1. Introduction
According to the UNDESA [
1,
2], approximately 55% of the global population resides in urban areas, with projections indicating that this figure will soon reach 60%, driven by rapid urbanization, in less developed countries. A region or country’s urbanization is a social process of the rural population moving to the cities and living in the cities. Urbanization has obvious impacts on or relationships to the nation’s economy, society, and environment [
3,
4]. The driving forces of urbanization, the impact of urbanization, and the complex relationship between urbanization and economic development are key areas of research that garner significant attention and offer compelling avenues for exploration [
5].
In the past few decades, developing countries have experienced urban population growth in city areas [
6]. Africa is projected to have the world’s highest urbanization rate due to its young population and rapid rural–urban migration: the UN estimates that by 2050, 60% of Africa’s population will reside in cities, driven by a projected 1.3 billion increase in urban dwellers—the largest absolute growth globally [
7,
8,
9,
10]. While urbanization in Africa is also seen as an opportunity for African countries to boost their economy and solve urban poverty [
11], it has not effectively translated into economic growth [
12]. Current studies also showcase that unemployment and poverty continue to constrain the development of the African economy [
5,
13]. And the weak urban economy has slowed down the urbanization process in some African countries, and even led to the retrogression of urbanization [
14,
15].
The process of urbanization involves not only rural–urban migration, but also a series of processes including economic growth, employment transfer, urban consumption level growth, and living standard improvement [
15]. While Africa is expected to have the highest urbanization rate globally, it is essential to evaluate the quality of this urbanization in a judicious manner. Moreover, the rapid growth of urban populations and economic development in Africa may not be well-coordinated [
16]. Therefore, it is essential to further measure the coordination between the two and analyze the associated impact mechanisms.
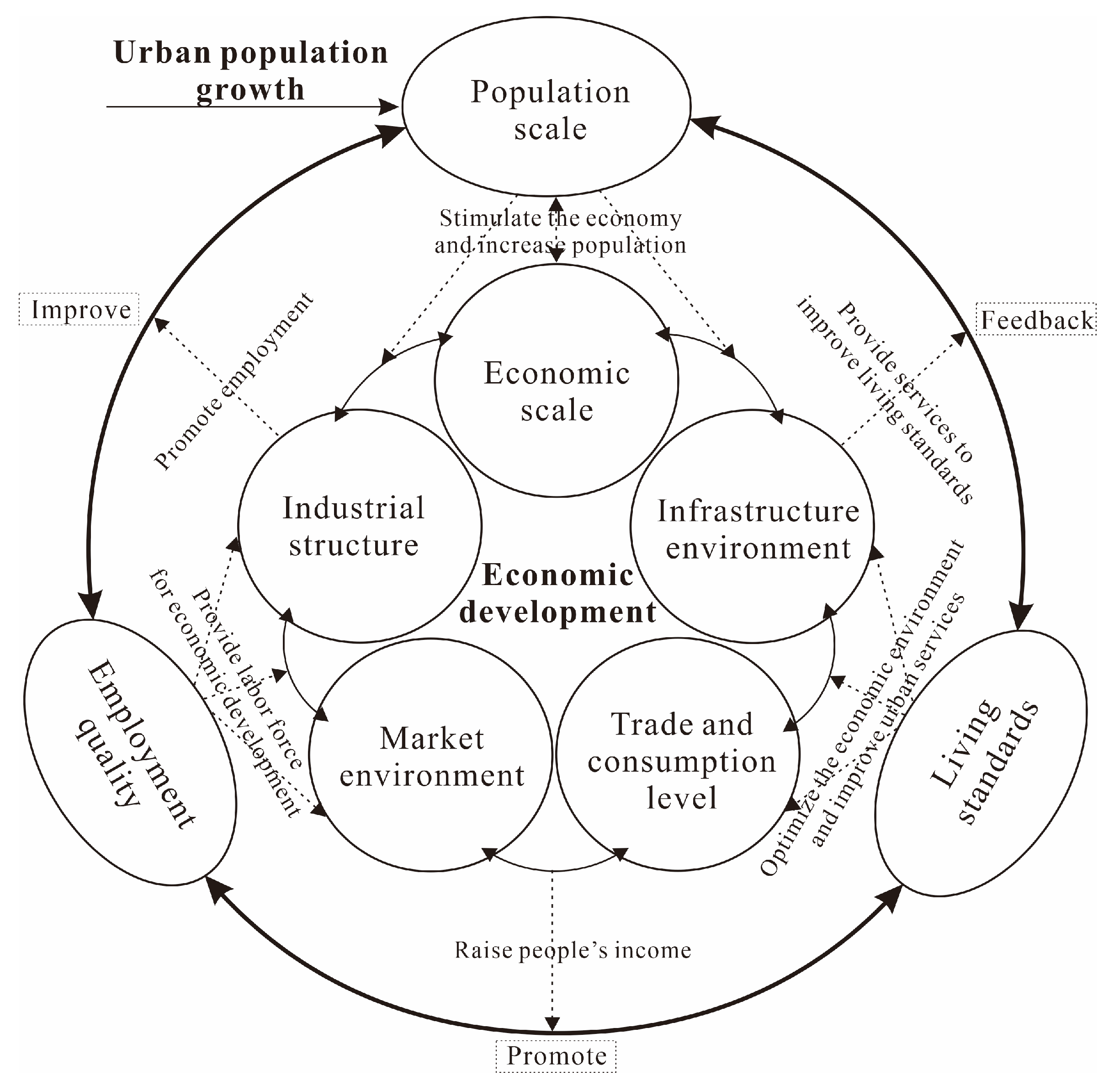
In this study, urbanization is defined as the comprehensive process of rural–urban migration, economic restructuring, and social transformation. Urban population growth specifically refers to changes in population structure and employment shifts toward non-agricultural sectors. Urban economic development encompasses changes in economic scale, industrial structure, the market environment, trade and consumption levels, and the infrastructure environment under the influence of urban population growth, as outlined in
Section 2. This study hypothesizes that there exists an asymmetric coupling dynamic relationship between urban population growth and economic development in African countries, where the level of economic development often lags behind population growth. Factors related to industrialization and governance are identified as key drivers of coordinated development. Under this hypothesis, this paper first analyzes the coupling and coordination relationship between urban population growth and economic development, constructs an indicator system to systematically evaluate the relative quality of their development and the coupling coordination degree, and uses the GeoDetector tool to analyze the influence mechanism of coordination. The specific research framework is shown in
Figure 1.
