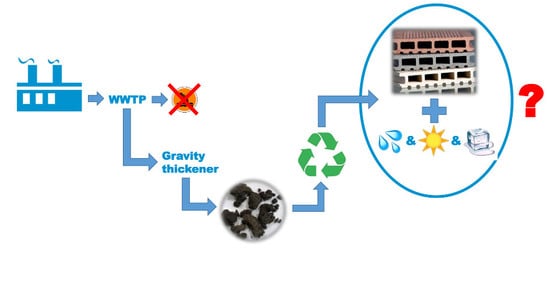
The Impact of Primary Sludge on the Physical Features of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Composites
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Work Methods
2.2.1. Moisture Properties
2.2.2. Impact Test After Freeze-Thawing Cycles
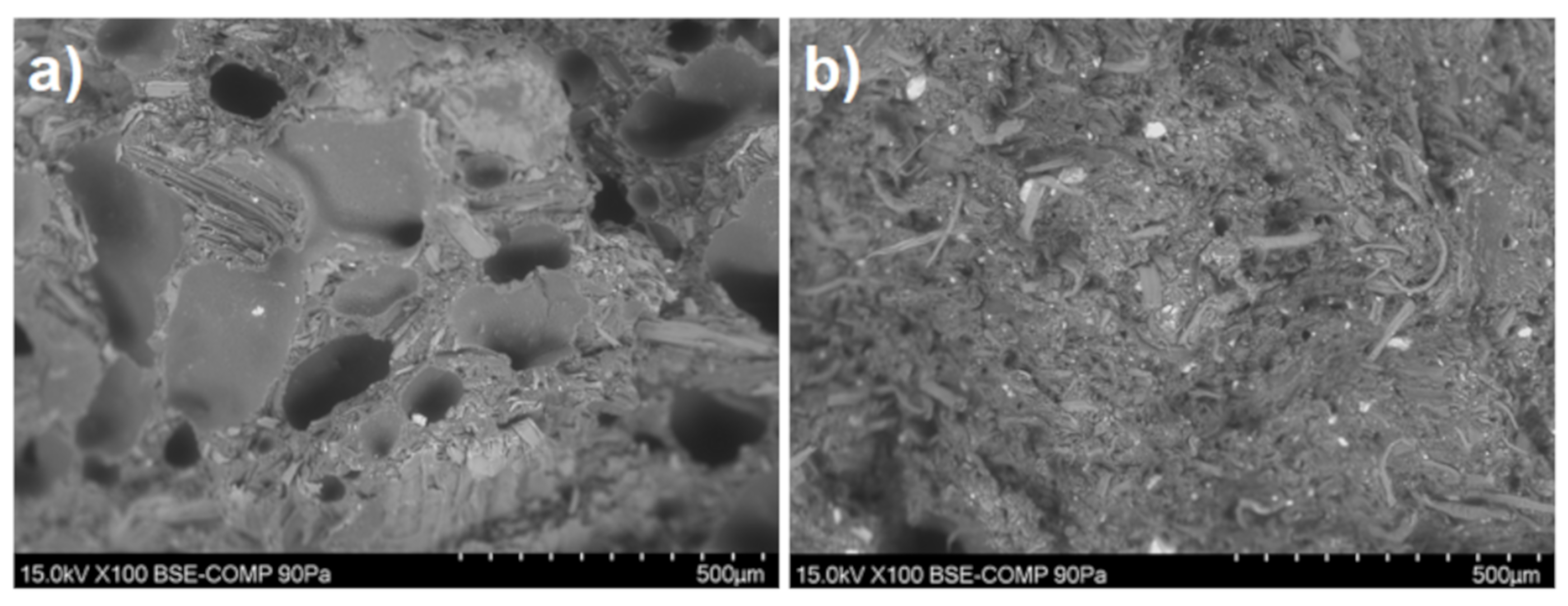
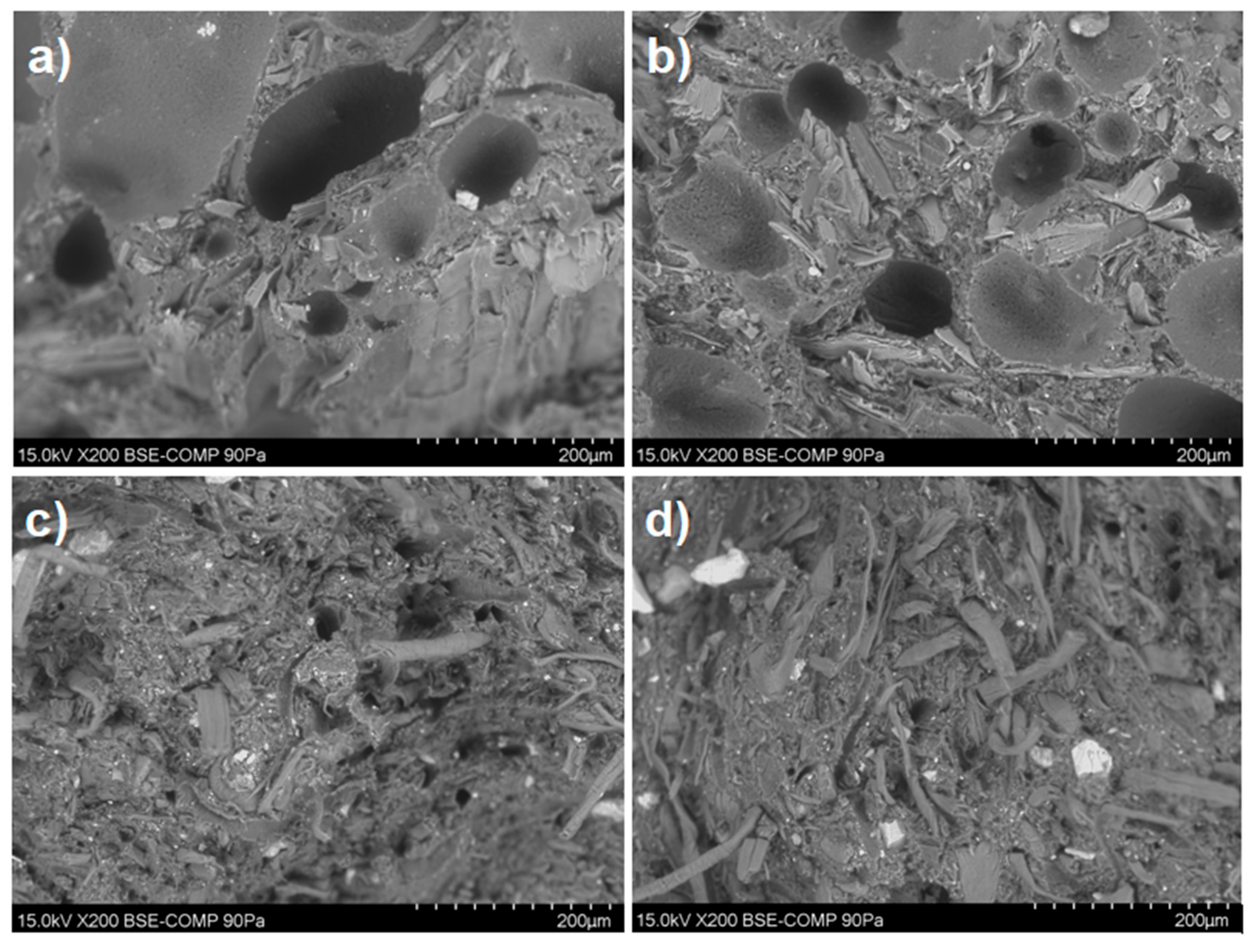
2.2.3. SEM Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Material Characterization
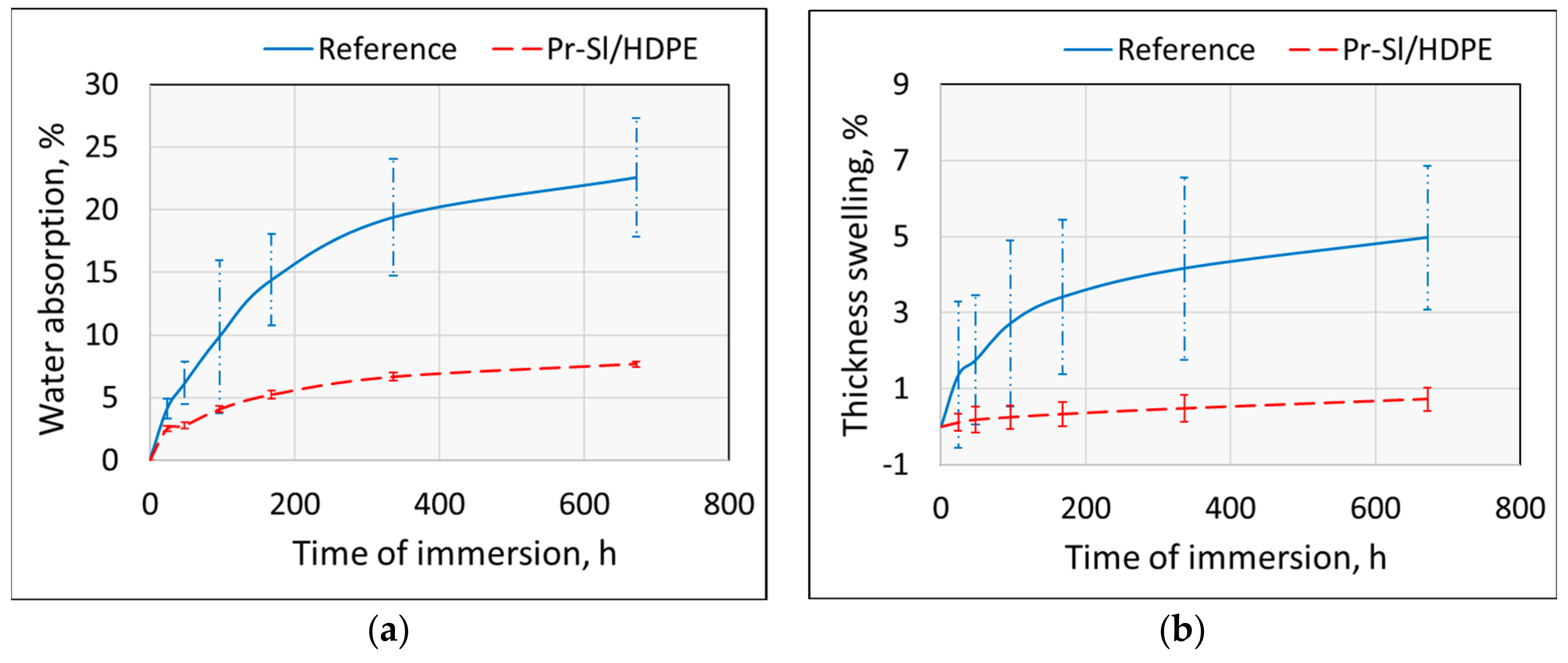
3.2. Moisture Properties
3.3. Freeze-Thawing Durability of Materials
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Cabrera, M.N. Pulp Mill Wastewater: Characteristics and Treatment. In Biological Wastewater Treatment and Resources Recovery; Farooq, R., Ed.; IntechOpen: London, UK, 2017; Chapter 7; pp. 119–139. [Google Scholar]
