A High-Efficiency Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting and Management Circuit Based on Full-Bridge Rectification
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Output Energy Modeling
3. Circuit Implementation
3.1. Cross-Coupled Rectifier Bridge Circuit
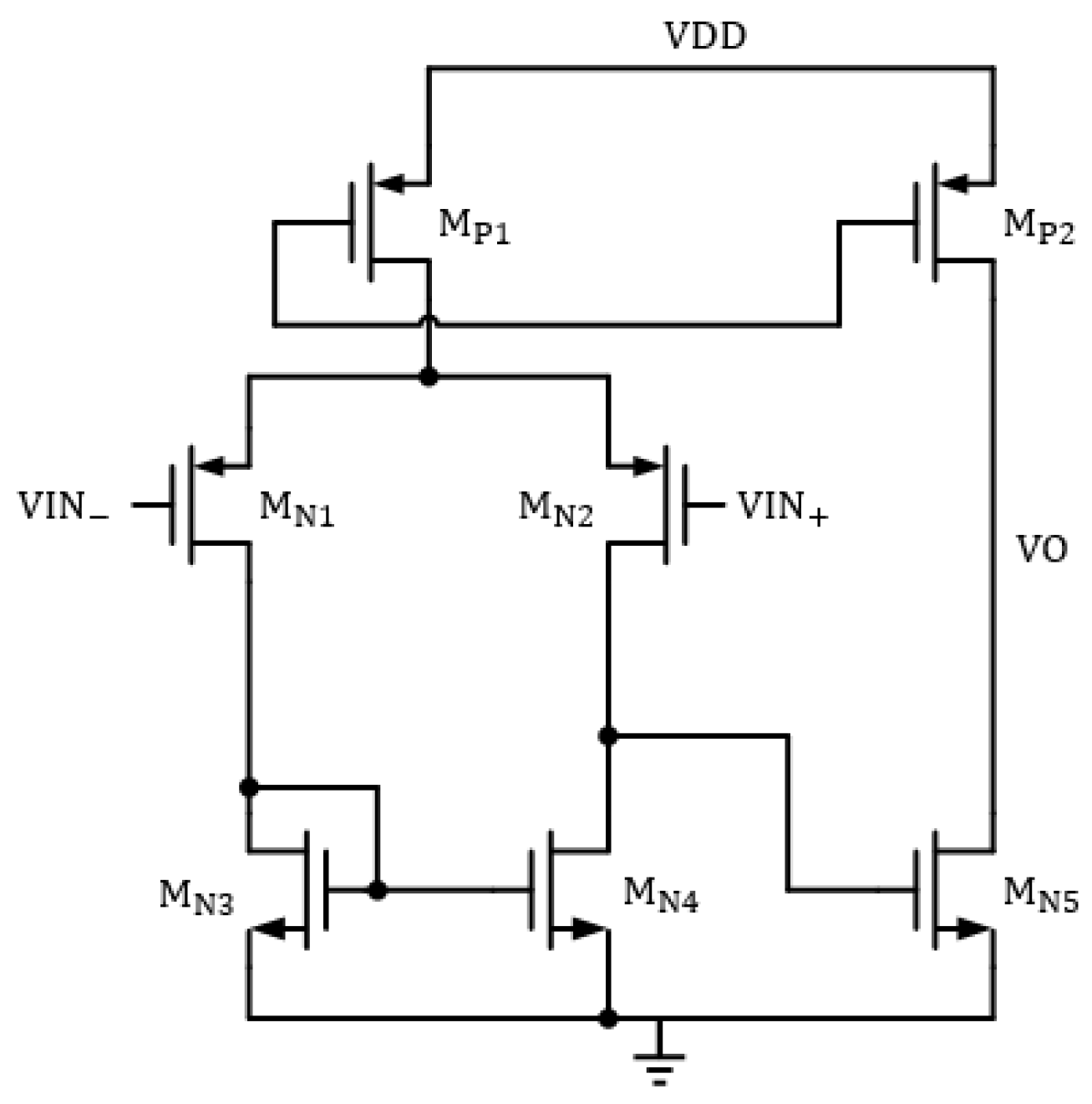
3.2. Reference Source Circuit
3.3. Energy Management Circuit
3.4. System-Level Simulation
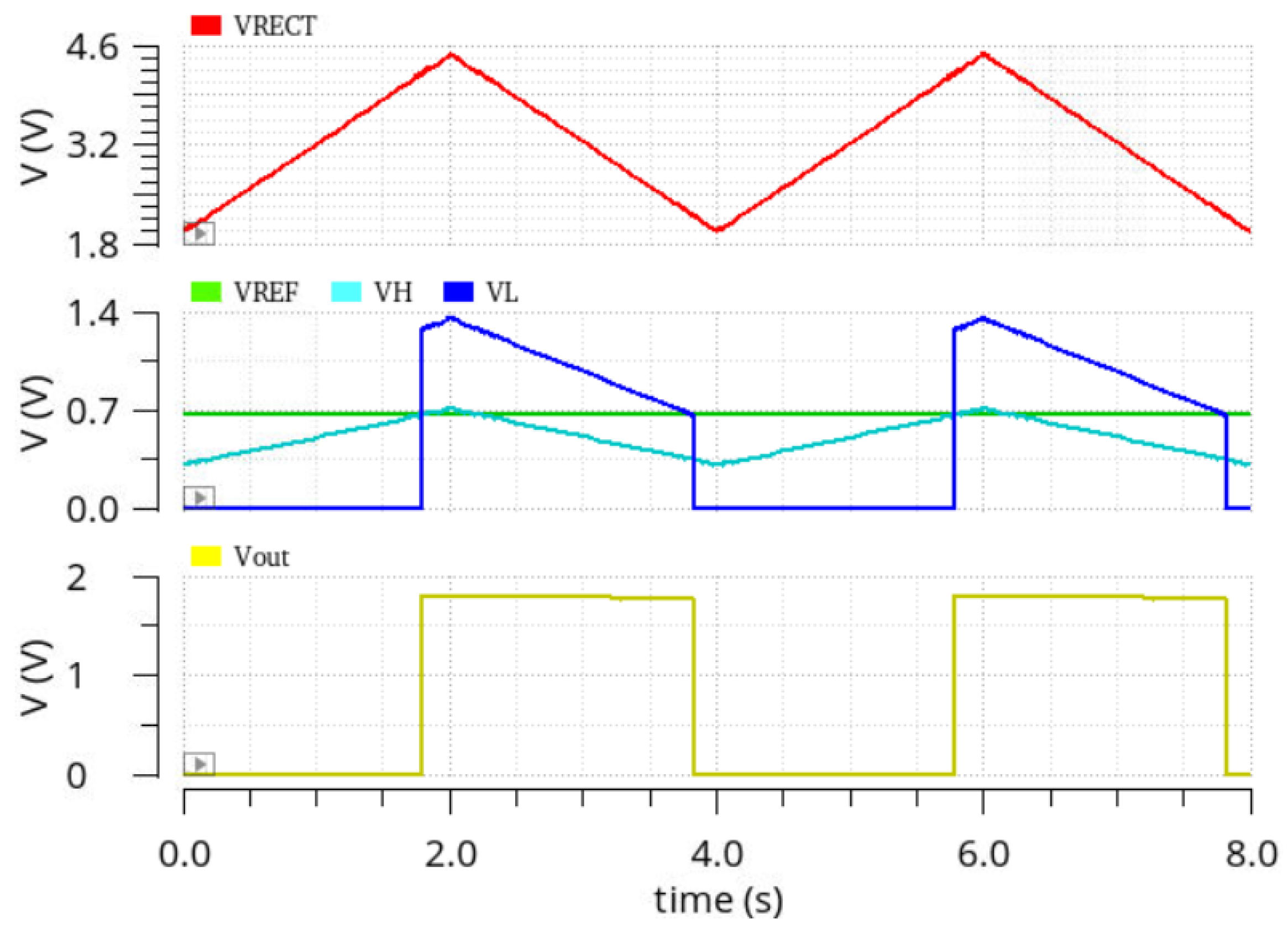
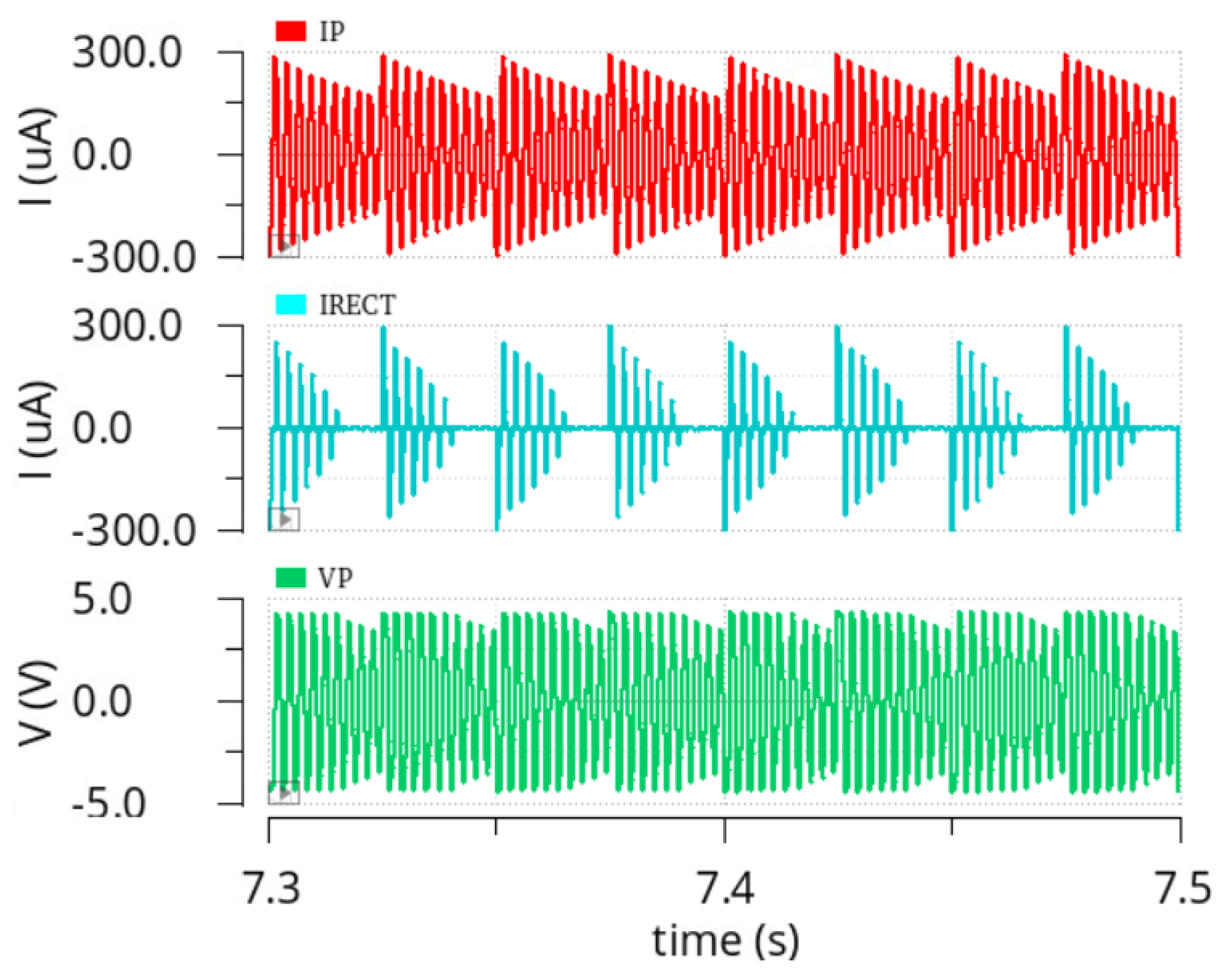
4. Measurement Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| FBR | Full-Bridge Rectifier |
| PEH | Piezoelectric Energy Harvester |
| LDO | Low Dropout Regulator |
| BGR | Bandgap Reference |
References
- Agarkhed, J.; Ankalgi, R. Energy efficient smart home monitoring system in wireless sensor network. In Proceedings of the Power and Computing Technologies (ICCPCT), 2016 International Conference on Circuit, Nagercoil, India, 18–19 March 2016; pp. 1–7. [Google Scholar]
- Ruiz-Garcia, L.; Lunadei, L.; Barreiro, P.; Robla, J.I. A Review of Wireless Sensor Technologies and Applications in Agriculture and Food Industry: State of the Art and Current Trends. Sensors 2009, 9, 4728–4750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oudenhoven, J.F.M.; Vullers, R.J.M.; Schaijk, R.V. A review of the present situation and future developments of micro-batteries for wireless autonomous sensor systems. Int. J. Energy Res. 2012, 36, 1139–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akyildiz, I.F.; Su, W.; Sankarasubramaniam, Y. Wireless sensor networks: A survey. Comput. Netw. 2002, 38, 393–422. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-Lozano, J.J.; Martín-Guzmán, M.; Martín-Ávila, J.; García-Cerezo, A. A wireless sensor network for urban traffic characterization and trend monitoring. Sensors 2015, 15, 26143–26169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulukus, S.; Yener, A.; Erkip, E.; Simeone, O.; Zorzi, M.; Grover, P.; Huang, K. Energy harvesting wireless communications: A review of recent advances. IEEE J. Sel. Areas Commun. 2015, 33, 360–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shaikh, F.K.; Zeadally, S. Energy harvesting in wireless sensor networks: A comprehensive review. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2016, 55, 1041–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roundy, S.; Steingart, D.; Frechette, L.; Wright, P.; Rabaey, J. Power sources for wireless sensor networks. In Proceedings of the European Workshop on Wireless Sensor Networks, Berlin, Germany, 19–21 January 2004; pp. 1–17. [Google Scholar]
- Sue, C.Y.; Tsai, N.C. Human powered MEMS-based energy harvest devices. Appl. Energy 2012, 93, 390–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xi, Y.; Guo, H.; Zi, Y.; Li, X.; Wang, J.; Deng, J.; Li, S.; Hu, C.; Cao, X.; Wang, Z.L. Multifunctional TENG for Blue Energy Scavenging and Self-Powered Wind-Speed Sensor. Adv. Energy Mater. 2017, 7, 1602397.1–1602397.6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradiso, J.A.; Starner, T. Energy scavenging for mobile and wireless electronics. IEEE Pervasive Comput. 