Toad Venom Antiproliferative Activities on Metastatic Melanoma: Bio-Guided Fractionation and Screening of the Compounds of Two Different Venoms
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Extraction of Toad Venom
2.2. Preparation of Standard Solutions
2.3. UHPLC Instrumentation and Analysis
2.4. Cell Lines and Culture
2.5. Effectors
2.6. Viability Assay
2.7. qPCR Analysis
2.8. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
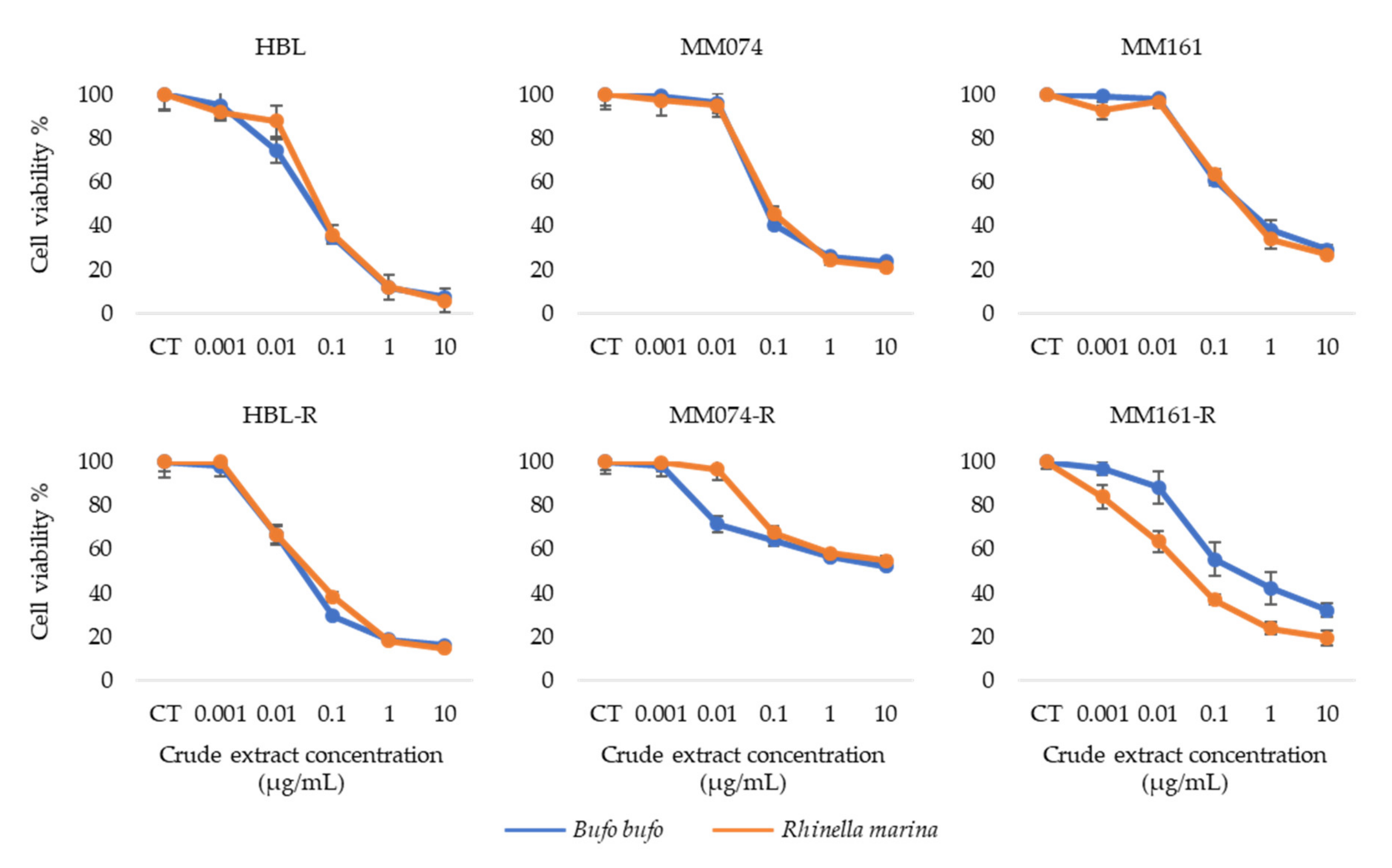
3.1. Antiproliferative Activity of Crude Extracts
3.2. UHPLC Analysis of Rhinella Marina Crude Extract Fractions
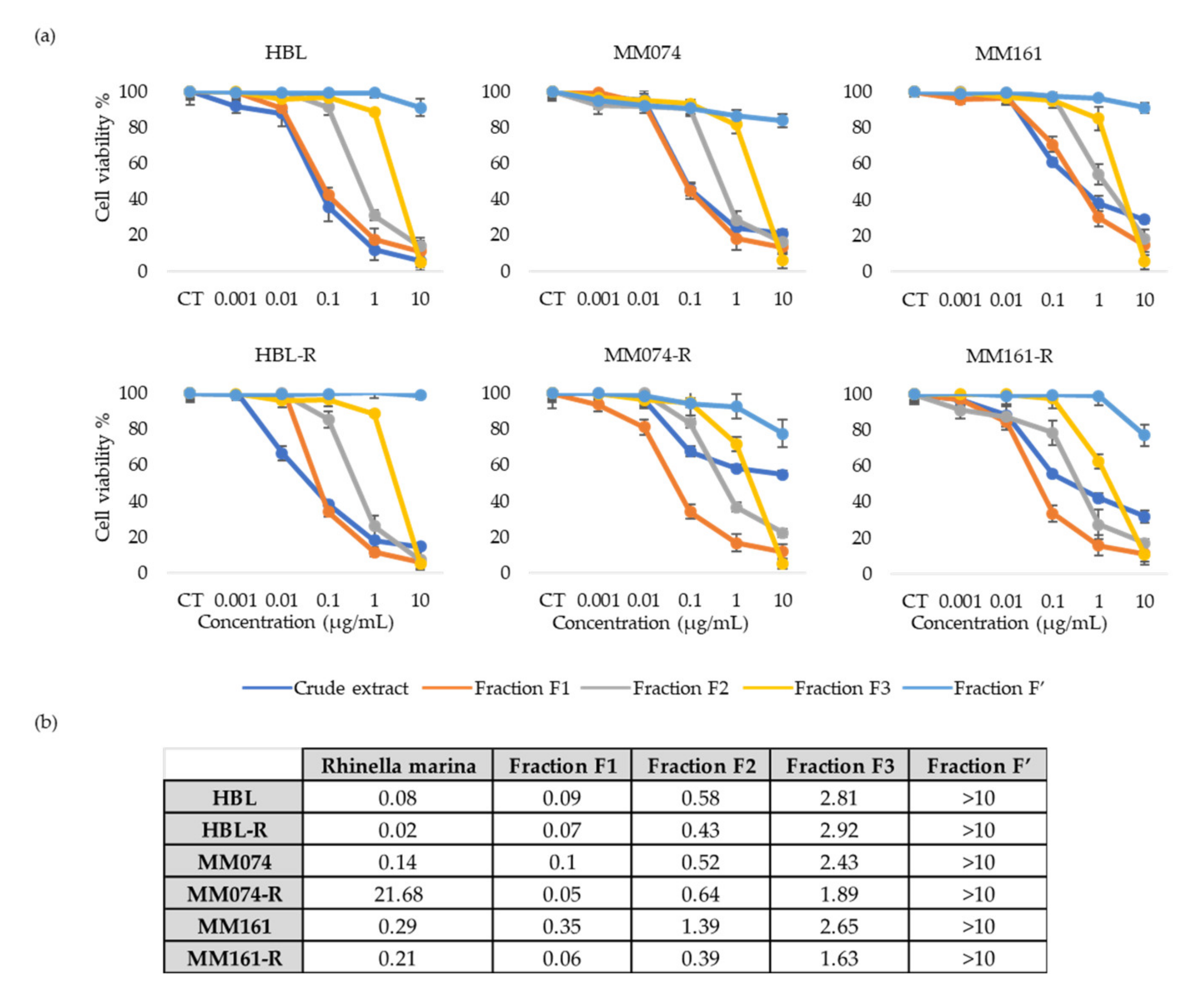
3.3. Antiproliferative Activity of Rhinella Marina Venom Fractions
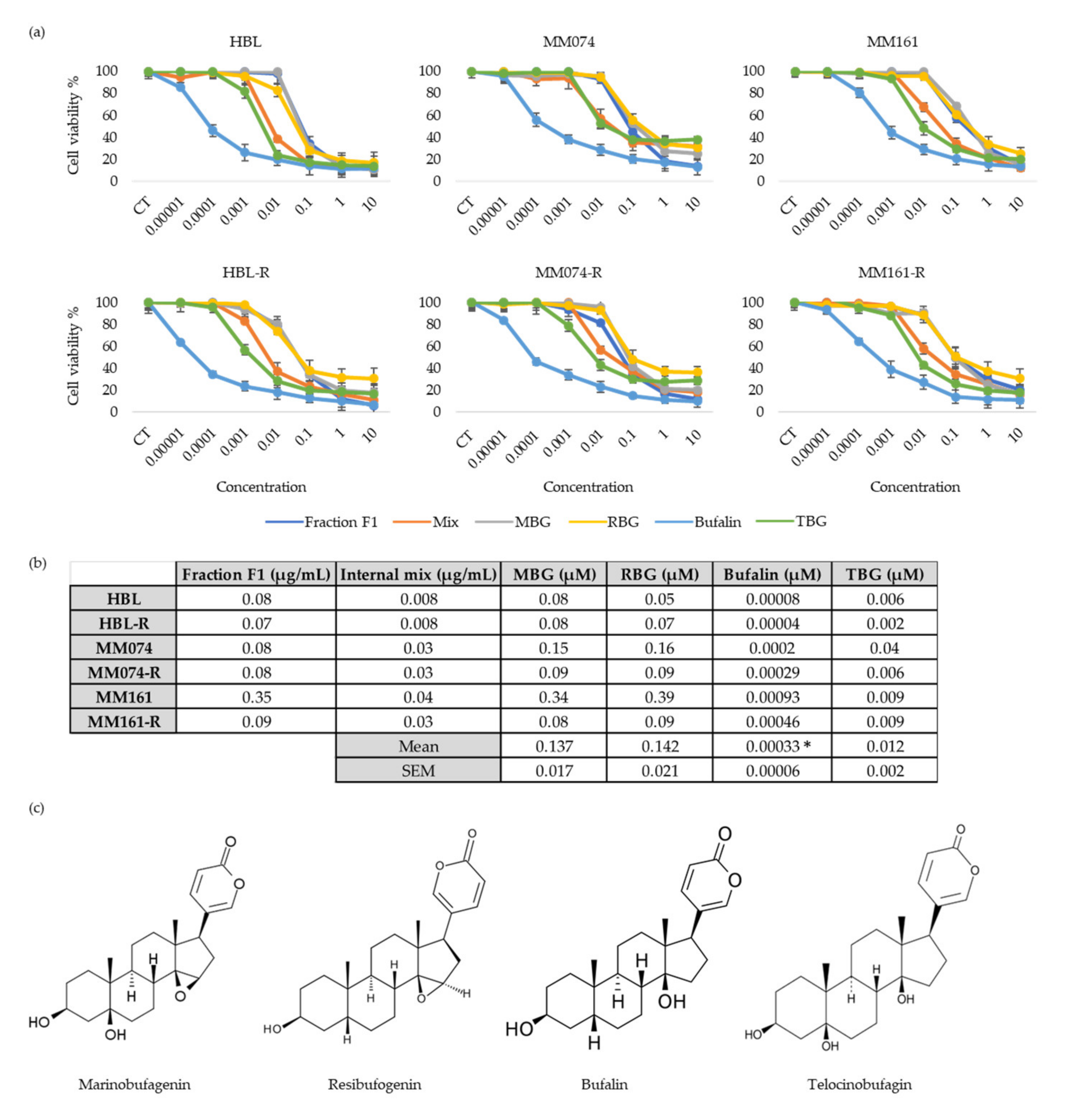
3.4. Antiproliferative Activity of “Fraction F1” Compounds
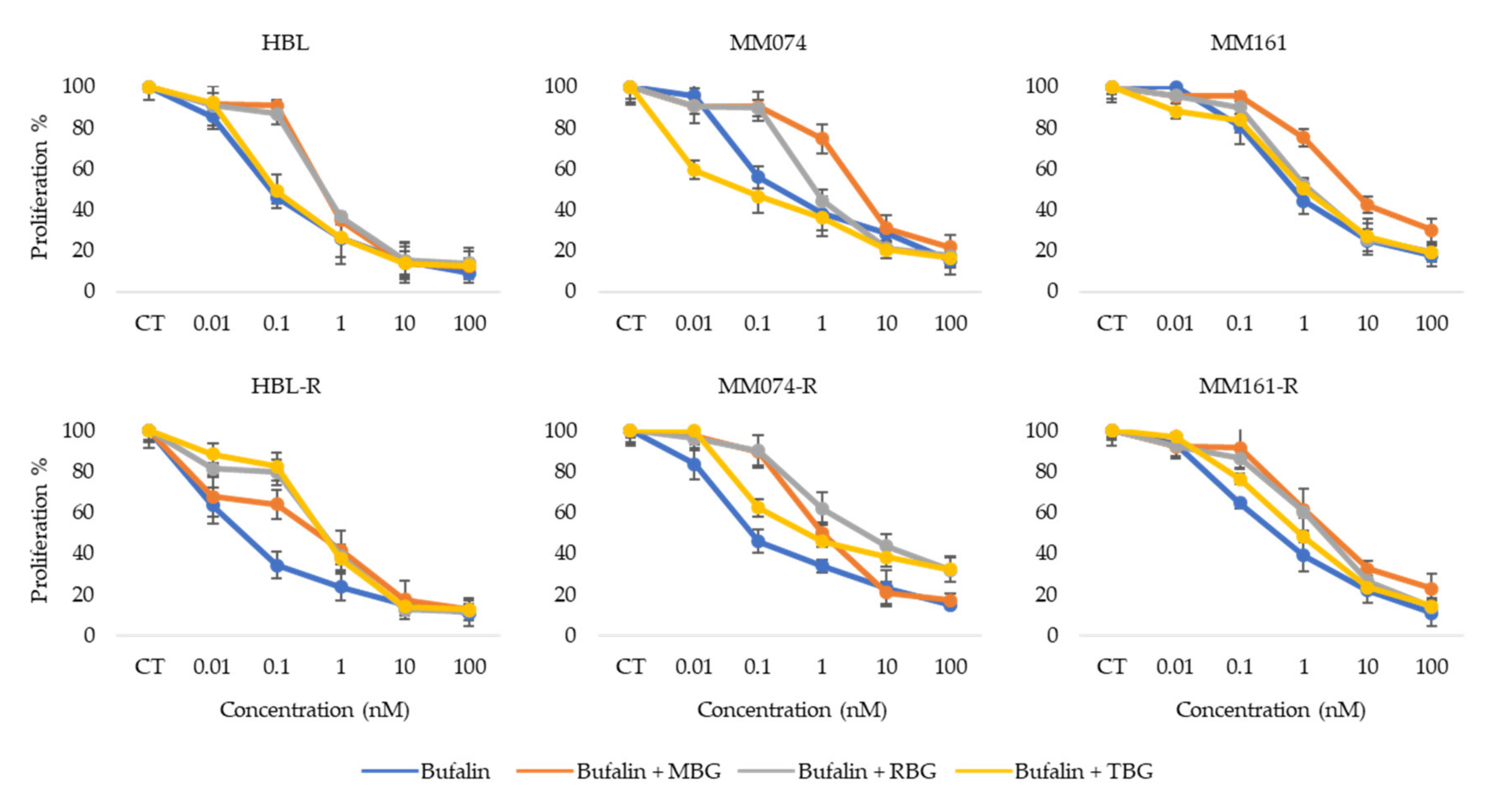
3.5. Antiproliferative Activity of Bufalin Combined with other Bufadienolides
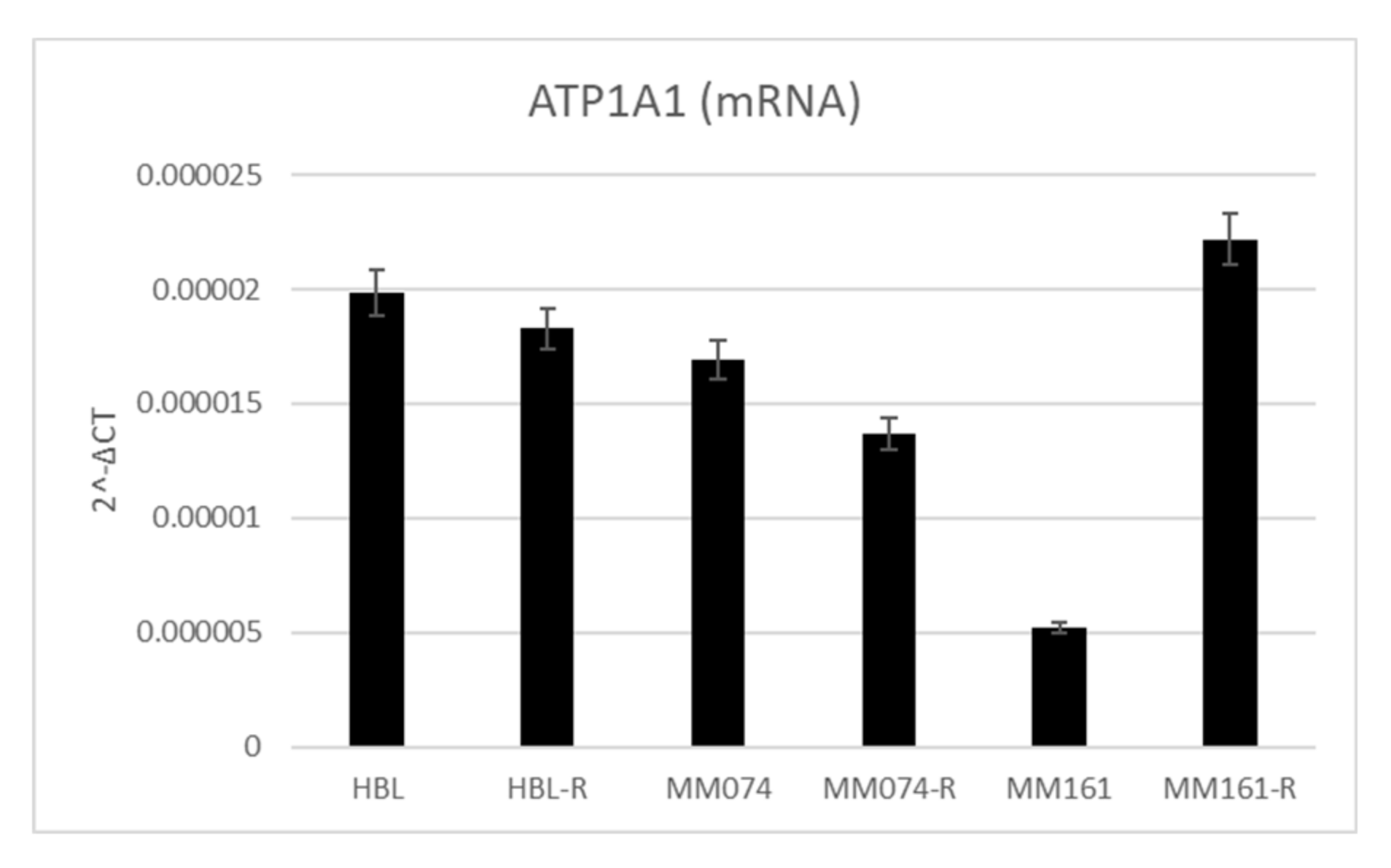
3.6. Na+/K+-ATPase Pump Expression in Sensitive and Resistant Melanoma Cell Lines
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mort, R.L.; Jackson, I.J.; Patton, E.E. The melanocyte lineage in development and disease. Dev. Camb. Engl. 2015, 142, 1387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Millet, A.; Martin, A.R.; Ronco, C.; Rocchi, S.; Benhida, R. Metastatic melanoma: Insights into the evolution of the treatments and future challenges. Med. Res. Rev. 2017, 37, 98–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lo, J.A.; Fisher, D.E. The melanoma revolution: From UV carcinogenesis to a new era in therapeutics. Science 2014, 346, 945–949. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siegel, R.L.; Miller, K.D.; Jemal, A. Cancer statistics, 2020. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2020, 70, 7–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davey, R.J.; van der Westhuizen, A.; Bowden, N.A. Metastatic melanoma treatment: Combining old and new therapies. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2016, 98, 242–253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- National Cancer Institute (US). PDQ adult treatment editorial board melanoma treatment (PDQ®). Patient version. In PDQ Cancer Information Summaries; National Cancer Institute (US): Bethesda, MD, USA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Hayward, N.K.; Wilmott, J.S.; Waddell, N.; Johansson, P.A.; Field, M.A.; Nones, K.; Patch, A.