Dynamics and Drivers of Ecosystem Service Values in the Qionglai–Daxiangling Region of China’s Giant Panda National Park (1990–2020)
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Study Area and Methods
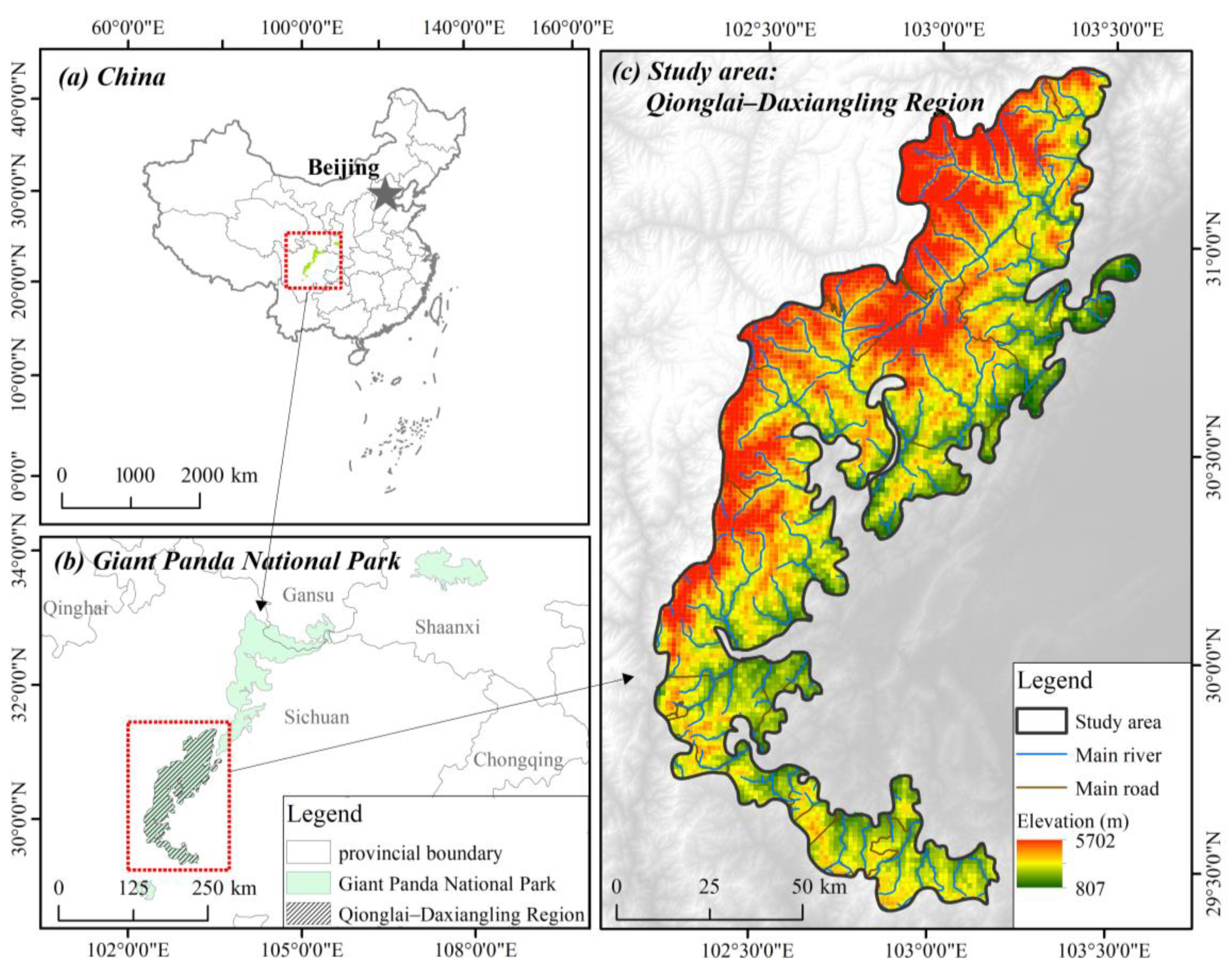
2.1. Study Area
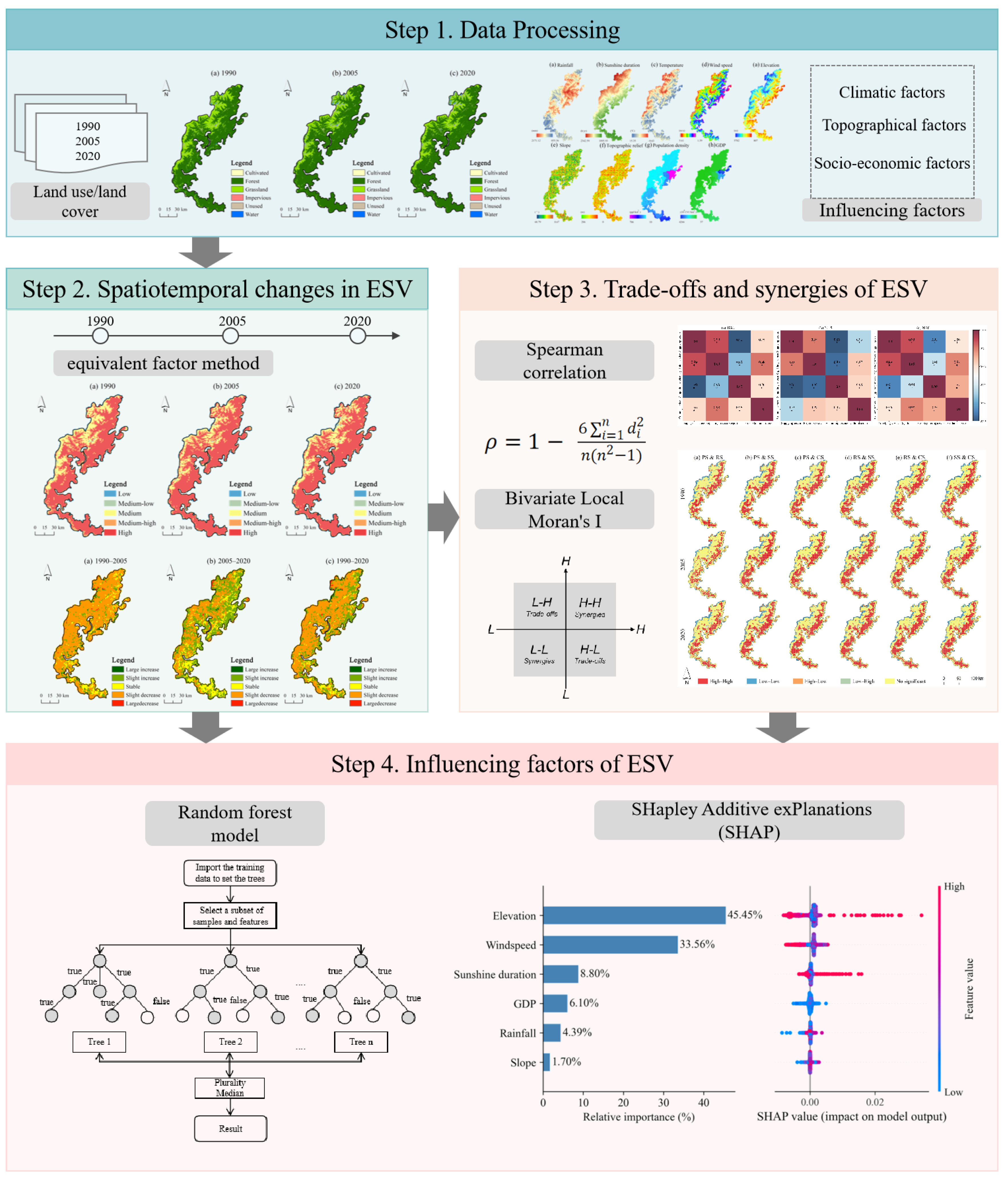
2.2. Methods
2.2.1. Coefficient Adjustment and Calculation of ESV
2.2.2. Trade-Off and Synergy Analysis of ESV
- (1)
- Linear Correlation Analysis
- (2)
- Bivariate Local Moran’s I (Bivariate LISA)
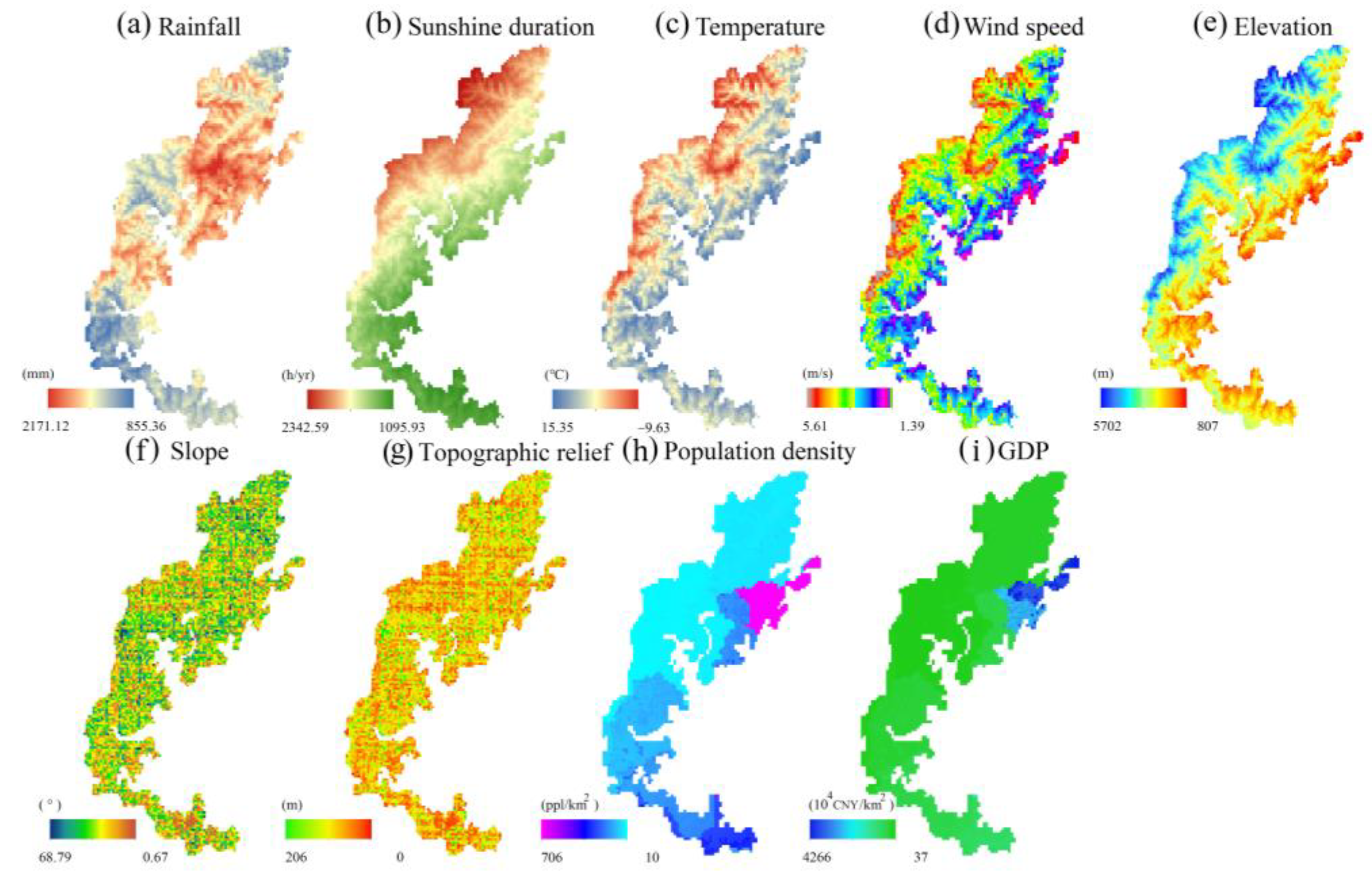
2.2.3. Factors Influencing ESV in the Study Area
- (1)
- Climatic factors
- (2)
- Topographical factors
- (3)
- Socioeconomic factors
2.3. Data Source and Processing
3. Results
3.1. Spatiotemporal Variation in Land Use and ESV
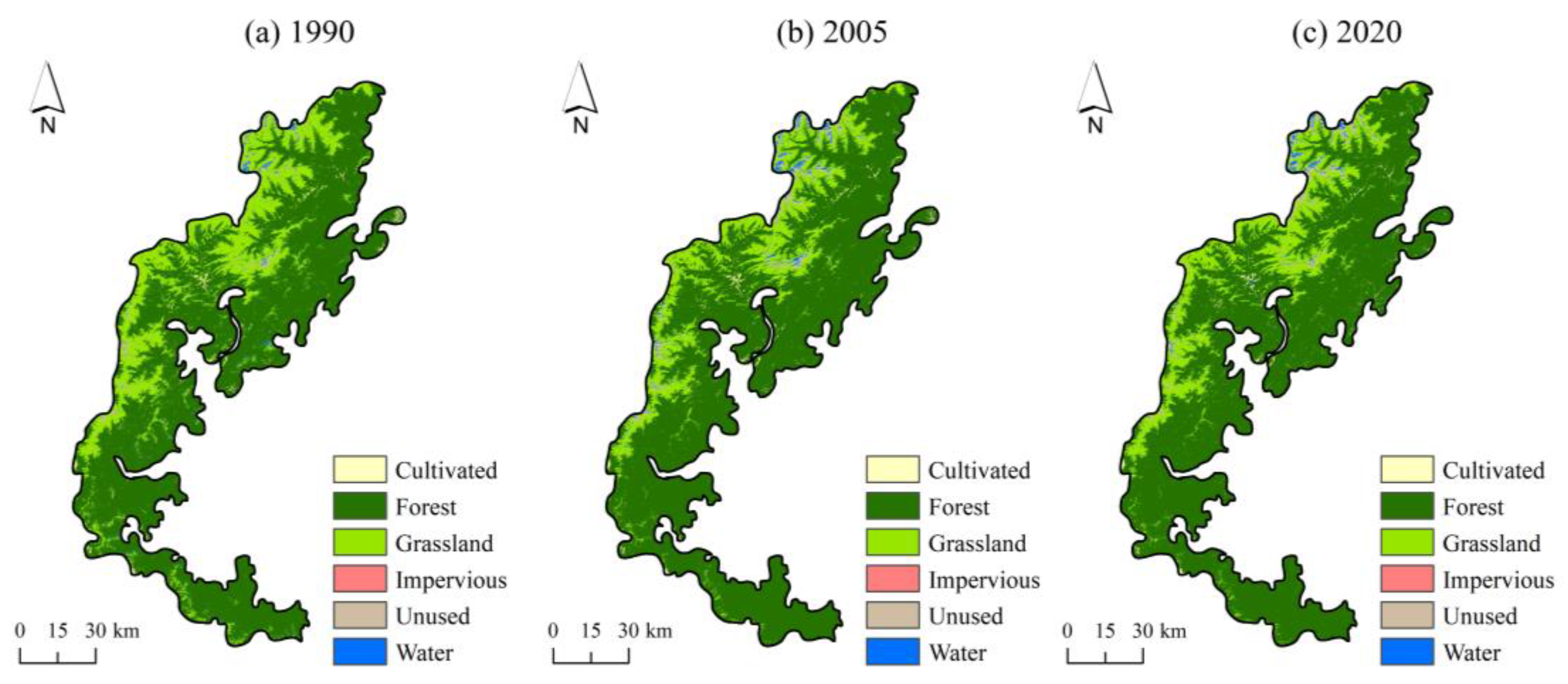
3.1.1. Changes in Land-Use/Land-Cover (LULC)
3.1.2. Changes in ESV
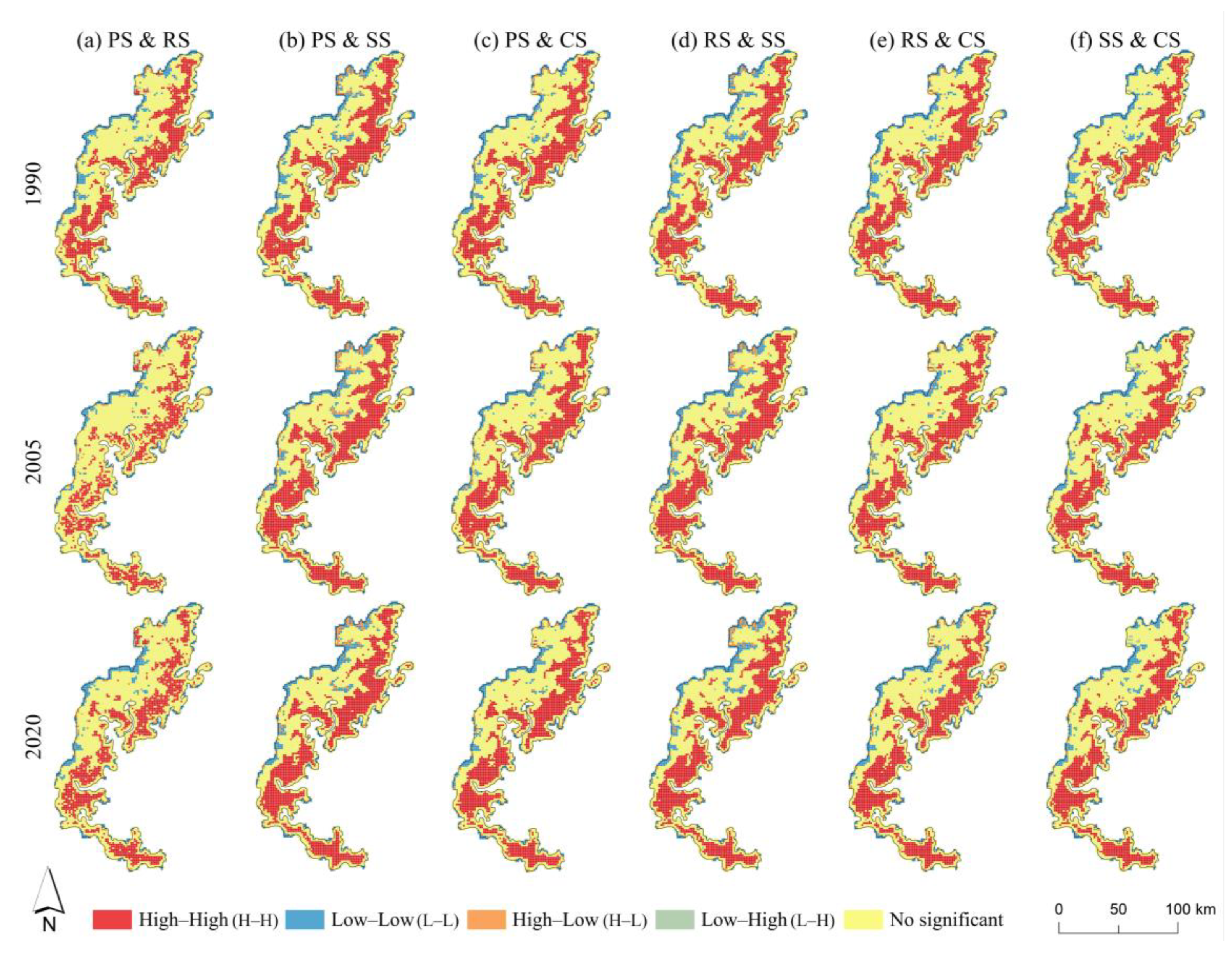
3.2. Trade-Offs and Synergies Among ESVs
3.3. Influencing Factors of ESV
4. Discussion
4.1. The Importance of ESV in National Parks
4.2. Changes in ESV and Their Responses to Land Use Changes
4.3. Implications of ESV Trade-Offs and Synergies
4.4. Interpretation of Influencing Factors of ESV
4.5. Limitations and Future Directions
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| CICES | Common International Classification of Ecosystem Services |
| CV | cross-validation |
| DEM | digital elevation model |
| ESV | ecosystem service value |
| GDP | gross domestic product |
| GPNP | Giant Panda National Park |
| LISA | Local Indicators of Spatial Association |
| LULC | land use/land cover |
| MAPE | mean absolute percentage error |
| MEA | Millennium Ecosystem Assessment |
| PAM | physical assessment method |
| QDR | Qionglai–Daxiangling region |
| RFFP | Returning Farmland to Forest Program |
| RMSE | root mean square error |
| SHAP | Shapley Additive exPlanations |
| VAM | value assessment method |
| VIF | variance inflation factor |
Appendix A
| Primary Services | Secondary Services | Cultivated | Forest | Grassland | Water | Unused |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provisioning Services | Food production | 1.00 | 0.25 | 0.23 | 0.44 | 0.00 |
| Raw material production | 0.31 | 0.58 | 0.34 | 0.24 | 0.00 | |
| Water supply | −0.78 | 0.30 | 0.19 | 4.35 | 0.00 | |
| Regulating Services | Gas regulation | 0.80 | 1.91 | 1.21 | 0.95 | 0.02 |
| Climate regulation | 0.42 | 5.71 | 3.19 | 2.14 | 0.00 | |
| Purifying the environment | 0.12 | 1.67 | 1.05 | 3.10 | 0.10 | |
| Hydrological regulation | 1.01 | 3.74 | 2.34 | 44.53 | 0.03 | |
| Supporting Services | Soil conservation | 0.72 | 2.32 | 1.47 | 1.08 | 0.02 |
| Maintaining nutrient circulation | 0.14 | 0.18 | 0.11 | 0.08 | 0.00 | |
| Biodiversity | 0.15 | 2.12 | 1.34 | 3.48 | 0.02 | |
| Cultural Services | Aesthetic landscape | 0.07 | 0.93 | 0.59 | 2.24 | 0.01 |
| Year | Statistical Scope | Rice | Wheat | Corn | Beans | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Sown Area (ha) | Grain Yield (kg/ha) | Price (CNY/kg) | Sown Area (ha) | Grain Yield (kg/ha) | Price (CNY/kg) | Sown Area (ha) | Grain Yield (kg/ha) | Price (CNY/kg) | Sown Area (ha) | Grain Yield (kg/ha) | Price (CNY/kg) | ||
| 1990 | Sichuan Province | 2,300,000 | 7394.78 | 1,680,000 | 3398.21 | 1,199,000 | 4054.21 | 343,000 | 1848.40 | ||||
| China (national) | 33,064,000 | 6211.95 | 0.58 | 30,753,000 | 3454.95 | 0.61 | 21,401,000 | 5374.28 | 0.44 | 9,163,000 | 1506.22 | 1.17 | |
| 2005 | Sichuan Province | 1,995,000 | 7655.22 | 1,360,000 | 3993.53 | 1,185,000 | 5414.58 | 520,000 | 2364.51 | ||||
