Abstract
This paper presents a review of the field of systems thinking and strategic management The evolution of the areas of interest between systems thinking and strategic management follows similar patterns with more prescriptive developments occurring within the 1960s until 1980s; then, an increasing focus on emergence and transformation emerged in later years. From the review, there seems to exist synergies between multiple strands in Systems Thinking and Strategic Management. Suggestions to facilitate the interaction between both fields are proposed, considering the type of processes to generate strategies and the perspectives employed to visualize the organizations as systems. Hopefully, the paper can contribute to embedding systemic approaches to the strategic management of organizations and society.
1. Introduction
Strategies are typically influenced by the following factors: multiple conflicting objectives, limited directly relevant data, diverse interested stakeholders, different decision alternatives, and long timescales and horizons [1]. Simultaneously, organizations operate within increasingly dynamic and complex environments facing multiple and destabilizing forces [2]. Strategic decision making has many characteristics of unstructured problems: multiple actors who are tightly interconnected in networks whose decisions cannot be ignored because the decisions impact on each other. Moreover, they do not usually agree and have conflicting interests due to their different beliefs, values and mental models [3]. These decisions are usually approached by two separate areas of knowledge: systems thinking and strategic management.
On the one hand, systems thinking (ST) refers to perspectives, concepts, frameworks, approaches, methodologies, and interventions focused on understanding interrelationships between entities or parts generating emergent behavior, as the field is highly fragmented with different schools that developed over time from the 1950s [4]. On the other hand, strategic management (SM), which originated in the 1960s, is also a fragmented field with different schools reflecting the different interests of scholars over time from defining successful strategies (prescriptive schools) to describing unstructured processes (descriptive schools), focusing on the process to develop strategies (strategy process) as well as the type of strategies (strategy content). While there are a number of scholars who have attempted to combine both areas of knowledge, e.g., [5,6,7]), there is not an overarching framework to define their integration. Thus, the research question for this article is: how can ST and SM be integrated?
There may be few possible alternatives to answer this question. One alternative is to adapt tools and frameworks in ST so they can be used jointly with SM tools and frameworks. In this way, the barriers for the potential users that know SM will be lower. Another alternative is to embed ST perspectives into SM so tools and frameworks in SM become systemic. A final alternative is to identify where ST standard tools and frameworks can be applied in terms of SM, e.g., finding a suitable matching, which is the approach taken in this article. The methodology to develop this review involves the selection of a few relevant scholar articles and books that summarize and describe SM and ST fields for two reasons: first, they are extensive fields which cannot be summarized in one article, and second, there are excellent summaries and description of the components of both fields. The key contribution of this paper is to offer a framework where more cross-fertilization between SM and ST can be developed in the future.
This paper is structured as follows: Section 2 introduces ST including a brief description of popular tools and methods. Section 3 presents a general overview of the field of SM from a perspective of the schools existing in the field. Section 4 synthesizes the interventions as part of a framework. The conclusion, the limitations, and some ideas for further research conclude this article.
2. Systems Thinking
2.1. An Introduction to Systems Thinking
Ackoff [8] defines “a system is a whole consisting of two or more parts (1) each of which can affect the performance or properties of the whole, (2) none of which can have an independent effect on the whole, and (3) no subgroup of which can have an independent effect on the whole. A system is a whole that cannot be divided into independent parts or subgroups of parts”. (p. 175). He identifies three types of systems, which can be used to characterize organizations:
- Mechanical systems are systems whose behavior is regular, determined by the internal structureand specific laws, e.g. clocks. This was the typical business in the 19th century, where employees were replaceable machine parts performing unskilled work and the business was run directly by the owner.
- Organismic systems have purposes of their own, but their constituent parts have not goal or purpose and are open. Therefore, they have to be considered together with their environments. Organizations that originated after the end of World War I were examples of this type. The fundamental change was the appearance of managers that replaced owners with workers who were more specialized and skilled. However, the focus was productivity and autocratic hierarchies.
- Social systems are open systems with purposes of their own as a system, as well as their constituent parts. Thus, organizations are intrinsically integrated internally, e.g., people playing more important roles, and externally, e.g., society. Since they cannot be divided, the performance is not equal to the sum of the actions taken separately. Therefore, analytic thinking, which consists of separating components and treating them separately, can be counterproductive. Instead, synthesis, which involves understanding components as parts of a larger system, can help to understand the performance of an organization.
Another important contribution to understanding approaches employed on ST is Boulding’s hierarchy of complexity [9]. This framework arranges the complexity existing in different empirical fields with a level of abstraction that is appropriate to understand their emergent properties [4]. The framework helps to identify a mismatch between the theories used for analysis with the level of complexity of the issue being study. The hierarchy has nine hierarchical levels (adapted from [9], table 1):
Level 1. Structures and frameworks showing static behavior are studied using verbal or pictorial description.
Level 2. Mechanistic structures with predetermined motion are investigated using classical natural science.
Level 3. Control mechanisms using closed-loop control are studied using cybernetics.
Level 4. Open systems exhibiting structural self-maintenance can be investigated using theories of metabolism.
Level 5. Lower organisms with functional parts showing blue-printed growth and reproduction are researched through botany.
Level 6. Animals with a brain to guide behavior and capable of learning can be studied by zoology.
Level 7. People with self-consciousness who use symbolic language are investigated using biology and psychology.
Level 8. Socio-cultural systems, which are defined by the existence of roles, communication and transmission of values, are researched using history, sociology, anthropology and behavioral science.
Level 9. Transcendental systems, inescapable unknowns, without any scientific discipline to study them, e.g., the idea of God.
Jackson [9] suggests a classification for the approaches employed in ST combining the two previous concepts: types of systems and hierarchy of complexity of analysis.
- Functionalist ST. ST methods, e.g., Systems Engineering, Systems Analysis, and Socio-Technical Systems Thinking, in this category use mechanistic (level 1–3) or organismic (level 4–6) models to understand systems. They focus on efficiency and survival of systems using scientific methods to learn about the nature of the parts of the system and their interrelationships internally and externally. In terms of the analysis, their approaches focus on representing the systems as mechanistic structures managed through close-loop control mechanisms.
