Evolution Trends, Spatial Differentiation, and Convergence Characteristics of Urban Ecological Economic Resilience in China
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Research Design and Methodology
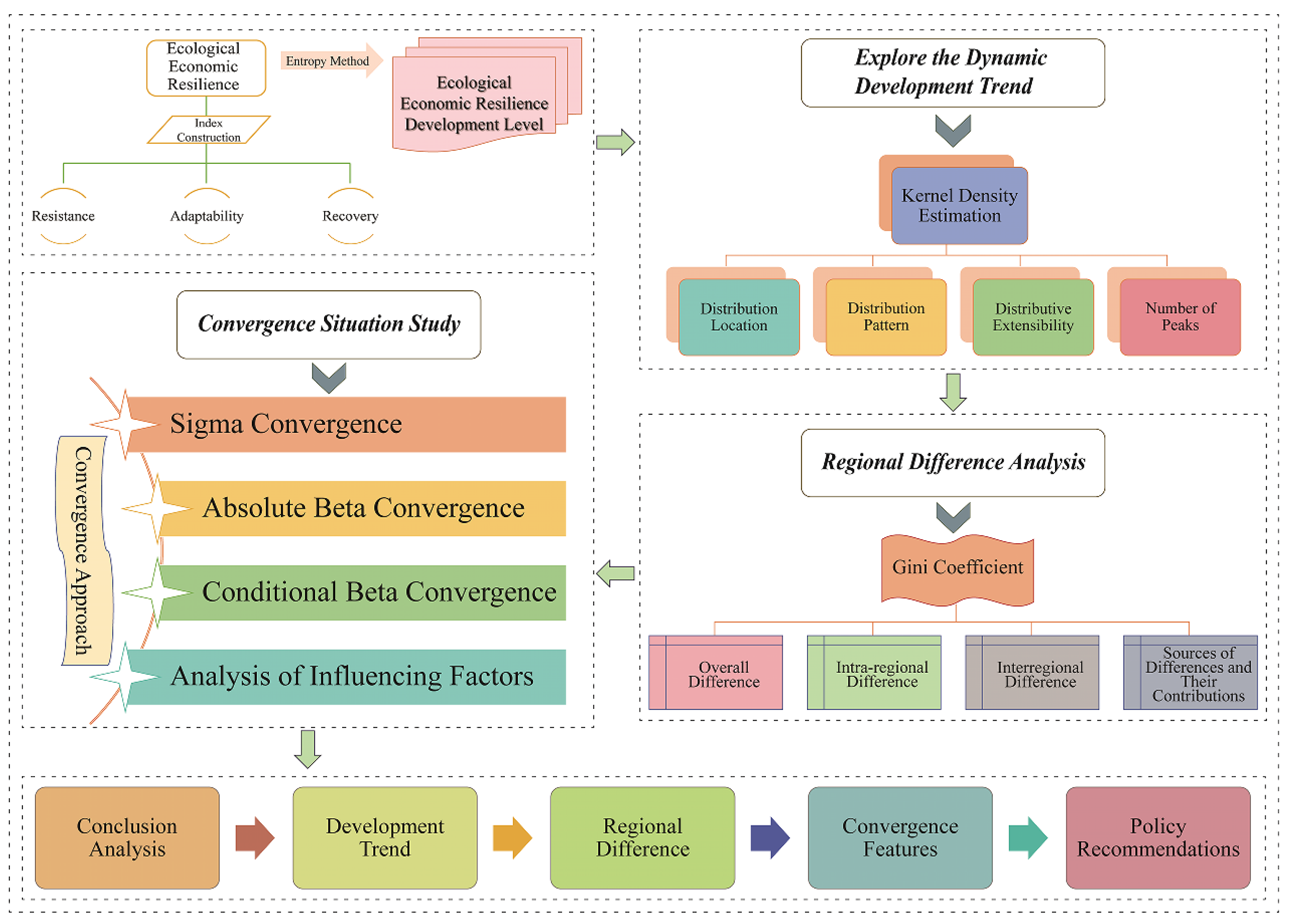
2.1. Evaluation Model for Ecological Economic Resilience
2.2. Research Methodology
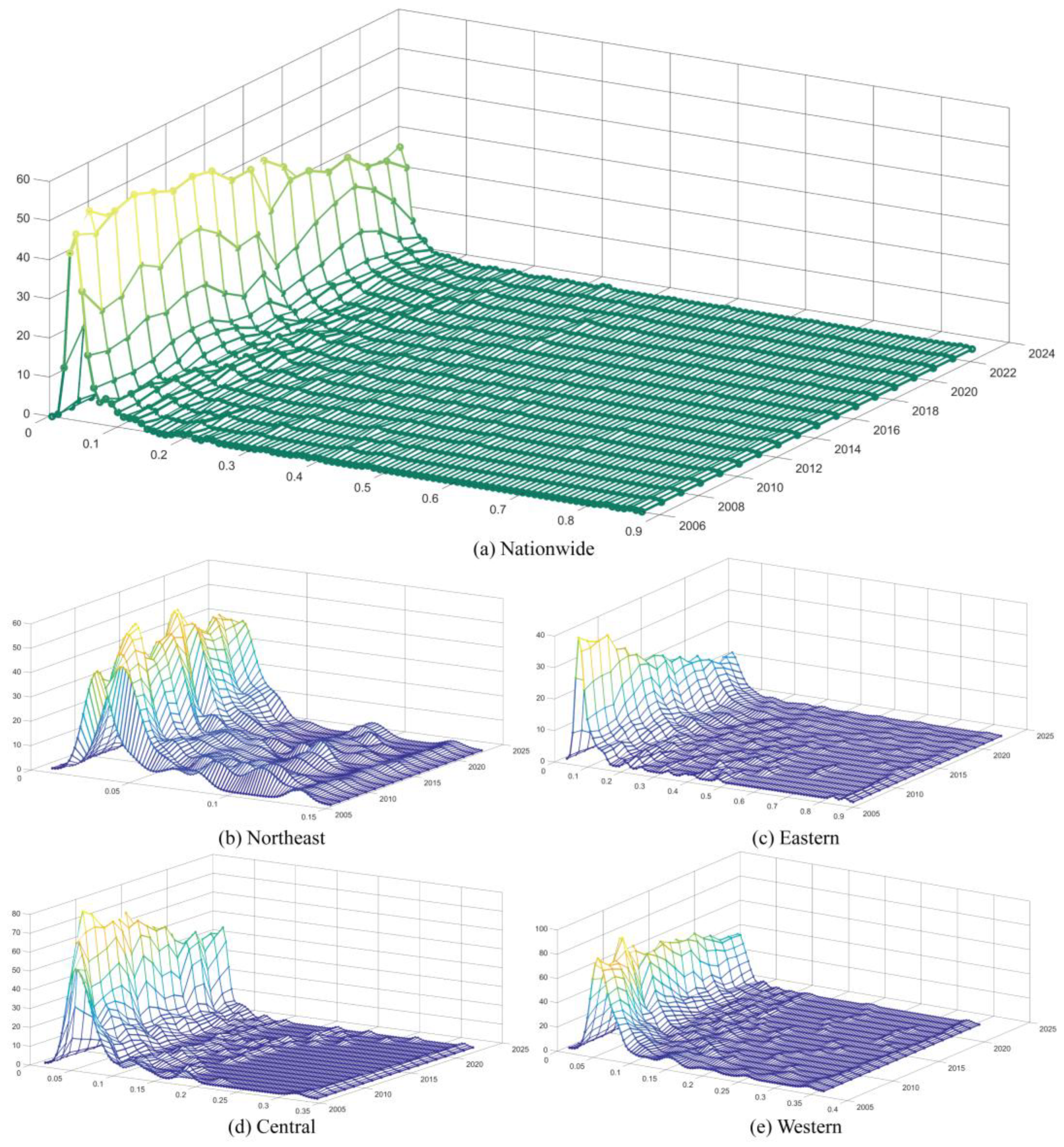
2.2.1. Kernel Density Estimation
2.2.2. Dagum Gini Coefficient
2.2.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Test
2.2.4. Convergence Test
3. Empirical Results Analysis
3.1. Analysis of the Evolutionary Patterns of Ecological Economic Resilience
3.2. Spatial Variation Analysis of Ecological Economic Resilience
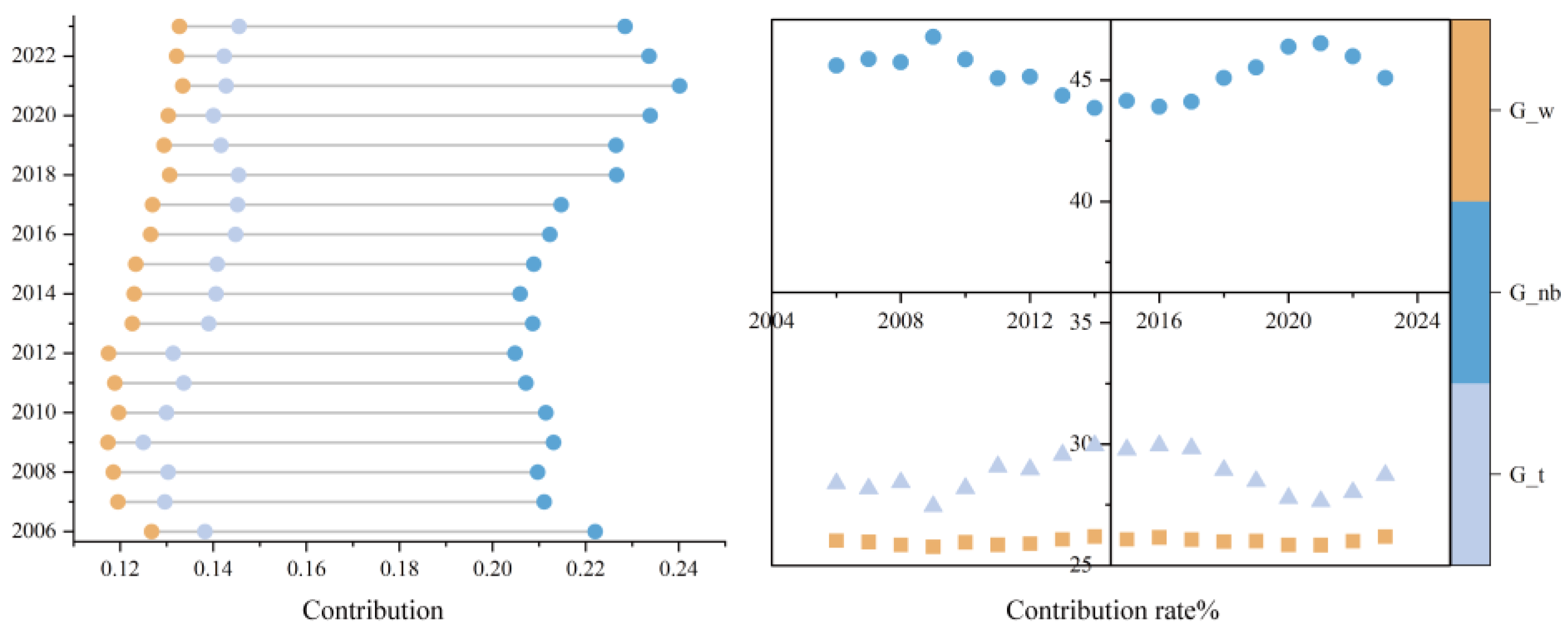
3.2.1. Overall Differences and Intra-Regional Differences
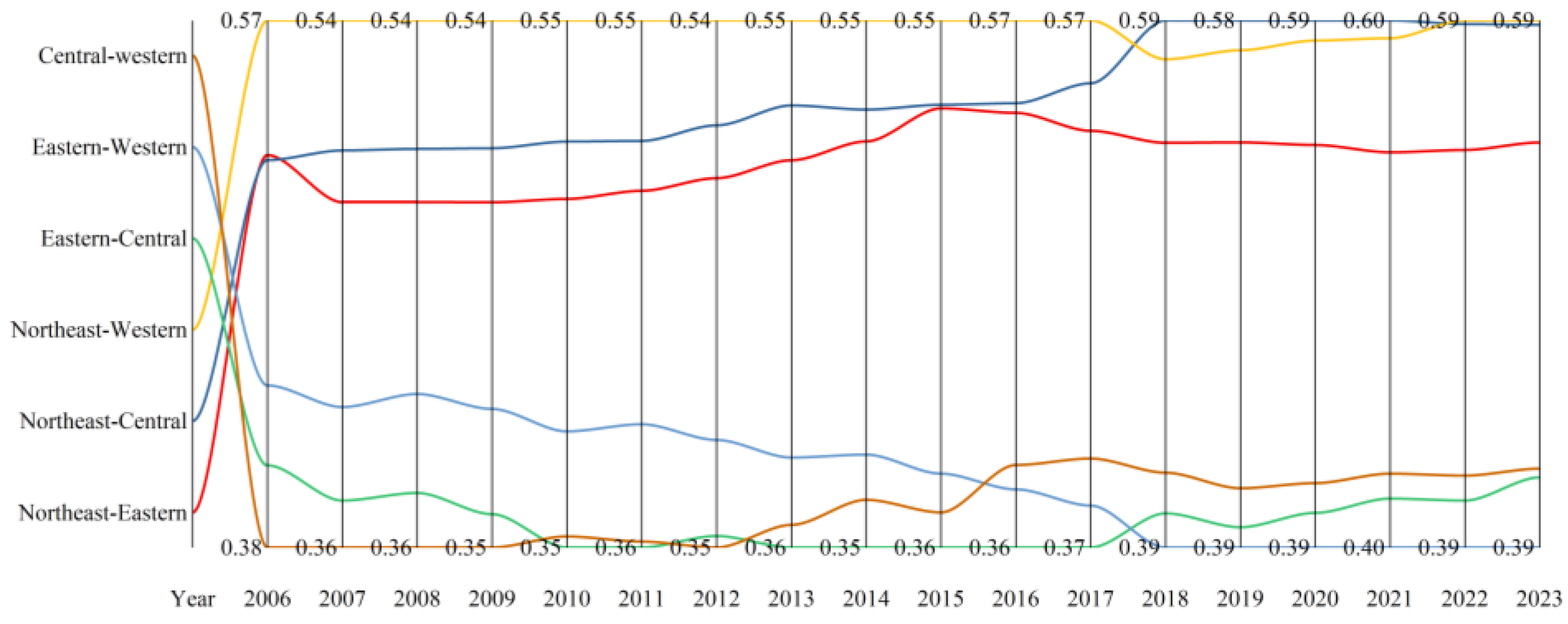
3.2.2. Inter-Regional Differences
3.2.3. Sources of Variation and Their Contributions
3.3. Convergence Pattern Analysis of Ecological Economic Resilience
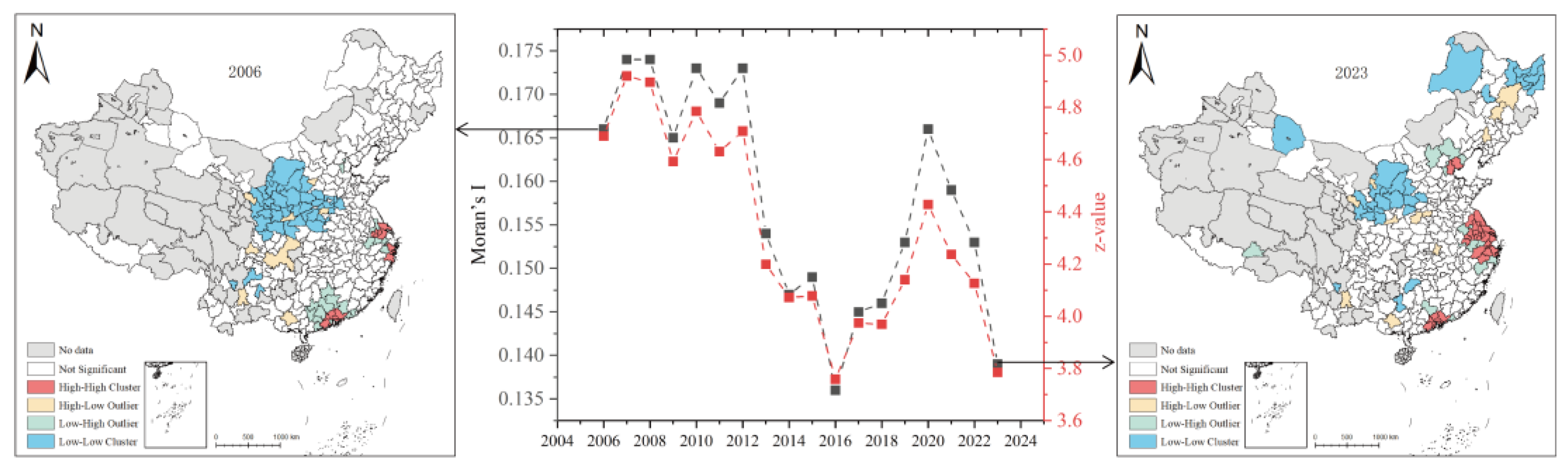
3.3.1. Spatial Correlation Test
3.3.2. Convergence Test and Result Analysis
3.3.3. Convergence Test and Result Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Panzeri, A.; Bertamini, M.; Butter, S.; Levita, L.; Gibson-Miller, J.; Vidotto, G.; Bennett, K.M. Factors impacting resilience as a result of exposure to COVID-19: The ecological resilience model. PLoS ONE 2021, 16, e0256041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tao, J.; Wang, Z.; Li, J. The spatial effect of digital economy on public psychological resilience during the diffusive crisis. Front. Public Health 2023, 11, 1156367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baho, D.L.; Allen, C.R.; Garmestani, A.S.; Fried-Petersen, H.B.; Renes, S.E.; Gunderson, L.H.; Angeler, D.G. A quantitative framework for assessing ecological resilience. Ecol. Soc. A J. Integr. Sci. Resil. Sustain. 