Low Power Clock Network Design
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Skew Mitigation Techniques
2.1. Skew and Power—Definitions and Background
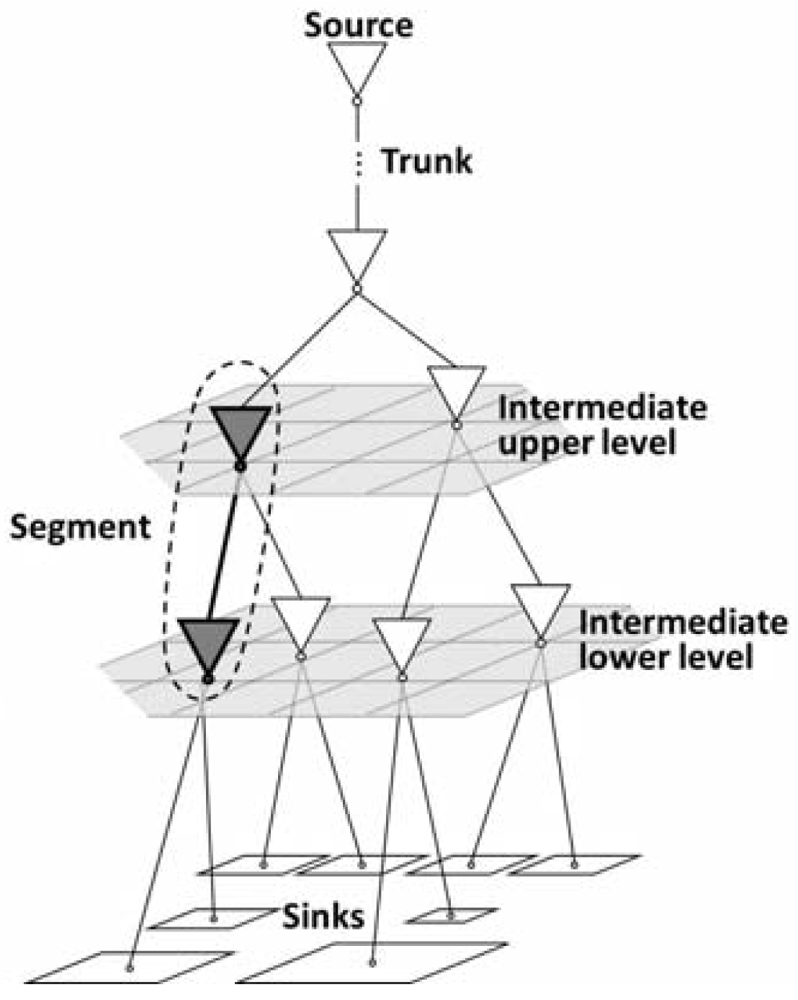
2.2. Clock Tree Topology
2.3. Mesh-Based Clock Topology
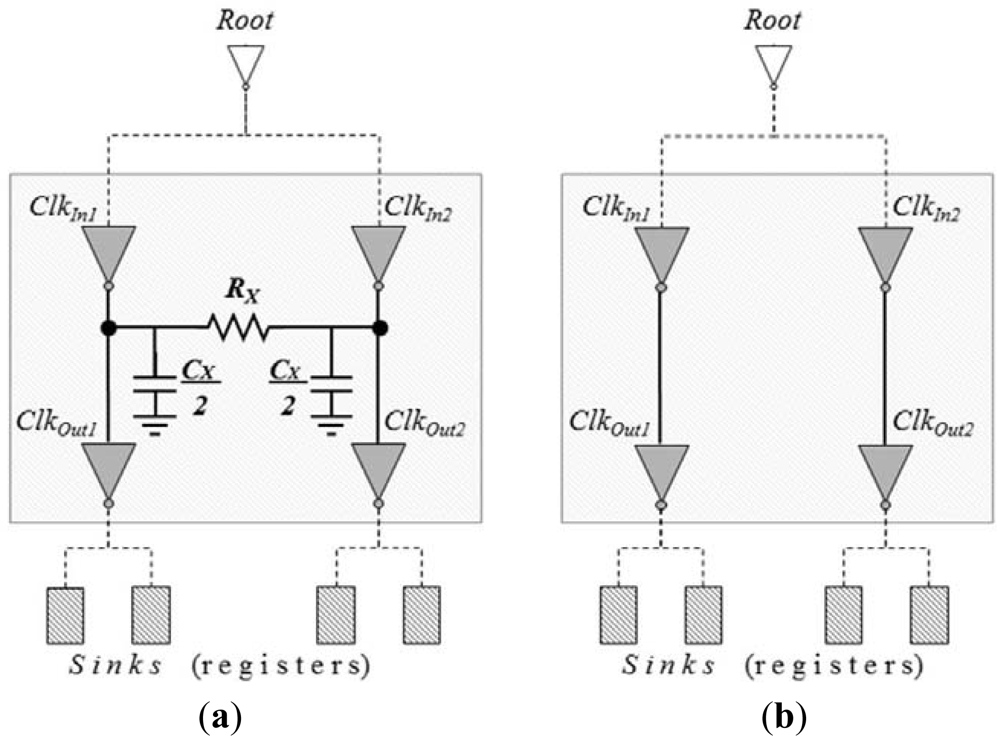
2.4. Crosslink-Based Clock Topology
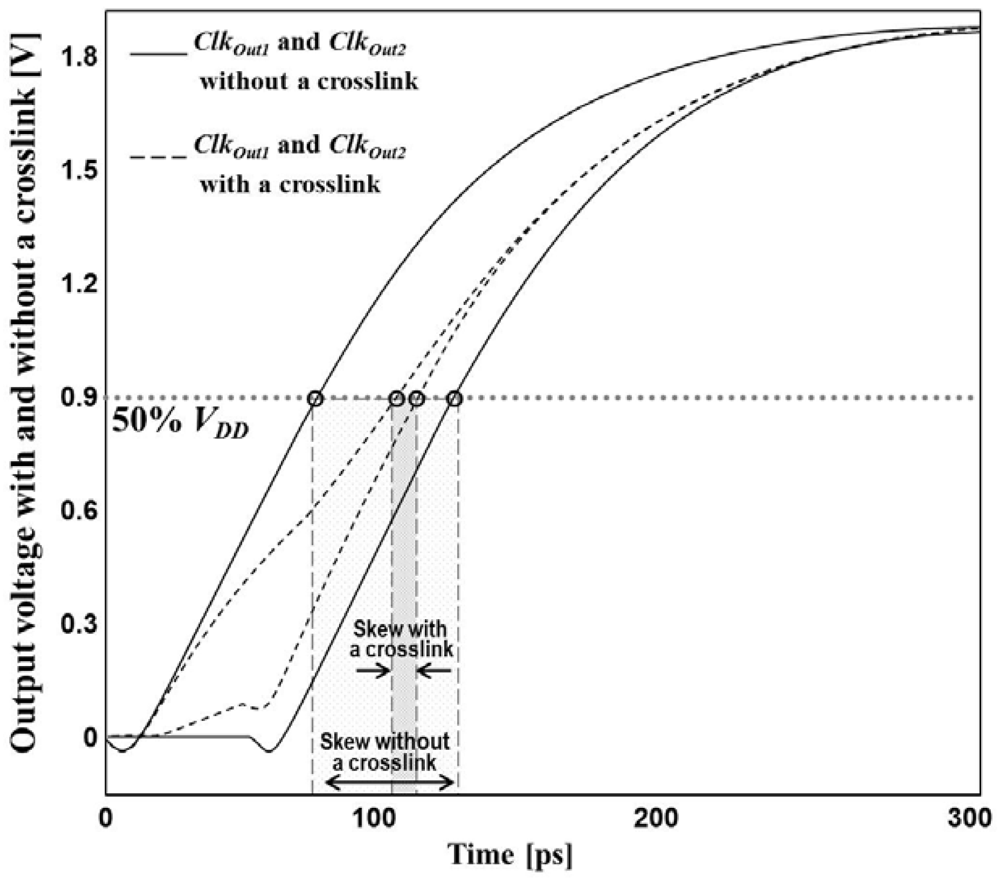
2.4.1. Power and Skew Tradeoffs in Simplified Crosslink-Based Clock Networks
2.4.2. Guidelines for Crosslink Insertion in a Clock Distribution Network
Rule 1: Location of Crosslinks within a Clock Tree
Rule 2: Location of Crosslink within a Clock Tree Section
Rule 3: Crosslink Parameters
3. Metrics for Power Efficient Clock Networks: Crosslink vs. Mesh-Based Topologies
Local and intermediate interconnect
Global interconnect
Optimum width and thickness (wOPT, tOPT)
4. Simulation Results
5. Summary










| Maximum Skew Due to Moderate Variations | Skew Violations Count | Energy per Cycle by Added Non-Tree Elements (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ps) | (% of TP) | (#) | (%) | SPICE | Analytic | |
