The Utility of Genomic and Transcriptomic Data in the Construction of Proxy Protein Sequence Databases for Unsequenced Tree Nuts
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
3. Results
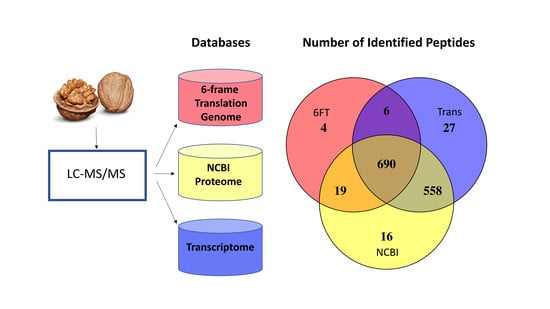
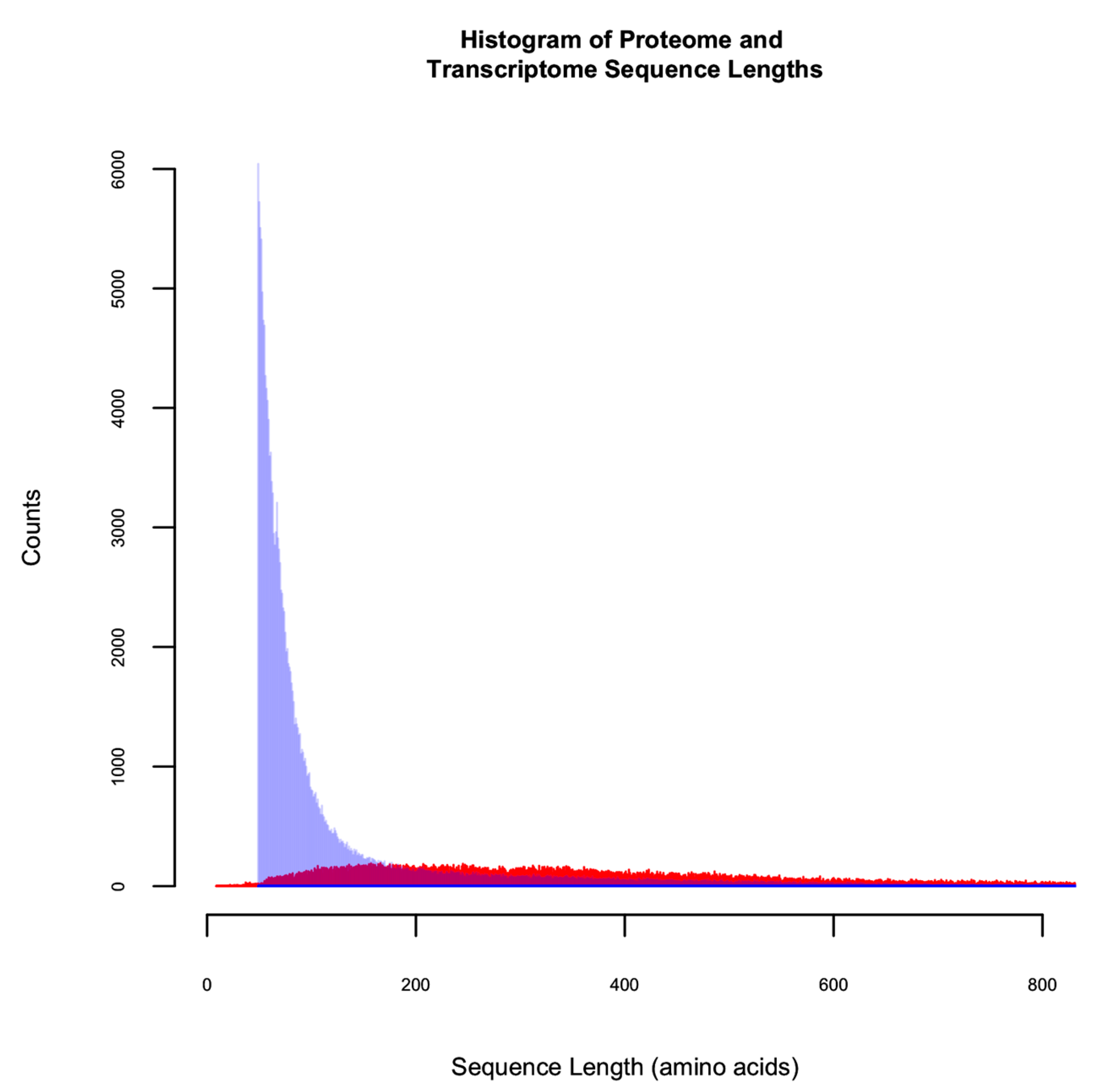
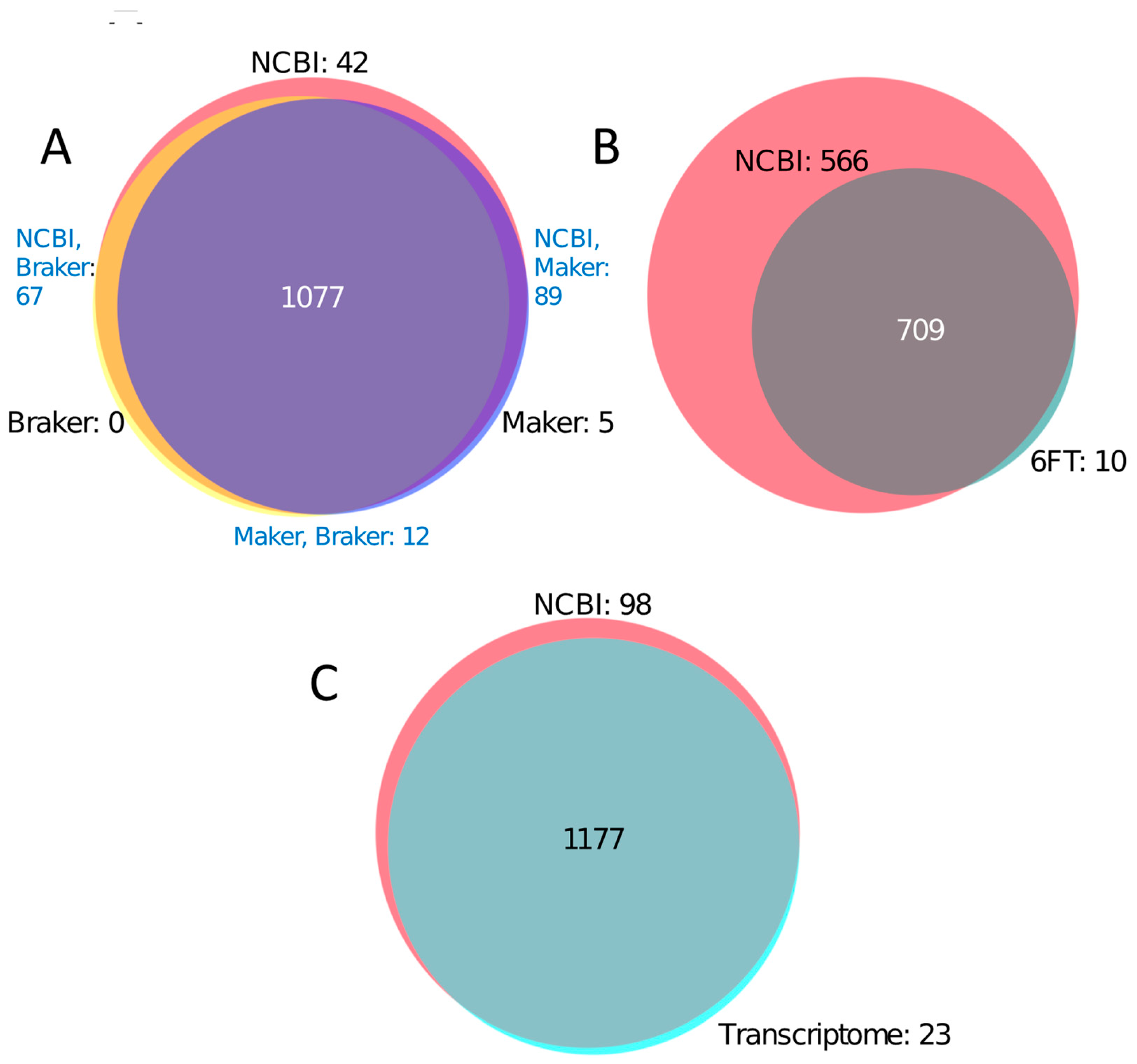
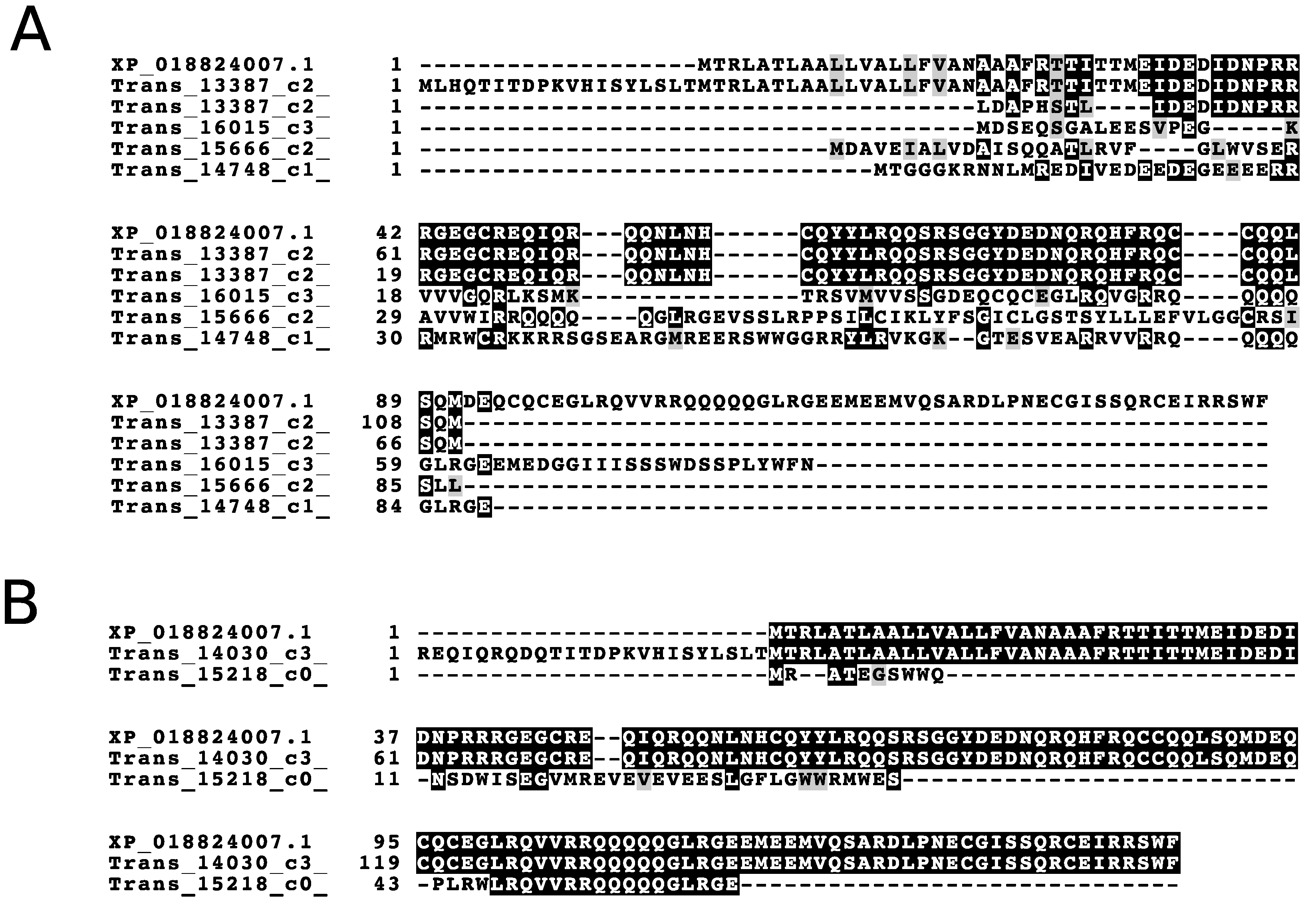
3.1. The Utility of Databases Built from a 6FT of the Genome, Three Proteomes, and a Six-Frame Translation of a Transcriptome Assembled Using Default Parameters
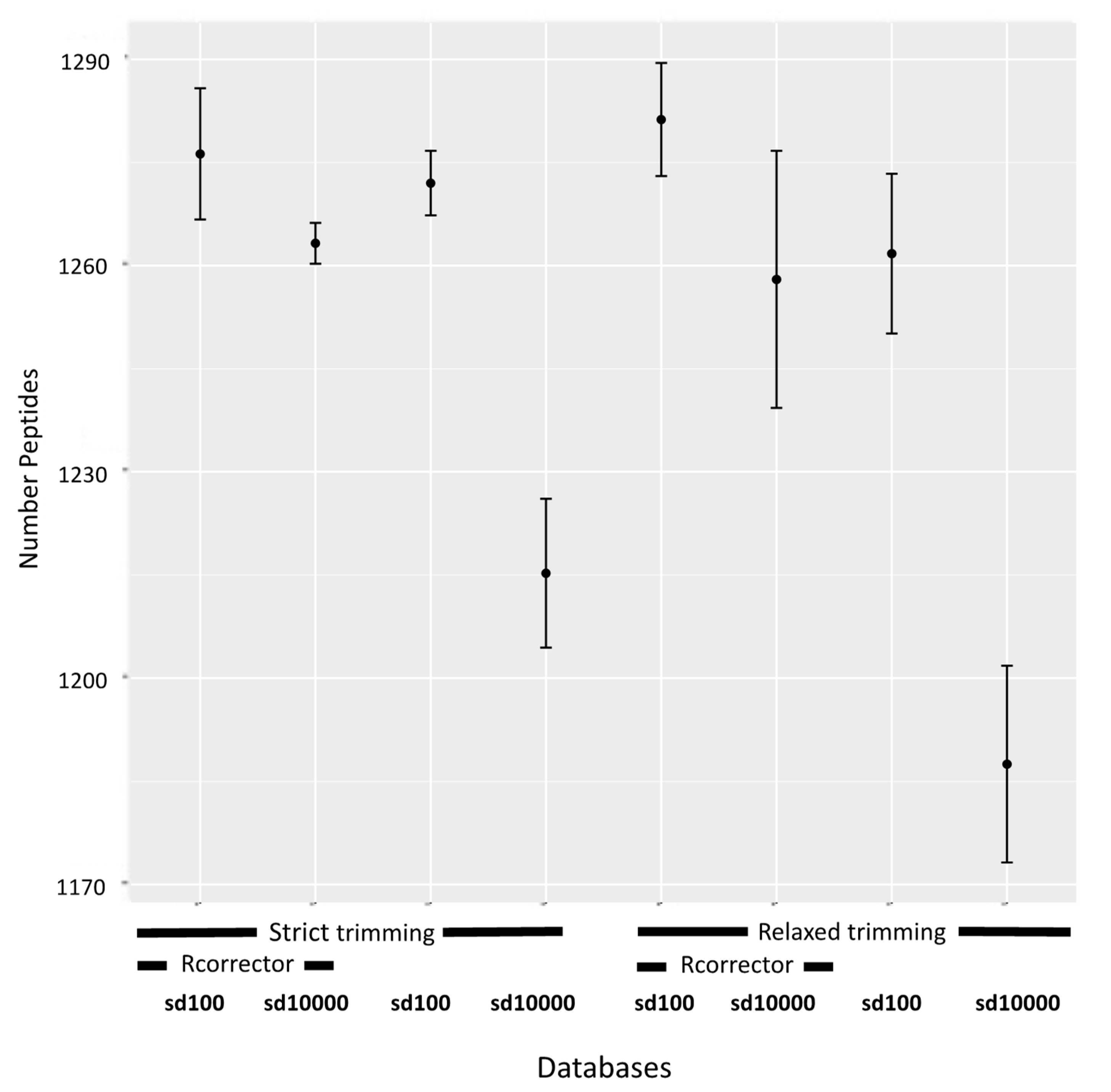
3.2. The Utility of Translated Transcriptomic Databases Assembled Using Varying Read Processing Parameters for Peptide Identifications
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- de Souza, R.G.M.; Machado Schincaglia, R.; Duarte Pimentel, G.; Mota, J.F. Nuts and Human Health Outcomes: A Systematic Review. Nutrients 2017, 9, 1311. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bock, S.A.; Munoz-Furlong, A.; Sampson, H.A. Fatalities Due to Anaphylactic Reactions to Foods. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2001, 107, 191–193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Further Fatalities Caused by Anaphylactic Reactions to Food, 2001–2006. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2007, 119, 1016–1018. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weinberger, T.; Sicherer, S. Current Perspectives on Tree Nut Allergy: A Review. J. Asthma Allergy 2018, 11, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poms, R.E.; Agazzi, M.E.; Bau, A.; Brohee, M.; Capelletti, C.; Norgaard, J.V.; Anklam, E. Inter-laboratory validation study of five commercial elisa test kits for the determination of peanut proteins in biscuits and dark chocolate. Food Addit. Contam. 2005, 22, 104–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Niemann, L.; Taylor, S.L.; Hefle, S.L. Detection of Walnut Residues in Foods Using an Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. J. Food Sci. 2009, 74, T51–T57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, K.; Sloan, A.; McCorrister, S.; Babiuk, S.; Bowden, T.R.; Wang, G.; Knox, J.D. Fit-for-Purpose Curated Database Application in Mass Spectrometry-Based Targeted Protein Identification and Validation. BMC Res. Notes 2014, 7, 444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Xiong, W.; McFarland, M.A.; Pirone, C.; Parker, C.H. Selection of Tree Nut Allergen Peptide Markers: A Need for Improved Protein Sequence Databases. J. AOAC Int. 2019, 102, 1263–1270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nesvizhskii, A.I. Proteogenomics: Concepts, Applications and Computational Strategies. Nat. Methods 2014, 11, 1114–1125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armengaud, J.; Trapp, J.; Pible, O.; Geffard, O.; Chaumot, A.; Hartmann, E.M. Non-Model Organisms, a Species Endangered by Proteogenomics. J. Proteom. 