Effects of Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Visually Guided Learning of Grip Force Control
Abstract
:1. Introduction
2. Experimental Section
2.1. Participants
2.2. Procedure
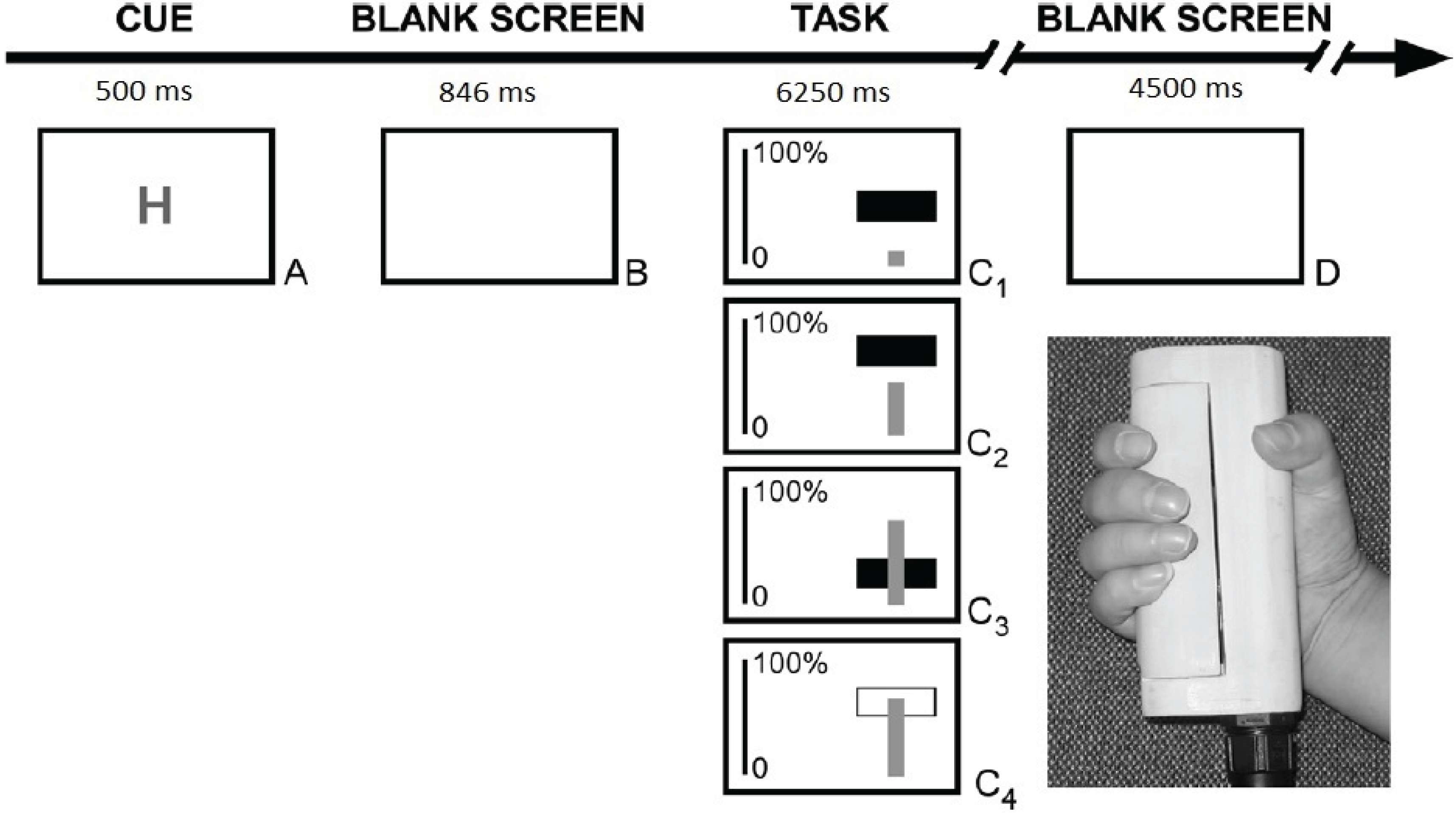
2.3. Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation
2.4. Experimental Protocol
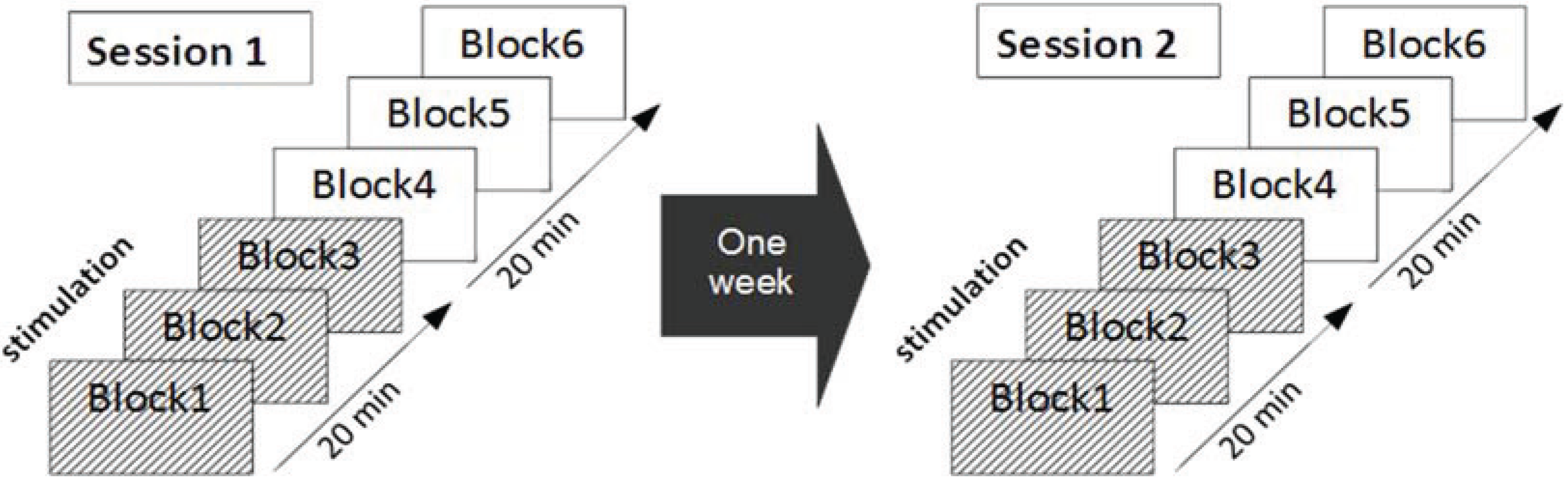
2.5. Data Analysis
3. Results
3.1. General Learning Effect
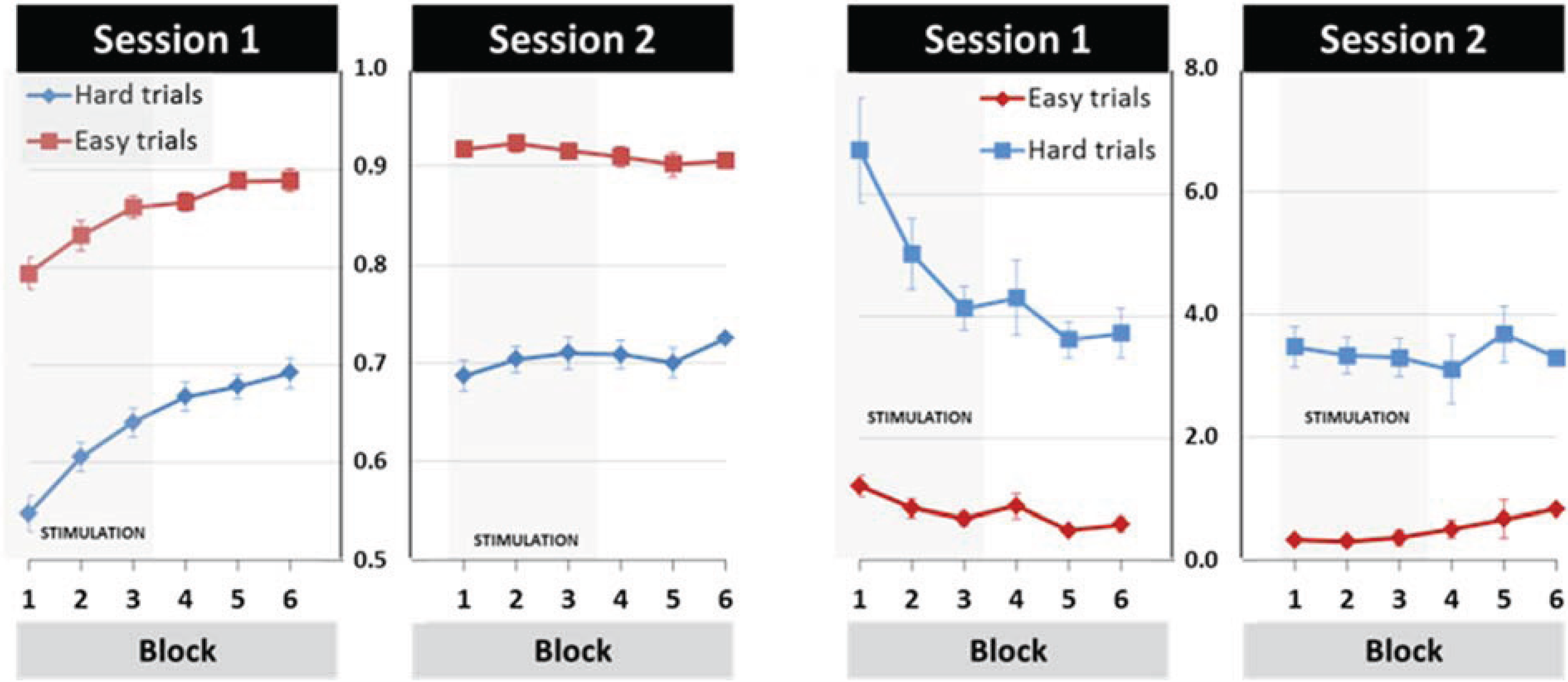
3.2. Modulation of Learning and Performance by tDCS Stimulation
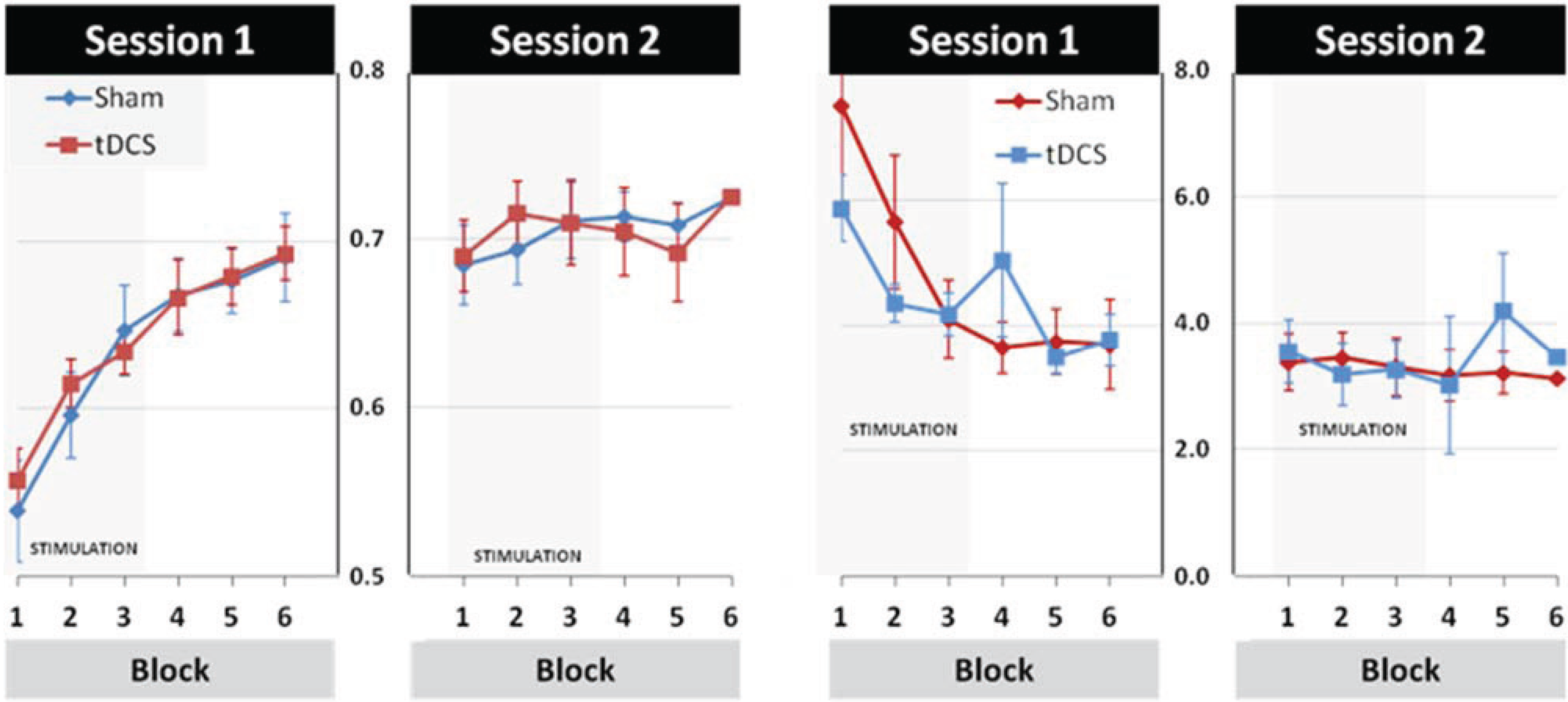
3.3. Effects of tDCS Stimulation on Early Learning and Retention
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Calautti, C.; Baron, J.C. Functional neuroimaging studies of motor recovery after stroke in adults: A review. Stroke 2003, 34, 1553–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hummel, F.C.; Cohen, L.G. Non-invasive brain stimulation: A new strategy to improve neurorehabilitation after stroke? Lancet Neurol. 2006, 5, 708–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liew, S.L.; Santarnecchi, E.; Buch, E.R.; Cohen, L.G. Non-invasive brain stimulation in neurorehabilitation: Local and distant effects for motor recovery. Front Hum. Neurosci. 2014, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, J.; Robertson, E.; Krakauer, J.W.; Rothwell, J.; Marshall, L.; Gerloff, C.; Wassermann, E.; Pascual-Leone, A.; Hummel, F.; Celnik, P.A.; et al. Consensus: “Can tDCS and TMS enhance motor learning and memory formation?”. Brain Stimul. 2008, 1, 363–369. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schulz, R.; Gerloff, C.; Hummel, F.C. Non-invasive brain stimulation in neurological diseases. Neuropharmacology 2013, 64, 579–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitsche, M.A.; Doemkes, S.; Karaköse, T.; Antal, A.; Liebetanz, D.; Lang, N.; Tergau, F.; Paulus, W. Shaping the effects of transcranial direct current stimulation of the human motor cortex. J. Neurophysiol. 