Does Digital Village Construction Empower the Green Allocation of Agricultural Water Resources?
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
3. Theoretical Analysis
3.1. Relationship between Digital Villages and the Efficiency of Green Allocation of Agricultural Water Resources
3.2. Spatial Spillover Effects of Digital Villages on the Efficiency of Green Allocation of Agricultural Water Resources
4. Model Setup and Indicator Selection
4.1. Model Setting
4.1.1. SE-SBM Model for Non-Consensual Outputs
4.1.2. Spatial Autocorrelation Analysis
4.1.3. Spatial Econometric Model
4.1.4. Spatial Econometric Model
4.2. Figures, Tables and Schemes
4.2.1. Dependent Variables
4.2.2. Explanatory Variables
4.2.3. Control Variables
4.2.4. Data Sources and Descriptive Statistics
5. Empirical Results and Analysis
5.1. Measurement of Agricultural Green Water Use Efficiency
5.2. Baseline Regression Analysis of Digital Villages and the Efficiency of Green Allocation of Agricultural Water Resources
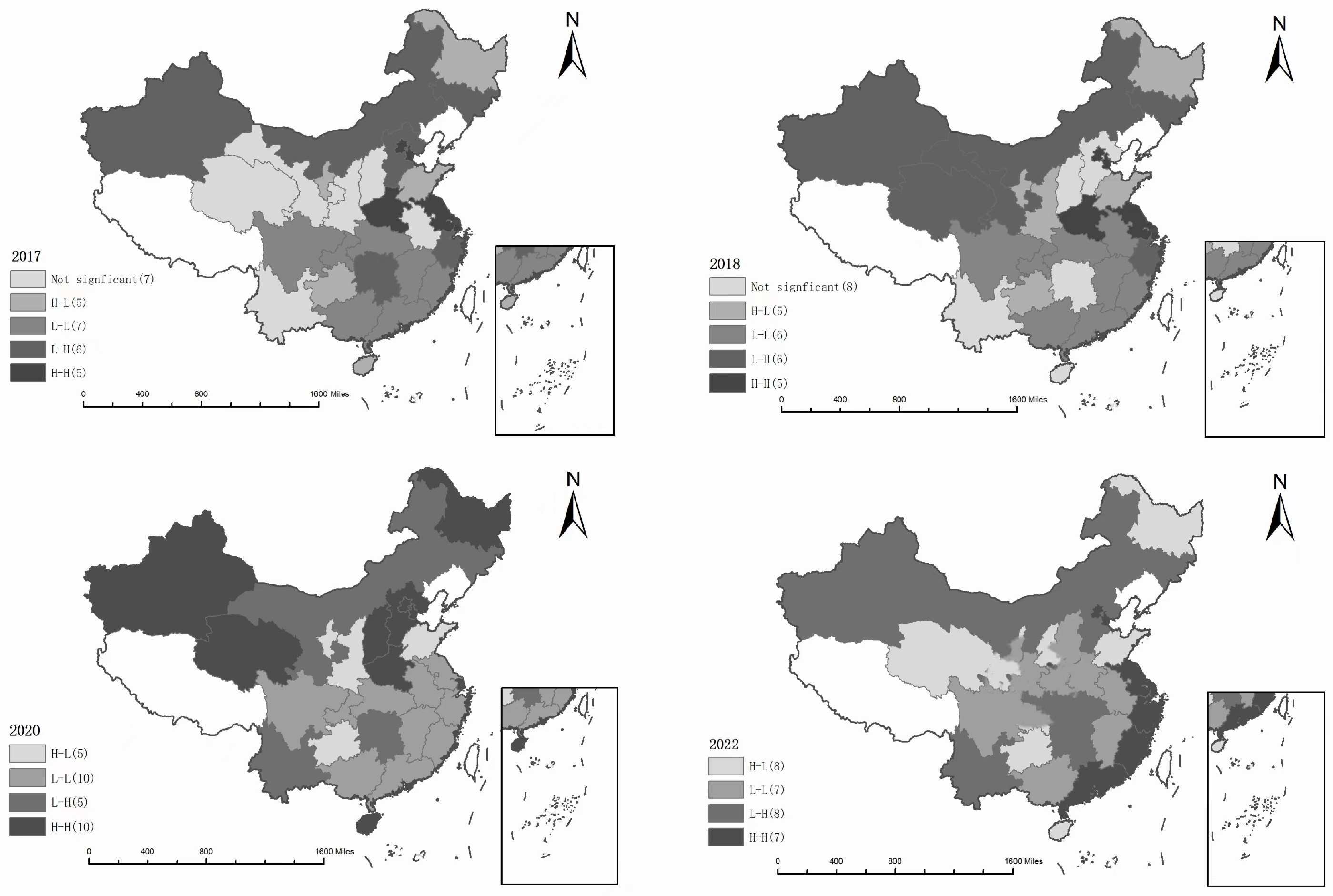
5.3. Spatial Autocorrelation Test
5.4. Analysis of Empirical Results of Spatial Effects
5.5. Decomposition of Spatial Effects
6. Robustness Test
6.1. Changing the Dependent Variable and Sample Data
6.2. Changing Spatial Weight Matrices
7. Conclusions, Limitations, and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gong, X.S.; Du, J. Digital Economy, Green Innovation, and Corporate Green Total Factor Productivity. Stat. Decis. 2024, 40, 35–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, J.Z.; Tao, X.H.; Xu, L. Geographical Agglomeration Characteristics and Spatio-temporal Evolution Mechanism of Digital Poverty in China. Econ. Geogr. 2019, 39, 169–179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, D.; Ying, R.Y. Study on the Relationship between Water Resources and Agricultural Economic Growth in China—Based on the Panel VAR Model. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2012, 22, 161–166. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, Y.P.; Luo, D.M.; Cheng, Y.X. Study on the Basic Price of Regional Water Rights Trading Considering Ecological Compensation by the Full Cost Method. Water Resour. Econ. 2021, 39, 72–78+82. [Google Scholar]
- Luo, Z.L.; Zuo, Q.T.; Zhao, Z.N.; Song, M.L. Discrimination Standards and Gap Analysis for Water Ecological Civilization Construction. Ecol. Econ. 2015, 31, 159–163. [Google Scholar]
- Guo, Y.; Hu, Y.; Shi, K.; Bilan, Y. Valuation of Water Resource Green Efficiency Based on SBM–TOBIT Panel Model: Case Study from Henan Province, China. Sustainability 2020, 12, 6944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, C.Z.; Ma, Q.F.; Zhao, L.S. Driving Mechanism of Green Efficiency of Water Resources in China Based on GWR Model. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2020, 75, 1022–1035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karagiannis, G.; Tzouvelekas, V.; Xepapadeas, A. Measuring irrigation water efficiency with a stochastic production frontier. Environ. Resour. Econ. 2003, 26, 57–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- lo Storto, C. Benchmarking operational efficiency in the integrated water service provision. Benchmarking Int. J. 2014, 21, 917–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tone, K. A slacks-based measure of efficiency in data envelopment analysis. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2001, 130, 498–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lins, M.P.E.; Gomes, E.G.; Soares de Mello, J.C.C.B.; Soares de Mello, A.J.R. Olympic ranking based on a zero-sum gains DEA model. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2003, 148, 312–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, G.; Jiang, H.; Zhang, S.; Bao, K.; Zhu, Y. Spatial–temporal differentiation and driving factors of water resources green efficiency in the Huaihe River Basin. Water Supply 2023, 23, 2043–2061. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Chen, P. Applying the three-stage SBM-DEA model to evaluate energy efficiency and impact factors in RCEP countries. Energy 2022, 241, 122917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Q.N.; Zhang, F.F.; Mai, Q.; Wu, G.Y. Spatial Spillover Network and Improvement Path of China’s Grain Production Efficiency. Acta Geogr. Sin. 2022, 77, 996–1008. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, S.Y.; Song, S.B.; Wang, X.J.; Wang, B.X. Quantitative Analysis of Regional Water Use Impact Factors Based on LMDI and STIRPAT Models. Water Resour. Hydropower Eng. 2021, 52, 30–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Federbush, M.S.; Muys, J.C., Jr. Israel and Water—(What’s Next for the) “Turn around Nation”: How Israel’s Leadership in Advanced Water Technologies Can Enhance Global Economic Growth and Diplomatic Relations. Am. Foreign Policy Interests 2012, 34, 309–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Fu, Z.; Wang, J.; Zhang, L. Farmers’ adoption of water-saving irrigation technology alleviates water scarcity in metropolis suburbs: A case study of Beijing, China. Agric. Water Manag. 2019, 212, 349–357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Blanke, A.; Rozelle, S.; Lohmar, B.; Wang, J.; Huang, J. Water-saving technology and saving water in China. Agric. Water Manag. 2007, 87, 139–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Innovation and government intervention: A comparison of Singapore and Hong Kong. Res. Policy 2018, 47, 399–412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, L.; Zhou, Y.X. Study on Water Use Efficiency of China’s Grain Production Based on DEA-Malmquist Model. China Agric. Resour. Zoning 2018, 39, 192–199. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, Q.; Wu, R.W.; Wang, H.R. Spatial Pattern and Interactions of Agricultural Water Use Efficiency in China: 1998–2013. J. Quant. Tech. Econ. 2017, 34, 72–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Lu, Q. Empirical Analysis of Regional Differences and Convergence Test of Agricultural Water Resources Utilization Efficiency in China. Soft Sci. 2014, 28, 133–137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murdoch, J. Networking rurality: Emergent complexity in the countryside. In Handbook of Rural Studies; Sage: Thousand Oaks, CA, USA, 2006; pp. 171–184. [Google Scholar]
- Yu, J.; Meng, Q.S.; Zhang, Y.; Jin, J. Digital Entrepreneurship: New Trends in Entrepreneurship Theory and Practice in the Digital Age. Stud. Sci. Sci. 2018, 36, 1801–1808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jansson, A. Mediatization, Spatial Coherence, and Social Sustainability: The Role of Digital Media Networks in a Swedish Countryside Community. Cult. Unbound J. Curr. Cult. Res. 2010, 2, 177–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Peng, Q.; Jin, C.; Ren, J.; Fu, Y.; Yue, X. Whether the digital economy will successfully encourage the integration of urban and rural development: A case study in China. Chin. J. Popul. Resour. Environ. 