Structural and Functional Peculiarities of α-Crystallin
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Samples
2.2. Electron Microscopy and Negative Staining
2.3. X-ray Analysis
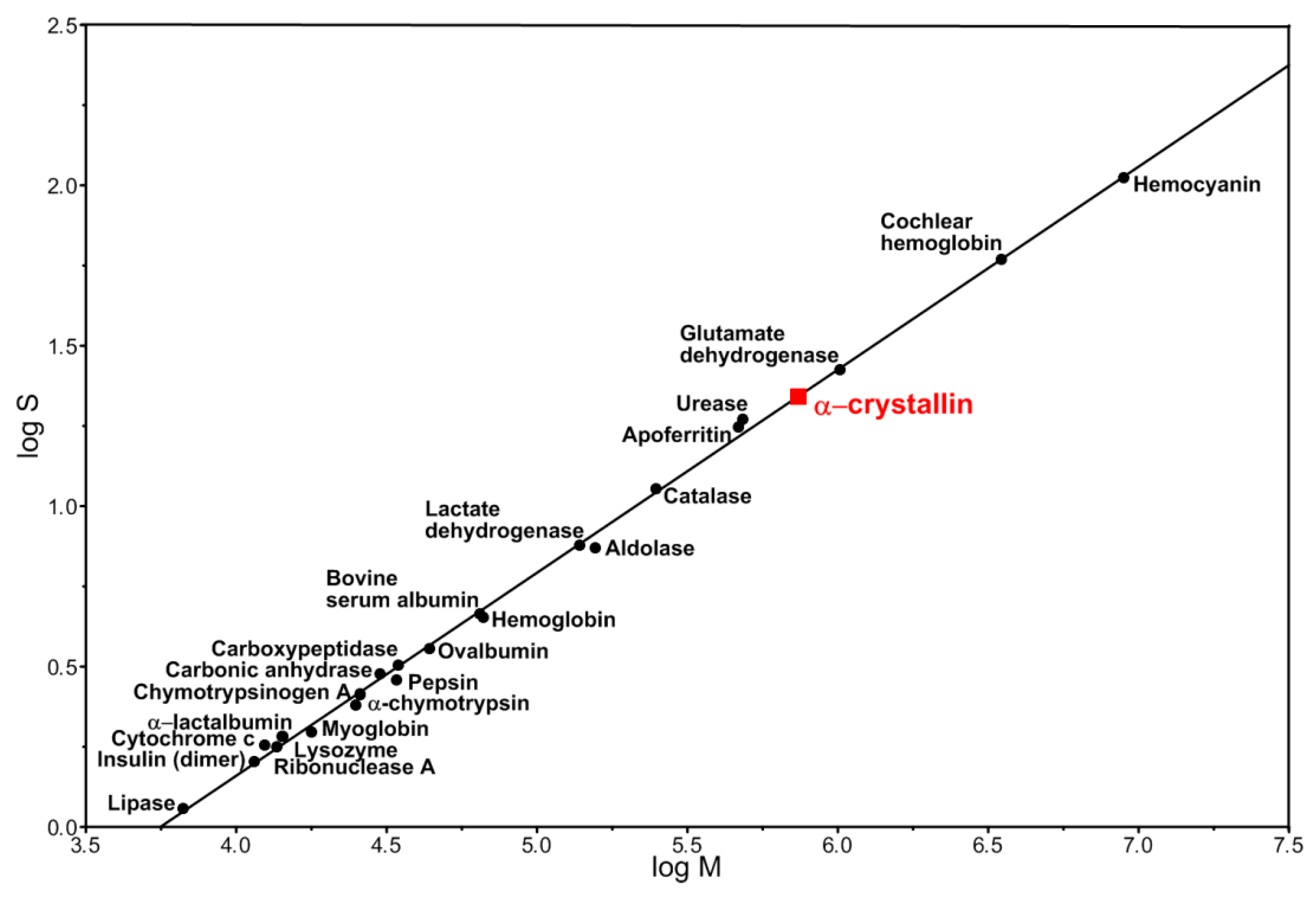
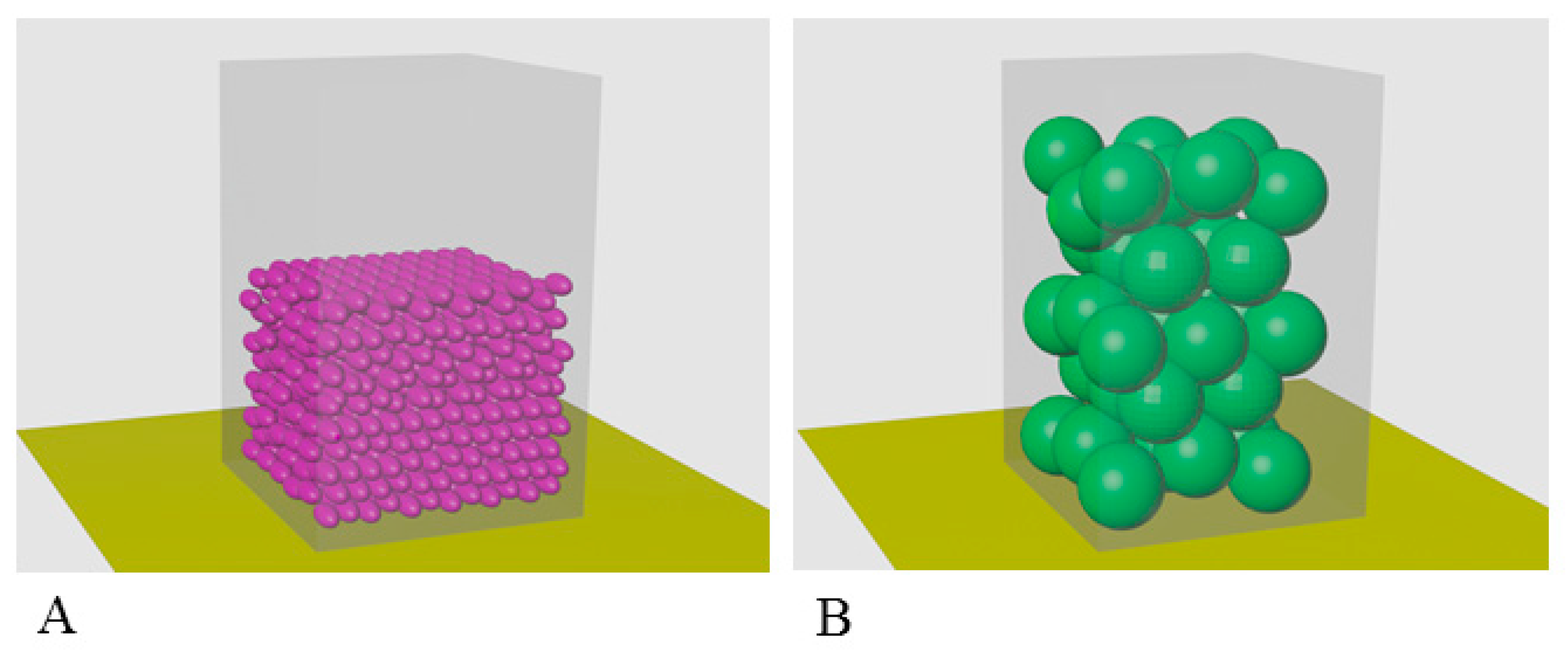
2.4. Calculation of Occupancy of a Unit Volume by α-Crystallin
3. Results
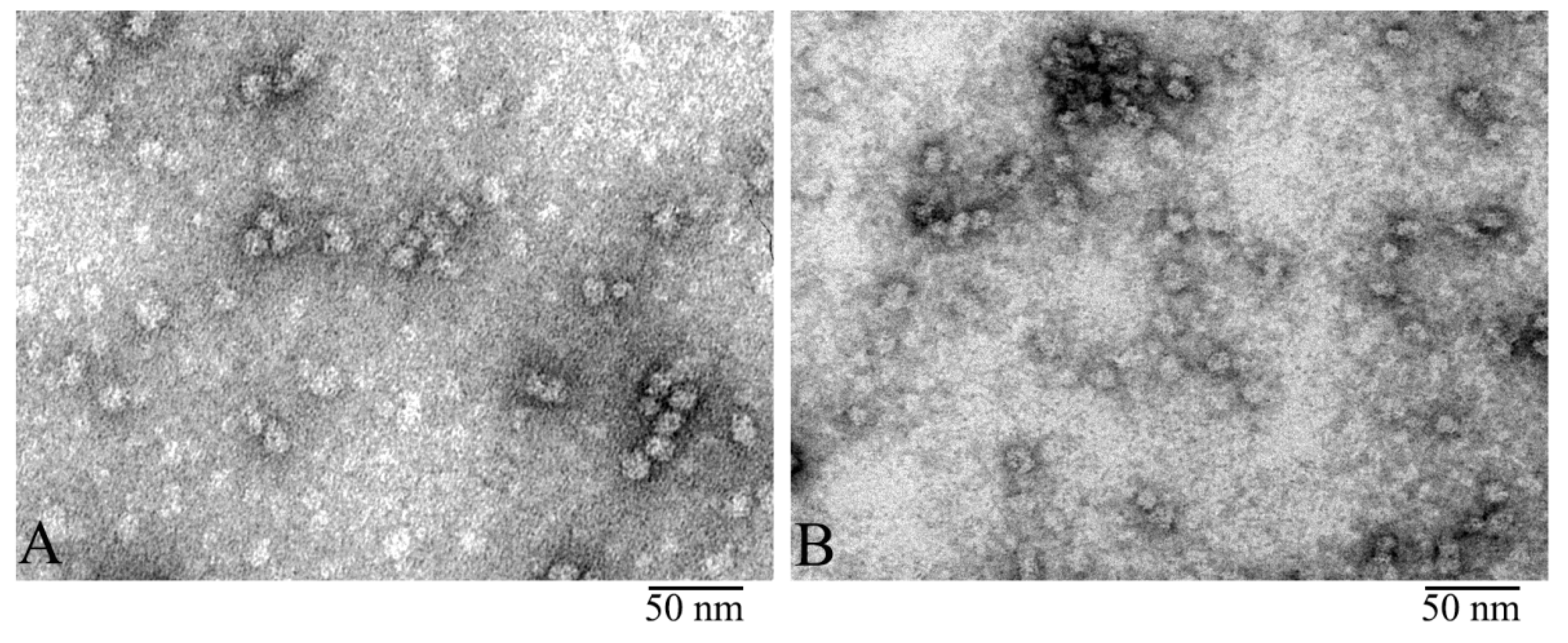
3.1. Electron Microscopy Analysis of α-Crystallin
3.2. Comparison of α-Crystallin from Cortex and Nuclear Region
3.3. Three Dimensional (3D) Reconstruction
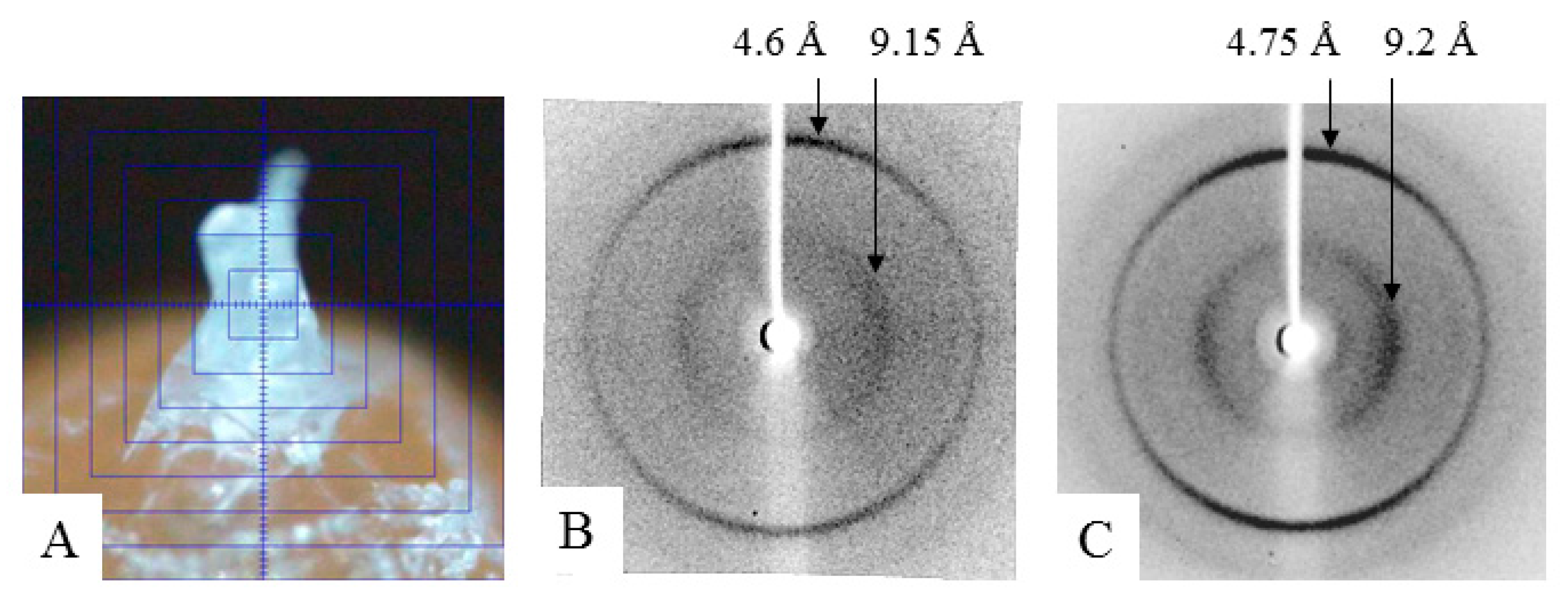
3.4. X-ray Diffraction Analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
- Both the heterogeneity of α-crystallin complexes and the fact of their formation represent some evolutionary adaptations. At high concentrations of α-crystallin in the eye lens, the heterogeneity of the α-crystallin complexes prevents protein crystallization. An increase in the activity of chaperone during the dissociation of complexes suggests that α-crystallin remains inactive in these complexes, which allows its discrete use under stress.
- It is impossible to obtain a reliable model of α-crystallin.
- αA-Crystallin is likely a specific lens chaperone.
- At a very high concentration, α-crystallin in eye lens can have a gel-like state; that is, the eye lens is a biogel.
- In vivo, due to the molecular crowding conditions, everything may be quite different from in vitro conditions, which leads to the conclusion that a more thorough analysis of the accumulated data is necessary.
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Benedek, G. Why the eye lens is transparent. Nature 1983, 302, 383–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delaye, M.; Tardieu, A. Short-range order of crystallin proteins accounts for eye lens transparency. Nature 1983, 302, 415–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Philipson, B. Distribution of protein within lenses with X-ray cataract. Invest Ophthalmol. 1969, 8, 271–280. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pierscionek, B.K.; Augusteyn, R.C. The refractive index and protein distribution in the blue eye trevally lens. J. Am. Optom. Assoc. 1995, 66, 739–743. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Pierscionek, B.K.; Chan, D.Y. Refractive index gradient of human lenses. Optom. Vis. Sci. 1989, 66, 822–829. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vérétout, F.; Delaye, M.; Tardieu, A. Molecular basis of eye lens transparency. Osmotic pressure and X-ray analysis of alpha-crystallin solutions. J. Mol. Biol. 1989, 205, 713–728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagerholm, P.P.; Philipson, B.T.; Lindström, B. Normal human lens—The distribution of protein. Exp. Eye Res. 1981, 33, 615–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemendal, H.; de Jong, W.; Jaenicke, R.; Lubsen, N.H.; Slingsby, C.; Tardieu, A. Ageing and vision: structure, stability and function of lens crystallins. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2004, 86, 407–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Jong, W.W.; Caspers, G.J.; Leunissen, J.A. Genealogy of the alpha-crystallin small heat-shock protein superfamily. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1998, 22, 151–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, J. Alpha-crystallin. Exp. Eye Res. 2003, 76, 145–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shiliaev, N.G.; Selivanova, O.M.; Galzitskaya, O.V. Search for conserved amino acid residues of the α-crystallin proteins of vertebrates. J. Bioinform. Comput. Biol. 2016, 14, 1641004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bloemendal, H. The vertebrate eye lens. Science 1977, 197, 127–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Quax-Jeuken, Y.; Quax, W.; van Rens, G.; Khan, P.M.; Bloemendal, H. Complete structure of the alpha B-crystallin gene: conservation of the exon-intron distribution in the two nonlinked alpha-crystallin genes. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1985, 82, 5819–5823. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ngo, J.T.; Klisak, I.; Dubin, R.A.; Piatigorsky, J.; Mohandas, T.; Sparkes, R.S.; Bateman, J.B. Assignment of the alpha B-crystallin gene to human chromosome 11. Genomics 1989, 5, 665–669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Srinivasan, A.N.; Nagineni, C.N.; Bhat, S.P. alpha A-crystallin is expressed in non-ocular tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 23337–23341. [Google Scholar]
