Abstract
The high sedimentation rate of Rawapening Lake is both an environmental challenge and a potential resource. Seedlings currently rely on single-use plastic polybags, which contribute significantly to plastic waste. The use of mineral soil as a growing medium can accelerate natural resource depletion. This study aims to evaluate the feasibility and sustainability of utilizing lake sediment as an alternative seedling media through soil block technology. An integrated Life Cycle Assessment was conducted to quantify the environmental impacts, and Multidimensional Scaling was applied to assess sustainability across environmental, technological, economic, social, and institutional dimensions. Field data from ten seedling producers using soil blocks and ten using polybags were analyzed. The results showed that soil block media reduced Global Warming Potential by 48% compared to polybags, increased phosphorus and organic matter content, and was more financially efficient, with an increase in productivity of 90.24% and a revenue cost ratio of 24.56%. Sustainability analysis classified the innovation as moderately sustainable, with the highest scores in the environmental and technological dimensions. Institutional support was identified as a limiting factor. These findings suggest that sediment-based soil block media are a viable, lower-impact alternative for seedling production, although scaling up will require policy and institutional support.
1. Introduction
The rapid sedimentation of Rawapening Lake, located in Central Java, Indonesia, has become a critical environmental concern, threatening the lake’s ecological stability and reducing its functional capacity [1]. This sedimentation is largely driven by watershed erosion and compounded by the decay of invasive water hyacinths, which release peat and organic matter into the lake [2,3,4]. The accumulation of sediments not only degrades aquatic ecosystems but also hampers the lake’s economic and ecological services, including fisheries, tourism, and agricultural water supply [5]. Simultaneously, agricultural nursery practices in Indonesia remain heavily reliant on plastic polybags and mineral soils, contributing to over 500,000 kg of plastic waste annually and exacerbating land degradation through excessive soil extraction [6,7]. These dual environmental issues, lake sedimentation and unsustainable nursery practices, highlight the urgent need for innovative, circular, and sustainable solutions in agriculture [8].
Reducing Global Warming Potential (GWP) is a growing concern in agricultural sustainability, especially in nursery systems where plastic containers and peat-based media are major contributors to greenhouse gas emissions. Recent Life Cycle Assessment (LCA) studies have demonstrated that replacing plastic pots and conventional substrates with composted or sediment-based media can reduce CO2-equivalent emissions by up to 23% [9,10]. Biochar and sediment-based soil blocks have also been shown to improve water retention and soil health while lowering greenhouse gas (GHG) footprints in nurseries [11]. These findings emphasize the need to evaluate sustainable alternatives using robust environmental indicators such as GWP.
Previous studies have explored the utilization of organic waste and alternative growing media in soilless agriculture and seedling production, with soil block technology gaining traction in Western countries since the 1970s [12,13]. Soil blocks, composed of compressed organic materials such as cocopeat, manure, and compost, have shown advantages in improving seedling quality, root development, and transplant success [14,15]. In tropical regions, the use of invasive water hyacinth and lake sediments has also been considered as agricultural inputs due to their high nutrient content and soil-enhancing properties [4,16].
Lake sediments, especially those from eutrophic tropical lakes, are often rich in macronutrients such as phosphorus (P) and nitrogen (N), as well as organic matter that can improve soil structure and nutrient availability. For example, field studies using lake sediments in Estonia reported P concentrations of up to 75 g/m3 more than three times that of surrounding soils and improved plant biomass [17]. Similarly, experiments in Poland and China found that sediment amendments enhanced plant growth and nutrient uptake, although careful management is needed to mitigate potential risks such as nutrient leaching or heavy metal accumulation [18,19,20]. When combined with stabilizing agents such as biochar, sediment-based media can provide both agronomic benefits and environmental safety [21].
However, most of these efforts have focused narrowly on technical or environmental aspects without a comprehensive evaluation of the long-term feasibility, economic viability, and social acceptance of such technologies, particularly in developing countries like Indonesia [22,23]. Despite these advancements, there remains a significant gap in the literature regarding the holistic evaluation of soil block technology, particularly those utilizing lake sediments as the primary growing media. Prior studies have not adequately assessed the environmental trade-offs, socio-economic benefits, or institutional challenges associated with the adoption of soil blocks in real agricultural systems [24,25]. Furthermore, the integration of comprehensive tools such as LCA for quantifying environmental impacts and Multidimensional Scaling (MDS) for evaluating sustainability across multiple dimensions has yet to be applied in this context [26,27].
This study addresses these research gaps by investigating the multidimensional feasibility of using Rawapening Lake sediment as a core component of soil block seedling media. Specifically, it aims to (1) assess the environmental, technological, and economic performance of soil block media in comparison with conventional polybag-based systems using LCA; and (2) evaluate the sustainability of the soil block media across five dimensions environmental, technological, economic, social, and institutional using MDS [28,29]. The novelty of this research lies in its integrated methodological approach and its focus on utilizing locally sourced agricultural and aquatic waste materials as part of a circular economy model for sustainable nursery practices [30,31].
The findings of this study are expected to provide empirical evidence supporting the reuse of lake sediments as a sustainable innovation in seedling media production. This approach contributes not only to environmental impact reduction through lower greenhouse gas emissions and plastic waste reduction but also to enhanced agricultural input efficiency and improved circular resource management [32,33]. In doing so, this research informs future agricultural policy, patent development, and institutional strategies necessary to scale up soil block technology within Indonesia and in other regions facing similar environmental and agricultural challenges [34,35].
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Description of Study Area
The research locations, including the Wonosobo and Magelang Regencies in Central Java, Indonesia, were selected purposively. These areas were chosen because of the established seedling businesses employing the soil block method with Rawapening Lake sediment media. In the Wonosobo Regency, a soil block maker was utilized, whereas in the Magelang Regency, the soil block was manually produced.
The raw materials for the soil block formulation in Wonosobo were a combination of Rawapening Lake sediment, cocopeat, poultry manure, agricultural lime, and natural phosphate. The raw materials used to formulate the Magelang soil block were a combination of topsoil, Rawapening Lake sediment, and poultry manure. The raw materials used for soil block at research sites, namely Rawapening Lake sediment, cocopeat, and poultry manure, had different chemical characteristics (Table 1).

Table 1.
Chemical characteristics of Rawapening Lake sediment, cocopeat, and poultry manure.
Rawapening Lake sediment is derived from the in situ decay of invasive water hyacinths and the accumulation of organic matter. As a result, it contains elevated levels of organic carbon, nitrogen, phosphorus, and humic substances, which act as slow-release nutrient pools that are favorable for plant growth [36,37]. When blended with cocopeat, a lignocellulosic material with high porosity and water-holding capacity, the mixture creates a physically optimal environment that facilitates root expansion and aeration [38]. Poultry manure provides a source of rapidly mineralizable nutrients, especially N and P, and introduces beneficial microbial consortia that accelerate organic matter decomposition and nutrient mineralization [39,40]. This combination enhances the physical, chemical, and biological properties of seedling substrates. Sediment supplies baseline macro- and micronutrients with buffering capacity, cocopeat improves moisture retention and structural stability, and poultry manure boosts nutrient turnover via microbial stimulation. The synergy among these components leads to increased cation exchange capacity (CEC), sustained nutrient availability, and enhanced seedling vigor, which collectively explain why this mixture outperforms conventional mineral soil plus fertilizer combinations, which often lack a balanced structure or consistent nutrient release [6,40].
The research samples were strategically chosen through purposive sampling, comprising ten seedling producers who utilized soil blocks and ten conventional seedling producers. Additional respondents included Rawapening Lake sediment media providers, practitioners, researchers, and policymakers who underwent in-depth interviews. In-depth interviews with respondents were conducted in October and November 2023 to collect primary data. The interview tool was a structured questionnaire containing questions that assessed respondents’ evaluations of attributes across various sustainability dimensions, including environmental, technological, economic, social, and institutional.
2.2. Life Cycle Inventory
As outlined in the preceding section, sediment from Rawapening Lake has the potential to be used as a seedling media. Its utilization is combined with several other components such as biomass waste, cocopeat and livestock waste as sources of nutrients for plant growth. To evaluate the environmental benefits of using soil blocks compared to traditional polybags, LCA was conducted. LCA is a widely known method for evaluating the environmental impact of a product and the processes involved in making the product [26,41]. This methodology offers a clear and transparent framework for calculating the flow of materials and energy, as well as the environmental impacts associated with each stage of a product’s life cycle. In this study, LCA will be applied to assess the environmental impacts of producing soil blocks made from Rawapening sediment. The analysis will cover the entire life cycle of the process, including stages such as sediment collection, until they are ready to be moved to the field. Specifically, the cradle-to-gate approach will be used. The aim is to identify the GWP of the production of soil blocks and polybag seedling media that are ready to be used in the nursery of one-piece soil blocks as a reference. The boundary is the production process of soil blocks and polybag seedling media to produce planting media used for one-piece soil blocks.
