A Bond Graph Approach for the Modeling and Simulation of a Buck Converter
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. The Bond Graph Theory
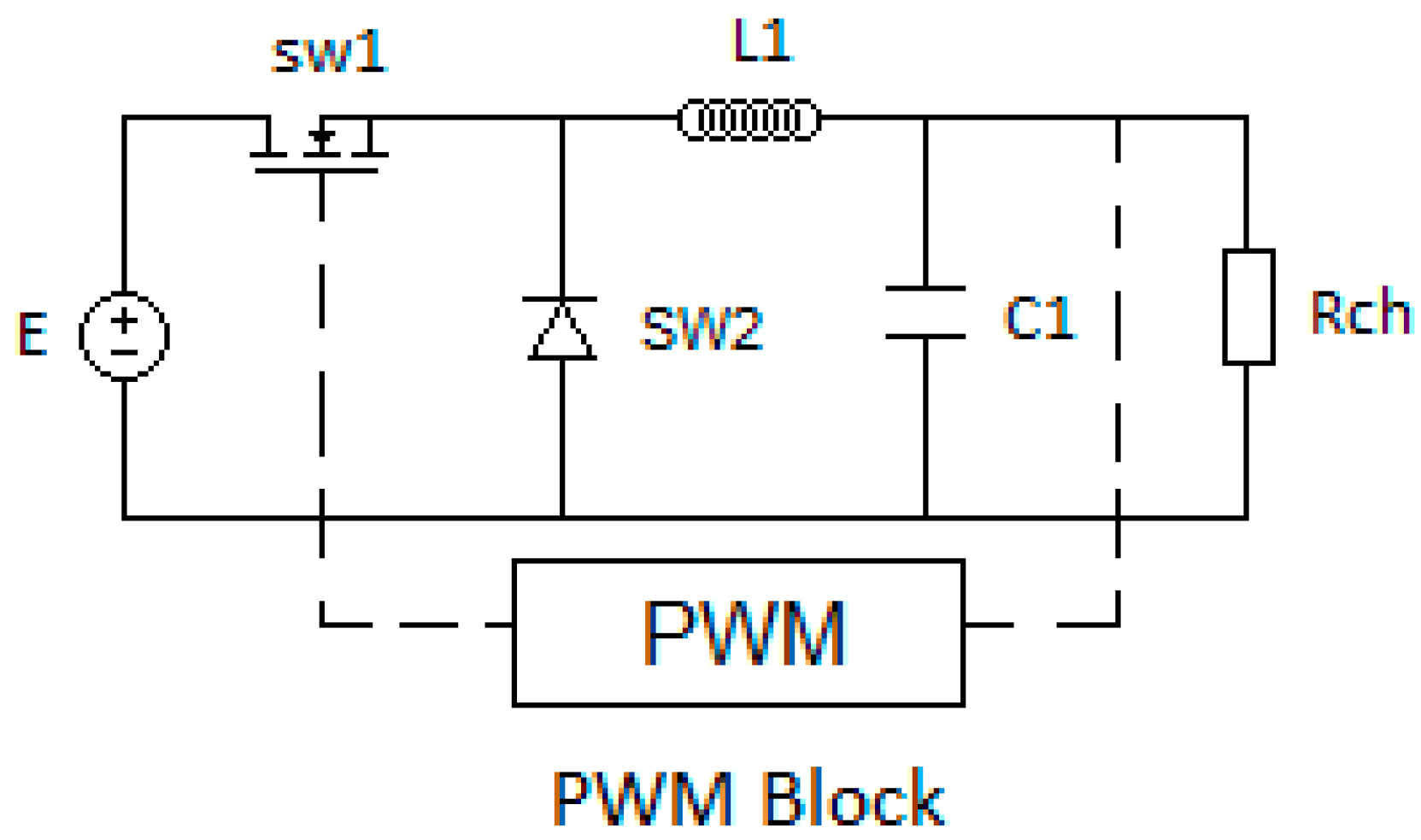
3. The Buck Bond Graph Model
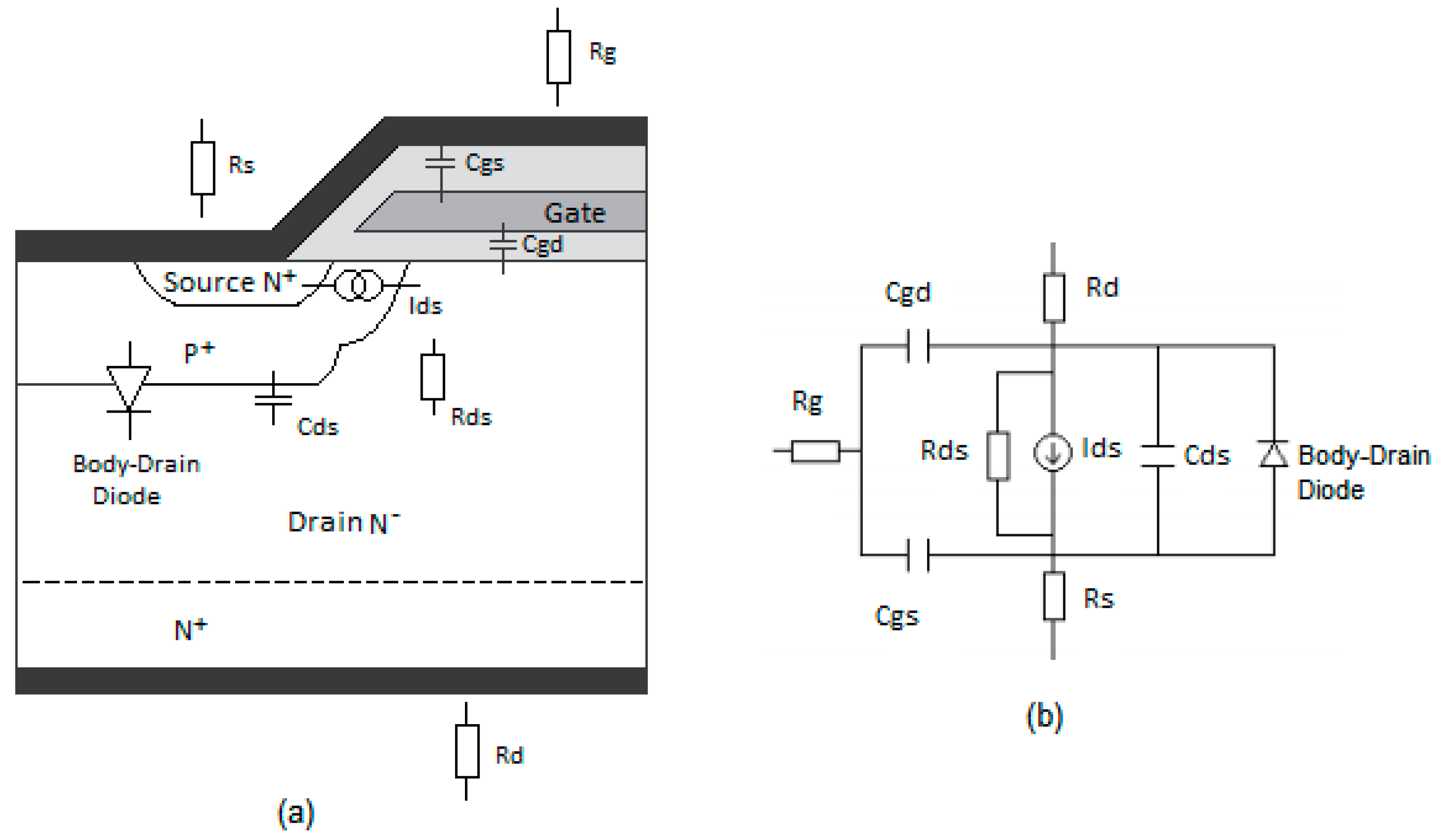
