies. In particular, black micritic limestones were found in the NE direction, while thin reddish limestones on the flanks of rock wrinkles were identified in the SW. Towards the end of the Lower Bajocian, the underwater seabed decreased in depth and the development of the upper Bajocian carbonate platform initiated. The extensive phase of the Mesozoic led to the opening of the basins occupied today by the Middle Atlas.
The TMA region (Figure 1) is characterized by a landscape of slightly subhorizontal structures, with highly fractured Liassic limestone and dolomite bedrock. The structures form a large karst plateau along the NE-SW direction at an altitude ranging between 700 to 2200 m bordered to the north by the Saiss basin and to the SE by the Middle Atlas. The TMA is affected by two major fracturing systems in the Mesozoic, Cenozoic and Quaternary formations, related to Hercynian tectonics and a post Hercynian event. A NE-SW oriented longitudinal fracturing system, incorporate Triassic and post-Hercynian bedrock units, similar to existing transversal fracturing system oriented NW-SE to ESE-WNW. It is this phenomenon in the NW-SE extension that has favored the generation of NE-SW fractures [35,36,37]. The Cenozoic was marked by the N-S compression and WNW-ESE extension that favored the genesis of the N-S to ESE-WNW fractures. During the Middle and Upper Quaternary, the second extensive phase of intense volcanic activity occurred (e.g., the Outigui and El Koudiate volcanoes) and the generation of the Tizi N’Tretten accident [38]. These fracturation systems (NE-SW, NW-SE and flexures) led to the current structural relations of the TMA. The set of Tizi N’Tretten faults divides the TMA into the North West and South East regions. The NW region is formed by the Causses d’Imouzzère, Ain Leuh, Ifrane and the Causse d El Hajeb, while southern part by the Causses of Annonceur and El Menzel, Guigou and the Oum Er-Rbia basin.
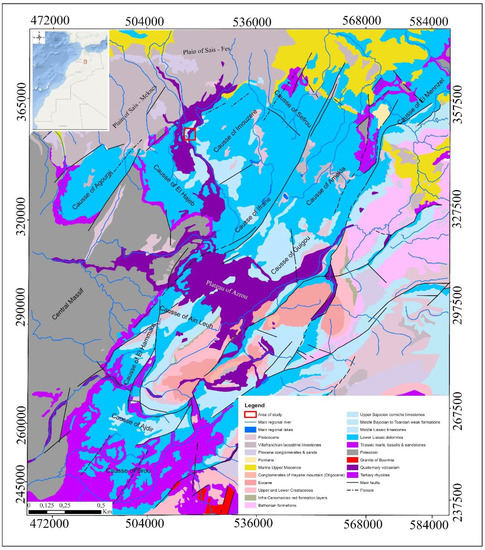
Figure 1.
Geologic stretch of the TMA of Morocco with red boxes indicating the location of the area of study on Moroccan as well as on TMA scales.
As part of the TMA, the Causse of El Hajeb is lithostratigraphically dominated by weathered basalts, red clays and sandstones of the Triassic period, carbonate rocks (dolomite and limestone) of the Jurassic era, and basalts, clay, and alluvial deposits of the Quaternary era. These formations are slightly deformed and gently folded in Jurassic carbonate rocks with approximately 20°–50° dip values. In addition, they are reversely covered with Paleozoic basement units composed of sandstone and pelite arranged as turbidity sequences [39]. The latter surrounds the southern part of the little Causse of Agourai oriented to the NE-SW and outcrops the SW limit of the Causse of El Hajeb. The carbonate rocks are affected by many fractures oriented NE-SW and NW-SE and define the structural framework of this area, with numerous blocks and narrow distensive structures corresponding to half-grabens [40]. Initial information on the Karstic phenomena in the Atlas Middle Causse was collected from studies carried out in the Atlas Middle Causse [13,14,41]. The development of different karstic forms in the TMA is conditioned in part by the presence of the subhumid to humid climate characterized by low temperatures and by the abundance of winter snow. These conditions favor the dissolution of the highly fractured Liassic dolomitic and limestone rocks and evaporite rocks of the Triassic, with different karstic forms developed in deep layers as well as close to the surface (e.g., avens, sinkholes, galleries, collapse chasms, caves, lapiez, polje and porches). Some of these karst landforms are invisible on the surface, unlike the very frequent sinkholes with diameters ranging from 15 to 12 m. This is often due to the accumulation of snow which led to the collapse of roofs of underground galleries and the pockets of salt dissolution during the Triassic, or due to equipment used in agricultural activities. Accumulated alteration products of carbonate rocks or reddish clay minerals are often located at the bottom of the karst depressions. This accumulation leads to the formation of clay residues that can circulate in the groundwater to the exit at the sources.
In regions where the Plio-Quaternary basaltic flows overlaid on calcareous substratum, large sinkholes, with depths ranging from 20 to 30 m, are visible on the surface. This karstic environment hosts an important underground aquifer in which the meteoric water (snow or rain) infiltrates through cracks and voids drains [6,42] and recharges the groundwater aquifer. Groundwater formed in carbonate rocks in the Lower and Middle Liassic rocks arrives on the surface at the level of local lake system in the basins and at the levels of the waters springs (resurgences or exsurgences), particularly at the point of contact with the TMA and Saiss Basin. During periods of intense rainfall, water turbidity is observed [36], reducing water quality. This turbidity can be attributed internally to the leaching of the karstic network in which meteoric water circulates, and also externally, at the level of infiltration within different karst landforms [7,41].
Our study region (Figure 2) has an approximate area of 3.5 km × 2.4 km and is located in the Causse of El Hajeb at 37 km, 45 km and 15 km from the regional main cities of Meknes, Fez and El Hajeb respectively. It is an area characterized by rich soil cover and abundant groundwater; these conditions have favored agricultural activities and regional economic development. The presences of fractured and weathered quaternary basalts deposed on major faults affecting Jurassic carbonate rocks have favored the development of subsidence sinkholes in or around agricultural fields. However, anthropogenic activities have increased the frequency of collapsed or subsidence sinkholes developed on superficial carbonate rocks of limited thickness. This can be attributed to the displacement of large basalts by trucks which subsequently apply pressure on the thin underground cavities roofs and eventually trigger their sudden collapse. In addition to this, the use of fertilizers and other types of chemicals alter the water surface composition, infiltrating through faults and fractures to gradually dissolve the carbonate rocks, and ultimately leading to the creation of karst cavities.
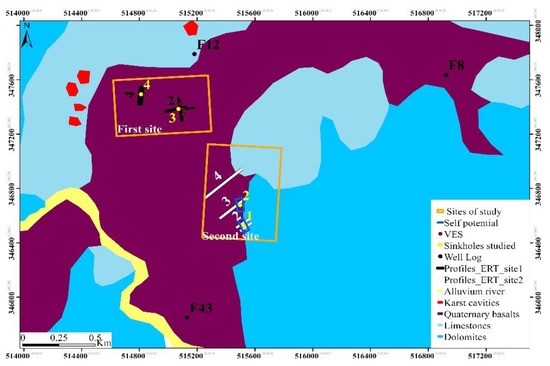
Figure 2.
Geological map extract of El Hajeb (1:100,000) indicating the study sites location. The first site represents area hosting buried sinkholes filled with basalts and dropout doline whereas the Second site represents area hosting funnel shaped collapse sinkhole with an approximate depth of 35 m and solution sinkhole with an approximate depth of 50 m.
3. Methodology and Datasets
The datasets consist of satellite imagery and measurements collected in the field. Satellite images were re-projected using a local coordinate system projection (Table 1) in order to minimize cartographic distortions and measurement errors during the planning of the fieldwork, as well for the determination of sinkhole locations. The remotely identified sinkhole locations were validated during the fieldwork. Furthermore, geophysical surveying was used to examine the vertical and horizontal extent of the sinkholes. Interpretations of geophysical data were based on borehole data, geologic information and on site direct observations.

Table 1.
The principle characteristics of the Moroccan Geographic coordinate system (Morocco Z1) used for the transformation of satellite imagery, GPS coordinate and DEM 84WGS UTM zone 30N projection system into Lambert Conic Conform.
The Figure 3 details the methodology followed in order to identify sinkholes presenting high risks to the environment and protection zones for groundwater resources in the Fez/Meknes region.
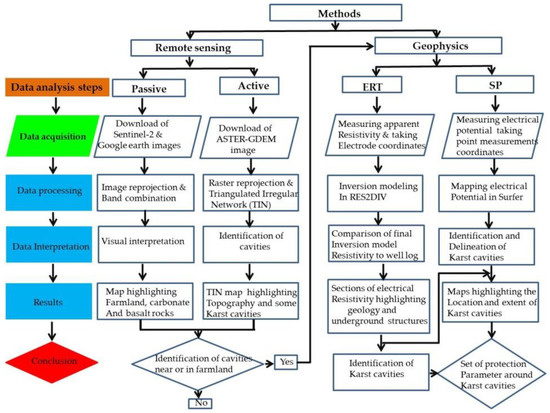
Figure 3.
Flowchart of the methodological steps adopted in this study.