2017, 22, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, G.; Tang, C.; Zhong, S.; Song, L. Multiscale study on differences in regional economic resilience in China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2023, 26, 29021–29055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, Y.; Zhou, H.Q.; Jin, X.M.; Shen, Y.F.; Yan, Y.Z. Assessing the Resilience of the Marine Economy: A Case Study of Southern China’s Marine Economy Circle. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 912462. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, X.; Gao, X.; Zhao, M.; Guo, Z.; Shen, W. Ecological space resilience assessment of Baiyangdian Basin from the perspective of evolutionary resilience. Front. Ecol. Evol. 2023, 11, 1200218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leitner, H.; Sheppard, E.; Webber, S. Globalizing urban resilience. Urban Geogr. 2018, 39, 1276–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datola, G. Implementing urban resilience in urban planning: A comprehensive framework for urban resilience evaluation. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2023, 98, 104821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ribeiro, P.J.G.; Gonçalves, L.A.P.J. Urban resilience: A conceptual framework. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2019, 50, 101625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Zhai, N.; Mu, H. Assessment of urban resilience and subsystem coupling coordination in the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei urban agglomeration. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2024, 100, 105058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Wang, J.; Zhang, J. Spatial distribution characteristics of natural ecological resilience in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2023, 342, 118133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enerlan, G.P. An analysis on the economic resilience and vulnerability of local economies in the Philippines to hydrometeorological disasters. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2023, 84, 103447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Zheng, X.; Wang, X.; Han, L.; Huang, Y.; Li, J.; Tao, Z. Economic resilience in California against two earthquakes. Int. J. Disaster Risk Reduct. 