An Ultra Low Power Integer-N PLL with a High-Gain Sampling Phase Detector for IOT Applications in 65 nm CMOS
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Exploring a 1.2 GHz INPLL Design with High-Gain LSPD
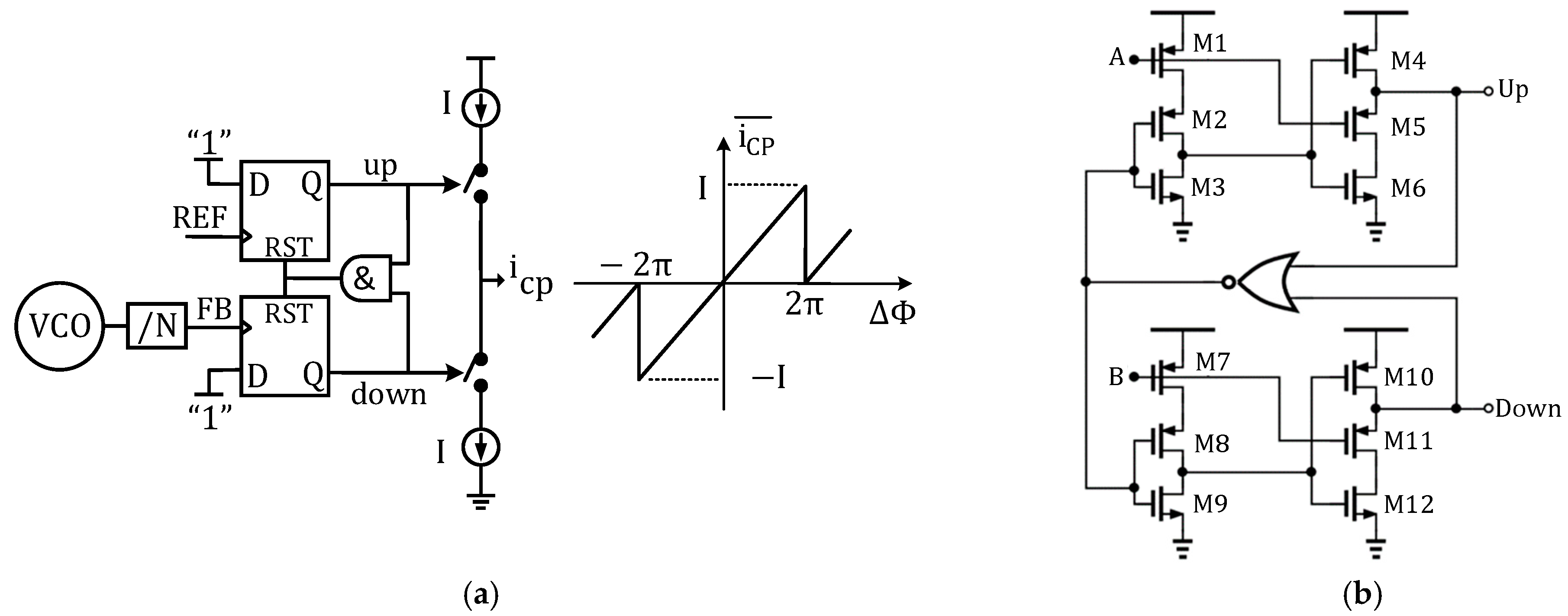
2.1. Constraints of Traditional PFD-CP PLL
2.2. Noise Contributions in Conventional PFD-CP PLL
3. Design of the Proposed PLL Utilizing LSPD
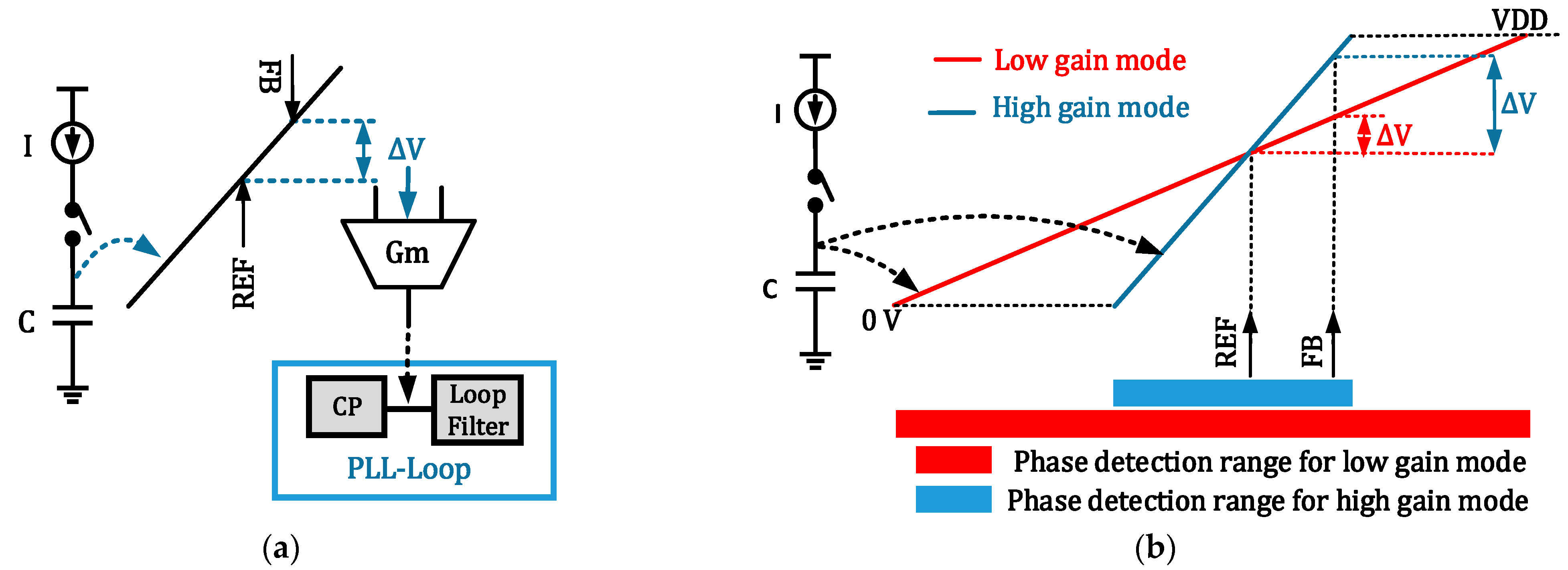
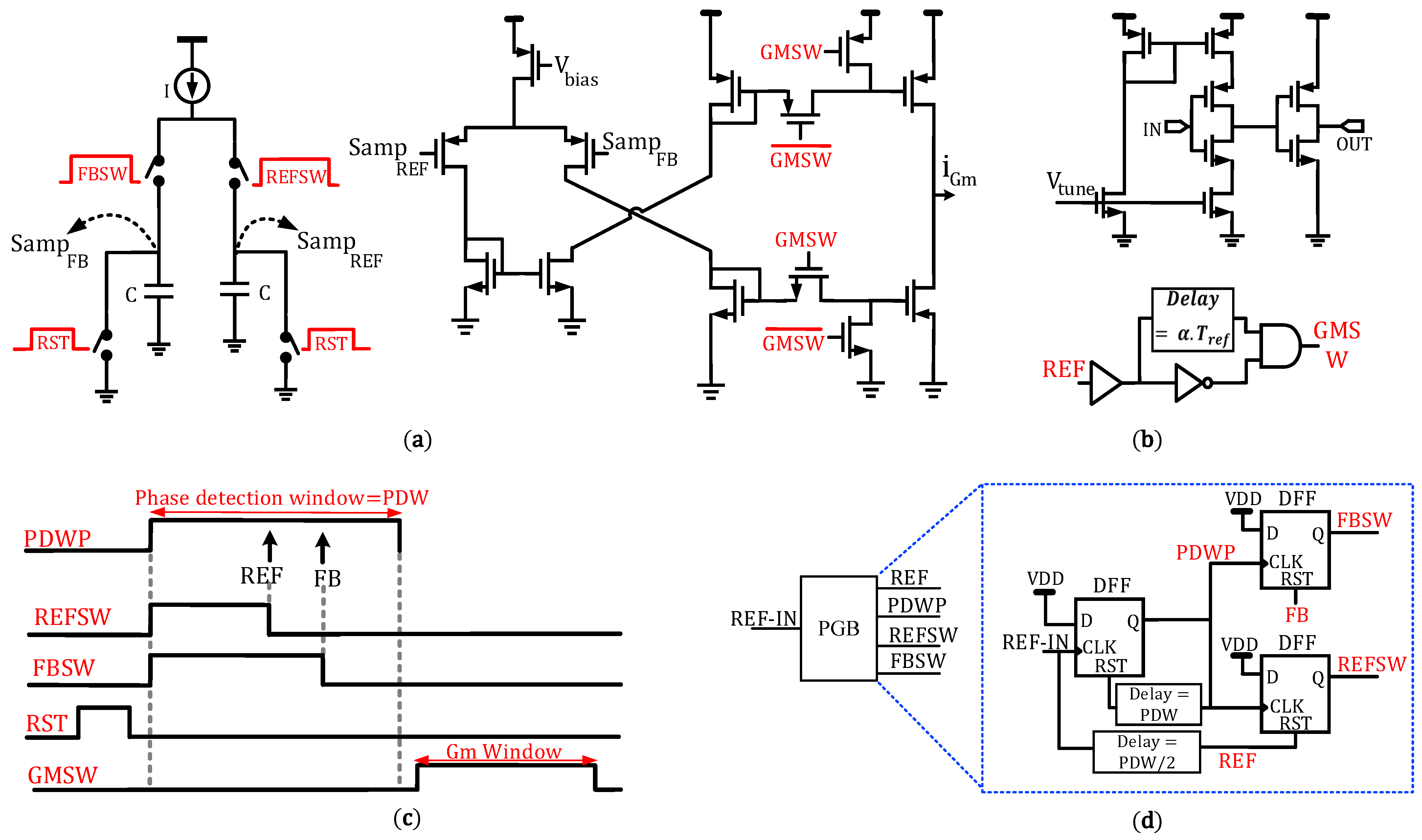
3.1. Proposed High-Gain LSPD
3.2. Proposed Sampling Integer-N PLL
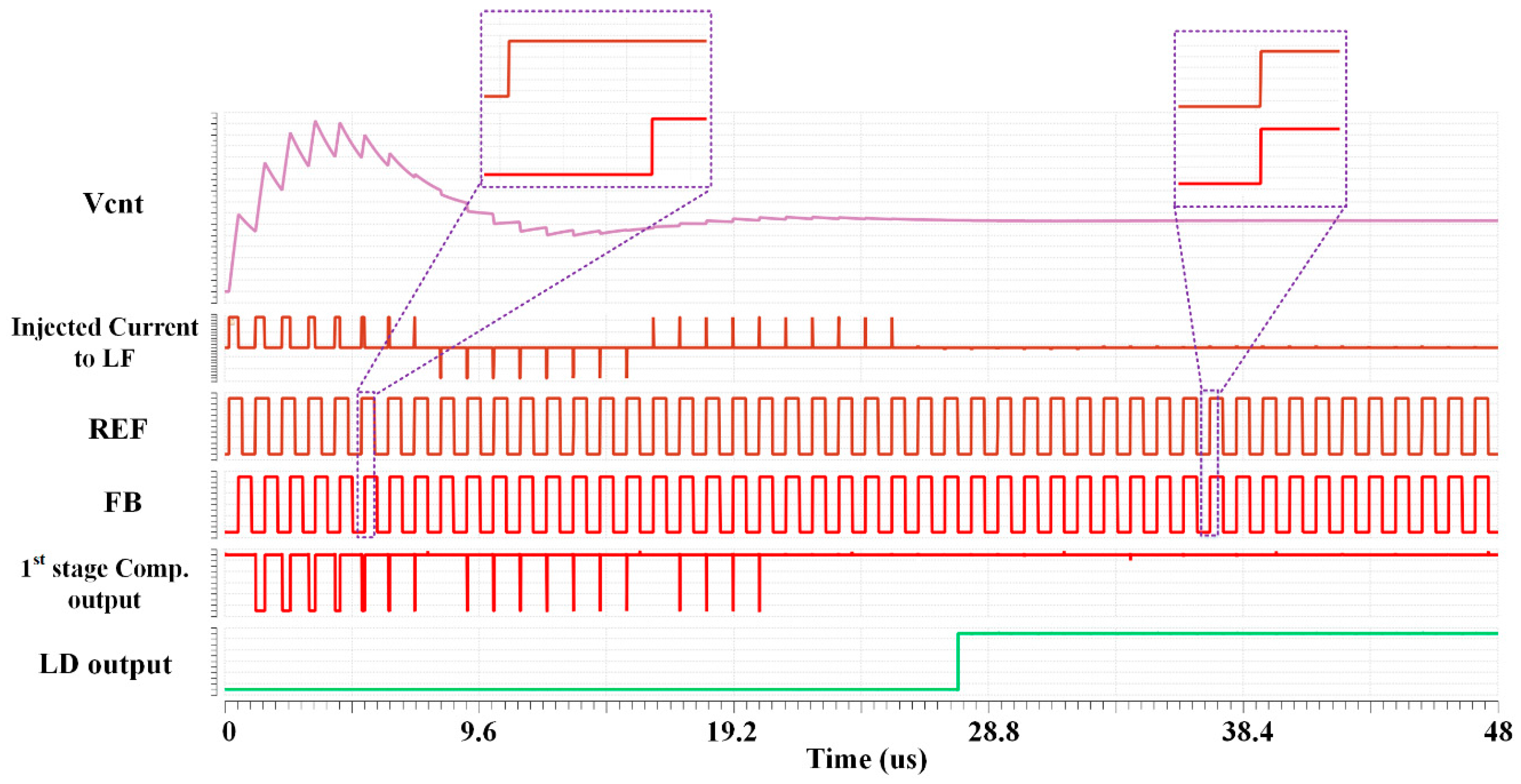
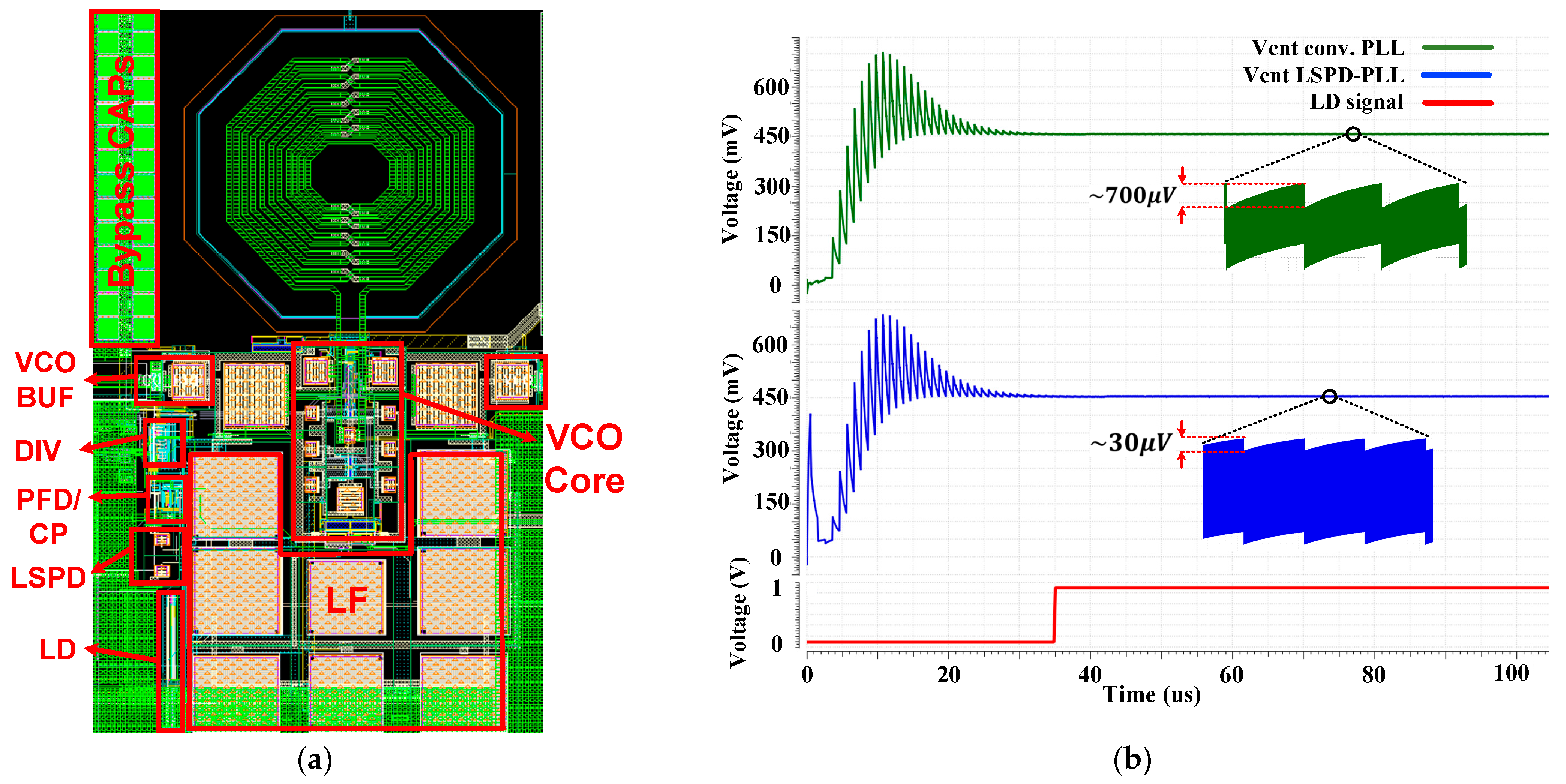
3.3. Lock Detector (LD) Block
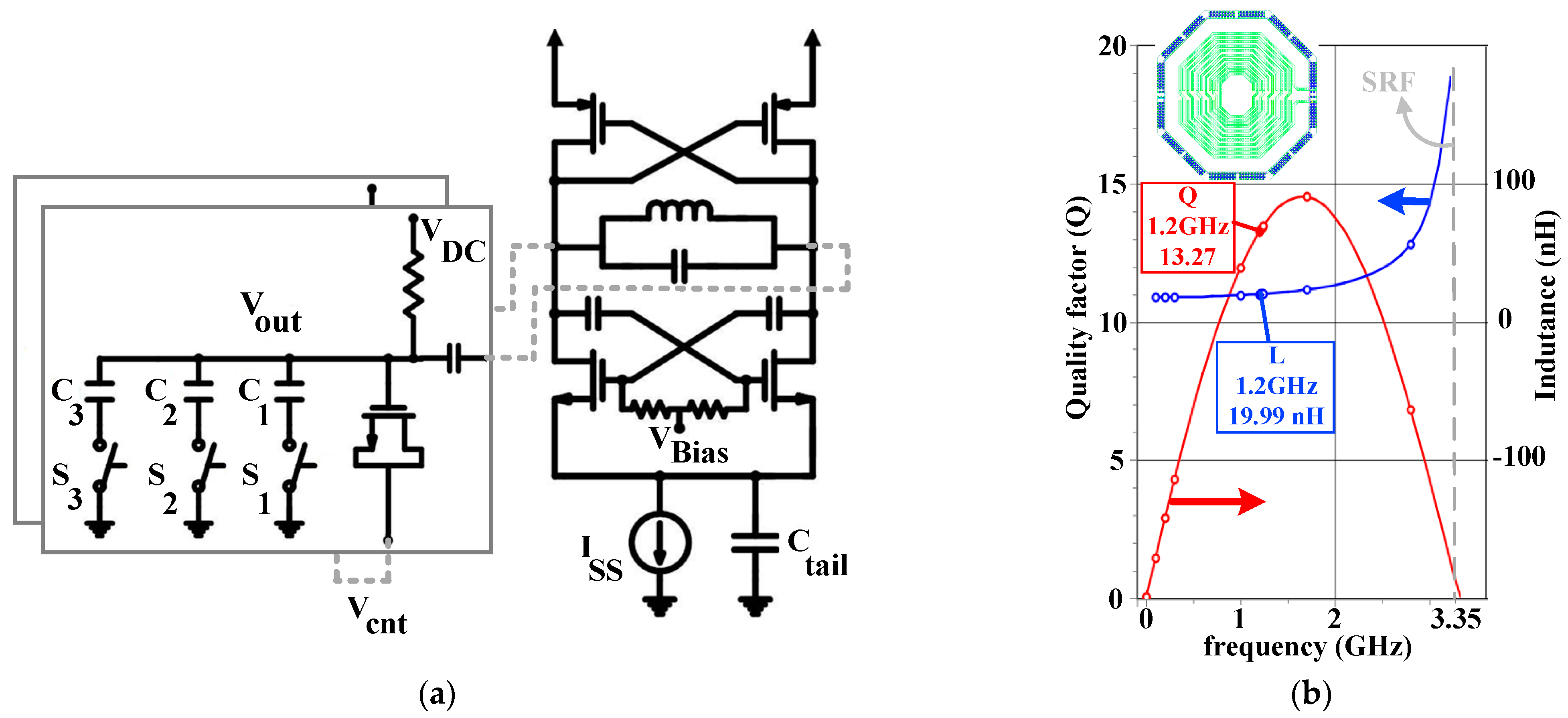
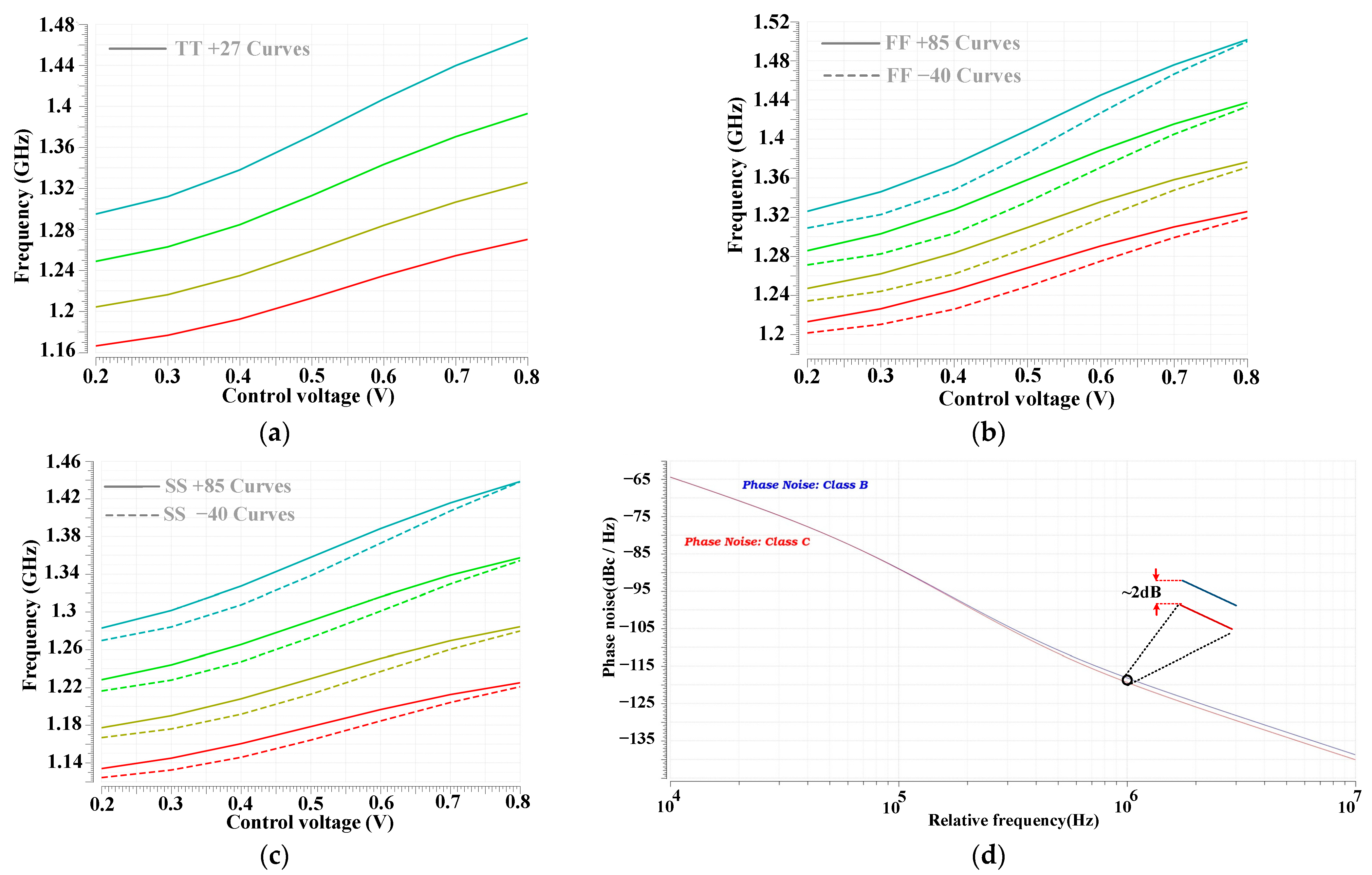
3.4. Low-Power Class-C CMOS LC VCO
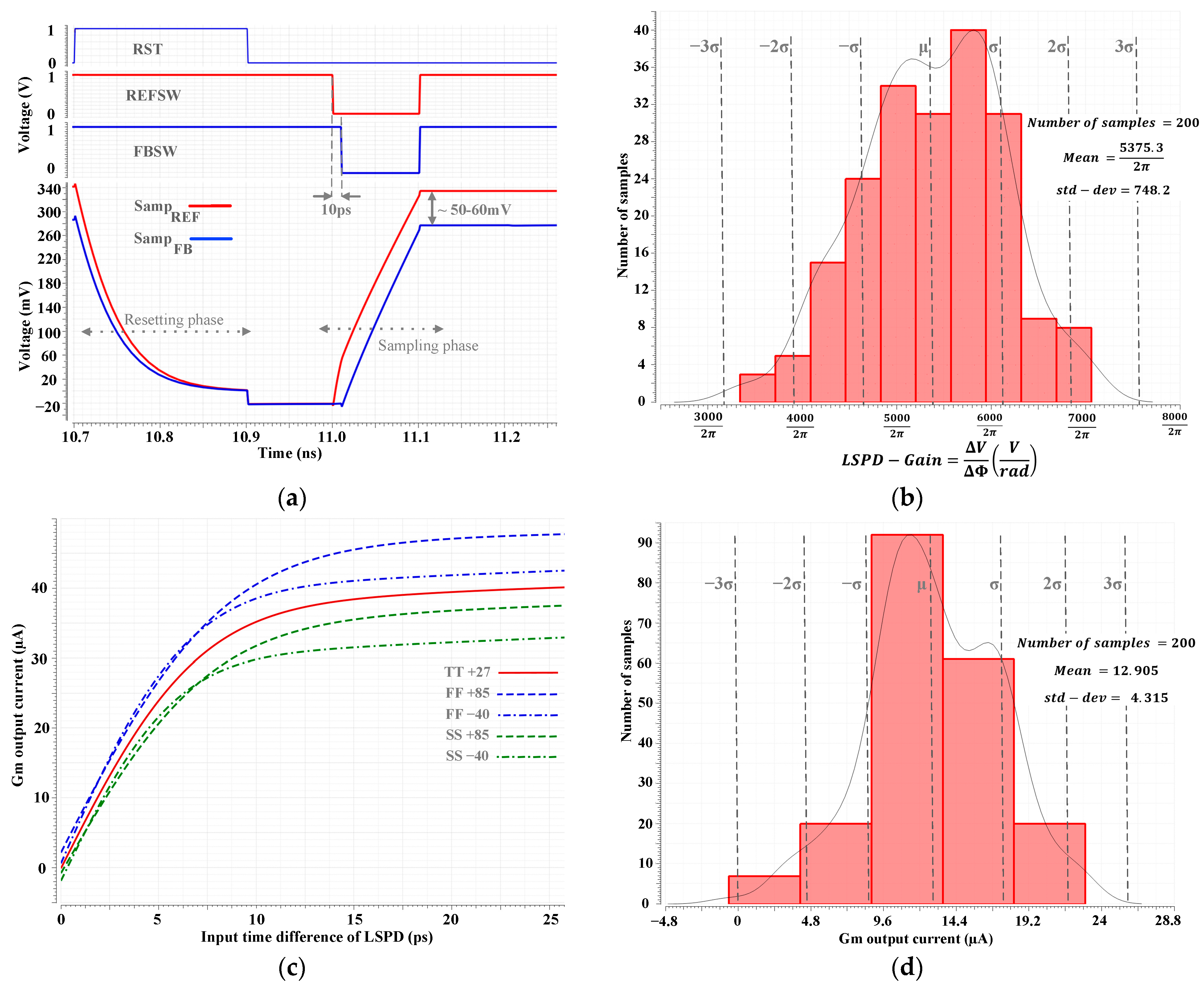
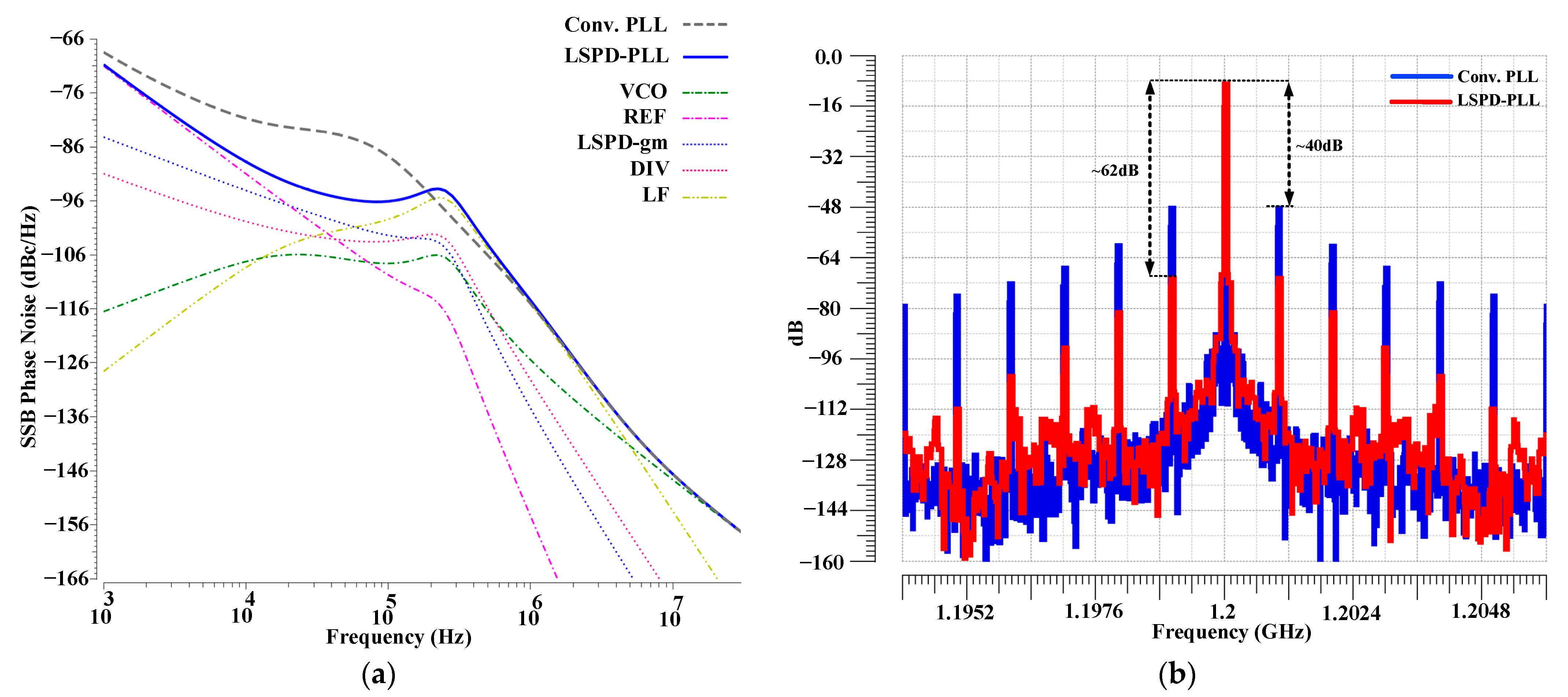
4. INPLL Simulation Results