- Thompson, G.; Swain, J.; Kay, M.; Forster, C.F. The treatment of pulp and paper mill effluent: A review. Bioresour. Technol. 2001, 77, 275–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zodi, S.; Louvet, J.-N.; Michon, C.; Potier, O.; Pons, M.-N.; Lapicque, F.; Leclerc, J.-P. Electrocoagulation as tertiary treatment for paper mill wastewater: Removal of non-biodegradable organic pollution and arsenic. Sep. Purif. Technol. 2011, 81, 62–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younas, T.; Bano, N.; Zafar, W.; Qadir, U. Wastewater Treatment Method Selection for Pulp and Paper Industry. In Proceedings of the 2018 Interntional Conference on Frontiers of Information Technology (FIT), Islamabad, Pakistan, 17–19 December 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Stoica, A.; Sandberg, M.; Holbe, O. Energy use and recovery strategies within wastewater treatment and sludge handling at pulp and paper mills. Bioresour. Technol. 2009, 100, 3497–3505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmood, T.; Elliott, A. A review of secondary sludge reduction technologies for the pulp and paper industry. Water Res. 2006, 40, 2093–2112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Directive 2008/98/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council. Available online: https://www.compostnetwork.info/wordpress/wp-content/uploads/CELEX_02008L0098-20180705_EN_TXT.pdf (accessed on 10 August 2019).