- Structuralist ST. In this classification, ST methods, e.g., System Dynamics, Viable Systems Model, search for key mechanisms or structures responsible for the system behavior. A structuralist approach leads analysts to identify the problems with the system and manipulate its design/structure to make it more effective over time (level 1–6). Their analytical lenses also focus on mechanistic and well-defined structures controlled by close-loop mechanisms. One criticism of these ST methods is their application to social systems because people through their motivations and actions define the emergent behavior of systems, and these methods don’t capture the subjective interpretations of the world.
- Interpretative ST. The ST methods, e.g., Soft Systems Methodology, Critical Systems Heuristic, Team Syntegrity, in this classification focus on the symbolic levels of complexity analysis (level 7–8), where system behavior originates from ‘images’ rather than direct stimuli, as the brain organizes information into knowledge structures or images. Therefore, these approaches work with the interpretation of the issues in systems by the actors in the system rather than defined and well-structured system models. Attention is paid to ensure sufficient accommodation between different views of the system to achieve ‘idealized designs’ of the system.
The implications for a social, or interpretative, perspective of systems, as implied in the third classification, is quite contrasting with respect to functionalist ST [10].
- Interpretative implies participatory decision-making processes, self-organization, free will, creativity, and spontaneity within democracy.
- Functionalist involves hierarchical decision-making processes, externally imposed order and control, deterministic behavior within a technocracy.
Another similar categorization of the field of ST is provided in [3]. They distinguish between ‘hard’ and ‘soft’ ST. Hard ST practice considers the real world can be modeled in an objective way with clear and established goals or objectives, so it can be optimized through models. On the other hand, soft ST assumes the real world is too complex to be modelled objectively and optimized. Soft ST can support structuring the understanding of the system and learning about problematic situations. Thus, debate and accommodation about the nature of the problem in the system rather than prescribing its solution is the main objective of soft ST.
Finally, Jackson [11] provides a useful grid for positioning the problem context that ST practitioners face, see Figure 1, which is based on a systems of systems methodology [12]. The grid has two axes representing the complexity of a problem: “type of systems” (y-axis) and “stakeholders” (x-axis). The type of systems can be simple, complicated and complex. Simple systems involve repeating patterns and consistent events with a clear cause-and-effect relationship this is easily identifiable, e.g., known knowns, with the existence of right answers suggesting a fact-based management [13]. Complicated systems have similar characteristics to simple, but experts are needed to uncover cause-and-effect relationships, e.g., known unknowns, with more than one right answer possible. Complex systems lack predictability, e.g., unknown unknowns, without clear answers, so there are competing ideas and a need for creative and innovative approaches. [13]. The horizontal axis indicates increasing divergence of values and/or interests for the people related to the system. In a “unitary” situation, there is clearly shared values and beliefs with related interests, or divergent values and beliefs are ignored. “Pluralist” indicates difference in terms of values and beliefs with similar interests. A “Coercive” situation shows multiple interests with opposing values and beliefs. Hard ST practice can be mostly located between unitary/pluralist and simple/complicated areas. Soft ST may be mapped on the pluralist/coercive and complicated/complex quadrants.
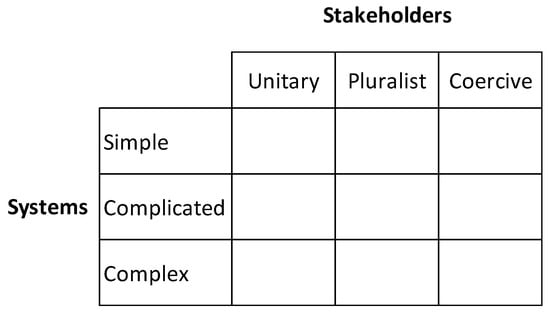
Figure 1.
Grid for problem contexts related to systems (adapted from [11], Figure 1).
To summarize, ST has two main strands: hard, or structuralist/functionalist, ST and soft, or interpretative/subjective, ST and each of them can be more suitable for different types of systems given their level of complexity. The next section presents a mapping of the methodologies in ST with respect to the grid.
2.2. ST Methodologies
This section does not intend to provide a detailed explanation of the ST methodologies and tools since there are multiple books explaining them in detail, e.g., [3,4,14]. To map the methodologies, I use Figure 1 and the classification indicated in [4].
Systems Engineering (SE) addresses systems’ problems building quantitative models with clear agreed objectives. The main objective is to design efficient systems by organizing their components [15]. SE shares many similarities with Operational Research (OR), and it is considered a hard ST [4]. SA (System Analysis) also shares similar characteristics with SE and OR. All of them make simple, unitary assumptions on working with systems: stakeholders’ agreement with objectives, and systems are modelled mathematically. Robustness Analysis (RA) supports decision-making when there is uncertainty about the future and decisions are sequential (by design or choice), especially in planning, with special consideration of their impact on the system [3]. The Vanguard Method (VM) is a method derived from business process improvement sources, e.g., Deming and Ohno, and comprises three stages: check (an analysis of the what and why of the current system), plan (exploration of potential solutions to eliminate waste), and do (implementation of solutions incrementally and by experiment) [4]. System Dynamics (SD) focus on the structural aspects of systems through identifying and mapping the dynamic interrelationships between multiple elements of the system. SD practice addresses the quality and quantity of interactions between elements, which makes it difficult to understand and infer the systems behavior, through feedback loops [16]. SD models can be quantitative or qualitative depending on the objective of its use: understanding the structure or simulating its behavior, respectively [17]. Organizational cybernetics [18] emphasizes communications and control to manage organizations. Viable System Model (VSM) facilitates seeing organizations as complex communications systems that control bureaucracies, hierarchies, and functional structures [18]. Socio-Technical Systems Thinking (STS) is an approach to design systems that enhance the quality of working life and humanism in organizations, especially during the implementation of technical innovations. It enhances multi-skilling and group decision making with flat hierarchies.