3.1. Remote Sensing and Geophysical Data Acquisition and Processing
Satellite images can optimally retrieve information on large-scale and remote areas. Unlike direct field measurements, the acquisition of satellite remote sensing data does not require administrative or local own authorization. Contrary to aerial photogrammetry (using drone), satellites have the ability to provide land cover and land use information at very large area in one single acquisition. In addition, the high temporal resolution, satellite allows the monitoring of natural phenomena as well as change detection of landscape. We used a multispectral Sentinel-2A image acquired on 30 March 2017 (specifications provided in Table 2), the Advanced Space borne Thermal Emission and Reflection Radiometer global digital elevation model (ASTER-GDEM) product Version 1 acquired on 17 October 2011 (provided by the Ministry of Economy, Trade, and Industry (METI) of Japan and the United States National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA)) and Google Earth image acquired on 19 July 2019.

Table 2.
Specifications of the Copernicus Sentinel-2 image employed in the data analysis.
3.2. Multispectral Sentinel-2A Image
The Copernicus Sentinel-2A satellite, along with its twin Sentinel-2B, is part of a satellite series developed by the European Union Earth Observation program. Launched on 23 June 2015 at an altitude of 786 km for a 7-year mission, the Sentinel-2A satellite monitors the Earth’s surface and the changes resulting from natural phenomena or human activities. It provides multispectral, high to medium spatial resolution images with 13 bands in the visible, near infrared (NIR) and shortwave infrared (SWIR) for a temporal resolution of 10 days (5 days when combined with Sentinel-2B). The data acquired by Sentinel satellites constellation is managed by the European Commission and distributed by the European Space Agency (ESA) via the Copernicus Open Access Hub. The images can be accessed and downloaded for free at https://scihub.copernicus.eu/dhus/#/home for regions located within 84° N and 56° S.
Sentinel-2 images are frequently applied in many fields, particularly for water management and land protection purposes [43], as well as the management of agricultural plots [44], the identification and monitoring of crops [45] and for the risk management of floods [46], forest fires [47], and coastal water contaminant [48]. Additional applications include geological mapping [49] and the monitoring of geological waste [50]. In the current study, we employed Sentinel-2A imagery in order to identify the extent of agricultural areas, the distribution of geological formations, and the location of potential karst landforms. Sentinel-2A data was combined with images from Google Earth and ASTER-GDEM, allowing us to identify land cover types in the Causse of El Hajeb.
The ASTER-GDEM (version 2), acquired on 17 October 2011 with a spatial resolution of 30 m, was downloaded from the US geological survey website (http://earthexplorer.usgs.gov).
3.2.1. Remote Sensing Data Processing and Interpretation
The detection and extraction of sinkholes via the analysis of remote sensing data was performed using a GIS-environment. Satellite imagery can provide precise information on vegetation, urban development, and bare soil. In the current study, we analyzed the vegetation and the bare soil, with the analysis procedure detailed as follows.
In the first step, we determined the geologic formation extent likely to host karst landforms. More specifically, the delineation of the outcrop geological formation was performed using the level-2A Sentinel-2A image using SNAP desktop (version 6.0, ESA, Paris, France) and ArcGIS (version 10.1, Esri, Redland, CA, USA). After resizing the spatial resolution of all bands to 10 m via SNAP desktop, ArcGIS was used for the re-projection to the local coordinates and false band combination using the SWIR, NIR, red bands. These bands were used based on the reflectance of land cover types, whereby vegetation exhibits a peak in the NIR band whereas carbonate rocks exhibits a peak in the SWIR band. The false color RGB image reveals the location of carbonate rocks, basalts, and red clays, as well as the vegetation within agricultural areas and numerous trees (Figure 4).
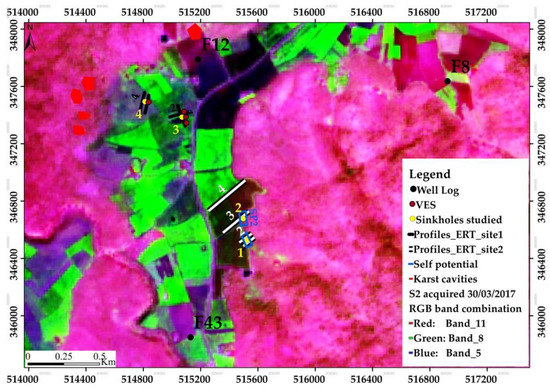
Figure 4.
False-color Sentinel-2 image (bands 11, 8, and 5) demonstrate the principle land cover types: vegetation (green colors), basalts (purple), and carbonate rocks (pink). Derived from a level-2A Sentinel-2A acquired on 30 March 2017 from the Copernicus Open Access Hub.
Second, sinkholes located on the geologic formations were extracted from the ASTER-GDEM using ArcGIS hydrological tool. The fill sinks is commonly used in hydrological studies to determine the flow direction of surface runoff without taking into account the effect of sinks and depression information recorded during DEM data processing. In a karst environment, these sinks and depressions can be related to the presence of cavities or sinkholes. It is possible to identify these karst landforms by subtracting the initial ASTER-GDEM raster from the output ASTER-GDEM raster derived from the fill sink algorithm. This technique has previously been used for the automatic delineation of karst sinkholes on high spatial resolution data [51,52,53]. In the current study, a 30 m spatial resolution was too course to identify individual sinkholes. Thus, we applied a triangulated irregular network (TIN) derived from ASTER-GDEM via the Delaunay triangulation method. This method has the advantage of forming triangles from nearby points, hence providing a good representation of the topography of a given area [54]. We computed the TIN in order to analyze the ASTER- GDEM karst depressions and compare their locations with the land cover information derived from the S-2A data, the geologic map of El Hajeb (published in 1975 with a scale of 1/100,000), and the Google Earth image (Figure 5). A detailed investigation was subsequently conducted during fieldwork in the study area, whereby the coordinates of the identified sinkholes were recorded using a GPS Garmin. These coordinates were then manually digitalized on TIN topography of the studied area in ArcGIS. In summary, sinkhole identification was conducted in five steps: (1) The identification of carbonate rocks (on geologic maps and multispectral images); (2) the delineation of karst depressions on ASTER- GDEM; (3) the identification of farmlands located in and near the karst depressions; (4) the identification of sinkholes and the recording of their coordinates in the field; and (5) the transformation of coordinates and digitization of sinkholes on the TIN elevation model.
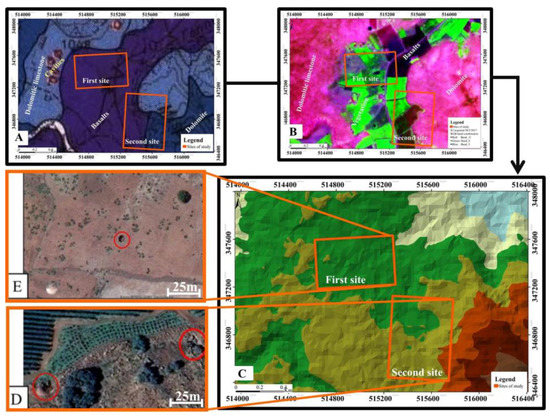
Figure 5.
Identification of sinkholes by comparing (A) a regional geological map of El Hajeb (B) a false color Sentinel-2A image using the SWIR, NIR and Red bands, (C) the TIN derived via the ASTER-GDEM, and a high spatial resolution Google image containing sinkholes (D,E) identified in agricultural areas.
Geophysical surveys were conducted on the second site in order to study the subsurface behavior of two sinkholes identified close to the farmland.
3.2.2. Geophysical Data Acquisition
In order to investigate surface and subsurface extensions of the identified sinkholes, we conducted geophysical surveys using electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) and Self-potential (SP). These non-invasive geoelectrical methods are generally employed in the measurements of electrical properties (electrical resistivity and electrical potential) of lithologic and pedologic formations in karst environments [55,56,57,58]. Advancements in equipment and software have increased both the speed and accuracy of the detection of sinkholes across different geologic formations. In particular, the application of non-polarizing electrodes combined with multimeters to measure ground surface electrical potential has previously been analyzed [59] to monitor SP anomalies associated with sinkholes. Furthermore, Zhou et al. [60] evaluated the advantages and disadvantages of different electrode configuration arrays for depth investigation, sensitivity to horizontal and vertical variations, and for the signal strength of electrode configurations by evaluating the resistivity of subsurface materials. The authors detected that images obtained using a dipole-dipole array were of a higher spatial resolution compared to those from the Wenner and Schlumberger arrays in displaying the sinkhole collapse areas. They concluded the dipole–dipole array as the most effective and less costly configuration in mapping karst hazards areas [60].
In the current study, four ERT profiles were acquired using a dipole-dipole array placed around two sinkholes. In addition, two SP surveys were conducted in order to produce a map of the electrical potential distribution at the ground surface. The fusion of ERT and SP was able to provide a clear picture of the sinkhole extension at the surface as well as underground. Geographic coordinates were registered for each measurement in order to enhance the geolocation precision of the studied sinkholes and the geo-electrical measurements. This allowed for the acquisition and processing of geophysical data and for the subsequent interpretation of the results.
