Clinical Veterinary Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) Studies in Dogs with Head and Neck Cancer: Bridging the Gap between Translational and Clinical Studies
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
- Confirmed histopathological diagnosis of head and neck cancer;
- Not amenable or unresponsive to alternative standard therapeutic options;
- Life expectancy with acceptable quality of life (QoL) of more than 1–2 months to ensure minimum follow-up time and clinical/cardiological status to tolerate prolonged (2 h) anesthesia during irradiation for BNCT;
- If the dog received previous treatment (surgery/chemotherapy), a minimum of 3 weeks should elapse between the end of this treatment and BNCT;
- No distant metastasis at initial presentation.
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hopewell, J.W.; Morris, G.M.; Schwint, A.; Coderre, J.A. The radiobiological principles of boron neutron capture therapy: A critical review. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2011, 69, 1756–1759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzi, E.C.; Cardoso, J.E.; Colombo, L.L.; Thorp, S.; Monti Hughes, A.; Molinari, A.J.; Garabalino, M.A.; Heber, E.M.; Miller, M.; Itoiz, M.E.; et al. Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) for liver metastasis: Therapeutic efficacy in an experimental model. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2012, 51, 331–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Monti Hughes, A.; Pozzi, E.; Thorp, S.I.; Curotto, P.; Medina, V.A.; Martinel Lamas, D.J.; Rivera, E.S.; Garabalino, M.A.; Farías, R.O.; Gonzalez., S.J.; et al. Histamine reduces boron neutron capture therapy-induced mucositis in an oral precancer model. Oral Dis. 2015, 21, 770–777. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kato, I.; Ono, K.; Sakurai, Y.; Ohmae, M.; Maruhashi, A.; Imahori, Y.; Kirihata, M.; Nakazawa, M.; Yura, Y. Effectiveness of BNCT for recurrent head and neck malignancies. Appl Radiat. Isot. 2004, 61, 1069–1073. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kreimann, E.L.; Itoiz, M.E.; Longhino, J.; Blaumann, H.; Calzetta, O.; Schwint, A.E. Boron neutron capture therapy for the treatment of oral cancer in the hamster cheek pouch model. Cancer Res. 2001, 61, 8638–8642. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trivillin, V.A.; Heber, E.M.; Nigg, D.W.; Itoiz, M.E.; Calzetta, O.; Blaumann, H.; Longhino, J.; Schwint, A.E. Therapeutic success of boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) mediated by a chemically non-selective boron agent in an experimental model of oral cancer: A new paradigm in BNCT radiobiology. Radiat. Res. 2006, 166, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Molinari, A.J.; Pozzi, E.C.; Monti Hughes, A.; Heber, E.M.; Garabalino, M.A.; Thorp, S.I.; Miller, M.; Itoiz, M.E.; Aromando, R.F.; Nigg, D.W.; et al. “Sequential” boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT): A novel approach to BNCT for the treatment of oral cancer in the hamster cheek pouch model. Radiat. Res. 2011, 175, 463–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Molinari, A.J.; Pozzi, E.C.; Monti Hughes, A.; Heber, E.M.; Garabalino, M.A.; Thorp, S.I.; Miller, M.; Itoiz, M.E.; Aromando, R.F.; Nigg, D.W.; et al. Tumor blood vessel “normalization” improves the therapeutic efficacy of boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) in experimental oral cancer. Radiat. Res. 2012, 177, 59–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schwint, A.E.; Trivillin, V.A. ‘Close-to-ideal’ tumor boron targeting for boron neutron capture therapy is possible with ‘less-than-ideal’ boron carriers approved for use in humans. Ther. Deliv. 2015, 6, 269–272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monti Hughes, A.; Longhino, J.; Boggio, E.; Medina, V.A.; Martinel Lamas, D.J.; Garabalino, M.A.; Heber, E.M.; Pozzi, E.C.C.; Itoiz, M.E.; Aromando, R.F.; et al. Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) translational studies in the hamster cheek pouch model of oral cancer at the new “B2” configuration of the RA-6 nuclear reactor. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2017, 56, 377–387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kato, I.; Fujita, Y.; Maruhashi, A.; Kumada, H.; Ohmae, M.; Kirihata, M.; Imahori, Y.; Suzuki, M.; Sakrai, Y.; Sumi, T.; et al. Effectiveness of boron neutron capture therapy for recurrent head and neck malignancies. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, S37–S42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kankaanranta, L.; Seppälä, T.; Koivunoro, H.; Saarilahti, K.; Atula, T.; Collan, J.; Salli, E.; Kortesniemi, M.; Uusi-Simola, J.; Välimäki, P.; et al. Boron neutron capture therapy in the treatment of locally recurred head-and-neck cancer: Final analysis of a phase I/II trial. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 82, e67–e75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, L.W.; Liu, Y.H.; Chou, F.I.; Jiang, S.H. Clinical trials for treating recurrent head and neck cancer with boron neutron capture therapy using the Tsing-Hua Open Pool Reactor. Cancer Commun. 