2023, 21, 13–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, D.; Zhu, Q. Innovation in emerging economies: Research on the digital economy driving high-quality green development. J. Bus. Res. 2022, 145, 801–813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peng, Z.; Dan, T. Digital dividend or digital divide? Digital economy and urban-rural income inequality in China. Telecommun. Policy 2023, 47, 102616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murthy, K.B.; Kalsie, A.; Shankar, R. Digital economy in a global perspective: Is there a digital divide? Transnatl. Corp. Rev. 2021, 13, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abukhader, S.M. Eco-efficiency in the era of electronic commerce—Should ‘Eco-Effectiveness’ approach be adopted? J. Clean. Prod. 2008, 16, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mendling, J.; Pentland, B.T.; Recker, J. Building a complementary agenda for business process management and digital innovation. Eur. J. Inf. Syst. 2020, 29, 208–219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agyapong, D. Implications of the digital economy for financial institutions in Ghana: An exploratory inquiry. Transnatl. Corp. Rev. 2021, 13, 51–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anselin, L.; Griffith, D.A. Do spatial effects really matter in regression analysis? Pap. Reg. Sci. 1988, 65, 11–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vu, K.M. Information and Communication Technology (ICT) and Singapore’s economic growth. Inf. Econ. Policy 2013, 25, 284–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Wu, M.J.; Chai, S.Y. Research on the coupling degree of urbanization process and village protection under the background of rural revitalization. J. Xinyang Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 34, 430–435. [Google Scholar]
- Li, J.L.; Chen, L.T.; Liu, M. The Impact of Internet Development on Regional Green Economic Efficiency in China. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2021, 31, 149–157. [Google Scholar]
- Vega-Carrillo, H.R.; Esparza-Garcia, I.R.; Sanchez, A. Features of a subcritical nuclear reactor. Ann. Nucl. Energy 2015, 75, 101–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.; Wu, Z. The Impact of Economic Disparities on Innovation Spillover and Technology Exchange: A Spatial Econometric Study Based on Economic Distance Matrix. Econ. Issues 2020, 78–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boschma, R.A. Proximity and innovation: A critical assessment. Reg. Stud. 2005, 39, 61–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, Y.P.; Jiang, C.Y.; Cui, Z.B. The Impact of Digital Finance on High-Quality Economic Development—Based on the Spatial Durbin Model. Technol. Econ. 2022, 41, 94–106. [Google Scholar]
- Cui, Y.C.; Han, Y.L.; Lü, N.; Zhu, H.H. Measurement of Agricultural Ecological Efficiency Based on the Super-efficiency SBM Model. Stat. Decis. 2020, 36, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, H.H.; Liu, X.M. Spatio-temporal Evolution of China’s Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity. China Manag. Sci. 2020, 28, 66–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, D.; Hao, S.; Sun, C. Evaluation and Spatial-Temporal Differentiation of Agricultural Ecological Efficiency Based on DEA-ESDA. Sci. Geogr. Sin. 2018, 38, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, J.F.; Tong, J.P.; Wang, H.M.; Wang, S. Study on the Spatial Effects of Global Technical Efficiency of Agricultural Water Use in the Yangtze River Economic Belt. Resour. Environ. Yangtze Basin 2018, 27, 2757–2765. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, G.L.; Wu, M.; Tai, Y.F. Analysis of the spatiotemporal pattern of coupling coordination between rural development and urbanization based on the perspective of rural revitalization: A case study of Henan Province. J. Xinyang Norm. Univ. (Nat. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 34, 68–75. [Google Scholar]
