Effects of Ettringite Formation on the Stability of Cement-Treated Sediments
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Characterization
2.3. Unconfined Compression Tests
2.4. Porosity/Cement Index ()
2.5. Thermogravimetric Tests
2.6. X-Ray Diffractometry and Fluorescence Tests
2.7. Text Refinement Using AI Tools
3. Results
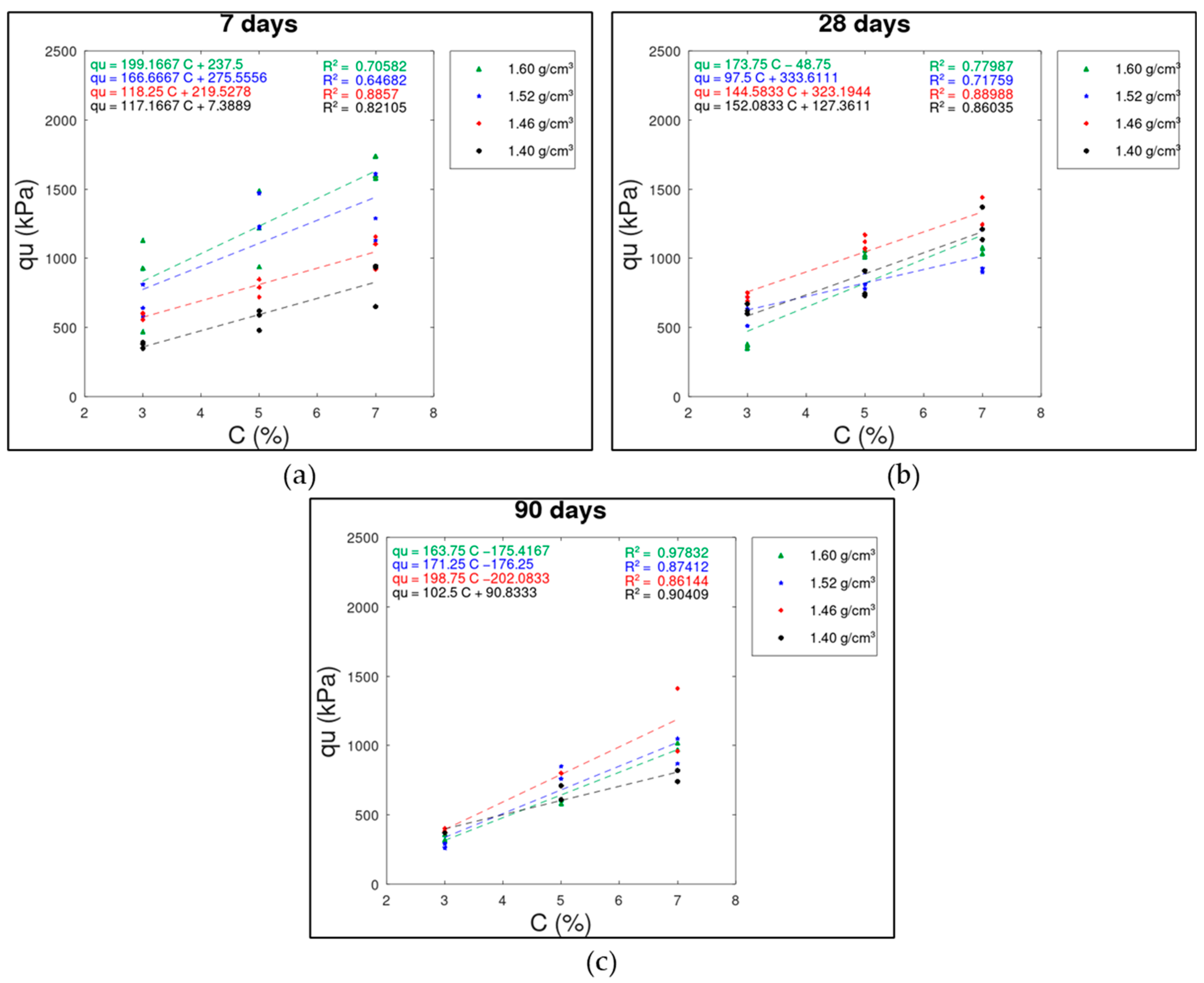
3.1. Cement Content (C) x UCS () Relationship
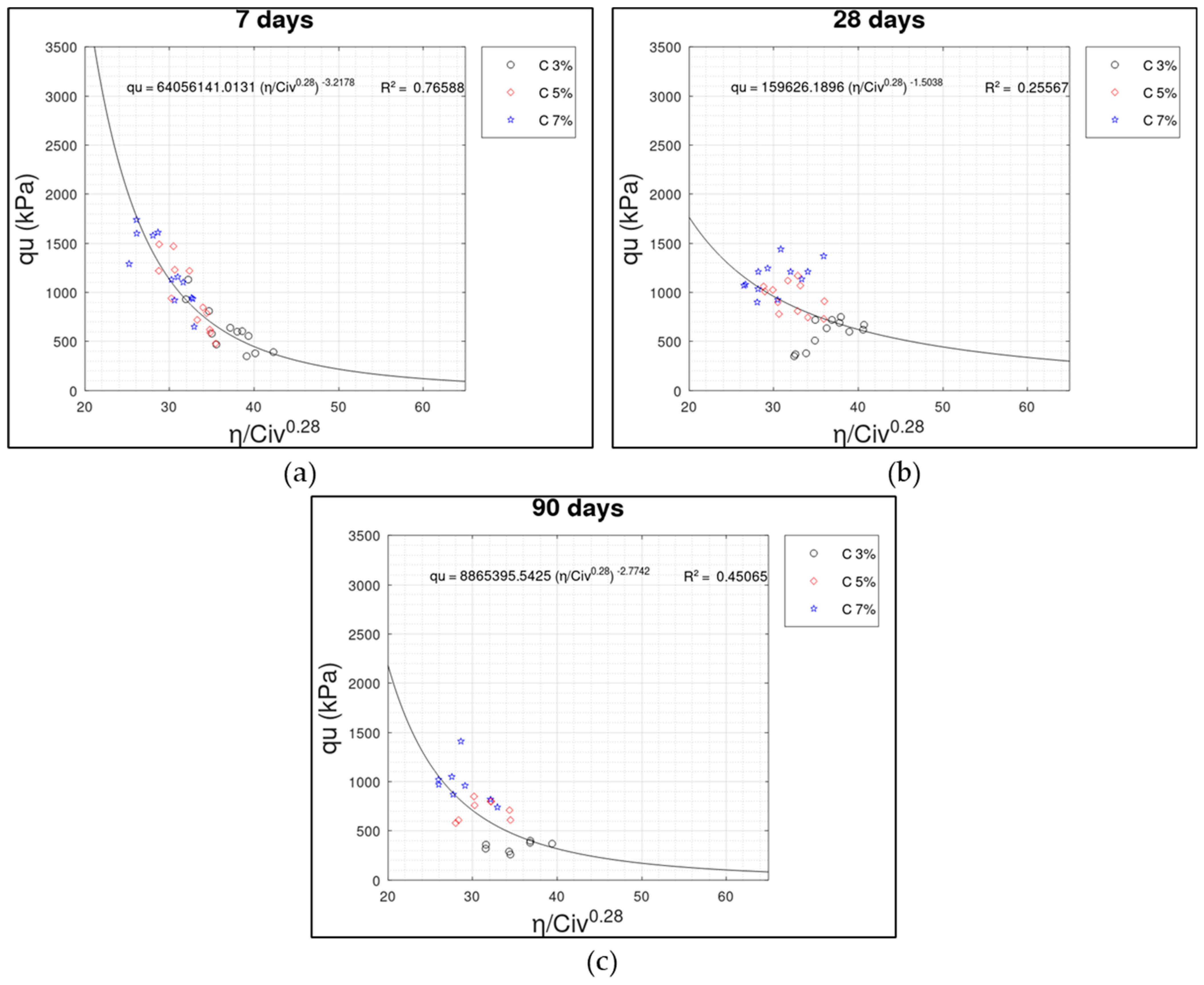