2014, 105, 5–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheynkman, G.M.; Shortreed, M.R.; Cesnik, A.J.; Smith, L.M. Proteogenomics: Integrating Next-Generation Sequencing and Mass Spectrometry to Characterize Human Proteomic Variation. Annu. Rev. Anal. Chem. 2016, 9, 521–545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, V.C.; Barker, G.; Heesom, K.J.; Fan, J.; Bessant, C.; David, A.M. De Novo Derivation of Proteomes from Transcriptomes for Transcript and Protein Identification. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 1207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Slebos, R.J.; Wang, D.; Halvey, P.J.; Tabb, D.L.; Liebler, D.C.; Zhang, B. Protein Identification Using Customized Protein Sequence Databases Derived from Rna-Seq Data. J. Proteome Res. 2012, 11, 1009–1017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Zhang, B. Integrating Genomic, Transcriptomic, and Interactome Data to Improve Peptide and Protein Identification in Shotgun Proteomics. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 2715–2723. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sheynkman, G.M.; Shortreed, M.R.; Frey, B.L.; Scalf, M.; Smith, L.M. Large-Scale Mass Spectrometric Detection of Variant Peptides Resulting from Nonsynonymous Nucleotide Differences. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 228–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woo, S.; Cha, S.W.; Merrihew, G.; He, Y.; Castellana, N.; Guest, C.; MacCoss, M.; Bafna, V. Proteogenomic Database Construction Driven from Large Scale Rna-Seq Data. J. Proteome Res. 2014, 13, 21–28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sheynkman, G.M.; Shortreed, M.R.; Frey, B.L.; Smith, L.M. Discovery and Mass Spectrometric Analysis of Novel Splice-Junction Peptides Using Rna-Seq. Mol. Cell. Proteom. 