2008, 4, 18–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, Y.; Wu, T.; Zeng, Y.; Yang, J.; Chen, W.; Li, Z. A 15 mV-input and 71%-efficiency boost converter with 22 mV output ripple for thermoelectric energy harvesting application. Microelectron. J. 2022, 121, 105353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harb, A. Energy harvesting: State-of-the-art. Renew. Energy 2011, 36, 2641–2654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beeby, S.P.; Tudor, M.J.; White, N.M. Energy harvesting vibration sources for microsystems applications. Meas. Sci. Technol. 2006, 17, 175–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Jasim, A.; Chen, X. Energy harvesting technologies in roadway and bridge for different applications—A comprehensive review. Appl. Energy 2018, 212, 1083–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Y.K.; Sarker, S.; Lee, K.S.; Seo, H.W.; Kim, D.M. Piezoelectric materials for high performance energy harvesting devices. In Proceedings of the Pan Pacific Microelectronics Symposium, Big Island, HI, USA, 25–28 January 2016; pp. 1–4. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, T.; Islam, S.K.; Mahfouz, M.; To, G. A Low-Power CMOS Piezoelectric Transducer Based Energy Harvesting Circuit for Wearable Sensors for Medical Applications. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2017, 7, 33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agorastou, Z.; Kalenteridis, V.; Siskos, S. A 1.02 µW Autarkic Threshold-Based Sensing and Energy Harvesting Interface Using a Single Piezoelectric Element. J. Low Power Electr. Appl. 2021, 27, 33. [Google Scholar]