| China (national) | 28,847,000 | 6465 | 1.55 | 22,793,000 | 4887 | 1.38 | 26,358,000 | 6339 | 1.11 | 12,901,000 | 1983 | 2.57 | |
| 2020 | Sichuan Province | 1866000 | 7904.95 | 597,000 | 4134.37 | 1,839,000 | 5790.02 | 599,000 | 2316.08 | ||||
| China (national) | 30,076,000 | 7016.85 | 2.75 | 23,380,000 | 6454.95 | 2.28 | 41,264,000 | 7539.3 | 2.31 | 11,593,000 | 2003.4 | 4.86 | |
| Year | k (−) | P (CNY/ha/yr) |
|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 1.10 | 459.60 |
| 2005 | 1.04 | 1214.87 |
| 2020 | 0.91 | 2059.65 |
| Geometric mean | 1057.74 |

References
- Lahon, D.; Meraj, G.; Hashimoto, S.; Debnath, J.; Baba, A.M.; Farooq, M.; Islam, M.N.; Singh, S.K.; Kumar, P.; Kanga, S. Projected Trends in Ecosystem Service Valuation in Response to Land Use Land Cover Dynamics in Kishtwar High Altitude National Park, India. Landsc. Ecol. Eng. 2025, 21, 81–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Xue, H.; Li, A.; Ma, X.; Sun, A.; Zhang, J. Spatial-Temporal Differentiation and Influencing Factors of Ecosystem Health in Three-River-Source National Park. Ecol. Indic. 2025, 171, 113183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meetei, K.B.; Tsopoe, M.; Chandra, G.; Mukhopadhyay, D.; Giri, K. Ecosystem Productivity and Carbon Dynamics in Keibul Lamjao National Park, Manipur, India: A Gray Relational Analysis Perspective. Environ. Monit. Assess. 2025, 197, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Simeon, M.; Wana, D. Synergies and Trade-Offs among Key Ecosystem Services in Maze National Park and Its Environs, Southwestern Ethiopia. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2025, 57, e03398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loomis, J.; Richardson, L.; Dara, P.K.; Mueller, J.; Zabel, J.; Smalley, P.; Fitch, R.; Nolte, C.; Paterson, R. Ecosystem Service Values Provided by National Parks to Residential Property Owners. Ecol. Econ. 2024, 220, 108175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Tang, H.; Lei, J.; Song, X. Spatial Autocorrelation in Land Use Type and Ecosystem Service Value in Hainan Tropical Rain Forest National Park. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 137, 108727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Li, W.; Shi, S.; Gao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ding, Y. Spatio-Temporal Dynamics of Ecosystem Service Values in China’s Northeast Tiger-Leopard National Park from 2005 to 2020: Evidence from Environmental Factors and Land Use/Land Cover Changes. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 155, 110734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costanza, R.; D’Arge, R.; De Groot, R.; Farber, S.; Grasso, M.; Hannon, B.; Limburg, K.; Naeem, S.; O’neill, R.V.; Paruelo, J. The Value of the World’s Ecosystem Services and Natural Capital. Nature 1997, 387, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sannigrahi, S.; Chakraborti, S.; Joshi, P.K.; Keesstra, S.; Sen, S.; Paul, S.K.; Kreuter, U.; Sutton, P.C.; Jha, S.; Dang, K.B. Ecosystem Service Value Assessment of a Natural Reserve Region for Strengthening Protection and Conservation. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 244, 208–227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, T.; Chen, Y.; Shu, B.; Gao, M.; Qiu, J. Spatiotemporal evolution of ecosystem service value and topographic gradient effect in the Da-Xiao Liangshan Mountains in Sichuan Province, China. J. Mt. Sci. 2023, 20, 2344–2357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, X.; Li, J.; Ma, Q. Integrating green infrastructure, ecosystem services and nature-based solutions for urban sustainability: A comprehensive literature review. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, D.; Ding, X. Assessing the Impact of Desertification Dynamics on Regional Ecosystem Service Value in North China from 1981 to 2010. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 30, 172–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millennium Ecosystem Assessment. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being; Island Press: Washington, DC, USA, 2005; Volume 5. [Google Scholar]