2.3. Variable Selection for Multidimensional Analysis
A total of 34 attributes from all dimensions in the MDS analysis were selected through a two-stage process: first, a comprehensive literature review was conducted to compile a list of potential sustainability indicators; second, validation with in-depth interviews and discussion with key local stakeholders was carried out to ensure contextual relevance at the research site (Table 2). Each attribute was assessed using four ordinal categories: 0 = Bad, 1 = Less, 2 = Fairly, and 3 = Good. All attributes were treated with equal weight, in accordance with the standard Rapfish, which emphasizes exploration leverage factor identification. To validate the robustness of the MDS results and reduce the risk of subjectivity of attribute selection, a Monte Carlo simulation and stress test were applied.

Table 2.
Variable dimensions and attributes of multidimensional analysis.
2.4. Analytical Methods
The performance analysis aimed to assess the advantages of soil block technology for seedling media composed of Rawapening Lake sediment. The performance is based on three advantages: (i) soil block technology suppressing GWP (environmental), (ii) the nutrient content of soil block seedling media (technological), and (iii) the economic feasibility of soil block seedling media (economic).
The environmental performance of soil blocks as seedling media was obtained by LCA comparing the production processes of polybags. OpenLCA 2.02 software was used for the analysis along with the Ecoinvent 3.8 database (Swiss Centre for Life Cycle Inventories, 2018). The life cycle inventory (LCI), which contains comprehensive inventory data for various processes, including those related to agriculture and waste management, will be applied to this database. Life Cycle Impact Assessment (LCIA) was conducted using the Centrum voor Milieukunde Leiden (CIML) midpoints impact method to obtain the GWP of the two-seedling media.
The technological performance of the nutrient content of seedling media was assessed by comparing seedling media produced in Wonosobo (using soil block equipment) and Magelang (manually). The nutrient content of seedling media was analyzed in a soil laboratory at the Agricultural Faculty of Muhammadiyah Yogyakarta University, including pH, organic carbon, organic matter (OM), total nitrogen (N), total and available phosphorus (P), and total and available potassium (K).
The economic performance of business feasibility to assess business efficiency was evaluated by financial analysis in a life cycle production process of polybag seedling media compared to that of soil blocks. Financial feasibility analysis shows the feasibility of a farm by using input–output or production facilities as well as its labor requirements, as conducted by Krisdiana et al. [42] using basic measurements such as production costs, labor wages, income, profit, revenue to cost ratio (R/C), and marginal benefit cost ratio (MBCR). Higher R/C values reflect the efficiency of resource and production input use [43]. MBCR > 1 indicates that the implementation of new technology increases efficiency because it generates a higher profit value than the value of the costs sacrificed [42].
Data on production capacity and unit cost per tray were collected from primary sources through structured field observations and interviews with seedling producers in Wonosobo between October and November 2023. The production capacity for both the soil block and polybag systems was calculated based on actual work performance during a standard 7 h workday. Cost components were compiled from documented input–output records and further verified through semi-structured interviews with the same seedling producers.
Sustainability was analyzed using MDS. MDS is a method for representing the measurement of similarity or proximity between objects, which can be individuals, attributes, regions, countries, products, and others, and is visualized as a two-dimensional graph [44]. The analysis in this study was carried out using the “Rapid Appraisal Technique for Fisheries” (RAPFISH) version 3.1, adapted to the RAPsoilblock ordinance technique. Adaptations were made to refine and align the attributes within each sustainability dimension to suit the research context and scope of this study [27]. MDS computations were based on the Euclidean distance matrix technique, as prescribed by Mancell and Deutsch [28]:
Notes:
= Euclidean distances.
X,Y,Z = Attributes.
1, 2 = Observation.
RAPFISH applied the Alternating Least Squares Scaling (ALSCAL) algorithm for iterative processes aimed at obtaining the smallest error value, thereby setting the intercept to zero (a = 0):
d12 = bD12 + e
The iterative process halts when the stress value falls below 0.25; therefore, the model is considered viable if the stress level is under 0.25:
The results of the sustainability index analysis are categorized into four levels: unsustainable (0.00–25.00), less sustainable (>25.01–50.00), moderately sustainable (>50.01–75.00), and highly sustainable (>75.01–100.00) [29]. The attribute leverage evaluation was utilized to determine the most sensitive attributes concerning sustainability. Attributes with higher values contributed significantly to sustainability by affecting the “Root Mean Square” (RMS) changes along the X-axis. The greater the RMS change, the more sensitive the indicator’s role in enhancing sustainability status [45]. According to Darwis et al. [46], the “Stress and Squared Correlation” (RSQ) or R2 values indicated the level of precision in the analysis or the “goodness of fit”. A model was considered good if the stress value < 0.25 (approaching 0). “The stress and coefficient of determination” (R2) values indicate the quality of the generated model (goodness of fit). An R2 value is considered good if it is close to one. Monte Carlo simulation was used in MDS to assess robustness under data variability and validate that the dimensional structure is not due to random chance. With a 95% confidence interval, the simulation showed minimal differences Δ < 5% between MDS original and Monte Carlo simulated sustainability indices, indicating that the MDS configuration is stable and the results are statistically reliable.
3. Results and Discussion
3.1. Performance of Soil Block Technology for Seedling Media
3.1.1. Life Cycle Analysis of Soil Block Technology Suppressing Global Warming Potential
The inventory data of the seedling media used for the single seed was obtained in accordance with the field observations (Table 3). The life cycle inventory analysis of the two-seedling media (polybag and soil block) revealed notable differences in terms of material composition, energy consumption, and resource utilization, each reflecting a distinct environmental footprint. The units presented in Table 3 refer to either mass (gram) or volume (cm3 and liter), indicating the amount of each material used per single seedling. The polybag media, with a volume of 30 cm3, is characterized by a high reliance on synthetic substances and fossil-derived inputs. It incorporates diesel fuel, synthetic fertilizer SP-36, and plastic polybags, highlighting its dependence on nonrenewable resources. Additionally, it contains a lower proportion of organic materials, including manure and lake sediment, than the soil block.

Table 3.
Life Cycle Assessment inventory of seedling media for single-seed applications.
Conversely, the soil block media prioritizes the use of natural and biodegradable components. It uses a smaller amount of unleaded petrol for energy input and entirely omits synthetic fertilizers. Instead, the media consists of cocopeat, dolomite, and rock phosphate, along with a greater quantity of lake sediment, reinforcing its environmentally sustainable design. Water usage is minimal, and the exclusion of plastic materials further supports waste minimization.
Furthermore, the soil block media requires fewer chemical plant protection substances and utilizes smaller quantities of pesticides and insecticides than the polybag media. Although both media incorporated organic manure, the soil block contained a smaller amount, potentially compensated for by nutrient contributions from sediment and mineral additives.
In this study, GWP was selected as the primary indicator for environmental impact assessment because GWP is one of the most widely applied impact categories in the LCA approach [47], particularly because of its relevance to global climate change, which remains a central focus of international agreements such as the Paris Agreement and national sustainability agendas [48]. And, GWP is a requirement for assessing the company’s performance rating in environmental management carried out by the Indonesian Ministry of Environment and Forestry. Based on the life cycle inventory, the GWP of soil blocks and polybag seedling media production was calculated (Figure 1).
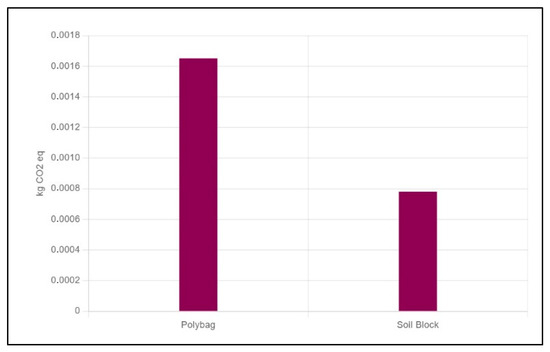
Figure 1.
Comparison of Global Warming Potential between soil blocks and polybag media used for single-seed applications.
The figure shows that the production of polybag seedling media has a higher GWP value than that of soil block media. This is primarily due to the inclusion of plastics, which have a high carbon footprint and contribute substantially to GHG emissions. According to Haase et al. [6], polybags, typically made of High-Density Polyethylene (HDPE) plastic, generate large amounts of waste and have major environmental impacts, especially because they are designed for single uses [7]. Furthermore, the use of polybags (especially the commonly used black plastic types in nurseries) can lead to substantial fluctuations in soil surface temperature. Young and Hammett [49] reported that the use of polybags increases soil temperature up to 49–50 °C due to their high heat absorption and low reflectivity when exposed to direct sunlight. Therefore, additional inorganic fertilizers are required in the planting media [50]. Replacing polybags with alternatives like soil blocks could not only reduce plastic waste but also create a more thermally stable environment for healthy seedling growth.