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gao, X.; Klumperink, E.A.M.; Bohsali, M.; Nauta, B. A 2.2 GHz 7.6 mW sub-sampling PLL with −126 dBc/Hz in-band phase noise and 0.15 psrms jitter in 0.18 µm CMOS. In Proceedings of the 2009 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference-Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 8–12 February 2009; pp. 392–394. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Klumperink, E.; Nauta, B. Sub-sampling PLL techniques. In Proceedings of the 2015 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), San Jose, CA, USA, 28–30 September 2015; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, D.G.; Mercier, P.P. A Sub-mW 2.4-GHz Active-Mixer-Adopted Sub-Sampling PLL Achieving an FoM of −256 dB. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2020, 55, 1542–1552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, J.; Krishnaswamy, H. A 2.4-GHz Reference-Sampling Phase-Locked Loop That Simultaneously Achieves Low-Noise and Low-Spur Performance. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2019, 54, 1407–1424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Memioglu, O.; Razavi, B. A 56GHz 23mW Fractional-N PLL with 110fs Jitter. In Proceedings of the 2022 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 20–26 February 2022; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2022; pp. 288–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkholy, A.; Talegaonkar, M.; Anand, T.; Kumar Hanumolu, P. Design and Analysis of Low-Power High-Frequency Robust Sub-Harmonic Injection-Locked Clock Multipliers. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2015, 50, 3160–3174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Mak, P.I.; Martins, R.P. A 3.78-GHz Type-I Sampling PLL With a Fully Passive KPD-Doubled Primary-Secondary S-PD Measuring 39.6-fsRMSJitter, −260.2-dB FOM, and −70.96-dBc Reference Spur. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2023, 70, 1463–1475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Zhao, B.; Mak, P.I.; Martins, R.P. A 3.6-GHz Type-II Sampling PLL With a Differential Parallel-Series Double-Edge S-PD Scoring 43.1-fsRMSJitter, −258.7-dB FOM, and −75.17-dBc Reference Spur. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2023, 31, 188–198. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yang, S.; Mak, P.I.; Martins, R.P. 16.8 A 25.4-to-29.5GHz 10.2 mW Isolated Sub-Sampling PLL Achieving −252.9 dB Jitter-Power FoM and −63dBc Reference Spur. In Proceedings of the 2019 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—(ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 17–21 February 2019; pp. 270–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Chen, Y.; Yuan, J.; Mak, P.I.; Martins, R.P. A 3.3-GHz Integer N-Type-II Sub-Sampling PLL Using a BFSK-Suppressed Push-Pull SS-PD and a Fast-Locking FLL Achieving −82.2-dBc REF Spur and −255-dB FOM. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2022, 30, 238–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagam, S.S.; Kinget, P.R. A Low-Jitter Ring-Oscillator Phase-Locked Loop Using Feedforward Noise Cancellation with a Sub-Sampling Phase Detector. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2018, 53, 703–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, B.D.; Shrimali, H. Design and implementation of a second order PLL based frequency synthesizer for implantable medical devices. Integration 2022, 86, 57–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kong, L.; Razavi, B. A 2.4-GHz 6.4-mW Fractional-N Inductorless RF Synthesizer. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2017, 52, 2117–2127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, J.; Krishnaswamy, H. A 0.0049mm2 2.3GHz sub-sampling ring-oscillator PLL with time-based loop filter achieving -236.2dB jitter-FOM. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2017; Volume 60, pp. 328–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Liu, Y.H.; Kuramochi, T.; van den Heuvel, J.; Busze, B.; Markulic, N.; Bachmann, C.; Philips, K. A 673 µW 1.8-to-2.5 GHz dividerless fractional-N digital PLL with an inherent frequency-capture capability and a phase-dithering spur mitigation for IoT applications. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference (ISSCC), San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–9 February 2017; Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers Inc.: New York, NY, USA, 2017; Volume 60, pp. 420–421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Ma, R.; Liu, S.; Ding, Z.; Zhang, P.; Zhu, Z. A 5-GHz Low-Power Low-Noise Integer-N Digital Subsampling PLL with SAR ADC PD. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2018, 66, 4078–4087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsu, C.W.; Tripurari, K.; Yu, S.A.; Kinget, P.R. A sub-sampling-assisted phase-frequency detector for low-noise plls with robust operation under supply interference. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2015, 62, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaidioz, D.; Cathelin, A.; Deval, Y. 28-nm FD-SOI CMOS Submilliwatt Ring Oscillator-Based Dual-Loop Integer-N PLL for 2.4-GHz Internet-of-Things Applications. IEEE Trans. Microw. Theory Tech. 2022, 70, 2207–2216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Yi, T. High Performance Injection-Locked PLL Architectures: An Overview. In Proceedings of the 2022 7th International Conference on Integrated Circuits and Microsystems (ICICM), Xi’an, China, 28–31 October 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tavakoli, J.; Yaghobi, H.; Sheikhaei, S. A 1.2 GHz adaptive bandwidth type-I PLL using a digital lock detector. In Proceedings of the 2020 28th Iranian Conference on Electrical Engineering (ICEE), Tabriz, Iran, 4–6 August 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Homayoun, A.; Razavi, B. Analysis of phase noise in phase/frequency detectors. IEEE Trans. Circuits Syst. I Regul. Pap. 2013, 60, 529–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Razavi, B. RF Microelectronics; Prentice Hall: New York, NY, USA, 2012; Available online: https://www.pearson.com/en-us/subject-catalog/p/rf-microelectronics/P200000000562/9780132901055?tab=table-of-contents (accessed on 14 December 2023).