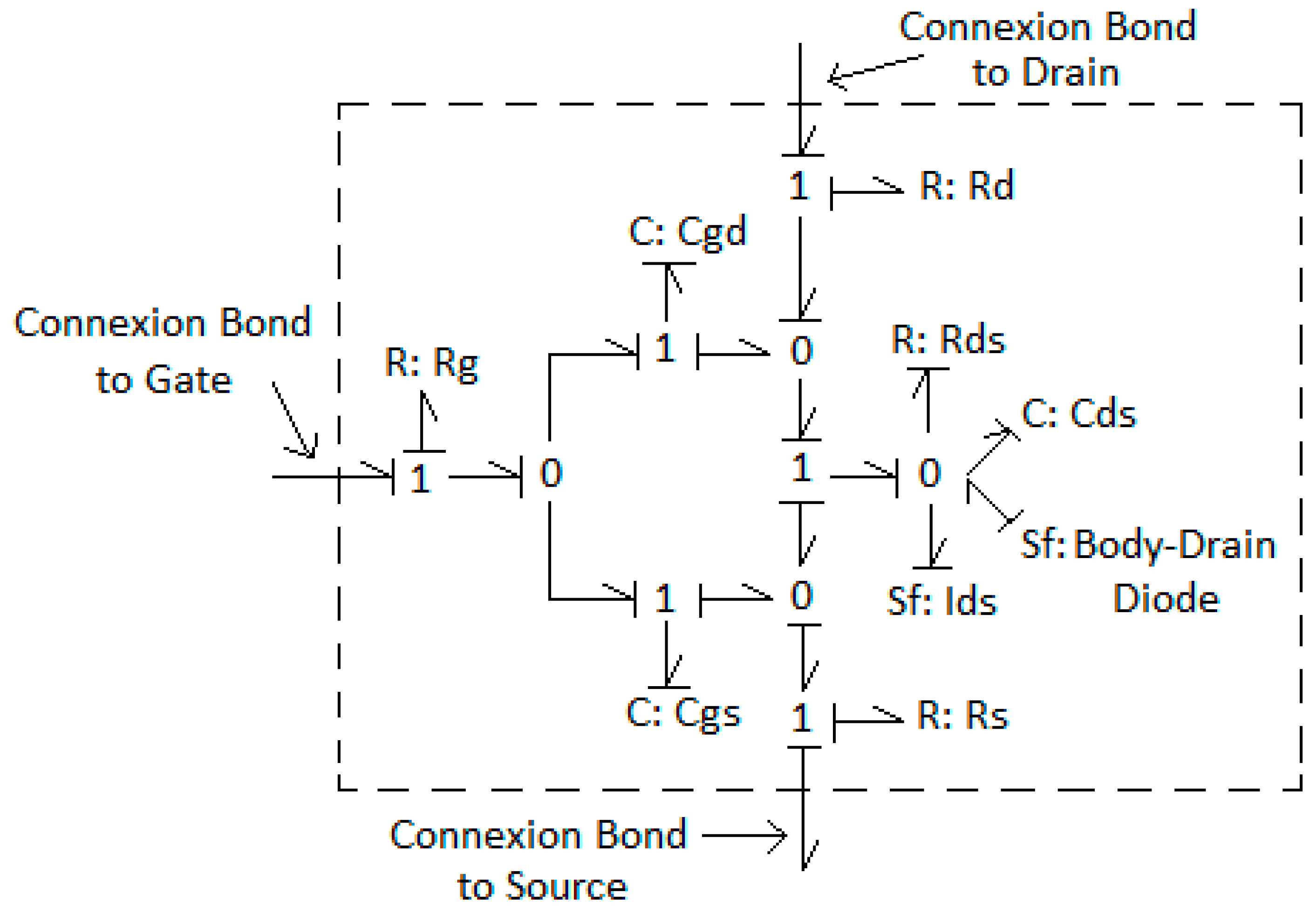
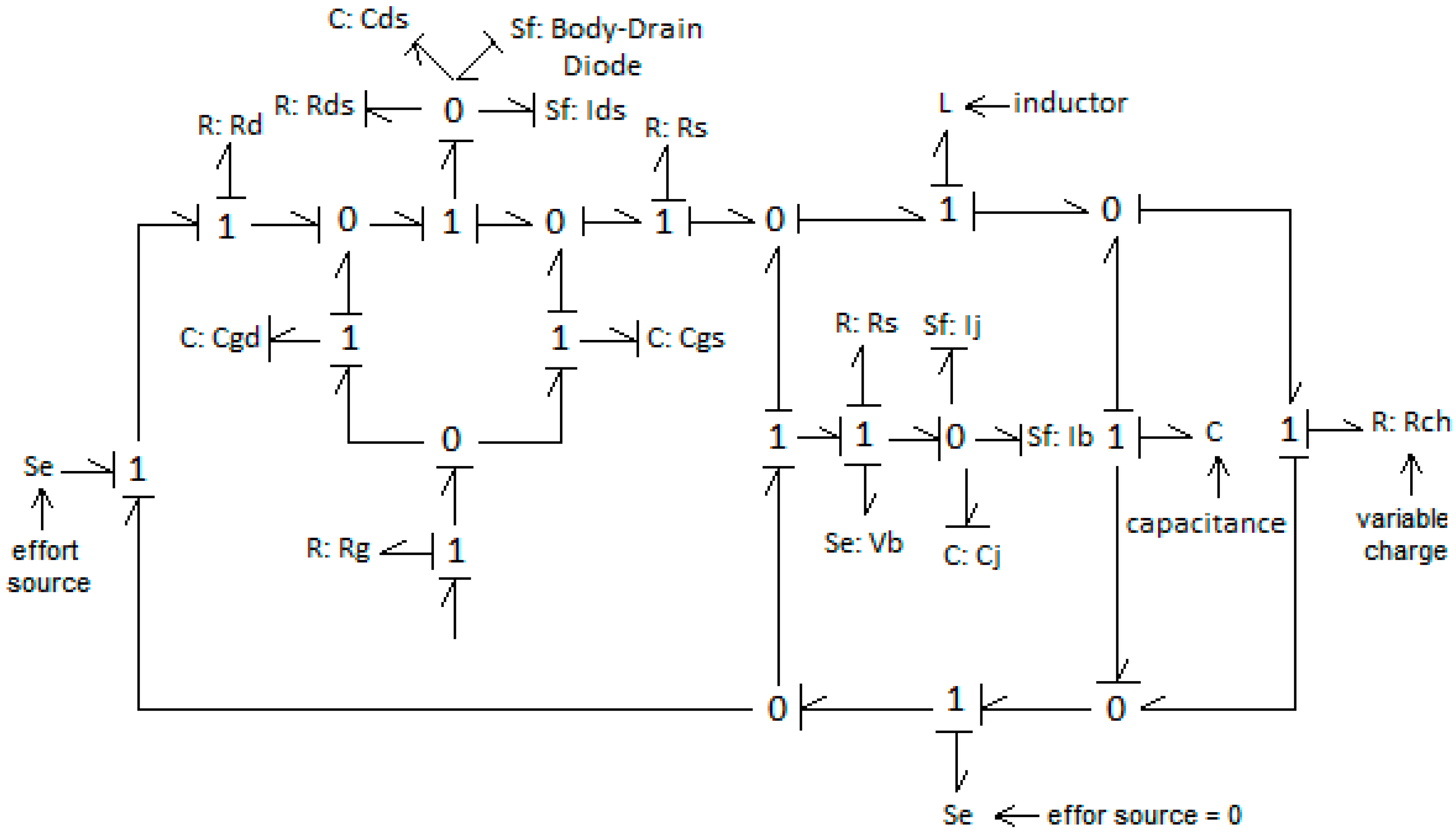
3.1. Power MOSFET Bond Graph Sub-Model Description
- The capacitances Cds, Cgd and Cgs that simulate the drain-source, gate-source, and gate-drain capacitances, respectively;