In contrast, soil block media has emerged as a more sustainable alternative owing to its use of renewable and biodegradable inputs, absence of plastic packaging, and lower dependence on agrochemicals. These results align well with the goals of sustainable agricultural practices, which aim to reduce waste, conserve resources, and minimize environmental harm. The results of this LCA indicate that soil blocks made with locally sourced and biodegradable materials offer a significantly lower environmental impact, contributing to more sustainable farming practices.
The results of LCA calculations related to GHG emissions from the use of soil blocks present promising opportunities for sustainable development. Sediment is often considered as waste and the transition to sediment-based seedling media aims to reduce GHG emissions, with a range of GHG emission reductions of 48% when compared to polybags. In addition, soil blocks contain essential nutrients and organic matter that can improve soil structure and fertility, thus supporting strong plant growth while reducing the need for chemical fertilizers that contribute to GHG emissions [51]. The use of fertilizers is an important aspect because it shows the potential of soil block sediment as a resource that can contribute to reducing the depletion of natural resources by substituting chemical fertilizers. Thus, sedimentation seedling media is a multifaceted strategy that can contribute significantly to reducing the environmental footprint of agriculture while encouraging resilience to climate change.
Greenhouse gas emissions play a significant role in influencing soil erosion and biodiversity dynamics. The mechanisms by which GHG emissions influence soil erosion and biodiversity are related to the physical properties of the soil and its biological activity. Climate change, exacerbated by increased GHG emissions, leads to changes in precipitation patterns, soil moisture, and temperature, all of which can accelerate soil erosion [52]. Soil biodiversity is highly dependent on stable conditions, as GHG emissions cause climate disruptions, resulting in the decline of soil organisms vital to soil health and function [53]. Changes in GHG levels can alter nutrient cycling and the decomposition of organic matter, which sustain soil microorganisms, thereby impacting broader biodiversity within the ecosystem [54].
To further explore the environmental impacts of soil blocks as seedling media, future studies should expand the LCA scope to include additional impact categories beyond GWP, such as acidification, eutrophication, water consumption, and biodiversity loss. This would allow for a more comprehensive and detailed evaluation of the environmental trade-offs associated with soil block production and the reuse of lake sediments as seedling media.
3.1.2. Potential Nutrient-Rich Content of Soil Block Seedling Media Based on Rawapening Lake Sediment
The media analysis revealed that the Wonosobo and Magelang soil block seedling media formulation contained higher levels of essential nutrients across all parameters, including pH, organic carbon, organic matter, total and available phosphorus, and total and available potassium, than mineral soil media (Table 4).

Table 4.
Chemical characteristics of seedling media of Rawapening Lake sediment.
The term mineral soil media in this study refers to naturally occurring soil materials composed primarily of inorganic mineral particles such as volcanic, alluvial, or entisol soils that are commonly used in horticultural nurseries in Central Java. These soils are rich in sand, silt, and clay minerals but contain low levels of organic matter. They are typically sourced through topsoil extraction in agricultural or riverine areas and widely applied as conventional substrates in seedling production [55,56]. In this experiment, mineral soil was obtained from a local horticultural nursery supplier in Wonosobo Regency, which routinely collects topsoil from nearby agricultural areas for commercial seedling propagation. The soil was air-dried, sieved (2 mm), and mixed with organic fertilizer (chicken manure) according to common local nursery practices [57]. This soil served as the control treatment to compare with the sediment-based soil block formulations.
Among the three-seedling media, Wonosobo seedling media with a mixture of Rawapening Lake sediment, cocopeat, and chicken manure had a higher chemical content than Magelang soil blocks or mineral soil media. Sediments in the form of peat have good chemical characteristics such as seedling media because of the high content of organic matter and other elements good for seed growth, and they have physical characteristics that are light but able to bind high amounts of water [15,58]. According to the research results of Gowthami et al. [59], cocopeat is a commonly used media seedling raw material because of its chemical content that is suitable for seed growth, namely, its higher levels of total N, total P, total K, and organic carbon compared to soil media. Organic manure plays an important role in seedling media because it contains high levels of organic C and other chemicals that are important for seed growth [15].
In addition, the use of biomass waste reduces dependence on mineral soils, which can have a negative impact on the environment when used in large quantities. This approach supports sustainable agriculture by recycling waste materials and reducing the need for new soil extractions. The use of sediment–organic waste mixtures can improve soil properties, such as CEC and pH balance, which are essential for optimal plant growth. These mixtures also have a minimal risk of metal mobility, making them safe for agricultural use [58]. Utilization of residual biomass can lead to a more environmentally friendly agricultural system [60].
This shows that seedling media containing a mixture of biomass wastes were of better quality than media with mineral soil as the main component (Table 5). The superior characteristics of the seedling media composed of Rawapening Lake sediment show that, technologically, the right mixture of biomass waste can be a promising seedling media technology for the seedling industry, which is more profitable for environmentally friendly agricultural activities.

Table 5.
The economic feasibility of soil block seedling media.
3.1.3. The Economic Feasibility of Soil Block Seedling Media Business Based on Rawapening Lake Sediment
The implementation of soil block technology in the production of seedling media has been shown to enhance labor productivity by 90.24% (Table 5). This substantial increase in production capacity is attributable to improved resource utilization, whereby identical time inputs yield significantly higher output volumes. These findings are consistent with those of Goswami and Daultani [61], who emphasize that operational efficiency and strategic application of appropriate technologies are critical pathways for optimizing production capacity. Furthermore, the present study demonstrates that the adoption of soil block molding technology can lead to a 90.24% increase in revenue and a 92.74% increase in producer profitability, underscoring its potential as an effective tool for enhancing the economic performance of seedling production systems.
The production of seedling media using soil block technology reduced the production cost by IDR 3589, representing a 24.67% increase in cost efficiency. This cost efficiency is primarily driven by the optimization of labor wages, which contributes 60.78% to the overall reduction. Production efficiency in enterprises is influenced by many factors, with labor wage optimization being the most dominant [62]. Soil block seedling media is also more feasible, as indicated by a higher R/C of 2.28 compared to 1.72 for polybag media. Although both methods are financially viable, the soil block method is 24.56% more cost-efficient than the polybag method [43]. The soil block seedling business also exhibits a MBCR of 1.36, meaning that for every additional IDR 1 invested due to the adoption of the technology, an additional return of IDR 1.36 is generated. The implementation of soil block technology increases costs by IDR 782,402 but simultaneously raises revenue by IDR 1,151,198, resulting in a net benefit of IDR 285,196. Several studies have reported MBCR values greater than 1, indicating enhanced efficiency and financial feasibility of the production process [63,64].
Soil block technology offers significant economic and productivity advantages for vegetable seedling production. Its application can increase output from 8 to 82 trays per worker per day (7 h), over ten times higher than plastic polybags. Production costs per tray are reduced by 24.7%, from IDR 14,550 to IDR 10,961. On a 10,000-hectare scale, this translates to a 19.29% cost saving and a 43.94% increase in net profit, highlighting its potential for sustainable, large-scale adoption.
Importantly, soil block seedlings are sold at similar prices to those grown in polybags, meaning no additional cost burden for farmers. Therefore, the key to wider adoption lies in farmer training and outreach on the benefits of this technology [65].
A major challenge is ensuring sustainable access to raw materials such as sediment and cocopeat. This requires investment in processing equipment by growing media enterprises and access to soil block machinery for farmers. Institutional support through subsidies, partnerships, or cooperative-based procurement is essential to enable collective and long-term adoption.
Performance analysis confirmed that the soil block seedling media outperformed polybag-based media across environmental, technological, and economic dimensions. However, despite its development since 2017, the downstream adoption of soil block technology is yet to replace polybag systems. The current analysis remains partial in scope; thus, further investigation of other influencing dimensions, including social and institutional factors is required to comprehensively understand the adoption barriers. A multidimensional analysis is crucial for holistically assessing sustainability and identifying the key factors that drive performance across all five dimensions.
3.2. Sustainability of Soil Block Seedling Media Business: A Multidimensional Approach
3.2.1. Sustainability and Validity Models
The results of the sustainability index indicate that the environmental, technological, economic, and social dimensions are considered ‘moderately sustainable’, whereas the institutional dimension remains in the ‘less sustainable’ category. Among these dimensions, the environmental dimension exhibits the highest index value at 73.22, whereas the institutional dimension ranks the lowest at 36.96 (Table 6). The sustainability level of the seedling media soil block based on the Rawapening Lake sediment falls within the “moderately sustainable” category (59.70).

