Simple Summary
The basement membrane (BM), a thin protein matrix in the extracellular space, provides vital information to organs to maintain their physiological functions. However, we do not know which of the proteins in this matrix are important in which organ and what happens in these organs when they are lost. Genes that encode BM components are highly conserved between Drosophila and humans. This makes the fruit fly an interesting genetic model system to study genes that might be important for reproductive biology and human health. The Drosophila ovary, the female’s reproductive organ, constantly produces eggs. Nidogen (Ndg), one of the main components of the BM, plays an important role in maintaining reproductive fitness. Loss of Ndg results in reduced egg production in aging flies, which can be associated with the death of egg precursors.
Abstract
The basement membrane (BM) is a specialized extracellular matrix that provides crucial structural support to tissues and organs. Mutations in BM genes can affect this structural support and are often associated with human diseases, including fibrosis, diabetes, and cancer, and are considered a hallmark of aging. However, how the BM maintains this support in organs with constant mechanical stress is largely unknown. In the Drosophila ovary, the BM provides the mechanical cues that are required for egg development. We discovered that the glycoprotein Ndg is important for maintaining organ integrity during egg production. Loss of Ndg results in a reduced number of progeny due to unfertilized eggs. Furthermore, we observed a decreased number of developing eggs and a premature death of egg chambers during development. Our results suggest that Ndg plays an important role in fertility.
1. Introduction
The basement membrane (BM) is a specialized extracellular matrix (ECM) that plays a crucial role in tissue morphogenesis and homeostasis, maintaining the structural integrity and function of tissues [1,2,3]. BMs are mainly composed of Laminins and Collagen IV, which form separate networks, as well as further components that link these networks, like the proteoglycan Perlecan and the glycoprotein Nidogen (Ndg) [4]. Ndg plays a pivotal function in preserving tissue homeostasis and dynamics by integrating diverse components of the ECM and modulating their molecular architecture and mechanical stability [5,6,7,8].
The function of Ndg is evident in a variety of phenotypes observed in different species. In mice, the functional loss of one of the two Ndg genes neither results in lethality nor disrupts the formation of the BM. However, Ndg1 mutant animals exhibit neurological phenotypes, including spontaneous seizures and loss of hind leg control [9,10,11]. Double mutants also exhibit no embryonic lethality or disturbance to the formation of the BM, but perinatal lethality occurs due to incorrect formation of the BM-associated ECM, which disturbs heart and lung development, as well as causes syndactyly [5,12]. Analyses of nid-1 mutants in C. elegans are also vital and fertile and show no abnormalities in the structure of the BM. However, fertility is reduced [13]. The animals exhibit movement disorders and the orientation of the longitudinal nerves as well as the arrangement of the neuromuscular connections are disturbed [13,14,15,16]. Finally, loss of nid1a in Danio rerio results in a reduction in body length [17]. Similarly, neurological defects in Drosophila, such as movement and orientation disorders, could be explained by defects in the innervation of the peripheral nervous system (PNS) and the incorrect arrangement of cilia in neurons. In addition, a role of Ndg for the stability and permeability of the BM could be shown in larval visceral muscles [7]. Thus, the current understanding of the role of Ndg is that it strengthens the BM and ensures its barrier function. Consequently, loss of Ndg function results in malformation of various organs, disturbed growth, and altered behavior across different species. At a molecular level, the interaction between Ndg and integrins may play a role in cell attachment. This is evidenced by the binding of Ndg-1 to αvβ3 and α3β1 dimers [18,19], as well as by a study showing that Ndg-1 acts as a tumor suppressor by mediating the polarization of macrophages through interaction with αvβ3 integrin [20]. A previous study has proposed that a complex of integrin, Ndg, and laminin regulates the stem cell niche and epidermal maintenance [21]. Furthermore, Ndg has been associated with several diseases by altering adhesion and signaling pathways. For example, Ndg-1 was identified as a novel biomarker in patients with acute myeloid leukemia [22], Ndg-2 activated the Akt signaling pathway in patients with glioma [23], and overexpression of Ndg-2 in a mouse model led to hepatosteatosis and atherosclerosis [24].
To study the function of Ndg, the Drosophila ovary is a well-suited model to study the mechanical functions of BM in vivo. The fact that Ndg null mutants are viable [7] and that only one gene encodes for Ndg [25] simplifies the analysis of Ndg function in Drosophila. The Drosophila ovaries are the paired reproductive organs of female flies and are composed of 16 ovarioles each. The germarium, located at the tip of these ovarioles and comprising the stem cell niche, produces egg chambers, the precursors of eggs. These are pushed towards the oviduct by a surrounding muscle sheet, where they are subsequently fertilised and laid. Finally, the entire ovary is surrounded and attached together with a thin muscle network called the peritoneal sheath [26,27]. Both, the germarium together with all egg chamber stages as well as the surrounding muscle sheets are surrounded by a Ndg-containing BM [6,28]. However, the molecular mechanisms by which Ndg maintains tissue integrity, and how loss of Ndg function can lead to behavioral disorders, reduced fertility, and human disease, are not yet fully understood.