| Clock tree | 51.56 | 5.16 | 64 | 53.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| With local crosslinks | 31.26 | 3.13 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.07 | 0.23 (EX,MAX) |
| With global crosslinks | 32.03 | 3.20 | 0 | 0.00 | 1.20 | 2.53 (EX,MAX) |
| With intermediate-level sparse mesh | 34.91 | 3.49 | 0 | 0.00 | 3.76 (EMESH) | N/A |
| With intermediate-level dense mesh | 35.62 | 3.56 | 0 | 0.00 | 5.97 (EMESH) | N/A |
| Maximum to Skew Due Large Variations | Skew Violations Count | Energy per Cycle Added by Non-Tree Elements (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ps) | (% of TP) | (#) | (%) | SPICE | Analytic | |
| Clock tree | 71.28 | 7.13 | 64 | 53.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| With local crosslinks | 35.96 | 3.60 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.08 | 0.24 (EX,MAX) |
| With global crosslinks | 34.61 | 3.46 | 0 | 0.00 | 1.34 | 2.80 (EX,MAX) |
| With intermediate-level sparse mesh | 67.18 | 6.72 | 28 | 23.33 | 3.75 (EMESH) | N/A |
| With intermediate-level dense mesh | 66.49 | 6.65 | 28 | 23.33 | 5.91 (EMESH) | N/A |
| With sink-level sparse mesh | 53.27 | 5.33 | 2 | 1.67 | 4.07 (EMESH) | N/A |
| With sink-level dense mesh | 46.16 | 4.62 | 0 | 0.00 | 6.28 (EMESH) | N/A |
| Maximum Skew Due to Moderate Variations | Skew Violations Count | Energy per Cycle Added by Non-Tree Elements (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ps) | (% of TP) | (#) | (%) | SPICE | Analytic | |
| Clock tree | 77.81 | 7.78 | 64 | 53.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| With local crosslinks | 45.01 | 4.50 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.80 | 0.82 (EX,MAX) |
| With global crosslinks | 43.64 | 4.36 | 0 | 0.00 | 0.98 | 2.64 (EX,MAX) |
| With intermediate-level sparse mesh | 43.00 | 4.30 | 0 | 0.00 | 3.45 (EMESH) | N/A |
| With intermediate-level dense mesh | 43.00 | 4.30 | 0 | 0.00 | 5.48 (EMESH) | N/A |
| Maximum Skew Due to Large Variations | Skew Violations Count | Energy per Cycle Added by Non-Tree Elements (%) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| (ps) | (% of TP) | (#) | (%) | SPICE | Analytic | |