2018, 38, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Axiak-Bechtel, S.M.; Maitz, C.A.; Selting, K.A.; Bryan, J.N. Preclinical imaging and treatment of cancer: The use of animal models beyond rodents. Q. J. Nucl. Med. Mol. Imaging 2015, 59, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gavin, P.R.; Kraft, S.L.; Wendling, L.R.; Miller, D.L. Canine spontaneous brain tumors-a large animal model for BNCT. Strahlenther. Onkol. 1989, 165, 225–228. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- MacEwen, E.G. Spontaneous tumors in dogs and cats: Models for the study of cancer biology and treatment. Cancer Metastasis Rev. 1990, 9, 125–136. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maglietti, F.; Tellado, M.; Olaiz, N.; Michinski, S.; Marshall, G. Minimally Invasive Electrochemotherapy Procedure for Treating Nasal Duct Tumors in Dogs using a Single Needle Electrode. Radiol. Oncol. 2017, 51, 422–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dos Anjos, D.S.; Bueno, C.; Magalhães, L.F.; Magalhães, G.M.; Mattos-Junior, E.; Pinto, M.M.R.; De Nardi, A.B.; Brunner, C.H.M.; Leis-Filho, A.F.; Calazans, S.G.; et al. Electrochemotherapy induces tumor regression and decreases the proliferative index in canine cutaneous squamous cell carcinoma. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 15819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Riccardo, F.; Aurisicchio, L.; Impellizeri, J.A.; Cavallo, F. The importance of comparative oncology in translational medicine. Cancer Immunol. Immunother. 2015, 64, 137–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bronson, R.T. Variation in age at death of dogs of different sexes and breeds. Am. J. Vet. Res. 1982, 43, 2057–2059. [Google Scholar]
- González, S.J.; Bonomi, M.R.; Santa Cruz, G.A.; Blaumann, H.R.; Calzetta Larrieu, O.A.; Menéndez, P.; Jiménez Rebagliati, R.; Longhino, J.; Feld, D.B.; Dagrosa, M.A.; et al. First BNCT treatment of a skin melanoma in Argentina: Dosimetric analysis and clinical outcome. Appl Radiat. Isot. 2004, 61, 1101–1105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Almela, R.M.; Ansón, A.A. Review of Immunotherapeutic Strategies in Canine Malignant Melanoma. Vet. Sci. 2019, 6, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, S.J.; Santa Cruz, G.A.; Kiger, W.S.; Goorley, J.T.; Palmer, M.R.; Busse, P.M.; Zamenhof, R. NCTPlan, the New PC version of MacNCTPlan: Improvements and Verification of a BNCT Treatment Planning System. In Proceedings of the 10th International Congress on Neutron Capture Therapy, Essen, Germany, 8–13 September 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Kankaanranta, L.; Seppälä, T.; Koivunoro, H.; Saarilahti, K.; Atula, T.; Collan, J.; Salli, E.; Kortesniemi, M.; Uusi-Simola, J.; Mäkitie, A.; et al. Boron neutron capture therapy in the treatment of locally recurred head and neck cancer. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2007, 69, 475–482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coderre, J.A.; Elowitz, E.H.; Chadha, M.; Bergland, R.; Capala, J.; Joel, D.D.; Liu, H.B.; Slatkin, D.N.; Chanana, A.D. Boron neutron capture therapy for glioblastoma multiforme using p-boronophenylalanine and epithermal neutrons: Trial design and early clinical results. J. Neurooncol. 1997, 33, 141–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Menéndez, P.R.; Roth, B.M.; Pereira, M.D.; Casal, M.R.; González, S.J.; Feld, D.B.; Santa Cruz, G.A.; Kessler, J.; Longhino, J.; Blaumann, H.; et al. BNCT for skin melanoma in extremities: Updated Argentine clinical results. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, S50–S53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González, S.J.; Pozzi, E.C.C.; Monti Hughes, A.; Provenzano, L.; Koivunoro, H.; Carando, D.G.; Thorp, S.I.; Casal, M.R.; Bortolussi, S.; Trivillin, V.A.; et al. Photon iso-effective dose for cancer treatment with mixed field radiation based on dose–response assessment from human and an animal model: Clinical application to boron neutron capture therapy for head and neck cancer. Phys. Med. Biol. 2017, 62, 7938–7958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sonis, S.T.; Peterson, R.L.; Edwards, L.J.; Lucey, C.A.; Wang, L.; Mason, L.; Login, G.; Ymamkawa, M.; Moses, G.; Bouchard, P.; et al. Defining mechanisms of action of interleukin-11 on the progression of radiation-induced oral mucositis in hamsters. Oral Oncol. 2000, 36, 373–381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- López-Castaño, F.; Oñate-Sánchez, R.E.; Roldán-Chicano, R.; Cabrerizo-Merino, M.C. Measurement of secondary mucositis to oncohematologic treatment by means of different scale. Review. Med. Oral Patol. Oral Cir. Bucal. 2005, 10, 412–421. [Google Scholar]