2013, 12, 2341–2353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z.; Thompson, D.A.; Amit, I.; Chen, Z.; Mauceli, E.; Hacohen, N.; Gnirke, A.; et al. Full-Length Transcriptome Assembly from Rna-Seq Data without a Reference Genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Honaas, L.A.; Eric, K.; Wafula, N.J.; Wickett, J.P.; Der, Y.Z.; Patrick, P.; Edger, N.S.; Altman, J.; Pires, C.; Leebens-Mack, J.H.; et al. Selecting Superior De Novo Transcriptome Assemblies: Lessons Learned by Leveraging the Best Plant Genome. PLoS ONE 2016, 11, e0146062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith-Unna, R.; Boursnell, C.; Patro, R.; Hibberd, J.M.; Steven, K. Transrate: Reference-Free Quality Assessment of De Novo Transcriptome Assemblies. Genome Res. 2016, 26, 1134–1144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, B.; Fillmore, N.; Bai, Y.; Collins, M.; Thomson, J.A.; Stewart, R.; Dewey, C.N. Evaluation of De Novo Transcriptome Assemblies from Rna-Seq Data. Genome Biol. 2014, 15, 553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luge, T.; Fischer, C.; Sauer, S. Efficient Application of De Novo Rna Assemblers for Proteomics Informed by Transcriptomics. J. Proteome Res. 2016, 15, 3938–3943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perkins, D.N.; Pappin, D.J.; Creasy, D.M.; Cottrell, J.S. Probability-Based