Do Supply Chain Management, ESG Sustainability Practices, and ICT Have an Impact on Environmental Sustainability?
Abstract
1. Introduction
- ❖
- Does global supply chain management impact CO2 emissions in China?
- ❖
- Does Information and Communication Technology influence China’s CO2 emissions?
- ❖
- Does ESG sustainability impact China’s CO2 emissions?
- ❖
- Does patent innovations impact China’s CO2 emissions?
Contribution of Study
2. Theoretical Framework and Literature Review
2.1. Theoretical Framework
2.2. Literature Review
3. Data and Methods
3.1. Data
3.2. Empirical Methods
3.2.1. Wavelet Power Spectrum
3.2.2. Wavelet Coherency (WTC)
3.2.3. Partial Wavelet Coherence (PWC)
3.2.4. Multiple Wavelet Coherence
3.2.5. Wavelet Granger Causality
4. Findings and Discussion
4.1. Descriptive Statistics
4.2. Nonlinearity Test Result
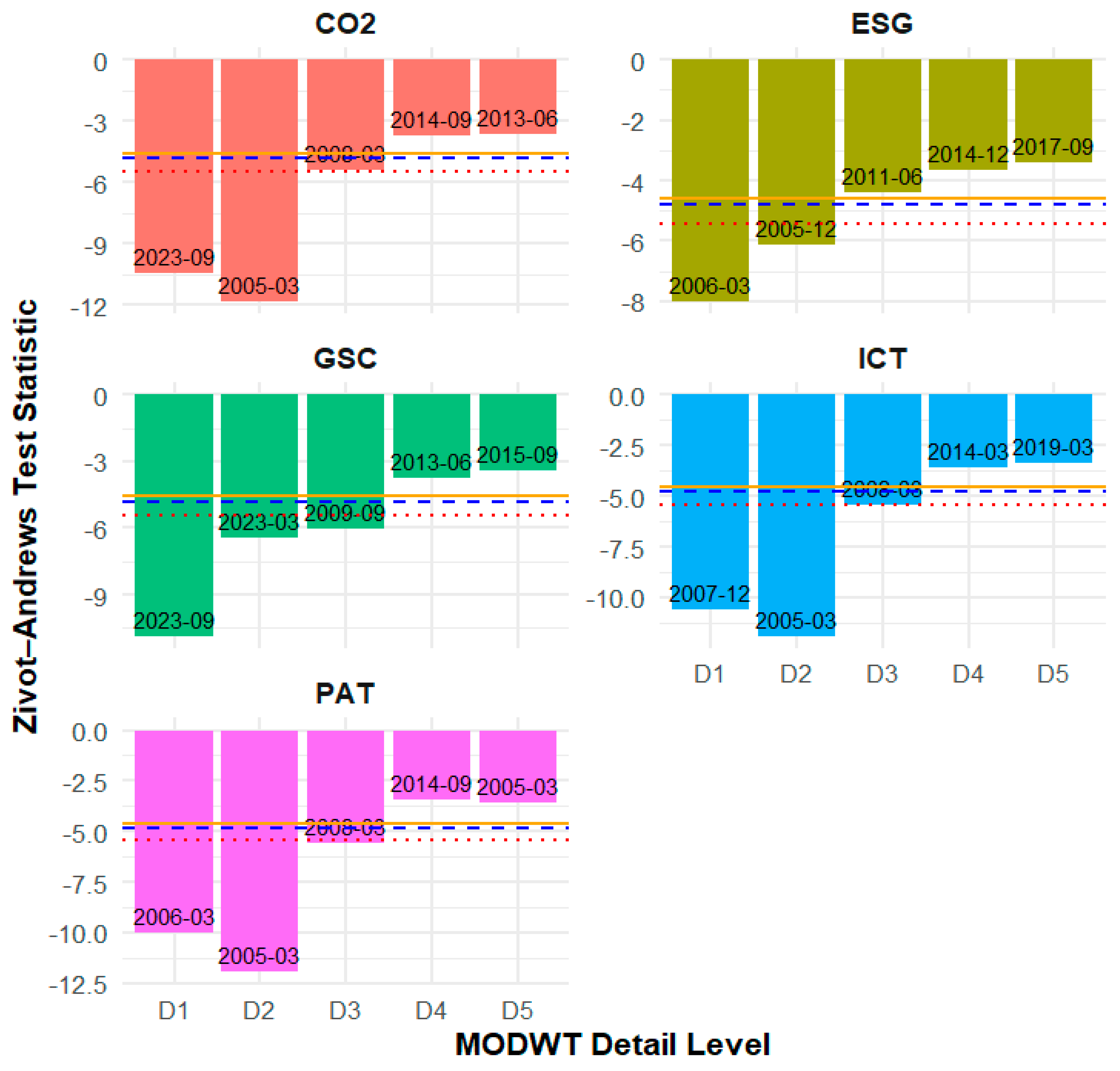
4.3. Stationarity Test Result
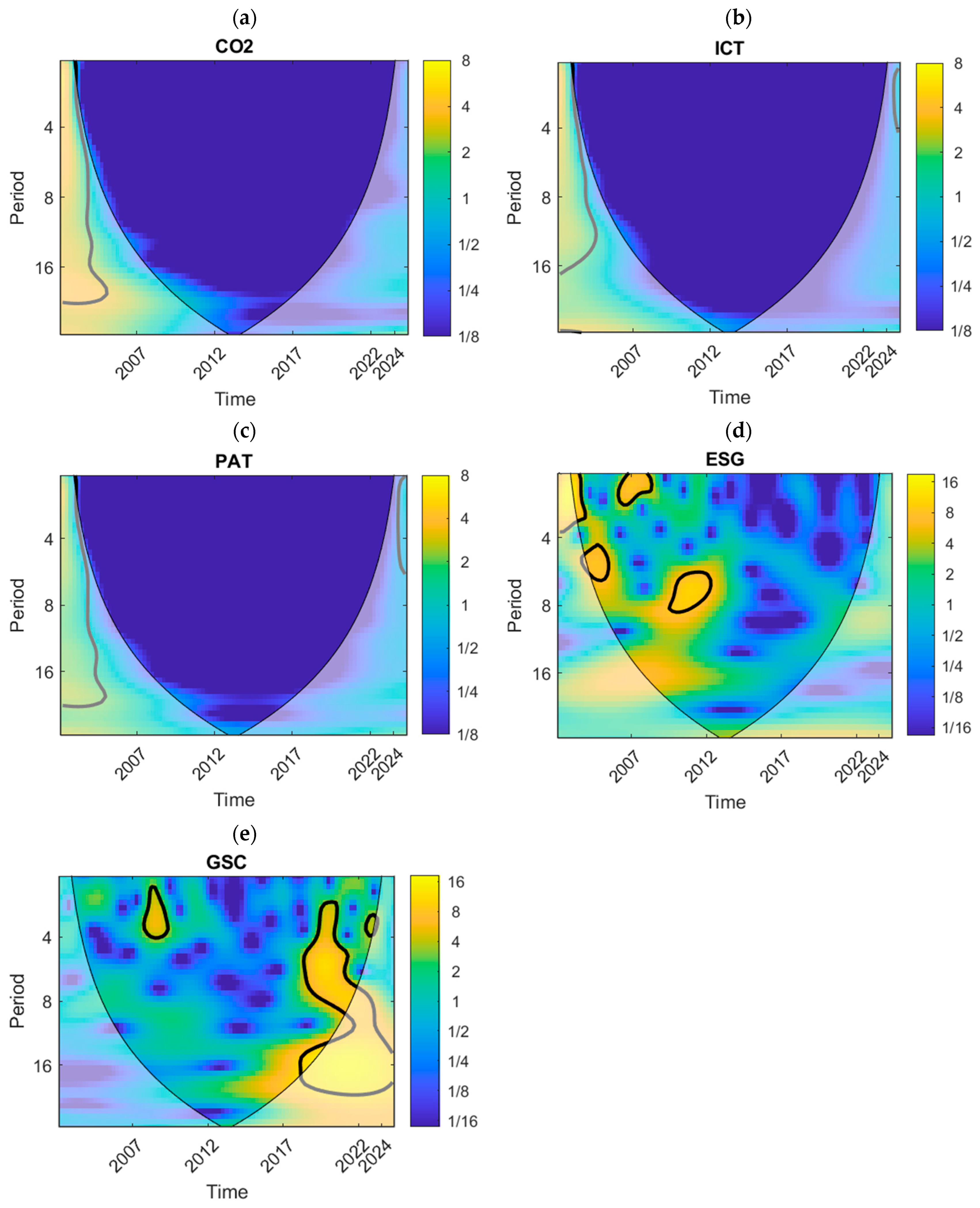
4.4. Wavelet Power Result
4.5. Wavelet Coherence Result
4.6. Multiple Wavelet Coherence
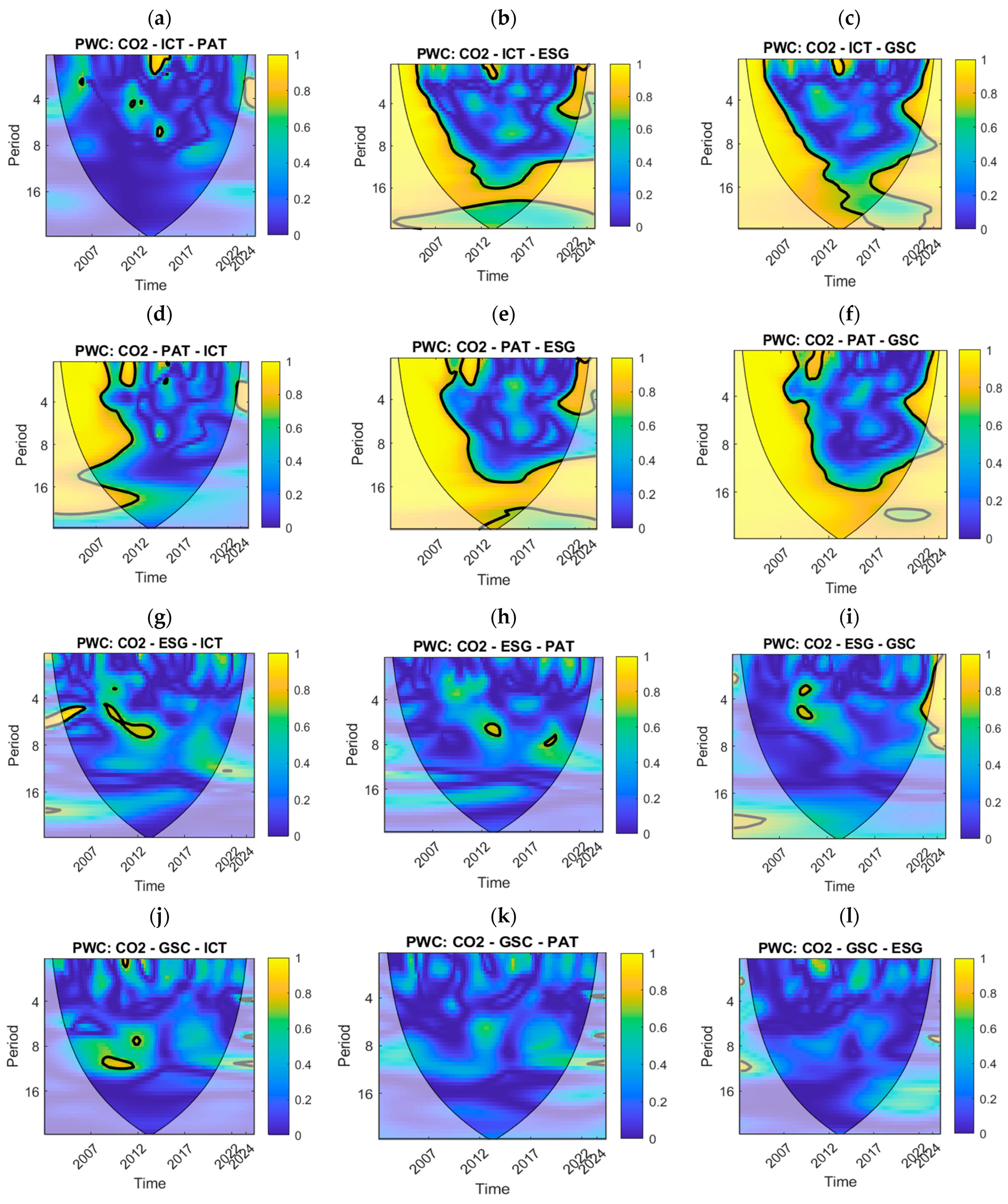
4.7. Partial Wavelet Coherence
4.8. Wavelet Granger Causality Result
5. Conclusions and Policy Recommendations
5.1. Conclusions
5.2. Policy Recommendations
5.3. Limitation and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Correction Statement
References
- Carbon Brief Analysis: Clean Energy Just Put China’s CO2 Emissions into Reverse for First Time. 2025. Available online: https://www.carbonbrief.org/analysis-clean-energy-just-put-chinas-co2-emissions-into-reverse-for-first-time/ (accessed on 4 April 2025).