- Bajpai, P. Options for utilization of waste. In Management of Pulp and Paper Mill Waste, 1st ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2015; pp. 79–180. [Google Scholar]
- Modolo, R.; Ferreira, V.M.; Machado, L.M.; Rodrigues, M.; Coelho, I. Construction materials as a waste management solution for cellulose sludge. Waste Manag. 2011, 31, 370–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soucy, J.; Koubaa, A.; Migneault, S.; Riedl, B. Chemical composition and surface properties of paper mill sludge and their impact on high density polyethylene (HDPE) composites. J. Wood Chem. Technol. 2015, 36, 77–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malaiskiene, J.; Kizinievic, O.; Kizinievic, V.; Boris, R. The impact of primary sludge from paper industry on the properties of hardened cement paste and mortar. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 172, 553–561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Demir, I.; Baspinar, M.S.; Orhan, M. Utilization of kraft pulp production residues in clay brick production. Build. Environ. 2005, 40, 1533–1537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mari, E.L.; Moran, S.R.; Austria, C.O. Paper mill sludge as fiber additive for asphalt road pavement. Philipp. J. Sci. 2009, 138, 29–36. [Google Scholar]
- Hýsek, Š.; Podlena, M.; Bartsch, H.; Wenderdel, C.; Böhm, M. Effect of wheat husk surface pre-treatment on the properties of husk-based composite materials. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2018, 125, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klyosov, A.A. Wood-Plastic Composites, 1st ed.; John Wiley Sons Inc: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Soucy, J.; Koubaa, A.; Migneault, S.; Riedl, B. The potential of paper mill sludge for wood-plastic composites. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2014, 54, 248–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahtela, V.; Mustonen, K.; Kärki, T. The effect of primary sludge on the mechanical perfromance of high-density polyethylene composites. Ind. Crop. Prod. 2017, 104, 129–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- European Standard. Composites Made from Cellulose-Based Materials and Thermoplastic (Usually Called Wood-Polymer Composites (WPC) or Natural Fibre Composites (NFC)). Part 1: Test Methods for Characterisation of Compounds and Products; EN 15534-1:2014 + A1:2017; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- European Standard. Particleboards and Fibreboards. Determination of Swelling in Thickness after Immersion in Water; EN 317:1993; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 1993. [Google Scholar]
- European Committee for Standardization. Plastic. Determination of Charpy Impact Properties. Part 1: Non-Instrumented Impact Test; EN ISO 179-1:2010; European Committee for Standardization: Brussels, Belgium, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Martikka, O.; Kärki, T. Promoting recycling of mixed waste polymers in wood-polymer composites using compatibilizers. Recycling 2019, 4, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butylina, S.; Martikka, O.; Kärki, T. Properties of wood fibre-polypropylene composites: Effect of wood fibre source. Appl. Compos. Mater. 2011, 18, 101–111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huuhilo, T.; Martikka, O.; Butylina, S.; Kärki, T. Impact of mineral fillers to the moisture resistance of wood-plastic composites. Baltic For. 2010, 16, 126–131. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.; Stark, N.M.; Tshabalala, M.A.; Gao, J.; Fan, Y. Properties of wood-plastic composites (WPCs) reinforced with extracted and delignified wood flour. Holzforchung 2014, 68, 933–940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyvärinen, M.; Ronkanen, M.; Kärki, T. The effect of the use of construction and demolition waste on the mechanical and moisture properties of a wood-plastic composite. Compos. Struct. 