Contrasting Assembly and Network Roles of Abundant and Rare Bacteria in Reservoir and Soil Habitats
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
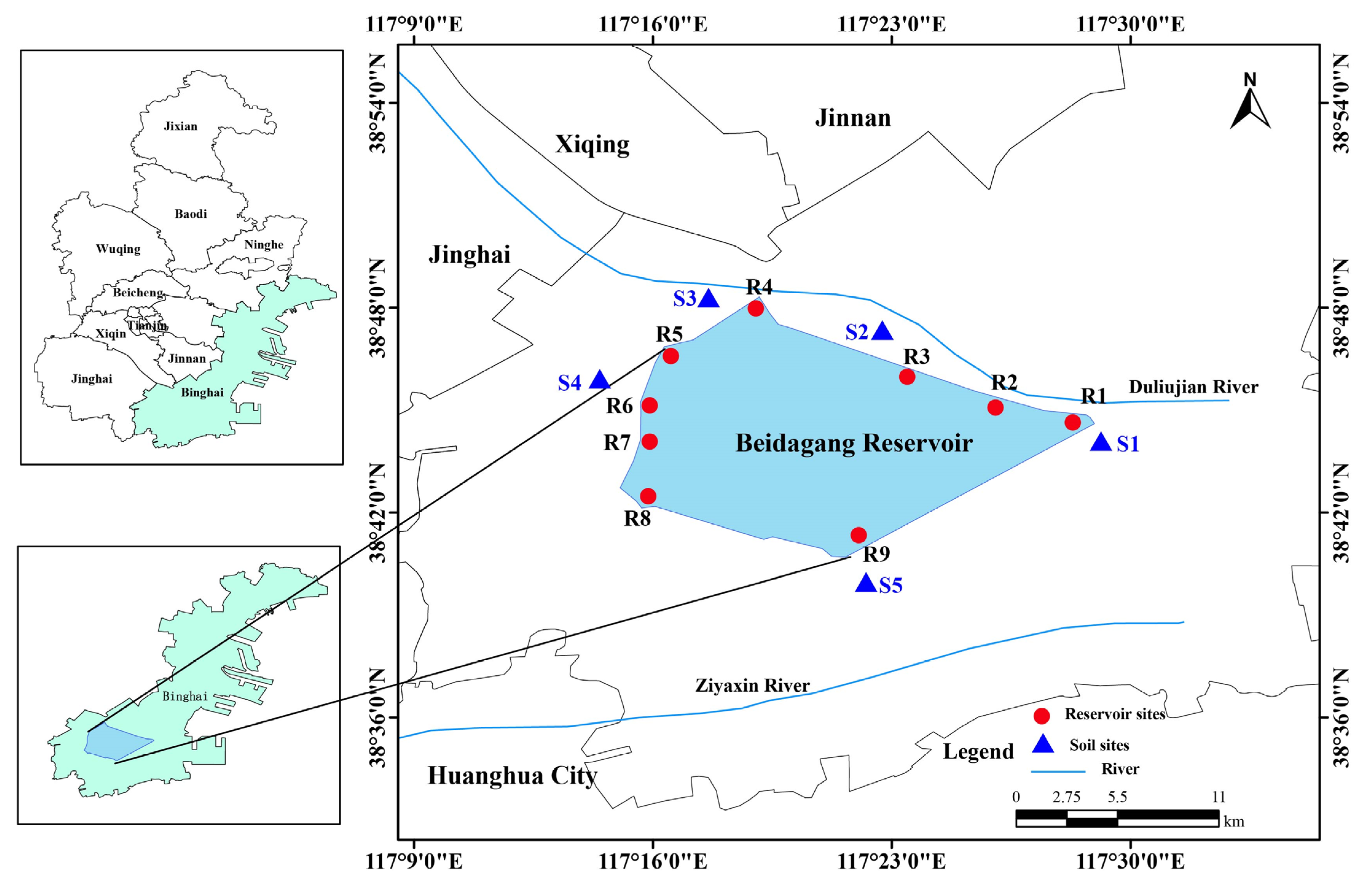
2.1. Sample Collection and Physicochemical Analysis
2.2. DNA Extraction, PCR Amplification, and Sequencing Analysis
2.3. Statistical Analyses
3. Results
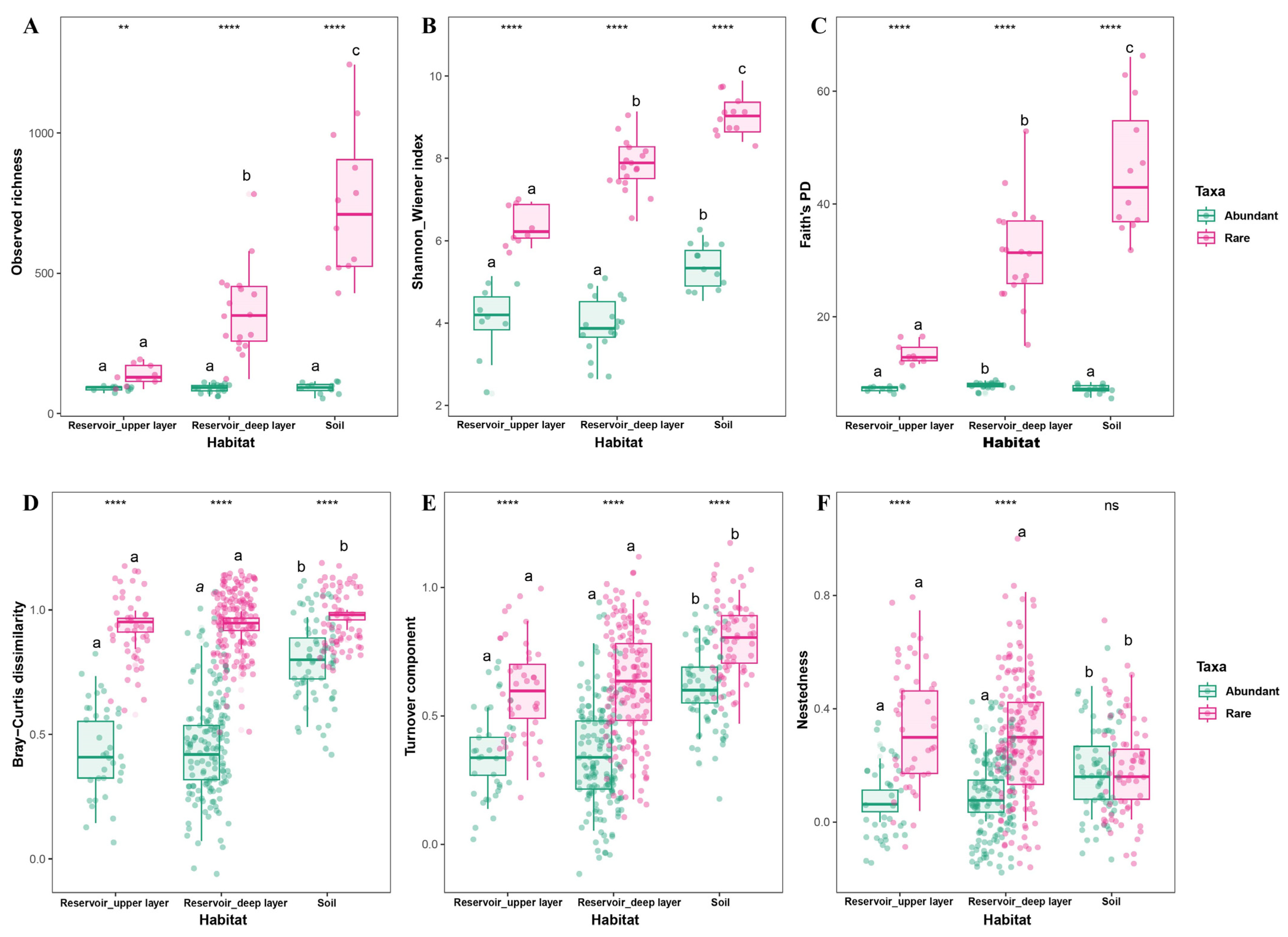
3.1. Community Structure and Diversity of Abundant and Rare Taxa in Reservoir and Adjacent Soil
3.2. Community Composition of Abundant and Rare Taxa in the Reservoir and Adjacent Soil
3.3. Influencing Factors and Assembly Mechanisms of Abundant and Rare Bacterial Taxa
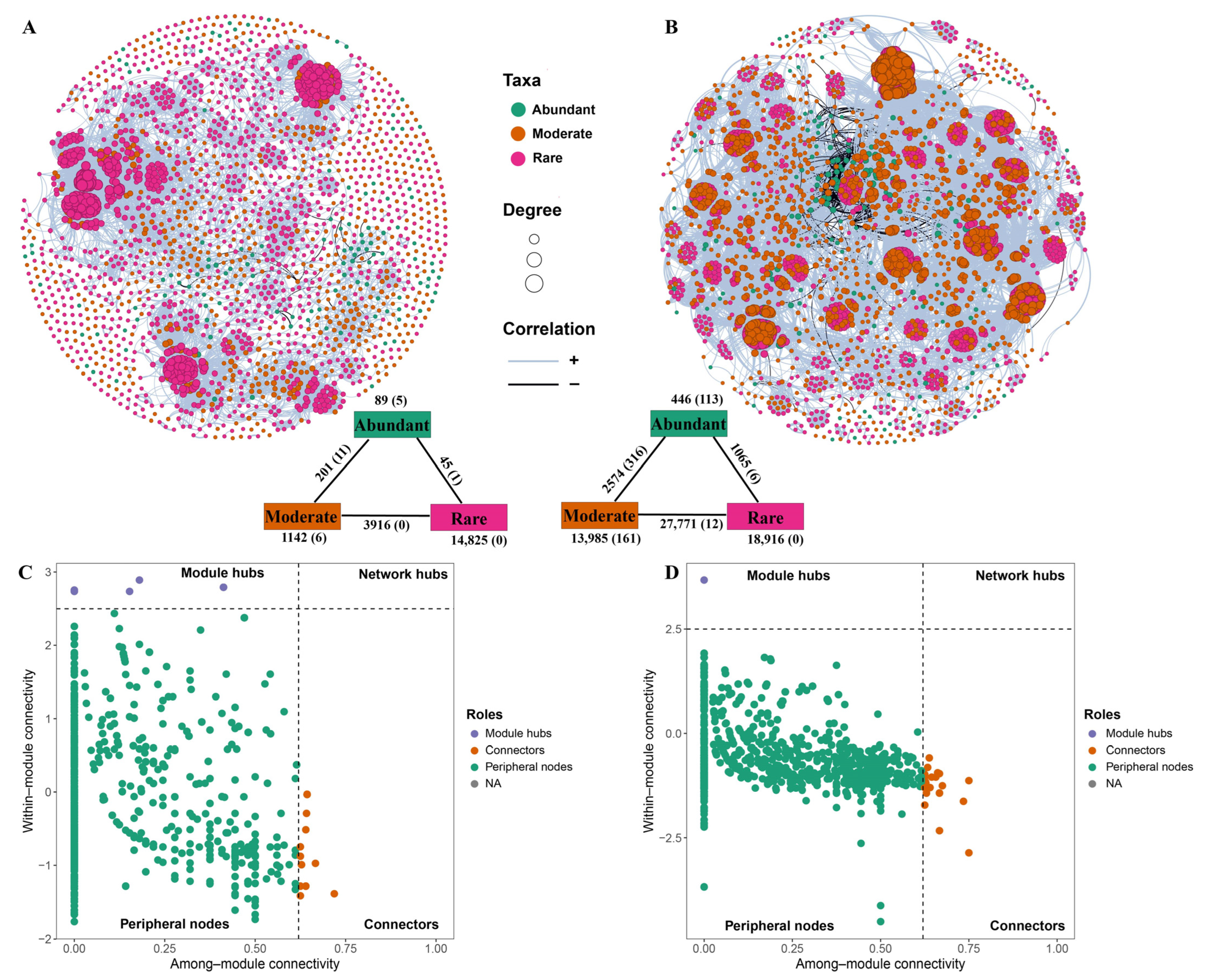
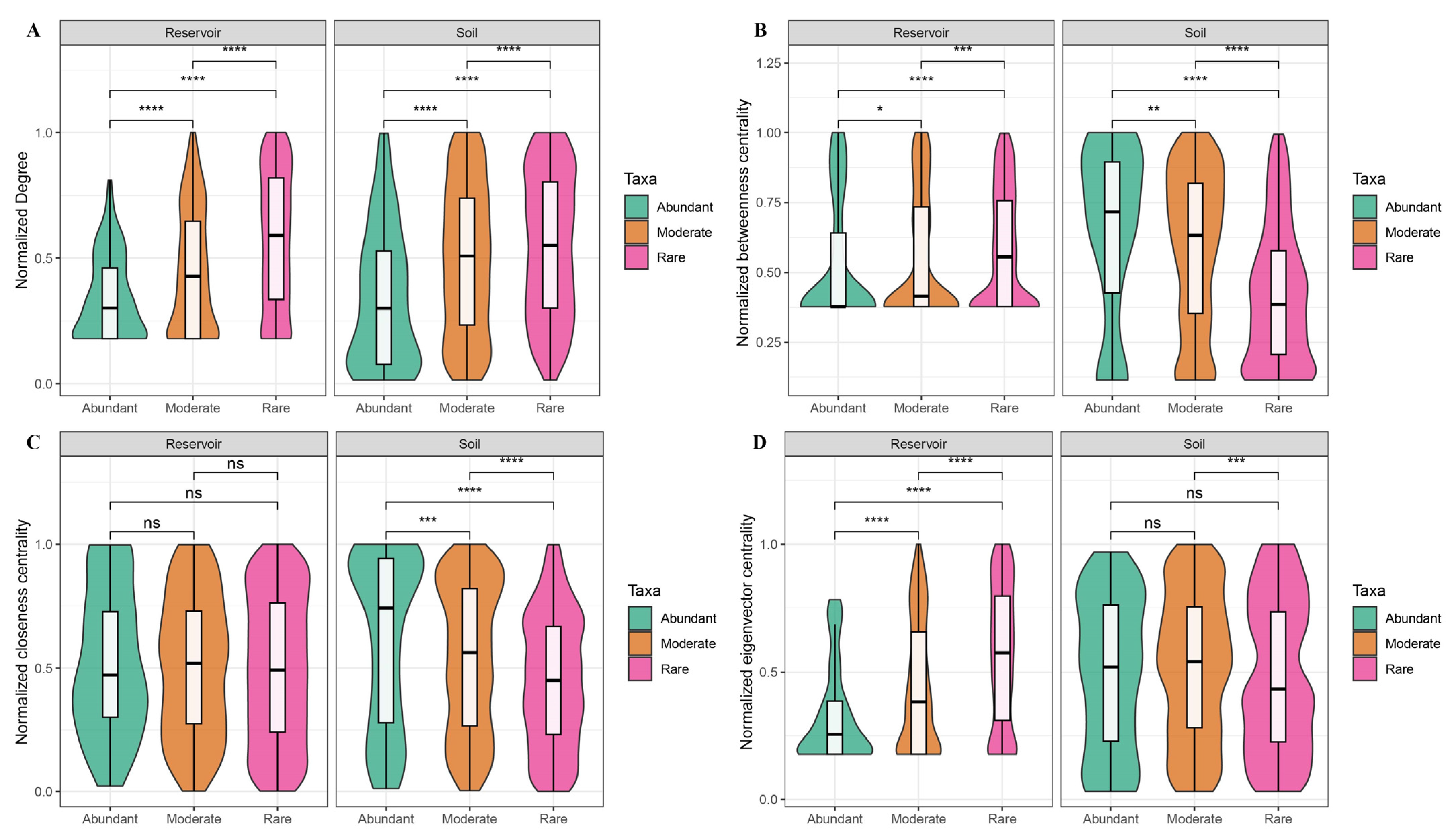
3.4. Co-Occurrence Networks of the Bacterial Community in the Reservoir and Soil
4. Discussion
4.1. The Community Structure of Abundant and Rare Taxa in the Reservoir and Adjacent Soil
4.2. Influencing Environmental Factors and Assembly Mechanisms of Abundant and Rare Taxa in Reservoir Water and Adjacent Soil
4.3. The Ecological Role of Abundant and Rare Taxa in the Network of the Reservoir and Adjacent Soil
4.4. Limitations of This Study
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Eh | Oxidation-reduction potential |
| TDS | Total dissolved solids |
| DOC | Dissolved organic carbon |
| TN | Total nitrogen |
| TP | Total phosphorus |
| NH4+–N | Ammonia nitrogen |
| TSS | Total soil salt |
| TOC | Total organic carbon |
| CEC | Cation exchange capacity |
| PCR | Polymerase chain reaction |
| ASV | Amplicon sequence variant |
| PCoA | Principal coordinates analysis |
| PERMANOVA | Permutational multivariate analysis of variance |
| NMDS | Non-metric multidimensional scaling |
| ANOSIM | Analysis of similarity |
| Faith’s PD | Faith’s phylogenetic diversity |
| LEfSe | Linear discriminant analysis effect size |
| CCA | Canonical correspondence analysis |
| βNTI | β-nearest taxon index |
| RCbray | Bray–Curtis-based Raup–Crick |
| MEMs | Moran’s eigenvector maps |
References
- Hopkinson, C.S.; Wolanski, E.; Cahoon, D.R.; Perillo, G.M.E.; Brinson, M.M. Chapter 1—Coastal Wetlands: A Synthesis. In Coastal Wetlands, 2nd ed.; Perillo, G.M.E., Wolanski, E., Cahoon, D.R., Hopkinson, C.S., Eds.; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2019; pp. 1–75. [Google Scholar]
- Jin, G.Q.; Mo, Y.M.; Li, M.D.; Tang, H.W.; Qi, Y.Z.; Li, L.; Barry, D.A. Desalinization and salinization: A review of major challenges for coastal reservoirs. J. Coast. Res. 2019, 35, 664–672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.M.; Jin, G.Q.; Zhang, C.M.; Xu, J.; Tang, H.W.; Shen, C.J.; Scheuermann, A.; Li, L. Combined effect of inland groundwater input and tides on flow and salinization in the coastal reservoir and adjacent aquifer. J. Hydrol. 