Here, we identify Ndg as an important gene for maintaining fertility in female Drosophila flies. We discovered an unknown link between a BM component, age, and the number of offspring in the fruit fly. Ndg mutants exhibit accelerated reduced fertility in aging flies, which correlates with the residual level of Ndg protein in the respective mutant. We observed ovarioles with an empty muscle sheet towards the oviduct and premature apoptotic egg chambers in affected amorphic Ndg mutants. Together, these results suggest a role for Ndg in maintaining the integrity of the BM and the ovary’s ability to continuously produce eggs.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fly Stocks and Genetics
The fly stocks used were white1118 [Bloomington Drosophila Stock Center (BDSC), 3605, Bloomington, IN, USA] NdgΔ0.4, and NdgΔ1.4 [7] (deletion generated from Mi{ET1}MB04184, P{hsILMiT} and P{Δ2–3}99B), Df Ndg (BDSC_23666) [29], and vkg::GFP [Drosophila Genetic Resource Center (DGRC), 110626, Kyoto, Japan] [30]. Flies were kept at 25 °C on standard food [31]; white1118 control flies were used because the NdgΔ0.4 and NdgΔ1.4 mutants used have the white1118 mutant background.
2.2. Immunohistochemistry
Ovaries from flies with the indicated age were dissected in PBS and fixed with 4% formaldehyde in PBS. Rabbit anti-Nidogen (Ndg) antibody [32] was used with a dilution of 1:500 and rabbit anti-green fluorescent protein (GFP, Abcam, ab290, Cambridge, UK) was used with a dilution of 1:500. Alexa Cy-coupled secondary antibodies were purchased from Dianova, Hamburg, GER and Jackson ImmunoResearch, Cambridgeshire, UK and Hoechst 55,380 (1:1000, Sigma Aldrich, 94403, St. Louis, MO, USA) and rhodamine–phalloidin (1:200, Thermo Fisher Scientific, R415, Waltham, MA, USA). Embryos were embedded in Fluoromount-G (Southern Biotech, 0100-01, Birmingham, AL, USA) before visualization under a Leica TCS SP2 (Leica, Wetzlar, Germany) or Olympus FV1000 confocal microscope (Olympus, Tokyo, Japan). For comparison of Ndg protein levels in the controls and Ndg mutants, we used the same laser intensity and settings.
2.3. Fertility Test
In order to investigate the fertility of females, 15 virgin flies of the desired genotype were collected and mated with 5 young males of the control genotype w1118 and kept at 25 °C in deposition vials. Flies were transferred to fresh vials every 24 h. Once the parents had reached the target age, the deposits were incubated at 25 °C for at least two hours to allow further development. The eggs obtained from the deposits were dechorionized, fixed, and de-vitellinized. The eggs were transferred directly to PBS with 0.1% Tween, stained with Hoechst, washed, and then analyzed. Eggs in which no DNA staining could be detected were interpreted as unfertilized.
2.4. Quantification of Egg Chamber Amount and Premature Apoptotic Egg Chambers
Flies were aged at 25 °C for 5 to 13 days, respectively, after which their ovaries were dissected in PBS. The ovarioles were loosened and fixed in 4% formaldehyde in PBS. The ovaries were stained with Hoechst, and the total number of egg chambers and the number of egg chambers per stage of oogenesis (grouped into stages 1–6, 7–12, and 13–14) were determined. Egg chamber stages of oogenesis were determined as previously described [26]. Premature apoptotic egg chambers were identified by condensed nuclei via the oversaturated fluorescence intensity of Hoechst staining. We counted egg chambers as prematurely apoptotic if apoptotic follicle or nurse cell nuclei appeared prior to stage 11 or 14, respectively, as these cells typically undergo apoptosis in these stages [33].
2.5. Statistical Analysis
The data were tested for equal variance and normal distribution, and statistical significance was subsequently calculated using a two-sided Student’s t-test for the comparison of two groups, and a Student’s t-test with Bonferroni correction for multiple comparisons, using R (version 2025.05.1+513) [34].