2022, 76, 102993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Watson, P.; Deller, S. Tourism and economic resilience. Tour. Econ. 2022, 28, 1193–1215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, K.; Hu, B.; Li, X.; Niu, T.; Zhang, L. Exploration of coupling effects in the digital economy and eco-economic system resilience in urban areas: Case study of the Beijing-Tianjin-Hebei Urban Agglomeration. Sustainability 2023, 15, 7258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Zhang, Y.; Liu, C.; Hu, F.; Zhou, S.; Zhu, J. Emergy-based assessment and suggestions for sustainable development of regional ecological economy: A case study of Anhui province, China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 2988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Wang, C.; Mao, G.; Wang, M.; Hsu, W.-L. An empirical study on the ecological economy of the Huai River in China. Water 2020, 12, 2162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.-C.; Yan, J.; Li, T. Ecological resilience of city clusters in the middle reaches of Yangtze river. J. Clean. Prod. 2024, 443, 141082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lu, X.; Zhu, J.; Zhou, M.; Zhang, Y. Is digital economy the driving force for improving the tourism economic resilience? Evidence from China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2024, 26, 1–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, D.; Zhao, Z.; Li, J.; Boamah, V. Research on coupling coordination degree of digital finance and economic resilience in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Nat. Hazards 2024, 120, 14279–14309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, L. Study of regional variations and convergence in ecological resilience of Chinese cities. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 154, 110667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Yuan, X.; Liu, G.; Ren, R. The evaluation of wetland reconstruction with nature-based solutions for eco-economic sustainable development. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 160, 111936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, Y.; Wu, X. The spatiotemporal relationship between tourism eco-efficiency and economic resilience from coupling perspectives in China. Sustainability 2023, 15, 10039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Yi, P.; Zhang, D.; Zhou, Y. Assessment of coordinated development between social economy and ecological environment: Case study of resource-based cities in Northeastern China. Sustain. Cities Soc. 2020, 59, 102208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valdez-Rojas, C.; Beas-Luna, R.; Lorda, J. Using a social-ecological systems perspective to identify context specific actions to build resilience in small scale fisheries in Mexico. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 904859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, B.M.; Boumans, R.; Fath, B.D. Prototype of social-ecological system’s resilience analysis using a dynamic index. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 141, 109113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, X.; Yu, Y.; Yang, S. Urban resilience for urban sustainability: Concepts, dimensions, and perspectives. Sustainability 2022, 14, 2481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miranti, R.C.; Mendez, C. Social and economic convergence across districts in indonesia: A spatial econometric approach. Bull. Indones. Econ. Stud. 2023, 59, 421–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xiao, Y. How environmental awareness affects the spatial convergence of urban economic resilience: Evidence from China. Front. Environ. Sci. 2023, 11, 1326701. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, N.; Tabandeh, A.; Gardoni, P. Regional resilience analysis: A multiscale approach to optimize the resilience of interdependent infrastructure. Comput.-Aided Civ. Infrastruct. Eng. 2020, 35, 1315–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhai, X.; Sun, C.; Zou, W.; Hao, S. Spatiotemporal characteristic and evolution of China’s marine economic resilience. Ocean Coast. Manag. 