-M.; Kakavand, H.; Alexandrov, L.B.; Burke, H.; et al. Whole-genome landscapes of major melanoma subtypes. Nature 2017, 545, 175–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lerner, B.A.; Stewart, L.A.; Horowitz, D.P.; Carvajal, R.D. Mucosal melanoma: New insights and therapeutic options for a unique and aggressive disease. Oncol. Williston Park N 2017, 31, e23–e32. [Google Scholar]
- Amaral, T.; Sinnberg, T.; Meier, F.; Krepler, C.; Levesque, M.; Niessner, H.; Garbe, C. The mitogen-activated protein kinase pathway in melanoma part I—Activation and primary resistance mechanisms to BRAF inhibition. Eur. J. Cancer 2017, 73, 85–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gopalakrishnakone, P.; Cruz, L.J.; Luo, S. Toxinology. In Toxins and Drug Discovery; Springer: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2017; ISBN 978-94-007-6451-4. [Google Scholar]
- Krenn, L.; Kopp, B. Bufadienolides from animal and plant sources. Phytochemistry 1998, 48, 1–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa-Neto, E.M. Animal-based medicines: Biological prospection and the sustainable use of zootherapeutic resources. An. Acad. Bras. Cienc. 2005, 77, 33–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, W.; Luo, H.; Zhang, Y.; Shan, L.; Li, H.; Yang, M.; Liu, R.; Zhang, W. Simultaneous determination of five main active bufadienolides of Chan Su in rat plasma by liquid chromatography tandem mass spectrometry. J. Chromatogr. B Analyt. Technol. Biomed. Life Sci. 2007, 859, 157–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Sousa, L.Q.; Machado, K.; Oliveira, S.F.D.C.; Araújo, L.D.S.; Monção-Filho, E.D.S.; Cavalcante, A.; Vieira-Júnior, G.M.; Ferreira, P.M.P. Bufadienolides from amphibians: A promising source of anticancer prototypes for radical innovation, apoptosis triggering and Na+/K+-ATPase inhibition. Toxicon 2017, 127, 63–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perera Córdova, W.H.; Leitão, S.G.; Cunha-Filho, G.; Bosch, R.A.; Alonso, I.P.; Pereda-Miranda, R.; Gervou, R.; Touza, N.A.; Quintas, L.E.M.; Noël, F. Bufadienolides from parotoid gland secretions of Cuban toad Peltophryne fustiger (Bufonidae): Inhibition of human kidney Na+/K+-ATPase activity. Toxicon 2016, 110, 27–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.; Lee, Y.; Choi, Y.J.; Han, K.