- Lee, T.Z.; Liu, Y.-W. High efficiency active rectifier with low-power self-biased comparator for low-frequency piezoelectric vibration energy harvesting of AUV. Microelectron. J. 2024, 146, 156–167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, J.; Xia, Y.; Xia, H. ReL-SSHI rectifier based piezoelectric energy harvesting circuit with MPPT control technique. Microelectron. J. 2022, 121, 141–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erturk, A.; Inman, D.J. A Distributed Parameter Electromechanical Model for Cantilevered Piezoelectric Energy Harvesters. J. Vib. Acoust. 2008, 130, 1257–1261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elvin, N.G.; Elvin, A.A. A General Equivalent Circuit Model for Piezoelectric Generators. J. Intell. Mater. Syst. Struct. 2009, 20, 3–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roundy, S.; Wright, P.K. A piezoelectric vibration based generator for wireless electronics. Smart Mater. Struct. 2004, 13, 1131–1142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renaud, M.; Karakaya, K.; Sterken, T.; Fiorini, P.; Hoof, C.V.; Puers, R. Fabrication, modeling and characterization of MEMS piezoelectric vibration harvesters. Sens. Actuators A Phys. 2008, 145–146, 380–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, B.; Xie, M.; Aw, K.C.; Hu, A.P.; Gao, W. An impact based frequency up-conversion mechanism for low frequency vibration energy harvesting. In Proceedings of the Transducers and Eurosensors, Barcelona, Spain, 16–20 June 2013; pp. 1344–1347. [Google Scholar]