3.2. Porosity/Cement Index () x UCS () Relationship
3.3. Curing Time x UCS () Relationship
3.4. X-Ray Fluorescence Analysis
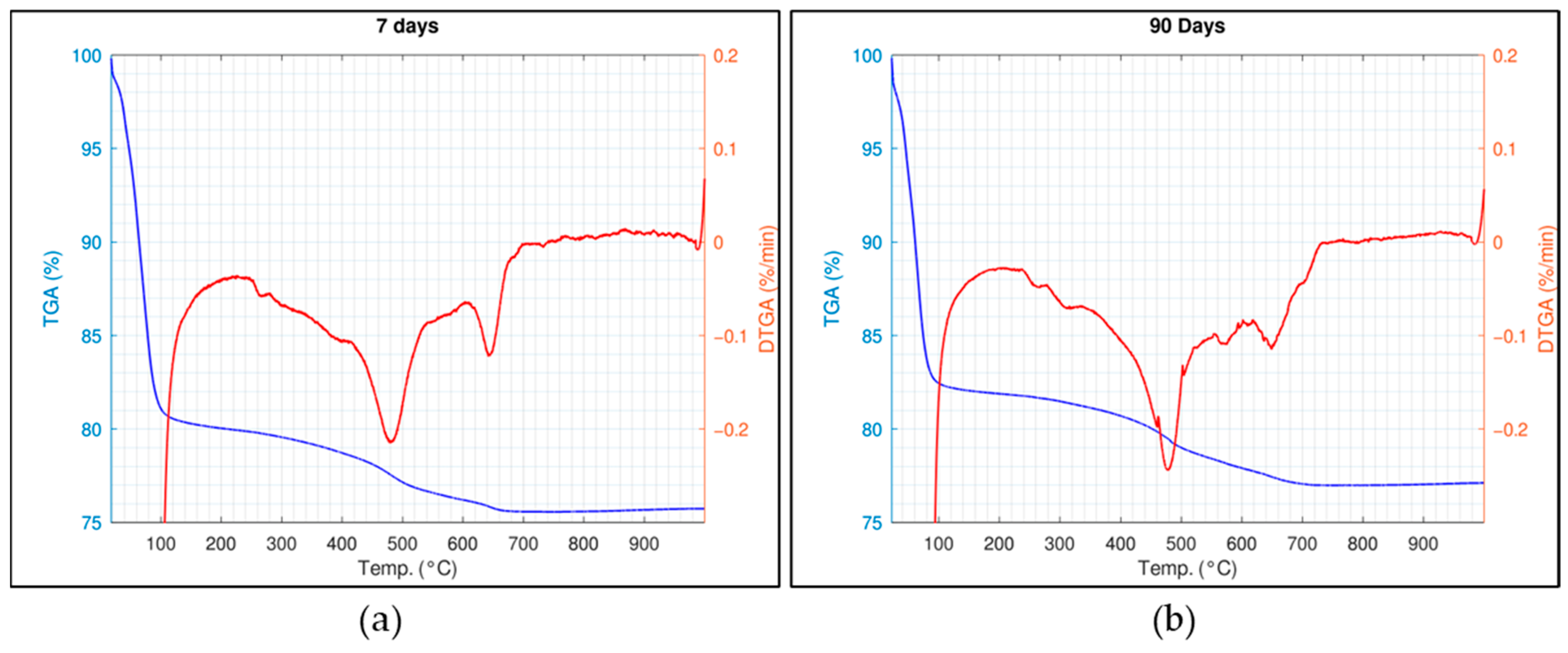
3.5. Thermogravimetric Analysis
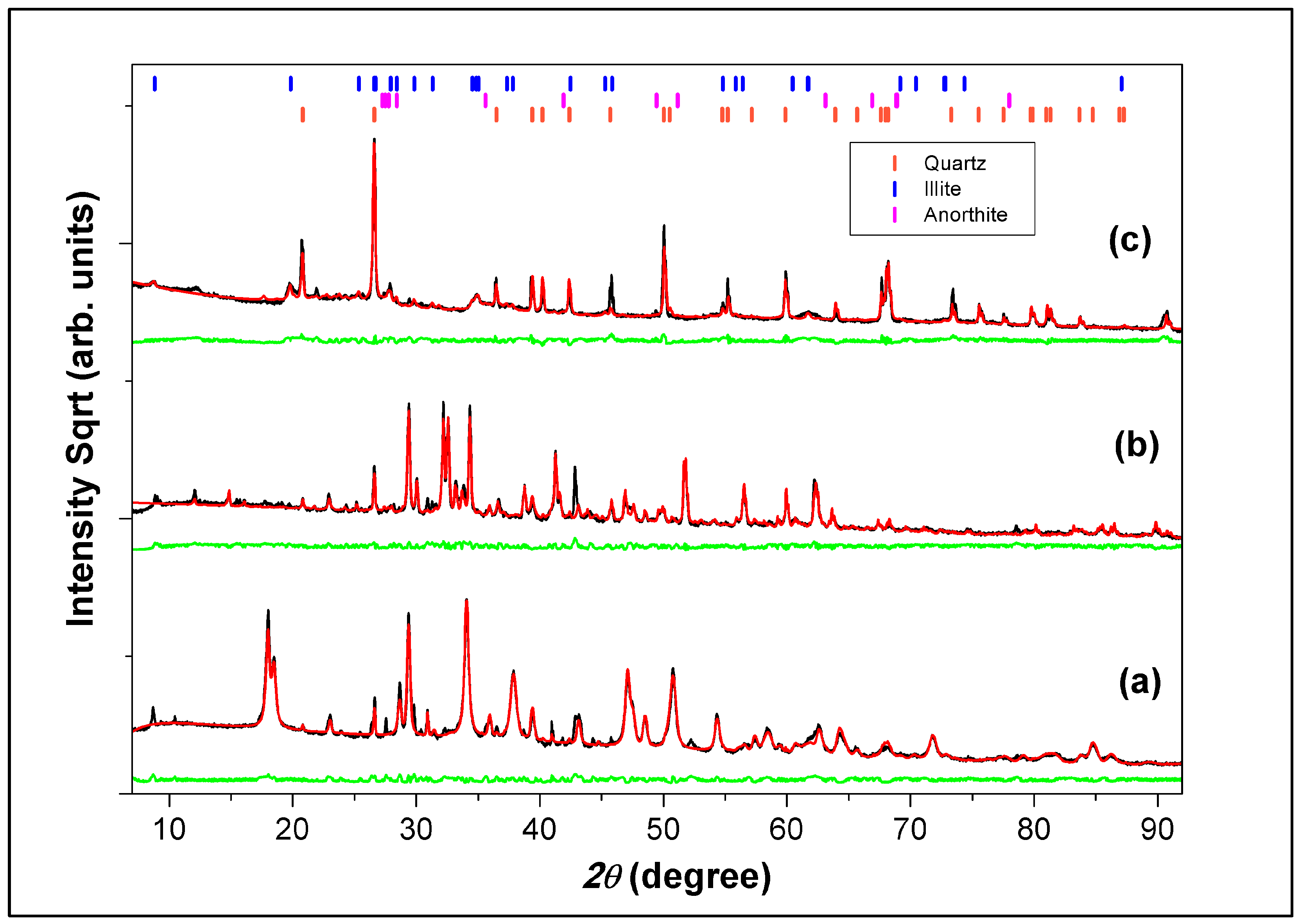
3.6. X-Ray Diffractometry Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- The combination of chemical stabilizers with compaction shows potential as a technique for stabilizing sediments from the Port of Rio Grande.
- The presence of sulfates in these sediments poses a challenge to their stabilization using calcium-based compounds like Portland cement and lime, despite the promising results observed with shorter curing times.
- Low-calcium stabilizers should be considered for these sediments, with particular attention paid to the risk of ettringite formation over longer curing times.
- Extended curing age evaluations are essential, as strength loss mechanisms may only become apparent beyond the typical 28-day period.
- Non-calcium stabilizers are preferable for stabilizing sulfate-bearing soils. Their efficacy in these sediments and their practical application at larger scales warrant further investigation.
- The combination of advanced chemical analysis with mechanical performance testing offers a comprehensive approach to understanding long-term stabilization behavior, which is essential for practical engineering applications.