Electrical Resistivity Survey Using ERT
ERT, an active geophysical prospecting method, measures the electrical resistivity (Equation (1)) following the injection of an electric current into the ground at the level of the electrodes. The circulation of this current depends on the chemical composition, lithology and underground structures of the prospected zone.
where ρ (Ωm) is resistivity and σ (S/m) is conductivity.
Electrical resistivity surveying is based on Ohm’s Law, which governs the flow of the current injected into the ground. Equation (2) is Ohm´s Law in vector form for the current density flow in a continuous medium [61] and demonstrates the relationship between the current density and the conductivity of soil and geologic formations.
where J (A m−2 )is current density and E (V/m) is the electric field intensity.
The gradient expressed in Equation (3) shows the relationship between electric field intensity and electrical potential:
where Φ (V) is electrical potential due to point sources.
The combination of Equations (2) and (3) gives the relation of current density with electrical potential and the conductivity expressed as follows:
During the ERT surveying process, the positions of the electrodes are determined by the X, Y, and Z coordinates. These electrodes are the current source (I). The relationship between current density (J) and the current (I) is given by Equation (5):
where ∆V is the elemental volume surrounding the electrodes and δ is the Dirac delta function. Following Ohm’s Law, where the current is considered to spread in all direction, Equation (4) can be rewritten in terms of the potential distribution in the ground due to a point current source as follows:
The resolution process in Equation (6) allows us to determine the electrical potential at the ground surface due to point current sources.
Apparent resistivity ERT field measurements of soil and geologic formations are conducted by injecting a current into the ground through two current electrodes (C1 and C2) and measuring the resulting voltage difference at two potential electrodes (P1 and P2) expressed by Equation (7) as follows:
where is the apparent resistivity, K is a geometric factor that depends on the arrangement of the electrodes, I is the electrical current and the electrical potential.
Note that the instrument used to measure geologic and soil formation resistivity generally records the resistance values as follows:
The apparent resistivity is determined by incorporating geometric factor K. For ERT surveys conducted using a dipole-dipole array, K is expressed as follows:
where π is the constant, a is horizontal electrode spacing (for current source electrodes or potential measuring electrodes) and n is an integer representing the number of spacing times between current source electrodes and potential measuring electrodes as shown on Figure 6.
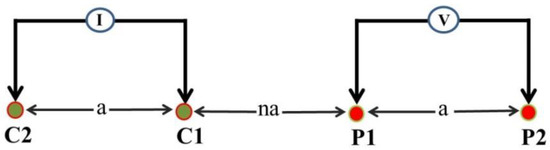
Figure 6.
Dipole-dipole array configuration for resistivity surveys for n = 1, where C1 and C2 represent the current source electrodes and P1 and P2 the potential measuring electrodes.
The final apparent resistivity measured by ERT using a dipole-dipole array can thus be written as follows:
The investigation depth depends on the length of the profile used, and the spatial resolution of a resistivity model section is a function of the distance between the electrodes.
During the ERT survey process, the electrode separation (a) is kept constant while n is constantly increased in order to measure the resistivity of deep structures. Potential measurements are performed at several points at different depths for each electrode. The Figure 7 illustrates an example of ERT survey for dipole-dipole configuration with 14 electrodes, during the acquisition of apparent resistivity; two electrodes are taken as the current source while the rest are used for potential measurements. The results obtained from several positions form a pseudosection of the apparent measured resistivity. The measurements are automatically controlled via an algorithm located in the acquisition instrument which selects the appropriate four electrodes for each measurement.
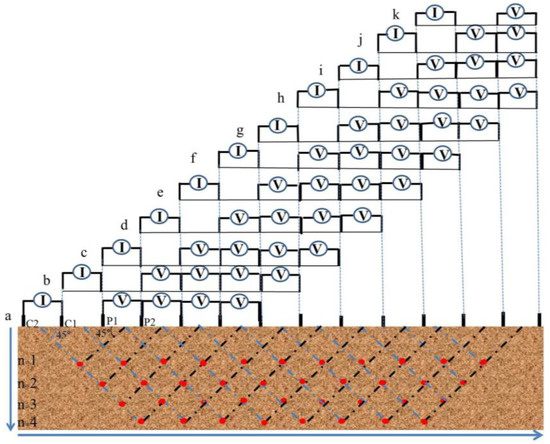
Figure 7.
ERT survey example: The plot of the dipole-dipole apparent resistivity on a pseudosection. Electrical potential measurements are performed at several positions for every current source location (from a to k). We used a 2 m spacing distance for both the current electrodes (C1, C2) and potential electrodes (P1, P2). The separation of current electrodes (I) and potential electrodes (V) is equal to n × 2 m. The arrows indicate the orientation of the measurements; the red dots indicate the measurement location at the intersection of two lines, at 45 degrees, to the center of the current and potential electrodes.
During the ERT measurements with a dipole-dipole array, we set the electrode separation to 2 m for three profiles and 5 m for one profile for 64 electrodes. From the measurements, we were able to obtain a 2D subsurface electrical model where the variation of resistivity revealed the location of the sinkholes and different enclosing geologic formations. The acquisition equipment (Figure 8) is manufactured by IRIS instruments and includes a Syscal PRO resistivity meter that measures the apparent resistivity, a 12 volt battery, 64 stainless steel electrodes, four yellow colored cables to connect the electrodes to the resistivity meter, four cable connectors and a Garmin GPS to register the geographic coordinates of the electrodes.
Figure 8.
The acquisition equipment manufactured by IRIS and includes battery, resistivimeter, electrodes, coil, cables, and cable connector.
SP Field Measurements
SP is a passive geophysical prospecting method that measures the distribution of natural electrical potential at the ground surface. This electrical potential is related to the electric charge polarization mechanisms observed in the porous or microcracked medium due to the chemical potential gradient of the carriers of ionic or electronic charges. The origin of this gradient makes it possible to distinguish the SP anomaly in three main categories. We distinguish the SP signal of (1) electrochemical origin (fluid diffusion through pedologic and lithologic contacts), (2) electrokinetic phenomena (underground water flow through pores, fractures, and cavities), and (3) thermal origin (namely subterranean temperature). SP can generally be attributed to underground stream flows in fractured and porous areas such as karstic environments. The SP method has previously been employed to determine the location of subsurface cavities [62] and the preferential groundwater flow pathways in sinkholes [59], and to investigate the vertical infiltration of water from agricultural ditches into sinkholes [63]. Furthermore, Ikard et al. [64] applied the fusion of SP with ERT to identify the occurrence of preferential groundwater seepage in karst terrain.
In the current study, we performed SP signal measurements at the ground surface using non-polarizing electrodes connected to a multimeter in voltage mode (with impedance at 10 MΩ) via an electric cable. Equation (11) represents the relationship between the electrical current density at point M and the measured SP signal at non-polarizing electrode P. This electrical potential signal φ (mV) can be computed as follows:
where jS is the source current density (in both saturated and unsaturated conditions), K(P,M) is the kernel connecting the φ(P) signal measured at a set of non-polarizing electrodes P (with respect to a reference electrode) and the source of current at point M in the conducting ground. It is important to note that this kernel depends on a number of factors including the number of measurement stations at the ground surface (Figure 9) as well as the distribution of resistivity [55]. The total current density is expressed as follows (Equation (12)) [65,66]:
where j is the electrical current density (A m2), σ is the electric conductivity of the porous material, φ is the SP, Qv is the excess charge of the diffuse layer of the pore water per unit pore volume and depends on the permeability of the porous material, θ is the water content, θs is the porosity, and u is the Darcy velocity.
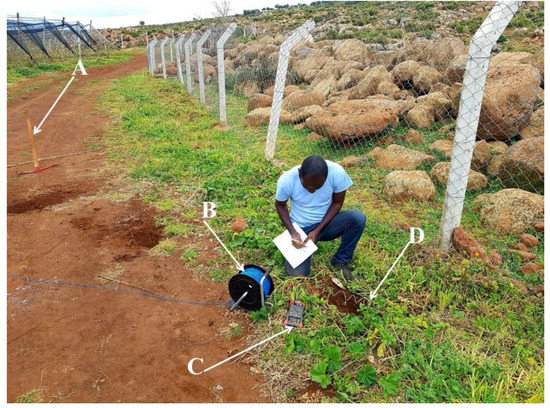

Figure 9.
An example of SP measurement station at the ground surface on which a pickaxe (A) is used to dig a shallow hole with 30 cm of depth where one non-polarizing electrode (D) connected to a multimeter (C) and another fixed non-polarizing electrode via an electrical cable (B) is introduced to take SP signal.