2021, 600, 126575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Zhang, Q.; Su, S.; Zhang, X.; Xiao, H. Salinity Gradients Override Hydraulic Connectivity in Shaping Bacterial Community Assembly and Network Stability at a Coastal Aquifer–Reservoir Interface. Microorganisms 2025, 13, 1611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mao, D.; Wang, Y.; Guo, Q.; Li, D.; Liu, S.; Meng, J.; Hu, L. Heterogeneous reservoir seepage characterized by geophysical, hydrochemical, and hydrologic methods. Geophysics 2024, 89, B401–B413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hillel, D. Introduction to Environmental Soil Physics; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2003. [Google Scholar]
- Garcia, C.A.; Huntington, J.M.; Buto, S.G.; Moreo, M.T.; Smith, J.L.; Andraski, B.J. Groundwater Discharge by Evapotranspiration, Dixie Valley, West-Central Nevada, March 2009-September 2011; 2330-7102; US Geological Survey: Reston, VA, USA, 2014. [Google Scholar]
- Newton, R.J.; Jones, S.E.; Eiler, A.; McMahon, K.D.; Bertilsson, S. A Guide to the Natural History of Freshwater Lake Bacteria. Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2011, 75, 14–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.; Wang, J.; Li, J.; Liu, G.; Dong, Q.g.; Zou, Y.; Chau, H.W.; Zhang, C. Different roles of core and noncore bacterial taxa in maintaining soil multinutrient cycling and microbial network stability in arid fertigation agroecosystems. J. Appl. Ecol. 2022, 59, 2154–2165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Qi, X.; Yuan, Y.; Zhou, H.; Rong, X.; Dang, Z.; Yin, H. Deciphering the distinct successional patterns and potential roles of abundant and rare microbial taxa of urban riverine plastisphere. J. Hazard. Mater. 2023, 450, 131080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyirabuhoro, P.; Liu, M.; Xiao, P.; Liu, L.; Yu, Z.; Wang, L.; Yang, J. Seasonal variability of conditionally rare taxa in the water column bacterioplankton community of subtropical reservoirs in China. Microb. Ecol. 2020, 80, 14–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nyirabuhoro, P.; Gao, X.; Ndayishimiye, J.C.; Xiao, P.; Mo, Y.; Ganjidoust, H.; Yang, J. Responses of abundant and rare bacterioplankton to temporal change in a subtropical urban reservoir. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiab036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dang, C.; Wang, J.; He, Y.; Yang, S.; Chen, Y.; Liu, T.; Fu, J.; Chen, Q.; Ni, J. Rare biosphere regulates the planktonic and sedimentary bacteria by disparate ecological processes in a large source water reservoir. Water Res. 2022, 216, 118296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xue, Y.Y.; Chen, H.H.; Yang, J.R.; Liu, M.; Huang, B.Q.; Yang, J. Distinct patterns and processes of abundant and rare eukaryotic plankton communities following a reservoir cyanobacterial bloom. ISME J. 2018, 12, 2263–2277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.; Lu, Y.; Wei, G.; Jiao, S. Rare species-driven diversity–ecosystem multifunctionality relationships are promoted by stochastic community assembly. MBio 2022, 13, e00449-22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lennon, J.T.; Jones, S.E. Microbial seed banks: The ecological and evolutionary implications of dormancy. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2011, 9, 119–130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Debroas, D.; Hugoni, M.; Domaizon, I. Evidence for an active rare biosphere within freshwater protists community. Mol. Ecol. 2015, 24, 1236–1247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, L.; Niu, W.; Li, G.; Du, Y.; Sun, J.; Zhang, Q.; Siddique, K.H.M. Crucial role of rare taxa in preserving bacterial community stability. Land Degrad. Dev. 2023, 35, 1397–1410. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, M.D.; Neufeld, J.D. Ecology and exploration of the rare biosphere. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2015, 13, 217–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pascoal, F.; Costa, R.; Magalhães, C. The microbial rare biosphere: Current concepts, methods and ecological principles. FEMS Microbiol. Ecol. 2021, 97, fiaa227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dini-Andreote, F.; Stegen, J.C.; Van Elsas, J.D.; Salles, J.F. Disentangling mechanisms that mediate the balance between stochastic and deterministic processes in microbial succession. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2015, 112, E1326–E1332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.Z.; Ning, D.L. Stochastic community assembly: Does it matter in microbial ecology? Microbiol. Mol. Biol. Rev. 2017, 81, e00002–e00017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stegen, J.C.; Lin, X.; Fredrickson, J.K.; Chen, X.; Kennedy, D.W.; Murray, C.J.; Rockhold, M.L.; Konopka, A. Quantifying community assembly processes and identifying features that impose them. ISME J. 2013, 7, 2069–2079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hubbell, S.P. The Unified Neutral Theory of Biodiversity and Biogeography; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, J.; Hein, T.; Yuan, Q.; Shu, W.; Huang, X.; Zhang, X.; Wang, L. Co-occurrence patterns and assembly processes of abundant and rare bacterioplankton in plain river network areas of eastern China. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 150, 110204. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, R.; Wang, D.; Jia, S.; Li, Q.; Liu, S.; Zhang, X.X. Dynamics of bacterioplankton communities in the estuary areas of the Taihu Lake: Distinct ecological mechanisms of abundant and rare communities. Environ. Res. 2024, 242, 117782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Cheng, K.; Li, K.; Jin, Y.; He, X. Deciphering the diversity patterns and community assembly of rare and abundant bacterial communities in a wetland system. Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 838, 156334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, G.F.; Peng, D.; Tripathi, B.M.; Zhang, Y.H.; Chu, H.Y. Distinct community assembly processes of abundant and rare soil bacteria in coastal wetlands along an inundation gradient. mSystems 2020, 5, e01150-20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, X.; Mansoldo, F.R.P.; An, J.; Kou, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Zeng, J.; Vermelho, A.B.; Yao, M. Microbial habitat specificity largely affects microbial co-occurrence patterns and functional profiles in wetland soils. Geoderma 2022, 418, 115866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, K.; Ren, Z.; Ma, J.; Chen, N.; Liu, J. Differential patterns and assembly processes of bacterial communities from distinct microhabitats in a subtropical estuary. Front. Mar. Sci. 2022, 9, 1039387. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.; Chen, C.; Grossart, H.P.; Liu, Y. Community assembly characteristics of abundant and rare bacterial taxa in water, sediment and riparian soil of Wujiang river, China. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2025, 297, 118262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, S.; Li, K.; Hu, J.; Wang, F.; Chen, D.; Zhang, Z.; Li, T.; Li, L.; Tao, J.; Liu, D.; et al. Distinct assembly mechanisms of microbial sub-communities with different rarity along the Nu River. J. Soils Sediments 2022, 22, 1530–1545. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morriën, E.; Hannula, S.E.; Snoek, L.B.; Helmsing, N.R.; Zweers, H.; De Hollander, M.; Soto, R.L.; Bouffaud, M.-L.; Buée, M.; Dimmers, W. Soil networks become more connected and take up more carbon as nature restoration progresses. Nat. Commun. 2017, 8, 14349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, Q.; Wang, S.; Hou, W.; Feng, K.; Li, F.; Hai, W.; Zhang, Y.; Sun, Y.; Deng, Y. Temperature and microbial interactions drive the deterministic assembly processes in sediments of hot springs. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 772, 145465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Huang, J.; Xia, Y.; Yang, Y.; Yu, Y.; Zhou, K.; Lin, L.; Li, X.; Li, B. Spatial distribution and assembly processes of bacterial communities in riverine and coastal ecosystems of a rapidly urbanizing megacity in China. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 934, 173298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faust, K.; Raes, J. Microbial interactions: From networks to models. Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2012, 10, 538–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newman, M.E.J. Modularity and community structure in networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 8577–8582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, Z.; Xiao, M.; Yue, F.; Yi, Y.; Mostofa, K. Seasonal Variations of Dissolved Organic Matter by Fluorescent Analysis in a Typical River Catchment in Northern China. Water 2021, 13, 494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Page, A.L.; Miller, R.H.; Keeney, D.R. Methods of Soil Analysis, Part 2, Chemical and Microbiological Properties; Americal Society of Agronomy, Inc.: Madison, WI, USA, 1982. [Google Scholar]
- Jackson, M.L. Soil Chemical Analysis; Pretice-Hall, Inc.: Englewood Cliffs, NJ, USA, 1958. [Google Scholar]
- HJ 634-2012; Soil Determination of Ammonium, Nitrite, and Nitrate Nitrogen Potassium Chloride Solution Extraction-Spectrophotometric Methods. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2012.