- Wu, X.; Chen, P.; Sonis, S.T.; Lingen, M.W.; Berger, A.; Toback, F.G. A novel Peptide to treat oral mucositis blocks endothelial and epithelial cell apoptosis. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 2012, 83, e409–e415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rao, M.; Trivillin, V.A.; Heber, E.M.; Cantarelli, M.A.; Itoiz, M.E.; Nigg, D.W.; Rebagliati, R.J.; Batistoni, D.; Schwint, A.E. BNCT of 3 cases of spontaneous head and neck cancer in feline patients. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2004, 61, 947–952. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trivillin, V.A.; Heber, E.M.; Rao, M.; Cantarelli, M.A.; Itoiz, M.E.; Nigg, D.W.; Calzetta, O.; Blaumann, H.; Longhino, J.; Schwint, A.E. Boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) for the treatment of spontaneous nasal planum squamous cell carcinoma in felines. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2008, 47, 147–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ono, K.; Masunaga, S.; Suzuki, M.; Kinashi, Y.; Takagaki, M.; Akaboshi, M. The combined effect of boronophenylalanine and borocaptate in boron neutron capture therapy for SCCVII tumors in mice. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1999, 43, 431–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wittig, A.; Sauerwein, W.A.; Coderre, J.A. Mechanisms of transport of p-borono-phenylalanine through the cell membrane in vitro. Radiat. Res. 2000, 153, 173–180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garabalino, M.A.; Olaiz, N.; Portu, A.; Saint Martin, G.; Thorp, S.I.; Pozzi, E.C.C.; Curotto, P.; Itoiz, M.E.; Monti Hughes, A.; Colombo, L.L.; et al. Electroporation optimizes the uptake of boron-10 by tumor for boron neutron capture therapy (BNCT) mediated by GB-10: A boron biodistribution study in the hamster cheek pouch oral cancer model. Radiat. Environ. Biophys. 2019, 58, 455–467. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benczik, J.; Seppälä, T.; Snellman, M.; Joensuu, H.; Morris, G.M.; Hopewell, J.W. Evaluation of the relative biological effectiveness of a clinical epithermal neutron beam using dog brain. Radiat. Res. 2003, 159, 199–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Coderre, J.A.; Gavin, P.R.; Capala, J.; Ma, R.; Morris, G.M.; Button, T.M.; Aziz, T.; Peress, N.S. Tolerance of the normal canine brain to epithermal neutron irradiation in the presence of p-boronophenylalanine. J. Neurooncol. 2000, 48, 27–40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takeuchi, A. Possible application of boron neutron capture therapy to canine osteosarcoma. Nihon Juigaku Zasshi 1985, 47, 869–878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gavin, P.R.; Kraft, S.L.; DeHaan, C.E.; Swartz, C.D.; Griebenow, M.L. Large animal normal tissue tolerance with boron neutron capture. Int. J. Radiat. Oncol. Biol. Phys. 1994, 28, 1099–1106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraft, S.L.; Gavin, P.R.; DeHaan, C.E.; Leathers, C.W.; Bauer, W.F.; Miller, D.L.; Dorn, R.V., 3rd. Borocaptate sodium: A potential boron delivery compound for boron neutron capture therapy evaluated in dogs with spontaneous intracranial tumors. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1992, 89, 11973–11977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraft, S.L.; Gavin, P.R.; Leathers, C.W.; DeHaan, C.E.; Bauer, W.F.; Miller, D.L.; Dorn III, R.V.; Griebenow, M.L. Biodistribution of Boron in Dogs with Spontaneous Intracranial Tumors following Borocaptate Sodium Administration. Cancer Res. 1994, 54, 1259–1263. [Google Scholar]
- Mitin, V.N.; Kulakov, V.N.; Khokhlov, V.F.; Sheino, I.N.; Arnopolskaya, A.M.; Kozlovskaya, N.G.; Zaitsev, K.N.; Portnov, A.A. Comparison of BNCT and GdNCT efficacy in treatment of canine cancer. Appl. Radiat. Isot. 2009, 67, S299–S301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
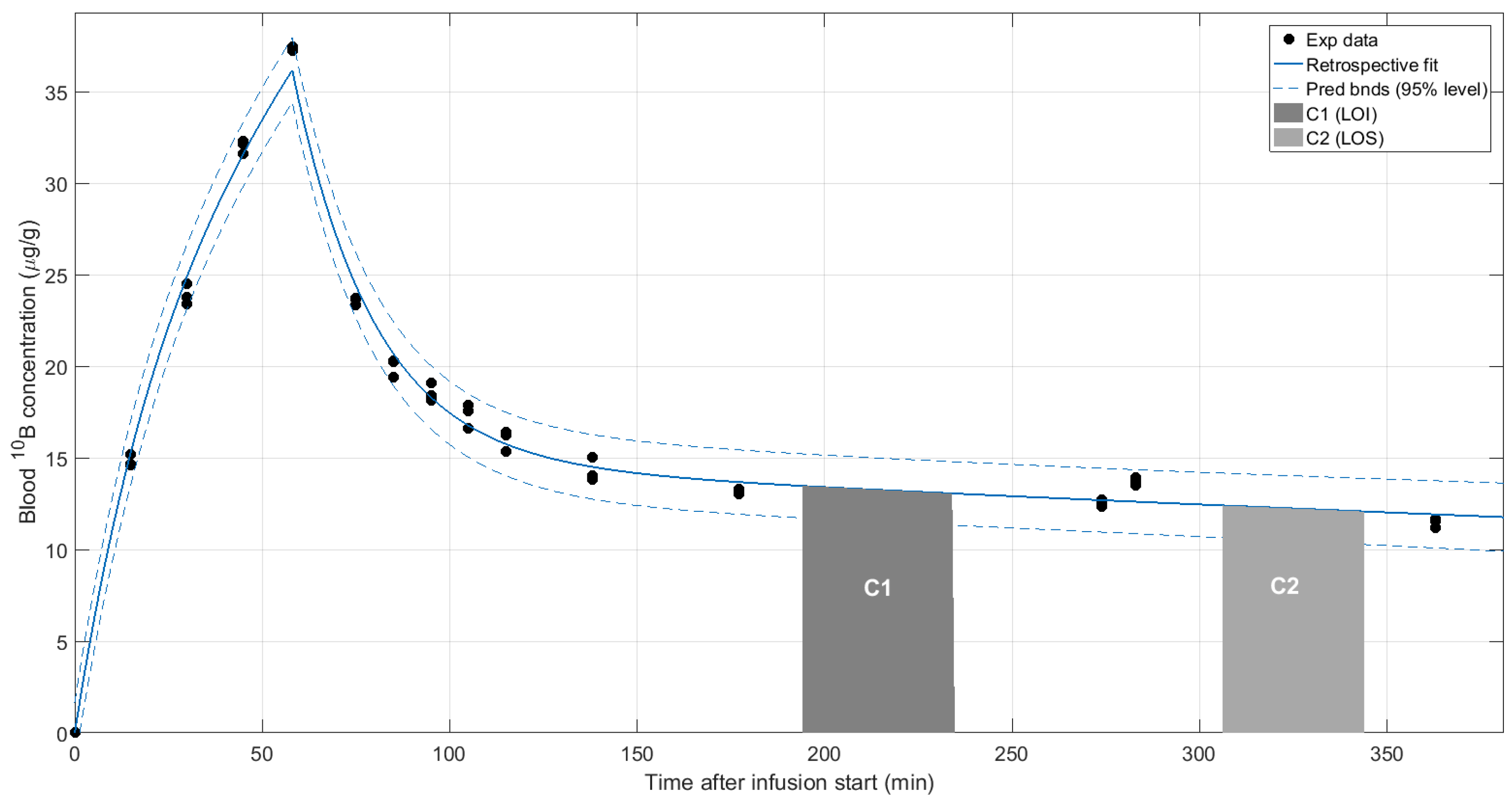

| Tumor Total Doses, Mean (Min, Max) | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Dog | BNCT Application | Absorbed | RBE-Weighted |
| Lucy | BNCT1 | 5 (3, 6) | 13 (8, 15) |
| BNCT2 | 6 (4, 8) | 17 (10, 22) | |
| Senshi | BNCT1 | 6 (3, 7) | 16 (7, 20) |
| BNCT2 | 6 (3, 7) | 16 (7, 20) | |
| Mora I | BNCT1 | 11 (7, 14) | 28 (17, 37) |
| BNCT2 | 3 (2, 4) | 8 (4, 10) | |
| Mora II | BNCT1 | 7 (5, 9) | 17 (12, 22) |
| BNCT2 | 6 (5, 8) | 17 (12, 22) | |
| Jake | BNCT1 | 10 (7, 11) | 26 (18, 31) |
| BNCT2 | 10 (7, 11) | 26 (18, 31) | |
| Normal Tissue Total Doses, Mean (Min, Max) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| RBE-Weighted | Absorbed (Max) | |||||
| Dog | BNCT Appl. | Left Eye Dmax = 6.5 Gy-eq | Right Eye Dmax = 6.5 Gy-eq | Brain Dmean = 7 Gy-eq | Skin Dmax = 22 Gy-eq | Mucosa Gy |
| Lucy | BNCT1 | 4.3 (3.6, 4.9) | 4.3 (3.6, 5.0) | 2.8 (1.1, 5.1) | 3.0 (0.2, 7.7) | 3.6 |
| BNCT2 | 4.3 (3.5, 5.0) | 5.7 (5.4, 6.2) | 3.4 (1.6, 5.6) | 4.3 (0.2, 10.6) | 5.0 | |
| Senshi | BNCT1 | 5.9 (5.2, 6.5) | 5.5 (5.0, 6.0) | 2.3 (0.9, 5.5) | 3.5 (0.2, 9.8) | 4.7 |
| BNCT2 | 6.1 (5.4, 6.7) | 5.7 (5.2, 6.2) | 2.3 (0.9, 5.7) | 3.6 (0.2, 10.0) | 4.9 | |
| Mora I | BNCT1 | 4.5 (3.2, 5.5) | 9.4 (7.9, 10.4) | 6.0 (3.8, 8.2) | 6.8 (0.7, 17.6) | 9.3 |
| BNCT2 | 1.5 (1.1, 1.8) | 2.7 (2.3, 3.2) | 1.9 (1.2, 2.7) | 1.9 (0.2, 5.1) | 2.6 | |
| Mora II | BNCT1 | 2.3 (1.8, 2.8) | 4.7 (3.6, 5.6) | 3.1 (1.8, 5.0) | 4.6 (0.9, 7.4) | 6.9 |