3.3. Geophysical Data Processing and Interpretation
3.3.1. ERT Data Processing
The apparent resistivity values obtained in the field represent the resistivity of homogeneous ground, with constant resistance values associated with the same electrode arrangement [55]. In order to obtain the true resistivity of the soil and geologic formations, computer inversion techniques are generally applied to determine the true subsurface resistivity from the apparent resistivity values [67]. These inversion techniques are made up of computer based algorithms. In particular, for ERT surveys, RES2DINV software, developed by Dr. M.H. Loke, is employed for the processing of 2D data. This program applies the conventional smoothness-constrained least-squares algorithm [68] as the default inversion method. More specifically, a 2D model of the subsurface is determined by first creating a large number of blocks and subsequently applying the least-squares inversion scheme to determine the appropriate resistivity for each block. By doing so, the calculated apparent resistivity values agree with the measured apparent resistivity values determined from the field surveying [61]. During the processing of the data, the difference between the calculated and measured apparent resistivity values is computed using, for example, the root-mean-squared (RMS) error (Equation (13)). This difference is reduced by adjusting the resistivity of the model blocks over a number of iterations. The optimum 2D model is chosen at the iteration where the change in the root mean square error (RMSE) is minimal.
where ρca is the calculated apparent resistivity (using RES2DINV), ρma is the measured apparent resistivity (on the field), and n is the number of points surveyed.
In the current study, ERT profiles acquired around four sinkholes were processed using the RES2DINV (version 4.8.10. 64-bit, GEOTOMO SOFTWARE, Gelugor, Penang, Malaysia) inversion software to map the electrical resistivity in two dimensions (vertically and horizontally). This updated version of RES2DINV softwares, dating 2 May 2018, is capable of processing 60,000 acquired data points for a maximum number of 6000 electrodes and 40 maximum model layers.
3.3.2. From SP Data Acquisition to SP Signal Maps
The measured SP signals are electrical potentials primarily attributed to the circulation of water in the saturated zone [16] or to the percolation of water seeping into the vadose zone. We used simple equipment consisting of two non-polarizing electrodes, a very high sensitivity multimeter and a coil of electric cable. The measurements values were then written down in a table on a field notebook. We chose to make an acquisition of electrical potential via a mesh of 2 m inter-measurements with a fixed and mobile electrode, allowing us to subsequently determine electrical potential variation maps around the sinkholes. In laboratory, SP data was saved in Excel (version 2010, Microsoft Corporation, Redmond, WA, USA) spreadsheets and then processed using the Surfer (version 13, Golden Software LLC Company, Golden, CO, USA) to output the electrical potential maps.
3.3.3. Boreholes Data and Geophysical Data Interpretation of the Second Site
The Figure 10 shows the location of geophysical measurements (ERT and SP) conducted around the sinkholes developed on the second site with geological formations dominated by basalts, dolomitic limestone, and dolomites.
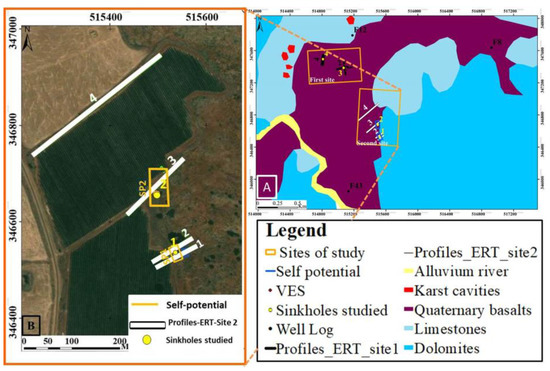
Figure 10.
Position map indicating the location (B) of the ERT profiles, SP and the sinkholes of the second site (A).
As previously mentioned, the SP signal can originate from different sources. Thus, in order to determine the origin of the measured SP signal, and to subsequently facilitate its interpretation, we combined the SP results with those derived from the ERT method. This allows for an improved understanding of the underground polarization mechanism that is responsible for the electrical potentials measured at the surface. We assumed that the dominant process contributing to the SP signal was the electro filtration electrokinetic phenomena generated by the streaming potential gradient from underground water flows through pores, fractures, and cavities in this karst environment.
The 2D model of subsurface true resistivity represents the resistivity values of geologic formations, soils, and other materials. An accurate interpretation of the model must be based on the electrical properties of the present materials in order to translate the resistivity model into a geologic model.
To do this, the subsurface materials and geologic formations of the surveyed area must be identified. This information can be obtained by conducting a number of borehole loggings and by determining the subsurface true geologic composition.
During the drilling of this borehole, different subsurface geology information (such as the lithology and the thickness of geological formation layers, their structural and composition as well as the water table level is saved in the form of stratigratic logs. The Figure 11, Figure 12 and Figure 13 represent the logs of boreholes F8, F12 and F48 located near the studied sinkholes (Figure 10). In particular, they contain descriptions of the stratigraphic composition of the surveyed area dominated by basalts, clays, sandy dolomites, fractured limestones, and dolomite. At the drilled point, the presence of cavities was identified by the free fall of the hammer deep in the borehole and was reported on borehole log as shown on the Figure 11, Figure 12 and Figure 13.
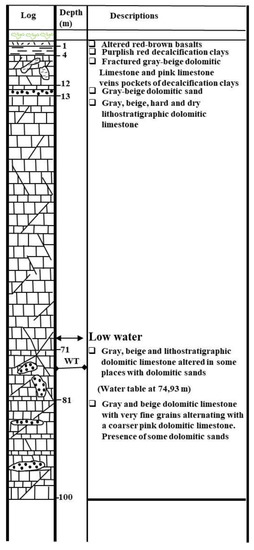
Figure 11.
Borehole log F8 from 1982 with final depth of 100 m where water table was identified at 74.9 m of depth.
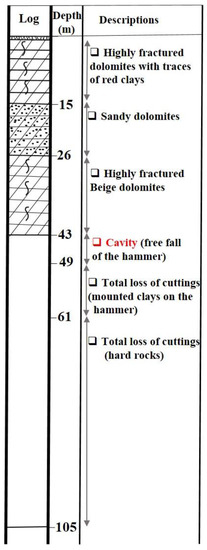
Figure 12.
Borehole log F12 from 1986 with final depth of 105 m where water table was identified at 5.6 m of depth.
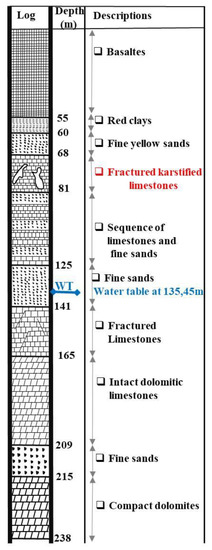
Figure 13.
Borehole log from 1998 with final depth of 238 m where water table was identified at 136 m of depth.
Following the determination of subsurface geologic formations of the study area, the locations of the formations must be identified on the 2D true resistivity model. Volcanic rocks such as basalts have a resistivity of 103–1.3 × 107 (dry) Ωm, sedimentary rocks such as sandstone, limestone and dolomite have values of 1–6.4 × 108 Ωm, 50–107 Ωm and 3.5 × 102–5 × 103 Ωm respectively, while soil (clay and alluvium) values are measured as 1–100 Ωm and 10–800 Ωm respectively [69]. The resistivity value is a function of various factors, such as the degree of porosity, fracturing and the type and the quantity of material filled in these voids. The combination of this information allows for the identification of structures and types of geological formations at the subsurface as well as at the horizontal extent of the studied sinkholes.
4. Results and Discussion
The measurements from the remote sensing and applied geophysical techniques were analyzed with the ultimate aim of identifying and protecting the sinkholes in the study area. The study was conducted in order to contribute to the big effort launched in the region of Fez/Meknes for climate change adaptation with a focus on groundwater resource protection. First, karst depressions and agricultural areas were identified using Sentinel-2A, ASTER-GDEM and Google Earth images. Based on the surface reflectance and morphology contained in the imagery, the interpretation of visual features of the 3-band false color Sentinel-2A image and TIN topographic model conducted in conjunction with geologic information and fieldwork measurements allowed us to identify sinkholes and karst cavities at the two study sites. Remote sensing measurements were used to identify the location and horizontal extent of the sinkholes, while geophysical surveys were conducted in order to determine their subsurface location and extent. The methods were able to delineate the soil and geological materials of the study area. Furthermore, geophysical data was acquired at the second site, whereby we identified collapse and solution sinkholes located close to agricultural fields.
4.1. Sinkholes Identified Remotely
The processed satellite imagery reveals that sinkholes are located in areas occupied by basalts and come into contact with carbonate rocks. In particular, these areas possess fertile and rich soil suitable for agricultural activity. In addition, the presence of fractured limestone and dolomite allow for the water infiltration and retention, thus making the area more attractive as farmland. Figure 14 presents the TIN elevation model computed from the ASTER-GDEM on which we digitalized the identified sinkholes and other karst cavities. Variations in the elevation and the interpolation of triangles representing nearest point elevations indicate that these karst landforms are developed on large to small depressions. These depressions are expressed by subcircular surface features with low elevation located in areas occupied by basalts and with their contact with carbonate rocks. On-site observations confirmed the location and characteristics of different karst landforms that were identified remotely (Table 3). Different types of sinkholes, such as collapse, solution, and dropout doline, were observed (Figure 15).