Table 6.
Sustainability assessment scores by dimension.
The MDS configuration produced a stress value ranging from 0.15 to 0.16 (stress < 0.25) and an R2 value between 0.94 and 0.95 (close to 1), indicating a good model fit with high reliability in representing the multidimensional sustainability attributes and accurately reflecting the input data. Monte Carlo simulation was used to test the robustness of the MDS results. The differences between original and Monte Carlo simulated sustainability indices were all below the Δ < 5% threshold, ranging from 0.10 to 0.52. This indicates that the MDS configuration is generally stable and reliable under data variation. Slightly higher deviations in the social and institutional dimensions suggest greater variability in perception, but overall, the results confirm the consistency and validity of the dimensional structure.
The technology employed in this study prioritizes environmentally friendly practices that utilize waste materials from local sources, initially of low economic value, and transforms them into higher-value products. The utilization of Rawapening Lake sediment waste from erosion, cocopeat from coconut waste, and organic fertilizer from animal manure waste, as well as the minimization of plastic polybag and mineral soil usage, highlight why the environmental dimension in this study exhibited the highest sustainability index compared to other dimensions. Over the past few decades, many industries have recognized the critical importance of the environmental dimension in sustainability. As a result, they have incorporated ‘key environmental value drivers’ in their business strategies, thereby enhancing product value at the consumer level [66].
3.2.2. Environmental Dimension
In the leverage evaluation of the six attributes comprising the environmental dimension, three attributes stand out as particularly sensitive, namely, the potential of agricultural biomass waste utilization, a reduction in pollution from plastic polybags, and a decrease in mineral soil or mineral soil exploitation, with respective RMS values of 5.73, 4.62, and 4.44 (Figure 2).
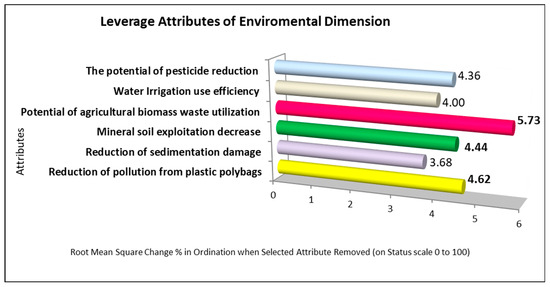
Figure 2.
Leverage analysis of environmental dimension attributes.
Environmental sustainability in this study was supported by the utilization of locally available agricultural biomass waste. The soil block formulation consists of Rawapening Lake sediment, cocopeat, and poultry manure materials abundant near the study site. Converting this biomass into soil blocks not only reduces the environmental impact but also adds economic value by producing high-quality seedling media. Rawapening Lake generates substantial sediment annually, as stated by Nugroho [67].
Hristov et al. [66] report 501,628.6 tons and Sadewo et al. [68] report 2350.44 tons from the sub-watershed alone. This abundant sediment supply offers significant potential as a raw material for soil blocks, supporting both environmental management and sustainable resource utilization in the lake area. Rawapening Lake sediment has been shown to improve soil attributes, influence microbial activities, enhance plant growth, and positively affect the nutrition of vegetable plants [69]. Sediments have a richer nutrient content and a different particle composition than regular soil (Table 2), making sediment usage more advantageous [13].
The reduction in pollution from plastic polybags is the second most significant factor impacting the sustainability of the environment. Roeswitawati et al. [70] mentioned that organic media made from water hyacinth and coconut fiber, combined with goat manure, produced the best results, as evidenced by plant height, leaf count, flower count, and fruit count parameters. The substantial use of container-less seedling media can also effectively decrease polybag usage [71], provide a more sustainable and environmentally friendly planting alternative [72], promote better seedling growth, and offer more environmentally friendly benefits [73].
The third most influential factor impacting the sustainability of the environmental dimension was the reduction in mineral soil exploitation. The utilization of sediment waste in soil block media provides a sustainable solution for reducing the environmental damage caused by mineral soil excavation [74,75]. Utilizing lake sediment as a substitute for mineral soil in soil block production offers a sustainable alternative that enhances soil fertility, moisture retention, and porosity, potentially improving crop productivity [76,77]. Additionally, the use of sediment, cocopeat, and organic fertilizer can create sustainable mineral soil-free soil block media [78], reduce heavy metal contamination, and support environmentally friendly farming practices [58]. Excessive mineral soil use, particularly with agrochemicals, tillage, and improper machinery, leads to erosion, nutrient loss, and declining soil organic carbon, ultimately reducing soil health and yield [79,80].
The use of soil blocks offers a sustainable alternative to plastic polybags, as supported by both MDS (RMS = 4.62) and LCA results, which show a substantial reduction in GWP due to minimized plastic production and waste. The results from the MDS analysis were aligned with the findings from the LCA results. LCA clearly indicates that the use of Rawapening Lake sediment in soil block production significantly reduces GWP compared to conventional seedling media, and this supports the high sensitivity observed in the MDS analysis for factors such as biomass waste utilization, plastic polybag pollution reduction, and mineral soil exploitation reduction. The LCA results further highlight that soil blocks contribute to environmental sustainability by avoiding the use of plastics and reducing dependency on synthetic fertilizers. This alignment confirms that both MDS and LCA emphasize the importance of utilizing local resources and minimizing environmental harm to enhance the sustainability of agricultural practices.
3.2.3. Technological Dimension
In the leverage evaluation of the eight attributes comprising the technological dimension, three attributes stand out as sensitive to the sustainability of nursery businesses—time and cost savings, increasing growing media production capacity, and ease of formulation and preparation—with RMS values of 2.69, 1.51, and 1.28, respectively (Figure 3). The soil block method for seedling media stands out as the most critical attribute in the technological dimension, offering significant time and cost efficiency. Time and cost savings are among the most important attributes of sustainability in a business, as they directly affect efficiency and the price of seeds per unit. Cheaper seed prices increase product competitiveness, making them easier to market.
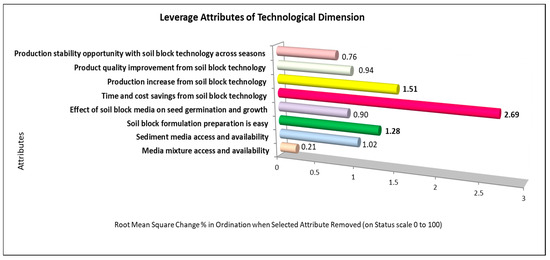
Figure 3.
Leverage analysis of technological dimension attributes.
One of the key characteristics of the technical dimension is the ease with which the soil block seedling media can be prepared. This quality is strongly tied to two other essential attributes: the first is that using soil block technology saves time and money, and the second is that it increases the production of seedling media. These characteristics are closely associated and help achieve moderately sustainable values in sustainability analysis. From the results of in-depth interviews with seedling media business actors, it is known that the production process of soil block media is simpler because it only requires two stages: first, mixing raw materials according to the composition, and second, making soil blocks using a soil block maker, producing 91 blocks in one process, with the results being directly arranged in wooden trays. Meanwhile, the production method of seedling media with plastic polybags goes through three stages: first mixing the raw materials and then putting the media mixture into plastic polybags one by one, followed by arranging the plastic media one by one into wooden trays. Therefore, soil block technology for seedling media saves time and labor and increases production because, in the same amount of time, more soil block media is produced compared to polybag seedling media.
As an illustration, using a soil block maker, one worker can produce 8800 seedling media, whereas conventional plastic methods can only yield 4200 seedling media per day (eight working hours). Using a soil block maker increases the technical performance by 109% compared to conventional methods. This demonstrates that technology can save time and labor. The use of a soil block maker also enhances economic performance. The production cost per unit of seedling media using the sediment-based Rawapening soil block method was 50% more efficient than conventional methods. Research by Haase et al. [6] indicated that nursery management with soilless technology and using insulated containers without polybags is more efficient in terms of time use when compared to the nursery process using plastic polybags.