- Du, J.J.; Zhang, Y.D.; Liu, B.M.; Dong, R.H. The Impact and Mechanism of Digital Villages on Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity. China Popul. Resour. Environ. 2023, 33, 165–175. [Google Scholar]
- Shen, F.; Ye, W. Digital Rural Development: Strategic Choices for Achieving High-Quality Rural Revitalization. J. Nanjing Agric. Univ. (Soc. Sci. Ed.) 2021, 21, 41–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Y.; Niu, Z.H. Agricultural Informatization, Spatial Spillover Effects, and Agricultural Green Total Factor Productivity—Based on SBM-ML Index Method and Spatial Durbin Model. Stat. Inf. Forum 2018, 33, 66–75. [Google Scholar]
- Benos, N.; Karagiannis, S. Do education quality and spillovers matter? Evidence on human capital and productivity in Greece. Econ. Model. 2016, 54, 563–573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Indicator | Variable | Variable Description |
|---|---|---|
| Input | Water Resource Input | Agricultural Water Footprint (100 million m3) |
| Land Input | Total Cultivated Area (thousand hectares) | |
| Energy Input | Agricultural Electricity Consumption (100 million kWh) | |
| Power Input | Total Agricultural Machinery Power (10,000 kW) | |
| Labor Input | Primary Industry Workforce (10,000 persons) | |
| Output | Desired Output | Total Agricultural Output Value (CNY 100 million) |
| Rural Social Development Index (%) | ||
| Undesired Output | Agricultural Grey Water Footprint (100 million m3) |
| Indicator Category | Variable | Measurement Method |
|---|---|---|
| Digital Foundation | Internet Penetration Rate (%) | Number of netizens in the region/Total population of the region |
| Mobile Phone Coverage (units per 100 households) | Number of mobile phones owned per 100 rural households | |
| Fixed Investment in Digital Industry (CNY 10,000) | Fixed asset investment in information transmission, computer services, and software industries | |
| Business Digitalization | Number of Enterprise Websites (websites per 100 enterprises) | Number of websites owned per 100 enterprises |
| E-commerce Participation Rate (%) | Proportion of enterprises engaged in e-commerce activities | |
| E-commerce Sale Volume (CNY 100 million) | Total amount of goods and services sold based on online orders | |
| Circulation Digitalization | Rural Postal Service Level (outlets per person) | Population served per rural postal service outlet |
| Rural Retail Level (%) | Rural retail sales/Total societal retail sales | |
| Proportion of Villages with Postal Service (Logistics) (%) | Villages with postal service/Total number of villages | |
| Living Digitalization | Rural Network Investment Quantity and Scale (-) | Digital Inclusive Finance County Investment Index |
| Rural Network Payment Quantity and Scale (-) | Digital Inclusive Finance County Mobile Payment Index | |
| Farmers’ Transportation and Communication Expenditure Level (%) | Proportion of farmers’ expenditures on transportation and communication | |
| Effective Invention Patent Rate (%) | Number of granted invention patents/Number of patent applications |