3. Results
3.1. Nidogen Is Required for Reproductive Fitness in Aging Flies
Ndg is one of the major components of the BM. The loss of Ndg reveals roles in BM stability, barrier function, and nervous system patterning, although Ndg null mutants are viable [7]. To investigate a potential role of Ndg for Drosophila fertility, we used our previously generated NdgΔ0.4 and NdgΔ1.4 mutants (Figure 1A) [7]. Immunohistochemical analysis of Drosophila embryos using a specific Ndg antibody, as well as Western blot analysis, revealed that NdgΔ0.4 is a hypomorphic allele, while NdgΔ1.4 is amorphic. This is attributed to the fact that the hypomorphic allele shows residual expression, whereas the amorphic alleles do not [7,35]. To test if Ndg antibody staining of the ovary led to similar results, we repeated this experiment. We stained the ovaries of 5-day old w1118 control flies as well as NdgΔ0.4 and NdgΔ1.4 mutants and co-stained the ovary with F-actin, which allows us to show muscles and discriminate between different stages of egg chamber development (Figure 1B–D’). In control flies, we observed prominently Ndg localization in BMs of the muscle sheets as well as of the epithelial follicle cells of the egg chambers (Figure 1B,B’). In NdgΔ0.4, only a small amount of Ndg can be detected in the BM (Figure 1C,C’), while the specific Ndg signal was abolished in the NdgΔ1.4 mutants (Figure 1D,D’). Ndg is known to ensure proper fertility in C. elegans [13]. To test if the loss of Ndg affects female fertility, we quantified the percentage of non-fertilized eggs with progressive age over time from day 5 to day 13 (Figure 1E). During this period, the number of unfertilized eggs in the control group also began to increase slightly (Figure 1E). While in 5-day old flies, NdgΔ1.4 mutants showed a significantly higher percentage of non-fertilized eggs compared to controls (by ∼6.4% and ∼19.2%, respectively), while NdgΔ0.4 mutants did not (∼7%); furthermore, 7- to 13-day-old females showed significant differences between controls compared to both Ndg mutants alleles (listed in the order of controls, NdgΔ0.4, and NdgΔ1.4: ∼8%, ∼17%, and ∼33% for 7-day-old flies, ∼11%, ∼25%, and ∼49% for 9-day-old flies, ∼17%, ∼28%, and ∼59% for 11-day-old flies, ∼18%, ∼46%, and ∼71% for 13-day-old flies) (Figure 1E). Thus, a reduction in Ndg protein levels affects female fertility with higher effects in older flies.
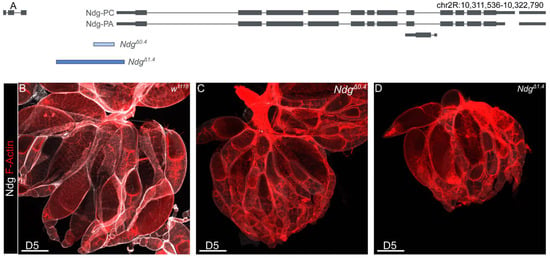
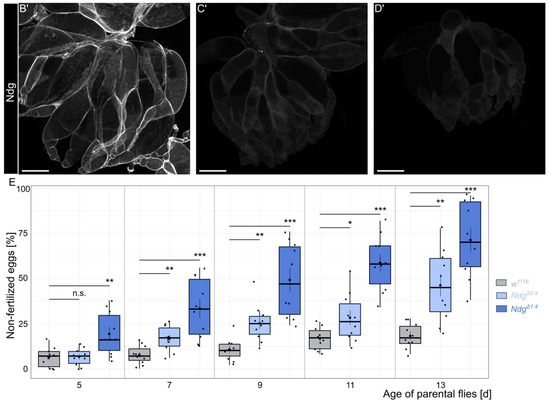
Figure 1.
Role of Nidogen for Drosophila fertility. (A) Schematic overview of the Nidogen gene and deleted regions of NdgΔ0.4 (indicated in light blue) and NdgΔ1.4 (indicated in dark blue) mutants. (B–D’) Ovaries of w1118 controls (B), NdgΔ0.4 (C), and NdgΔ1.4 (D) 5-day-old flies stained with anti-Nidogen antibody (white) and (B–D) for F-actin (red). Control ovaries show strong Ndg protein localization (B,B’), while Ndg mutants show apparent reduced Ndg signal for NdgΔ0.4 (C,C’) and abolished Ndg signal for NdgΔ1.4 (D,D’). Scale bars = 200 µm. (E) Boxplots showing the percentage of non-fertilized eggs of w1118 controls (gray), NdgΔ0.4 (light blue), and NdgΔ1.4 (dark blue) genotypes laid by parental flies aged 5–13 days. Boxplots indicate the median, the 25th percentile, and the 75th percentile. Means (central black point); and individual measurements (smaller black points/scatterplot) are shown. * p < 0.025, ** p < 0.005, *** p < 0.0005 (Student’s t-test with Bonferroni correction). n.s. = not significant. n = 10 replicates of 50 eggs each.