- The resistances Rd, Rg and Rs that represent the equivalent resistance of the drain, gate, and source, respectively;
- The resistance Rds that represents the total resistance between the drain and the source (the body-drain diode); and
- The controlled current source Ids, whose associated equations are:
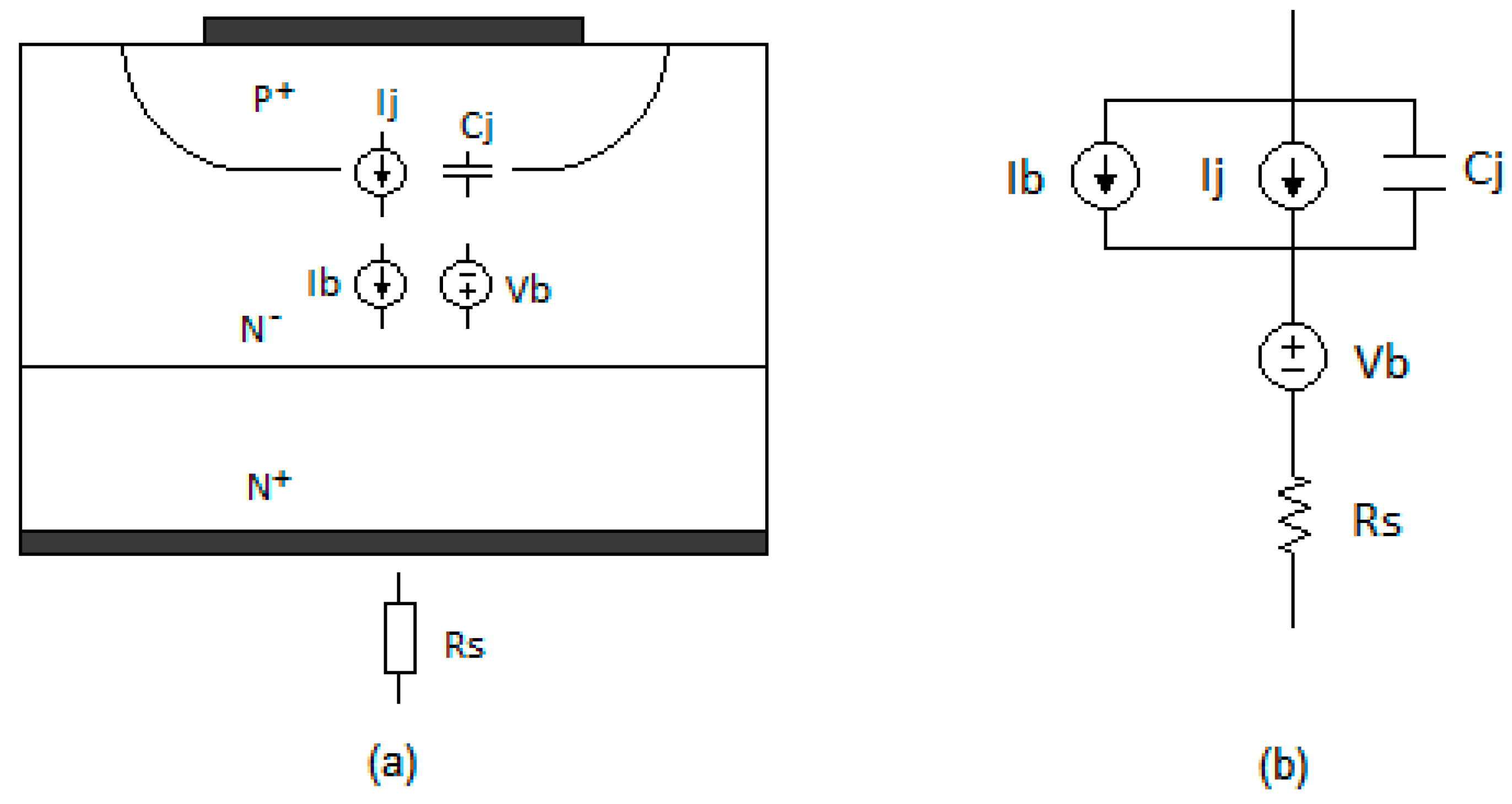
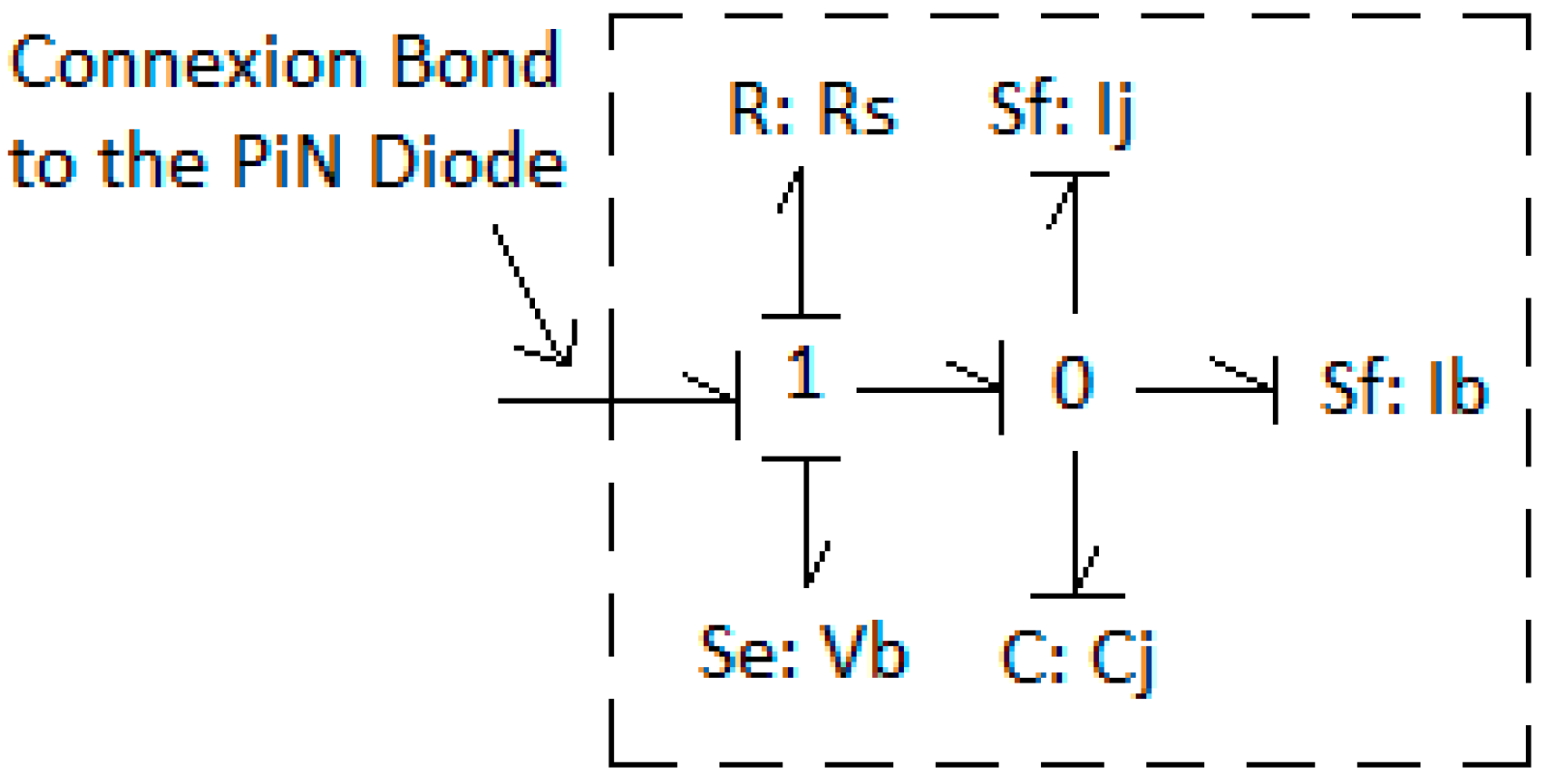
3.2. PiN Diode Bond Graph Model Description
- The current junction source Ij defined by the following equation:where is the junction voltage and is the thermal voltage.