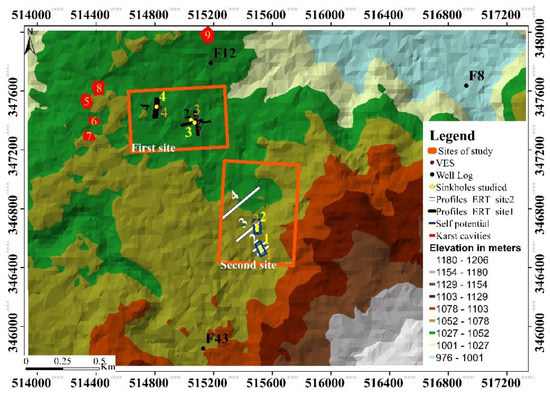
Figure 14.
TIN topography of studied area highlighting the variation in topography and the locations of the studies sinkholes.

Table 3.
Karst landforms characteristics identified in the Causse of El Hajeb.
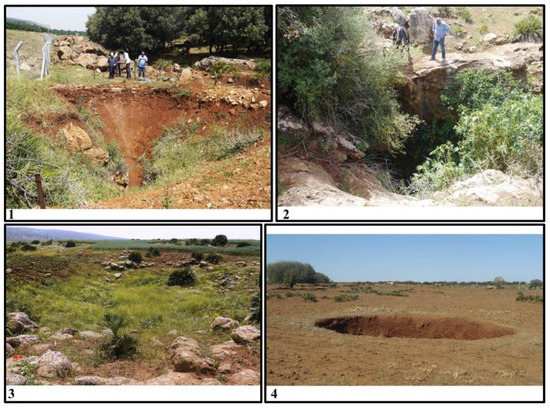

Figure 15.
Photographs of sinkholes identified during fieldwork observations. (1) Funnel shaped collapse sinkhole with an approximate depth of 35 m, (2) solution sinkhole with an approximate depth of 50 m, (3) buried sinkholes filled with basalts, and (4) dropout doline.
Table 3 reports the key characteristics of karst landforms identified via the satellite imagery and confirmed using on-site observations. The distance from farmland value calculated from the sinkhole or cavity location represents the distance a polluting substance used in agricultural activities would have travel in order to reach the fractured carbonate rocks to eventually end up in the groundwater aquifer. Knowledge of the surface morphology and outcrop geology can help to determine the type of protection perimeter structure required to protect these sinkholes.
4.2. ERT
The location of the karst cavities was observed in areas with very low electrical resistivity values compared to the whole resistivity model section values. The 2D Resistivity model was chosen for the 7th iteration with RMSE (absolute errors) of 8.9, 9.4, 11.3 and 14 for different electrical resistivity profiles conducted during of the field surveys.
Figure 16, Figure 17, Figure 18 and Figure 19 represent the 2D resistivity model sections obtained from the ERT profiles conducted around sinkholes and cavities identified at the second site (Figure 14). The results of the ERT survey obtained following seven iterations reveals the electrical resistivity of subsurface materials, with higher values representing resistive geological formations whereas lower values represent conductive materials. Based on the borehole logging information, we were able to determine the subsurface geological formations belonging to these materials. The resistivity model allowed us to identify soil materials and red clays on the surface and inside the sinkhole cavities with values ranging from 3 to 60 Ωm. These sinkholes are located in high resistive host rocks, namely dolomitic limestone, fractured limestone, and dolomite, with resistivity values ranging from 165 to 4000 Ωm.
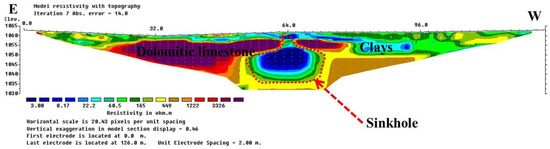
Figure 16.
Resistivity model section for ERT profile P1, representing the variation in electrical resistivity values obtained following the inversion of apparent resistivity values for seven iterations with absolute error of 14.0. This profile was acquired in the southeast of the first sinkhole identified at 64 m from the first electrode. The continuity of the vertical anomaly demonstrates that the development of the sinkhole in carbonate rocks, reaching a 30 m depth from the surface where the cavity is visible (Figure 15).
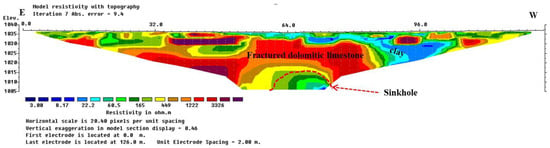
Figure 17.
Resistivity model section for ERT profile P2, representing the variation of electrical resistivity values obtained following the inversion of apparent resistivity values for seven iterations with absolute error of 9.4. This profile was acquired in the northwest of the first sinkhole identified at 70 m from the first electrode. Vertical anomaly analysis demonstrates the development of the sinkhole in carbonate rocks, reaching deep into fractured dolomitic limestone.
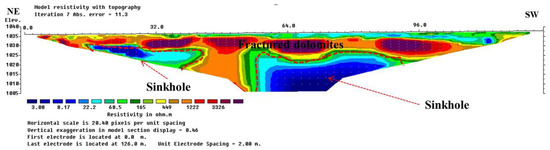
Figure 18.
Resistivity model section for ERT profile P3 representing the variation of electrical resistivity values obtained following the inversion of apparent resistivity values for seven iterations with absolute error of 11.3. This profile was acquired in the northwest of the second sinkhole, approximately 30 m in size and identified at 70 m from the first electrode. Vertical anomaly analysis shows that the sinkhole is developed in carbonate rocks and reaches deep into fractured dolomitic limestone. In addition, a second sinkhole was identified 32 m from the first electrode.
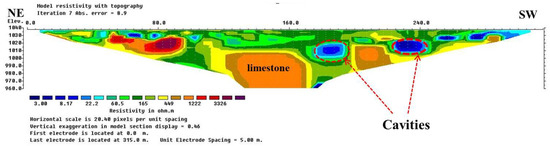
Figure 19.
Resistivity model section for ERT profile P4 representing the variation of electrical resistivity values obtained following the inversion of the apparent resistivity values for seven iterations with absolute error of 8.9. This profile was acquired in the northwest of the second sinkhole identified, at 185 m from the first electrode. Vertical anomaly analysis shows that the sinkhole is developed in carbonate rocks and reaches deep into fractured limestone. In addition, two small cavities were identified at 190 m and 240 m from the first electrode.
The resistivity model sections for the ERT profiles derived from surveying conducted around the Funnel shaped collapse sinkhole and the solution sinkhole, (Figure 15), exhibit low resistivity values, indicating that theses cavities, developed in fractured dolomitic limestone, are filled with conductive materials. These resistivity low values, shown on the Figure 16, are attributed to the clay filled in the Funnel shaped sinkhole. Furthermore, the sinkhole was observed to become deeper, and its continuity was identified in the northwest of Figure 17.
The resistivity model section of the ERT profiles obtained for the survey conducted in the northwest of sinkhole (2) indicate a number of sinkholes not observed at the surface. These sinkholes exhibit low resistivity values, indicating that they are filled with conductive materials, well developed in depth and are hosted by fractured dolomite and limestone. The results of the ERT survey (Figure 18 and Figure 19) present resistivity low values for a sinkhole well-developed bellow fractured limestone. The resistivity models were derived using cells with a width of 2.0 m (Figure 18) and 5.0 m (Figure 19). The sinkholes are denoted by the low resistivity anomaly at the 26 m and 64 m horizontal distance marks from NE to the SW for Figure 18. Other underground cavities can be identified at 185 m and 232 m horizontal distance marks from NE to the SW as seen on the Figure 19. These sections demonstrate the connectivity of the two sinkholes, with greater depths from the SE to the NW. In addition, the fractured limestone in Figure 18 is affected by a sinkhole of approximately 30 m in size that is accessible at the surface. This shows the complexity of this karst system.
4.3. SP
The analysis of the ERT measurements allows us to determine the vertical extent of subsurface sinkholes and buried cavities, while the results of the SP measurements provide their subsurface horizontal extant. SP signal measurements conducted around identified sinkholes were processed and presented on the maps of electrical potential (Figure 20 and Figure 21). Two maps were produced from the data, with areas of 756 m2 and 2760 m2. The results exhibit several anomalies, with very high SP values linked to the level of the sinkholes (more than 10 mV). These high values are a result of materials that fill the sinkhole, which are essentially composed of clays and soil erosion materials. The continuity of these anomalies reveals the subsurface extent of the sinkholes from the SE to the NW.
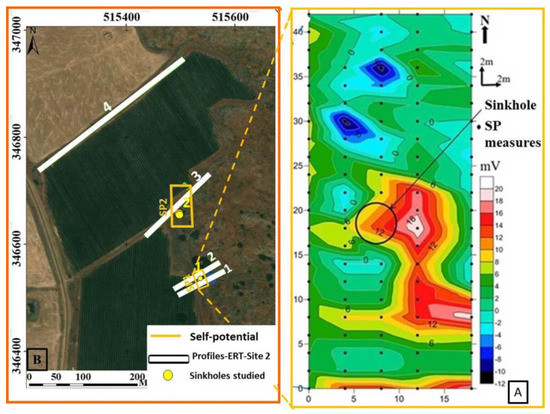
Figure 20.