2023, 238, 106562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Y.; Fan, H.; Lei, X.; Wan, J. A runoff probability density prediction method based on B-spline quantile regression and kernel density estimation. Applied Mathematical Modelling. 2021, 93, 852–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Z.; Zhang, S.; Li, F. The spatio-temporal dynamic evolution and variability pattern of urban green resilience in China based on multi-criteria decision-making. Sustainable Cities and Society. 2024, 116, 105887. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, L.; Liang, Y.; Shao, J.; Cheng, Y.; Zhou, Q.; Zhang, J. Moran’s index-based tensor decomposition for eddy current pulsed thermography sequence processing. IEEE Trans. Instrum. Meas. 2021, 70, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrerias, M.J.; Ordoñez, J. New evidence on the role of regional clusters and convergence in China (1952–2008). China Econ. Rev. 2012, 23, 1120–1133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Li, C.; Si, Y. Spatio-temporal autocorrelation measures for nonstationary series: A new temporally detrended spatio-temporal Moran’s index. Phys. Lett. A 2016, 380, 106–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cui, Y.; Khan, S.U.; Deng, Y.; Zhao, M. Spatiotemporal heterogeneity, convergence and its impact factors: Perspective of carbon emission intensity and carbon emission per capita considering carbon sink effect. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 92, 106699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, D.; Peng, B.; Wu, J.; Zhang, Z. The convergence of total-factor energy efficiency across Chinese cities: A distribution dynamics approach. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2024, 69, 406–416. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, J.E.; Lee, J.; Islam, M.T.; Nazlioglu, S. Stochastic convergence of per capita greenhouse gas emissions: New unit root tests with breaks and a factor structure. Energy Econ. 2022, 113, 106201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, Y.; Jia, J.; Ju, M.; Chen, C.; Zhou, Y.; Zhong, Y. Multi-perspective analysis of household carbon dioxide emissions from direct energy consumption by the methods of logarithmic mean divisia index and σ convergence in Central China. Sustainability 2021, 13, 9285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Hao, Y. Rethinking China’s environmental target responsibility system: Province-level convergence analysis of pollutant emission intensities in China. J. Clean. Prod. 2020, 242, 118472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dun, S.; Xiao, L.; Long, D. Is the New Urbanization Beneficial to Improve the Ecological Civilization Quality in the Western Region? Inq. Into Econ. 2018, 7, 164–173. [Google Scholar]
- Min, W.; Jiuli, H. Is Campaign-Style Governance Effective? Civilized City Campaign and Urban Sanitation. J. World Econ. 2022, 45, 212–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Que, X.; Huang, J.; Ralph, J.; Zhang, J.; Prabhu, A.; Morrison, S.; Ma, X. Using adjacency matrix to explore remarkable associations in big and small mineral data. Geosci. Front. 2024, 15, 101823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, J.; Wu, H.; Zhang, X. Research on the impact of sand and dust weather on the social-ecological system resilience based on the DPWSIR model—Taking the arid cities of Northwest China as an example. Ecol. Indic. 2024, 166, 112314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]



| Dimensional Designations | Nuclear Factors | Fundamental Indicators |
|---|---|---|
| Resistance | Social Development | Proportion of Land Area in Built-up Areas |
| Total Volume of Urban Water Supply | ||
| Population Density | ||
| Total Industrial Output Above Designated Size | ||
| Pollutant Emissions | Industrial Wastewater Discharge (10,000 tons) | |
| Industrial Sulfur Dioxide Emission (metric tons) | ||
| Industrial Smoke and Dust Emission (metric tons) | ||
| Industrial Nitrogen Oxides Emission (metric tons) | ||