In terms of pluralist, there are multiple methods (see Figure 2). A Strategic Choice Approach (SCA) also supports decision making by focusing on the interconnectedness of decision problems while managing uncertainty [19]. It has four modes of decision-making: shaping mode, designing mode, comparing mode, and choosing mode [19]. Strategic Options Development (SODA) is a framework to design problem solving interventions for messy problems. It involves the development of a facilitated model that is politically feasible and shows the interconnectedness between issues, problems, strategies, and options [20]. Interactive planning (IP) is a method generated by Ackoff. IP aims at creating the ideal organization through a process of idealization with all relevant stakeholders through a planning process [21]. By creating the ideal organizations, participants can obtain new knowledge and adapt to the situation [21]. IP is implemented in a series of stages: mess formulation, ends planning, means planning, resource planning and implementation, and control planning. The first two stages are the idealization tasks, and the rest are the planning tasks. The second method is the Soft System Methodology (SSM) [22]. It is a highly participative method to address problems in systems through exploring participants’ perceptions about them which lead to a model of a desirable future system of activities. It involves considering the situation in an unstructured form and transforms it into a visual representation, called a ‘rich picture’. Then, possible future systems that address the problem are discussed and agreed into an action plan. Strategic assumption surfacing and testing (SAST) is a methodology to confront messes or wicked problems (interconnected, complicated, uncertain, ambiguous, and with societal constraints) by focusing on the formulation of the problem, as it is more relevant than problem solving [4]. The methodology is participative, adversarial, integrative, and managerial supporting, and it is applied in four stages: group formation, assumption surfacing, dialectical debate, and synthesis [4]. RA, SODA, and SCA are also considered Problem Structuring Methods/Soft ST [3], or Soft OR, because they focus on structuring problems [4]. However, they share similar characteristics with other ST methods, especially those focused on pluralism, e.g., SSM.
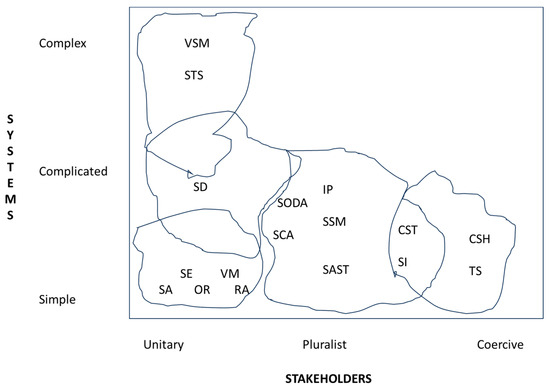
Figure 2.
ST methodologies classified according to type of systems/stakeholder involvement (partially adapted from [4], p 512), and include methods from [3]. Note: The mapping, in terms of clouds encompassing the methods, is an approximation without specific measurements to define the shapes and size of the figures. VSM (Viable System Model), STS (Socio-technical System), SD (System Dynamics), SE (Systems Engineering), SA (System Analysis), OR (Operational Research), VM (Vanguard Method), IP (Interactive Planning), SSM (Soft System Methodologies), SAST (Strategic Assumption Surfacing and Testing), CSH (Critical Systems Heuristic), TS (Team Syntegrity), CST (Critical System Thinking), SI (Systemic Intervention), SODA (Strategic Options Development Analysis), SCA (Strategic Choice Approach), RA (Robustness Analysis).
Finally, there are two methods that focus on pluralism but aren’t included in Jackson’s [4] original map. One is Critical Systems Thinking (CST) [4] whose aim is to understand the strengths and weaknesses of each ST method before combining them to address problems in systems. The second method called Systemic Intervention (SI) [23] is also a pluralistic approach that provides a rationale combining, mostly ST methods to question the boundaries defined in systems before addressing the problems in the system. Defining and reflecting on the boundaries of the system is a critical aspect of the use of systems-based methods to facilitate the selection and integration of multiple stakeholders. Mingers and Brocklesby [24] emphasize the attractiveness of using multimethodology in systemic practices in real-world problem situations because systems are highly complex and multi-dimensional.
The final set of methods associated with coerciveness are Critical Systems Heuristics (CSH) [25] and Team Syntegrity (TS) [4]. CSH fundamentally focuses on the existence of “coercive simple systems” [4]. CSH consist of a set of questions to achieve holistic awareness of situations regarding the values and motivations built into the views of situations held by stakeholders and efforts to improve them; the power structures influencing the definition of a problem and its solution; the knowledge that defines an information relevant for the issues; and the moral aspects of the consequences of the action or no action regarding the situation. In CSH, these questions inform four dimensions of problems, sources of motivation, control, knowledge, and legitimacy, that define their boundaries [25]. Team Syntegrity (TS) focuses on providing non-hierarchical, equitable, and participative decision-making processes where diverse views are shared to achieve consented innovative solutions with a ST perspective [4].
3. Strategic Management
One of the challenges to map out the potential contributions of ST to SM is to find sources that provide a broad perspective on the field of SM. In this case, the book by Mintzberg et al. [26] Strategy Safari is a good source to understand the field of SM in general terms, but it “… is a field review, not a literature review”. However, the schools are partial views of the same phenomenon, so their combination is what makes a complete depiction of SM as practice, as Mintzberg et al. said. Mintzberg et al. [26] classify SM into ten different schools:
The Design School: strategy formation as a process of conception.
The Planning School: strategy formation as a formal process.
The Positioning School: strategy formation as an analytical process.
The Entrepreneurial School: strategy formation as a visionary process.
The Cognitive School: strategy formation as a mental process.
The Learning School: strategy formation as an emergent process.
The Power School: strategy formation as a process of negotiation.
The Cultural School: strategy formation as a collective process.
The Environmental School: strategy formation as a reactive process.
The Configuration School: strategy formation as a process of transformation.