- Häyhä, T.; Franzese, P.P. Ecosystem Services Assessment: A Review under an Ecological-Economic and Systems Perspective. Ecol. Modell. 2014, 289, 124–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines-Young, R.; Potschin-Young, M. Revision of the Common International Classification for Ecosystem Services (CICES V5. 1): A Policy Brief. One Ecosyst. 2018, 3, e27108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tymchenko, I.V.; Havryliuk, R.B.; Stankiewicz-Volosianchuk, O.I.; Savchenko, S.A. Assessment of the Economic Value of Ecosystem Services of the Oleksandrivskyi Reservoir of the South Bug River Basin. J. Geol. Geogr. Geoecol. 2024, 33, 387–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grima, N.; Jutras-Perreault, M.-C.; Gobakken, T.; Ørka, H.O.; Vacik, H. Systematic Review for a Set of Indicators Supporting the Common International Classification of Ecosystem Services. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 147, 109978. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Liu, R.; Xue, C.; Xia, Z. Ecological Sensitivity Evaluation and Explanatory Power Analysis of the Giant Panda National Park in China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Yu, L.; Cao, Y.; Xu, Y.; Zhao, Z.; Zhuang, Y.; Liu, X.; Du, Z.; Liu, T.; Yang, B.; et al. Habitat Quality Dynamics in China’s First Group of National Parks in Recent Four Decades: Evidence from Land Use and Land Cover Changes. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 325, 116505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Yang, B.; Dai, Q.; Pan, H.; Zhong, X.; Ran, J.; Yang, X.; Gu, X.; Yang, Z.; Qi, D. Landscape-Scale Giant Panda Conservation Based on Metapopulations within China’s National Park System. Sci. Adv. 2022, 8, eabl8637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, W.; Wu, D.; Huang, L.; Liu, L. Spatial and Temporal Variations and Significance Identification of Ecosystem Services in the Sanjiangyuan National Park, China. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 6151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, S.; Hu, X.; Chen, H.; Wu, C.; Hong, W. Spatio-Temporal Variation of Ecosystem Service Values Adjusted by Vegetation Cover: A Case Study of Wuyishan National Park Pilot, China. J. For. Res. 2022, 33, 851–863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sohel, M.S.I.; Ahmed Mukul, S.; Burkhard, B. Landscape’s Capacities to Supply Ecosystem Services in Bangladesh: A Mapping Assessment for Lawachara National Park. Ecosyst. Serv. 2015, 12, 128–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bennett, D.; McGinnis, D. Coupled and Complex: Human–Environment Interaction in the Greater Yellowstone Ecosystem, USA. Geoforum 2008, 39, 833–845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mayer, M.; Woltering, M. Assessing and Valuing the Recreational Ecosystem Services of Germany’s National Parks Using Travel Cost Models. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 31, 371–386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Loc, H.H.; Irvine, K.N.; Suwanarit, A.; Vallikul, P.; Likitswat, F.; Sahavacharin, A.; Sovann, C.; Ha, L. Mainstreaming Ecosystem Services as Public Policy in South East Asia, from Theory to Practice. In Sustainability and Law: General and Specific Aspects; Mauerhofer, V., Rupo, D., Tarquinio, L., Eds.; Springer: Cham, Switzerland, 2020; pp. 631–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kibria, A.S.M.G.; Behie, A.; Costanza, R.; Groves, C.; Farrell, T. The Value of Ecosystem Services Obtained from the Protected Forest of Cambodia: The Case of Veun Sai-Siem Pang National Park. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 27–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagstad, K.J.; Semmens, D.J.; Waage, S.; Winthrop, R. A Comparative Assessment of Decision-Support Tools for Ecosystem Services Quantification and Valuation. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 5, 27–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, W.; Deng, X.; Yuan, Y.; Wang, Z.; Li, Z. Impacts of Land-Use Change on Valued Ecosystem Service in Rapidly Urbanized North China Plain. Ecol. Model. 2015, 318, 245–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jia, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, S. Evaluation of Agricultural Ecosystem Service Value in Arid and Semiarid Regions of Northwest China Based on the Equivalent Factor Method. Environ. Process. 2021, 8, 713–727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancini, M.S.; Galli, A.; Coscieme, L.; Niccolucci, V.; Lin, D.; Pulselli, F.M.; Bastianoni, S.; Marchettini, N. Exploring Ecosystem Services Assessment through Ecological Footprint Accounting. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 30, 228–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Harrison, P.A.; Dunford, R.; Barton, D.N.; Kelemen, E.; Martín-López, B.; Norton, L.; Termansen, M.; Saarikoski, H.; Hendriks, K.; Gómez-Baggethun, E.; et al. Selecting Methods for Ecosystem Service Assessment: A Decision Tree Approach. Ecosyst. Serv. 2018, 29, 481–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valencia Torres, A.; Tiwari, C.; Atkinson, S.F. Progress in Ecosystem Services Research: A Guide for Scholars and Practitioners. Ecosyst. Serv. 2021, 49, 101267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, T.; Li, W.; Qian, Z. Variations in Ecosystem Service Value in Response to Land Use Changes in Shenzhen. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1427–1435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, B.; Li, Y.; Wang, Y.; Zhang, B.; Yin, S.; Zhu, H.; Xing, Z. Evaluation of Ecosystem Service Value of Riparian Zone Using Land Use Data from 1986 to 2012. Ecol. Indic. 2016, 69, 873–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baniya, B.; Tang, Q.; Pokhrel, Y.; Xu, X. Vegetation Dynamics and Ecosystem Service Values Changes at National and Provincial Scales in Nepal from 2000 to 2017. Environ. Dev. 2019, 32, 100464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kianmehr, A.; Lim, T.C. Quantifying Interactive Cooling Effects of Morphological Parameters and Vegetation-Related Landscape Features during an Extreme Heat Event. Climate 2022, 4, 60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhen, L.; Zhang, L. Dynamic Changes in the Value of China’s Ecosystem Services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 26, 146–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Li, W.; Xie, G. Ecosystem Services Research in China: Progress and Perspective. Ecol. Econ. 2010, 69, 1389–1395. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gaodi, X.; Lin, Z.; Chunxia, L.; Yu, X.; Wenhua, L.I. Applying Value Transfer Method for Eco-Service Valuation in China. J. Resour. Ecol. 2010, 1, 51–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palomo, I.; Martín-López, B.; Potschin, M.; Haines-Young, R.; Montes, C. National Parks, Buffer Zones and Surrounding Lands: Mapping Ecosystem Service Flows. Ecosyst. Serv. 2013, 4, 104–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Yu, J.; Wu, W.; Hou, R.; Yang, Z.; Owens, J.R.; Gu, X.; Xiang, Z.; Qi, D. Evaluating the Efficacy of Zoning Designations for National Park Management. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2021, 27, e01562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ellison, A.M.; Liu, W.; Chen, D. Establish an Environmentally Sustainable Giant Panda National Park in the Qinling Mountains. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 979–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Pimm, S.L.; Xu, W.; Shi, X.; Xiao, Y.; Kong, L.; Fan, X.; Ouyang, Z. Relationship between Giant Panda Populations and Selected Ecosystem Services. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 44, 101130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, Q.; Fei, Y.; Yang, H.; Gu, X.; Songer, M. Giant Panda National Park, a Step towards Streamlining Protected Areas and Cohesive Conservation Management in China. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2020, 22, e00947. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ai, M.; Chen, X.; Yu, Q. Spatial Correlation Analysis between Human Disturbance Intensity (HDI) and Ecosystem Services Value (ESV) in the Chengdu-Chongqing Urban Agglomeration. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Zhu, L.; Dou, L.; Wu, M.; Guo, Y. Estimation of Ecosystem Service Value in Huixian Karst National Wetland Park Based on Equivalent Factor Method. Int. J. Digit. Earth 2025, 18, 2494073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, G.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, L.; Chen, W.; Li, S. Improvement of the Evaluation Method for Ecosystem Service Value Based on Per Unit Area. J. Nat. Resour. 2015, 30, 1243–1254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Wang, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, D.; Chen, J.; Liang, E. Trade-Offs and Synergies of Ecosystem Services and Their Threshold Effects in the Largest Tableland of the Loess Plateau. Glob. Ecol. Conserv. 2023, 48, e02706. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, R.; Chen, J.; Cui, S.; Li, L.; Qian, J.; Zhao, H.; Huang, G. A Data-Driven Framework to Identify Influencing Factors for Soil Heavy Metal Contaminations Using Random Forest and Bivariate Local Moran’s I: A Case Study. J. Environ. Manag. 2025, 375, 124172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ding, X.; Shu, Y.; Tang, X.; Ma, J. Identifying Driving Factors of Basin Ecosystem Service Value Based on Local Bivariate Spatial Correlation Patterns. Land 2022, 11, 1852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Ao, Y.; Ke, J.; Lu, Y.; Liang, Y. To Walk or not to Walk? Examining Non-linear Effects of Streetscape Greenery on Walking Propensity of Older Adults. J. Transp. Geogr. 2021, 94, 103099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yu, B.; Liang, Y.; Lu, Y.; Li, W. Time-varying and Non-linear Associations Between Metro Ridership and the Built Environment. Tunn. Undergr. Space Technol. 2023, 132, 104931. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, Y.; Zhao, B.; Peng, S.; Li, K.; Yin, Y.; Zhang, J. Effects of Cultural Landscape Service Features in National Forest Parks on Visitors’ Sentiments: A Nationwide Social Media-Based Analysis in China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2024, 67, 101614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lundberg, S.M.; Lee, S.