Map of SP signal (A) measured around the funnel shaped collapse sinkhole (B) with high values (10 to 20 mV) indicating the horizontal extent of the sinkhole whereas the low values (6 to −12 mV) indicate the extent of the hosting rock. The black circle indicates the position of the sinkhole as observed to the ground surface.
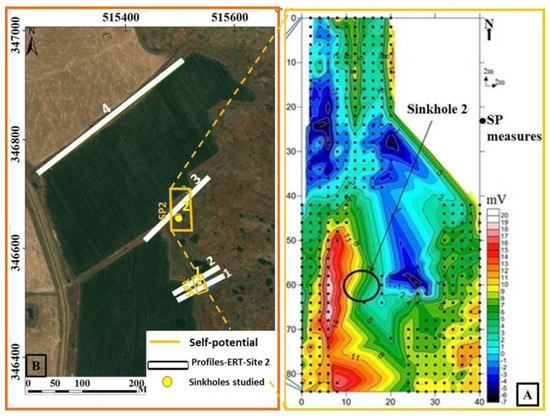
Figure 21.
Map of SP signal (A) measured around the solution sinkhole (B) with high values (10 to 20 mV) indicating the horizontal extent of the sinkhole while the low values (6 to −7 mV) indicate distribution of the hosting rock. The black circle indicates the accessible part of the sinkhole from the ground surface.
4.4. Protection Zoning of Sinkholes
In natural environments, the solubility of calcite and dolomite minerals depends on pH, which is largely controlled by carbon dioxide (CO2) partial pressure [70]. In agricultural areas, the chemicals and fertilizers used for the protection and growth of crops change the surface runoff pH, which in turns influences the solubility of these minerals. Cavities formed by the gradual dissolution of carbonate rocks may lead to the development of ground subsidence or sinkhole formations. While infrastructure damage or the loss of human live can occur during the development of sinkholes, hydrogeological hazards are more common in karst environments.
The key factors controlling karstification processes in the TMA are discussed in detail in [9,71] and include the following: lithology, geomorphological settings and adjacent aquifers, water table fluctuations (variations in the piezometric level), faults and structures affecting carbonate rocks (tectono-structures), Mediterranean climate and precipitation regimes, surface runoff and its physicochemical properties, and regional land cover and land use.
Amraoui et al. [9] and Howell et al. [10] investigated the hydrochemistry of the principle water springs located in the piedmont of TMA and identified the contribution of sinkholes (from the surface as well as from internal gradual erosion) to the turbidity of these springs.
Internal erosion and deformational processes are generally controlled by different factors [72] including water table fluctuations (variations in the piezometric level), hydraulic gradient and mechanical properties of carbonate rocks (which may control dissolution processes), subsurface karst and void networks generated by dissolution, and surface run-off and its physicochemical properties flowing in sinkholes and cavities.
Figure 22 depicts the derived protection zones to weaken the key effects controlling karstification processes in the study area, and for the eventual reduction of the impact of sinkholes on the turbidity observed on the main water sources in the Fez/Meknes region. The zones indicate areas which require protection, with anthropic activities prohibited within the zones. In particular, they indicate highly vulnerable areas surrounding the sinkholes, and their protection will minimize the effects of agricultural activity and land reclaiming for agricultural needs conducted in the Causse of El Hajeb.
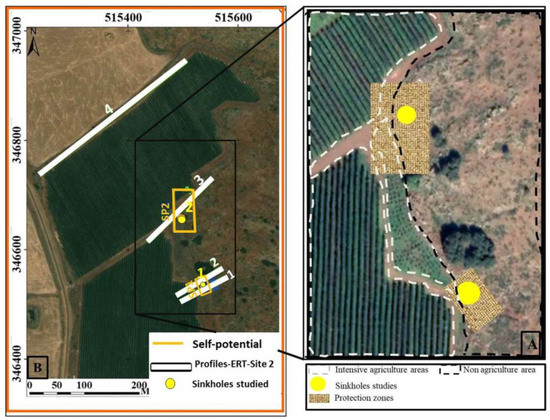
Figure 22.
Map indicating the location of geophysical measurements (SP and ERT) and the sinkholes studied (B) as well as the zoom in indicating the location of landcover (farmland and non-agriculture carbonate rocks) and the proposed protection zones (A). Note that these sinkholes are located in the contact of intensive agricultural area and carbonate rocks. The protection of these sinkholes requires the implementation of protection zone covering their whole horizontal extent.
The results obtained in the current study highlight the advantage of combining multiple methods for natural hazards studies. In particular, remote sensing imagery is able to provide surface land cover information with the exact location of different karst landforms over large areas, while ERT measurements can supply us with subsurface vertical information of sinkholes according to variations in depth. Furthermore, SP measurements complement the ERT results by providing the horizontal extent of subsurface cavities. This information can be applied to determine protection zones for the identified sinkholes.
4.5. Assessment of Measurements and Sinkhole Delineation Precisions
By taking 22.2 Ωm as the model resistivity value at the limit of sinkholes and their hosting rocks, we can determine the error propagation of the resistivity chosen for sinkhole delineation on model section of each ERT profiles. The relationship between the obtained model resistivity and the measured resistivity can be expressed as follow (Equation (14)):
While the absolute errors indicate the precision of equipment used to take the measurement, the accuracy of the results can be evaluated by examining the relative uncertainty.
The relative uncertainty is the ratio between absolute error and the value of modeled resistivity multiple by 100 (Equation (15)). The large percentage of relative uncertainty means less precision of the measured resistivity. This can be explored to evaluate the accuracy of the results for each ERT profile.
The Table 4 shows uncertainty parameters examined to determine the precision of the resistivity model section for ERT profiles and eventually its usage for the delineation of sinkhole. We noticed that for ERT profiles (P1 and P3) acquired too close to the sinkholes, absolute errors and relative uncertainty are very high. This can be explained by electrical property of materials filled in the sinkhole cavities where their variations can be affecting the precision of equipment. On the Figure 23 we can observe the resistivity values which can be mistaken during the delineation of the sinkhole for each profile. We noticed that the delineation of the sinkhole for ERT profile (P1) requires particular attention due to the highly variable resistivity between the sinkhole and the hosting rocks.

Table 4.
Precision measurement parameters estimated on the level of sinkhole.
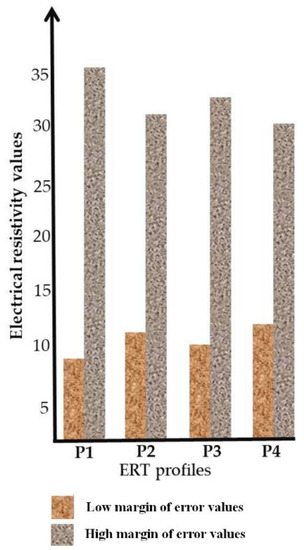
Figure 23.
Error propagation of electrical resistivity for different ERT profiles, this figure shows the margin of error (low and high resistivity values) for sinkhole delineation on resistivity model section.
5. Conclusions
The protection of sinkholes requires precise information on their location, shape, subsurface extent, and host rocks in order to determine a protection perimeter. The current study examines the potential of remote sensing and applied geophysics in mapping sinkholes and karst cavities. More specifically, Sentinel-2; ASTER-GDEM and Google Images were combined with fieldwork and GPS information to identify sinkholes in the Causse of El Hajeb. Electrical resistivity and electrical potential, acquired using ERT and SP respectively, provided subsurface extent and host rock information of the identified sinkholes. The results provide insights into the questions raised by the influence of water table fluctuations and their influence on karst aquifers. Subsurface sinkhole locations, their filling materials and host rocks suggest the presence of a complex subsurface network of karst conduits with numerous underground cavities developed in this area. This confirms the vulnerability of karst environments, where the development of sinkholes presents environmental and geo-hazards risks.
We conclude that the combination of remote sensing and applied geophysics can effectively be applied for the sinkhole risk mitigation process, where satellite images and electrical resistivity can delineate geological formations and anthropic activities for both large and small areas. In addition, precision accuracy assessment provided the degree of confidence for subsurface sinkhole delineation process. Groundwater pollution risks posed by these sinkholes should be mitigated by establishing and implementing a protection perimeter, as well as reducing anthropic activities conducted nearby. The results of this study can aid decision makers involved in water management and water protection in implementing protection zones for the studied sinkholes. In addition, future research will be conducted on the sinkholes identified on the first site and also employ corrective measures by mobilizing local population. For this we recommend measures including the reduction of groundwater withdrawal, which contributes to the decline of the water table, as well as rational agricultural practices and water usage.