The first three schools prescribe the formulation of strategies, called prescriptive schools, from unique designs to specific positions in markets through the extremely analytical and formal process of planning. The next six schools describe aspects of the process of strategy development, called descriptive schools. The first three schools focus on individuals, as strategy makers, from visioning (entrepreneurial) to a process of learning through a micro analysis of the mental process to create strategies (cognitive processes). The following three schools address the impact of other actors in the process: culture, power, and the environment. The power school treats strategy as a process of negotiation compared with the cultural school which indicates that culture shapes strategy. The final school, configuration, combines the others in terms of process, content, organizational structures, and contexts, e.g., distinct stages or episodes on the life cycle of organization. Thus, this last school will not be considered further.
An interesting aspect of Mintzberg et al.’s [26] book is the definition of strategy as five Ps. First, strategy is a Plan or course of action into the future. Second, strategy is a Pattern or consistent behavior over time, e.g., companies targeting certain market segments or launching specific types of products. Additionally, strategies are not necessarily all intended but they may originate from practice or solutions to problems, or emergent strategies. Third, strategy can be a Position such as selecting the position of a product in specific markets. Fourth, strategy as a Perspective starts looking inside the organization, e.g., inside the heads of the strategists or considering only the internal aspects of the organization, to come out with a grand strategy. Finally, strategy can be a ploy, or specific maneuvers to win against the competition.
For each aspect of the process and content of strategies, there can be inferred some advantages and disadvantages. For example, when strategy defines the direction, it helps to set the path for the organization, but it can also blind the organization to opportunities or hide threats. However, there are key considerations with respect to strategy: it concerns internal (organization) and external (environment) factors; it is complex due to set of combinations that can occur; it affects the future of the organization; it involves the output (content) as well as the making (process); it can appear as deliberate or emergent; and it comprises conceptual as well as analytical activities.
Table 1 presents a summary of the schools from Mintzberg et al.’s [26] book. The first concept, summary, captures the main messages from each school, for example, the design school aims to achieve fit between internal and external aspects of the organization but practitioners following the school focus on a thoughtful design of the strategy. The first three schools have actions associated with analytical activities comprising deliberate processes of conscious thought. On the other hand, the next three schools capture activities directly related to the mental aspects of strategic making: envisioning, framing, and learning. The following three schools address actions related to struggle: grab, coalesce, or cope.
The next group of concepts describe the process (activities to generate strategies) and context (actors developing strategies, organizational and environmental conceptualizations) dimensions of the school. The outcomes of the strategy process vary from formal and deliberate plans, including the first three schools together with environmental, to patterns (learning, power) through perspectives (entrepreneurial, cognitive, and cultural). Additionally, the first row describes the rich variation in the process suggested by each school with only three schools being a deliberate process with different levels of formalization and the rest implying emergent, informal, messy processes influenced by either the person doing the strategy or other forces in the organization, power, or culture. Another outcome of strategies is organizational change, which can be large from incremental and occasional (for strategies considering mostly stable systems) to revolutionary and continuous (for strategies emerging from dynamic processes). Another important concept is the Key actors responsible for the development of the strategy. More analytical actors generate strategies that are more stable or focus on incremental change, e.g., planning, compared with situations that involved more actors, or less analytical actors, e.g., power or cultural school or entrepreneurial school. Related to the actors is the style of leadership needed in each school: supportive of analytical and formal procedures for schools emphasizing the role of planning, and dominant in those schools that concentrate the decision on one person, but they seem to be less dominant on schools that assume the participation of multiple people on the process.
The last two concepts in this group are Conceptualization of the Organization and Conceptualization of the Environment. The first concept indicates the assumptions employed during the strategy development processes with respect to the characteristics of the organization. Schools are better suited to different types of the organization; when the potential for the implementation of the strategy is considered, in general, organizations tend to accept change and they need to be stable and ordered to foster more analytical approaches. However, the organizational life cycle can also be critical for the development of a certain school. The second concept captures the easiness to understand and manage the environment of the organization during the strategy process, as well as the conditions perceived about the external environments that the strategic decision makers have: from simple, stable, and understandable to complex, dynamic, and incomprehensible.

Table 1.
Summary of the strategy schools (adapted from [26], Table 12.1).
Table 1.
Summary of the strategy schools (adapted from [26], Table 12.1).