- Climate Tracker Climate Tracker China. 2025. Available online: https://climateactiontracker.org/countries/china/ (accessed on 20 June 2025).
- de Mariz, F.; Aristizábal, L.; Andrade Álvarez, D. Fiduciary duty for directors and managers in the light of anti-ESG sentiment: An analysis of Delaware Law. Appl. Econ. 2025, 57, 4309–4320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özkan, O.; Naimoğlu, M.; Dam, M.M. The Impact of ESG-Related, Financial, and Geopolitical Uncertainties on the Renewable Energy Transition in the United States. Bus. Strategy Environ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baratta, A.; Cimino, A.; Longo, F.; Solina, V.; Verteramo, S. The Impact of ESG Practices in Industry with a Focus on Carbon Emissions: Insights and Future Perspectives. Sustainability 2023, 15, 6685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Işık, C.; Ongan, S.; Islam, H.; Pinzon, S.; Jabeen, G. Navigating sustainability: Unveiling the interconnected dynamics of ESG factors and SDGs in BRICS-11. Sustain. Dev. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qian, Y.; Liu, Y. Improve carbon emission efficiency: What role does the ESG initiatives play? J. Environ. Manag. 2024, 367, 122016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalia, D.; Aggarwal, D. Examining impact of ESG score on financial performance of healthcare companies. J. Glob. Responsib. 2022, 14, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, T.S. Response of sectoral CO2 emissions to climate and economic policy uncertainties: A multi-frequency quantile analysis. Appl. Econ. 2025, 1, 1–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, Y. US-China tensions, global supply chains pressure, and global economy. Econ. Lett. 2025, 250, 112283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maeno, K.; Tokito, S.; Kagawa, S. CO2 mitigation through global supply chain restructuring. Energy Econ. 2022, 105, 105768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qin, M.; Su, C.-W.; Umar, M.; Lobonţ, O.-R.; Manta, A.G. Are climate and geopolitics the challenges to sustainable development? Novel evidence from the global supply chain. Econ. Anal. Policy 2023, 77, 748–763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eti, S.; Dinçer, H.; Gökalp, Y.; Yüksel, S.; Kararoğlu, D. Identifying Key Issues to Handle the Inflation Problem in the Healthcare Industry Caused by Energy Prices: An Evaluation with Decision-Making Models. In Managing Inflation and Supply Chain Disruptions in the Global Economy; IGI Global: Hershey, PA, USA, 2023; pp. 162–178. ISBN 978-1-66845-876-1. [Google Scholar]
- Hu, G.; Gozgor, G.; Lu, Z.; Mahalik, M.K.; Pal, S. Determinants of renewable stock returns: The role of global supply chain pressure. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2024, 191, 114182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adams, S.; Adedoyin, F.; Olaniran, E.; Bekun, F.V. Energy consumption, economic policy uncertainty and carbon emissions; causality evidence from resource rich economies. Econ. Anal. Policy 2020, 68, 179–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Özkan, O.; Olanrewaju, V.O.; Uzun, B. Do fossil-fuel subsidies, Fintech innovation, and digital ICT transform ecological quality in Turkey? Evidence from modified cross-quantile regression. Appl. Econ. 2025, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Añón Higón, D.; Gholami, R.; Shirazi, F. ICT and environmental sustainability: A global perspective. Telemat. Inform. 2017, 34, 85–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Liu, C. The impact of ICT industry on CO2 emissions: A regional analysis in China. Renew. Sustain. Energy Rev. 2015, 44, 12–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uddin, M.; Rashid, M.H.U.; Ahamad, S.; Ehigiamusoe, K.U. Impact of militarization, energy consumption, and ICT on CO2 emissions in G20 countries. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 11771–11793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adedoyin, F.F.; Gumede, M.I.; Bekun, F.V.; Etokakpan, M.U.; Balsalobre-lorente, D. Modelling coal rent, economic growth and CO2 emissions: Does regulatory quality matter in BRICS economies? Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 710, 136284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Acheampong, A.O.; Dzator, J.; Dzator, M.; Salim, R. Unveiling the effect of transport infrastructure and technological innovation on economic growth, energy consumption and CO2 emissions. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 182, 121843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Olanrewaju, V.O.; Özkan, O.; Ali, S. How does Digital Technology Influence Natural Resource Use: A Global Perspective. Comput. Econ. 2024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Hu, S.; Li, R. Could information and communication technology (ICT) reduce carbon emissions? The role of trade openness and financial development. Telecommun. Policy 2024, 48, 102699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memari, A.; Rahim, A.R.A.; Ahmad, R.; Hassan, A. A literature review on green supply chain modelling for optimising CO2 emission. Int. J. Oper. Res. 2016, 26, 509–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiwari, S.; Si Mohammed, K.; Mentel, G.; Majewski, S.; Shahzadi, I. Role of circular economy, energy transition, environmental policy stringency, and supply chain pressure on CO2 emissions in emerging economies. Geosci. Front. 2024, 15, 101682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akram, R.; Ibrahim, R.L.; Wang, Z.; Adebayo, T.S.; Irfan, M. Neutralizing the surging emissions amidst natural resource dependence, eco-innovation, and green energy in G7 countries: Insights for global environmental sustainability. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 344, 118560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Ozsahin, D.U.; Olanrewaju, V.O.; Uzun, B. Decoding the environmental role of nuclear and renewable energy consumption: A time-frequency perspective. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2025, 223, 111660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costantiello, A.; Leogrande, A. The Determinants of CO2 Emissions in the Context of ESG Models at World Level. Available online: https://mpra.ub.uni-muenchen.de/117110/ (accessed on 8 July 2025).
- Özkan, O.; Destek, M.A.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Esmaeili, P. Unlocking the impact of international financial support to infrastructure, energy efficiency, and ICT on CO2 emissions in India. Energy Policy 2024, 194, 114340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Liu, J. Impact of supply chain digitalization, business enterprise R&D expenditure and government budget allocations for R&D: A roadmap towards carbon neutrality. Energy Econ. 2025, 141, 108057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prakash, N. Income disparities and environmental dynamics: Exploring varied impacts of renewable energy, innovations, and economic growth on CO2 emissions. Renew. Energy 2025, 243, 122596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bilgili, F.; Balsalobre-Lorente, D.; Kuşkaya, S.; Alnour, M.; Önderol, S.; Hoque, M.E. Are research and development on energy efficiency and energy sources effective in the level of CO2 emissions? Fresh evidence from EU data. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, C.; Ren, X.; Wang, Z.; Yan, C. Heterogeneous impacts of renewable energy and environmental patents on CO2 emission—Evidence from the BRIICS. Sci. Total Environ. 2019, 668, 1328–1338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ibrahim, R.L.; Awosusi, A.A.; Ajide, K.B.; Ozdeser, H. Exploring the renewable energy-environmental sustainability pathways: What do the interplay of technological innovation, structural change, and urbanization portends for BRICS? Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2025, 27, 191–211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adebayo, T.S.; Kirikkaleli, D. Impact of renewable energy consumption, globalization, and technological innovation on environmental degradation in Japan: Application of wavelet tools. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 16057–16082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- WDI World Development Indicator. 2024. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org (accessed on 1 April 2024).
- OWD Our Worldindata. 2024. Available online: https://ourworldindata.org/ (accessed on 20 October 2024).
- PU Policy Uncertainty. 2024. Available online: https://www.policyuncertainty.com (accessed on 4 January 2024).