- The current base source Ib, whose relations are as follows:where is the injected charge level at the junction and is the total charge in the central region, where:and
- The voltage base source Vb, equal to:
- The junction capacitance Cj
- The equivalent resistance Rs
3.3. Derivation of the Buck Bond Graph Model
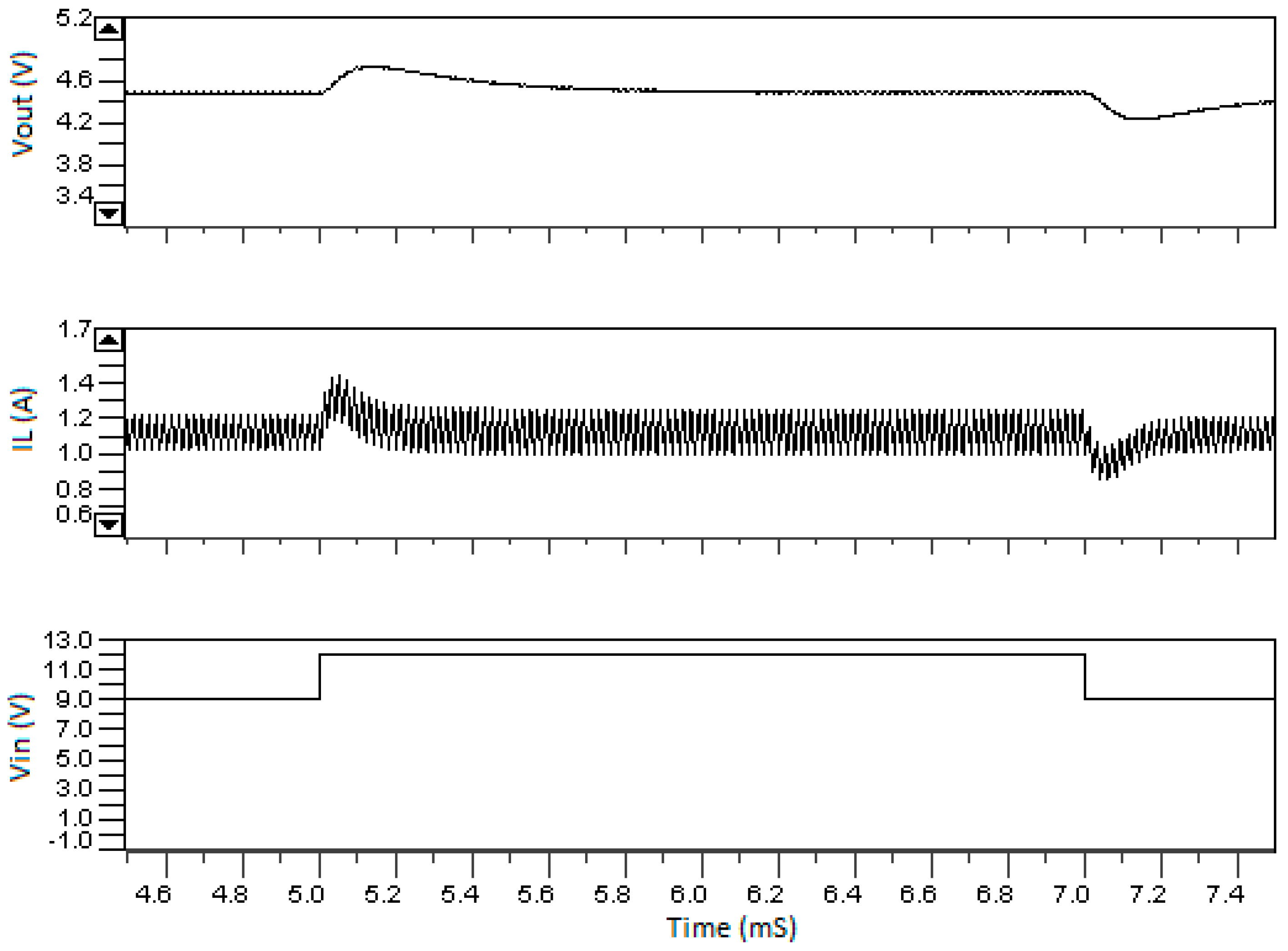
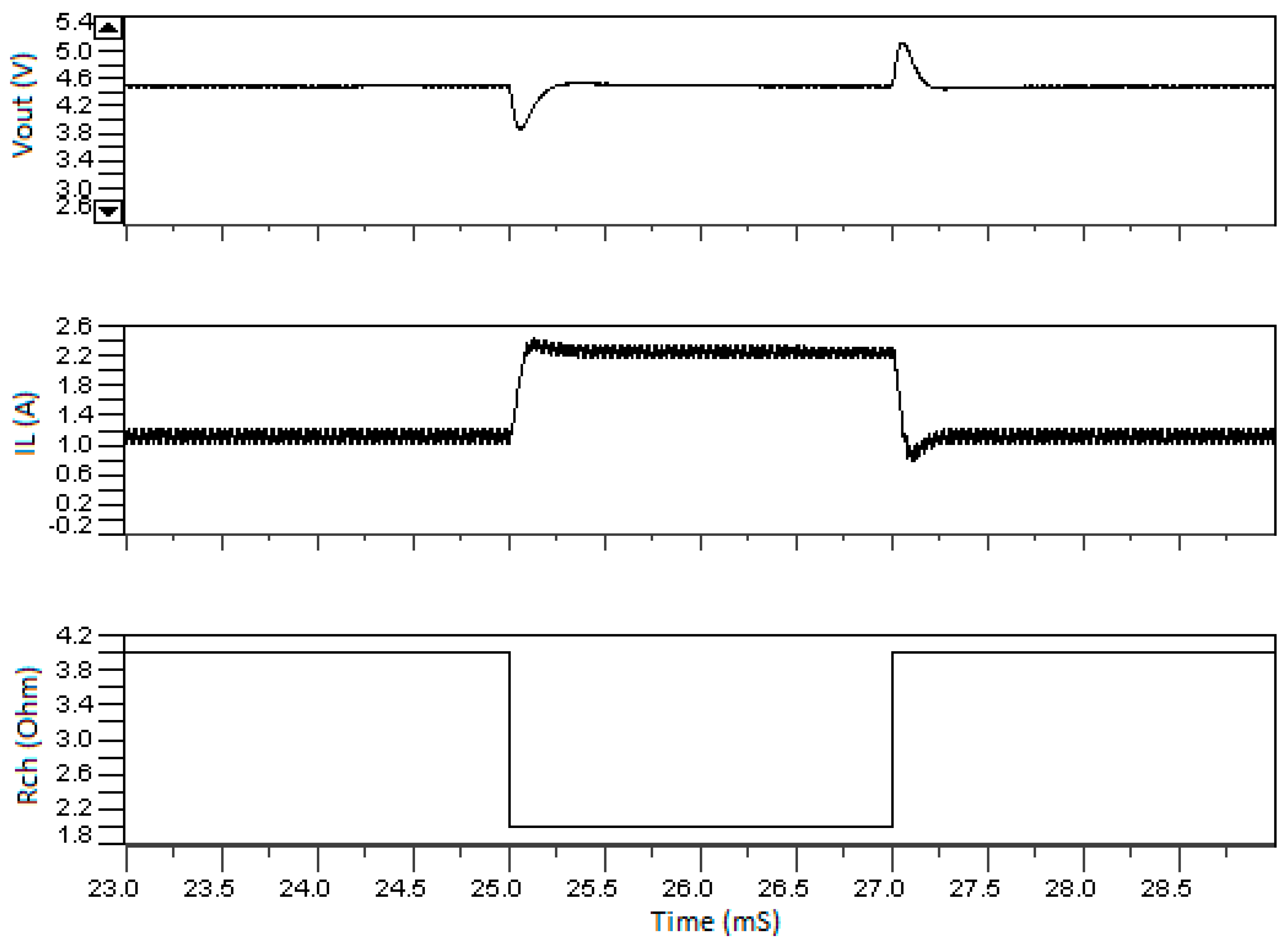
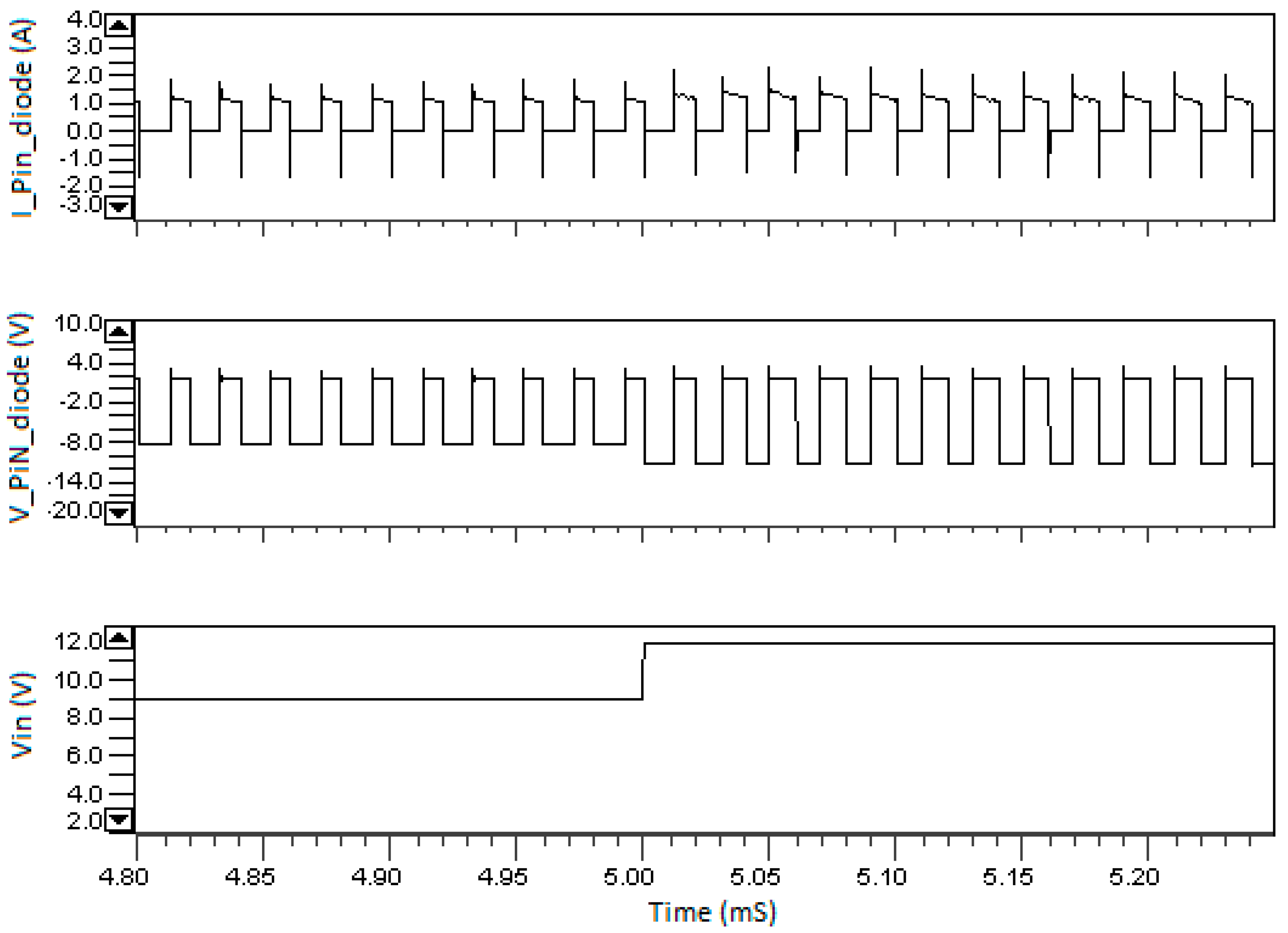
4. Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Acknowledgments
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Borutzky, W. Bond Graph Methodology—Development and Analysis of Multidisciplinary Dynamic System Models; Springer: London, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Buisson, J.; Cormerais, H.; Richard, P.Y. Analysis of the bond graph model of hybrid physical systems with ideal switches. Proc. Inst. Mech. Eng. Part I 2002, 216, 47–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borutzky, W. Bond Graph Model-Based Fault Diagnosis of Hybrid Systems; Springer: Cham, Switzerland; Heidelberg, Germany, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Asher, G.M. The robust modelling of variable topology circuits using bond graphs. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bond Graph Modelling (ICBGM’93), La Jolla, CA, USA, 17–20 January 1993. [Google Scholar]
- Umarikar, A.C.; Umanand, L. Modelling of switching systems in bond graphs using the concept of switched power junctions. J. Frankl. Inst. 2005, 342, 131–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Besbes, K. Modeling an insulated gate bipolar transistor using bond graph techniques. Int. J. Numer. Model. 