Author Contributions
Methodology, A.M., M.B.; validation, M.B., H.B., G.R., A.C., G.B., S.L., A.M.; software, A.A., A.M.; Writing—original draft, A.M., S.L., G.R.; writing—review & editing, A.C., G.B., G.R., S.L., M.B., A.M.; supervision, M.B., G.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Regional Council of Fès-Meknès in the framework of calls for Research Development and Innovation projects granted in September 2016.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Fairbridge, R.W. The Encyclopaedia of Geomorphology; Reinhold Book Corporation: New York, NY, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Intrieri, E.; Gigli, G.; Nocentini, M.; Lombardi, L.; Mugnai, F.; Casagli, N. Sinkhole monitoring and early warning: An experimental and successful GB-InSAR application. Geomorphology 2015, 241, 304–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisio, S.; Caramanna, G.; Ciotoli, G. Sinkholes in Italy: First results on the inventory and analysis. Geol. Soc. Spec. Public 2007, 279, 23–45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauro, U. Dolines and sinkholes: Aspects of evolution and problems of classification. Acta Carsol. 2003, 32, 41–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzirafuti, A.; Boualoul, M.; Randazzo, G.; Lanza, S.; Allaoui, A.; El Ouardi, H.; Habibi, M.; Ouhaddach, H. The use of remote sensing for water protection in the karst environment of the Tabular Middle Atlas/the causse of El Hajeb/Morocco. In Earth Observation Advancements in a Changing World; Chirici, G., Gianinetto, M., Eds.; AIT Series, Trends in Earth Observation; Italian Society of Remote Sensing: Firenze, Italy, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Hinaje, S.; Aït Brahim, L. Les bassins lacustres du Moyen Atlas (Maroc): Exemple d’activité tectonique polyphasée associée à des structures d’effondrement. Comun. Inst. Geol. Mineiro 2002, 89, 283–294. [Google Scholar]
- Miche, H.; Saracco, G.; Mayer, A.; Qarqori, K.; Rouai, M.; Dekayir, A.; Chalikakis, K.; Emblanch, C. Hydrochemical constraints between the karst tabular Middle Atlas Causses and the Saïs basin (Morocco): Implications of groundwater circulation. J. Hydrogeol. 2018, 26, 71–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allaoui, A. Contribution des Etudes Structurales, Géophysiques et Hydrochimiques à la Compréhension des Ecoulements des Eaux Souterraines du Causse d’Agouray vers le Bassin de Saïss, (Maroc) [Contribution of Structural, Geophysical and Hydrochemical Studies to the Comprehension of Groundwater floWs from the Causse d’Agouray to the Saïss Basin, (Morocco)]. Ph.D. Thesis, Moulay Ismail University, Meknes, Morocco, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Amraoui, F.; Razack, M.; Bouchaou, L. Turbidity dynamics in karstic systems. Example of Ribaa and Bittit springs in the Middle Atlas (Morocco). Hydrol. Sci. J. 2003, 48, 971–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Howell, B.; Fryar, A.; Benaabidate, A.E.; Bouchaou, L.; Farhaoui, M. Variable responses of karst springs to recharge in the Middle Atlas region of Morocco. Hydrogeol. J. 2019, 27, 1693–1710. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esper, J.; Frank, D.C.; Büntgen, U.; Verstege, A.; Luterbacher, J.; Xoplaki, E. Long-term drought severity variations in Morocco. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, L17702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdim, B.; Amyay, M. Environmental vulnerability and agriculture in the karstic domain: Landscape indicators and cases in the Atlas Highlands, Morocco. Int. J. Speleol. 1999, 28B, 119–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aouragh, M.H.; Essahlaoui, A.; Ouali, A.E.; Hmaidi, A.E.; Kamel, S. Groundwater potential of Middle Atlas plateaus, Morocco, using fuzzy logic approach, GIS and remote sensing. Geomat. Hazards Risk 2017, 8, 194–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tennevin, M. Paysages karstiques du Moyen Atlas septentrional. Méditerranée 1978, 32, 23–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mhiyaoui, H.; Manar, A.; Remmal, T.; Boujamaaoui, M.; El Kamel, F.; Amar, M.; El Amrani, I. Deep quaternary volcanic structures in the central Middle Atlas (Morocco): Contributions of aeromagnetic mapping (structures profondes du volcanisme quaternaire du Moyen Atlas central (Maroc): Apports de la cartographie aéromagnétique. Bull. Inst. Sci. Rabat Sci. T. 2016, 38, 111–125. [Google Scholar]
- Qarqori, K.; Rouai, M.; Moreau, F.; Saracco, G.; Dauteuil, O.; Hermitte, D.; Boualoul, M.; Le Carlier de Veslud, C. Geoelectrical tomography investigating and modeling of fractures network around Bittit spring (Middle Atlas, Morocco). Int. J. Geophys. 2012, 489634, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufmann, G.; Romanov, D.; Tippelt, T.; Vienken, T.; Werban, U.; Dietrich, P.; Mai, F.; Borner, F. Mapping and modeling of collapse sinkholes in soluble rock: The Münsterdorf site, northern Germany. J. Appl. Geophys. 2018, 154, 64–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Čeru, T.; Dolenec, M.; Gosar, A. Application of ground penetrating Radar Supported by Mineralogical-Geochemical Methods for Mapping Unroofed Cave Sediments. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 639. [Google Scholar]
- Zini, L.; Calligaris, C.; Forte, E.; Petronio, L.; Zavagno, E.; Boccali, C.; Cucchi, F. A multidisciplinary approach in sinkhole analysis: The Quinis Village case study (NE-Italy). Eng. Geol. 2015, 197, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, M.; Polom, U.; Trabs, S.; Dahm, T. Sinkholes in the city of Hamburg—New urban shear-wave reflection seismic system enables high-resolution imaging of subrosion structures. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 78, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barbara, T.; Halima, A.; Abdessamad, C.; Fatima, E.B.; Mohamed, C. Remote Sensing and GIS Contribution to the Investigation of Karst Landscapes in NW-Morocco. Geosciences 2014, 4, 50–72. [Google Scholar]
- Christoph, S.; Olaf, B.; Bernhard, E. Combining digital elevation data (SRTM/ASTER), high resolution satellite imagery (Quickbird) and GIS for geomorphological mapping: A multi-component case study on Mediterranean karst in Central Crete. Geomorphology 2009, 112, 106–112. [Google Scholar]
- Kim, Y.J.; Nam, B.H.; Youn, H. Sinkhole Detection and Characterization Using LiDAR-Derived DEM with Logistic Regression. Remote Sens. 2019, 11, 1592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galve, J.P.; Castañeda, C.; Gutiérrez, F.; Herrera, G. Assessing sinkhole activity in the Ebro Valley mantled evaporite karst using advanced DInSAR. Geomorphology 2015, 229, 30–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billi, A.; Fillippis, L.; Poncia, P.P.; Sella, P.; Faccenna, C. Hidden Sinkholes and Karst cavities in Travertine plateau of the highly-populated geothermal seismic territory (Tivoli, central Italy). Geomophology 2016, 255, 63–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, A.M.; El-Kaliouby, H.M.; Zabramawi, Y.A. Integration of remote sensing and electrical resistivity methods in sinkhole investigation in Saudi Arabia. J. Appl. Geophys. 2012, 87, 28–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rizzo, E.; Giampaolo, V.; Capozzoli, L.; Grimaldi, S. Deep Electrical Resistivity Tomography for the Hydrogeological Setting of Muro Lucano Mounts Aquifer (Basilicata, Southern Italy). Geofluids 2019, 2019, 6594983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baudon, C.; Fabuel-Perez, I.; Redfern, J. Structural style and evolution of a Late Triassic rift basin in the Central High Atlas, Morocco: Controls on sediment deposition. Geol. J. 2009, 44, 677–691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Michard, A. Elément de géologie marocaine. Notes et Mém. Serv. Géol. Maroc. 1976, 252, 408. [Google Scholar]
- Laville, E.; Petit, J.P. Role of synsedimentary strike-slip faults in the formation of the Moroccan Triassic basins. Geology 1984, 12, 424–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fedan, B. Evolution géodynamique d’un basin intra-plaque sur décrochement: Le Moyen Atlas Maroc Durant le Méso-Cénozoïque. Trav. Inst. Sci. Rabat. 1989, 18, 1–142. [Google Scholar]
- Manspeizer, W.; Puffer, J.H.; Cousminer, H.L. Separation of Morocco and eastern North America: A Triassic-Liassic stratigraphic record. Geol. Soc. Am. Bull. 1978, 89, 901–920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warme, J.E. Evolution of the Jurassic High-Atlas Rift, Morocco: Transtension, Structural and Eustatic Controls on Carbonate Facies, Tectonic Inversion. Guidebook, AAPG Field Seminar, 24 September–1 October 1989. Colorado School of Mines, Golden, Colorado, Publication Number 9. 1989. Available online: http://www.worldcat.org/title/evolution-of-the-jurassic-high-atlas-rift-morocco-transtension-structural-and-eustatic-controls-on-carbonate-deposition-tectonic-inversion/oclc/20552972 (accessed on 30 June 2016).