-S.; Chung, H.W. Cyto-/genotoxic effects of the ethanol extract of Chan Su, a traditional Chinese medicine, in human cancer cell lines. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2014, 152, 372–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clarke, B.T. The natural history of amphibian skin secretions, their normal functioning and potential medical applications. Biol. Rev. Camb. Philos. Soc. 1997, 72, 365–379. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Daly, J.W.; Myers, C.W.; Whittaker, N. Further classification of skin alkaloids from neotropical poison frogs (Dendrobatidae), with a general survey of toxic/noxious substances in the amphibia. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 1987, 25, 1023–1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Utkin, Y.N. Animal venom studies: Current benefits and future developments. World J. Biol. Chem. 2015, 6, 28–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Q.; Zhou, X.; Zhang, M.; Bi, L.; Miao, S.; Cao, W.; Xie, Y.; Sun, J.; Tang, H.; Li, Y.; et al. Angel of human health: Current research updates in toad medicine. Am. J. Transl. Res. 2015, 7, 1–14. [Google Scholar]
- Gao, F.; Wang, X.; Li, Z.; Zhou, A.; Tiffany-Castiglioni, E.; Xie, L.; Qian, Y. Identification of anti-tumor components from toad venom. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 15–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Machado, K.; De Sousa, L.Q.; Lima, D.J.B.; Soares, B.M.; Cavalcanti, B.C.; Maranhão, S.; Noronha, J.D.C.D.; Rodrigues, D.D.J.; Militão, G.C.G.; Chaves, M.H.; et al. Marinobufagin, a molecule from poisonous frogs, causes biochemical, morphological and cell cycle changes in human neoplasms and vegetal cells. Toxicol. Lett. 2018, 285, 121–131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez, C.; Rollins-Smith, L.; Ibáñez, R.; Durant-Archibold, A.A.; Gutiérrez, M. Toxins and pharmacologically active compounds from species of the family Bufonidae (Amphibia, Anura). J. Ethnopharmacol. 2017, 198, 235–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathieu, V.; Pirker, C.; Martin de Lassalle, E.; Vernier, M.; Mijatovic, T.; DeNeve, N.; Gaussin, J.-F.; Dehoux, M.; Lefranc, F.; Berger, W.; et al. The sodium pump α1 sub-unit: A disease progression–related target for metastatic melanoma treatment. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2009, 13, 3960–3972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, M.; Yang, G.; Lin, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhang, H.; Su, Y. Determination of endogenous bufalin in serum of patients with hepatocellular carcinoma based on HPLC-MS/MS. Front. Oncol. 2019, 9, 1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdelfatah, S.; Lu, X.; Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Efferth, T. Cytotoxicity and antimitotic activity of Rhinella schneideri and Rhinella marina venoms. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2019, 242, 112049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmeda-Hirschmann, G.; Quispe, C.; Arana, G.V.; Theoduloz, C.; Urra, F.A.; Cárdenas, C. Antiproliferative activity and chemical composition of the venom from the Amazonian toad Rhinella marina (Anura: Bufonidae). Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2016, 121, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia, I.J.P.; De Oliveira, G.C.; Valadares, J.M.D.M.; Banfi, F.F.; Andrade, S.N.; Freitas, T.R.; Filho, E.D.S.M.; Santos, H.D.L.; Júnior, G.M.V.; Chaves, M.H.; et al. New bufadienolides extracted from Rhinella marina inhibit Na, K-ATPase and induce apoptosis by activating caspases 3 and 9 in human breast and ovarian cancer cells. Steroids 2019, 152, 108490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lenaerts, C.; Wells, M.; Hambÿe, S.; Blankert, B. Marinobufagenin extraction from Rhinella marina toad glands: Alternative approaches for a systematized strategy. J. Sep. Sci. 2019, 42, 1384–1392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jing, J.; Ren, W.C.; Li, C.; Bose, U.; Parekh, H.S.; Wei, M.Q. Rapid identification of primary constituents in parotoid gland secretions of the Australian cane toad using HPLC/MS-Q-TOF. Biomed. Chromatogr. BMC 2013, 27, 685–687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, H.; Zehl, M.; Leitner, A.; Wu, X.; Wang, Z.; Kopp, B. Comparison of toad venoms from different Bufo species by HPLC and LC-DAD-MS/MS. J. Ethnopharmacol. 2010, 131, 368–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.M.P.; Lima, D.J.B.; Debiasi, B.W.; Soares, B.M.; Machado, K.D.C.; Noronha, J.D.C.; Rodrigues, D.D.J.; Sinhorin, A.P.; Pessoa, C.; Vieira, G.M. Antiproliferative activity of Rhinella marina and Rhaebo guttatus venom extracts from Southern Amazon. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2013, 72, 43–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Yu, Z.; Yang, Z.J.; Zhu, G.; Fong, W. Comprehensive chemical analysis of Venenum Bufonis by using liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization tandem mass spectrometry. J. Pharm. Biomed. Anal. 2011, 56, 210–220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Xue, X.; Zhang, X.; Liang, X. Systematic screening and characterization of novel bufadienolides from toad skin using ultra-performance liquid chromatography/electrospray ionization quadrupole time-of-flight mass spectrometry. Rapid Commun. Mass Spectrom. RCM 2010, 24, 667–678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heus, F.; Otvos, R.A.; Aspers, R.L.E.G.; van Elk, R.; Halff, J.I.; Ehlers, A.W.; Dutertre, S.; Lewis, R.J.; Wijmenga, S.; Smit, A.B.; et al. Miniaturized bioaffinity assessment coupled to mass spectrometry for guided purification of bioactives from toad and cone snail. Biology 2014, 3, 139–156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Medeiros, D.S.S.; Rego, T.B.; Santos, A.P.D.A.; Pontes, A.S.; Moreira-Dill, L.S.; Matos, N.B.; Zuliani, J.P.; Stábeli, R.G.; Teles, C.B.G.; Soares, A.M.; et al. Biochemical and biological profile of parotoid secretion of the Amazonian Rhinella marina (Anura: Bufonidae). BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mondal, A.; Gandhi, A.; Fimognari, C.; Atanasov, A.G.; Bishayee, A. Alkaloids for cancer prevention and therapy: Current progress and future perspectives. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2019, 858, 172472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slingerland, M.; Cerella, C.; Guchelaar, H.J.; Diederich, M.; Gelderblom, H. Cardiac glycosides in cancer therapy: From preclinical investigations towards clinical trials. Invest. New Drugs 2013, 31, 1087–1094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, Y.; Banuls, L.; Urban, E.; Gelbcke, M.; Dufrasne, F.; Kopp, B.; Kiss, R.; Zehl, M. Structure-activity relationship analysis of bufadienolide-induced in vitro growth inhibitory effects on mouse and human cancer cells. J. Nat. Prod. 2013, 76, 1078–1084. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Bi, Z. Bufalin inhibited the growth of human osteosarcoma MG-63 cells via down-regulation of Bcl-2/Bax and triggering of the mitochondrial pathway. Tumour Biol. J. Int. Soc. Oncodevelopmental. Biol. Med. 2014, 35, 4885–4890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mijatovic, T.; Van Quaquebeke, E.; Delest, B.; Debeir, O.; Darro, F.; Kiss, R. Cardiotonic steroids on the road to anti-cancer therapy. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2007, 1776, 32–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagrov, A.Y.; Shapiro, J.I.; Fedorova, O.V. Endogenous cardiotonic steroids: Physiology, pharmacology, and novel therapeutic targets. Pharmacol. Rev. 2009, 61, 9–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kennedy, D.J.; Shrestha, K.; Sheehey, B.; Li, X.S.; Guggilam, A.; Wu, Y.; Finucan, M.; Gabi, A.; Medert, C.M.; Westfall, K.; et al. Elevated plasma marinobufagenin, an endogenous cardiotonic steroid, is associated with right ventricular dysfunction and nitrative stress in heart failure. Circ. Heart Fail. 2015, 8, 1068–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lenaerts, C.; Bond, L.; Tuytten, R.; Blankert, B. Revealing of endogenous Marinobufagin by an ultra-specific and sensitive UHPLC-MS/MS assay in pregnant women. Talanta 2018, 187, 193–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rassler, B. The renin-angiotensin system in the development of salt-sensitive hypertension in animal models and humans. Pharmaceuticals 2010, 3, 940–960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botelho, A.F.M.; Pierezan, F.; Soto-Blanco, B.; Melo, M.M. A review of cardiac glycosides: Structure, toxicokinetics, clinical signs, diagnosis and antineoplastic potential. Toxicon Off. J. Int. Soc. Toxinol. 2019, 158, 63–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dmitrieva, R.I.; Bagrov, A.Y.; Lalli, E.; Sassone-Corsi, P.; Stocco, D.M.; Doris, P.A. Mammalian bufadienolide is synthesized from cholesterol in the adrenal cortex by a pathway that is independent of cholesterol side-chain cleavage. Hypertension 2000, 36, 442–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirahanchi, Y.; Aeddula, N.R. Physiology, sodium potassium pump (Na+ K+ Pump). In StatPearls; StatPearls Publishing: Treasure Island, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Xie, C.-M.; Lin, X.-T.; Wu, D.; Tan, Y.; Cheng, C.H.K.; Zhang, J. Cardiac glycoside bufalin blocks cancer cell growth by inhibition of Aurora A and Aurora B activation via PI3K-Akt pathway. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13783–13795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Horisberger, J.-D. Recent insights into the structure and mechanism of the sodium pump. Biol. Physiol. 