1995, 8, 51–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garrab, H.; Allard, B.; Morel, H.; Ghedira, S.; Besbes, K. Role of the temperature distribution on the pn junction behavior in the electro-thermal simulation. Int. J. Numer. Model. 2004, 17, 539–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morel, H.; Allard, B.; Ghedira, S.; Ammous, A. A bond graph model of the PN junction. Simul. Ser. 1997, 29, 325–330. [Google Scholar]
- Alexander, H.S. Model Engineering in Mixed-Signal Circuit Design: A Guide to Generating Accurate Behavioral Models in VHDL-AMS; Springer: New York, NY, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ashenden, P.J.; Peterson, G.D.; Teegarden, D.A. The System Designer’s Guide to VHDL-AMS: Analog, Mixed-Signal, and Mixed-Technology Modeling; Elsevier: Laguna Hills, CA, USA, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Ibrahim, T. Contribution au Développement de Modèles Pour L’électronique de Puissance en VHDL-AMS. Ph.D. Dissertation, INSA-Lyon, Villeurbanne, France, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Ma, C.L.; Lauritzen, P.O. A simple power diode model with forward and reverse recovery. IEEE Trans. Power Electron. 1993, 8, 342–346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borusky, W. Bond graphs and object oriented modeling—A comparison. Syst. Control. Eng. 2002, 216, 21–33. [Google Scholar]
- Maehne, T.; Vachoux, A.; Leblebici, Y. Development of a bond graph based model of computation for systemc-ams. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on PhD Research in Microelectronics and Electronics, Istanbul, Turkey, 22–25 June 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Pecheux, F.; Allard, B.; Lallement, C.; Vachoux, A.; Morel, H. Modeling and simulation of multi-discipline systems using bond graphs and VHDL-AMS. In Proceedings of the International Conference on Bond Graph Modeling and Simulation (ICBGM), New Orleans, LA, USA, 23–27 January 2005; pp. 149–155. [Google Scholar]