| Adaptability | Economic Strength | Per Capita GDP |
| The Advanced Transformation of Industrial Structure (Proportion of the Added Value of the Tertiary Industry in GDP (%)) | ||
| Local General Budgetary Revenue in Fiscal Affairs | ||
| Environmental Protection Investment | Urban Construction and Maintenance Expenditure | |
| Investment in Landscape Gardening | ||
| Investment in Cityscape and Sanitation | ||
| Investment in Sewerage and Waste Disposal | ||
| Governance Efficiency | Comprehensive Utilization Rate (%) of General Industrial Solid Waste | |
| Sanitary Treatment Rate (%) of Domestic Waste | ||
| Sewage Treatment Rate (%) | ||
| Environmental Quality | PM2.5 | |
| recoverability | Innovation-Driven Development | The Proportion of Education and Science Expenditures in Public Budget Expenditure |
| The Place-Occupying Ratio of Information Transmission, Computer Services, and Software Industry Practitioners in Total Employment | ||
| The Number of Granted Green Patents | ||
| Ecological Restoration | Per Capita Road Area | |
| Per Capita Green Space in Parks | ||
| Urban Green Space Coverage Rate in Built-up Areas |
| Region | Nationwide | Northeast | Eastern | Central | Western |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | SDM | SAR | SDM | SAR | SDM |
| −0.2509 *** (0.0086) | −0.3420 *** (0.0265) | −0.2649 *** (0.0164) | −0.3252 *** (0.0155) | −0.1751 *** (0.0164) | |
| 0.1251 *** (0.0128) | — | 0.0863 *** (0.0233) | — | 0.0369 * (0.0215) | |
| 0.0478 ** (0.0195) | −0.1433 ** (0.0562) | 0.0105 (0.0357) | −0.0550 (0.0401) | 0.0396 (0.0293) | |
| 0.0160 | 0.0233 | 0.0171 | 0.0219 | 0.0107 | |
| Time effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Individual effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 0.1021 | 0.2330 | 0.0666 | 0.0706 | 0.0392 |
| Region | Nationwide | Northeast | Eastern | Central | Western |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Model | SDM | SDM | SDM | SDM | SDM |
| −0.3318 *** (0.0092) | −0.4561 *** (0.0290) | −0.3650 *** (0.0167) | −0.4524 *** (0.0176) | −0.2597 *** (0.0172) | |