2007, 97, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nitsche, M.A.; Paulus, W. Excitability changes induced in the human motor cortex by weak transcranial direct current stimulation. J. Physiol. 2000, 527, 633–639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fritsch, B.; Reis, J.; Martinowich, K.; Schambra, H.M.; Ji, Y.; Cohen, L.G.; Lu, B. Direct current stimulation promotes BDNF-dependent synaptic plasticity: Potential implications for motor learning. Neuron 2010, 66, 198–204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Utz, K.S.; Dimova, V.; Oppenländer, K.; Kerkhoff, G. Electrified minds: Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) and Galvanic Vestibular Stimulation (GVS) as methods of non-invasive brain stimulation in neuropsychology—A review of current data and future implications. Neuropsychologia 2010, 48, 2789–2810. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeyemo, B.O.; Simis, M.; Macea, D.D.; Fregni, F. Systematic review of parameters of stimulation, clinical trial design characteristics, and motor outcomes in non-invasive brain stimulation in stroke. Front Psychiatry 2012, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwardson, M.A.; Lucas, T.H.; Carey, J.R.; Fetz, E.E. New modalities of brain stimulation for stroke rehabilitation. Exp. Brain Res. 2013, 224, 335–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowak, D.A.; Grefkes, C.; Ameli, M.; Fink, G.R. Interhemispheric competition after stroke: Brain stimulation to enhance recovery of function of the affected hand. Neurorehabil. Neural Repair 2009, 23, 641–656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fregni, F.; Boggio, P.S.; Santos, M.C.; Lima, M.; Vieira, A.L.; Rigonatti, S.P.; Silva, M.T.; Barbosa, E.R.; Nitsche, M.A.; Pascual-Leone, A. Noninvasive cortical stimulation with transcranial direct current stimulation in Parkinson’s disease. Mov. Disord. 