- Zrafi, R.; Ghedira, S.; Dhahri, Y.; Besbes, K. Simple VHDL-AMS PiN Diode Model Using Bond Graph Techniques. In Proceedings of the IEEE 16th International Conference on Sciences and Techniques of Automatic Control & Computer Engineering -STA’2015, Monastir, Tunisia, 21–23 December 2015; pp. 551–556. [Google Scholar]
- Zrafi, R.; Ghedira, S.; Dhahri, Y.; Besbes, K. Bond graph based automated modeling of switch-mode power converters using VHDL-AMS. In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Control, Automation and Diagnosis (ICCAD), Hammamet, Tunisia, 19–21 January 2017. [Google Scholar]
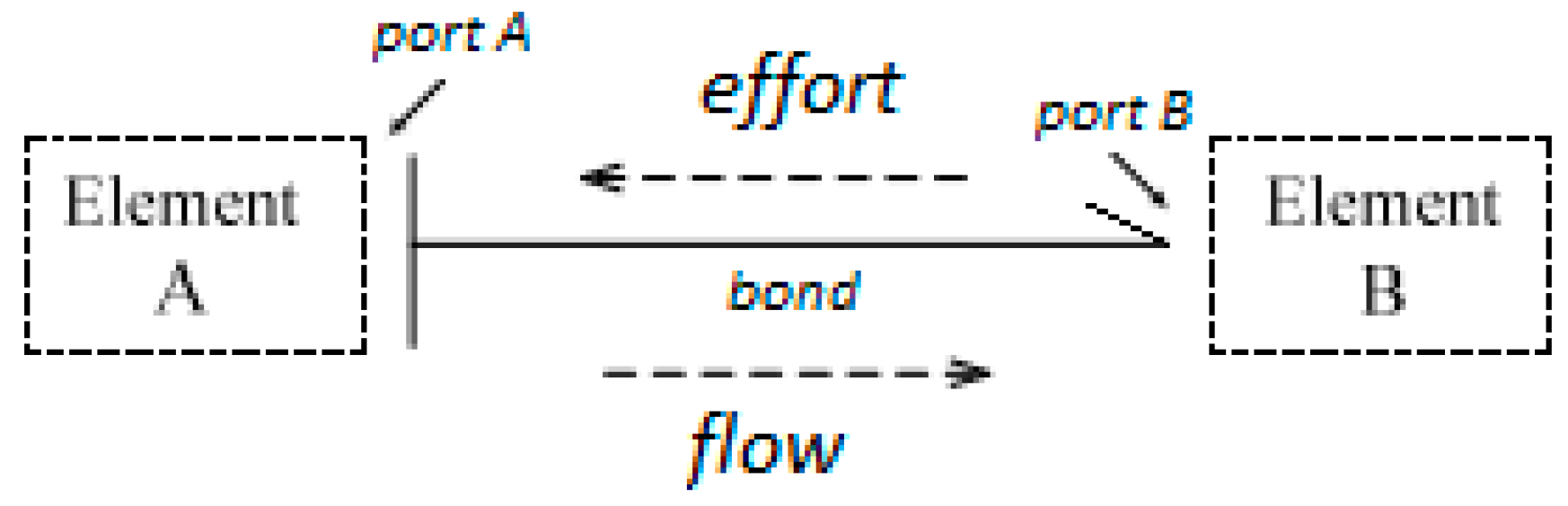


| Physical Domain | Flow Variable | Effort Variable |
|---|---|---|
| Electrical | Current | Voltage |
| Mechanical | Velocity | Force |
| Hydraulic | Volume flow | Pressure |
| Thermal | Entropy flow | Temperature |
| Parameters | Description | Values | Unity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Teta | Transverse electric field factor of the MOSFET | 3.5 | |
| Kplin | Linear transconductance | 9.0 | A/ |
| Kpsat | Saturation transconductance | 15.0 | A/ |
| vt | Threshold voltage | 3.5 | V |
| Rd | Equivalent resistance of the drain | 0.02 | Ω |
| Rs | Equivalent resistance of the source | 0.038 | Ω |
| Rg | Equivalent resistance of the gate | 0.09 | Ω |
| Rds | Resistance between the drain and the source | 1.5 × 106 | Ω |
| Cds0 | Drain-source capacity at zero level polarization | 5.2 × 10−9 | F |
| Is0 | Saturation current of the body-drain diode | 4.0 × 10−9 | A |
| PB | Potential of the MOSFET base | 0.8 | V |
| MJ | Gradient coefficient | 1.0 | – |