2004, 19, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Puschett, J.B. Marinobufagenin predicts and resibufogenin prevents preeclampsia: A review of the evidence. Am. J. Perinatol. 2012, 29, 777–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hsiao, Y.-P.; Yu, C.-S.; Yu, C.-C.; Yang, J.-S.; Chiang, J.-H.; Lu, C.-C.; Huang, H.-Y.; Tang, N.-Y.; Yang, J.-H.; Huang, A.-C.; et al. Triggering apoptotic death of human malignant melanoma A375.S2 cells by bufalin: Involvement of caspase cascade-dependent and independent mitochondrial signaling pathways. ECAM 2012, 2012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yoshida, T.; Kuroiwa, Y. Stimulation of melanin synthesis of B16-F10 mouse melanoma cells by bufalin. Life Sci. 1992, 51, 17–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, X.; Ng, T.T.H.; Sham, K.W.Y.; Zhang, L.; Chan, M.T.V.; Wu, W.K.K.; Cheng, C.H.K. Bufalin, a traditional Chinese medicine compound, prevents tumor formation in two murine models of colorectal cancer. Cancer Prev. Res. Phila. 2019, 12, 653–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Tian, X.; Liu, X.; Gong, P. Bufalin inhibits human breast cancer tumorigenesis by inducing cell death through the ROS-mediated RIP1/RIP3/PARP-1 pathways. Carcinogenesis 2018, 39, 700–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lan, Y.-L.; Zou, Y.-J.; Lou, J.-C.; Xing, J.-S.; Wang, X.; Zou, S.; Ma, B.-B.; Ding, Y.; Zhang, B. The sodium pump α1 subunit regulates bufalin sensitivity of human glioblastoma cells through the p53 signaling pathway. Cell Biol. Toxicol. 2019, 35, 521–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, C.-S.; Wang, J.; Chen, J.; Kuo, K.T.; Tang, J.; Gao, H.; Chen, L.; Chen, Z.; Meng, Z. New therapeutic aspects of steroidal cardiac glycosides: The anticancer properties of Huachansu and its main active constituent Bufalin. Cancer Cell Int. 2019, 19, 92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, D.; Zhou, W.-Y.; Lin, X.-T.; Fang, L.; Xie, C.-M. Bufalin induces apoptosis via mitochondrial ROS-mediated caspase-3 activation in HCT-116 and SW620 human colon cancer cells. Drug Chem. Toxicol. 2019, 42, 444–450. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Luan, J.; Duan, H.; Zhang, F.; Yagasaki, K.; Zhang, G. Effects of bufalin on the proliferation of human lung cancer cells and its molecular mechanisms of action. Cytotechnology 2010, 62, 573–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