- Wilmsen, M.; Neuweiler, F. Biosedimentology of the Early Jurassic post-extinction carbonate depositional system, central High Atlas rift basin, Morocco. Sedimentology 2008, 55, 773–807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mattauer, M.; Tapponier, P.; Proust, F. Sur les mécanismes de formation des chaines intracontinentales. L’exemple des chaines atlasiques du Maroc. Bull. Soc. Geol. Fr. 1977, 7, 521–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arboleya, M.; Teixell, L.A.; Charroud, M.; Julivert, M. A structural transect through the High and Middle Atlas of Morocco. J. Afr. Earth Sci. 2004, 39, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qarqori, K. Contribution à l’étude du Réservoir Discontinu et Karstique des Causses Moyen-Atlasiques et de sa Jonction Avec le Bassin de Saïs par Télédétection Spatiale et Imagerie Géophysique [Contribution to the study of the discontinuous and karstic reservoir of the Middle Atlasic Causses and its junction with the Saïs Basin by Remote Sensing and Geophysical Imagery]. Ph.D. Thesis, Moulay Ismail University, Meknes, Morocco, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Gomez, F.; Barazangi, M.; Bensaid, M. Active tectonism in the intracontinental Middle Atlas Mountains of Morocco: Simultaneous crustal shortening and extension. J. Geol. Soc. Lond. 1996, 153, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouya, N.; El-Ouardi, H.; Habibou, E.H. Geologic interpretation of the aeromagnetic survey in the Agourai area (Central Morocco). Centr. Europ. Geol. 2013, 56, 381–395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- El-Ouardi, H.; Boualoul, M.; Ouhaddach, H.; Habib, M.; Muzarafuti, A.; Allaoui, A.; Amine, A. Fault analysis and its relationship with karst structures affecting lower Jurassic limestone in the Agourai plateau (Middle Atlas, Morocco). Geogaceta 2018, 63, 119–122. [Google Scholar]
- Amraoui, F. Contribution à la Connaissance des Aquifères Karstiques: Cas du Lias de la Plaine du Saïs et Du Causse Moyen Atlasique Tabulaire (Maroc). [Contribution to the Knowledge of Karstic Aquifers: Case of the Lias of the Saïs Plain and the Middle Atlas Moyen Causse (Morocco)]. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Hassan II Ain Chock, Casablanca, Morocco, 2005. [Google Scholar]
- Shalev, E.; Lyakhovsky, V.; Yechieli, Y. Salt dissolution and sinkhole formation along the Dead Sea shore. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bousbih, S.; Zribi, M.; El Hajj, M.; Baghdadi, N.; Lili-Chabaane, Z.; Gao, Q.; Fanise, P. Soil Moisture and Irrigation Mapping in A Semi-Arid Region, Based on the Synergetic Use of Sentinel-1 and Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2018, 10, 1953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzia, V.; Khaliq, A.; Chiaberge, M. Improvement in Land Cover and Crop Classification based on Temporal Features Learning from Sentinel-2 Data Using Recurrent-Convolutional Neural Network (R-CNN). Appl. Sci. 2020, 10, 238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, M.D.; Baez-Villanueva, O.M.; Bui, D.D.; Nguyen, P.T.; Ribbe, L. Harmonization of Landsat and Sentinel 2 for Crop Monitoring in Drought Prone Areas: Case Studies of Ninh Thuan (Vietnam) and Bekaa (Lebanon). Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffi, A.; Stroppiana, D.; Brivio, P.A.; Bordogna, G.; Boschetti, M. Towards an automated approach to map flooded areas from Sentinel-2 MSI data and soft integration of water spectral features. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinf. 2020, 84, 101951. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pulvirenti, L.; Squicciarino, G.; Fiori, E.; Fiorucci, P.; Ferraris, L.; Negro, D.; Gollini, A.; Severino, M.; Puca, S. An Automatic Processing Chain for Near Real-Time Mapping of Burned Forest Areas Using Sentinel-2 Data. Remote Sens. 2020, 12, 674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muzirafuti, A.; Randazzo, G.; Lanza, S.; Crupi, A.; Cascio, M.; Barreca, G.; Gregorio, F. Sentinel-2 images for the monitoring of dissolved contaminants on Sicily’s South-east coast. In Proceedings of the 21th EGU General Assembly, Vienna, Austria, 7–12 April 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Van der Meer, F.D.; van der Werff, H.M.A.; van Ruitenbeek, F.J.A. Potential of ESA’s Sentinel-2 for geological applications. Remote Sens. Environ. 2014, 148, 124–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mielke, C.; Boesche, N.; Rogass, C.; Kaufmann, H.; Gauert, C.; de Wit, M. Spaceborne mine waste mineralogy monitoring in South Africa, applications for modern push-broom missions: Hyperion/OLI and EnMAP/Sentinel-2. Remote Sens. 2014, 6, 6790–6816. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Deng, C.; Chen, Z. Automated delineation of karst sinkholes from lidar-derived digital elevation models. Geomorphology 2016, 266, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doctor, D.H.; Young, J.A. An Evaluation of Automated GIS Tools for Delineating Karst Sinkholes and Closed Depressions from 1-Meter LIDAR-Derived Digital Elevation Data. In Proceedings of the 13th Multidisciplinary Conference on Sinkholes and the Engineering and Environmental Impacts of Karst, Carlsbad, NM, USA, 1 May–15 August 2013; pp. 449–458. [Google Scholar]
- Boualla, O.; Mehdi, K.; Zourarah, B. Collapse dolines susceptibility mapping in Doukkala Abda (Western Morocco) by using GIS matrix method (GMM) Model. Earth Syst. Environ. 2016, 2, 1–18. [Google Scholar]
- Ivanov, V.Y.; Vivoni, E.; Bras, R.L.; Entekhabi, D. Catchment hydrologic response with a fully distributed triangulated irregular network model. Water Resour. Res. 2004, 40, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardani, A.; Revil, A.; Boleve, A.; Dupont, J.P.; Barrash, W.; Malama, B. Tomography of the Darcy velocity from self-potential measurements. Geophy. Res. Lett. 2007, 34, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardani, A.; Dupont, J.P.; Revil, A. Self-potential signals associated with preferential ground water flow pathways in sinkholes. J. Geophys. Res. 2006, 111, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Tao, M.; Chen, X.; Binley, A. Evaluation of electrical resistivity tomography (ERT) for mapping the soil–rock interface in karstic environments. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 439–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Q.; Chen, X.; Tao, M.; Binley, A. Characterization of karst structures using quasi-3D electrical resistivity tomography. Environ. Earth Sci. 2019, 78, 285–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jardani, A.; Revil, A.; Santos, F.; Fauchard, C.; Dupont, J.P. Detection of preferential infiltration pathways using joint inversion of self-potential and EM-34 conductivity data. Geoph. Prospect. 2007, 55, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, W.; Beck, B.F.; Adam, A.L. Effective electrode array in mapping karst hazards in electrical resistivity tomography. Environ. Geol. 2002, 42, 922–928. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loke, M.H. Tutorial: 2D and 3D Electrical Imaging Surveys; University of Alberta: Edmonton, AB, Canada, 2004; Available online: https://sites.ualberta.ca/~unsworth/UA-classes/223/loke_course_notes.pdf (accessed on 1 January 2020).
- Jardani, A.; Revil, A.; Dupont, J.P. 3D self-potential tomography applied to the determination of cavities. Geophys. Res. Lett. 2006, 33, L13401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boleve, A.; Revil, A.; Janod, F.; Mattiuzzo, J.L.; Jardani, A. Forward modeling and validation of a new formulation to compute self-potential signals associated with ground water flow. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 11, 1661–1671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ikard, S.; Pease, E. Preferential groundwater seepage in karst terrane inferred from geoelectric measurements. Near Surf. Geophs. 2019, 17, 43–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revil, A.; Linde, N.; Cerepi, A.; Jougnot, D.; Matthai, S.; Finsterle, S. Electrokinetic coupling in unsaturated porous media. J. Colloid Interface Sci. 2007, 313, 315–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Boleve, A.; Revil, A.; Janod, F.; Mattiuzzo, J.L.; Jardani, A. A new formulation to compute self-potential signals associated with ground water flow. Hydrol. Earth Syst. Sci. 2007, 4, 1429–1463. [Google Scholar]
- Loke, M.H.; Chambers, J.E.; Rucker, D.F.; Kuras, O.; Wilkinson, P.B. Recent developments in the direct-current geoelectrical imaging method. J. Appl. Geophys. 2013, 95, 135–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- deGroot-Hedlin, C.; Constable, S. Occam’s inversion to generate smooth, two dimensional models form magnetotelluric data. Geophysics 1990, 55, 1613–1624. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Telford, W.M.; Geldart, L.P.; Sheriff, R.E. Applied Geophysics. Chapter 5 Electrical Properties of Rocks and Minerals; Cambridge University Press Retrieval: Cambridge, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Gutiérrez, F.; Cooper, A.H.; Johnson, K.S. Identification, prediction and mitigation of sinkhole hazards in evaporite karst areas. Environ. Geol. 2008, 53, 1007–1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martin, J. Le Moyen Atlas Central. Etude Géomorphologique. [The Central Middle Atlas. Geomorphological Study]. Ph.D. Thesis, Université Paris Diderot - Paris 7, Paris, France, 1976. [Google Scholar]
- Waltham, T.; Bell, F.; Culshaw, M. Sinkholes and Subsidence; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2005; p. 382. [Google Scholar]
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).