- Torrence, C.; Compo, G.P. A Practical Guide to Wavelet Analysis. Bull. Am. Meteorol. Soc. 1998, 79, 61–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mihanović, H.; Orlić, M.; Pasarić, Z. Diurnal thermocline oscillations driven by tidal flow around an island in the Middle Adriatic. J. Mar. Syst. 2009, 78, S157–S168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abdelbaky, A.; Liu, T.; Mingyang, X.; Shahzad, M.F.; Hassanein, A. Real Earnings Management and ESG Performance in China: The Mediating Role of Corporate Innovations. Int. J. Financ. Econ. 2025. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Broadstock, D.C.; Chan, K.; Cheng, L.T.W.; Wang, X. The role of ESG performance during times of financial crisis: Evidence from COVID-19 in China. Financ. Res. Lett. 2021, 38, 101716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, K.; Ahmed, S. A predictive analysis of CO2 emissions, environmental policy stringency, and economic growth in China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2018, 25, 16091–16100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Razzaq, A.; Sharif, A.; An, H.; Aloui, C. Testing the directional predictability between carbon trading and sectoral stocks in China: New insights using cross-quantilogram and rolling window causality approaches. Technol. Forecast. Soc. Change 2022, 182, 121846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afshan, S.; Yaqoob, T. The potency of eco-innovation, natural resource and financial development on ecological footprint: A quantile-ARDL-based evidence from China. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. 2022, 29, 50675–50685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, H.; Yi, J.; Chen, A.; Peng, D.; Yang, J. Green technology innovation and CO2 emission in China: Evidence from a spatial-temporal analysis and a nonlinear spatial durbin model. Energy Policy 2023, 172, 113338. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flammer, C. Green bonds and carbon emissions. Oxf. Rev. Econ. Policy 2023, 39, 752–764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Author(s) | Period | Nation(s) | Method(s) | Finding(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Impact of ESG on CO2 | ||||
| Baratta et al. [5] | Not defined | Global | Bibliometric Analysis | ESG ↓ CO2 |
| Akram et al. [28] | 2011–2020 | 193 countries | ANN | ESG ↓ CO2 |
| Özkan et al. [4] | 2002 to 2023 | United States | KRLS | ESG ↑ CO2 |
| Qian et al. [7] | Not defined | Chinese companies | Mechanism analysis | ESG ↓ CO2 |
| Impact of ICT on CO2 | ||||
| Zhang & Liu [18] | 2000–2010 | China | PCSE | ICT ↓ CO2 |
| Añón et al. [17] | 1995 to 2010 | 142 economies | POLS | ICT ↑ CO2 |
| Uddin et al. [19] | 1980 to 2019 | G20 countries | GMM | ICT ↑ CO2 |
| Özkan et al. [29] | 2000–2021 | India | MMQR | ICT ↓ CO2 |
| Wang et al. [23] | 2006 to 2017 | 92 countries | Threshold regression | ICT ↓ CO2 |
| Impact of GSC on CO2 | ||||
| Tiwari et al. [25] | 1997 to 2020 | Emerging economies | QARDL | GSC ↑ CO2 |
| Memari et al. [24] | Undefined | Global | Undefined | GSC ↑ CO2 |
| Maeno et al. [11] | Undefined | Japan | SEM | GSC ↑ CO2 |
| Li & Liu [30] | 2000Q1 to 2022Q4. | United States | WQQR | GSC ↑ CO2 |
| Impact of PAT on CO2 | ||||
| Ibrahim et al. [34] | 1992 to 2019 | BRICS | MMQR | PAT ↑ CO2 |
| Bilgili et al. [32] | 1990–2019 | European Union | PVAR) | PAT ↓ CO2 |
| Cheng et al. [33] | 1990–2019 | Arab countries | FMOLS | PAT ↓ CO2 |
| Prakash [31] | 1990–2020 | 190 countries | CCEMG | PAT ↓ CO2 |
| Adebayo & Kirikkaleli [35] | 1990–2016 | Japan | Wavelet Tools | PAT ↑ CO2 |
| Abbreviation | Variables | Measurement | Sources |
|---|---|---|---|
| PAT | Patent innovations | Number of patent resident | WDI [36] |
| ICT | Information and Communication Technology | Individuals using the Internet (% of population) | WDI [36] |
| CO2 | Carbon emissions | Metric tons per capita | OWD [37] |
| GSC | Global supply chain management | Index | |
| ESG | Environmental sustainability, governance sustainability uncertainty | Index | PU [38] |
| CO2 | ICT | PAT | ESG | GSC | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Minimum | 1.235 | 1.664 | 3.609 | 2.377 | −1.313 |