| Variable | N | Mean | P50 | SD | Min | Max | Vif |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Efficiency | 330.000 | 0.789 | 0.764 | 0.141 | 0.486 | 1.311 | --- |
| Digital | 330.000 | 0.391 | 0.393 | 0.074 | 0.224 | 0.600 | 1.44 |
| Finance | 330.000 | 3.296 | 3.434 | 1.521 | 0.175 | 7.581 | 1.43 |
| ML | 330.000 | 0.638 | 0.574 | 0.229 | 0.264 | 1.387 | 1.21 |
| OP | 330.000 | 0.007 | 0.003 | 0.034 | 0.000 | 0.503 | 1.06 |
| Creative | 330.000 | 0.035 | 0.033 | 0.017 | 0.009 | 0.081 | 1.05 |
| Region | 2011 | 2012 | 2013 | 2014 | 2015 | 2016 | 2017 | 2018 | 2019 | 2020 | 2021 | 2022 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| East | 0.74 | 0.74 | 0.78 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.85 | 0.93 | 0.92 | 1.02 | 1.03 |
| Central | 0.64 | 0.66 | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.72 | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.82 | 0.84 | 0.83 | 0.85 |
| West | 0.62 | 0.65 | 0.69 | 0.71 | 0.75 | 0.77 | 0.74 | 0.77 | 0.81 | 0.90 | 0.91 | 0.93 |
| Northeast | 0.69 | 0.68 | 0.72 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.74 | 0.83 | 0.83 | 0.81 | 0.84 | 0.84 | 0.84 |
| National | 0.68 | 0.69 | 0.72 | 0.77 | 0.79 | 0.78 | 0.78 | 0.80 | 0.86 | 0.89 | 0.93 | 0.94 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | (4) | (5) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Digital | 0.329 * | 0.293 * | 0.376 ** | 0.367 ** | 0.366 ** |
| (1.79) | (1.66) | (2.11) | (2.02) | (2.02) | |
| Finance | 0.040 *** | 0.043 *** | 0.043 *** | 0.043 *** | |
| (4.92) | (5.27) | (5.27) | (5.29) | ||
| ML | −0.112 ** | −0.109 ** | −0.111 ** | ||
| (−2.51) | (−2.38) | (−2.42) | |||
| OP | −0.037 | −0.032 | |||
| (−0.29) | (−0.25) | ||||
| Creative | 0.802 | ||||
| (0.68) | |||||
| Constant | 0.569 *** | 0.421 *** | 0.452 *** | 0.453 *** | 0.426 *** |
| (9.36) | (6.41) | (6.82) | (6.81) | (5.48) | |
| year | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| state | yes | yes | yes | yes | yes |
| Observations | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 | 330 |
| R2 | 0.581 | 0.614 | 0.622 | 0.622 | 0.623 |
| Variables | z | I | Variables | z | I |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| e2011 | 1.392 | 0.109 * | x2011 | 3.478 | 0.353 *** |
| e2012 | 1.782 | 0.154 ** | x2012 | 4.339 | 0.449 *** |
| e2013 | 2.546 | 0.240 *** | x2013 | 3.570 | 0.358 *** |
| e2014 | 3.223 | 0.324 *** | x2014 | 3.971 | 0.407 *** |
| e2015 | 2.128 | 0.203 ** | x2015 | 3.365 | 0.341 *** |
| e2016 | 2.095 | 0.197 ** | x2016 | 1.865 | 0.174 ** |
| e2017 | 0.536 | 0.024 | x2017 | 1.917 | 0.180 ** |
| e2018 | 0.413 | 0.011 | x2018 | 1.943 | 0.181 ** |
| e2019 | 1.349 | 0.117 * | x2019 | 2.222 | 0.214 ** |
| e2020 | 0.764 | 0.052 | x2020 | 2.188 | 0.211 ** |
| e2021 | 0.774 | 0.052 | x2021 | 1.697 | 0.155 ** |
| e2022 | 0.793 | 0.049 | x2022 | 1.893 | 0.147 ** |
| Test Statistics | Economic Geography Matrix | Adjacency Matrix | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Value | p-Value | Value | p-Value | |
| LM-lag | 62.40 | 0.000 | 59.21 | 0.000 |
| Robust LM-lag | 28.40 | 0.000 | 8.59 | 0.000 |
| LM-error | 34.22 | 0.000 | 91.91 | 0.000 |
| Robust LM-error | 0.22 | 0.637 | 41.29 | 0.000 |
| Hausman test | 32.61 | 0.001 | 33.24 | 0.001 |
| LR test spatial lag | 67.47 | 0.000 | 43.82 | 0.000 |
| LR test spatial error | 68.92 | 0.000 | 46.18 | 0.000 |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Digital | 0.5640 *** (4.18) | |
| Construction | 0.1171 * (1.75) | |