-I. A Unified Approach to Interpreting Model Predictions. Adv. Neural Inf. Process. Syst. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Kruk, M. SHAP-NET, a Network Based on Shapley Values as a New Tool to Improve the Explainability of the XGBoost-SHAP Model for the Problem of Water Quality. Environ. Model. Softw. 2025, 188, 106403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Batunacun; Wieland, R.; Lakes, T.; Nendel, C. Using Shapley Additive Explanations to Interpret Extreme Gradient Boosting Predictions of Grassland Degradation in Xilingol, China. Geosci. Model Dev. 2021, 14, 1493–1510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen Van, L.; Nguyen, G.V.; Yeon, M.; Thi-Tuyet Do, M.; Lee, G. Unveiling Environmental Drivers of Soil Erosion in South Korea through SHAP-Informed Machine Learning. Land Use Policy 2025, 155, 107592. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholami, H.; Darvishi, E.; Moradi, N.; Mohammadifar, A.; Song, Y.; Li, Y.; Niu, B.; Kaskaoutis, D.; Pradhan, B. An Interpretable (Explainable) Model Based on Machine Learning and SHAP Interpretation Technique for Mapping Wind Erosion Hazard. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2024, 31, 64628–64643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Najjar, H.A.H.; Pradhan, B.; Beydoun, G.; Sarkar, R.; Park, H.-J.; Alamri, A. A Novel Method Using Explainable Artificial Intelligence (XAI)-Based Shapley Additive Explanations for Spatial Landslide Prediction Using Time-Series SAR Dataset. Gondwana Res. 2023, 123, 107–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Tian, H. Insights from Optimized Non-Landslide Sampling and SHAP Explainability for Landslide Susceptibility Prediction. Appl. Sci. 2025, 15, 1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Yang, H.; Yu, B.; Lu, Y.; Cui, J.; Lin, D. Exploring Non-linear and Synergistic Effects of Green Spaces on Active Travel Using Crowdsourced Data and Interpretable Machine Learning. Travel Behav. Soc. 2024, 34, 100673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Qin, T.; Yan, D.; Liu, S.; Feng, J.; Wang, Q.; Liu, H.; Gao, H. Analysis of the Evolution of Ecosystem Service Value and Its Driving Factors in the Yellow River Source Area, China. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Amani-Beni, M.; Zhang, R.; Wei, D. Evolution of population distribution and its influencing factors in the poverty-stricken mountainous region of Southwest China from 2000 to 2020. Humanit. Soc. Sci. Commun. 2024, 11, 1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinda, J.A.; Trac, C.J.; Zhai, D.; Harrell, S. Dual-Function Forests in the Returning Farmland to Forest Program and the Flexibility of Environmental Policy in China. Geoforum 2017, 78, 119–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Wang, W.; Chen, J.; Zhang, Z. Assessing Effects of the Returning Farmland to Forest Program on Vegetation Cover Changes at Multiple Spatial Scales: The Case of Northwest Yunnan, China. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 304, 114303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Z.; Shang, X.; Zhang, T.; Yun, J. Coupled Regulatory Mechanisms and Synergy/Trade-off Strategies of Human Activity and Climate Change on Ecosystem Service Value in the Loess Hilly Fragile Region of Northern Shaanxi, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 143, 109325. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wang, M.; Lan, T.; Xu, Z.; Wu, J.; Liu, Q.; Peng, J. Distinguishing the Effects of Land Use Policies on Ecosystem Services and Their Trade-Offs Based on Multi-Scenario Simulations. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 151, 102864. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, L.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Ying, L. Effects of Agricultural Land Consolidation on Ecosystem Services: Trade-Offs and Synergies. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 264, 121412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cord, A.F.; Bartkowski, B.; Beckmann, M.; Dittrich, A.; Hermans-Neumann, K.; Kaim, A.; Lienhoop, N.; Locher-Krause, K.; Priess, J.; Schröter-Schlaack, C.; et al. Towards Systematic Analyses of Ecosystem Service Trade-Offs and Synergies: Main Concepts, Methods and the Road Ahead. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 28, 264–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, J.; Jin, X.; Xu, W.; Yang, F.; Wang, S.; Zhou, Y. Assessing Trade-Offs and Synergies among Multiple Land Use Functional Efficiencies: Integrating Ideal Reference and Key Indicators for Sustainable Landscape Management. Appl. Geogr. 2023, 158, 103037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Landscape Sustainability Science: Ecosystem Services and Human Well-Being in Changing Landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2013, 28, 999–1023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, M.; Xueqian, S.; Gai, Q.; Basirialmahjough, M.; Yuan, H. Improving Robustness of Water Supply System Using a Multi-Objective Robust Optimization Framework. Environ. Res. 2023, 232, 116270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moudi, M.; Galoie, M.; Yuan, H.; Motamedi, A.; Huang, P.; Shafi, M. Dynamic Multi-Objective Programming Model for Improving Consumer Satisfaction within Water Supply System under Uncertain Environment. J. Environ. Manag. 2021, 293, 112897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahdi, M.; Xueqian, S.; Yuan, H.; Amani-Beni, M. Enhancing Equitable Water Distribution in Agriculture: A Novel Optimal Framework for Irrigation Equity Index Improvement Under Diverse Adaptation Strategies. Water Resour. Manag. 2024, 38, 2669–2685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, H.; Xu, X.; Tang, J.; Wang, Z.; Miao, C. Understanding the Key Factors and Future Trends of Ecosystem Service Value to Support the Decision Management in the Cluster Cities around the Yellow River Floodplain Area. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Lu, Y.; Cao, M.; Wang, R.; Chen, J. Assessing Accessibility to Peri-urban Parks Considering Supply, Demand, and Traffic Conditions. Landsc. Urban Plan. 2025, 257, 105313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Han, R.; Yang, S.; Yang, Y.; Tang, X.; Qu, W. Identification of Bundles and Driving Factors of Ecosystem Services at Multiple Scales in the Eastern China Region. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 158, 111378. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, L.; Chau, K.W.; Szeto, W.Y.; Cui, X.; Wang, X. Accessibility to Transit, by Transit, and Property Prices: Spatially Varying Relationships. Transport. Res. Part D-Transport. Environ. 2020, 85, 102387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]





| Primary Services | Secondary Services | Cultivated | Forest | Grassland | Water | Unused |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Provisioning Services | Food production | 1060.91 | 267.08 | 246.81 | 461.88 | 0.00 |
| Raw material production | 324.73 | 613.49 | 363.16 | 257.38 | 0.00 | |
| Water supply | −819.75 | 317.32 | 200.97 | 4597.64 | 0.00 | |
| Regulating Services | Gas regulation | 848.31 | 2017.64 | 1276.34 | 1004.85 | 21.15 |
| Climate regulation | 447.42 | 6037.05 | 3374.19 | 2267.09 | 0.00 | |