| BNCT2 | 1.9 (1.5, 2.3) | 4.0 (3.1, 4.8) | 2.5 (1.4, 4.2) | 4.0 (0.4, 10.5) | 6.7 | |
| Jake | BNCT1 | 4.3 (3.1, 5.7) | 4.0 (3.0, 5.4) | 1.5 (0.7, 4.0) | 3.4 (0.4, 15.3) | 7.7 |
| BNCT2 | 4.3 (3.1, 5.7) | 4.0 (3.0, 5.4) | 1.5 (0.7, 4.0) | 3.4 (0.4, 15.3) | 7.7 | |
| Patient | Histology/Pre-Treatment Tumor Volume (TV) | Complementary Treatment | BPA-BNCT | Response | Toxicity | Clinical Evaluation |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
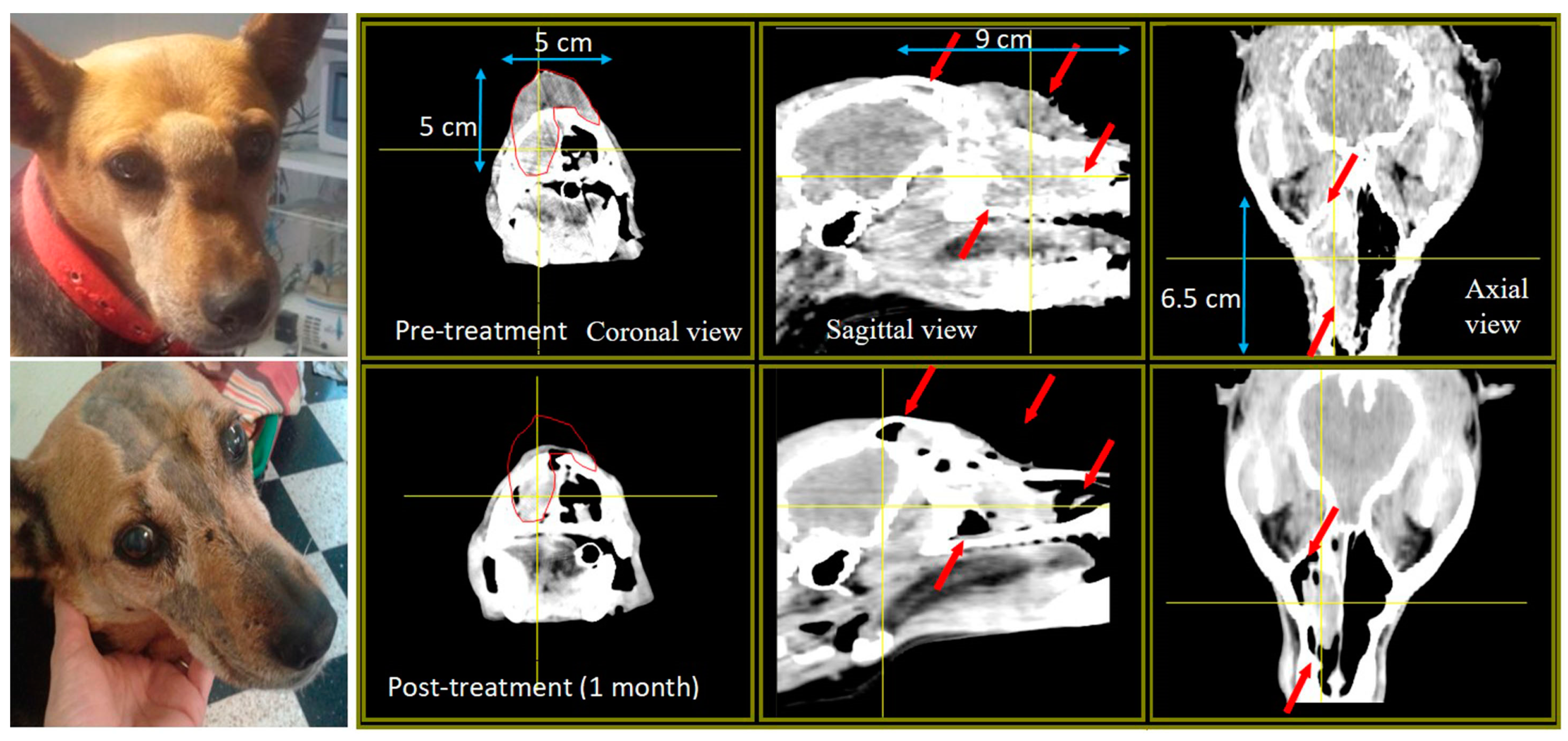
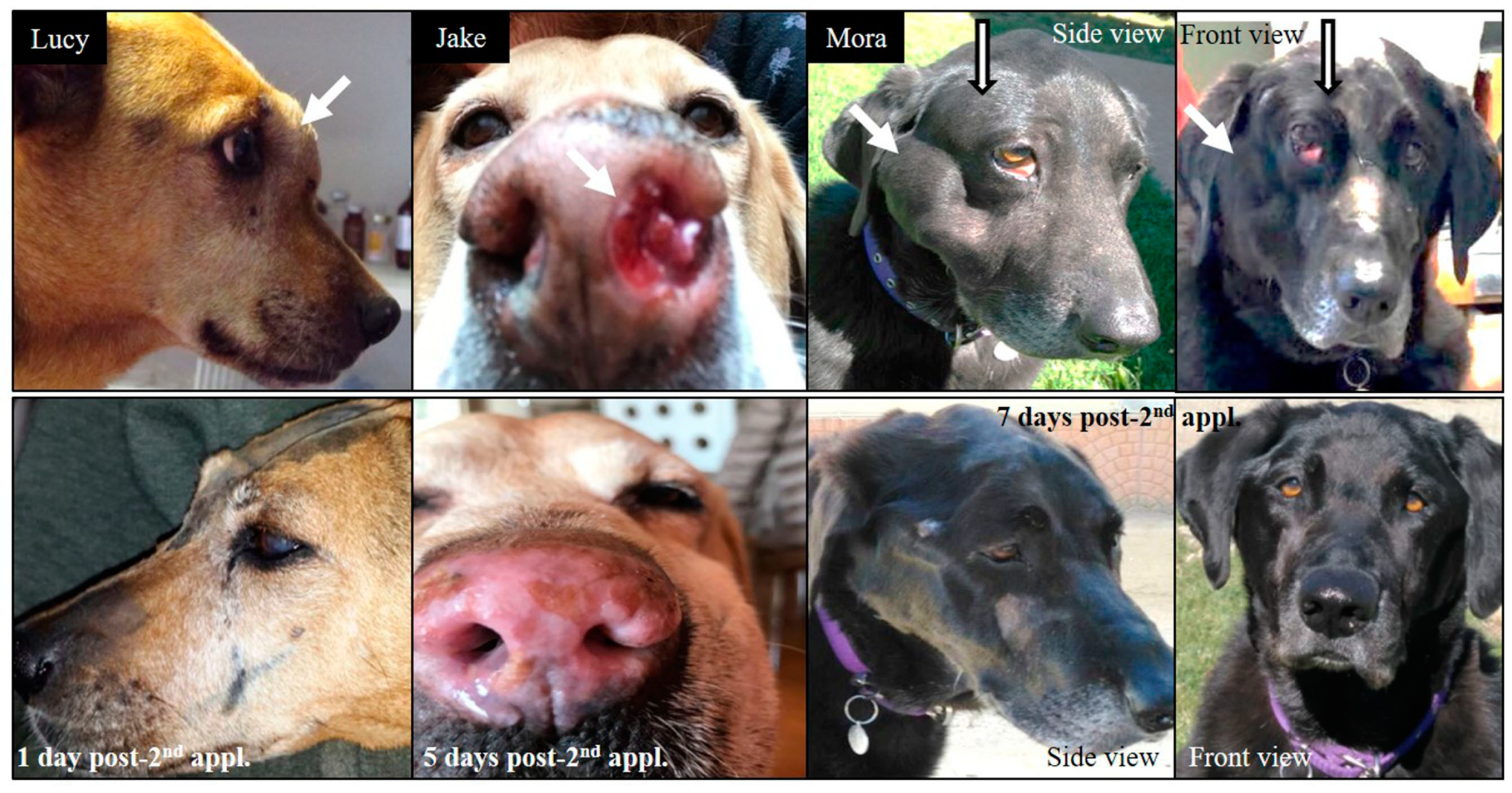
| Mixed-breed Lucy 12 years old | SCC nasal cavity and paranasal sinuses with bone destruction Pre-treatment TV: 51 cm3 Re-treatment Pre re-treatment TV: 77 cm3 | Chemo-therapy pre-BNCT | 2 appl., 3 weeks apart; 2 portals per appl. Re-treatment with full dose BNCT, 10 months after the first BNCT treatment, due to local tumor regrowth | Partial response (PR) TV 1 month post 1st treatment BNCT: 25 cm3 Cause of death: euthanasia due to recurrence and decline Survival post 1st treatment: 13.5 months Survival post re-treatment: 3 months | Mild nasal keratosis Mild mucositis Mild somnolence Re-treatment: Mild somnolence and eye irritation | Positive tumor response and clinical benefit For 8 months, optimum clinical signs and no protruding tumor mass. Re-treatment due to tumor regrowth at 10 months post 1st treatment Initial positive response, recurrence and decline 3 months after re-treatment |
| Alsatian Senshi 9–10 years old | Nasal chondrosarcoma TV: 105 cm3 | Chemo-therapy pre-BNCT | 2 appl., 3.5 weeks apart; 3 portals per appl. | PR TV 1 month post-BNCT: 57 cm3 Cause of death: euthanasia due to recurrence and decline Survival post BNCT: 10 months | Mild somnolence Mild–moderate nasal mucositis | Positive tumor response and clinical benefit |
| Labrador Mora I 9 years old | Oral amelanotic melanoma TV: 342 cm3 | 5 surgeries Immuno-therapy pre-BNCT | 2 appl., 5 weeks apart; 2 portals/appl. | PR TV 1 month post 1st appl.: 284 cm3 TV 2.5 months post 1st appl.: 149 cm3 Cause of death: Euthanasia due to lung metastasis diagnosed 2 months post BNCT Survival post 1st appl.: 2.5 months | Moderate mucositis | Positive tumor response and clinical benefit |
| Labrador Mora II 11 years old | Oral amelanotic melanoma TV: 12 cm3 | Surgery pre-BNCT Immuno-therapy 10 weeks post BNCT when liver and lung metastases were diagnosed | 2 appl., 4.5 weeks apart; 2 portals per appl. | PR TV 1 month post 1st appl.: 2.9 cm3 TV 2 months post 1st appl.: 0.60 cm3 Cause of death: recurrence and lung metastasis Survival post BNCT: 1 year | Mild mucositis | Positive but short-term tumor response and clinical benefit |