| Clock tree | 96.83 | 9.68 | 64 | 53.33 | 0.00 | 0.00 |
| With local crosslinks | 61.86 | 6.19 | 16 | 13.33 | >0.79 | >1.39 (EX,MAX) |
| With global crosslinks | 60.77 | 6.08 | 16 | 13.33 | >1.07 | >3.31 (EX,MAX) |
| With intermediate-level sparse mesh | 47.84 | 4.78 | 0 | 0.00 | 3.43 (EMESH) | N/A |
| With intermediate-level dense mesh | 39.39 | 3.94 | 0 | 0.00 | 5.44 (EMESH) | N/A |
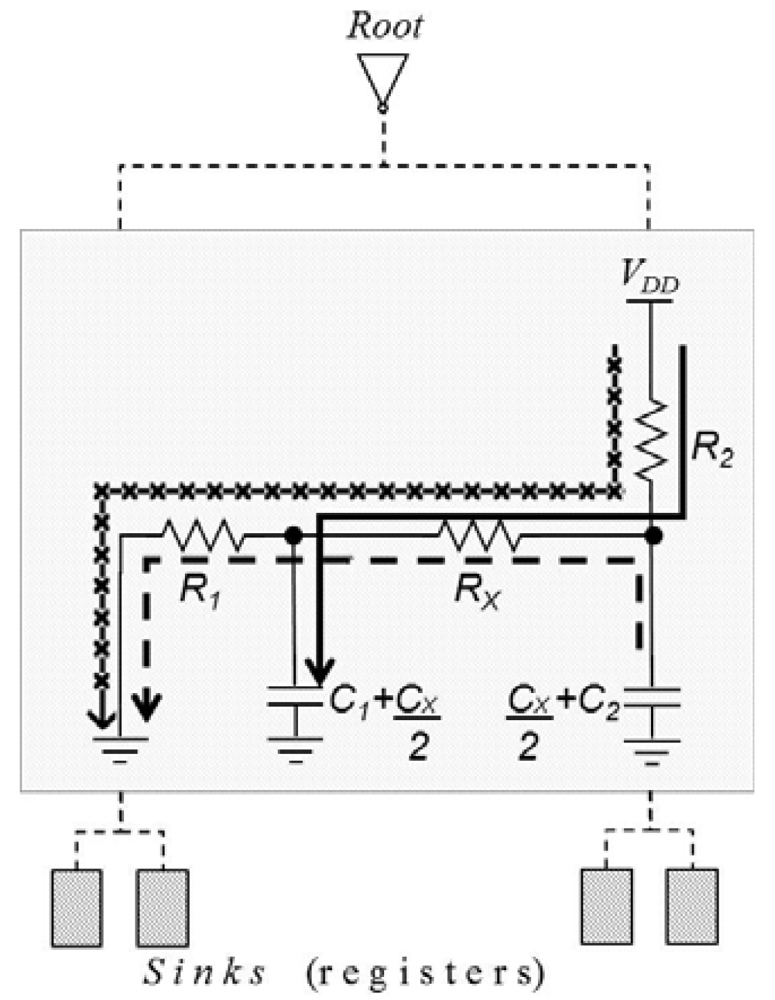
Appendix A: Total Energy Consumed in a Clock Tree Section with a Crosslink
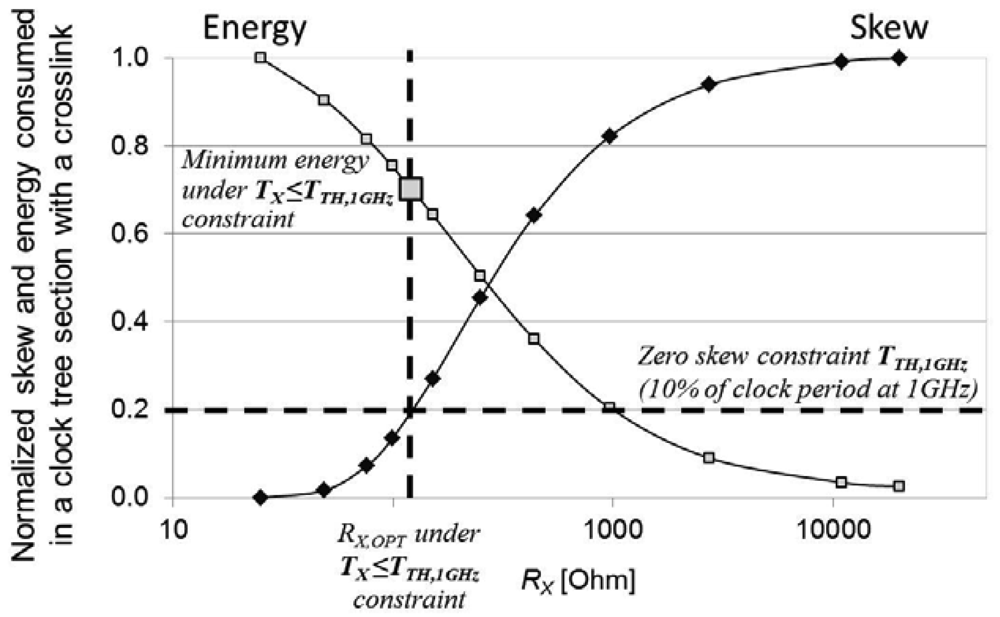
Appendix B: Crosslink Parameters for Low Power Design under the Zero Skew Constraint



References
- Kourtev, I.S.; Friedman, E.G. Timing Optimization through Clock Skew Scheduling, 2nd ed.; Springer Science + Business Media: Boston, MA, USA, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Xi, J.G.; Dai, W.W.M. Buffer Insertion and Sizing under Process Variations for Low Power Clock Distribution. Proceedings of the 32st Conference on Design Automation, San Francisco, CA, USA, 12–16 June 1995; pp. 491–496.