Another benefit of soil block technology is its nutritional value. Soil blocks have excellent nutrient content to support seed growth during seeding and after transplanting to the fields. Comparative analysis showed that soil blocks without mineral soil contained higher macronutrient levels without additional inorganic fertilizers, unlike mineral soil-based media, which require nutrient supplementation (Table 5). According to Grossnickle and MacDonald [81], seedlings grown in media with optimal nutrient reserves can enhance shoot growth after transplanting. Seedling growth is a crucial factor influencing crop production [82], and the increased production of some crops is generally followed by increased farmer income [83]. According to Fuentes-Peñailillo et al. [84], healthy seedling growth supports plant growth and development in the subsequent field phase, thus enabling plants to achieve maximum production. As Gruda [85] stated, soilless seedling technology can improve water use efficiency because peat sediment has high water retention capabilities. Moreover, Rawapening Lake sediment is a readily available natural waste that must be removed from the lake to prevent worsening sedimentation [86]. Based on the explanations above, seedling media preparation becomes a sensitive attribute as it is easier to perform than conventional seedling methods using polybags, and this ease leads to practices that consider environmental conservation. This research technology is compatible with the recommendations of the Food and Agriculture Organization (FAO) [35], where the concept of sustainable development must manage and conserve natural resources (the use of Rawapening Lake sediments) and orient more efficient technological changes (from conventional technology to the use of soil block technology) to meet sustainable human needs for current and future generations. The depletion of natural resources and environmental degradation must be reversed towards the discovery of new and renewable resource reserves accompanied by environmental quality improvement. Therefore, soil block technology can be one of the future technological solutions because it is environmentally friendly, utilizing biomass waste to produce high-value products.
3.2.4. Economic Dimension
In the leverage evaluation of the six attributes comprising the economic dimension, three attributes stand out as sensitive to sustainability price of seedling media, income increase opportunities, and input production access with RMS values of 1.88, 1.18, and 0.87, respectively (Figure 4). The price of the seedling media is the most sensitive factor affecting sustainability in the economic dimension. Product pricing is crucial because it affects consumer purchasing behavior; the cheaper a product, the more units will be sold [87]. The price of soil block seedling media in the research location is competitive because it has the same price as that of polybag media (IDR 25,000). At the same price level, the product quality of the soil block media was better. From the producer’s perspective, soil block media seedling production is faster and more efficient [6], meaning that in the same period of time, soil block media production produces more quantity with fewer resources (cost, labor, time, and raw materials).
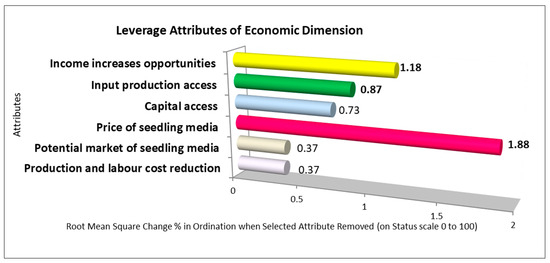
Figure 4.
Leverage analysis of economic dimension attributes.
The second sensitive attribute that affects economic sustainability is the potential opportunity for increased income. The production speed and resource efficiency of soil block seedling media were directly proportional to the potential for increased income, as evidenced by the fact that the income of soil block seedling media producers increased by 90.24% compared to polybag media (Table 6). In addition, soil block seedling media can increase production capacity because they can be produced in large quantities in a shorter time. As Mutunga and Owino [22] stated, increasing production capacity has a positive impact on increasing income.
The third crucial factor affecting economic sustainability is the accessibility of production inputs or raw materials. The ease with which business actors can access raw materials (such as organic fertilizer, Rawapening Lake sediment, cocopeat, dolomite, natural phosphate, and labor) has a positive effect on increasing production [88,89] and supports the sustainability of a business. As Hulopi et al. [89] showed, supporting activities in the upstream agribusiness subsystem has a significant effect on increasing production. In addition, all raw materials as production inputs are domestic and environmentally friendly, utilizing waste such as Rawapening sedimentary peat, cocopeat, and organic fertilizer. Economically, the utilization of domestic raw materials can improve business performance and maintain sustainable growth [90].
3.2.5. Social Dimension
Of the eight variables examined, the two most sensitive to sustainability were enhanced female participation (RMS = 3.72) and the chance to strengthen community resilience (RMS = 2.86) (Figure 5). Women’s participation is vital because they are careful, thorough, and capable of multitasking in nursery settings. Furthermore, flexible working hours enable women to fulfill their domestic responsibilities while contributing financially [91]. This aligns with the principle of gender equality and has been shown to boost productivity [92].
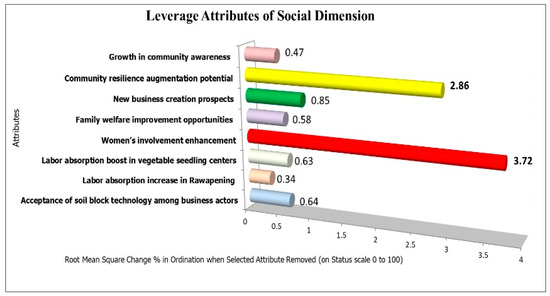
Figure 5.
Leverage analysis of social dimension attributes.
Opportunities for community resilience can be realized by empowering women, developing social networks, and enhancing social inclusion. Individual and family well-being improves when women have greater access to resources and participate in decision-making [93]. On the other hand, robust social networks and collaboration among farmers, seed producers, academics, and other stakeholders will foster solidarity and creativity in the development of nursery businesses [94]. This strategy allows vulnerable groups such as smallholder farmers and the impoverished to participate actively, thus contributing to the reduction in social inequities at the local level.
Other attributes, such as labor absorption and increased community awareness, show low leverage values, which need to be improved through participatory education and outreach so that the social impact of this innovation can be more widespread. It is also important to complement the role of women’s empowerment and strengthen social networks so that all elements of society, including vulnerable groups, can be actively involved in the nursery business and share benefits more evenly.
3.2.6. Institutional Dimension
The leverage analysis within the institutional dimension identified three key attributes critical for the sustainability of soil block nursery businesses: government support (RMS 3.82), private sector support (RMS 3.56), and the presence of marketing institution support (RMS 2.51) (Figure 6). Government support is expected to focus on providing production facilities, marketing assistance, and capacity building through training programs. However, current support remains inconsistent and limited, as highlighted by Komalawati et al. [34], who emphasized the government’s crucial role in ensuring business sustainability through regulations, funding, and promotion. Similarly, private sector support, such as corporate collaborations and Corporate Social Responsibility (CSR) initiatives, has been underutilized, while nursery associations continue to prioritize traditional plastic or polybag packaging. Marketing poses a major challenge due to farmers’ limited awareness of the quality advantages of soil block media seedlings.
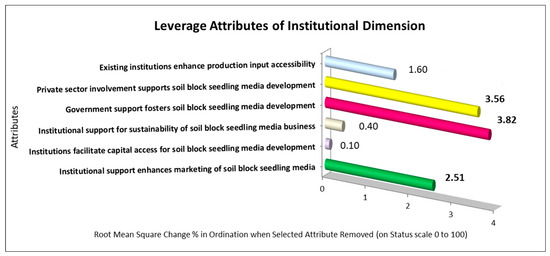
Figure 6.
Leverage analysis of institutional dimension attributes.
To ensure effective and sustainable support, a dedicated institution is needed to coordinate the development of soil block seedling media businesses. This institution can manage capital, provide production inputs, and facilitate marketing knowledge and training for business operators [95,96]. Currently, the lack of a specialized institution has led to fragmented government and private sector support, which hinders businesses’ sustainability. Therefore, this study underscores the necessity of establishing a dedicated institution supported by stakeholder commitment, the government, and the private sector to address coordination gaps and enhance the growth of soil block nursery businesses.
4. Conclusions and Recommendations
This study assessed the feasibility and sustainability of soil block seedling media utilizing Rawapening Lake sediment through integrated LCA and MDS. The soil block system demonstrated a 48% reduction in GWP, improved nutrient content, and higher economic efficiency compared to conventional polybag media.
The RAPsoilblock method, a practical analytical tool for assessing the sustainability of soil blocks as agricultural seedling media, indicates that the environmental dimension holds the highest sustainability index, classified as moderately sustainable. This is followed by the technological, economic, and social dimensions, which also fall within the same sustainability category, reflecting a relatively balanced performance across these aspects. In contrast, the institutional dimension recorded the lowest index, placing it in the less sustainable category. The institutional dimension was identified as the weakest link, indicating limited policy and structural support for broader adoption. These findings highlight the need for institutional strengthening, market development, and social empowerment, particularly enhancing community involvement and women’s participation, to ensure long-term sustainability.