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mirlean, N.; Calliari, L.; Johannesson, K. Dredging in an Estuary Causes Contamination by Fluid Mud on a Tourist Ocean Beach. Evidence via REE Ratios. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2020, 159, 111495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calliari, L.J.; Machado, A.A.; Marroig, P.; Vinzon, S.; Gianuca, N. Mud Deposits at Cassino Beach: Role of Dredging. Geo-Mar. Lett. 2020, 40, 1031–1043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Larrosa, C.; Lotero, A.; Bastos, C.; Servi, S.; Consoli, N.C. Stabilization of Dredging Material from Rio Grande Harbor with Alkali-Activated Cements to Produce Masonry Elements. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2023, 35, 04023018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Fagundes, D.F.; Pimpão, C.Y.; Servi, S.P. Mechanical Behaviour of Dredging Waste in the Port of Rio Grande by Adding Stabilizing Agents. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2024, 18, 433–443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.-F.; Chen, C.-W.; Ju, Y.-R.; Kao, C.-M.; Dong, C.-D. Impact of Disposal of Dredged Material on Sediment Quality in the Kaohsiung Ocean Dredged Material Disposal Site, Taiwan. Chemosphere 2018, 191, 555–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donázar-Aramendía, I.; Sánchez-Moyano, J.E.; García-Asencio, I.; Miró, J.M.; Megina, C.; García-Gómez, J.C. Impact of Dredged-Material Disposal on Soft-Bottom Communities in a Recurrent Marine Dumping Area near to Guadalquivir Estuary, Spain. Mar. Environ. Res. 2018, 139, 64–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svensson, N.; Norén, A.; Modin, O.; Karlfeldt Fedje, K.; Rauch, S.; Strömvall, A.-M.; Andersson-Sköld, Y. Integrated Cost and Environmental Impact Assessment of Management Options for Dredged Sediment. Waste Manag. 2022, 138, 30–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.F.; Zhu, W.; Zhang, C.L. Yielding and Shear Behaviour of Cement-Treated Dredged Materials. Eng. Geol. 2009, 103, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amar, M.; Benzerzour, M.; Kleib, J.; Abriak, N.-E. From Dredged Sediment to Supplementary Cementitious Material: Characterization, Treatment, and Reuse. Int. J. Sediment Res. 2021, 36, 92–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Dong, C.; Zhang, C.; Xu, K. A Dredged Material Solidification Treatment for Fill Soils in East China: A Case History. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2017, 35, 865–872. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shinsha, H.; Kumagai, T. Material Properties of Solidified Soil Grains Produced from Dredged Marine Clay. Soils Found. 2018, 58, 678–688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yoobanpot, N.; Jamsawang, P.; Simarat, P.; Jongpradist, P.; Likitlersuang, S. Sustainable Reuse of Dredged Sediments as Pavement Materials by Cement and Fly Ash Stabilization. J. Soils Sediments 2020, 20, 3807–3823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Li, D.; Lang, L. Evaluation of Strength Development in Cemented Dredged Sediment Admixing Recycled Glass Powder. Constr. Build. Mater. 2022, 342, 127996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maherzi, W.; Benzerzour, M.; Mamindy-Pajany, Y.; Van Veen, E.; Boutouil, M.; Abriak, N.E. Beneficial Reuse of Brest-Harbor (France)-Dredged Sediment as Alternative Material in Road Building: Laboratory Investigations. Environ. Technol. 2018, 39, 566–580. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kourtaa, S.; Chabannes, M.; Becquart, F.; Abriak, N.-E. Hydration of Lime—Marine Sediment Blends: Influence of Mineralogical Composition and Lime Content. Adv. Powder Technol. 2023, 34, 104043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rađenović, D.; Kerkez, Đ.; Pilipović, D.T.; Dubovina, M.; Grba, N.; Krčmar, D.; Dalmacija, B. Long-Term Application of Stabilization/Solidification Technique on Highly Contaminated Sediments with Environment Risk Assessment. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 684, 186–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chatain, V.; Benzaazoua, M.; Loustau Cazalet, M.; Bouzahzah, H.; Delolme, C.; Gautier, M.; Blanc, D.; De Brauer, C. Mineralogical Study and Leaching Behavior of a Stabilized Harbor Sediment with Hydraulic Binder. Env. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2013, 20, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, N.C.; Foppa, D.; Festugato, L.; Heineck, K.S. Key Parameters for Strength Control of Artificially Cemented Soils. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2007, 133, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, N.C.; Rosa, A.D.; Saldanha, R.B. Variables Governing Strength of Compacted Soil–Fly Ash–Lime Mixtures. J. Mater. Civ. Eng. 2011, 23, 432–440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Consoli, N.C.; Prietto, P.D.M.; Da Silva Lopes, L.; Winter, D. Control Factors for the Long Term Compressive Strength of Lime Treated Sandy Clay Soil. Transp. Geotech. 2014, 1, 129–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheuermann, H.C.; Martins, C.G.; Menezes, R.J.W.; Dornelles, L.E.; Consoli, N.C. The Effect of Key Parameters on the Strength of a Dispersive Soil Stabilized with Sustainable Binders. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2021, 39, 5395–5404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, I.; Nierwinski, H.; Freitas Fagundes, D.; Pinheiro Maria, R. Geotechnical Characterization of Dredged Material from Rio Grande’s Port, Brazil. In Proceedings of the 7th International Conference on Geotechnical and Geophysical Site Characterization, CIMNE, Barcelona, Spain, 18–21 June 2024. [Google Scholar]
- Sherwood, P.T. The Stabilization with Cement of Weathered and Sulphate-Bearing Clays. Géotechnique 1957, 7, 179–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hunter, D. Lime-Induced Heave in Sulfate-Bearing Clay Soils. J. Geotech. Eng. 1988, 114, 150–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dermatas, D. Ettringite-Induced Swelling in Soils: State-of-the-Art. Appl. Mech. Rev. 1995, 48, 659–673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anburuvel, A. The Engineering Behind Soil Stabilization with Additives: A State-of-the-Art Review. Geotech. Geol. Eng. 2024, 42, 1–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Divet, L.; Randriambololona, R. Delayed Ettringite Formation: The Effect of Temperature and Basicity on the Interaction of Sulphate and C-S-H Phase. Cem. Concr. Res. 1998, 28, 357–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henke, K.R.; Robl, T.L.; Rathbone, R.F. Effects of Calcium Sulfate and Aluminum Crystal Forms on the Kinetics of Ettringite Formation. In Proceedings of the 2007 World of Coal Ash (WOCA), Covington, KY, USA, 7–10 May 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Barman, D.; Dash, S.K. Stabilization of Expansive Soils Using Chemical Additives: A Review. J. Rock Mech. Geotech. Eng. 2022, 14, 1319–1342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raja, P.S.K.; Thyagaraj, T. Effect of Short-Term Sulphate Contamination on Lime-Stabilized Expansive Soil. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2021, 15, 964–976. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, G. Sulphate Attack and Ettringite Formation in the Lime and Cement Stabilized Marine Clays. Ocean Eng. 2005, 32, 1133–1159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, G.; Murali, K.; Srinivasaraghavan, R. Effect of Chlorides and Sulphates on Lime Treated Marine Clays. Soils Found. 1997, 37, 105–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajasekaran, G.; Narasimha Rao, S. Sulphate Attack in Lime-Treated Marine Clay. Mar. Georesources Geotechnol. 2005, 23, 93–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chrysochoou, M.; Grubb, D.G.; Malasavage, N.E. Assessment of Sulfate-Induced Swell in Stabilized Dredged Material: Is Ettringite Always a Problem? J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2012, 138, 407–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yi, Y.; Li, C.; Liu, S.; Al-Tabbaa, A. Resistance of MgO–GGBS and CS–GGBS Stabilised Marine Soft Clays to Sodium Sulfate Attack. Géotechnique 2014, 64, 673–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM D2487-17; Standard Practice for Classification of Soils for Engineering Purposes (Unified Soil Classification System). ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2017.