| Labrador Jake 12 years old | Nasal SCC (poorly differentiated) Myasthenia TV: 29 cm3 | 1 surgery pre-BNCT Palliative chemo-therapy 7 months post BNCT, after regrowth | 2 appl., 4.5 weeks apart; 2 portals per appl. | PR as revealed by complete reduction in visible tumor volume and improvement in quality of life Cause of death: euthanasia due to recurrence and decline No CT scan 1 month post treatment Survival: 8.5 months post-BNCT | Moderate–severe mucositis that responded to medication | Positive tumor response and clinical benefit |
© 2020 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Schwint, A.E.; Monti Hughes, A.; Garabalino, M.A.; Santa Cruz, G.A.; González, S.J.; Longhino, J.; Provenzano, L.; Oña, P.; Rao, M.; Cantarelli, M.d.l.Á.; et al. Clinical Veterinary Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) Studies in Dogs with Head and Neck Cancer: Bridging the Gap between Translational and Clinical Studies. Biology 2020, 9, 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9100327
Schwint AE, Monti Hughes A, Garabalino MA, Santa Cruz GA, González SJ, Longhino J, Provenzano L, Oña P, Rao M, Cantarelli MdlÁ, et al. Clinical Veterinary Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) Studies in Dogs with Head and Neck Cancer: Bridging the Gap between Translational and Clinical Studies. Biology. 2020; 9(10):327. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9100327
Chicago/Turabian StyleSchwint, Amanda E., Andrea Monti Hughes, Marcela A. Garabalino, Gustavo A. Santa Cruz, Sara J. González, Juan Longhino, Lucas Provenzano, Paulina Oña, Monica Rao, María de los Ángeles Cantarelli, and et al. 2020. "Clinical Veterinary Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) Studies in Dogs with Head and Neck Cancer: Bridging the Gap between Translational and Clinical Studies" Biology 9, no. 10: 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9100327
APA StyleSchwint, A. E., Monti Hughes, A., Garabalino, M. A., Santa Cruz, G. A., González, S. J., Longhino, J., Provenzano, L., Oña, P., Rao, M., Cantarelli, M. d. l. Á., Leiras, A., Olivera, M. S., Trivillin, V. A., Alessandrini, P., Brollo, F., Boggio, E., Costa, H., Ventimiglia, R., Binia, S., ... Santa Cruz, I. S. (2020). Clinical Veterinary Boron Neutron Capture Therapy (BNCT) Studies in Dogs with Head and Neck Cancer: Bridging the Gap between Translational and Clinical Studies. Biology, 9(10), 327. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology9100327