Future research should consider scalability by analyzing long-term sediment supply logistics, capital support mechanisms for farmers, and the potential of cooperative models to facilitate shared use of soil block machines. This study is limited by its geographic scope and sample size and lacks a long-term impact assessment. Future research should broaden the analysis, include temporal dynamics, and engage policy stakeholders to facilitate scaling-up and commercialization of this environmentally friendly innovation.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, M.D.P., C.C., A.S.R., A.K.P., K.K., F.I., F.D.A., J.T., W.W., I.N.D., H.B., S.G., R.R., V.D., M.S. and R.H.P.; methodology, M.D.P., C.C., A.S.R., S.M., A.K.P., K.K., F.I., F.D.A., J.T., W.W., I.N.D., H.B., S.S., B.N., S.G., R.R., V.D., M.S. and R.H.P.; software, C.C., A.S.R., A.K.P., K.K., F.I., I.N.D. and H.B.; validation, M.D.P., C.C., S.M., A.K.P., K.K., F.I., J.T., W.W., H.B., S.S., B.N., A.A.W., S.G., R.R., V.D., M.S. and R.H.P.; formal analysis, M.D.P., C.C., A.S.R., A.K.P., F.I., J.T., I.N.D., H.B., S.S., B.N., A.A.W., S.G., R.R., V.D., M.S. and R.H.P.; data curation, M.D.P., C.C., A.S.R., S.M., K.K., F.D.A., J.T., W.W., S.S., B.N., A.A.W. and S.G.; investigation, M.D.P., C.C., A.S.R.,S.M., K.K., F.D.A., J.T., W.W., S.S. and B.N.; resources, M.D.P., S.M., F.D.A., W.W., I.N.D., H.B., S.S., B.N., A.A.W., R.R., V.D., M.S. and R.H.P.; writing—original draft preparation, M.D.P., C.C., A.S.R., A.K.P., K.K., F.I., F.D.A., J.T., W.W., I.N.D., H.B., S.S., B.N., S.G., R.R., V.D., M.S. and R.H.P.; writing—review and editing, M.D.P., C.C., A.S.R., S.M., A.K.P., K.K., F.I., F.D.A., J.T., W.W., I.N.D., H.B., B.N., A.A.W., S.G., R.R., V.D., M.S. and R.H.P.; visualization, C.C., A.S.R., A.K.P., K.K., F.I., J.T., I.N.D., H.B., S.S., A.A.W., S.G., R.R., V.D., M.S. and R.H.P.; supervision, M.D.P., S.M., A.K.P., F.I., F.D.A., W.W., S.S., B.N. and A.A.W.; project administration, M.D.P., A.S.R., S.M., K.K., F.D.A. and A.A.W.; funding acquisition, M.D.P., C.C., S.M., F.D.A., J.T., I.N.D., A.A.W., S.G. and R.R., V.D., M.S. and R.H.P.; All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the Education Fund Management Institution (LPDP) in collaboration with the National Research and Innovation Agency (BRIN), through a competition scheme on Innovation Research for Advanced Indonesia (RIIM) batch 3 for 2023–2024, with contract numbers B-839/II.7.5/FR.06/5/2023 and B-1066/III.3/FR.06/5/2023.
Institutional Review Board Statement
This protocol was approved by the Ethical Committee of Social Studies and Humanities, National Research and Innovation Agency (Project ID: 07052023000069) on 16 May 2023.
Data Availability Statement
Data will be made available by the corresponding authors upon request.
Acknowledgments
The authors thank the National Research and Innovation Agency of Indonesia for the RIIM program funding and Eka Mardiono, a nursery businesses soil block media owner in Wonosobo Regency, who developed the soil block method based on Rawapening Lake Sediment media.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- Piranti, A.S. Pengendalian Eutrofikasi Danau Rawapening; UNSOED Press: Purwokerto, Indonesia, 2021; p. 72. ISBN 978-623-7144-34-2. [Google Scholar]
- Chapungu, L.; Mudyazhezha, O.C.; Mudzengi, B. Socio-ecological impacts of water hyacinth (Eichhornia crassipes) under dry climatic conditions: The case of Shagashe River in Masvingo, Zimbabwe. J. Environ. Sci. Public Health 2018, 2, 36–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Djihouessi, M.B.; Olokotum, M.; Chabi, L.C.; Mouftaou, F.; Aina, M.P. Paradigm shifts for sustainable management of water hyacinth in tropical ecosystems: A review and overview of current challenges. Environ. Chall. 2023, 11, 100705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gunnarsson, C.C.; Petersen, C.M. Water hyacinths as a resource in agriculture and energy production: A literature review. Waste Manag. 2007, 27, 117–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Güereña, D.; Neufeldt, H.; Berazneva, J.; Duby, S. Water hyacinth control in Lake Victoria: Transforming an ecological catastrophe into economic, social, and environmental benefits. Sustain. Prod. Consum. 2015, 3, 59–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haase, D.I.; Bouzza, K.; Emerton, L.; Friday, J.B.; Lieberg, B.; Aldrete, A.; Davis, A.S. The high cost of the low-cost polybag system: A review of nursery seedling production systems. Land 2021, 10, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stafford, W.; Russo, V.; Nahman, A. A comparative cradle-to-grave life cycle assessment of single-use plastic shopping bags and various alternatives available in South Africa. Int. J. Life Cycle Assess. 2022, 27, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Novita, A.A.; Ngindana, R.; Putra, E.; Virgiyansha, D. Development and challenges in the implementation of sustainable development goals (SDGs) in Indonesia: A systematic literature review. J. Inov. Ilmu Sos. Dan Polit. JISoP 2023, 5, 189–196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kasper, G.; Kapp, G.; Seidel, C. Greenhouse gas emissions in horticulture: Potentials for reduction using alternative substrates. Acta Hortic. 2019, 1242, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gheewala, S.H.; Beri, N.P.; Maliwan, N. Environmental performance of soilless cultivation using organic substrates: A comparative LCA of growing media. J. Clean. Prod. 2023, 403, 136872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, X.; Zhou, G.; Zhang, H.; Zhang, S. Biochar-based growing media reduce N2O and CH4 emissions in nursery production. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 722, 137896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danso, H.; Martinson, B.; Ali, M.; Mant, C. Performance characteristics of enhanced soil blocks: A quantitative review. Build. Res. Inf. 2015, 43, 253–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, A.; Nair, A.; Thoms, A. Evaluating the soil block method and growing media in organic vegetable transplant production. HortScience 2024, 59, 542–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Cao, H.; Yuan, Q.; Luoa, S.; Liu, Z. Component optimization of dairy manure vermicompost, straw and peat in seedling compressed substrates using simplex-centroid design. J. Air Waste Manag. Assoc. 2018, 68, 215–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mechergui, T.; Vanderschaaf, C.L.; Pardos, M. From Waste to Plant Production: Cattle Dung Compost as an Alternative Nursery Substrate to Commercial Peat for Producing Lettuce Plants. HortScience 2024, 59, 1489–1496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, F.; Bai, N.; Chu, X.; He, Y.; Zhang, H.; Li, H. Effects of lake sediment on soil properties, crop growth, and the phod-harboring microbial community. Agriculture 2022, 12, 2065. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ge, X.; Chen, X.; Liu, M.; Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Tran, H.-T.; Joseph, S.; Zhang, T. Toward a Better Understanding of Phosphorus Nonpoint Source Pollution from Soil to Water and the Application of Amendment Materials: Research Trends. Water 2023, 15, 1531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Różyło, K.; Szymańska, M.; Kalembasa, S.; Jaremko, D. The use of lake sediment for fertilization: Effect on soil fertility and crop yield. Agronomy 2021, 11, 165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, C.; Nan, Z.; Wang, H.; Jin, P. Plant growth and heavy metal bioavailability changes in a loess subsoil amended with municipal sludge compost. J. Soils Sediments 2017, 17, 2797–2809. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, H.; Liu, Z. Effect of sediment-based growing medium with biochar on nutrient release and lettuce yield. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2023, 30, 103058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brigham, R.D.; Pelini, S.; Xu, Z.; Vázquez-Ortega, A. Assessing the effects of lake-dredged sediments on soil health: Agricultural and environmental implications for northwestern Ohio. J. Environ. Qual. 2021, 50, 494–503. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mutunga, D.; Owino, E. Effect of Production Capacity on the Financial Performance of Manufacturing Firms in Kenya. J. Econ. 2017, 1, 15–24. Available online: https://stratfordjournals.org/journals/index.php/journal-of-economics/article/view/86 (accessed on 23 February 2025).
- Unhelkar, B.; Joshi, S.; Sharma, M.; Prakashf, S.; Mani, A.K.; Prasad, M. Enhancing supply chain performance using RFID technology and decision support systems in the industry 4.0–A systematic literature review. Int. J. Inf. Manag. Data Insights 2022, 2, 100084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espolov, T.; Espolov, A.; Satanbekov, N.; Tireuov, K.; Mukash, J.; Suleimenov, Z. Economic trend in developing sustainable agriculture and organic farming. Int. J. Sustain. Dev. Plann. 2023, 18, 1885–1891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, A.; Sen, K.K.; Mochida, T.; Yoshimoto, Y.; Kishimoto, K. Overcoming barriers to proactive plastic recycling toward a sustainable future. Environ. Chall. 2024, 17, 101040. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO14040; Environmental Management-Life Cycle Assessment: Principles and Framework. International Standard Organization (ISO): Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Bai, C.; Dallasega, P.; Orzes, G.; Sarkis, J. Industry 4.0 technologies assessment: A sustainability perspective. Int. J. Prod. Econ. 2020, 229, 107776. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancell, S.A.; Deutsch, C.V. Multidimensional scaling. In Geostatistics Lessons; Deutsch, J.L., Ed.; Resource Modeling Solutions: Calgary, AB, Canada, 2019; pp. 1–10. Available online: https://geostatisticslessons.com/lessons/mds (accessed on 23 June 2025).