- Fagundes, D.F.; Rammah, K.I.; Almeida, M.S.S.; Pequeno, J.; Oliveira, J.R.M.S.; Borges, R.G. Strength Behaviour Analysis of an Offshore Brazilian Marine Clay. In Proceedings of the Volume 4: Offshore Geotechnics; Ronald W. Yeung Honoring Symposium on Offshore and Ship Hydrodynamics, Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 1–6 July 2012; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: Rio de Janeiro, Brazil, 2012; pp. 1–9. [Google Scholar]
- Valerio, B.S.B.; Alves, A.M.L.; Fontoura, J.A.S.; Nunez, V.F. Geotechnical, Microscopic and Mineralogical Characterization of Surficial Sediments Nearshore the Southern Coast of Brazil. Int. J. Geotech. Eng. 2024, 18, 13–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM International. Specification for Portland Cement; ASTM: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rietveld, H.M. A Profile Refinement Method for Nuclear and Magnetic Structures. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 1969, 2, 65–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- FIZ Karlsruhe ICSD. Available online: https://icsd.products.fiz-karlsruhe.de/en/about/about-icsd (accessed on 10 August 2024).
- Coelho, A.A. TOPAS and TOPAS-Academic: An Optimization Program Integrating Computer Algebra and Crystallographic Objects Written in C++. J. Appl. Crystallogr. 2018, 51, 210–218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mitchell, J.K. Soil Improvement—State-of-the Art Report. In Proceedings of the 10th International Conference on Soil Mechanics and Foundation Engineering, Estocolmo, Sweden, 15–19 June 1981; International Society for Soil Mechanics and Geotechnical Engineering: London, UK, 1981; p. 58. [Google Scholar]
- Nicholson, P. Soil Improvement & Ground Modification Methods, 1st ed.; Elsevier: Waltham, MA, USA, 2014; ISBN 978-0-12-408076-8. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, D.X.; Abriak, N.E.; Zentar, R.; Xu, W. Solidification/Stabilization of Dredged Marine Sediments for Road Construction. Environ. Technol. 2012, 33, 95–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zentar, R.; Wang, H.; Wang, D. Comparative Study of Stabilization/Solidification of Dredged Sediments with Ordinary Portland Cement and Calcium Sulfo-Aluminate Cement in the Framework of Valorization in Road Construction Material. Constr. Build. Mater. 2021, 279, 122447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, H.; Jeong, Y.; Bae, S.; Jun, Y.; Yoon, S.; Eun Oh, J. A Study of Thermal Decomposition of Phases in Cementitious Systems Using HT-XRD and TG. Constr. Build. Mater. 2018, 169, 648–661. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puppala, A.J.; Griffin, J.A.; Hoyos, L.R.; Chomtid, S. Studies on Sulfate-Resistant Cement Stabilization Methods to Address Sulfate-Induced Soil Heave. J. Geotech. Geoenviron. Eng. 2004, 130, 391–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.; Li, R.; Xiao, H. Treating Sulfate-Bearing Soil by Using Sodium Silicate and NaOH-Activated Ground Granulated Blast-Furnace Slag. Acta Geotech. 2024, 19, 3129–3138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khadka, S.D.; Jayawickrama, P.W.; Senadheera, S.; Segvic, B. Stabilization of Highly Expansive Soils Containing Sulfate Using Metakaolin and Fly Ash Based Geopolymer Modified with Lime and Gypsum. Transp. Geotech. 2020, 23, 100327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nontikansak, M.; Chaiyapoom, P.; Siriwatwechakul, W.; Jongvisuttisun, P.; Snguanyat, C. Control the Early-Stage Hydration of Expansive Additive from Calcium Sulfoaluminate Clinker by Polymer Encapsulation. Cement 2022, 8, 100021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Y.; Qian, C. Improved Ettringite Stabilization by Calcium Carbonate and Calcium Nitrate Additions in Ternary PC-CSA-C$ Systems. Cem. Concr. Res. 2024, 175, 107383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]