| Concept | Design | Planning | Positioning | Entrepreneurial | Cognitive | Learning | Power | Cultural | Environmental |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Summary | This school focuses on achieving congruence between the organization (in terms of strengths and weaknesses) with the environment (in terms of threats and opportunities). | This school considers strategy as a highly formalized program of activities with strong quantitative focus through budgeting and numerical scenarios. | For this school, strategy is an analytical process of the competitive dimensions leading to generic strategies and the arrangement of initiatives in portfolios. | Strategy is about envisioning, leading to bold actions originated by the insights of the entrepreneur. | Strategy is in the mind of the leaders, as frames, imagination, or maps. The critical components are perceptions, interpretations, bounded rationality, and cognitive styles. | Strategy is about learning, incrementalism and emergence. A combination of sense-making, entrepreneurialism, and venturing. | In this school, strategy is about bargaining, conflict, and grabbing. It also entails managing coalitions (networks, alliances), stakeholders, and political games. | This school considers strategies are driven by values, beliefs and myths. Aspects such as culture, ideology and symbolism define the development of strategies | Strategy involves reacting to the environment in different ways: coping, capitulating, adapting, evolving, or disappearing if the conditions are not appropriate. |
| Strategy development process | The development of strategies follows a planned approach aiming for unique, informal and simple strategies that may imply occasional changes. | This process to develop strategies consists of detailed plans decomposing strategies into sub-strategies and programs. It is a formal and deliberate process leading to incremental change. | This process is driven by economic analysis that leads planned positions in markets sustained by a defined and deliberate set of competitive actions (ploys). Strategies derive into piecemeal, frequent changes. | This process is about creating a personal, unique perspective (vision) about a place in the market (niche). Therefore, strategies are mostly visionary, intuitive, and emergent. Change is mostly opportunistic and revolutionary. | This process is focused on the micro-behavior of the top management team leading to the generation of strategies. No specific recipes but the interaction of mental perspectives are critical to generate mostly emergent strategies that may or may not change. | This process is informal, emergent, messy, and continuous. The main outcomes are strategies as patterns of unique actions. Change is mostly incremental. | Developing strategies is a political process leading to patterns of actions, some of them cooperative and other conflictive/aggressive. The outcomes are messy and emergent leading to frequent changes. | Strategy development process is an exercise of collective perspectives, unique and ideological. The resulting strategies are constrained by the collective ideology with infrequent changes. | Strategy development involves finding specific positions in markets/industries and adapting to them passively. Strategies can lead to no change or radical changes depending on the environment. |
| Key actors responsible for the development of the strategy | Strategies are designed by the chief executive officer, who is the architect designing the organization as it sees it, in a dominant and judgmental manner. | The key actors are the staff in the corporate planning area; the planners, who elaborate procedures that are followed by managers to develop the strategies. | The main role in the process is taken by analysts, who generate the portfolio of market positions. Managers are responsive to this analysis. | The only actor is the entrepreneurial leader, who has a dominant position and she/he is driven by her/his intuition. | The leaders working alone or in teams. Their cognition has the main role | Everyone can be responsible for the strategy as a learning process. | Anyone with power inside the organization. | There aren’t any specific actors responsible for the strategy since it is a collective effort. However, symbolic leaders may drive the process. | There aren’t any specific actors. However, the most relevant roles are related to the analysis of the environment. |
| Conceptualization of the Organization) | The organization is considered as a formal machine, highly structured, and centralized in the figure of the CEO, with the assumption that it can accept changes, if needed, easily so it can be reconfigured without any problem. | Organizations are large centralized, formalized machines organized in divisions. The structure is easy to decompose and its activities arranged into programs followed by the decision makers. | Similarly to the previous two schools, organizations are considered large centralized and formalized machines competing preferably in commodity or mass markets at global scale.Change is good if the change implies creating a competitive advantage or doesn’t change. | The organization is conceptualized as simple but centralized around the entrepreneurial leader and ready to change. They are usually small in size and startups or large and in turnaround processes. | The organization can take any shape as it depends on the conceptualization of the leaders in terms of structure. | The organization is a professional adhocracy highly decentralized and flexible. The organization is continuously evolving, especially during unprecedented change. | There is no specific conceptualization but it may be conflictive, disjointed, and uncontrollable (micro) with continuous political challenges, either blockages or flux. | The organizations are driven by a mission shared collectively in a cohesive way and supported by norms. It is a stagnant organization with significant inertia. | Organizations are formal machines, centralized and accustomed to their market/industry as they are mature. |
| Conceptualization of the Environment aspects | The environment is considered to be expedient and easy to understand in categories, e.g., social, political, technical, and stable. | The environment is assumed to be manageable and controlled as a list of factors that can be predicted and are stable. | The environment is competitively demanding but analyzable, and ultimately acquiescent to the organization. The environment tends to be stable with enough historical data. | The environment is dynamic and full of opportunities, which are clearly understood by the leader. The organization is able to maneuver around the niches with ease. | The environment can be overwhelming due to its dynamics and complexity. On the other hand, it can be perceived in an extremely simplified way. | There is an elaborate conceptualization of the environment, which is unpredictable and dynamically complex. | The environment is contentious and divisive, but negotiable leading to control or cooperation. | The environment doesn’t have major impact, and it is passive, unless there are incidents/threats that affect the organization. | The environment defines the past, present and future of the organization, so it is highly relevant and exigent for the organization. The environment is also competitive and clearly delineated. |
4. Integration of Systems Thinking with Strategic Management
This section focuses on the integration of ST with SM considering three alternatives mentioned in the introduction. The first alternative is to simplify the ST methods to fit with SM. No examples were encountered, but there may be frameworks designed by consultants that can satisfy this requirement. An approximation can be found in Kunc’s [27] book where some chapters provide examples that could be useful to think about this alternative. A second alternative, which considers embedding ST into SM, does not have clear examples unless from SM scholars. One potential example may be Brown and Eisenhardt’s [28] book on strategy as structured chaos. The last alternative is represented in Table 2 showing a potential allocation of the ST method to each SM school.
Table 2 employs the concepts defined in Section 2. The first concept is the type of system implied in the definition of the school, which can be mechanical, organismic, or social. Clearly, the first three schools together with the Environmental school have a conceptualization of organizations as mechanical systems with regular behavior shaped by internal structure and economic laws easily shaped into the strategies identified by the main actors. The other schools have a mix between organismic and social depending on the role of people on shaping the development of strategies through visioning activities, learning processes, power struggle, and cultural influence. The level of complexity, as presented in Figure 1, indicates the conceptualization of the systems underpinning the formation and implementation of strategies. Schools mostly driven by individual actors have a simplistic concept of the organization, e.g., SWOT analysis to design strategies is a very simplistic tool. However, most of the schools tend to have a complicated or complex perspective, albeit implicit, in their conceptualization of the system due to multiple actors involved in the process, the existence of different forces, the amount of information to be processed, etc. I use the term implicit because Mintzberg et al. [26] had a comment suggesting that complexity is not addressed in ST in terms of the content of strategies. A dimension aligned with the second term, as presented is Figure 1, Section 2, is the acknowledgement of the impact of divergent values, beliefs and interests, as Unitary/Pluralist/Coercive, which tend to be recognized in schools that consider the impact of people on the process, pluralist/coercive, as either positive or a source of struggle. For formal schools, organizations are highly malleable. The fourth term, Functionalist/Structuralist/Interpretative, provides a potential classification of the ST approaches that can be employed considering the type of system and the complexity. The schools that tend to be more analytical in their strategic making processes seem to be better served by functionalist or structuralist ST approaches. On the other hand, schools that recognize the role of people can benefit from interpretative ST approaches, but with a caveat since it depends on the role of the central actor. The last line includes the different ST methods that can be associated or employed in each school of strategy. The allocation is based on Figure 2, Section 2. While there is only one method in each school, the best approach is methodological pluralism, as suggested in Section 2, so the combination of more than one ST method with SM methods depending on the step of the strategic development process, the organizational situation and other factors should be considered.
