Histological Study on Digestive System of Triplophysa yarkandensis in Saline-Alkali and Freshwater Environments: Adaptive Mechanisms
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Materials
2.2. Tissue Collection and Processing
2.3. Histological Analysis
2.4. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
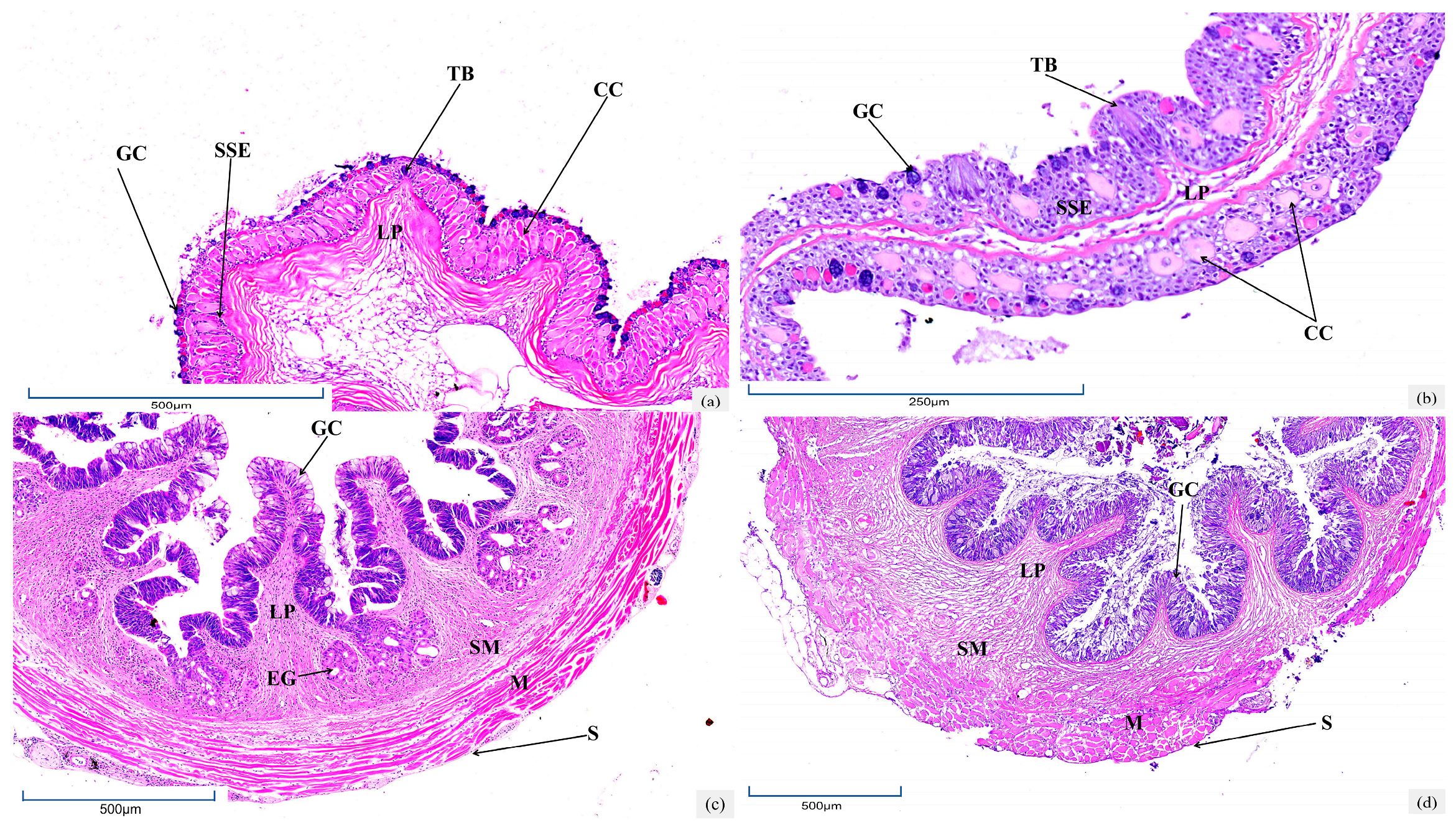
3.1. Histological Characteristics of Oropharyngeal Cavity
3.2. Histological Characteristics of Esophagus
3.3. Histological Characteristics of Cardia, Stomach, and Pylorus
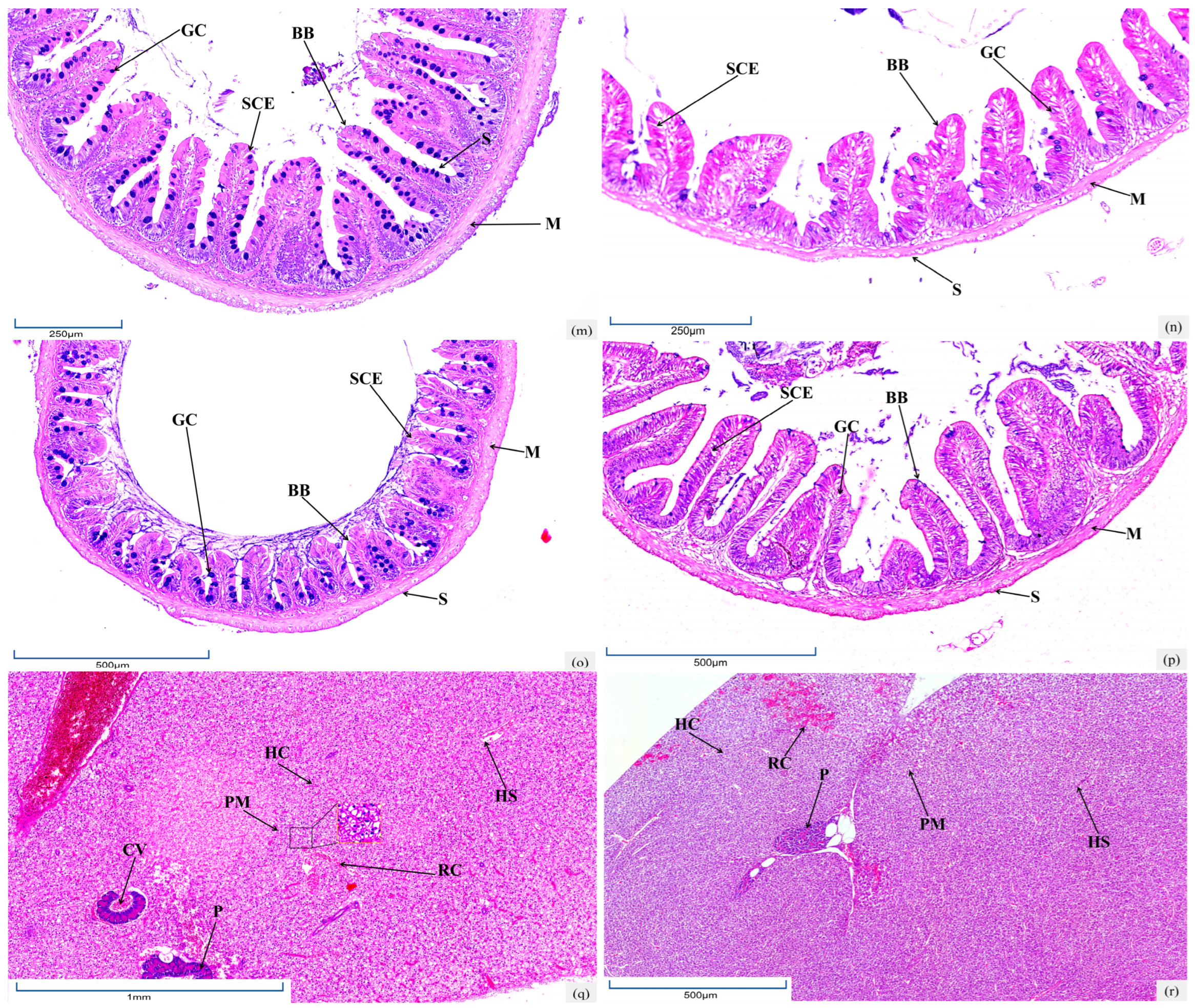
3.4. Histological Characteristics of Intestine
3.5. Histological Characteristics of Hepatopancreas
4. Discussion
4.1. Adaptive Remodeling of Digestive Tract Structure and Enhancement of Barrier Function
4.2. Stress Response and Metabolic Regulation of Hepatopancreas
4.3. Molecular Mechanisms Underlying Digestive System Adaptation
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hwang, P.-P.; Lee, T.-H. New insights into fish ion regulation and mitochondrion-rich cells. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2007, 148, 479–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tong, C.; Li, M. Genomic signature of accelerated evolution in a saline-alkaline lake-dwelling Schizothoracine fish. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2020, 149, 341–347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassani, A.; Azapagic, A.; Shokri, N. Global predictions of primary soil salinization under changing climate in the 21st century. Nat. Commun. 2021, 12, 6663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Chen, Y.; Wang, W.; Xia, Z.; Li, X.; Kayumba, P.M. Hydrochemical characteristics and evolution of groundwater in the dried-up river oasis of the Tarim Basin, Central Asia. J. Arid Land 2021, 13, 977–994. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.-A.; Hou, J.; Yao, N.; Xie, C.; Li, D. Comparative transcriptome analysis of Triplophysa yarkandensis in response to salinity and alkalinity stress. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D Genom. Proteom. 2020, 33, 100629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evans, T.G.; Kültz, D. The cellular stress response in fish exposed to salinity fluctuations. J. Exp. Zool. Part A Ecol. Integr. Physiol. 2020, 333, 421–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, L.; Jin, Y.; Wu, Y.; Sun, S. Effects of carbonate alkalinity on growth and intestinal health of Macrobrachium rosenbergii. J. Fish. Sci. China 2024, 31, 926–939. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Z.; Zhang, L.; Wei, J.; Hao, H.; Hamid, S.M.; Gao, S.; Li, W.; Nie, Z. Morphological and Histological Analysis of the Gastrointestinal Systems in Triplophysa strauchii and Triplophysa tenuis: Insights into Digestive Adaptations. Animals 2025, 15, 1095. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, H.; Yao, T.; Zhang, T.; Sun, M.; Ning, Z.; Chen, Y.; Mu, W. Effects of chronic saline-alkaline stress on gill, liver and intestinal histology, biochemical, and immune indexes in Amur minnow (Phoxinus lagowskii). Aquaculture 2024, 579, 740153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, S.-H.; Leu, J.-H.; Yang, C.-H.; Fang, M.-J.; Huang, C.-J.; Hwang, P.-P. Gene Expression of Na+-K+-ATPase a1 and a3 Subunits in Gills of the Teleost Oreochromis mossambicus, Adapted to Different Environmental Salinities. Mar. Biotechnol. 2002, 4, 379–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Z.; Hao, H.; Wei, J.; Wu, H.; Hamid, S.M.; Lv, R.; Lu, H.; Nie, Z. Morphology, Age, and Growth of Triplophysa strauchii in Sayram Lake, Xinjiang, China. Animals 2025, 15, 1039. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, S.; Stockwell, C.A.; Snider, M.R.; Wisenden, B.D. Epidermal Club Cells in Fishes: A Case for Ecoimmunological Analysis. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azizi, S.; Kochanian, P.; Peyghan, R.; Khansari, A.; Bastami, K.D. Chloride cell morphometrics of Common carp, Cyprinus carpio, in response to different salinities. Comp. Clin. Pathol. 2011, 20, 363–367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huerta-Aguirre, G.; Paredes-Ramos, K.M.; Becerra-Amezcua, M.P.; Hernández-Calderas, I.; Matadamas-Guzman, M.; Guzmán-García, X. Histopathological Analysis of the Intestine from Mugil cephalus on Environment Reference Sites. In Pollution of Water Bodies in Latin America: Impact of Contaminants on Species of Ecological Interest; Gómez-Oliván, L.M., Ed.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2019; pp. 319–328. [Google Scholar]
- Marshall, W.S.; Breves, J.P.; Doohan, E.M.; Tipsmark, C.K.; Kelly, S.P.; Robertson, G.N.; Schulte, P.M. Claudin-10 isoform expression and cation selectivity change with salinity in salt-secreting epithelia of Fundulus heteroclitus. J. Exp. Biol. 2018, 221, jeb168906. [Google Scholar]