- Tang, Q. Micro-Energy Harvester Based on Coupling of Two-Stage Vibrational Structures; Microelectronics and Solid-State Electronics; University of Chinese Academy of Sciences: Beijing, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J. Research on High-Efficiency Energy Capture of Piezoelectric Energy Harvesters and Technologies for Self-Powered Wireless Sensor Nodes; Soochow University: Suzhou, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Niu, D.; Huang, Z.; Jiang, M.; Inoue, Y. A Sub-O.3 V CMOS Rectifier for Energy Harvesting Applications. In Proceedings of the IEEE 54th International Midwest Symposium on Circuits and Systems, Seoul, Republic of Korea, 7–10 August 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Belal, E.; Mostafa, H.; Said, M.S. Comparison between Active AC-DC Converters For Low Power Energy Harvesting Systems. In Proceedings of the 27th International Conference on Microelectronics, Casablanca, Morocco, 20–23 December 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Yeo, K.H.; Ali, S.H.M.; Menon, P.S.; Islam, M.S. Comparison of CMOS Rectifiers for Micropower Energy Harvesters. In Proceedings of the IEEE Conference on Energy Conversion (CENCON), Johor Bahru, Malaysia, 19–20 October 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Navidi, M.M.; Graham, D.W. A Low-Power Voltage Reference Cell with a 1.5 V Output. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2018, 8, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Lu, Z.; Xu, K.; Dai, H.; Wu, Z.; Yu, X. A Sub-1-V Nanopower MOS-Only Voltage Reference. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2023, 14, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, N.; Mirhassani, M. Ultra low-power negative DC voltage generator based on a proposed level shifter and voltage reference. Microelectron. J. 2021, 113, 155–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.; Huang, Y.; Luo, Y.; Tan, H.Z. An ultra-low-power CMOS voltage reference generator based on body bias technique. Microelectron. J. 2013, 44, 1145–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisi, A.; Finocchiaro, A.; Papotto, G.; Palmisano, G. Nano-power CMOS voltage reference for RF-powered systems. IEEE Trans. Circ. Syst. II Express Briefs 2018, 65, 1425–1429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadass, Y.K.; Chandrakasan, A.P. An Efficient Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting Interface Circuit Using a Bias-Flip Rectifier and Shared Inductor. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2010, 45, 189–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, L.; Do, X.-D.; Lee, S.-G.; Ha, D.S. A Self-Powered and Optimal SSHI Circuit Integrated with an Active Rectifier for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2017, 64, 537–549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, S.; Seshia, A.A. An Inductorless Bias-Flip Rectifier for Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 2746–2757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
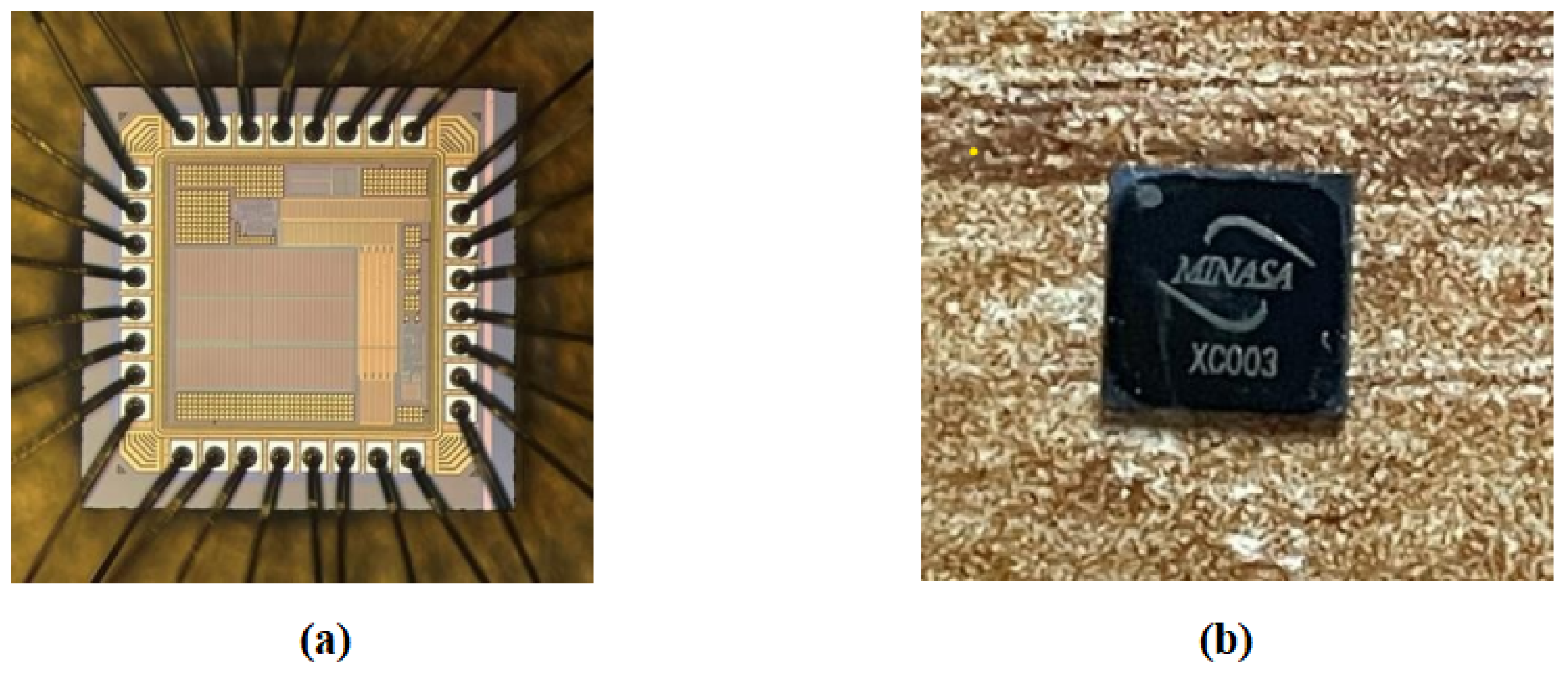

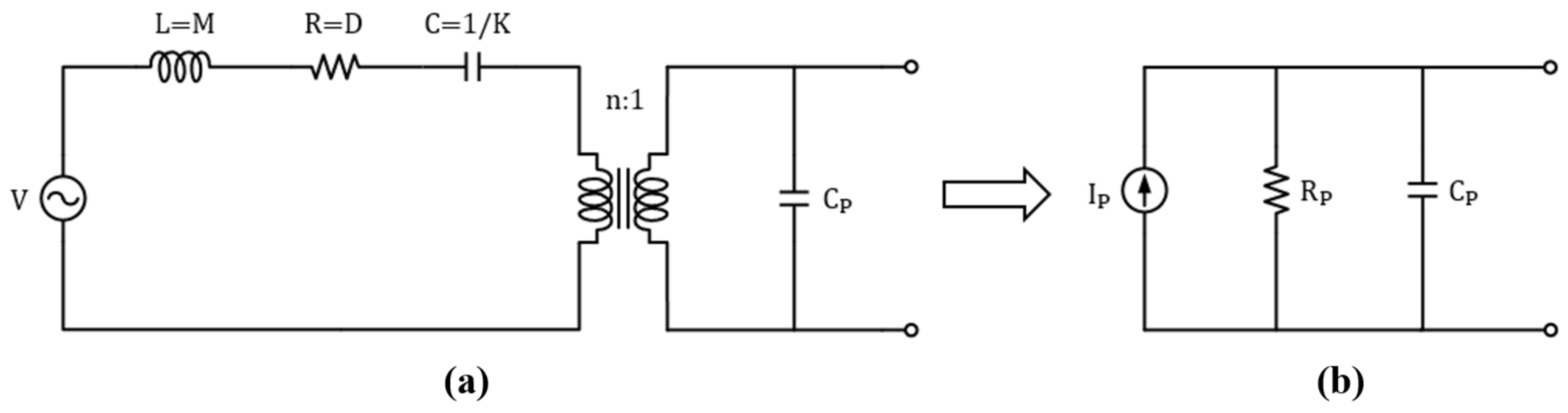


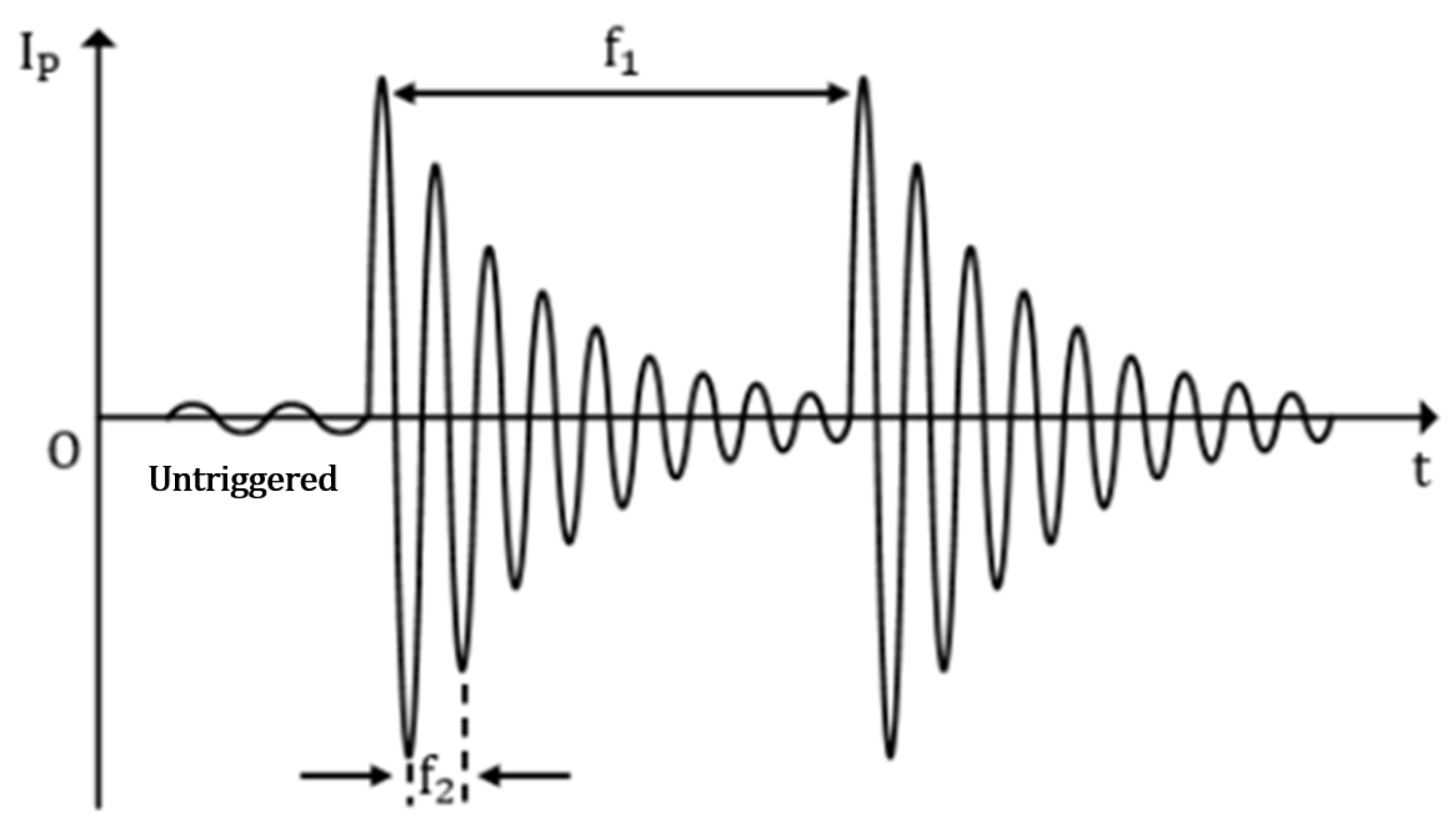
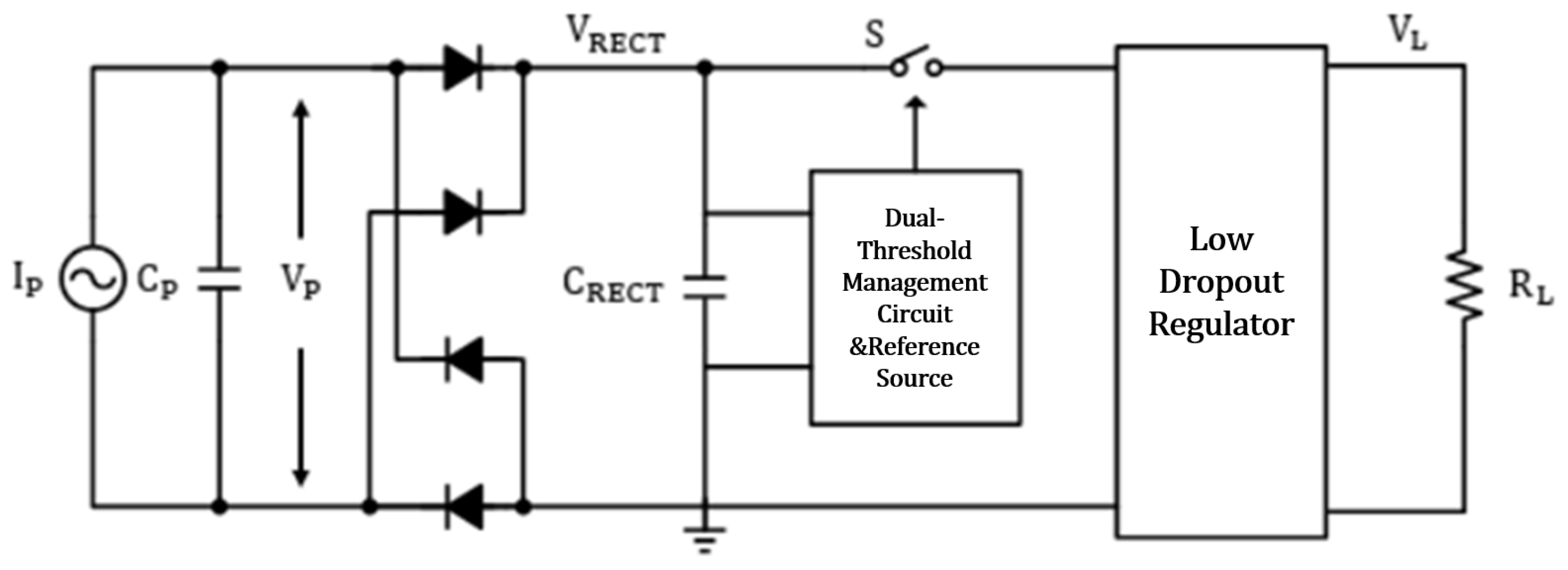
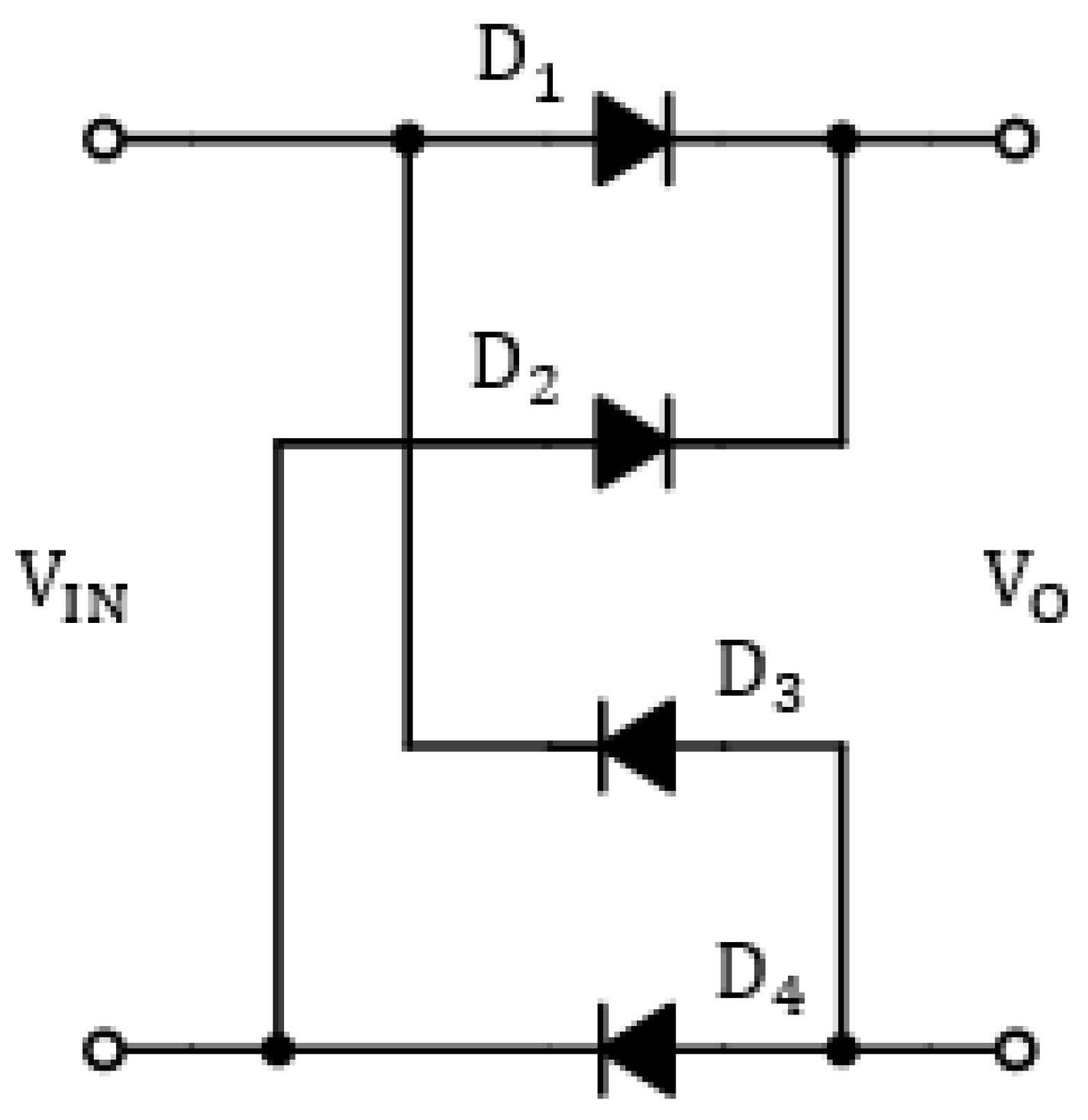
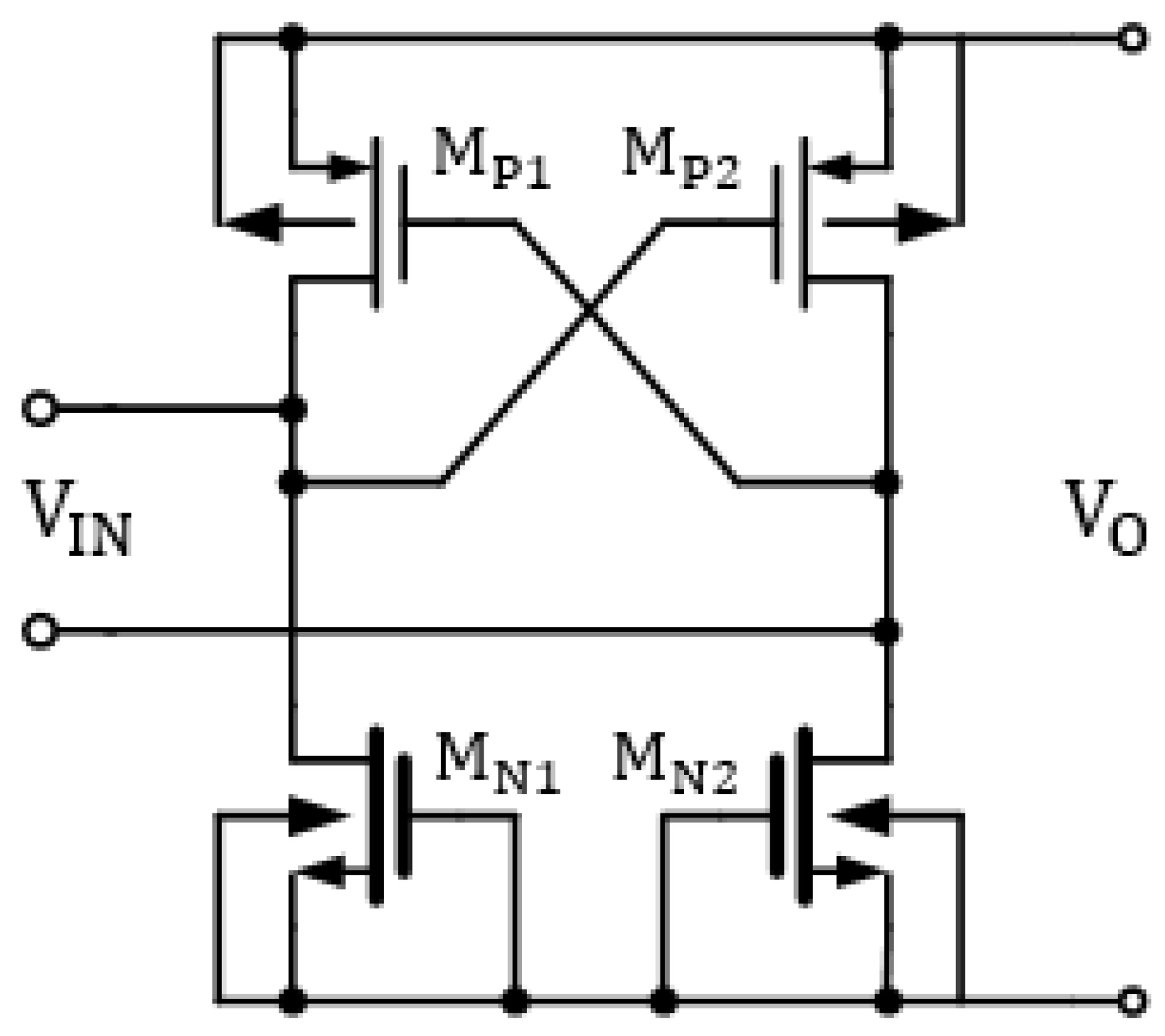

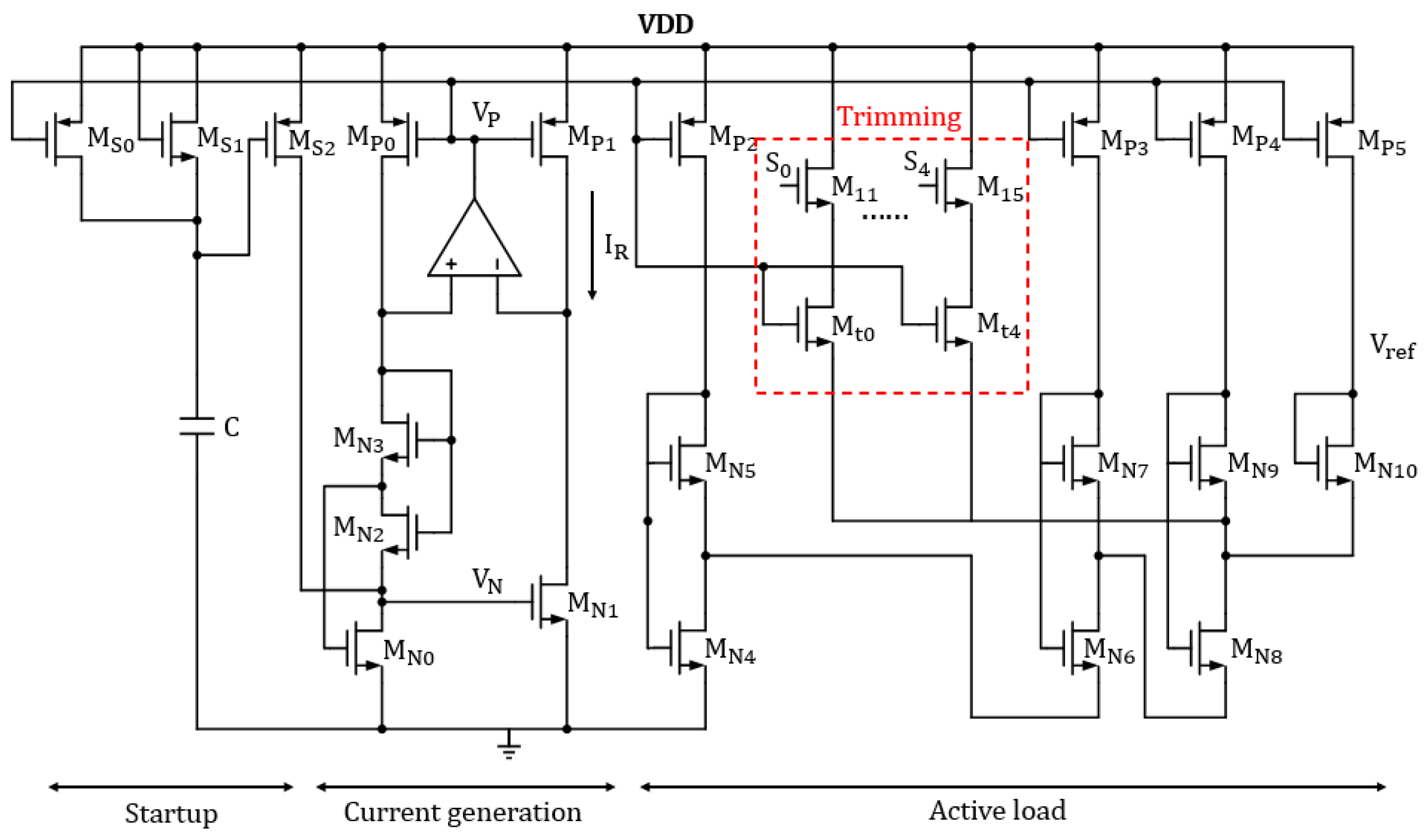
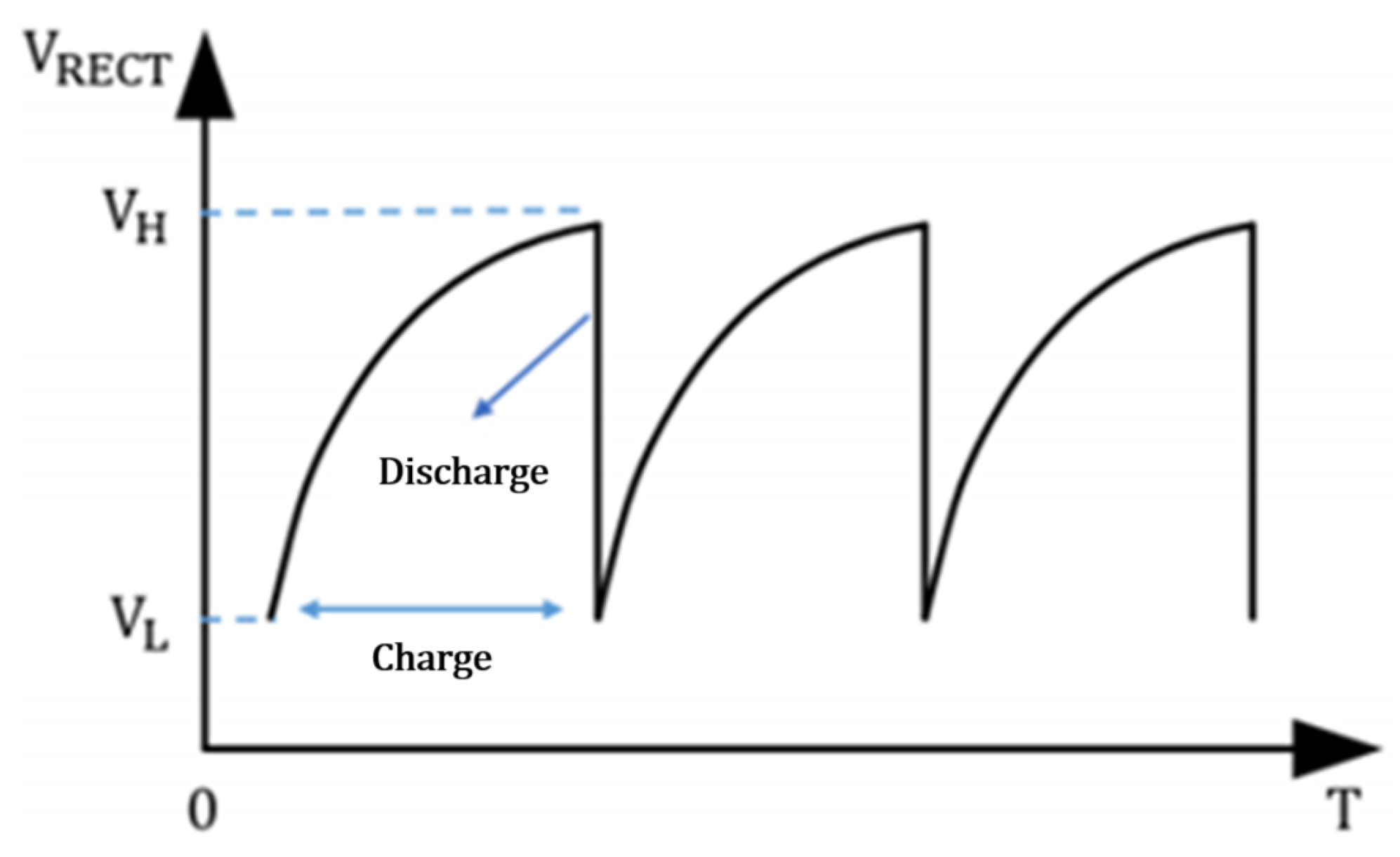
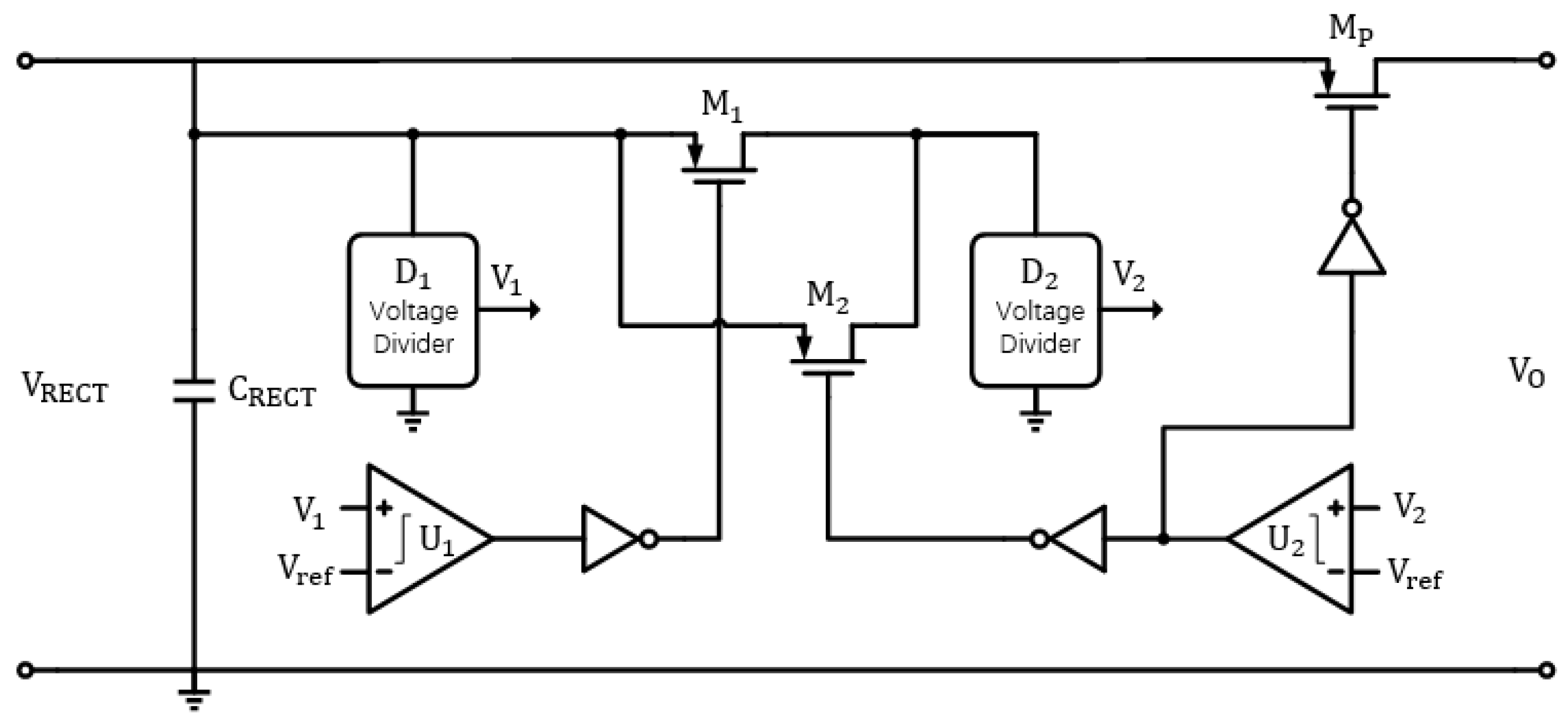






| Parameter | Symbol | Value |
|---|---|---|
| Two-stage vibrator spacing | G | 0.8 mm |
| Base thickness of beryllium bronze sheet | 100.0 m | |
| PZT thickness | 60.0 m | |
| PZT length | 5.0 mm | |
| Low-frequency-induced vibrator length | 12.5 mm | |
| High-frequency power generation vibrator length | 11.0 mm | |
| Low-frequency-induced vibrator width | 8.0 mm | |
| High-frequency power generation vibrator width | 4.5 mm | |
| Piezoelectric coupling coefficient | −5.0 × 10 m/V | |
| PZT dielectric constant | 4500 | |
| Magnetic residual magnetic | 950.0 | |
| Quality block quality | 350.0 |
| Ref. | [36] | [37] | [38] | This Work |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Year | 2010 | 2017 | 2017 | 2024 |
| Process | 0.35 m | 0.25 m | 0.35 m | 0.11 m |
| Structure | FBR | SSHI | SSHC | FBR |
| Parasitic Capacitance | 12 nF | 19 nF | 45 nF | 20 nF |
| Vibration Frequency | 225 Hz | 144 Hz | 92 Hz | 400 Hz |
| Presence of Maximum Power Point | No | No | No | No |
| Power Consumption | <2 W | 11.5 W | ≈1.7 W | <1 W |
| Energy Extraction Power | 32.5 W | 136 W | 161.8 W | 234 W |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Liu, S.; Chen, S.; Gao, W.; Zhang, J.; Xu, D.; Chen, F.; Lu, Z.; Yu, X. A High-Efficiency Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting and Management Circuit Based on Full-Bridge Rectification. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2024, 14, 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea14040049
Liu S, Chen S, Gao W, Zhang J, Xu D, Chen F, Lu Z, Yu X. A High-Efficiency Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting and Management Circuit Based on Full-Bridge Rectification. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications. 2024; 14(4):49. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea14040049
Chicago/Turabian StyleLiu, Shuhan, Suhao Chen, Wei Gao, Jiabin Zhang, Dacheng Xu, Fang Chen, Zhenghao Lu, and Xiaopeng Yu. 2024. "A High-Efficiency Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting and Management Circuit Based on Full-Bridge Rectification" Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications 14, no. 4: 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea14040049
APA StyleLiu, S., Chen, S., Gao, W., Zhang, J., Xu, D., Chen, F., Lu, Z., & Yu, X. (2024). A High-Efficiency Piezoelectric Energy Harvesting and Management Circuit Based on Full-Bridge Rectification. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications, 14(4), 49. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea14040049