At the end of Table 2, a sample of academic articles showing applications of ST in SM is presented, as well as books, which have plenty of examples of applications to illustrate their different methods in more than one case study. The examples fit more than one school because the cases are not clearly delineated in one specific school since SM issues comprise more than one school, as mentioned in Section 4.
In more detail, Andrade and Loureiro [29] describe a case study conducted in a science, technology, and innovation institution operating in Brazil. In their study, they compared the strategic planning cycles using traditional methodologies to develop strategies with SE. SE involves a structured analysis to identify requirements and attributes of the product life cycle, manufacturing processes, and the organization structure, including requirements, functional, and physical analyses.
Torres et al. [2] present a protocol for supporting strategy development using SD in small organizations. The protocol, which was applied in five companies, involved the development of a quantitative model to generate scenarios of alternative strategic situations. The development of the model employed an interactive modelling process [30]. Through the projects, managers using SD could identify structural aspects of their business, e.g., causal relationships and feedback loops among key resources, and external forces affecting the business, increasing the number of new strategic ideas. The work also involved evaluating the effectiveness of this protocol one year after the intervention. Managers who were not able to generate alternative strategic ideas to overcome the challenges identified with the SD model found it difficult to manage the uncertainties arising in the environment compared with the managers who demonstrated learning from the modelling process and by using the model.
Cavana et al. [31] provide an example of the use of ST/SD in the Power Strategy School. They suggest that power dynamics are key for the formulation and implementation of policies originated from SD models. Their article synthesizes the experience and knowledge of experts in SD. They created a “Power and Influence” archetype to show the dynamics of public support over a campaign, which are driven by the indifference of the public to give their support. The archetype can be extended to organizational situations where power is a critical factor in the creation of strategies and the driving of strategic change.
Espinosa et al. [32] describe an action research case study where a team of consultants supported the process of strategy implementation in a Latin American multinational corporation using an adapted version of VSM. The corporation was a large construction company based in Colombia that embarked on a strategy to expand operations to the Latin American market. The consulting team developed a structured survey and semi-structured interviews to conduct an in-depth VSM diagnosis to facilitate the international expansion. After discussions with the executive team, they agreed on a proposal for restructuring the organization in terms of new structures, roles, processes, and teams required to implement the strategy.
Haftor [33] presents a case study using IP to support a comprehensive development of a medical department of a Nordic subsidiary within a pharmaceutical company. The case study involved action research applying IP. The author found a positive impact from most tasks. The overall impression was the execution of the IP process generated increased quality and productivity of the operational execution, but the method had issues in terms of leadership and a limited customer orientation for the new operations.
Bhattacharjya and Venable [34] explain the use of SSM to support strategic information systems planning (SISP) in a non-profit organization. They found that SSM could be adapted to address the culture and situation of a non-profit organization. The project was considered after an initial consultation with a software vendor, and it had the support of the CEO who felt that the staff’s perception of information system issues might be different from his own. The perceptions needed to be brought out during the SISP. The problem situation was investigated using interviews with management team members and other key staff. The consultants constructed the problem situation using common SSM/ST diagrams augmented with other traditional strategic planning analyses, e.g., SWOT, critical success factors, Porter’s Five Forces, etc. The outcome was a three-year strategic information system plan for the organization with some information systems identified for development or procurement, e.g., activity reporting system, web-based retail system, a system for performing detailed analysis of fundraising campaigns, etc.
Chowdhury [35] presents two consultancy case studies integrating three ST methods, CSH, SSM, and VSM, under the concept of Holistic Flexibility. Holistic flexibility is a conceptual lens for a more egalitarian and democratic stance for ST through methodological flexibility. The case studies articulate the benefits and limitations of methodological flexibility, where CSH was used to address issues of boundary definition.
Ufua et al. [36] developed a project with a food production company in the Niger Delta Region of Nigeria using SI together with community OR perspectives and lean management approaches. The objectives were waste minimization and value development considering the ‘usual’ stakeholders of a company and its local community. In the project, they were able to systemic co-create innovations between the company and its community rather than only considering the traditional view of reducing costs and ensuring regulatory compliance for lean management.
Jackson [4] discusses a very interesting case study using CST. The case study involved facilitating the redesign of the operating procedures of an executive committee of a voluntary service institution. The work involved a ‘creativity phase’ using cognitive mapping and a ‘choice phase’ where SSM was the dominant method supported by VSM. During the project, there was a constant critical reflection of the benefits and issues for each ST method.
Finally, there are six books that are worth mentioning in this subsection, arranged by time of publication. Firstly, Rosenhead and Mingers [3] covers comprehensively a number of Soft OR, or PSM, methods clearly illustrated with a number of case studies, and strongly related to strategic problems. Secondly, Herrscher’s [37] book on systemic planning presents a set of chapters discussing the positioning of the book with respect to ST, followed by the biggest issues dealt in planning before introducing a set of tools mixing IP, SSM, and strategic management. The book finishes with a systemic model for planning illustrated with five case studies. Thirdly, Ackermann and Eden’s [38] book addresses the challenge of how to build robust strategies that want to be implemented. It works on the premise that the process of strategy making is both analytical and social, obtained through strategic conversations, also known as ‘strategy forum’. They advocate that strategy is originated as part of a negotiation process where different perspectives are surfaced and respected and subject to negotiation to combine them into an accepted strategy. Fourthly, Kunc [39] provides an edited collection of mostly strategic applications of SD used as hard (quantitative) and soft (qualitative) ST (model). The multiple cases show the approaches and outcomes obtained from using ST to facilitate the generation of strategies, develop scenarios, and facilitate policy making. As a further example of SD and the Design and/or Planning Strategy Schools is the book from Warren [40] where he uses SD in an interactive method to design a system of resources for different types of businesses.