- Tsai, J.L.; Chen, T.H.; Chen, C.C.P. Zero skew clock-tree optimization with buffer insertion/sizing and wire sizing. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aid. Des. Int. 2004, 23, 565–572. [Google Scholar]
- Pullela, S.; Menezes, N.; Omar, J.; Pillage, L.T. Skew and delay optimization for reliable buffered clock trees. Proceedings of the 1993 IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, Santa Clara, CA, USA, 7–11 November 1993; pp. 556–562.
- Li, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, W. Wire sizing for non-tree topology. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Int. 2007, 26, 872–880. [Google Scholar]
- Friedman, E.G. Clock distribution networks in synchronous digital integrated circuits. Proc. IEEE 2001, 89, 665–692. [Google Scholar]
- Abdelhadi, A.; Ginosar, R.; Kolodny, A.; Friedman, E.G. Timing-Driven Variation-Aware Nonuniform Clock MeshSynthesis. Proceedings of the 20th ACM Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI 2009, Providence, RI, USA; 2010; pp. 250–257. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaram, A.; Pan, D.Z. MeshWorks: A comprehensive framework for optimized clock mesh networks synthesis. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aid. Des. Int. 2010, 29, 1945–1958. [Google Scholar]
- Wilke, G.R. Analysis and Optimization of Mesh-Based Clock Distribution Architectures. Ph.D. Thesis, Federal University of Rio Grande do Sul, Porte Alegre, Brazil, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Venkataraman, G.; Feng, Z.; Hu, J.; Li, P. Combinatorial Algorithms for Fast Clock Mesh Optimization. Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, San Jose, CA, USA, 7–11 November 2010; pp. 563–567.
- Ye, X.; Li, P.; Zhao, M.; Panda, R.; Hu, J. Scalable analysis of mesh-based clock distribution networks using application-specific reduced order modeling. IEEE Trans. Comput. Aided Des. Int. 2010, 29, 1342–1353. [Google Scholar]
- Feng, Z.; Li, P.; Hu, J. Efficient Model Update for General Link-Insertion Networks. Proceedings of the 7th IEEE International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design, San Jose, CA, USA, 27–29 March 2006; pp. 43–50.
- Ye, X.; Zhao, M.; Panda, R.; Li, P.; Hu, J. Accelerating Clock Mesh Simulation Using Matrix-Level Macromodels and Dynamic Time Step Rounding. Proceedings of the 9th IEEE International Symposium on Quality Electronic Design, San Jose, CA, USA, 17–19 March 2008; pp. 627–632.
- Sobczyk, A.L.; Łuczyk, A.W.; Pleskacz, W.A. Power Dissipation in Basic Global Clock Distribution Networks. Proceedings of the 10th IEEE Workshop Design and Diagnostics of Electronic Circuits and Systems, Kraków, Poland, 11–13 April 2007; pp. 1–4.
- Mori, M.; Chen, H.; Yao, B.; Cheng, C.K. A Multiple Level Network Approach for Clock Skew Minimization with Process Variations. Proceedings of the IEEE Asia and South Pacific Design Automation Conference, Yokohama, Japan, 27–30 January 2004; pp. 263–268.
- Restle, P.J.; Carter, C.A.; Eckhardt, J.P.; Krauter, B.L.; McCredie, B.D.; Jenkins, K.A.; Weger, A.J.; Mule, A.V. The Clock Distribution of the Power4 Microprocessor. Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 4–6 February 2002; pp. 1.144–1.145.
- Xanthopoulos, T.; Bailey, D.W.; Gangwar, A.K.; Gowan, M.K.; Jain, A.K.; Prewitt, B.K. The Design and Analysis of the Clock Distribution Network for a 1.2 GHz Alpha Microprocessor. Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 5–7 February 2001; pp. 402–403.