2. Literature Review and Theoretical Framework
2.1. The Link Between Urban Population Growth and Economic Development
The relationship between urban population growth and economic development represents a significant focal point within the field of urbanization research [
5,
17]. Recent studies shed light on the intricate relationship between urban population growth and economic growth, as well as the correlation between urban size and economic development [
18]. The process of urban population growth can promote economic development. Additionally, urbanization plays a pivotal role in alleviating poverty in rural areas, which is mainly achieved by increasing the demand for agricultural products and adding more non-agricultural jobs [
19]. The increasing population in urban areas leads to a greater number of individuals participating in non-agricultural production. At the same time, the growth of the urban population generates an increased demand for goods and services within the urban economy, thereby positively impacting its expansion [
20]. The positive effect of urban population growth on the urban economy is not static. Rapid urban population growth rates are often accompanied by challenges such as increasing unemployment rates and the expansion of slum populations within cities. The rapid and unreasonable expansion of urban areas also contributes to various environmental problems and management crises, ultimately posing a threat to economic development [
21,
22].
Studies on African countries indicate that rural–urban migration can have several positive effects on economic development. These include an upsurge in the demand for housing, enhancements in intraurban transportation, an increase in consumption demand, and the overall promotion of economic development [
23]. Beauchemin and Bocquier [
24] also highlighted the importance of urban population growth for economic development. However, their results indicated that the slowdown of urbanization led by economic recession is occurring in some African cities. Potts [
25] also found evidence suggesting that urban poverty and unemployment have contributed to a decline in urbanization rates in certain African countries. While existing studies highlight the positive impacts of urban migration on consumption and the risks of unplanned urbanization, they predominantly rely on qualitative approaches or single indicators. Few studies have systematically analyzed the dynamic interactions between population and economic systems or quantified coordination levels across African countries, creating a research gap, which is addressed by this study’s coupling coordination model and multi-indicator framework.
2.2. Theoretical Framework of Coupling Coordination
In this study, a coupled coordination model is employed to elucidate the relationship between population change and economic development within the context of urbanization. The coupling coordination model, adapted from physics, has gained traction in urbanization research to analyze interactive dynamics between complex systems [
26]. The degree of system coordination is employed to assess the level of harmony within the system by measuring the disparities among static systems [
27,
28]. As one of the approaches for measuring interactive effects, the coupling coordination degree is now widely applied in different research fields, including urbanization [
29], tourism [
30], economy [
31], etc. These interactions between urban population growth and economic development are complicated, as they simultaneously involve various system components; meanwhile they dynamically change over time. Overall, the increase in urbanites brought by urban population growth can facilitate the shift in employment structure and lifestyles towards non-agricultural development. This, in turn, exerts influence on multiple dimensions of economic development, including economic scale, industrial structure, the market environment, trade, and consumption levels, as well as infrastructure conditions. As economic quality improves, it further enhances the attractiveness of cities for rural populations, thereby facilitating the process of urban population growth. In the context of urban population growth and economic development, this framework helps quantify how population structure shifts and economic transformations mutually reinforce or constrain each other. For African countries, where urbanization is rapid but often disjointed from economic progress [
12,
16], this model offers a critical tool to unpack systemic bottlenecks.
Several studies have examined the correlation between urban population growth and economic development in Africa. However, it is important to note that these studies primarily rely on qualitative research methodologies and utilize a restricted set of indicators [
4,
13,
32]. Most research cannot comprehensively and accurately reflect the development level of urban population growth and economic development in Africa. Moreover, it remains challenging to objectively capture the level of coordination between urban population growth and economic development in Africa. Unlike prior studies in Africa that use simple correlation analysis [
13] or static indices [
4], this study employs a dynamic coupling coordination model to capture reciprocal interactions. For example, while Onjala and K’Akumu analyzed urbanization–economic links in Kenya, they did not account for multi-dimensional system interactions or spatial heterogeneity [
4], which our coupling coordination model and geographic detector will addresses. Consequently, building upon the foundation of coupling coordination theory, this study develops an integrated indicator system comprising two hierarchical levels and eight subsystems (shown in
Figure 2). The economic development system is conceptualized as comprising five subsystems, including economic scale, industrial structure, market environment, trade, and infrastructure (
Figure 2). Each subsystem dynamically interacts with changes in urban scale, employment structure, and lifestyle brought about by urban population growth. The aim is to investigate the quality of urban population growth and economic development, along with the coordination between the two. This endeavor contributes to the enrichment of the knowledge base in this domain and offers valuable insights for the urbanization development of African nations.
3. Materials and Methods
To enhance the scientific rigor of indicator weighting, this paper adopts a combination of subjective scoring and objective weight calculation to determine the indicator weights of the evaluation system. Specifically, the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) and entropy method are currently the two most commonly used indicator weight calculation methods, with mature technologies. Moreover, their evaluation processes are relatively independent and do not affect each other. By comparing their calculation results, comprehensive consideration of the combined weights of the indicator system can be achieved.