Finally, Jackson [4] offers a comprehensive tour to ST with chapters explaining the theory underpinning ST, followed by applications of ST and different case studies exemplifying the use of ST mostly in strategic issues.

Table 2.
ST analysis of the Strategy Schools and a potential matching of ST methods with each of them (own elaboration).
Table 2.
ST analysis of the Strategy Schools and a potential matching of ST methods with each of them (own elaboration).
| Concept | Design | Planning | Positioning | Entrepreneurial | Cognitive | Learning | Power | Cultural | Environmental |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Type of system | Mechanical | Mechanical | Mechanical | Social | Mechanical/Organismic | Organismic/Social | Social | Social | Mechanical |
| Complexity | Simple | Complicated/Complex | Simple | Simple | Complicated/Complex | Complicated/Complex | Complicated | Complicated | Simple/Complicated |
| Unitary/Pluralist/Coercive | Unitary | Unitary/Pluralist (if participative) | Unitary | Unitary | Unitary/Pluralist | Unitary/Pluralist | Coercive | Pluralist/Coercive | Unitary |
| Functionalist/Structuralist/Interpretative | Functionalist/Structuralist | Functionalist | Structuralist | Structuralist | Structuralist/Interpretative | Structuralist/Interpretative | Interpretative | Interpretative | Structuralist |
| ST Methods | SE/SA/OR/VSM/SD/VM/STS/SCA | SE/SA/SD/VSM/IP/VM/RA/OR/SCA | SE/SA/SD/RA/OR | SD/SSM/SODA/SCA | SD/SODA/SSM/SAST/CSH | SD/SODA/SSM/SAST/CSH/TS | CSH/CST/SI/TS/STS/SD | CSH/CST/SI/TS/STS/SD | SE/SA/OR/VSM/SD/VM/STS/SCA/CST |
| ST examples and resources | [29,32,37,39,40] | [3,29,33,37,39,40] | [3,29,37,39] | [2,3,38] | [2,38] | [3,35,39] | [3,4,31,35,38,39] | [4,34,38,39] | [27,36] |
5. Conclusions, Limitations, and Ideas for Further Research
Ackoff [41] suggests that few organizations adopt ST because organizations are not conducive to learning and there is a lack of knowledge or understanding of ST in organizations. Another reason can be use of incorrect ST tools given the context of its use in SM processes, or the limited opportunities for using ST given there aren’t many organizations ready for its use. Therefore, it is necessary to show what, how, and when ST tools can be used to address strategic issues, which is presented in Table 2.
Strategic management has managed to become very successful in business for a number of reasons. Firstly, the extensive set of tools and frameworks that are widely taught in all managerial courses. Secondly, the tools and frameworks are taught through case studies that facilitate its use in a real context. Thirdly, the tools and frameworks are simple or well designed to support a simple use in a systematic way. Therefore, they provide clear vantages for its use and adoption, but they are not systemic even though they are addressing systemic issues.
Strategic management have been benefitting, as a brief revision of the field suggests, from the contribution that systems thinking can make, moving from analysis or intuition to synthesis and systemic mental models, but it is highly fragmented in terms of ST tools and SM issues. Therefore, it is necessary to have frameworks that help to select the right set of methods appropriate for the content and process of the strategy. The intention of this article has been to improve the understanding of the fit of ST with SM (see Table 2). Critically, the mapping of ST tools with respect to the conceptualization of the type of systems employed by decision makers and the involvement of stakeholders in the strategy development process can provide a quick guide to match ST tools with SM issues. Another important contribution of the paper is to showcase the diversity of ST tools and methods, which have different strengths and weaknesses according to the SM issues. However, it is not a one-to-one match as explained previously, and, certainly, more than one ST method can support more than one SM practice, as shown in Table 2.
This paper has several limitations but the most important is this is not a systematic review of the literature to account for existing research and uncover patterns of association between strategic management with systems thinking, especially considering the two alternatives without examples mentioned in Section 4. Definitively, future research can perform a systematic literature review and map the existing research with respect to the dimensions indicated in Table 1 and Table 2, given the extensive activity in these fields. The use of another framework, such as the Johari window [42], can be useful to categorize the relationship/synergies between ST and SM. Another important avenue for future research is the approach to document the synergies, which are generated by the different alternatives of interaction, between both fields through research. Gary et al. [43] present a variety of approaches that have been used and can be used from the system dynamics perspective. However, a review of the applications mentioned in Section 4 indicates a preference in systems thinking for specific applications or action research, which are not widely adopted among strategy scholars or journals. Future research may be needed to address this important gap and provide guidelines to facilitate the exchanges between fields. Finally, the intersection of complexity theory, ST, and SM can be a fruitful area to uncover other aspects missed in this review.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Data Availability Statement
The original contributions presented in the study are included in the article, further inquiries can be directed to the corresponding author.
Conflicts of Interest
The author declares no conflict of interest.