- Razavi, B. Design of CMOS Phase-Locked Loops; Cambridge University Press: Cambridge, UK, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levantino, S.; Romanò, L.; Pellerano, S.; Samori, C.; Lacaita, A.L. Phase noise in digital frequency dividers. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2004, 39, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, A.; Andreani, P. A 1.4mW 4.90-to-5.65GHz class-C CMOS VCO with an average FoM of 194.5 dBc/Hz. In Proceedings of the 2008 IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference—Digest of Technical Papers, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–7 February 2008; Volume 51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lacaita, N.; Bassi, M.; Mazzanti, A.; Svelto, F. A K-Band low-noise bipolar Class-C VCO for 5G backhaul systems in 55 nm BiCMOS technology. In Proceedings of the 2017 IEEE Bipolar/BiCMOS Circuits and Technology Meeting (BCTM), Miami, FL, USA, 19–21 October 2017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lohrabi Pour, F.; Hong, S.K.; Ha, D.S. A Temperature-Compensated Class-C Oscillator with an Adaptive Automatic Amplitude Controller in 180-nm CMOS. IEEE Microw. Wirel. Technol. Lett. 2023, 33, 567–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hajimiri, A.; Lee, T.H. A general theory of phase noise in electrical oscillators. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 1998, 33, 179–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, A.; Andreani, P. Class-C harmonic CMOS VCOs, with a general result on phase noise. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2008, 43, 2716–2729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazzanti, A.; Andreani, P. A push-pull class-C CMOS VCO. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2013, 48, 724–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masnadi, A.; Mahani, M.; Lavasani, H.M.; Mirabbasi, S.; Shekhar, S.; Zavari, R.; Djahanshahi, H. A Compact Dual-Core 26.1-to-29.9 GHz Coupled-CMOS LC-VCO with Implicit Common-Mode Resonance and FoM of-191 dBc/Hz at 10 MHz. In Proceedings of the 2020 IEEE Custom Integrated Circuits Conference (CICC), Boston, MA, USA, 22–25 March 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




| Corner & Temp. | Supply (V) | Power Consumption | Output Swing (mV) | Phase Noise @ 1 MHz (dBc/Hz) | Phase Noise @ 3 MHz (dBc/Hz) | FOM @ 3 MHz (dB) | (MHz/V) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| TT, 27 | 1 | 150.1 | 380 | −119.6 | −129.5 | 189.7 | 153 |
| 1.05 | 152.4 | 383 | −120.4 | −129.6 | 189.8 | 155.1 | |
| 0.95 | 147.5 | 375 | −117.1 | −125 | 185.3 | 144 | |
| FF, 85 | 1 | 150.5 | 300 | −117.5 | −127.4 | 187.6 | 129 |
| 1.05 | 152.9 | 303 | −118.2 | −127.6 | 187.7 | 131 | |
| 0.95 | 148.1 | 296.5 | −114.8 | −123 | 183.3 | 122.5 | |
| FF, −40 | 1 | 150.1 | 343 | −122 | −131.8 | 192 | 150 |
| 1.05 | 152.5 | 346.5 | −122.7 | −131.9 | 192 | 152 | |
| 0.95 | 147.4 | 339 | −119.7 | −127 | 187.3 | 142 | |
| SS, 85 | 1 | 151 | 348 | −119.1 | −128.8 | 189 | 155 |
| 1.05 | 153.4 | 351.5 | −117.3 | −127.3 | 187.5 | 157 | |
| 0.95 | 148.6 | 344 | −115.4 | −126.9 | 187.5 | 146.5 | |
| SS, −40 | 1 | 151.5 | 412 | −123 | −131.8 | 192 | 181 |
| 1.05 | 154 | 416 | −121 | −130.2 | 190.4 | 183.5 | |
| 0.95 | 149 | 407.5 | −119.2 | −129.7 | 190 | 171 |
| This Work | [11] | [12] | [13] | [14] | [3] | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PLL topology (INPLLs) | Analog | Sub-sampling | Analog | Type-I Analog | Sub-sampling | Sub-sampling |
| Phase detection method | LSPD | SSPD | Conv. PFD-CP | XOR-PD & MSSF-LF | SSPD | SSPD |
| Technology | 65 nm | 65 nm | 130 nm | 45 nm | 65 nm | 65 nm |
| Supply voltage (V) | 1 | 0.935 | 1.2 | 1 | 1.2 | 1 |
| Ref. Frequency (MHz) | 1 | 49.15 | 8.66 | 22.6 | 192 | 100 |
| Output frequency (GHz) | 1.18–1.43 | 2.4 | 1.8 | 2.4 | 2.3 | 2.4 |
| Power dissipation | 350 | 5860 | 740 | 4000 | 4600 | 900 |
| IPN (dBc) (10 kHz to 10 MHz) | −37 | −44 | −18 | −39.6 | −42 | −55 |
| Rms Jitter (ps) | 2.9 | 0.63 | 15.97 | 0.97 | 0.72 | 0.161 |
| Reference spur (dBc) | −62 | −55.2 | −52 | −65 | −37 | −67 |
| Channel Selection | Y | N | N | N | N | N |
| [31] | −236.25 | −236.3 | −217.24 | −234.1 | −236 | −256 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Tavakoli, J.; Lavasani, H.M.; Sheikhaei, S. An Ultra Low Power Integer-N PLL with a High-Gain Sampling Phase Detector for IOT Applications in 65 nm CMOS. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2023, 13, 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea13040065
Tavakoli J, Lavasani HM, Sheikhaei S. An Ultra Low Power Integer-N PLL with a High-Gain Sampling Phase Detector for IOT Applications in 65 nm CMOS. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications. 2023; 13(4):65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea13040065
Chicago/Turabian StyleTavakoli, Javad, Hossein Miri Lavasani, and Samad Sheikhaei. 2023. "An Ultra Low Power Integer-N PLL with a High-Gain Sampling Phase Detector for IOT Applications in 65 nm CMOS" Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications 13, no. 4: 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea13040065
APA StyleTavakoli, J., Lavasani, H. M., & Sheikhaei, S. (2023). An Ultra Low Power Integer-N PLL with a High-Gain Sampling Phase Detector for IOT Applications in 65 nm CMOS. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications, 13(4), 65. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea13040065