3.2. Premature Apoptosis in Egg Chambers of Ndg Mutant Flies
To examine the reason for the lack of fertility of aging Ndg mutants, we studied the morphology of the ovaries using DNA and F-actin staining as well as the Collagen IV signal (Figure 2). We started to test if the Collagen IV signal is disturbed by visualizing Collagen IV with a GFP-tagged vkg::GFP fly line (vkg encodes the Drosophila Collagen IVa2 subunit). We tested the Collagen IV fluorescence signal in 5-day-old and 13-day-old controls as well as in a transheterozygous situation with the previously mentioned NdgΔ1.4 allele and a deficiency allele, where the Ndg locus is completely deleted [25], recombined with vkg::GFP. This strategy allows us on the one hand to study ovary morphology in a genetic null background and on the other hand it reduces the possibility of potential off-target phenotypes due to the independent Ndg alleles. While the Collagen IV signal is constantly high between different ages and genotypes (Figure 2A–D), Ndg mutant ovaries of 13-day-old flies are smaller and contain empty ovarioles that only show the BM of collapsed muscle sheets, missing the matured egg chambers within (Figure 2D, arrows). We next validated if we are able to observe similar phenotypes in the strong NdgΔ1.4 mutants and we found the same phenotype (Figure 2E–E’’). While some ovarioles are still filled with egg chambers of later stages (Figure 2E), parts of the ovarioles are only filled with early- and mid-staged egg chambers and are empty towards the oviduct (Figure 2E’,E’’, arrowheads). This partial lack of late egg chambers in the ovarioles is reflected by significant differences in the number of egg chambers in 5- to 13-day-old flies (∼125 and ∼85 at day 5, ∼95 and ∼60 at day 9, and ∼60 and ∼33 at day 13, respectively) (Figure 2F–G’). While follicle cell nuclei start to typically condense during stage 14 and nurse cell nuclei start to die from stage 11 on [33], we observed nuclei that condensate prematurely in earlier stages (Figure 2E’’, arrowhead, and Figure 2H). In particular, the presence of prematurely dying egg chambers correlates with ovarioles where no later egg chambers can be observed (compare Figure 2E’, and Figure 2E’’). In conclusion, in Ndg mutant ovaries, the number of egg chambers is reduced, especially that of later stages, and egg chambers prematurely die during development.
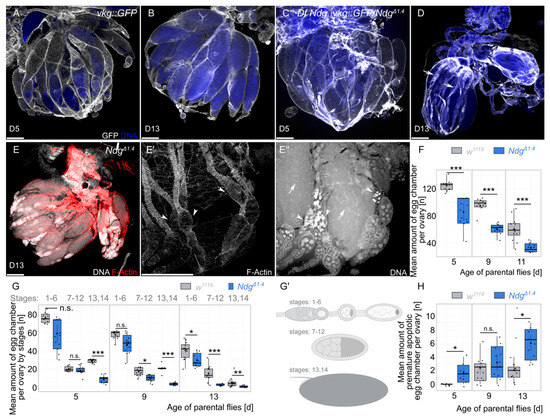
Figure 2.
Morphological defects of Ndg mutants. (A–D) Anti-GFP antibody (white) and DNA (blue) staining on ovaries of 5-day-old (A,C) and 13-day-old (B,D) flies with the vkg::GFP control (A,B) and Df Ndg, vkg::GFP/NdgΔ1.4 (C,D) genotypes. (E–E’’) F-actin (red) and DNA (white) staining on NdgΔ1.4 mutants. In contrast to the controls (B), 13-day-old Ndg mutant conditions show partially empty ovarioles and highly condensed nuclei of mid-stage egg chambers (D–E’’). Scale bars = 200 µm. (F) Boxplots showing mean amount of egg chambers per ovary of w1118 controls (gray) and NdgΔ1.4 (dark blue) genotypes of 5-, 9-, and 13-day-old flies. (G) Boxplots showing mean amount of egg chambers per ovary by stages of w1118 controls (gray) and NdgΔ1.4 (dark blue) genotypes of 5-, 9-, and 13-day-old flies. (G’) Schematic illustration related to G, showing groups of stages 16, 7–12, and 13–14. (H) Boxplots showing mean amount of premature apoptotic egg chambers per ovary by stages of w1118 controls (gray) and NdgΔ1.4 (dark blue) genotypes of 5-, 9- and 13-day old flies. Boxplots indicate the median, the 25th percentile, and the 75th percentile. Points indicate outliers below the 25th percentile or above the 75th percentile. Means (central black point); and individual measurements (smaller black points/scatterplot) are shown. * p < 0.05, ** p < 0.01, and *** p < 0.001 (Student’s t-test). n.s. = not significant. n = 12 ovaries of ≥6 flies.