3.1. Data Sources and Evaluation Indexes
In accordance with the definitions of urban population growth and economic development outlined in this paper, the evaluation system for assessing the quality of urban population growth comprises three subsystems: population structure, employment structure, and living standards. Additionally, the evaluation system for economic development quality encompasses five subsystems: economic scale, industrial structure, the market environment, trade and consumption levels, and the infrastructure environment. The data utilized in this study were sourced from World Bank Open Data (
https://data.worldbank.org/, accessed on 15 January 2025) and African Development Bank Group Statistics (
https://www.afdb.org/en/knowledge/statistics, accessed on 15 January 2025). To ensure comparability, the values of GDP per capita, national income per capita, and consumption per capita were converted into 2010 USD. The study focused on the period from 2001 to 2020, which was divided into four stages: 2001–2005, 2006–2010, 2011–2015, and 2016–2020. Due to data limitations, Somalia and South Sudan were excluded as non-study areas. In order to minimize the statistical errors, the average values (X
ij) of different periods were utilized as the initial values for these countries.
3.2. Indicator Weight Calculation
3.2.1. The Entropy Weight Method
The entropy weight method is a kind of objective weight method which uses entropy to express the size of the information. Generally, the greater the difference between attribute values, the greater the amount of information the entropy value contains, so the smaller the entropy value, the greater the entropy weight is [
29]. The indicator’s weight signifies the relative significance of each element in contributing to the overall system. The entropy weight method is employed to determine the weights of indicators based on their effect size, mitigating the disproportionate influence of experts’ subjective knowledge. This method has been extensively applied in various fields such as economics and urbanization [
29,
33].
All objects need to be converted into dimensionless indicators to eliminate statistical errors caused by different indicator magnitudes. The methods are as follows:
For moderate indicators:
where
is the value of indicator
j of country
i;
and
are the maximum and minimum value of the indicator
j;
is the optimum value of the indicator
j;
n is the number of indicators;
is the weights calculated using the entropy weight method. The specific calculation process can be found in Zhang’s research [
34].
3.2.2. Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP)
Assigning weights through the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP) is essentially a subjective decision-making approach. It involves decomposing complex problems into distinct decision elements, structuring these elements into hierarchical levels, and using expert scoring to conduct pairwise comparisons of importance at the indicator level. This process determines the priority ranking of each indicator relative to the decision objective, thereby deriving indicator weights. AHP has been widely applied in socioeconomic evaluation and target decision-making [
35]. The operational process of this method can be referenced in Lee’s research [
36].
Five relevant experts in the research field were recruited to conduct scoring in accordance with the Analytic Hierarchy Process (AHP). The results in
Table 1 indicate that the weight calculation results passed the consistency check. Hereafter, we use
to denote the indicator weights calculated by the AHP method.
3.2.3. Comprehensive Weight Calculation
The determination of comprehensive weights
needs to be as close as possible to both subjective and objective weight values, thereby ensuring the rationality of the evaluation system’s weights. According to the minimum information entropy theory [
29], it is concluded that the minimum information entropy
satisfies the following relationship with subjective weights, objective weights, and comprehensive weights:
Equation (4) should also satisfy
Finally, the comprehensive weight
is optimally solved using the Lagrange multiplier method:
The evaluation system and the calculation results of the indicator weights are shown in
Table 2. On this basis, the development quality
is calculated by the following formula:
is the comprehensive weight of indicator j.
Table 2.
Index system used for evaluation of relationship between urban population growth and economic development.
Table 2.
Index system used for evaluation of relationship between urban population growth and economic development.
| System | Subsystem | Index | We (%) | Wa (%) | Wn (%) |
|---|
Urban
population growth system | Population scale | Urban population (% of total population) | 8.392 | 6.665 | 7.695 |
| Population in the largest city (% of urban population) | 2.988 | 4.165 | 3.630 |
| Economically active population (% of total population) | 5.893 | 8.264% | 7.180 |
| Employment quality | Employment in industry (% of total employment) | 12.092 | 12.336 | 12.566 |
| Employment in agriculture (% of total employment) | 8.374 | 3.771 | 5.782 |
| Unemployment, total (% of total labor force) | 2.893 | 9.366 | 5.356 |
Living
standards | Population living in slums (% of urban population) | 9.288 | 18.260 | 13.399 |
| Adjusted net national income per capita (constant 2015 USD) | 30.569 | 22.305 | 26.867 |
| Adjusted savings: net national savings (% of GNI) | 19.511 | 14.870 | 17.525 |
| Economic development system | Economic scale | GDP per capita (constant 2015 USD) | 20.327 | 6.184 | 12.287 |
| GDP per capita growth (annual %) | 1.511 | 5.354 | 3.117 |
| Gross fixed capital formation per capita (constant 2015 USD) | 21.143 | 11.975 | 17.437 |
| Industrial structure | Agriculture value added (% of GDP) | 1.480 | 2.942 | 2.287 |
| Manufacturing value added (% of GDP) | 6.691 | 9.455 | 8.716 |
| Services, value added (% of GDP) | 3.412 | 5.836 | 4.890 |
| Market environment | Inflation, consumer prices (annual %) | 0.254 | 3.715 | 1.064 |
| Foreign direct investment, net inflows (% of GDP) | 5.459 | 5.062 | 5.761 |
| Cost of business start-up procedures (% of GNI per capita) | 0.547 | 5.571 | 1.913 |
| Trade and consumption level | Trade surplus value (% of GDP) | 3.112 | 6.816% | 5.047 |
| Final consumption expenditure per capita (constant 2015 USD) | 19.223 | 13.228 | 17.475 |
| Export value index (2000 = 100) | 0.313 | 4.157% | 1.250 |
| Infrastructure environment | Mobile cellular subscriptions (per 100 people) | 11.885 | 8.058% | 10.725 |
| Access to electricity, urban (% of urban population) | 2.862 | 6.194 | 4.614 |
| Access to basic drinking water services, urban (% of urban population) | 1.781 | 5.453 | 3.415 |
3.3. Coupling Coordination Index
According to the definition of coupling coordination and previous research experience, the coupling coordination degree of the urban population growth and economic development systems was calculated as follows:
where D is the coupling coordination degree;
C is the coupling degree between the two systems;
T is the comprehensive coordination index between the two systems;
E is the relative development degree;
and
are the comprehensive evaluation indexes of the urban population growth and economic development systems; and
α and
β are undetermined coefficients. Given the theoretical parity of the population and economic systems in urbanization, equal weights (
α =
β = 0.5) are adopted to avoid subjective bias. This aligns with studies treating urban–rural or economy–environment systems as interdependent [
26,
29]. All statistical analyses were conducted using the SPSS statistical software package (SPSS v 22.0, IBM, Armonk, NY, USA).