| NB | Concentration in the MOSFET base | 5.4 × 1021 | |
| Coxd | Gate oxide capacity | 0.045 × 10−9 | F |
| Agd | Equivalent surface of the gate-drain area | 4.0 × 10−6 | |
| Cgs | Grid-source equivalent capacity | 0.4 × 10−9 | F |
| Parameters | Description | Values | Unity |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rs | Serial resistance | 30.0 × 10−3 | Ω |
| Ise | Recombination current | 1.0 × 10−23 | A |
| TM | Carriers transit time | 8.2 × 10−9 | ns |
| TAU | Carriers lifetime | 1.3 × 10−7 | ns |
| RM0 | Initial resistance | 0.1 | Ω |
| M | Gradient coefficient | 0.55 | – |
| Cj0 | Junction capacitance | 3.0 × 10−9 | F |
| Is | Saturation current | 1.0 × 10−12 | A |
© 2018 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zrafi, R.; Ghedira, S.; Besbes, K. A Bond Graph Approach for the Modeling and Simulation of a Buck Converter. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2018, 8, 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea8010002
Zrafi R, Ghedira S, Besbes K. A Bond Graph Approach for the Modeling and Simulation of a Buck Converter. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications. 2018; 8(1):2. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea8010002
Chicago/Turabian StyleZrafi, Rached, Sami Ghedira, and Kamel Besbes. 2018. "A Bond Graph Approach for the Modeling and Simulation of a Buck Converter" Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications 8, no. 1: 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea8010002
APA StyleZrafi, R., Ghedira, S., & Besbes, K. (2018). A Bond Graph Approach for the Modeling and Simulation of a Buck Converter. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications, 8(1), 2. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea8010002