References
- Kunc, M.; O’brien, F.A. The role of business analytics in supporting strategy processes: Opportunities and limitations. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2019, 70, 974–985. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, J.P.; Kunc, M.; O’Brien, F. Supporting strategy using system dynamics. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2017, 260, 1081–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosenhead, J.; Mingers, J. (Eds.) Rational Analysis for a Problematic World Revisited, 2nd ed.; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M. Critical Systems Thinking and the Management of Complexity; Wiley: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Gregory, A. A systems approach to strategic management. In Proceedings of the 51st Annual Meeting of the ISSS-2007, Tokyo, Japan, 5–10 August 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Pourahmadi, B.; Kalkowska, J. Characterizing the Relationship between Growth and Development in the Context of Strategic Management via Systems Thinking: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2022, 14, 5561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grewatsch, S.; Kennedy, S.; Bansal, P. Tackling wicked problems in strategic management with systems thinking. Strat. Organ. 2023, 21, 721–732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackoff, R.L. Systems thinking and thinking systems. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 1994, 10, 175–188. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.C. Fifty years of systems thinking for management. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 2009, 60, S24–S32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammond, D. Exploring the genealogy of systems thinking. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2002, 19, 429–439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.C. How We Understand “Complexity” Makes a Difference: Lessons from Critical Systems Thinking and the COVID-19 Pandemic in the UK. Systems 2020, 8, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, M.C.; Keys, P. Towards a system of systems methodologies. J. Oper. Res. Soc. 1984, 35, 473–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snowden, D.J.; Boone, M.E. A leader’s framework for decision making. Harv. Bus. Rev. 2007, 85, 68. [Google Scholar]
- Midgley, G. Systems Thinking, Volumes I–IV; Sage Publications: London, UK, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Nielsen, C.B.; Larsen, P.G.; Fitzgerald, J.; Woodcock, J.; Peleska, J. Systems of systems engineering: Basic concepts, model-based techniques, and research directions. ACM Comput. Surv. (CSUR) 2015, 48, 1–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morecroft, J.D. Strategic Modelling and Business Dynamics: A Feedback Systems Approach; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Kunc, M. System dynamics: A soft and hard approach to modelling. In 2017 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2017; pp. 597–606. [Google Scholar]
- Beer, S. Brain of the Firm; Allen Lane: London, UK, 1972. [Google Scholar]
- Friend, J. The Strategic Choice Approach—Chapter 6. In Rational Analysis for a Problematic World Revisited, 2nd ed.; Rosenhead, J., Mingers, J., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Eden, C.; Ackermann, F. SODA—The Principles—Chapter 2. In Rational Analysis for a Problematic World Revisited, 2nd ed.; Rosenhead, J., Mingers, J., Eds.; John Wiley and Sons Ltd.: Chichester, UK, 2001. [Google Scholar]
- Ackoff, R.L. A Brief Guide to Interactive Planning and Idealized Design. 2001. Available online: https://ackoffcenter.blogs.com/ackoff_center_weblog/2003/10/a_brief_guide_t.html (accessed on 19 March 2006).
- Checkland, P.; Scholes, J. Soft Systems Methodology in Action; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 1990. [Google Scholar]
- Midgley, G. Systemic Intervention: Philosophy, Methodology, and Practice; Kluwer/Plenum: New York, NY, USA, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Mingers, J. Rational Analysis for a Problematic World Revisited, 2nd methodologies. Omega 1997, 25, 489–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ulrich, W.; Reynolds, M. Critical systems heuristics. In Systems Approaches to Managing Change: A Practical Guide; Reynolds, M., Holwell, S., Eds.; Springer: London, UK, 2010; pp. 243–292. [Google Scholar]
- Mintzberg, H.; Ahlstrand, B.; Lampel, J.B. Strategy Safari, 2nd ed.; FT Publishing: London, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Kunc, M. Strategic Analytics: Integrating Management Science and Strategy; John Wiley & Sons: Hoboken, NJ, USA, 2018. [Google Scholar]
- Brown, S.L.; Eisenhardt, K.M. Competing on the Edge: Strategy as Structured Chaos; Harvard Business Press: Brighton, MA, USA, 1998. [Google Scholar]
- Andrade, H.S.; Loureiro, G. A Comparative Analysis of Strategic Planning Based on a Systems Engineering Approach. Bus. Ethic- Leadersh. 2020, 4, 86–95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kunc, M. System dynamics: A behavioral modeling method. In 2016 Winter Simulation Conference (WSC); IEEE: New York, NY, USA, 2016; pp. 53–64. [Google Scholar]
- Cavana, R.Y.; Forgie, V.E.; van den Belt, M.; Cody, J.R.; Romera, A.J.; Wang, K.; Browne, C.A. A “Power and Influence” political archetype: The dynamics of public support. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2019, 35, 70–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espinosa, A.; Reficco, E.; Martínez, A.; Guzmán, D. A methodology for sup- porting strategy implementation based on the VSM: A case study in a Latin- American multi-national. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2015, 240, 202–212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haftor, D.M. An Evaluation of R.L. Ackoff’s Interactive Planning: A Case-based Approach. Syst. Pract. Action Res. 2011, 24, 355–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhattacharjya, J.; Venable, J. Adapting soft systems methodology for strategic information systems planning: An action research study in a non-profit organisation in Australia. In Proceedings of the 17th Australasian Conference on Information Systems 2006 Proceedings, Adelaide, Australia, 6–8 December 2006; p. 8. [Google Scholar]
- Chowdhury, R. Methodological Flexibility in Systems Thinking: Musings from the Standpoint of a Systems Consultant. Syst. Pract. Action Res. 2023, 36, 59–86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ufua, D.E.; Papadopoulos, T.; Midgley, G. Systemic Lean Intervention: Enhancing Lean with Community Operational Research. Eur. J. Oper. Res. 2018, 268, 1134–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrscher, E. Planeamiento Sistémico: Un Enfoque Estratégico en la Turbulencia; Ediciones Granica: Buenos Aires, Argentina, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ackermann, F.; Eden, C. Making Strategy: Mapping Out Strategic Success; Sage: Newcastle upon Tyne, UK, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Kunc, M. (Ed.) System Dynamics: Soft and Hard Operational Research; Springer: Berlin/Heidelberg, Germany, 2017. [Google Scholar]
- Warren, K. Strategic Management Dynamics; John Wiley & Sons: Chichester, UK, 2008. [Google Scholar]
- Ackoff, R.L. Why few organizations adopt systems thinking. Syst. Res. Behav. Sci. 2006, 23, 705–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luft, J.; Ingham, H. The johari window. Hum. Relat. Train. News 1961, 5, 6–7. [Google Scholar]
- Gary, M.S.; Kunc, M.; Morecroft, J.D.W.; Rockart, S.F. System dynamics and strategy. Syst. Dyn. Rev. 2008, 24, 407–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2024 by the author. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).