| Operation | 0.2340 *** (3.14) | |
| Circulate | −0.2622 *** (−2.80) | |
| Life | 0.1846 * (1.73) | |
| Finance | 0.0102 ** (2.17) | 0.0263 *** (4.41) |
| ML | 0.0565 * (1.95) | 0.0879 *** (2.91) |
| OP | 0.3483 ** (2.02) | 0.1542 (0.91) |
| Creative | −2.0761 *** (−3.27) | −2.1264 *** (−2.99) |
| ρ | −0.0917 ** (−2.11) | −0.1545 * (−1.88) |
| λ | 0.0100 *** (12.83) | 0.0092 *** (12.78) |
| W×Digital | −0.7282 *** (−2.62) | |
| W×Construction | 0.1181 (0.92) | |
| W×Operation | −0.4329 ** (−2.37) | |
| W×Circulate | −0.3341 * (−1.96) | |
| W×Life | −0.0800 (−0.39) | |
| W×Finance | −0.0447 *** (−4.11) | −0.0362 *** (−2.89) |
| W×ML | 0.4454 *** (6.79) | 0.4995 *** (7.16) |
| W×OP | −1.0681 (−1.21) | −1.2883 (−1.49) |
| W×Creative | 3.6684 *** (2.65) | 4.0400 ** (2.40) |
| ID | NO | NO |
| YEAR | YES | YES |
| N | 330 | 330 |
| R2 | 0.239 | 0.425 |
| LR_Direct | LR_Indirect | LR_Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Digital | 0.589 *** | −0.718 *** | −0.129 |
| (0.00) | (0.01) | (0.64) | |
| Finance | 0.011 ** | −0.043 *** | −0.031 *** |
| (0.02) | (0.00) | (0.00) | |
| ML | 0.048 * | 0.412 *** | 0.460 *** |
| (0.09) | (0.00) | (0.00) | |
| OP | 0.369 ** | −0.976 | −0.606 |
| (0.03) | (0.23) | (0.47) | |
| Creative | −2.189 *** | 3.609 *** | 1.420 |
| (0.00) | (0.00) | (0.15) |
| (1) | (2) | |
|---|---|---|
| Digital | 0.3857 *** | 1.0962 *** |
| (0.1345) | (0.2942) | |
| Finance | 0.0242 *** | 0.0308 *** |
| (0.0048) | (0.0103) | |
| ML | 0.1547 *** | −0.0470 |
| (0.0314) | (0.0625) | |
| OP | 0.1049 | 0.9723 *** |
| (0.1571) | (0.3756) | |
| Creative | −2.8459 *** | −2.2483 |
| (0.5774) | (1.3840) | |
| ρ | −0.2812 *** | −0.0481 |
| (0.0878) | (0.0828) | |
| λ | 0.0079 *** | 0.0476 *** |
| (0.0007) | (0.0037) | |
| N | 286 | 330 |
| (1) | (2) | (3) | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Distance | Adjacency | Economic | |
| Digital | 0.8414 *** | 0.4185 ** | 0.5640 *** |
| (0.1373) | (0.1625) | (0.1348) | |
| Finance | −0.0000 | −0.0023 | 0.0102 ** |
| (0.0037) | (0.0041) | (0.0047) | |
| ML | 0.0214 | 0.0132 | 0.0565 * |
| (0.0332) | (0.0328) | (0.0290) | |
| OP | 0.4471 *** | 0.3400 * | 0.3483 ** |
| (0.1650) | (0.1839) | (0.1722) | |
| Creative | −1.8101 *** | −1.5655 *** | −2.0761 *** |
| (0.4928) | (0.5884) | (0.6340) | |
| ρ | −0.6837 *** | 0.0351 | −0.0917 |
| (0.2262) | (0.0849) | (0.0827) | |
| λ | 0.0087 *** | 0.0107 *** | 0.0100 *** |
| (0.0007) | (0.0008) | (0.0008) | |
| N | 330 | 330 | 330 |
| R2 | 0.407 | 0.375 | 0.239 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhao, L.; Chen, H.; Ding, X.; Chen, Y. Does Digital Village Construction Empower the Green Allocation of Agricultural Water Resources? Systems 2024, 12, 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12060214
Zhao L, Chen H, Ding X, Chen Y. Does Digital Village Construction Empower the Green Allocation of Agricultural Water Resources? Systems. 2024; 12(6):214. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12060214
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhao, Li, Haining Chen, Xuhui Ding, and Yifan Chen. 2024. "Does Digital Village Construction Empower the Green Allocation of Agricultural Water Resources?" Systems 12, no. 6: 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12060214
APA StyleZhao, L., Chen, H., Ding, X., & Chen, Y. (2024). Does Digital Village Construction Empower the Green Allocation of Agricultural Water Resources? Systems, 12(6), 214. https://doi.org/10.3390/systems12060214