4. Discussion
The integrity of BMs is the key to the proper functioning of tissues and organs. The Drosophila ovary must sustain constant mechanical stress for ongoing egg production. The work described here provides insights into the role of Ndg to mediate the proper BM integrity. Drosophila encodes only one Ndg gene and in our NdgΔ1.4 mutant, Ndg protein is completely abolished (Figure 1D,D’) [7]. In Ndg mutants, the number of eggs produced per day is significantly reduced, which is an effect that increases with the aging of flies. In aged flies, we observed a reduced number of egg chambers present in the ovary; in particular, aged flies lacking late egg chamber stages in a part of the ovarioles. Finally, our data show that ovarioles without late egg chambers show prematurely dying egg chambers, which seem to get stuck in the ovariole.
Ndg is one of the most abundant proteins in the BM and has multiple binding partners including all major components, namely Laminin, Collagen IV, and Perlecan [36,37,38]. These multiple interactions have been shown to influence the mechanical properties of the BM. In particular, loss of Ndg have been shown to influence BM stiffness in the egg chamber [28], maintain BM topology in the wing disc [39], and modulate Collagen IV turnover during Drosophila embryonic development [40] as well as in C. elegans larval pharynx [41]. These effects occur at the molecular level and manifest as behavioral disorders, defective innervation, reduced body size, impaired lung and heart development, and syndactyly across different organisms [5,12,13,14,15,16,17]. Interestingly, similar to our results in Drosophila, in C. elegans, the fertility is also reduced, which has been determined by a reduced number of laid eggs [13]. However, in this study the number of eggs in the uterus was not significantly different between controls and Ndg mutants, which might be indicating that Ndg has distinct functions in Drosophila egg development. In the Drosophila visceral musculature, ultrastructural analyses revealed a perforated BM [7], which resulted in strong phenotypes, particularly in tissues under tension. Such defects could affect the physiology of the muscle sheet surrounding the ovary and impair fertility. The defects in the ovary could be due to mechanical stress, which the BM without Ndg may not be able to withstand adequately. Since BM stiffness not only affects migration but also the maintenance of tissue homeostasis and stem cell differentiation [42]. Thus, our results showing prematurely dying egg chambers might indicate a disturbance in the homeostasis of the stem cell niches in the ovary. BM components play an essential role in testes and ovaries in the positioning of the stem cell niche and thus for the maintenance of further differentiation processes [43,44,45,46]. It would be interesting to see if Ndg is also required for fertility in other organisms or if mutations in Ndg genes are a genetic condition associated with infertility in humans.
One thing we could not clarify in our study is the question: How is the premature dying of egg chamber related to the fertility defects? Dying egg chambers might stick in the muscle sheet that is required for its contraction to push forward developing egg chambers that are necessary for fertilization. Therefore, apoptotic egg chambers may interfere with egg activation and fertilization in the uterus. Egg activation depends on mechanical stress [47], which may be absent if BM integrity is compromised.
We identified a role of Drosophila Ndg for female reproductive fitness. Loss of Ndg reduces the number of laid eggs, with progressively stronger effects with age. Furthermore, in aged flies we observed fewer developing egg chambers and more prematurely dying egg chambers, which stuck in the ovarioles. Based on our findings and previous results in other species, we can now speculate that Ndg plays a conserved role in reproductive fitness across the animal kingdom. We hypothesize that Ndg is required in the BM to sustain the mechanical stress of the ovary during ongoing egg production and to maintain the microenvironment that regulates stem cell differentiation.
5. Conclusions
Ndg is one of the most highly conserved BM components, but its precise role is not yet fully understood. This study and others underline its role in maintaining tissue and organ integrity. However, further analyses are needed to explain the defects in terms of reduced fertility. Additionally, the roles of Ndg in barrier function and BM stability are also aspects that influence fitness. While Ndg itself may not be essential for viability, these results align with previous findings, providing a clearer picture of how Ndg can affect reproductive fitness.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, U.T.; methodology, U.T.; validation, U.T.; formal analysis, U.T.; investigation, U.T.; resources, A.H.; data curation, U.T.; writing—original draft preparation, U.T.; writing—review and editing, U.T. and A.H.; visualization, U.T.; supervision, A.H.; project administration, A.H.; funding acquisition, U.T. and A.H. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This work was funded by the Deutsche Forschungsgemeinschaft (DFG, German Research Foundation)—project number 562367279 (TO 1599/3-1 to UT) and project number 272140094 (HO 2559/5-3 to AH).