- HJ 889-2017; Soil Determination of Cation Exchange Capacity (CEC) Hexaamminecobalt Trichloride Solution Extraction-Spectrophotometric Method. Ministry of Ecology and Environment of the People’s Republic of China: Beijing, China, 2017.
- Nossa, C.W.; Oberdorf, W.E.; Yang, L.; Aas, J.A.; Paster, B.J.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Brodie, E.L.; Malamud, D.; Poles, M.A.; Pei, Z. Design of 16S rRNA gene primers for 454 pyrosequencing of the human foregut microbiome. World J. Gastroenterol. 2010, 16, 4135–4144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Z.; DeSantis, T.Z.; Andersen, G.L.; Knight, R. Accurate taxonomy assignments from 16S rRNA sequences produced by highly parallel pyrosequencers. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36, e120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Callahan, B.J.; McMurdie, P.J.; Rosen, M.J.; Han, A.W.; Johnson, A.J.A.; Holmes, S.P. DADA2: High-resolution sample inference from Illumina amplicon data. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 581–583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quast, C.; Pruesse, E.; Yilmaz, P.; Gerken, J.; Schweer, T.; Yarza, P.; Peplies, J.; Glöckner, F.O. The SILVA ribosomal RNA gene database project: Improved data processing and web-based tools. Nucleic Acids Res. 2013, 41, 590–596. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Jin, L.; Zhang, C.; Li, S.; Zhou, T.; Hua, Z.; Wang, L.; Ji, S.; Wang, Y.; Gan, Y.; et al. Destabilized microbial networks with distinct performances of abundant and rare biospheres in maintaining networks under increasing salinity stress. iMeta 2023, 2, e79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Li, P.; Yin, M.; Wang, J.; Sun, Y.; Ju, W.; Liu, L.; Li, Z.H. Deciphering characterization of seasonal variations in microbial communities of marine ranching: Diversity, co-occurrence network patterns, and assembly processes. Mar. Pollut. Bull. 2023, 197, 115739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gobet, A.; Quince, C.; Ramette, A. Multivariate Cutoff Level Analysis (MultiCoLA) of large community data sets. Nucleic Acids Res. 2010, 38, e155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Yang, J.; Yu, Z.; Wilkinson, D.M. The biogeography of abundant and rare bacterioplankton in the lakes and reservoirs of China. ISME J. 2015, 9, 2068–2077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katoh, K.; Standley, D.M. MAFFT Multiple Sequence Alignment Software Version 7: Improvements in Performance and Usability. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2013, 30, 772–780. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, M.N.; Dehal, P.S.; Arkin, A.P. FastTree 2–approximately maximum-likelihood trees for large alignments. PLoS ONE 2010, 5, e9490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kembel, S.W.; Cowan, P.D.; Helmus, M.R.; Cornwell, W.K.; Morlon, H.; Ackerly, D.D.; Blomberg, S.P.; Webb, C.O. Picante: R tools for integrating phylogenies and ecology. Bioinformatics 2010, 26, 1463–1464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, C.; Gunina, A.; Luo, Y.; Wang, J.; He, J.