| Parameters | Value |
|---|---|
| Initial water content (%) | 110 |
| Organic matter content (%) | 7.71 |
| Grain size > 63 μm (%) | 48 |
| 63 μm > Grain size > 2 μm (%) | 24 |
| Grain size < 2 μm (%) | 28 |
| Classification (USCS) | CL |
| Liquid limit (%) | 49 |
| Plastic limit (%) | 19 |
| Plasticity index (%) | 30 |
| 2.53 | |
| (g/cm3) | 1.46 |
| (%) | 25.20 |
| (g/cm3) | 1.60 |
| (%) | 24.50 |
| pH | 7.89 |
| Phase | Description | DS (%) | PC (%) | HL (%) | ICSD |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| SiO2 | Quartz | 55.4 (0.90) | 2.51 (0.90) | 0.88 (0.06) | 174 |
| K(Al4Si2O9(OH)3) | Illite | 33.9 (0.80) | - | - | 90,144 |
| CaAl2(SiO4)2 | Anorthite | 10.7(0.90) | - | - | 22,022 |
| C3S | Tricalcium Silicate | - | 73.30 (0.50) | - | 94,742 |
| C2S | Dicalcium Silicate | - | 9.20 (0.50) | - | 79,550 |
| CaCO3 | Calcite | - | 7.70 (0.30) | 24.50 (0.20) | 79,673 |
| C4AF | Tetra calcium Aluminoferrite | - | 4.43 (0.19) | - | 9197 |
| C3A–Cubic | Tricalcium Aluminate | - | 2.86 (0.14) | - | 1841 |
| Ca(OH)2 | Portlandite | - | - | 41.00 (0.30) | 15,471 |
| Mg(OH)2 | Brucite | - | - | 31.80 (0.30) | 34,401 |
| CaMg(CO3)2 | Dolomite | - | - | 1.87 (0.17) | 10,404 |
| 8.92 | 10.34 | 9.22 |
| (g/cm3) | w (%) | HL (%) | PC (%) | Curing Time (Days) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1.40 (95% Standard) | 25 | 1 | 3, 5, 7 | 7, 28, 90 |
| 1.46 (100% Standard) | 25 | 1 | 3, 5, 7 | 7, 28, 90 |
| 1.52 (95% Modified) | 25 | 1 | 3, 5, 7 | 7, 28, 90 |
| 1.60 (100% Modified) | 25 | 1 | 3, 5, 7 | 7, 28, 90 |
| (g/cm3) | PC (%) | 7 Days | 28 Days | 90 Days | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (kPa) | σ (kPa) | (kPa) | σ (kPa) | (kPa) | σ (kPa) | ||
| 1.40 | 3 | 386 | 6 | 610 | 10 | 370 | * |
| 1.40 | 5 | 535 | 56 | 738 | 8 | 660 | 50 |
| 1.40 | 7 | 939 | 5 | 1173 | 38 | 780 | 40 |
| 1.46 | 3 | 603 | 3 | 705 | 15 | 390 | 10 |
| 1.46 | 5 | 818 | 29 | 1145 | 25 | 800 | * |
| 1.46 | 7 | 1130 | 27 | 1228 | 18 | 1185 | 225 |
| 1.52 | 3 | 610 | 30 | 678 | 43 | 275 | 15 |
| 1.52 | 5 | 1225 | 5 | 795 | 15 | 805 | 45 |
| 1.52 | 7 | 1210 | 80 | 913 | 13 | 960 | 90 |
| 1.60 | 3 | 1030 | 100 | 375 | 5 | 340 | 20 |
| 1.60 | 5 | 1355 | 135 | 1018 | 8 | 595 | 15 |
| 1.60 | 7 | 1670 | 70 | 1075 | 5 | 995 | 25 |
| Oxide | SiO2 | Al2O3 | Fe2O3 | K2O | CaO | SO3 | TiO2 | Other |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Content (%) | 51.84 | 19.78 | 16.63 | 4.18 | 2.40 | 2.07 | 1.75 | 1.33 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ribeiro, I.S.; Fagundes, D.d.F.; Nierwinski, H.P. Effects of Ettringite Formation on the Stability of Cement-Treated Sediments. Resources 2025, 14, 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14050073
Ribeiro IS, Fagundes DdF, Nierwinski HP. Effects of Ettringite Formation on the Stability of Cement-Treated Sediments. Resources. 2025; 14(5):73. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14050073
Chicago/Turabian StyleRibeiro, Inácio Soares, Diego de Freitas Fagundes, and Helena Paula Nierwinski. 2025. "Effects of Ettringite Formation on the Stability of Cement-Treated Sediments" Resources 14, no. 5: 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14050073
APA StyleRibeiro, I. S., Fagundes, D. d. F., & Nierwinski, H. P. (2025). Effects of Ettringite Formation on the Stability of Cement-Treated Sediments. Resources, 14(5), 73. https://doi.org/10.3390/resources14050073