3.4. Geographical Detector
GeoDetector is a new statistical method to detect spatial stratified heterogeneity and reveal the driving factors behind it. This method with no linear hypothesis has an elegant form and definite physical meaning [
37]. The q statistic in GeoDetector has already been applied in many fields of natural and social sciences and can be used to measure spatial stratified heterogeneity, detect explanatory factors, and analyze the interactive relationship between variables. The interaction detection tool of GeoDetector can explain the effect of the superposition of the two factors on the dependent variable and has a more plausible explanatory role than the regression model. The formula is as follows:
The value of the q statistic (0 ≤ q ≤ 1) indicates how much the coupling coordination degree is interpreted by the influencing factor (F). stands for the variance of the influencing factor (F), L denotes the number of influencing factor (F) to be divided, represents for the number units of type i, and N refers to the total number of all units.
4. Results
4.1. The Evolution of Urban Population Growth and Economic Development, 2001–2020
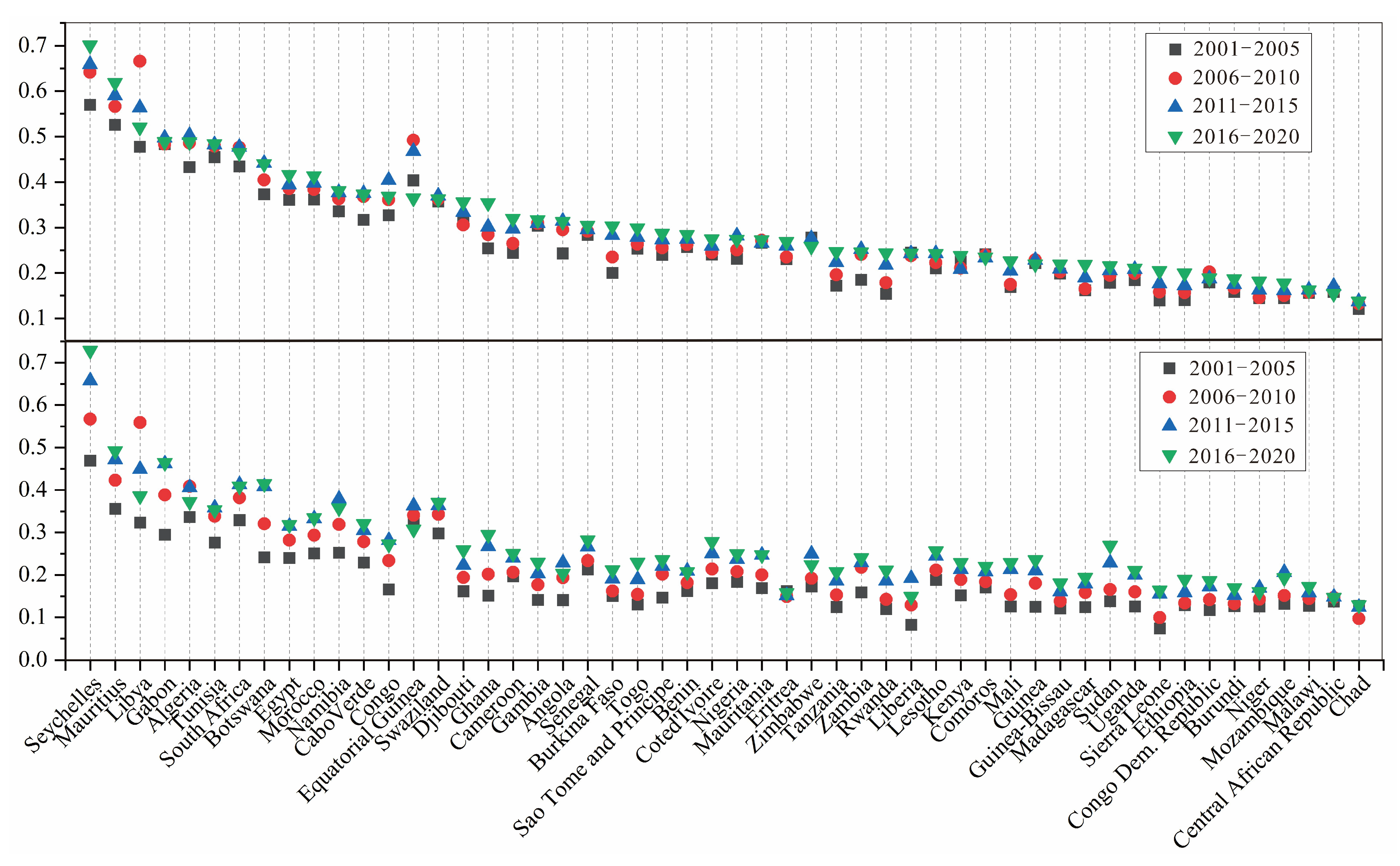
We assessed the quality of urban population growth and economic development in African countries over the period 2001–2020 according to Equation (7). The results are shown in
Figure 3 and
Table 3. Over the past 20 years, the average quality of urban population growth in African countries has shown an increase from 0.272 to 0.309. However, the overall level remains relatively low. The coefficient of variation fluctuates between 0.392 and 0.436, indicating large differences between African countries. The average quality of economic development of African countries increases from 0.158 to 0.217, with an overall level lower than the quality of urban population growth. The coefficient of variation, on the other hand, fluctuates between 0.402 and 0.498, with greater differences between African countries. Furthermore,
Figure 3 demonstrates a consistent spatial distribution pattern of urban population growth and economic development across African countries. Countries like Seychelles and Mauritius exhibit the highest overall levels, whereas countries like Chad and the Central African Republic have the lowest overall levels. This observation lends support to the existence of a closely intertwined coupling coordination mechanism between urban population growth and economic development in Africa.