-Z.; Kuzyakov, Y.; Hemp, A.; Classen, A.T.; Ge, Y. Contrasting patterns and drivers of soil bacterial and fungal diversity across a mountain gradient. Environ. Microbiol. 2020, 22, 3287–3301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Segata, N.; Izard, J.; Waldron, L.; Gevers, D.; Miropolsky, L.; Garrett, W.S.; Huttenhower, C. Metagenomic biomarker discovery and explanation. Genome Biol. 2011, 12, R60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Lian, C.; Wan, W.; Qiu, Z.; Luo, X.; Huang, Q.; Deng, Y.; Zhang, T.; Yu, K. Salinity-triggered homogeneous selection constrains the microbial function and stability in lakes. Appl. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2023, 107, 6591–6605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levins, R. Evolution in Changing Environments: Some Theoretical Explorations; Princeton University Press: Princeton, NJ, USA, 1968. [Google Scholar]
- Anderson, M.J.; Walsh, D.C. PERMANOVA, ANOSIM, and the Mantel test in the face of heterogeneous dispersions: What null hypothesis are you testing? Ecol. Monogr. 2013, 83, 557–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Legendre, P.; Legendre, L. Numerical Ecology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2012; Volume 24. [Google Scholar]
- Benjamini, Y.; Hochberg, Y. Controlling the false discovery rate: A practical and powerful approach to multiple testing. J. R. Stat. Soc. Ser. B Methodol. 1995, 57, 289–300. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Olesen, J.M.; Bascompte, J.; Dupont, Y.L.; Jordano, P. The modularity of pollination networks. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2007, 104, 19891–19896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guimerà, R.; Amaral, L.A.N. Functional cartography of complex metabolic networks. Nature 2005, 433, 895–900. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Strogatz, S.H. Exploring complex networks. Nature 2001, 410, 268–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Röttjers, L.; Faust, K. Can we predict keystones? Nat. Rev. Microbiol. 2019, 17, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shi, S.; Nuccio, E.E.; Shi, Z.J.; He, Z.; Zhou, J.; Firestone, M.K. The interconnected rhizosphere: High network complexity dominates rhizosphere assemblages. Ecol. Lett. 2016, 19, 926–936. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Delgado-Baquerizo, M.; Shi, Y.; Liu, X.; Yang, Y.; Chu, H. Co-existing water and sediment bacteria are driven by contrasting environmental factors across glacier-fed aquatic systems. Water Res. 2021, 198, 117139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, X.; He, Z.; Wang, Y.; Wang, F.; Zheng, Z.; Zuo, Y.; Cao, Y.; Yao, X.; She, Z.; Ge, Y.; et al. Assessment of soil microbial communities and diversity in typical coastal wetlands along a succession gradient: Implications for reconstructing the long-term evolution of coastal wetlands. Environ. Technol. Innov. 