2006, 21, 1693–1702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Butler, A.J.; Shuster, M.; O’Hara, E.; Hurley, K.; Middlebrooks, D.; Guilkey, K. A meta-analysis of the efficacy of anodal transcranial direct current stimulation for upper limb motor recovery in stroke survivors. J. Hand Ther. 2013, 26, 162–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elsner, B.; Kugler, J.; Pohl, M.; Mehrholz, J. Transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) for improving function and activities of daily living in patients after stroke. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2013, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O’Shea, J.; Boudrias, M.H.; Stagg, C.J.; Bachtiar, V.; Kischka, U.; Blicher, J.U.; Johansen-Berg, H. Predicting behavioural response to TDCS in chronic motor stroke. Neuroimage 2014, 85, 924–933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bastani, A.; Jaberzadeh, S. Does anodal transcranial direct current stimulation enhance excitability of the motor cortex and motor function in healthy individuals and subjects with stroke: A systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2012, 123, 644–657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antal, A.; Nitsche, M.A.; Kincses, T.Z.; Kruse, W.; Hoffmann, K.P.; Paulus, W. Facilitation of visuo-motor learning by transcranial direct current stimulation of the motor and extrastriate visual areas in humans. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2004, 19, 2888–2892. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vollmann, H.; Conde, V.; Sewerin, S.; Taubert, M.; Sehm, B.; Witte, O.W.; Villringer, A.; Ragert, P. Anodal transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) over supplementary motor area (SMA) but not pre-SMA promotes short-term visuomotor learning. Brain Stimul. 