- Sittadewi, E.H.; Tejakusuma, I.G.; Handayani, T.; Santoso, A.D.; Tohari, A.; Mulyono, A.; Zakaria, Z.; Budiman, E.B.; Fatahillah, H.E.H.; Fitriani, R. Novel Rap-Landslide Method for Assessing Agroforestry Sustainability in Landslide-Prone Areas. Resources 2025, 14, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nin, S.; Bonetti, D.; Antonetti, M.; Peruzzi, E.; Manzi, D.; Macci, C. Sediment-based growing media provides a window opportunity for environmentally friendly production of ornamental shrubs. Agronomy 2023, 13, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levacher, D.; Suriray, A.; Ndahirwa, D.; Zmamou, H.; Leblanc, N.; Shimpo, T. Sediment-based unfired bricks reinforced with waste flax fibers: Implementation, physical aspects and kinetics of air drying-part I. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kiani, M.; Raave, H.; Simojoki, A.; Tammeorg, O.; Tammeorg, P. Recycling Lake sediment to agriculture: Effects on plant growth, nutrient availability, and leaching. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 753, 141984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çakmakçı, R.; Salık, M.A.; Çakmakçı, S. Assessment and principles of environmentally sustainable food and agriculture systems. Agriculture 2023, 13, 1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Komalawati, K.; Hidayat, S.; Praptana, R.H.; Pertiwi, M.D.; Romdon, A.S.; Hidayat, Y.; Yuniati, D.; Syahyuti, S.; Ramadhan, R.P.; Saptana, S.; et al. Indrawanto, Community-government, and private partnership (CGPP): Revisiting the concept of community-based forest management. Int. For. Rev. 2023, 25, 310–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FAO. Building a Common Vision for Sustainable Food and Agriculture; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2014; Volume 56, Available online: https://openknowledge.fao.org/handle/20.500.14283/i3940e (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Zhang, Y.; Gu, X.; Xu, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, M. Effect of dredged lake sediment as a soil amendment on nutrient supply and rice growth. J. Environ. Manag. 2020, 254, 109808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Li, S.; Wu, J.; Wu, Y. Using lake sediments to improve urban soil fertility and plant productivity. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2020, 197, 110586. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turno, M.S.; Balingbing, C.A.; Apostol, O.B.; Mendoza, R.C. Growth performance of eggplant seedlings in cocopeat-based growing media with organic additives. Int. J. Agric. Technol. 2021, 17, 1677–1688. [Google Scholar]
- Sutejo, Y.; Setiawan, M.; Nugroho, W. Enhancing soil fertility and maize yield through poultry manure and microbial bioactivator. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 1041, 012016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adekiya, A.O.; Agbede, T.M.; Ejue, W.S.; Dunsin, O. Comparative effects of organic manure and chemical fertilizer on soil properties and maize yield. Agronomy 2023, 13, 1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ISO14044; Environmental Management-Life Cycle Assessment: Requirements and Guidelines. ISO: Geneva, Switzerland, 2006.
- Krisdiana, R.; Prasetiaswati, N.; Sutrisno, I.; Rozi, F.; Harsono, A.; Mejaya, M.J. Financial feasibility and competitiveness levels of soybean varieties in rice-based cropping system of Indonesia. Sustainability 2023, 13, 8334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salamba, H.N.; Malia, I.E.; Hutapea, R.; Rawung, J.B.M.; Sondakh, J.O.; Tandi, O.G. Agronomical and financial feasibility of sweet corn intercropped under the coconut-based farming system in North Sulawesi. In Proceedings of the 4th International Conference on Agribusiness and Rural Development (IConARD 2023), E3S Web of Conferences, Yogyakarta, Indonesia, 9–10 August 2023; EDP Sciences: Les Ulis, France, 2023; p. 02012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borg, I.; Mair, P. The choice of initial configurations in multidimensional scaling: Local minima, fit, and interpretability. Austrian J. Stat. 2017, 46, 19–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dahliani, L.; Maharani, M.D.D. Palm oil sustainable management using MDS model from social dimension. In Proceedings of the 5th International Conference on Community Development (AMCA 2018), Quezon City, Philippines, 19–20 July 2018; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2018; pp. 50–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Darwis, V.; Rachmawati, R.R.; Muslim, C.; Chanifah; Sembiring, A.; Ilham, N.; Mufidah, L.; Suhartini, S.H.; Basuki, R.S.; Rina, Y.; et al. Transformation of financial institutions grants from the government to inclusive financial institutions in Indonesia. PLoS ONE 2023, 18, e0286482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smurthwaite, M.; Jiang, L.; Williams, K.S. A review of the LCA literature investigating the methods by which distinct impact categories are compared: M. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 19113–19129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guinée, J.B. Selection of impact categories and classification of LCI results to impact categories. In Life Cycle Impact Assessment; Springer: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2015; pp. 17–37. [Google Scholar]
- Young, K.; Hammett, K.R.W. Temperature patterns in exposed black polyethylene plant containers. Agric. Meteorol. 1980, 21, 165–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wijayanto, F.; Khairuddin, M.S.; Alfitra, N.Z.; Tsaqif, N.; Hanafi, F.I. The Ecofriendly Polybag: Natural Polybag, as an Alternative for Plastic Polybag Problem. J. Integr. Sains Dan Qur’an JISQu 2022, 1, 1–7. Available online: https://jisqu.trensains.sch.id/index.php/journal/article/view/31 (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- Renella, G. Recycling and reuse of sediments in agriculture: Where is the problem. Sustainability 2021, 13, 1648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aide, M.; Braden, I.; Nakasagga, S.; Svenson, S. Improving forest soil health and ecosystem services to minimize the impact of climate change. Agric. Sci. 2023, 14, 1153–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hisano, M.; Searle, E.; Chen, H. Biodiversity as a solution to mitigate climate change impacts on the functioning of forest ecosystems. Biol. Rev. 2017, 93, 439–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaureguiberry, P.; Titeux, N.; Wiemers, M.; Bowler, D.; Coscieme, L.; Golden, A.; Purvis, A. The direct drivers of recent global anthropogenic biodiversity loss. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabm9982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riyanto, D.; Dianawati, M.; Sutardi; Susanto, H.; Sasongko, N.A.; Sri Ratmini, N.P.; Rejekiningrum, P.; Yustisia; Susilawati, H.L.; Hanafi, H.; et al. The Effect of P2O5 Fertilizer, Zeolite and Volcanic Soil Media from Different Altitudes on the Soil Mineral, Growth, Yield and Asiaticoside Content of Centella asiatica L. Sustainability 2022, 14, 15394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartikawati, R.; Hanudin, E.; Purwanto, B.H. Physico-Chemical Properties of Volcanic Soils under Different Perennial Plants from Upland Area of Mt. Merapi, Indonesia. Planta Trop. 2019, 7, 93–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nitisapto, M.; Maas, A.; Purwanto, B.H.; Sudira, P. Water Use Efficiency in Vertical Cropping System with Volcanic Ash Media by Using Biochar and Urban Waste Compost Fertilizer as Soil Amendment. Ilmu Pertan. Agric. Sci. 2021, 20, 45–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szara-Bąk, M.; Baran, A.; Klimkowicz-Pawlas, A. Recycling of bottom sediment to agriculture: Effects on plant growth and soil properties. J. Soils Sediments 2023, 23, 539–551. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gowthami, K.; Vidhya, D.; Muthuvel, I.; Djanaguiraman, M.; Jagadeeswaran, R. Cocopeat: An alternative to soil medium for propagation of papaya (Carica papaya L.). Plant Sci. Today 2024, 11, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tataru-Farmus, R.E.; Zaharia, C.; Suteu, D.; Blaga, A.C. Biomass-based soil in ecological agriculture: Characteristics and wheat grains development trends. J. Appl. Life Sci. Environ. 2022, LIV, 273–288. Available online: https://repository.iuls.ro/xmlui/handle/20.500.12811/2281 (accessed on 5 May 2025). [CrossRef]