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Data Availability Statement
Data reported in this paper will be shared by the corresponding author upon request.
Acknowledgments
This study used strains obtained from the BDSC (NIH P40OD018537), the VDRC, and the DGRC.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Abbreviations
The following abbreviations are used in this manuscript: BM, basement membrane; DNA, deoxyribonucleic acid; F-actin, filamentous actin; GFP, green fluorescent protein; Ndg, Nidogen; PBS, phosphate buffer saline.
References
- Töpfer, U. Basement Membrane Dynamics and Mechanics in Tissue Morphogenesis. Biol. Open 2023, 12, bio059980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sekiguchi, R.; Yamada, K.M. Basement Membranes in Development and Disease. In Current Topics in Developmental Biology; Elsevier: Amsterdam, The Netherlands, 2018; Volume 130, pp. 143–191. ISBN 978-0-12-809802-8. [Google Scholar]
- Yurchenco, P.D. Basement Membranes: Cell Scaffoldings and Signaling Platforms. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2011, 3, a004911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hohenester, E.; Yurchenco, P.D. Laminins in Basement Membrane Assembly. Cell Adhes. Migr. 2013, 7, 56–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bader, B.L.; Smyth, N.; Nedbal, S.; Miosge, N.; Baranowsky, A.; Mokkapati, S.; Murshed, M.; Nischt, R. Compound Genetic Ablation of Nidogen 1 and 2 Causes Basement Membrane Defects and Perinatal Lethality in Mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005, 25, 6846–6856. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, J.; Estrada, B.; Jacobs, S.; Sánchez-Sánchez, B.J.; Tang, J.; Ma, M.; Magadán-Corpas, P.; Pastor-Pareja, J.C.; Martín-Bermudo, M.D. Dissection of Nidogen Function in Drosophila Reveals Tissue-Specific Mechanisms of Basement Membrane Assembly. PLoS Genet. 2018, 14, e1007483. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wolfstetter, G.; Dahlitz, I.; Pfeifer, K.; Töpfer, U.; Alt, J.A.; Pfeifer, D.C.; Lakes-Harlan, R.; Baumgartner, S.; Palmer, R.H.; Holz, A. Characterization of Drosophila Nidogen/Entactin Reveals Roles in Basement Membrane Stability, Barrier Function and Nervous System Patterning. Development 2019, 146, dev168948. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töpfer, U.; Holz, A. Nidogen in Development and Disease. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2024, 12, 1380542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.; Chen, Y.; Lewis, M.; Hsieh, J.-C.; Reing, J.; Chaillet, J.R.; Howell, C.Y.; Melhem, M.; Inoue, S.; Kuszak, J.R.; et al. Neurologic Defects and Selective Disruption of Basement Membranes in Mice Lacking Entactin-1/Nidogen-1. Lab. Investig. 2002, 82, 1617–1630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murshed, M.; Smyth, N.; Miosge, N.; Karolat, J.; Krieg, T.; Paulsson, M.; Nischt, R. The Absence of Nidogen 1 Does Not Affect Murine Basement Membrane Formation. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2000, 20, 7007–7012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schymeinsky, J.; Nedbal, S.; Miosge, N.; Pöschl, E.; Rao, C.; Beier, D.R.; Skarnes, W.C.; Timpl, R.; Bader, B.L. Gene Structure and Functional Analysis of the Mouse Nidogen-2 Gene: Nidogen-2 Is Not Essential for Basement Membrane Formation in Mice. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2002, 22, 6820–6830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Böse, K.; Nischt, R.; Page, A.; Bader, B.L.; Paulsson, M.; Smyth, N. Loss of Nidogen-1 and -2 Results in Syndactyly and Changes in Limb Development. J. Biol. Chem. 2006, 281, 39620–39629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, S.H.; Kramer, J.M. Nidogen Is Nonessential and Not Required for Normal Type IV Collagen Localization in Caenorhabditis elegans. Mol. Biol. Cell 2000, 11, 3911–3923. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackley, B.D.; Kang, S.H.; Crew, J.R.; Suh, C.; Jin, Y.; Kramer, J.M. The Basement Membrane Components Nidogen and Type XVIII Collagen Regulate Organization of Neuromuscular Junctions in Caenorhabditis elegans. J. Neurosci. 2003, 23, 3577–3587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hobert, O.; Bülow, H. Development and Maintenance of Neuronal Architecture at the Ventral Midline of C. elegans. Curr. Opin. Neurobiol. 