4.2. Spatial and Temporal Evolution of the Coupling Coordination Degree
We calculated the coupling coordination degree between urban population growth and economic development in African countries over the period 2001–2020 according to Equation (8). The average coupling coordination degree of African countries has increased from 0.464 to 0.526 over the past 20 years. However, the overall level still remains relatively low. Previous studies [
31,
33] provide insights suggesting that when the coupling coordination degree (D) falls within the range of (0, 0.4), the urban population growth and economic development systems are considered uncoordinated. When D ∈ [0.4, 0.6], the system is characterized as barely coordinated, and when D ∈ (0.6, 1), the system is said to be in a state of coordinated development. Within these three states, further divisions can be made based on the synchronous relationship between urban population growth and economic development. The following classifications can be made: when
−
> 0.1, urban population growth quality lags behind economic development quality; when
−
> 0.1, economic development lags behind urban population growth; and when |
−
| < 0.1, urban population growth and economic development are in a relatively synchronous stage.
The division results of coupling coordination types are shown in
Table 4 and
Figure 4. As a whole, Northern and Southern Africa exhibit higher levels of coordination, while Eastern and Western Africa demonstrate relatively lower levels of coordination. From 2001 to 2020, although the number of African countries in a state of uncoordinated development decreased from 38 to 25, most African countries are still in a state of uncoordinated development, with Burundi and Chad having the lowest coupling coordination degree. At the same time, the number of countries with a coordinated development status increased from 7 to 13, with Seychelles and Mauritius having the highest coupling coordination. During these two decades, most African countries have been in a state where economic development lags behind urban population growth. On the other hand, the number of countries in a state of high-quality coordinated development (Type IX) has only increased from 0 to 4, accounting for less than 10% of the total.
4.3. Analysis of the Influencing Factors
The urban population growth and economic development systems are affected by multiple factors. Drawing upon previous research experience, urbanization speed, industrialization level, dependence on foreign trade, and government financial investment exert significant influences on the development of African countries. In addition, political stability and international aid are also major factors affecting the development of African countries. Therefore, we selected these relevant indicators and made them dimensionless according to Equations (1)–(3). With the help of GeoDetector 2015 software, the influencing factors of coupling coordination were systematically analyzed, and the results are shown in
Table 5. Industrialization, represented by X2 (manufacturing labor efficiency), emerged as the strongest driver (q = 0.568), confirming its critical role in bridging population growth and economic development. In contrast, urbanization speed was found to have the least significant impact on coordination (
p > 0.05).
The impact on the coordination of the urban population growth and economic development systems is not solely attributed to a single factor. Therefore, we used the interaction detector tool to analyze the superimposed influence strength of the influencing factors. The results, presented in
Table 6, reveal an overall increase in the influence strengths of all combined factors, except for the results involving the insignificant influencing factor X1. The strengths (q value) of X2∩X4, X3∩X4, X4∩X5, X4∩X6, and X5∩X6 are greater than the sum value of their two factors, indicating that the superposition of the above factors has a greater impact on system coordination.
5. Discussion
5.1. Coordination Dynamics Between Urban Population Growth and Economic Development
The absolute size of cities has increased rapidly in under-developed countries during the late 20th century, and city size is becoming less indicative of city living standards compare with the past [
38]. The conclusions of this paper also suggest that the contribution of urbanization speed to the quality of urbanization is not significant. Furthermore, it is observed that the overall urbanization quality of African countries remains relatively low, and the rapid urban population growth has not been accompanied by an equivalent level of economic development. In the process of urban population growth, a large number of rural surplus laborers are transferred to secondary industry for employment, which promotes the development of industrial scale and technological progress. Consequently, the agricultural sector’s contribution to the national economy gradually diminishes, while the tertiary sector experiences slight growth, driving structural transformation and economic upgrading. This process will also, in turn, affect the quality of urban population growth. However, it is worth mentioning that in many African countries, tertiary industry has become disproportionately larger than secondary industry. This imbalance poses challenges as it is not conducive to sustained and balanced economic development. The average proportion of Africa’s secondary industry was 26% of the total GDP in 2001 and 25.2% in 2020. Africa’s service sector accounted for 45.7% of the total GDP in 2000, and the value increased to 49.1% in 2016. Growth in the service sector has been largely dominated by informal, low-productivity work, making it difficult to create quality jobs [
39,
40].
Therefore, the rapid urban population growth has led to more employment growth in the informal sector within cities, but the quality of life of the urban population remains low. Under the influence of such urban population growth, various challenges emerge. Although economic scale experiences rapid growth, the industrial structure remains unbalanced, inhibiting the effective stimulation of the market environment and consumption levels. Additionally, insufficient fiscal revenue hampers government efforts to improve the infrastructure environment. Consequently, the lower quality of economic development further hinders the enhancement of urban population growth quality, resulting in an uncoordinated development scenario.