| Maximum | 2.128 | 4.356 | 7.102 | 3.894 | 4.251 |
| 1. Quartile | 1.721 | 3.082 | 4.967 | 2.765 | −0.458 |
| 3. Quartile | 2.016 | 4.149 | 6.852 | 3.283 | 0.298 |
| Mean | 1.854 | 3.518 | 5.877 | 3.033 | 0.127 |
| Median | 1.957 | 3.846 | 6.311 | 2.950 | −0.163 |
| SE mean | 0.025 | 0.087 | 0.118 | 0.037 | 0.109 |
| LCL mean | 1.804 | 3.344 | 5.642 | 2.959 | −0.088 |
| UCL mean | 1.904 | 3.691 | 6.112 | 3.107 | 0.343 |
| Variance | 0.056 | 0.679 | 1.244 | 0.123 | 1.048 |
| Stdev | 0.238 | 0.824 | 1.116 | 0.351 | 1.024 |
| Skewness | −1.044 | −0.927 | −0.584 | 0.433 | 1.950 |
| Kurtosis | −0.070 | −0.536 | −1.121 | −0.775 | 3.856 |
| JB | 16.712 *** | 14.032 *** | 9.549 *** | 4.823 * | 118.04 *** |
| Dimensions | CO2 | ICT | PAT | ESG | GSC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| M2 | 24.584 *** | 24.318 *** | 36.582 *** | 19.929 *** | 9.8861 *** |
| M3 | 26.176 *** | 25.852 *** | 39.070 *** | 19.716 *** | 10.312 *** |
| M4 | 28.181 *** | 27.744 *** | 42.225 *** | 19.922 *** | 10.494 *** |
| M5 | 31.132 *** | 30.504 *** | 46.860 *** | 20.601 *** | 10.908 *** |
| M6 | 35.196 *** | 34.294 *** | 53.253 *** | 21.851 *** | 11.368 *** |
| Frequency | Dependent Variables | Independent Variables | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CO2 | ESG | GSC | PAT | ICT | ||
| Original level | CO2 | 0.7456 | 0.7172 | 0.0320 | 0.0353 ** | |
| ESG | 0.530 | 0.1520 | 0.3819 | 0.1810 | ||
| GSC | 0.214 | 0.4000 | 0.5024 | 0.9890 | ||
| PAT | 0.952 | 0.2930 | 0.6365 | 0.6737 | ||
| ICT | 0.189 | 0.7557 | 0.6668 | 0.0213 | ||
| Level 1 | CO2 | 0.001 | 0.590 | 0.241 | 0.402 | |
| ESG | 0.174 | 0.392 | 0.129 | 0.104 | ||
| GSC | 0.110 | 0.365 | 0.136 | 0.127 | ||
| PAT | 0.293 | 0.001 *** | 0.555 | 0.950 | ||
| ICT | 0.441 | 0.001 *** | 0.504 | 0.954 | ||
| Level 2 | CO2 | 0.008 | 0.765 | 0.742 | 0.760 | |
| ESG | 0.388 | 0.204 | 0.385 | 0.386 | ||
| GSC | 0.227 | 0.719 | 0.126 | 0.146 | ||
| PAT | 0.648 | 0.010 ** | 0.936 | 0.527 | ||
| ICT | 0.978 | 0.013 ** | 0.915 | 0.680 | ||
| Level 3 | CO2 | 0.170 | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | |
| ESG | 0.003 *** | 0.011 ** | 0.002 *** | 0.000 *** | ||
| GSC | 0.000 *** | 0.366 | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | ||
| PAT | 0.001 *** | 0.052 * | 0.000 *** | 0.001 *** | ||
| ICT | 0.000 *** | 0.070 * | 0.000 *** | 0.002 *** | ||
| Level 4 | CO2 | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | |
| ESG | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | ||
| GSC | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | ||
| PAT | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.006 *** | ||
| ICT | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.002 *** | ||
| Level 5 | CO2 | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.001 *** | 0.000 *** | |
| ESG | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | ||
| GSC | 0.000 *** | 0.001 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | ||
| PAT | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.002 *** | ||
| ICT | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.000 *** | 0.051 * | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ben Salem, A.; Iyiola, K.; Alzubi, A. Do Supply Chain Management, ESG Sustainability Practices, and ICT Have an Impact on Environmental Sustainability? Systems 2025, 13, 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13090725
Ben Salem A, Iyiola K, Alzubi A. Do Supply Chain Management, ESG Sustainability Practices, and ICT Have an Impact on Environmental Sustainability? Systems. 2025; 13(9):725. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13090725
Chicago/Turabian StyleBen Salem, Abdurahim, Kolawole Iyiola, and Ahmad Alzubi. 2025. "Do Supply Chain Management, ESG Sustainability Practices, and ICT Have an Impact on Environmental Sustainability?" Systems 13, no. 9: 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13090725
APA StyleBen Salem, A., Iyiola, K., & Alzubi, A. (2025). Do Supply Chain Management, ESG Sustainability Practices, and ICT Have an Impact on Environmental Sustainability? Systems, 13(9), 725. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13090725