| Purifying the environment | 127.99 | 1769.07 | 1114.15 | 3282.52 | 105.77 | |
| Hydrological regulation | 1063.03 | 3950.66 | 2471.58 | 47,104.67 | 31.73 | |
| Supporting Services | Soil conservation | 765.80 | 2456.60 | 1554.88 | 1142.36 | 21.15 |
| Maintaining nutrient circulation | 149.14 | 187.75 | 119.88 | 88.14 | 0.00 | |
| Biodiversity | 162.89 | 2237.12 | 1413.85 | 3677.41 | 21.15 | |
| Cultural Services | Aesthetic landscape | 72.98 | 981.05 | 624.07 | 2365.81 | 10.58 |
| Total | 4203.46 | 20,834.82 | 12,759.86 | 66,249.75 | 211.55 | |
| Influencing Factors | Variables (Unit) | Min | Max | Mean | Std. Dev. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Climatic | Rainfall (mm) | 855.36 | 2171.12 | 1576.33 | 208.19 |
| Sunshine duration (h/yr) | 1095.93 | 2342.58 | 1622.45 | 284.04 | |
| Temperature (°C) | −9.63 | 15.35 | 5.50 | 4.55 | |
| Wind speed (m/s) | 1.39 | 5.62 | 3.30 | 0.75 | |
| Topographical | Elevation (m) | 807.00 | 5702.00 | 2859.11 | 896.96 |
| Slope (°) | 0.67 | 68.79 | 28.03 | 12.25 | |
| Topographic relief (m) | 0 | 206 | 43.24 | 23.28 | |
| Socioeconomic | Population density (persons/km2) | 10 | 706 | 69.17 | 105.15 |
| GDP (104 CNY/km2) | 37 | 4266 | 370.42 | 592.17 |
| Type | 1990 | 2005 | 2020 | Change (1990–2020) | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | Area (km2) | Percentage (%) | |
| Cultivated | 83.54 | 0.83 | 68.89 | 0.68 | 82.71 | 0.82 | −0.83 | −0.99 |
| Forest | 7462.20 | 74.16 | 7877.05 | 78.28 | 7869.82 | 78.21 | 407.62 | 5.46 |
| Grassland | 2322.15 | 23.08 | 1818.26 | 18.07 | 1842.46 | 18.31 | −479.69 | −20.66 |
| Water | 83.98 | 0.83 | 119.22 | 1.18 | 87.80 | 0.87 | 3.82 | 4.55 |
| Unused | 109.78 | 1.09 | 177.66 | 1.77 | 177.69 | 1.77 | 67.91 | 61.86 |
| Impervious | 0.57 | 0.01 | 1.14 | 0.01 | 1.74 | 0.02 | 1.17 | 205.26 |
| Ecosystem Type | ESV (CNY billion) | ESV Change | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1990 | 2005 | 2020 | 1990–2020 | |
| Cultivated | 0.35 | 0.29 | 0.34 | −0.54% |
| Forest | 155.06 | 163.69 | 163.53 | 5.46% |
| Grassland | 29.62 | 23.20 | 23.51 | −20.64% |
| Water | 5.56 | 7.90 | 5.82 | 4.62% |
| Unused | 0.02 | 0.04 | 0.04 | 61.87% |
| Total | 190.61 | 195.11 | 193.23 | 1.38% |
| Cross-Validation Schemes | RMSE | R2 | MAPE (%) |
|---|---|---|---|
| Random CV K-fold | 0.0046 | 0.56 | 6.98 |
| Spatial Grid Group K-fold (5 × 5) | 0.0049 | 0.46 | 7.70 |
| Spatial K-means Group K-fold (k = 16) | 0.0049 | 0.39 | 7.92 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Chen, Y.; Zhang, R.; Dehghanifarsani, L.; Amani-Beni, M. Dynamics and Drivers of Ecosystem Service Values in the Qionglai–Daxiangling Region of China’s Giant Panda National Park (1990–2020). Systems 2025, 13, 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13090807
Chen Y, Zhang R, Dehghanifarsani L, Amani-Beni M. Dynamics and Drivers of Ecosystem Service Values in the Qionglai–Daxiangling Region of China’s Giant Panda National Park (1990–2020). Systems. 2025; 13(9):807. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13090807
Chicago/Turabian StyleChen, Yang, Ruizhi Zhang, Laleh Dehghanifarsani, and Majid Amani-Beni. 2025. "Dynamics and Drivers of Ecosystem Service Values in the Qionglai–Daxiangling Region of China’s Giant Panda National Park (1990–2020)" Systems 13, no. 9: 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13090807
APA StyleChen, Y., Zhang, R., Dehghanifarsani, L., & Amani-Beni, M. (2025). Dynamics and Drivers of Ecosystem Service Values in the Qionglai–Daxiangling Region of China’s Giant Panda National Park (1990–2020). Systems, 13(9), 807. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13090807