2019, 210, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hosseinaei, O.; Wang, S.; Enayati, A.A.; Rials, T.G. Effects of hemicellulose extraction on properties of wood flour and wood-plastic composites. Compos. Part A 2012, 43, 686–694. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khonsari, A.; Taghiyari, H.R.; Karimi, A.; Tajvidi, M. Study on the effects of wood flour geometry on physical and mechanical properties of wood-plastic composites. Maderas Cienc. Tecnol. 2015, 17, 545–558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cerbu, C.; Cosereanu, C. Moisture effects on the mechanical behavior of fir wood flour/glass reinforced epoxy composite. BioResources 2016, 11, 8364–8385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migneault, S.; Koubaa, A.; Erchiqui, F.; Chaala, A.; Englund, K.; Krause, C.; Wolcott, M. Effect of fiber length on processing and properties of extruded wood-fiber/HDPE composites. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2008, 110, 1085–1092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamzeh, Y.; Ashori, A.; Mirzaei, B. Effects of waste paper sludge on the physico-mechanical properties of high density polyethylene/wood flour composite. J. Polym. Environ. 2011, 19, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Stark, N.M.; Tshabalala, M.A.; Gao, J.; Fan, Y. Weathering charasteristics of wood plastic composites reinforced with extracted or delignified wood flour. Materials 2016, 9, 610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, X.; Wang, W.; Huang, H. Resistance of paper mill sludge/wood fiber/high-density polyethylene composites to water immersion and thermotreatment. J. Appl. Polym. Sci. 2015, 132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Composite | HDPE | WF | Pr-Sl | MAPE | Lubricant |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Reference | 50 | 44 | - | 3 | 3 |
| Pr-Sl/HDPE | 50 | - | 44 | 3 | 3 |
| Element | Avg. (wt %) 1 | Sd 2 |
|---|---|---|
| Sodium (Na) | 0.47 | 0.39 |
| Magnesium (Mg) | 1.40 | 0.82 |
| Aluminium (Al) | 1.98 | 1.07 |
| Silicon (Si) | 3.95 | 2.38 |
| Chlorine (Cl) | 0.09 | 0.12 |
| Potassium (K) | 0.05 | 0.07 |
| Calcium (Ca) | 5.92 | 8.37 |
| Iron (Fe) | 0.35 | 0.49 |
| Zinc (Zn) | 0.06 | 0.09 |
| Molybdenum (Mo) | 1.03 | 1.46 |
| Reference Before Cycles | Reference After 3 Cycles | Pr-Sl/HDPE Before Cycles | Pr-Sl/HDPE After 3 Cycles | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact Strength (kJ/m2) | 4.25 | 3.09 | 6.37 | 6.91 |
| Standard deviation | ±0.51 | ±0.36 | ±0.66 | ±0.81 |
© 2019 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Mustonen, K.; Lahtela, V.; Kärki, T. The Impact of Primary Sludge on the Physical Features of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Composites. Resources 2019, 8, 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources8040184
Mustonen K, Lahtela V, Kärki T. The Impact of Primary Sludge on the Physical Features of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Composites. Resources. 2019; 8(4):184. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources8040184
Chicago/Turabian StyleMustonen, Kati, Ville Lahtela, and Timo Kärki. 2019. "The Impact of Primary Sludge on the Physical Features of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Composites" Resources 8, no. 4: 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources8040184
APA StyleMustonen, K., Lahtela, V., & Kärki, T. (2019). The Impact of Primary Sludge on the Physical Features of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) Composites. Resources, 8(4), 184. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources8040184