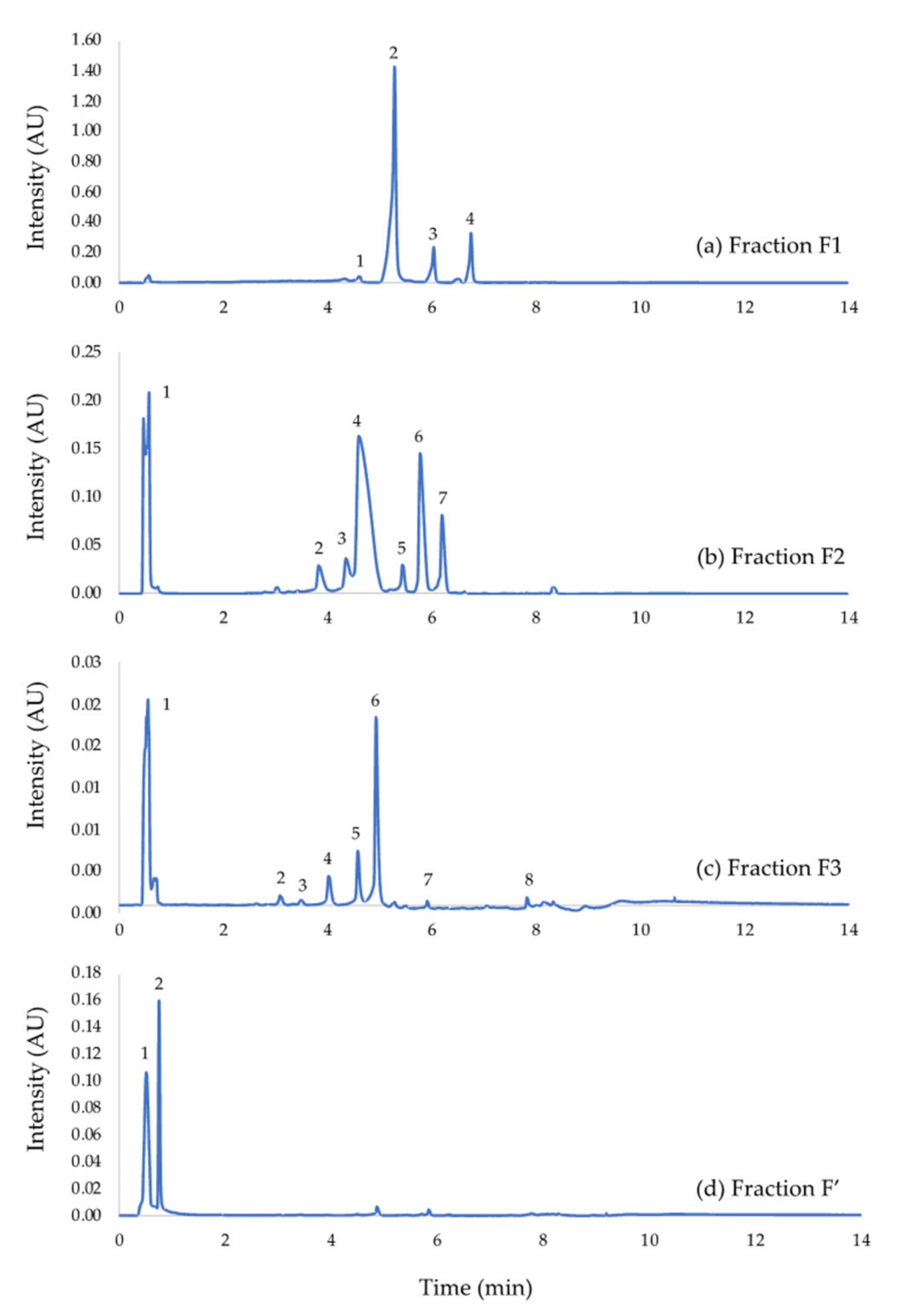
| Fraction | Compound Identification | Proportion (%) | Peak Number |
|---|---|---|---|
| Fraction F1 | Telocinobufagin | 2.48 | 1 |
| Marinobufagenin | 65.50 | 2 | |
| Bufalin | 8.88 | 3 | |
| Resibufogenin | 10.27 | 4 | |
| Fraction F2 | Suberoyl arginine | 20.05 | 1 |
| Marinobufagin−3-pimeloyl-arginine | 4.30 | 2 | |
| Telocinobufotoxin | 4.71 | 3 | |
| Marinobufotoxin | 41.06 | 4 | |
| Marinobufagin−3-adipate-arginine | 2.72 | 5 | |
| Bufalitoxin | 14.08 | 6 | |
| Resibufotoxin | 6.95 | 7 | |
| Fraction F3 | Suberoyl arginine | 47.83 | 1 |
| Marinobufagin−3-adipate-arginine | 1.47 | 2 | |
| Telocinobufagin−3-pimeloyl-arginine | 0.84 | 3 | |
| Marinobufagin−3-pimeloyl-arginine | 5.43 | 4 | |
| Telocinobufotoxin | 7.31 | 5 | |
| Marinobufotoxin | 28.93 | 6 | |
| Bufalitoxin | 0.67 | 7 | |
| Fraction F’ | Dehydrobufotenin | 51.00 | 1 |
| Suberoyl arginine | 30.31 | 2 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Soumoy, L.; Wells, M.; Najem, A.; Krayem, M.; Ghanem, G.; Hambye, S.; Saussez, S.; Blankert, B.; Journe, F. Toad Venom Antiproliferative Activities on Metastatic Melanoma: Bio-Guided Fractionation and Screening of the Compounds of Two Different Venoms. Biology 2020, 9, 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9080218
Soumoy L, Wells M, Najem A, Krayem M, Ghanem G, Hambye S, Saussez S, Blankert B, Journe F. Toad Venom Antiproliferative Activities on Metastatic Melanoma: Bio-Guided Fractionation and Screening of the Compounds of Two Different Venoms. Biology. 2020; 9(8):218. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9080218
Chicago/Turabian StyleSoumoy, Laura, Mathilde Wells, Ahmad Najem, Mohammad Krayem, Ghanem Ghanem, Stéphanie Hambye, Sven Saussez, Bertrand Blankert, and Fabrice Journe. 2020. "Toad Venom Antiproliferative Activities on Metastatic Melanoma: Bio-Guided Fractionation and Screening of the Compounds of Two Different Venoms" Biology 9, no. 8: 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9080218
APA StyleSoumoy, L., Wells, M., Najem, A., Krayem, M., Ghanem, G., Hambye, S., Saussez, S., Blankert, B., & Journe, F. (2020). Toad Venom Antiproliferative Activities on Metastatic Melanoma: Bio-Guided Fractionation and Screening of the Compounds of Two Different Venoms. Biology, 9(8), 218. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9080218