- Renkawek, K.; de Jong, W.W.; Merck, K.B.; Frenken, C.W.; van Workum, F.P.; Bosman, G.J. alpha B-crystallin is present in reactive glia in Creutzfeldt-Jakob disease. Acta. Neuropathol. 1992, 83, 324–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renkawek, K.; Voorter, C.E.; Bosman, G.J.; van Workum, F.P.; de Jong, W.W. Expression of alpha B-crystallin in Alzheimer’s disease. Acta. Neuropathol. 1994, 87, 155–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Noort, J.M.; van Sechel, A.C.; Bajramovic, J.J.; el Ouagmiri, M.; Polman, C.H.; Lassmann, H.; Ravid, R. The small heat-shock protein alpha B-crystallin as candidate autoantigen in multiple sclerosis. Nature 1995, 375, 798–801. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ousman, S.S.; Tomooka, B.H.; van Noort, J.M.; Wawrousek, E.F.; O’Connor, K.C.; Hafler, D.A.; Sobel, R.A.; Robinson, W.H.; Steinman, L. Protective and therapeutic role for alphaB-crystallin in autoimmune demyelination. Nature 2007, 448, 474–479. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Launay, N.; Tarze, A.; Vicart, P.; Lilienbaum, A. Serine 59 phosphorylation of alpha B-crystallin down-regulates its anti-apoptotic function by binding and sequestering Bcl-2 in breast cancer cells. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 37324–37332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pereira, M.B.M.; Santos, A.M.; Gonçalves, D.C.; Cardoso, A.C.; Consonni, S.R.; Gozzo, F.C.; Oliveira, P.S.; Pereira, A.H.M.; Figueiredo, A.R.; Tiroli-Cepeda, A.O.; et al. αB-crystallin interacts with and prevents stress-activated proteolysis of focal adhesion kinase by calpain in cardiomyocytes. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 5159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Groenen, P.J.; Merck, K.B.; de Jong, W.W.; Bloemendal, H. Structure and modifications of the junior chaperone alpha-crystallin. From lens transparency to molecular pathology. Eur. J. Biochem. 1994, 225, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Haslbeck, M.; Peschek, J.; Buchner, J.; Weinkauf, S. Structure and function of α-crystallins: Traversing from in vitro to in vivo. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016, 1860, 149–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Horwitz, J.; Huang, Q.L.; Ding, L.; Bova, M.P. Lens alpha-crystallin: chaperone-like properties. Meth. Enzymol. 1998, 290, 365–383. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Yu, C.-M.; Chang, G.-G.; Chang, H.-C.; Chiou, S.-H. Cloning and characterization of a thermostable catfish alphaB-crystallin with chaperone-like activity at high temperatures. Exp. Eye Res. 2004, 79, 249–261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemendal, H.; Groenewoud, G. One-step separation of the subunits of alpha-crystallin by chromatofocusing in 6 M urea. Anal. Biochem. 1981, 117, 327–329. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschek, J.; Braun, N.; Franzmann, T.M.; Georgalis, Y.; Haslbeck, M.; Weinkauf, S.; Buchner, J. The eye lens chaperone alpha-crystallin forms defined globular assemblies. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2009, 106, 13272–13277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, D.A.; Bova, M.P.; Huang, Q.L.; Mchaourab, H.S.; Stewart, P.L. Small heat-shock protein structures reveal a continuum from symmetric to variable assemblies. J. Mol. Biol. 2000, 298, 261–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Head, M.W.; Corbin, E.; Goldman, J.E. Coordinate and independent regulation of alpha B-crystallin and hsp27 expression in response to physiological stress. J. Cell. Physiol. 1994, 159, 41–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, J. Alpha-crystallin can function as a molecular chaperone. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1992, 89, 10449–10453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Derham, B.K.; Harding, J.J. Alpha-crystallin as a molecular chaperone. Prog. Retin. Eye. Res. 1999, 18, 463–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Horwitz, J.; Bova, M.P.; Ding, L.L.; Haley, D.A.; Stewart, P.L. Lens alpha-crystallin: function and structure. Eye (Lond.) 1999, 13, 403–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hook, D.W.; Harding, J.J. Protection of enzymes by alpha-crystallin acting as a molecular chaperone. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 1998, 22, 295–306. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Montfort, R.L.; Basha, E.; Friedrich, K.L.; Slingsby, C.; Vierling, E. Crystal structure and assembly of a eukaryotic small heat shock protein. Nat. Struct. Biol. 2001, 8, 1025–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haley, D.A.; Horwitz, J.; Stewart, P.L. The small heat-shock protein, alphaB-crystallin, has a variable quaternary structure. J. Mol. Biol. 1998, 277, 27–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jehle, S.; Vollmar, B.S.; Bardiaux, B.; Dove, K.K.; Rajagopal, P.; Gonen, T.; Oschkinat, H.; Klevit, R.E. N-terminal domain of alphaB-crystallin provides a conformational switch for multimerization and structural heterogeneity. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 6409–6414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peschek, J.; Braun, N.; Rohrberg, J.; Back, K.C.; Kriehuber, T.; Kastenmüller, A.; Weinkauf, S.; Buchner, J. Regulated structural transitions unleash the chaperone activity of αB-crystallin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2013, 110, E3780–E3789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaiser, C.J.O.; Peters, C.; Schmid, P.W.N.; Stavropoulou, M.; Zou, J.; Dahiya, V.; Mymrikov, E.V.; Rockel, B.; Asami, S.; Haslbeck, M.; et al. The structure and oxidation of the eye lens chaperone αA-crystallin. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2019, 26, 1141–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiou, S.H.; Azari, P.; Himmel, M.E.; Squire, P.G. Isolation and physical characterization of bovine lens crystallins. Int. J. Pept. Protein Res. 1979, 13, 409–417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khanova, H.A.; Markossian, K.A.; Kurganov, B.I.; Samoilov, A.M.; Kleimenov, S.Y.; Levitsky, D.I.; Yudin, I.K.; Timofeeva, A.C.; Muranov, K.O.; Ostrovsky, M.A. Mechanism of chaperone-like activity. Suppression of thermal aggregation of betaL-crystallin by alpha-crystallin. Biochemistry 2005, 44, 15480–15487. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Augusteyn, R.C.; Koretz, J.F.; Schurtenberger, P. The effect of phosphorylation on the structure of alpha-crystallin. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 1989, 999, 293–299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Kleef, F.S.; Hoenders, H.J. Population character and variety in subunit structure of high-molecular-weight proteins from the bovine eye lens. Eur. J. Biochem. 