- Kurd, N.A.; Barkarullah, J.S.; Dizon, R.O.; Fletcher, T.D.; Madland, P.D. A multigigahertz clocking scheme for the pentium 4 microprocessor. IEEE J. Solid-State Circuits 2001, 36, 1647–1653. [Google Scholar]
- Tam, S.; Leung, J.; Limaye, R.; Choy, S.; Vora, S.; Adachi, M. Clock Generation and Distribution of a Dual-Core Xeon Processor with 16MB L3 Cache. Proceedings of the IEEE International Solid-State Circuits Conference, San Francisco, CA, USA, 6–9 February 2006; pp. 1512–1521.
- Rajaram, A.; Pan, D.Z. Variation Tolerant Buffered Clock Network Synthesis with CrossLinks. Proceedings of the ACM International Symposium on Physical Design, San Jose, CA, USA, 9–12 April 2006; pp. 157–164.
- Vaisband, I.; Ginosar, R.; Kolodny, A.; Friedman, E.G. Power Efficient Tree-Based Crosslinks for Skew Reduction. Proceedings of the 19th ACM Great Lakes Symposium on VLSI, Boston, MA, USA, 10–12 May 2009; pp. 285–290.
- Venkataraman, G.; Jayakumar, N.; Hu, J.; Li, P.; Sunil, K.; Anand, R.; McGuinness, P.; Alpert, C. Practical Techniques to Reduce Skew and its Variations in Buffered Clock Networks. Proceedings of the IEEE/ACM International Conference on Computer-Aided Design, San Jose, CA, USA, 6–10 November 2005; pp. 592–596.
- Hu, S.; Li, Q.; Hu, J.; Li, P. Utilizing redundancy for timing critical interconnect. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2007, 15, 1067–1080. [Google Scholar]
- Samanta, R.; Hu, J.; Li, P. Discrete buffer and wire sizing for link-based non-tree clock networks. IEEE Trans. Very Large Scale Integr. Syst. 2010, 18, 1025–1035. [Google Scholar]
- Rajaram, A.; Pan, D.Z.; Hu, J. Improved Algorithms for Link Based Non-Tree Clock Network for Skew Variability Reduction. Proceedings of the ACM International Symposium on Physical Design, San Francisco, CA, USA, 3–6 April 2005; pp. 55–62.
- Rajaram, A.; Hu, J.; Mahapatra, R. Reducing Clock Skew Variability via CrossLinks. Proceedings of the 41st ACM/IEEE Design Automation Conference, San Diego, CA, USA, 7–11 June 2004; pp. 18–23.
- Mehrotra, V.; Boning, D. Technology Scaling Impact of Variation on Clock Skew and. Interconnect Delay. Proceedings of the IEEE International Interconnect Technology Conference, Burlingame, CA, USA, 3–6 June 2001; pp. 122–124.
- Predictive Technology Model. Available online: http://ptm.asu.edu (accessed on 14 May 2011).
- Adler, V.; Friedman, E.G. Delay and Power Expressions for a CMOS Inverter Driving a Resistive-Capacitive Load. Analog Integr. Circuit Signal 1997, 14, 29–39. [Google Scholar]
- Keisler, H.J. Elementary Calculus. An Infinitesimal Approach, 2nd ed.; Prindle, Weber & Schmidt: Boston, MA, USA, 1986. [Google Scholar]
© 2011 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/3.0/).
Share and Cite
Vaisband, I.; Friedman, E.G.; Ginosar, R.; Kolodny, A. Low Power Clock Network Design. J. Low Power Electron. Appl. 2011, 1, 219-246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea1010219
Vaisband I, Friedman EG, Ginosar R, Kolodny A. Low Power Clock Network Design. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications. 2011; 1(1):219-246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea1010219
Chicago/Turabian StyleVaisband, Inna, Eby G. Friedman, Ran Ginosar, and Avinoam Kolodny. 2011. "Low Power Clock Network Design" Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications 1, no. 1: 219-246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea1010219
APA StyleVaisband, I., Friedman, E. G., Ginosar, R., & Kolodny, A. (2011). Low Power Clock Network Design. Journal of Low Power Electronics and Applications, 1(1), 219-246. https://doi.org/10.3390/jlpea1010219