- Goswami, M.; Daultani, Y. Product quality optimization vs production capacity optimization: An analytical perspective. Int. J. Qual. Reliab. Manag. 2023, 40, 801–819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishrif, A.; Hammad, M.A. Multi-factor cost adjustment for enhanced export-oriented production capacity in manufacturing firms. Economies 2024, 12, 219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chanifah; Sahara, D.; Susila, A.; Triastono, J. Advantages of early-maturity soybean varieties as a farmer adaptation effort to climate change in Grobogan Regency. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2024, 1323, 012006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruma, K.F.; Kamruzzaman, M.; Jui, K.F.; Rahman, K.T.; Hasan, J. A comparative financial analysis of four crops based cropping patternswith existing cropping patternsin different locations of Bangladesh. Asian J. Res. Agric. For. 2023, 9, 110–123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rogers, E.M. Diffusion of Innovations, 1st ed.; Free Press: New York, NY, USA, 1962; 367p. [Google Scholar]
- Hristov, I.; Appolloni, A.; Chirico, A.; Cheng, W. The role of the environmental dimension in the performance management system: A systematic review and conceptual framework. J. Clean. Prod. 2021, 293, 126075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nugroho, N.P. Sediment export estimation from the catchment area of Lake Rawapening using InVEST model. IOP Conf. Ser. Earth Environ. Sci. 2022, 950, 012072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadewo, B.E.C.; Ni’am, M.F.; Poedjiastoeti, H. Prediksi laju sedimentasi di Sub DAS Rawapening Kabupaten Semarang. BRILIANT J. Ris. Dan Konseptual 2022, 7, 220–228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kebede, T.; Diriba, D.; Boki, A. The effect of organic solid waste compost on soil properties, growth, and yield of Swiss chard crop (Beta vulgaris L.). Sci. World J. 2023, 2023, 6175746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roeswitawati, D.; Fatonah, S.N.; Iriany, A. Study of the use of organic polybags based on water hyacinth and coconut fiber on growth and results of big red chili (Capsicum annum L.). In Proceedings of the 6th International Conference on Community Development (ICCD 2019), Bandar Seri Begawan, Brunei, 24–25 July 2019; Atlantis Press: Dordrecht, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 152–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younis, S.M.; Sheded, R.S.M.; Ali, T.H.; Ibrahim, M.M. Development of a drum seeding metering unit for sowing vegetable plug tray seedlings. Plant Arch. 2020, 20, 3119–3130. Available online: https://www.plantarchives.org/SPECIAL%20ISSUE%2020-1/204__3119-3130_.pdf (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Pudjiono, E.; Ahmad, A.M.; Subekti, R. Engineering tube casting machine of organic planting pouch. J. Teknol. Pertan. 2020, 2, 145–160. Available online: https://jtp.ub.ac.id/index.php/jtp/article/view/128/490 (accessed on 5 May 2025).
- Mwangi, W.; Kariuki, S.; Wagara, N. Substitution of plastics with organic pots in tree seedlings production for sustainable environmental conservation. E. Afr. J. Sci. Technol. Innov. 2021, 2, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferrans, L.; Schmieder, F.; Hogland, W. Dredged sediments: A new source of nutrients as a plant-growing substrate. In Proceedings of the 22th EGU General Assembly, EGU22, Vienna, Austria and Online, 23–27 May 2022; p. EGU22-13557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Z.; Li, C.; Omine, K.; Li, J.; Flemmy, S.O. Feasibility study of low-environmental-load methods for treating high-water-content Waste Dredged Clay (WDC)—A case study of WDC treatment at Kumamoto Prefecture Ohkirihata Reservoir in Japan. Sustainability 2023, 15, 8243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Han, M.; Dsouza, M.; Zhou, C.; Li, H.; Zhang, J.; Chen, C.; Yao, Q.; Zhong, C.; Zhou, H.; Gilbert, J.A.; et al. Agricultural risk factors influence microbial ecology in Honghu Lake. Genom. Proteom. Bioinform. 2018, 17, 76–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stenfert Kroese, J.; Batista, P.V.; Jacobs, S.R.; Breuer, L.; Quinton, J.N.; Rufino, M.C. Agricultural land is the main source of stream sediments after conversion of an African montane forest. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 14827. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Askarova, D.A.; Glebov, V.V.; Rodionova, O.M.; Anikina, E.V. Various approaches for reduction of heavy metal pollution of topsoil. AIP Conf. Proc. 2019, 2063, 040003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Yang, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Li, Y.; Sui, Y.; Tang, C.; Jin, J.; Liu, X. Reducing topsoil depth decreases the yield and nutrient uptake of maize and soybean grown in a glacial till. Land Degrad. Dev. 2021, 32, 2849–2860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Umeghalu, I.C.E.; Nwachukwu, C.P.; Umobi, C.O.; Uba, J.I.; Anonye, O.F. Agricultural land clearing is imperative for a successful agricultural mechanization program in Nigeria. Agrobiol. Rec. 2022, 10, 42–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grossnickle, S.C.; MacDonald, J.E. Why seedlings grow: Influence of plant attributes. New For. 2018, 49, 1–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haj Sghaier, A.; Tarnawa, Á.; Khaeim, H.; Kovács, G.P.; Gyuricza, C.; Kende, Z. The effects of temperature and water on the seed germination and seedling development of rapeseed (Brassica napus L.). Plants 2022, 11, 2819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abera, A.; Wana, D. Effects of agricultural land management practices on crop production and household income in Ojoje, Southern Ethiopia. J. Degraded Min. Lands Manag. 2024, 11, 5817–5828. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fuentes-Peñailillo, F.; Gutter, K.; Vega, R.; Silva, G.C. New generation sustainable technologies for soilless vegetable production. Horticulturae 2024, 10, 49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gruda, N.S. Increasing sustainability of growing media constituents and stand-alone substrates in soilless culture systems. Agronomy 2019, 9, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mardiatno, D.; Faridah, F.; Listyaningrum, N.; Hastari, N.R.F.; Rhosadi, I.; da Costa, A.D.S.; Rahmadana, A.D.W.; Lisan, A.R.A.K.; Sunarno, S.; Setiawan, M.A. A holistic review of lake rawapening management practices, indonesia: Pillar-based and object-based management. Water 2023, 15, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Yao, X.; Liu, Z.; Yang, Q. Impact of pricing and product information on consumer buying behavior with customer satisfaction in a mediating role. Front. Psychol. 2021, 12, 720151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pello, W.Y.; Renoat, E.; Banunaek, M.F. The effect of agricultural extension agent’s role and motivation on wet-rice cultivation technology innovation in East Kupang Sub District of Kupang Regency of East Nusa Tenggara Province. J. Penyul. 2019, 15, 184–194. Available online: https://journal.ipb.ac.id/index.php/jupe/article/view/27732/17742 (accessed on 7 May 2025).
- Hulopi, I.; Murtisari, A.; Boekoesoe, Y. Pengaruh kegiatan penunjang agribisnis terhadap produksi padi sawah di Kelurahan Dembe Jaya Kecamatan Kota Utara Kota Gorontalo. AGRINESIA J. Ilm. Agribisnis 2018, 2, 219–231. Available online: https://ejurnal.ung.ac.id/index.php/AGR/article/view/9666 (accessed on 6 May 2025).
- Nguyen, P.H.; Hsu-Hao, L.; Pham, H.A.; Thi, H.L.; Do, Q.M.; Nguyen, D.H.; Nguyen, T.H. Material sourcing characteristics andfirm performance: An empirical study in Vietnam. Mathematics 2022, 10, 1691. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Farnworth, C.R.; Galiè, A.; Gumucio, T.; Jumba, H.; Kramer, B.; Ragasa, C. Women’s seed entrepreneurship in aquaculture, maize, and poultry value chains in Ghana, Kenya, and Tanzania. Front. Sustain. Food Syst 2024, 8, 1198130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jirgi, A.J.; Oluwafemi, R.A.; Oseghale, A.I. Empirical Review of Women Participation in Some Agricultural Sub-Sectors of the Globe. J. Agripreneurship Sustain. Dev. 2020, 3, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chebet, N. The Role of Women on Agricultural Sector Growth. Int. J. Agric. 2023, 8, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicolopoulou, K.; Karataş-Özkan, M.; Vas, C.; Nouman, M. An incubation perspective on social innovation: The London Hub-a social incubator. R&D Manag. 2022, 47, 368–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krasachat, W.; Yaisawarng, S. Directional Distance Function Technical Efficiency of Chili Production in Thailand. Sustainability 2021, 13, 741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saptana; Sayekti, A.L.; Perwita, A.D.; Sayaka, B.; Gunawan, E.; Sukmaya, S.G.; Hayati, N.Q.; Yusuf; Sumaryanto; Yufdy, M.P.; et al. Analysis of competitive and comparative advantages of potato production in Indonesia. PLoS ONE 2023, 17, e0263633. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).