Protein Identification by Searching Sequence Databases Using Mass Spectrometry Data. Electrophoresis 1999, 20, 3551–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slotta, D.J.; McFarland, M.A.; Markey, S.P. Masssieve: Panning Ms/Ms Peptide Data for Proteins. Proteomics 2010, 10, 3035–3039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez-Garcia, P.J.; Crepeau, M.W.; Puiu, D.; Gonzalez-Ibeas, D.; Whalen, J.; Stevens, K.A.; Paul, R.; Butterfield, T.S.; Britton, M.T.; Reagan, R.L.; et al. The Walnut (Juglans Regia) Genome Sequence Reveals Diversity in Genes Coding for the Biosynthesis of Non-Structural Polyphenols. Plant. J. 2016, 87, 507–532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holt, C.; Yandell, M. Maker2: An Annotation Pipeline and Genome-Database Management Tool for Second-Generation Genome Projects. BMC Bioinform. 2011, 12, 491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoff, K.J.; Lange, S.; Lomsadze, A.; Borodovsky, M.; Stanke, M. Braker1: Unsupervised Rna-Seq-Based Genome Annotation with Genemark-Et and Augustus. Bioinformatics 2016, 32, 767–769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- NCBI. NCBI Eukaryotic Genome Annotation Pipeline. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/genome/annotation_euk/process/ (accessed on 3 July 2017).