1973, 40, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chebotareva, N.A.; Eronina, T.B.; Roman, S.G.; Poliansky, N.B.; Muranov, K.O.; Kurganov, B.I. Effect of crowding and chaperones on self-association, aggregation and reconstitution of apophosphorylase b. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2013, 60, 69–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spector, A.; Li, L.K.; Augusteyn, R.C.; Schneider, A.; Freund, T. α-Crystallin. The isolation and characterization of distinct macromolecular fractions. Biochem. J. 1971, 124, 337–343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serdyuk, I.N.; Zaccai, N.R.; Zaccai, G. Methods in molecular biophysics: structure, dynamics, function; Cambridge University Press: New York, NY, USA, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Clarke, M.J.; Artero, J.B.; Moulin, M.; Callow, P.; Carver, J.A.; Griffiths, P.C.; Haertlein, M.; Harding, J.J.; Meek, K.M.; Timmins, P.; et al. Investigation of γE-crystallin target protein binding to bovine lens alpha-crystallin by small-angle neutron scattering. BBA-Gen. Subjects 2010, 1800, 392–397. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meehan, S.; Knowles, T.P.J.; Baldwin, A.J.; Smith, J.F.; Squires, A.M.; Clements, P.; Treweek, T.M.; Ecroyd, H.; Tartaglia, G.G.; Vendruscolo, M.; et al. Characterisation of Amyloid Fibril Formation by Small Heat-shock Chaperone Proteins Human αA-, αB- and R120G αB-Crystallins. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 372, 470–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garvey, M.; Ecroyd, H.; Ray, N.J.; Gerrard, J.A.; Carver, J.A. Functional Amyloid Protection in the Eye Lens: Retention of α-Crystallin Molecular Chaperone Activity after Modification into Amyloid Fibrils. Biomolecules 2017, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Selivanova, O.M.; Glyakina, A.V.; Gorbunova, E.Y.; Mustaeva, L.G.; Suvorina, M.Y.; Grigorashvili, E.I.; Nikulin, A.D.; Dovidchenko, N.V.; Rekstina, V.V.; Kalebina, T.S.; et al. Structural model of amyloid fibrils for amyloidogenic peptide from Bgl2p-glucantransferase of S. cerevisiae cell wall and its modifying analog. New morphology of amyloid fibrils. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2016, 1864, 1489–1499. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woodard, D.; Bell, D.; Tipton, D.; Durrance, S.; Burnett, L.C.; Cole, L.; Li, B.; Xu, S. Gel formation in protein amyloid aggregation: a physical mechanism for cytotoxicity. PLoS ONE 2014, 9, e94789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bloemendal, H.; Berns, T.; Zweers, A.; Hoenders, H.; Benedetti, E.L. The state of aggregation of -crystallin detected after large-scale preparation by zonal centrifugation. Eur. J. Biochem. 1972, 24, 401–406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siezen, R.J.; Berger, H. The quaternary structure of bovine alpha-crystallin. Size and shape studies by sedimentation, small-angle X-ray scattering and quasi-elastic light scattering. Eur. J. Biochem. 1978, 91, 397–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siezen, R.J.; Bindels, J.G.; Hoenders, H.J. The quaternary structure of bovine alpha-crystallin. Size and charge microheterogeneity: more than 1000 different hybrids? Eur. J. Biochem. 1978, 91, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gu, L.; Abulimiti, A.; Li, W.; Chang, Z. Monodisperse Hsp16.3 Nonamer Exhibits Dynamic Dissociation and Reassociation, with the Nonamer Dissociation Prerequisite for Chaperone-like Activity. J. Mol. Biol. 2002, 319, 517–526. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Z.; Hanson, S.R.A.; Lampi, K.J.; David, L.L.; Smith, D.L.; Smith, J.B. Age-Related Changes in Human Lens Crystallins Identified by HPLC and Mass Spectrometry. Exp. Eye Res. 1998, 67, 21–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Brady, J.P.; Garland, D.; Duglas-Tabor, Y.; Robison, W.G., Jr.; Groome, A.; Wawrousek, E.F. Targeted disruption of the mouse alpha A-crystallin gene induces cataract and cytoplasmic inclusion bodies containing the small heat shock protein alpha B-crystallin. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 1997, 94, 884–889. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Goto, S.; Inaguma, Y.; Hasegawa, K.; Morishita, R.; Asano, T. Purification and characterization of a 20-kDa protein that is highly homologous to alpha B crystallin. J. Biol. Chem. 1994, 269, 15302–15309. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Kato, K.; Shinohara, H.; Goto, S.; Inaguma, Y.; Morishita, R.; Asano, T. Copurification of small heat shock protein with alpha B crystallin from human skeletal muscle. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 7718–7725. [Google Scholar]
- Mymrikov, E.V.; Seit-Nebi, A.S.; Gusev, N.B. Heterooligomeric complexes of human small heat shock proteins. Cell Stress Chaperon. 2012, 17, 157–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delcour, J.; Papaconstantinou, J. A change in the stoichiometry of assembly of bovine lens alpha-crystallin subunits in relation to cellular differentiation. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 1974, 57, 134–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vermorken, A.J.; Bloemendal, H. alpha-Crystallin polypeptides as markers of lens cell differentiation. Nature 1978, 271, 779–781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chiesa, R.; McDermott, M.J.; Spector, A. Differential synthesis and phosphorylation of the alpha-crystallin A and B chains during bovine lens fiber cell differentiation. Curr. Eye Res. 1989, 8, 151–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

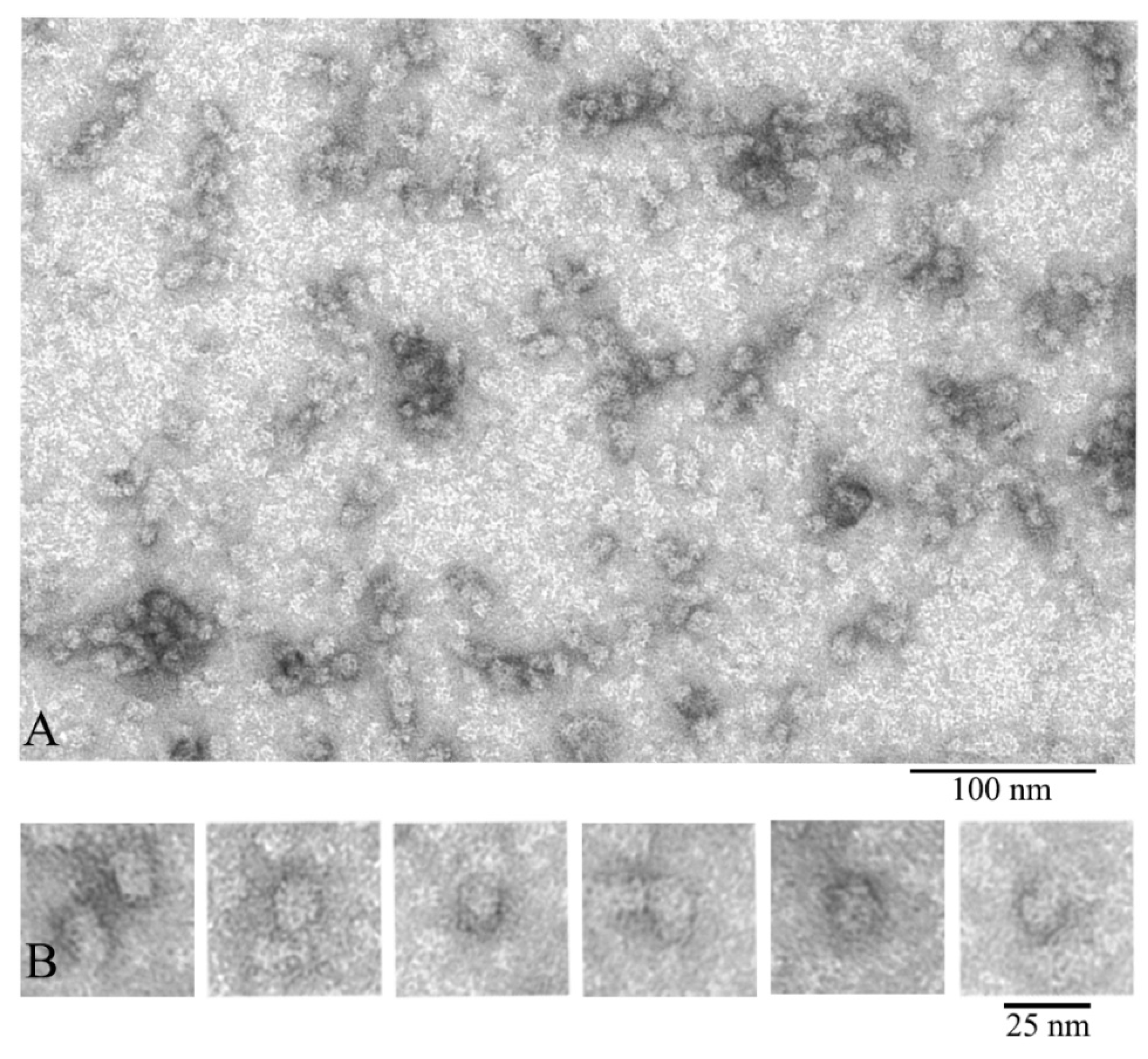

| Complex Diameter (nm) | Number of Complexes | Portion (%) |
|---|---|---|
| 12–14 | 605 | 53 |
| 15–19 | 309 | 27 |
| 20–25 | 229 | 20 |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Selivanova, O.M.; Galzitskaya, O.V. Structural and Functional Peculiarities of α-Crystallin. Biology 2020, 9, 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9040085
Selivanova OM, Galzitskaya OV. Structural and Functional Peculiarities of α-Crystallin. Biology. 2020; 9(4):85. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9040085
Chicago/Turabian StyleSelivanova, Olga M., and Oxana V. Galzitskaya. 2020. "Structural and Functional Peculiarities of α-Crystallin" Biology 9, no. 4: 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9040085
APA StyleSelivanova, O. M., & Galzitskaya, O. V. (2020). Structural and Functional Peculiarities of α-Crystallin. Biology, 9(4), 85. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9040085