5.2. Driving Mechanism of Coupling Coordination by Different Factors
Industrialization plays the most important role in the coordination of urban population growth and economic development in African countries. Industrialization-driven economic development is regarded as the main driver of urbanization [
41]. However, urban growth without the support of industrialization has limited effectiveness in terms of boosting employment and national income, called ‘growth without development’ [
42]. In the context of urbanization without industrialization, the population migration in African countries does not follow the pattern of labor migration in the traditional dual economy of urban–rural areas. The massive shift in new urban populations to lower-end services and the informal sector, characterized by fewer employment barriers, has resulted in an expanding share of services in the employment structure. Conversely, the growth of the industrial labor force has been sluggish. This limited industrialization has posed constraints on economic development and structural upgrading, resulting in low labor productivity. Consequently, the industrial sector’s growth has been stunted, making it challenging for cities to generate an adequate number of quality jobs to meet the demand of the population. In addition, most African countries export commodities based on agricultural commodities and primary industrial raw materials, and have low demand for manufacturing. International investors have become an important force in promoting industrialization. However, their limited incentives have posed challenges for overall economic development [
43]. Although the rapid urbanization process has provided an adequate labor force and consumer base for urban development, the overall growth of both the industrial sector and its productivity has been hindered by the low level of industrialization. Services and the informal sector, with higher marginal output, have emerged as the primary drivers of economic growth. As a result, the influence of urban population growth on human capital growth has not been sufficient to boost economic development [
39,
44], resulting in economic development generally lagging behind urban population growth.
Factors such as the foreign trade dependence ratio, government final consumption expenditure, ODA received per capita, and the political stability index all exert an influence on coordination. Restricted by the poor level of industrialization, most African countries mainly export agricultural products and industrial raw materials in their foreign trade, whereas manufactured goods constitute the main imported commodities [
45]. The foreign trade dependence ratio is not within a reasonable range, which is not conducive to improving economic quality and the living standards, while also making it difficult to promote rapid growth in government revenue. Political instability and weak governance undermine policy effectiveness by deterring foreign investment and misallocating public funds (X4). As shown in
Table 5, political stability (X6) explains 27.9% of coordination variation, underscoring the need for anti-corruption reforms and inclusive governance frameworks to sustain urbanization gains. The government’s insufficient hardware investment in urban renewal and infrastructure construction will also restrict economic development and the improvement in urban population growth.
5.3. The Future of Urbanization in Africa
Compared to other typical global regions, the relationship between population and economy in the urbanization process of Africa exhibits unique characteristics. The urbanization process in Global Northern countries is accompanied by industrial development and witnesses the complementary growth of urban populations and economies, achieving a relatively balanced and high level of development [
46]. The ‘Latin American trap’—high urbanization rates (often >70%) coupled with industrial stagnation and economic inequality—has been documented in studies like Gollin et al. [
42]. In Africa, this manifests as rapid urban growth without industrial job creation, pushing 60–70% of urban labor into low-productivity informal sectors [
39,
40]. Our GeoDetector results (
Table 5) reveal a critical insight: countries in Southern and Northern Africa with stronger industrial bases exhibit higher coupling coordination [
47], while Eastern and Central African nations suffer from low manufacturing labor efficiency (X2) and inadequate government investment (X4), leading to severe coordination deficits [
48].
According to our findings, the superposition of multiple factors will also enhance the impact on coordination. The influence strength of X2∩X4 is the highest, indicating that under the condition of improving the level of industrialization, increasing government investment can more effectively contribute to the coordinated development of the system. The influence strength of X5∩X6 shows the most significant increase, indicating that in a stable political environment, international aid can bring greater support to the coordinated development of the system. The superposition between factor X4 and other factors all yields a higher influence strength, indicating that improving national governance capacity and strengthening government investment in urbanization are fundamental to the ongoing coordination of urban population growth and economic development.
It is evident that industrialization should be prioritized as the primary avenue for future urbanization in Africa. African countries should gradually improve their manufacturing capabilities through the development of characteristic industries and the construction of industrial parks. Countries with low X2 and X4, such as Burundi and Chad, should establish industrial parks linked to urban infrastructure projects. For example, scaling manufacturing clusters in Ethiopia’s Addis Ababa—paired with government spending on logistics—could boost labor efficiency (X2) and reduce coordination deficits. This approach aims to improve labor productivity by generating more high-quality employment opportunities. Concurrently, efforts should be made to elevate residents’ income and consumption levels to stimulate domestic consumption demand and reduce dependence on foreign trade. To reduce over-reliance on low-value exports (X3), countries like Kenya and Ghana should formalize informal sectors and promote high-value agriculture processing, supported by government subsidies (X4). This could raise manufacturing’s share of GDP, as seen in Vietnam’s industrialization model [
43]. For resource-rich nations, adopting sovereign wealth funds could mitigate trade dependency risks by reinvesting export revenues into diversified industries. Moreover, upgrading of the industrial system can further support urban construction, restrain and reduce urban poverty growth, and promote the coordinated development of urbanization.
The government should invest more in key sectors of urban development such as infrastructure development, urban renewal, and scientific and technological innovation to create a basis for industrialization and urbanization. In nations with high political stability scores (X6), such as Botswana and Morocco, international aid (X5) should be channeled into skills training programs and digital infrastructure to amplify synergistic effects (X5∩X6). As advocated in Agenda 2063, “Africa must therefore, consolidate the positive turn around, using the opportunities of demographics, natural resources, urbanization, technology and trade as a springboard to ensure its transformation and renaissance to meet the people’s aspirations” [
49].
6. Conclusions
By constructing a coupling coordination model, this study explores the coordination and internal links between urban population growth and economic development, informing social practice through insights into interactive dynamics to guide sustainable urbanization policies in African countries. The findings are as follows:
A strong correlation between urban population growth and economic development is observed in African countries, and both indicators demonstrate a trend of sustained growth. However, the development quality varies greatly among different countries, with an overall tendency towards lower levels of quality, with economic growth trailing urban population expansion due to insufficient industrial job creation in most African countries.
The spatial distribution of the quality of urban population growth and economic development is relatively consistent, indicating a close coupling and coordination relationship between the two. Most African countries are in an uncoordinated or barely coordinated state of development, with only parts of Southern and Northern Africa being relatively coordinated.