- Trouern-Trend, A.J.; Falk, T.; Zaman, S.; Caballero, M.; Neale, D.B.; Langley, C.H.; Dandekar, A.M.; Stevens, K.A.; Wegrzyn., J.L. Comparative Genomics of Six Juglans Species Reveals Disease-Associated Gene Family Contractions. Plant. J. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wegrzyn, J.L.; Staton, M.A.; Street, N.R.; Main, D.; Grau, E.; Herndon, N.; Buehler, S.; Falk, T.; Zaman, S.; Ramnath, R.; et al. Cyberinfrastructure to Improve Forest Health and Productivity: The Role of Tree Databases in Connecting Genomes, Phenomes, and the Environment. Front. Plant. Sci. 2019, 10, 813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, S. Fastqc: A Quality Control Tool for High Throughput Sequence Data; The Babraham Institute: Cambridge, UK, 2010. [Google Scholar]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, O.F. The Silva Ribosomal Rna Gene Database Project: Improved Data Processing and Web-Based Tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, D590–D596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast Gapped-Read Alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat. Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- JGI. Bbduk from the Joint Genome Institute. Available online: https://github.com/BioInfoTools/BBMap/blob/master/sh/bbduk.sh (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Bolger, A.M.; Lohse, M.; Usadel, B. Trimmomatic: A Flexible Trimmer for Illumina Sequence Data. Bioinformatics 2014, 30, 2114–2120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. Transdecoder. Available online: https://github.com/TransDecoder/TransDecoder (accessed on 26 July 2018).