2003, 13, 70–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, S.; Wadsworth, W.G. Positioning of Longitudinal Nerves in C. elegans by Nidogen. Science 2000, 288, 150–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, P.; Ma, Z.; Guo, L.; Zhang, W.; Zhang, Q.; Zhao, T.; Jiang, K.; Peng, J.; Chen, J. Short Body Length Phenotype Is Compensated by the Upregulation of Nidogen Family Members in a Deleterious Nid1a Mutation of Zebrafish. J. Genet. Genom. 2017, 44, 553–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dedhar, S.; Jewell, K.; Rojiani, M.; Gray, V. The Receptor for the Basement Membrane Glycoprotein Entactin Is the Integrin Alpha 3/Beta 1. J. Biol. Chem. 1992, 267, 18908–18914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, L.-J.; Hsieh, J.-C.; Chung, A.E. Two Distinct Cell Attachment Sites in Entactin Are Revealed by Amino Acid Substitutions and Deletion of the RGD Sequence in the Cysteine-Rich Epidermal Growth Factor Repeat 2. J. Biol. Chem. 1995, 270, 15838–15843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caracuel-Peramos, R.; Rodríguez-Baena, F.J.; Redondo-García, S.; Villatoro-García, J.A.; García-Muñoz, A.; Peris-Torres, C.; Plaza-Calonge, M.C.; Rubio-Gayarre, A.; López-Millán, B.; Ricciardelli, C.; et al. Loss of the Extracellular Protease ADAMTS1 Reveals an Antitumorigenic Program Involving the Action of NIDOGEN-1 on Macrophage Polarization. OncoImmunology 2025, 14, 2508057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muffler, S.; Stark, H.-J.; Amoros, M.; Falkowska-Hansen, B.; Boehnke, K.; Bühring, H.-J.; Marmé, A.; Bickenbach, J.R.; Boukamp, P. A Stable Niche Supports Long-Term Maintenance of Human Epidermal Stem Cells in Organotypic Cultures. Stem Cells 2008, 26, 2506–2515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vanhooren, J.; Deneweth, L.; Pagliaro, L.; Ren, Z.; Giaimo, M.; Zamponi, R.; Roti, G.; Depreter, B.; Hofmans, M.; De Moerloose, B.; et al. Nidogen-1, a Player in KMT2A-Rearranged Pediatric Acute Myeloid Leukemia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3011. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lan, Z.; Xiao, Y.; Liao, Y.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, H.; Zhang, W. NID2 Affects Prognosis of Glioma via Activating the Akt Signaling Pathway. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 3859. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kathuria, I.; Prasad, A.; Sharma, B.K.; Aithabathula, R.V.; Ofosu-Boateng, M.; Gyamfi, M.A.; Jiang, J.; Park, F.; Singh, U.P.; Singla, B. Nidogen 2 Overexpression Promotes Hepatosteatosis and Atherosclerosis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2024, 25, 12782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Öztürk-Çolak, A.; Marygold, S.J.; Antonazzo, G.; Attrill, H.; Goutte-Gattat, D.; Jenkins, V.K.; Matthews, B.B.; Millburn, G.; Dos Santos, G.; Tabone, C.J.; et al. FlyBase: Updates to the Drosophila Genes and Genomes Database. Genetics 2024, 227, iyad211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spradling, A.C. Developmental Genetics of Oogenesis. In The Development of Drosophila Melanogaster; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory Press: Woodbury, NY, USA, 1993; pp. 1–70. [Google Scholar]
- Hudson, A.M.; Petrella, L.N.; Tanaka, A.J.; Cooley, L. Mononuclear Muscle Cells in Drosophila Ovaries Revealed by GFP Protein Traps. Dev. Biol. 2008, 314, 329–340. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Töpfer, U.; Guerra Santillán, K.Y.; Fischer-Friedrich, E.; Dahmann, C. Distinct Contributions of ECM Proteins to Basement Membrane Mechanical Properties in Drosophila. Development 2022, 149, dev200456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cook, R.K.; Christensen, S.J.; Deal, J.A.; Coburn, R.A.; Deal, M.E.; Gresens, J.M.; Kaufman, T.C.; Cook, K.R. The Generation of Chromosomal Deletions to Provide Extensive Coverage and Subdivision of the Drosophila melanogaster Genome. Genome Biol. 2012, 13, R21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morin, X.; Daneman, R.; Zavortink, M.; Chia, W. A Protein Trap Strategy to Detect GFP-Tagged Proteins Expressed from Their Endogenous Loci in Drosophila. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2001, 98, 15050–15055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M. Drosophila: A Laboratory Handbook; Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory: Woodbury, NY, USA, 1989; ISBN 0-87969-321-5. [Google Scholar]