2013, 6, 101–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saiote, C.; Polanía, R.; Rosenberger, K.; Paulus, W.; Antal, A. High-frequency TRNS reduces BOLD activity during visuomotor learning. PLOS ONE 2013, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, J.M.; Vazquez, A.; Pasricha, N.; de Xivry, J.J.; Celnik, P. Dissociating the roles of the cerebellum and motor cortex during adaptive learning: The motor cortex retains what the cerebellum learns. Cereb. Cortex 2011, 21, 1761–1770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saucedo Marquez, C.M.; Zhang, X.; Swinnen, S.P.; Meesen, R.; Wenderoth, N. Task-specific effect of transcranial direct current stimulation on motor learning. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halder, P.; Sterr, A.; Brem, S.; Bucher, K.; Kollias, S.; Brandeis, D. Electrophysiological evidence for cortical plasticity with movement repetition. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 21, 2271–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kranczioch, C.; Athanassiou, S.; Shen, S.; Gao, G.; Sterr, A. Short-term learning of a visually guided power-grip task is associated with dynamic changes in EEG oscillatory activity. Clin. Neurophysiol. 2008, 119, 1419–1430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sterr, A.; Shen, S.; Kranczioch, C.; Szameitat, A.J.; Hou, W.; Sorger, B. fMRI effects of task demand and feedback accuracy on grip force tracking. Neurosci. Lett. 2009, 457, 61–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Berker, A.O.; Bikson, M.; Bestmann, S. Predicting the behavioral impact of transcranial direct current stimulation: Issues and limitations. Front. Hum. Neurosci. 2013, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, N.; Siebner, H.R.; Ward, N.S.; Lee, L.; Nitsche, M.A.; Paulus, W.; Rothwell, J.C.; Lemon, R.N.; Frackowiak, R.S. How does transcranial DC stimulation of the primary motor cortex alter regional neuronal activity in the human brain? Eur. J. Neurosci. 2005, 22, 495–504. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, X.; Alsop, D.C.; Schlaug, G. Effects of transcranial direct current stimulation (tDCS) on human regional cerebral blood flow. Neuroimage 2011, 58, 26–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Notturno, F.; Marzetti, L.; Pizzella, V.; Uncini, A.; Zappasodi, F. Local and remote effects of transcranial direct current stimulation on the electrical activity of the motor cortical network. Hum. Brain Mapp. 2014, 35, 2220–2232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardwick, R.M.; Rottschy, C.; Miall, R.C.; Eickhoff, S.B. A quantitative meta-analysis and review of motor learning in the human brain. Neuroimage 2013, 67, 283–297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nishitani, N.; Uutela, K.; Shibasaki, H.; Hari, R. Cortical visuomotor integration during eye pursuit and eye-finger pursuit. J. Neurosci. 1999, 19, 2647–2657. [Google Scholar]
- Miall, R.C.; Reckess, G.Z.; Imamizu, H. The cerebellum coordinates eye and hand tracking movements. Nat. Neurosci. 2001, 4, 638–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krakauer, J.W.; Shadmehr, R. Consolidation of motor memory. Trends Neurosci. 2006, 29, 58–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reis, J.; Schambra, H.M.; Cohen, L.G.; Buch, E.R.; Fritsch, B.; Zarahn, E.; Celnik, P.A.; Krakauer, J.W. Noninvasive cortical stimulation enhances motor skill acquisition over multiple days through an effect on consolidation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2009, 106, 1590–1595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanes, J.N.; Donoghue, J.P. Plasticity and primary motor cortex. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 2000, 23, 393–415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sanes, J.N. Neocortical mechanisms in motor learning. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2003, 13, 225–231. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, T.; Sacco, P.; Nitsche, M.A.; Turner, D.L. Modulation of internal model formation during force field-induced motor learning by anodal transcranial direct current stimulation of primary motor cortex. J. Physiol. 2009, 587, 2949–2961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wiethoff, S.; Hamada, M.; Rothwell, J.C. Variability in Response to Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation of the Motor Cortex. Brain Stimul. 2014, 7, 468–475. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cramer, S.C.; Sur, M.; Dobkin, B.H.; O’Brien, C.; Sanger, T.D.; Trojanowski, J.Q.; Rumsey, J.M.; Hicks, R.; Cameron, J.; Chen, D.; et al. Harnessing neuroplasticity for clinical applications. Brain 2011, 134, 1591–1609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
© 2015 by the authors; licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Minarik, T.; Sauseng, P.; Dunne, L.; Berger, B.; Sterr, A. Effects of Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Visually Guided Learning of Grip Force Control. Biology 2015, 4, 173-186. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4010173
Minarik T, Sauseng P, Dunne L, Berger B, Sterr A. Effects of Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Visually Guided Learning of Grip Force Control. Biology. 2015; 4(1):173-186. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4010173
Chicago/Turabian StyleMinarik, Tamas, Paul Sauseng, Lewis Dunne, Barbara Berger, and Annette Sterr. 2015. "Effects of Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Visually Guided Learning of Grip Force Control" Biology 4, no. 1: 173-186. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4010173
APA StyleMinarik, T., Sauseng, P., Dunne, L., Berger, B., & Sterr, A. (2015). Effects of Anodal Transcranial Direct Current Stimulation on Visually Guided Learning of Grip Force Control. Biology, 4(1), 173-186. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology4010173