2025, 39, 104263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujakić, I.; Cabello-Yeves, P.J.; Villena-Alemany, C.; Piwosz, K.; Rodriguez-Valera, F.; Picazo, A.; Camacho, A.; Koblížek, M. Multi-environment ecogenomics analysis of the cosmopolitan phylum Gemmatimonadota. Microbiol. Spectr. 2023, 11, e01112-23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mujakić, I.; Piwosz, K.; Koblížek, M. Phylum Gemmatimonadota and Its Role in the Environment. Microorganisms 2022, 10, 151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- La, W.; Han, X.; Liu, C.Q.; Ding, H.; Liu, M.; Sun, F.; Li, S.; Lang, Y. Sulfate concentrations affect sulfate reduction pathways and methane consumption in coastal wetlands. Water Res. 2022, 217, 118441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, J.; Zou, X.; Qu, M.; Li, J. Groundwater depth regulates assembly processes of abundant and rare bacterial communities across arid inland river basin. J. Environ. Manag. 2022, 319, 115767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yue, F.; Li, S.; Li, X.; Lang, Y.; Hu, J.; Ding, H.; Liu, C. Spatial variations in water chemical components in a coastal zone of northern China: Insights from environmental isotopes. J. Hydrol. 2022, 612, 128054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Hao, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhao, X.; Fu, X.; Wang, W.; He, D.; Li, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; et al. Source identification of sedimentary organic carbon in coastal wetlands of the western Bohai Sea. Sci. Total Environ. 2024, 913, 169282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, Y.Y.; Peng, F.; Gao, X.; Xiao, P.; Logares, R.; Jeppesen, E.; Ren, K.; Xue, Y.; Yang, J. Low shifts in salinity determined assembly processes and network stability of microeukaryotic plankton communities in a subtropical urban reservoir. Microbiome 2021, 9, 128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhong, Z.P.; Liu, Y.; Miao, L.L.; Wang, F.; Chu, L.M.; Wang, J.L.; Liu, Z.P. Prokaryotic community structure driven by salinity and ionic concentrations in Plateau Lakes of the Tibetan Plateau. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2016, 82, 1846–1858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kang, E.; Song, B.; Wang, J.; Zhang, X.; Wang, J.; Li, M.; Yan, L.; Yan, Z.; Zhang, K.; et al. Soil salinity and nutrients availability drive patterns in bacterial community and diversity along succession gradient in the Yellow River Delta. Estuar. Coast. Shelf Sci. 2021, 262, 107621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rath, K.M.; Fierer, N.; Murphy, D.V.; Rousk, J. Linking bacterial community composition to soil salinity along environmental gradients. ISME J. 2019, 13, 836–846. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, J.; Chen, L.; Zhou, T.; Zhang, C.; Zhang, J.; Zhao, B. Salinity-driven differentiation of bacterial and fungal communities in coastal wetlands: Contrasting assembly processes and spatial dynamics. Environ. Res. 2025, 279, 121895. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Bai, J.; Tebbe, C.C.; Zhao, Q.; Jia, J.; Wang, W.; Wang, X.; Yu, L. Salinity controls soil microbial community structure and function in coastal estuarine wetlands. Environ. Microbiol. 2021, 23, 1020–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schober, P.; Boer, C.; Schwarte, L.A. Correlation Coefficients: Appropriate Use and Interpretation. Anesth. Analg. 2018, 126, 1763–1768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Konopka, A.; Lindemann, S.; Fredrickson, J. Dynamics in microbial communities: Unraveling mechanisms to identify principles. ISME J. 2015, 9, 1488–1495. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, X.; Gu, H.; Wang, Y.; Liu, J.; Yu, Z.; Li, Y.; Jin, J.; Liu, X.; Dai, Q.; Wang, G. Succession of soil bacterial communities and network patterns in response to conventional and biodegradable microplastics: A microcosmic study in Mollisol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2022, 436, 129218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu, L.; Tang, Q.; Li, H.; Li, Z. Damming river shapes distinct patterns and processes of planktonic bacterial and microeukaryotic communities. Environ. Microbiol. 2022, 24, 1760–1774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Poudel, R.; Jumpponen, A.; Schlatter, D.C.; Paulitz, T.; Gardener, B.M.; Kinkel, L.L.; Garrett, K. Microbiome networks: A systems framework for identifying candidate microbial assemblages for disease management. Phytopathology 2016, 106, 1083–1096. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, K.; Weisenhorn, P.; Gilbert, J.A.; Shi, Y.; Bai, Y.; Chu, H. Soil pH correlates with the co-occurrence and assemblage process of diazotrophic communities in rhizosphere and bulk soils of wheat fields. Soil Biol. Biochem. 2018, 121, 185–192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]




Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Zhang, C.; Li, H.; Li, M.; Su, S.; Xiao, H.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, Q. Contrasting Assembly and Network Roles of Abundant and Rare Bacteria in Reservoir and Soil Habitats. Biology 2025, 14, 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091291
Zhang C, Li H, Li M, Su S, Xiao H, Zhang X, Zhang Q. Contrasting Assembly and Network Roles of Abundant and Rare Bacteria in Reservoir and Soil Habitats. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091291
Chicago/Turabian StyleZhang, Cuixia, Haiming Li, Mengdi Li, Sihui Su, Han Xiao, Xiaodong Zhang, and Qian Zhang. 2025. "Contrasting Assembly and Network Roles of Abundant and Rare Bacteria in Reservoir and Soil Habitats" Biology 14, no. 9: 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091291
APA StyleZhang, C., Li, H., Li, M., Su, S., Xiao, H., Zhang, X., & Zhang, Q. (2025). Contrasting Assembly and Network Roles of Abundant and Rare Bacteria in Reservoir and Soil Habitats. Biology, 14(9), 1291. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091291