- Wolfstetter, G.; Shirinian, M.; Stute, C.; Grabbe, C.; Hummel, T.; Baumgartner, S.; Palmer, R.H.; Holz, A. Fusion of Circular and Longitudinal Muscles in Drosophila Is Independent of the Endoderm but Further Visceral Muscle Differentiation Requires a Close Contact between Mesoderm and Endoderm. Mech. Dev. 2009, 126, 721–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lebo, D.P.V.; McCall, K. Murder on the Ovarian Express: A Tale of Non-Autonomous Cell Death in the Drosophila Ovary. Cells 2021, 10, 1454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R Core Team. R: A Language and Environment for Statistical Computing; R Foundation for Statistical Computing: Vienna, Austria, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Töpfer, U. Analysen zur Regulation und Komposition der Extrazellulären Matrix von Drosophila melanogaster. Ph.D. Thesis, University of Gießen, Gießen, Germany, 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aumailley, M.; Wiedemann, H.; Mann, K.; Timpl, R. Binding of Nidogen and the Laminin-Nidogen Complex to Basement Membrane Collagen Type IV. Eur. J. Biochem. 1989, 184, 241–248. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mann, K.; Deutzmann, R.; Aumailley, M.; Timpl, R.; Raimondi, L.; Yamada, Y.; Pan, T.C.; Conway, D.; Chu, M.L. Amino Acid Sequence of Mouse Nidogen, a Multidomain Basement Membrane Protein with Binding Activity for Laminin, Collagen IV and Cells. EMBO J. 1989, 8, 65–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hopf, M.; Göhring, W.; Mann, K.; Timpl, R. Mapping of Binding Sites for Nidogens, Fibulin-2, Fibronectin and Heparin to Different IG Modules of Perlecan1. J. Mol. Biol. 2001, 311, 529–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santillán, K.Y.G.; Dahmann, C.; Fischer-Friedrich, E. ECM Proteins Shape Topographical Patterns in the Basement Membrane of Drosophila Wing Discs. Matrix Biol. 2025, 140, 78–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsubayashi, Y.; Sánchez-Sánchez, B.J.; Marcotti, S.; Serna-Morales, E.; Dragu, A.; Díaz-de-la-Loza, M.-C.; Vizcay-Barrena, G.; Fleck, R.A.; Stramer, B.M. Rapid Homeostatic Turnover of Embryonic ECM during Tissue Morphogenesis. Dev. Cell 2020, 54, 33–42.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keeley, D.P.; Hastie, E.; Jayadev, R.; Kelley, L.C.; Chi, Q.; Payne, S.G.; Jeger, J.L.; Hoffman, B.D.; Sherwood, D.R. Comprehensive Endogenous Tagging of Basement Membrane Components Reveals Dynamic Movement within the Matrix Scaffolding. Dev. Cell 2020, 54, 60–74.e7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handorf, A.M.; Zhou, Y.; Halanski, M.A.; Li, W.-J. Tissue Stiffness Dictates Development, Homeostasis, and Disease Progression. Organogenesis 2015, 11, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van De Bor, V.; Zimniak, G.; Papone, L.; Cerezo, D.; Malbouyres, M.; Juan, T.; Ruggiero, F.; Noselli, S. Companion Blood Cells Control Ovarian Stem Cell Niche Microenvironment and Homeostasis. Cell Rep. 2015, 13, 546–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papagiannouli, F.; Schardt, L.; Grajcarek, J.; Ha, N.; Lohmann, I. The Hox Gene Abd-B Controls Stem Cell Niche Function in the Drosophila Testis. Dev. Cell 2014, 28, 189–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Pearson, J.R.; Zurita, F.; Tomás-Gallardo, L.; Díaz-Torres, A.; Loza, M.D.C.D.; Franze, K.; Martín-Bermudo, M.D.; González-Reyes, A. ECM-Regulator Timp Is Required for Stem Cell Niche Organization and Cyst Production in the Drosophila Ovary. PLoS Genet. 2016, 12, e1005763. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanentzapf, G.; Devenport, D.; Godt, D.; Brown, N.H. Integrin-Dependent Anchoring of a Stem-Cell Niche. Nat. Cell Biol. 2007, 9, 1413–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Avilés-Pagán, E.E.; Orr-Weaver, T.L. Activating Embryonic Development in Drosophila. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2018, 84, 100–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).