Urbanization without industrialization restricts the transfer of the work force in different industries in African countries. The growth in industrial scale, human capital, and consumer groups resulting from urban population growth predominantly occurs within the informal sector, which acts as a key constraint on the coordinated development of the population and economy in African countries. In addition, foreign trade dependence, international aid, government investment, and political stability all exert influences on coordination. Notably, the interaction of political stability and government investment with other factors yields significant effects. Therefore, promoting industrial structure upgrading with industrialization, and improving the quality of population and economic development with stable policy support and continuous financial investment, should be the main approaches for achieving coordinated urbanization development in African countries.
As with many studies, this work also has certain limitations. One limitation arises from the potential inaccuracies in the statistical data from African countries, which may introduce biases in the calculation results. To mitigate this, we minimize the statistical error of the data by taking the average every 5 years. In addition, the indicators used in this study are based on per capita indicators and aggregate national data, which may obscure significant intra-country heterogeneities and fail to capture the nuanced dynamics of specific cities or regions. Further, the informal economy—a critical pillar of African urban livelihoods—is largely omitted from official statistics, leading to the potential underestimation of actual economic activities and their linkages with urban population growth. Although explaining the variations in development among countries of different sizes may present challenges, this approach allows for a better understanding of the common issues faced by Africa as a whole. In the future, we plan to collaborate with scholars in Africa to refine the indicator system, incorporating micro-level city data and non-market metrics to address these gaps.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization and methodology, H.R. and Z.Z.; software, H.R. and S.J.; validation, H.R., Z.Z., and S.J.; formal analysis, H.R.; data curation, S.J.; writing—original draft preparation, H.R.; writing—review and editing, S.J.; supervision, H.R. and Z.Z.; project administration, H.R.; funding acquisition, H.R. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, funding number 42301227.
Data Availability Statement
The data presented in this study are available on request from the corresponding author due to the need to maintain the integrity of the findings and to ensure that users understand the context and limitations of the data.
Acknowledgments
We thank the World Bank Group and the African Development Bank Group for providing data support for this study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
References
- UN-Habitat. World Cities Report 2022: Envisaging the Future of Cities. Available online: https://unhabitat.org/wcr/ (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- United Nations Department of Economic and Social Affairs (UNDESA). The World’s Cities in 2018. Available online: https://digitallibrary.un.org/record/3799524 (accessed on 12 December 2024).
- Wang, Y.; Geng, Q.; Si, X.; Kan, L. Coupling and Coordination Analysis of Urbanization, Economy and Environment of Shandong Province, China. Environ. Dev. Sustain. 2021, 23, 10397–10415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Onjala, J.; K’Akumu, O.A. Relational Patterns of Urbanisation and Economic Growth in Sub-Saharan Africa. Dev. S. Afr. 2016, 33, 234–246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ren, H.; Zhang, Z.; Das, P. Bibliometric Analysis on African Urbanization Studies: Patterns and Trends of Published Articles. S. Afr. Geogr. J. 2023, 105, 54–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henderson, J.V.; Turner, M.A. Urbanization in the Developing World: Too Early or Too Slow. J. Econ. Perspect. 2020, 34, 150–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyemang, F.S.; Silva, E.; Poku-Boansi, M. Understanding the Urban Spatial Structure of Sub-Saharan African Cities Using the Case of Urban Development Patterns of a Ghanaian City-Region. Habitat Int. 2019, 85, 21–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selod, H.; Shilpi, F. Rural-Urban Migration in Developing Countries: Lessons from the Literature. Reg. Sci. Urban Econ. 2021, 91, 103713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Julia, B.S.; Ciara, A. African Urban Futures; Institute for Security Studies: Pretoria, South Africa, 2016. [Google Scholar]
- Cobbinah, P.B.; Erdiaw-Kwasie, M.O.; Amoateng, P. Rethinking Sustainable Development within the Framework of Poverty and Urbanisation in Developing Countries. Environ. Dev. 2015, 13, 18–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Güneralp, B.; Lwasa, S.; Masundire, H.; Parnell, S.; Seto, K.C. Urbanization in Africa: Challenges and Opportunities for Conservation. Environ. Res. Lett. 2017, 13, 015002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- United Nations Economic Commission for Africa (UNECA). Economic Report on Africa 2017: Urbanization and Industrialization for Africa’s Transformation. Available online: https://www.uneca.org/era2021 (accessed on 20 January 2025).