| 0.1256 *** (0.0154) | 0.0730 (0.0676) | 0.1229 *** (0.0264) | 0.0368 *** (0.0408) | 0.0145 (0.0257) | |
| 0.0394 ** (0.0196) | −0.0830 (0.0610) | 0.0433 (0.0355) | −0.0709 * (0.0429) | 0.0320 (0.0295) | |
| LED | 0.0661 *** (0.0108) | 0.1120 *** (0.0351) | 0.0537 *** (0.0189) | 0.1162 *** (0.0235) | 0.0449 ** (0.0186) |
| IS | −0.0304 ** (0.0140) | −0.0315 (0.0342) | −0.0790 *** (0.0287) | −0.0573 (0.0365) | 0.0027 (0.0223) |
| UCE | 0.0116 *** (0.0009) | 0.0058 * 0.0033) | 0.0118 *** (0.0014) | 0.0139 *** (0.0016) | 0.0129 *** (0.0017) |
| UWSS | 0.0679 *** (0.0049) | 0.1288 *** (0.0171) | 0.1475 *** (0.0113) | 0.0911 *** (0.0111) | 0.0268 *** (0.0070) |
| ITER | 0.0048 *** (0.0007) | 0.0034 (0.0025) | 0.0014 (−0.0176) | 0.0032 *** (0.0011) | 0.0120 *** (0.0016) |
| 0.0224 | 0.0338 | 0.0252 | 0.0335 | 0.0167 | |
| Time effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| Individual effect | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes | Yes |
| 0.2049 | 0.2668 | 0.2304 | 0.3523 | 0.1577 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ran, X.; Ding, R.; Zhang, B. Evolution Trends, Spatial Differentiation, and Convergence Characteristics of Urban Ecological Economic Resilience in China. Systems 2025, 13, 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13080666
Ran X, Ding R, Zhang B. Evolution Trends, Spatial Differentiation, and Convergence Characteristics of Urban Ecological Economic Resilience in China. Systems. 2025; 13(8):666. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13080666
Chicago/Turabian StyleRan, Xiaofeng, Rui Ding, and Bowen Zhang. 2025. "Evolution Trends, Spatial Differentiation, and Convergence Characteristics of Urban Ecological Economic Resilience in China" Systems 13, no. 8: 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13080666
APA StyleRan, X., Ding, R., & Zhang, B. (2025). Evolution Trends, Spatial Differentiation, and Convergence Characteristics of Urban Ecological Economic Resilience in China. Systems, 13(8), 666. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems13080666