- Li, W.; Godzik, A. Cd-Hit: A Fast Program for Clustering and Comparing Large Sets of Protein or Nucleotide Sequences. Bioinformatics 2006, 22, 1658–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Global Proteome Machine Organization. Crap: The Global Proteome Machine. Available online: https://www.thegpm.org/GPM/repos.html (accessed on 1 November 2010).
- Song, L.; Florea, L. Rcorrector: Efficient and Accurate Error Correction for Illumina Rna-Seq Reads. Gigascience 2015, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- R_Core_Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2006; Available online: https://www.R-project.org (accessed on 20 March 2019).
- Mattison, C.P.; Rai, R.; Settlage, R.E.; Hinchliffe, D.J.; Madison, C.; Bland, J.M.; Brashear, S.; Graham, C.J.; Tarver, M.R.; Florane, C.; et al. Rna-Seq Analysis of Developing Pecan (Carya Illinoinensis) Embryos Reveals Parallel Expression Patterns among Allergen and Lipid Metabolism Genes. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2017, 65, 1443–1455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leinonen, R.; Sugawara, H.; Shumway, M. Collaboration on behalf of the International Nucleotide Sequence Database. The Sequence Read Archive. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, D19–D21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Del Fabbro, C.; Scalabrin, S.; Morgante, M.; Giorgi, F.M. An Extensive Evaluation of Read Trimming Effects on Illumina Ngs Data Analysis. PLoS ONE 2013, 8, e85024. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Macmanes, M.D. On the Optimal Trimming of High-Throughput Mrna Sequence Data. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haak, M.; Vinke, S.; Keller, W.; Droste, J.; Ruckert, C.; Kalinowski, J.; Pucker, B. High Quality De Novo Transcriptome Assembly of Croton Tiglium. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2018, 5, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, S.C.; Gaiti, F.; Tanurdzic, M. De Novo Plant Transcriptome Assembly and Annotation Using Illumina Rna-Seq Reads. Methods Mol. Biol. 2019, 1933, 265–275. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, D.; Horvath, D.; Li, P.; Liu, W. Rna Sequencing Characterizes Transcriptomes Differences in Cold Response between Northern and Southern Alternanthera Philoxeroides and Highlight Adaptations Associated with Northward Expansion. Front. Plant Sci. 2019, 10, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brown, C.T.; Howe, A.; Zhang, Q.; Pyrkosz, A.B.; Brom, T.H. A Reference-Free Algorithm for Computational Normalization of Shotgun Sequencing Data. arXiv 2012, arXiv:1203.4802 [q-bio.GN]. [Google Scholar]
- Durai, D.A.; Schulz, M.H. In Silico Read Normalization Using Set Multi-Cover Optimization. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, 3273–3280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Scarano, D.; Rao, R.; Corrado, G. In Silico Identification and Annotation of Non-Coding Rnas by Rna-Seq and De Novo Assembly of the Transcriptome of Tomato Fruits. PLoS ONE 2017, 12, e0171504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Yandell, M.; Ence, D. A Beginner’s Guide to Eukaryotic Genome Annotation. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 329–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kapp, E.A.; Schutz, F.; Connolly, L.M.; Chakel, J.A.; Meza, J.E.; Miller, C.A.; Fenyo, D.; Eng, J.K.; Adkins, J.N.; Omenn, G.S.; et al. An Evaluation, Comparison, and Accurate Benchmarking of Several Publicly Available Ms/Ms Search Algorithms: Sensitivity and Specificity Analysis. Proteomics 2005, 5, 3475–3490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Omenn, G.S.; States, D.J.; Adamski, M.; Blackwell, T.W.; Menon, R.; Hermjakob, H.; Apweiler, R.; Haab, B.B.; Simpson, R.J.; Eddes, J.S.; et al. Overview of the Hupo Plasma Proteome Project: Results from the Pilot Phase with 35 Collaborating Laboratories and Multiple Analytical Groups, Generating a Core Dataset of 3020 Proteins and a Publicly-Available Database. Proteomics 2005, 5, 3226–3245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfeiffer, F.; Grober, C.; Blank, M.; Handler, K.; Beyer, M.; Schultze, J.L.; Mayer, G. Systematic Evaluation of Error Rates and Causes in Short Samples in Next-Generation Sequencing. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 10950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- MacManes, M.D.; Eisen, M.B. Improving Transcriptome Assembly through Error Correction of High-Throughput Sequence Reads. PeerJ 2013, 1, e113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heydari, M.; Miclotte, G.; Demeester, P.; Van de Peer, Y.; Fostier, J. Evaluation of the Impact of Illumina Error Correction Tools on De Novo Genome Assembly. BMC Bioinform. 2017, 18, 374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carruthers, M.; Yurchenko, A.A.; Augley, J.J.; Adams, C.E.; Herzyk, P.; Elmer, K.R. De Novo Transcriptome Assembly, Annotation and Comparison of Four Ecological and Evolutionary Model Salmonid Fish Species. BMC Genom. 2018, 19, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kerr, S.C.; Gaiti, F.; Beveridge, C.A.; Tanurdzic, M. De Novo Transcriptome Assembly Reveals High Transcriptional Complexity in Pisum Sativum Axillary Buds and Shows Rapid Changes in Expression of Diurnally Regulated Genes. BMC Genom. 2017, 18, 221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paya-Milans, M.; Olmstead, J.W.; Nunez, G.; Rinehart, T.A.; Staton, M. Comprehensive Evaluation of Rna-Seq Analysis Pipelines in Diploid and Polyploid Species. Gigascience 2018, 7, giy132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, H.S.; Schulz, M.H.; McCauley, B.M.; Hinman, V.F.; Bar-Joseph, Z. Probabilistic Error Correction for Rna Sequencing. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, e109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haas, B.J.; Papanicolaou, A.; Yassour, M.; Grabherr, M.; Blood, P.D.; Bowden, J.; Couger, M.B.; Eccles, D.; Li, B.; Lieber, M.; et al. De Novo Transcript Sequence Reconstruction from Rna-Seq Using the Trinity Platform for Reference Generation and Analysis. Nat. Protoc. 2013, 8, 1494–1512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| SIZED | UNSIZED | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Database Type | Number of Sequences | Number of Residues | Number of Sequences | Number of Residues | Number of Identified Peptides |
| NCBI Proteome | 55,751 | 24,750,578 | 61,756 | 26,627,674 | 1275 |
| Maker Proteome | 32,621 | 13,113,315 | 76,087 | 26,627,669 | 1183 |
| Braker Proteome | 30,306 | 13,599,899 | 72,425 | 26,627,687 | 1156 |
| Translated transcriptome | 194,436 | 26,627,682 | 194,436 | 26,627,682 | 1200 |
| Six-frame Translation Genome | 172,954 | 679,657,178 | NA | NA | 719 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Pirone-Davies, C.; McFarland, M.A.; Parker, C.H.; Adachi, Y.; Croley, T.R. The Utility of Genomic and Transcriptomic Data in the Construction of Proxy Protein Sequence Databases for Unsequenced Tree Nuts. Biology 2020, 9, 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9050104
Pirone-Davies C, McFarland MA, Parker CH, Adachi Y, Croley TR. The Utility of Genomic and Transcriptomic Data in the Construction of Proxy Protein Sequence Databases for Unsequenced Tree Nuts. Biology. 2020; 9(5):104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9050104
Chicago/Turabian StylePirone-Davies, Cary, Melinda A. McFarland, Christine H. Parker, Yoko Adachi, and Timothy R. Croley. 2020. "The Utility of Genomic and Transcriptomic Data in the Construction of Proxy Protein Sequence Databases for Unsequenced Tree Nuts" Biology 9, no. 5: 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9050104
APA StylePirone-Davies, C., McFarland, M. A., Parker, C. H., Adachi, Y., & Croley, T. R. (2020). The Utility of Genomic and Transcriptomic Data in the Construction of Proxy Protein Sequence Databases for Unsequenced Tree Nuts. Biology, 9(5), 104. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9050104