- Turok, I.; McGranahan, G. Urbanization and Economic Growth: The Arguments and Evidence for Africa and Asia. Environ. Urban. 2013, 25, 465–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocquier, P. Analyzing Urbanization in Sub-Saharan Africa. In New Forms of Urbanization; Champion, T., Hugo, G., Eds.; Routledge: London, UK, 2017; pp. 133–150. [Google Scholar]
- Beri, P.B.; Mhonyera, G.; Nubong, G.F. Globalisation and Economic Growth in Africa: New Evidence from the Past Two Decades. S. Afr. J. Econ. Manag. Sci. 2022, 25, 4515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Behnisch, M.; Krüger, T.; Jaeger, J.A. Rapid Rise in Urban Sprawl: Global Hotspots and Trends Since 1990. PLoS Sustain. Transform. 2022, 1, e0000034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Xie, H. Interactive Relationship Among Urban Expansion, Economic Development, and Population Growth Since the Reform and Opening Up in China: An Analysis Based on a Vector Error Correction Model. Land 2019, 8, 153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, A.; Bakari, I. Impact of Population Growth on Economic Growth in Africa: A Dynamic Panel Data Approach (1980–2015). Pak. J. Humanit. Soc. Sci. 2018, 6, 412–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, X.; Zeng, F. Poverty Reduction in China: Does the Agricultural Products Circulation Infrastructure Matter in Rural and Urban Areas? Agriculture 2022, 12, 1208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahtta, R.; Fragkias, M.; Güneralp, B.; Mahendra, A.; Reba, M.; Wentz, E.A.; Seto, K.C. Urban Land Expansion: The Role of Population and Economic Growth for 300+ Cities. NPJ Urban Sustain. 2022, 2, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seto, K.C.; Güneralp, B.; Hutyra, L.R. Global Forecasts of Urban Expansion to 2030 and Direct Impacts on Biodiversity and Carbon Pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2012, 109, 16083–16088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thurlow, J.; Dorosh, P.; Davis, B. Demographic Change, Agriculture, and Rural Poverty. In Sustainable Food and Agriculture: An Integrated Approach; Campanhola, C., Pandey, S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 31–53. [Google Scholar]
- Ren, H.; Guo, W.; Zhang, Z.; Kisovi, L.M.; Das, P. Population Density and Spatial Patterns of Informal Settlements in Nairobi, Kenya. Sustainability 2020, 12, 7717. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beauchemin, C.; Bocquier, P. Migration and Urbanisation in Francophone West Africa: An Overview of the Recent Empirical Evidence. Urban Stud. 2004, 41, 2245–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Potts, D. The Slowing of Sub-Saharan Africa’s Urbanisation: Evidence and Implications for Urban Livelihoods. Environ. Urban. 2009, 21, 253–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Song, Q.; Zhou, N.; Liu, T.; Siehr, S.A.; Qi, Y. Investigation of a “Coupling Model” of Coordination Between Low-Carbon Development and Urbanization in China. Energy Policy 2018, 121, 346–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guan, D.; Gao, W.; Su, W.; Li, H.; Hokao, K. Modeling and Dynamic Assessment of Urban Economy-Resource-Environment System with a Coupled System Dynamics-Geographic Information System Model. Ecol. Indic. 2011, 11, 1333–1344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Fu, Y.; Lu, B.; Li, H.; Qu, Y.; Ibrahim, H.; Wang, J.; Ding, H.; Ma, S. Coupling Coordination Evaluation and Optimization of Water-Energy-Food System in the Yellow River Basin for Sustainable Development. Systems 2025, 13, 278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, P.; Wei, X.; Duan, Z. Coupling and Coordination Analysis in Urban Agglomerations of China: Urbanization and Ecological Security Perspectives. J. Clean. Prod. 2022, 365, 132730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Weng, G. The Coordinated Relationship Between the Tourism Economy System and the Tourism Governance System: Empirical Evidence from China. Systems 2025, 13, 301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Y.; Pang, X.; Zhou, C.; He, X. Coupling Coordination Degree Between the Socioeconomic and Eco-Environmental Benefits of Koktokay Global Geopark in China. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19, 8498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mason, A.; Lee, R.; NTA Network. Six Ways Population Change Will Affect the Global Economy. Popul. Dev. Rev. 2022, 48, 51–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, L.; Xue, M.G.; Hu, M.S. Dynamic Simulation and Assessment of the Coupling Coordination Degree of the Economy-Resource-Environment System: Case of Wuhan City in China. J. Environ. Manag. 2019, 230, 474–487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Li, E.; Xu, C. Assessment Model of Ecoenvironmental Vulnerability Based on Improved Entropy Weight Method. Sci. World J. 2014, 2014, 797814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awad, J.; Jung, C. Extracting the planning elements for sustainable urban regeneration in Dubai with AHP (analytic hierarchy process). Sustain. Cities Soc. 2022, 76, 103496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Lim, S. An analytic hierarchy process (AHP) approach for sustainable assessment of economy-based and community-based urban regeneration: The case of South Korea. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Qin, F.; Xu, C.; Li, B.; Guo, L.; Wang, Z. Evaluating the Suitability of Urban Development Land with a Geodetector. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 123, 107339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jedwab, R.; Vollrath, D. Urbanization Without Growth in Historical Perspective. Explor. Econ. Hist. 2015, 58, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Etim, E.; Daramola, O. The Informal Sector and Economic Growth of South Africa and Nigeria: A Comparative Systematic Review. J. Open Innov. Technol. Mark. Complex. 2020, 6, 134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yeboah, F.K.; Jayne, T.S. Africa’s Evolving Employment Trends. J. Dev. Stud. 2018, 54, 803–832. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, L.; Liu, Y. Urban-Industrial Development and Regional Economic Growth in a Developing Country: A Spatial Econometric Approach. SAGE Open 2022, 12, 21582440221102425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gollin, D.; Jedwab, R.; Vollrath, D. Urbanization with and Without Industrialization. J. Econ. Growth 2016, 21, 35–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gui-Diby, S.L.; Renard, M.F. Foreign Direct Investment Inflows and the Industrialization of African Countries. World Dev. 2015, 74, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ochinyabo, S. Rapid Population Growth and Economic Development Issues in Nigeria. J. Econ. Allied Res. 2021, 6, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Opoku, E.E.O.; Yan, I.K.M. Industrialisation as a Driver of Sustainable Economic Growth in Africa. J. Int. Trade Econ. Dev. 2019, 28, 30–56. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Zhang, H.; Liu, W.; Zhang, W. The Global Pattern of Urbanization and Economic Growth: Evidence from the Last Three Decades. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e103799. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andreoni, A.; Tregenna, F. Escaping the Middle-Income Technology Trap: A Comparative Analysis of Industrial Policies in China, Brazil and South Africa. Struct. Change Econ. Dyn. 2020, 54, 324–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Twum, A.K.; Agyemang, A.O. Realizing Sustainable Development Goals in Sub-Saharan Africa: The Role of Industrialization on Consumption-Based Carbon Emission. Sustain. Dev. 2024, 32, 2666–2677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- African Union. Second Continental Report on the Implementation of Agenda 2063. Available online: https://au.int/en/agenda2063 (accessed on 17 November 2024).
| Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).