- Younis, E.; Abdel-Warith, A.-W.; Al-Asgah, N.; Ebaid, H. Histopathological alterations in the liver and intestine of Nile tilapia Oreochromis niloticus exposed to long-term sublethal concentrations of cadmium chloride. Chin. J. Oceanol. Limnol. 2015, 33, 846–852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reverter, M.; Tapissier-Bontemps, N.; Lecchini, D.; Banaigs, B.; Sasal, P. Biological and Ecological Roles of External Fish Mucus: A Review. Fishes 2018, 3, 41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dildar, T.; Cui, W.; Ikhwanuddin, M.; Ma, H. Aquatic Organisms in Response to Salinity Stress: Ecological Impacts, Adaptive Mechanisms, and Resilience Strategies. Biology 2025, 14, 667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Edwards, S.L.; Marshall, W.S. 1-Principles and Patterns of Osmoregulation and Euryhalinity in Fishes. In Fish Physiology; McCormick, S.D., Farrell, A.P., Brauner, C.J., Eds.; Academic Press: Cambridge, MA, USA, 2012; Volume 32, pp. 1–44. [Google Scholar]
- Lin, S.-M.; Zhou, X.-M.; Zhou, Y.-L.; Kuang, W.-M.; Chen, Y.-J.; Luo, L.; Dai, F.-Y. Intestinal morphology, immunity and microbiota response to dietary fibers in largemouth bass, Micropterus salmoide. Fish Shellfish Immunol. 2020, 103, 135–142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ni, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Zheng, L.; Rong, N.; Yang, Y.; Gong, P.; Yang, Y.; Siwu, X.; Zhang, C.; Zhu, L.; et al. Bifidobacterium and Lactobacillus improve inflammatory bowel disease in zebrafish of different ages by regulating the intestinal mucosal barrier and microbiota. Life Sci. 2023, 324, 121699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.; Zhu, L.; Wei, Y.; Gao, P.; Liu, Y.; Zhou, K.; Sun, Z.; Lai, Q.; Yao, Z. Intestinal ion regulation exhibits a daily rhythm in Gymnocypris przewalskii exposed to high saline and alkaline water. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, L.; Chen, S.; Yao, C.; Li, D.; Li, L.; Tang, R. Nitrite induces endoplasmic reticulum stress and associates apoptosis of liver cells in grass carp (Ctenopharyngodon idella). Aquaculture 2019, 507, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dawood, M.A.O.; Noreldin, A.E.; Sewilam, H. Long term salinity disrupts the hepatic function, intestinal health, and gills antioxidative status in Nile tilapia stressed with hypoxia. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2021, 220, 112412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Balm, P.H.M.; Haenen, H.E.M.G.; Wendelaar Bonga, S.E. Regulation of interrenal function in freshwater and sea water adapted tilapia (Oreochromis mossambicus). Fish Physiol. Biochem. 1995, 14, 37–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hvas, M.; Nilsen, T.O.; Oppedal, F. Oxygen Uptake and Osmotic Balance of Atlantic Salmon in Relation to Exercise and Salinity Acclimation. Front. Mar. Sci. 2018, 5, 368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Zhang, Y.; Li, C.; Ai, K.; Li, K.; Li, H.; Yang, J. The evolutionarily conserved MAPK/Erk signaling promotes ancestral T-cell immunity in fish via c-Myc-mediated glycolysis. J. Biol. Chem. 2020, 295, 3000–3016. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moyson, S.; Liew, H.J.; Diricx, M.; Sinha, A.K.; Blust, R.; De Boeck, G. The combined effect of hypoxia and nutritional status on metabolic and ionoregulatory responses of common carp (Cyprinus carpio). Comp. Biochem. Physiol. A Mol. Integr. Physiol. 2015, 179, 133–143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Yao, M.; Li, S.; Wei, X.; Ding, L.; Han, S.; Wang, P.; Lv, B.; Chen, Z.; Sun, Y. Integrated application of multi-omics approach and biochemical assays provides insights into physiological responses to saline-alkaline stress in the gills of crucian carp (Carassius auratus). Sci. Total Environ. 2022, 822, 153622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Morphological Index | Group | Oropharyngeal Cavity | Esophagus | Cardia | Stomach | Pylorus | Foregut | Midgut | Hindgut |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Club cell (cell number/100 μm) | Saline-alkali water | 48.50 ± 2.68 a | - | - | - | - | - | - | - |
| Freshwater | 17.80 ± 2.04 c | - | - | - | - | - | - | - | |
| Mucosal fold height/μm | Saline-alkali water | - | 220.13 ± 36.68 a | 196.53 ± 84.95 a | 367.56 ± 66.07 a | 178.69 ± 21.12 a | 677.31 ± 24.60 a | 219.07 ± 41.07 a | 125.40 ± 7.92 a |
| Freshwater | - | 360.93 ± 115.51 c | 290.91 ± 31.85 c | 419.91 ± 64.04 c | 185.24 ± 17.48 c | 591.17 ± 10.05 c | 158.10 ± 15.05 c | 313.11 ± 36.59 c | |
| Mucosal fold width/μm | Saline-alkali water | - | 63.42 ± 20.86 a | 77.79 ± 28.89 a | 57.33 ± 5.21 a | 71.65 ± 17.56 a | 9.06 ± 2.47 a | 13.15 ± 3.62 a | 6.71 ± 1.44 a |
| Freshwater | - | 158.04 ± 55.29 c | 113.33 ± 12.04 c | 68.79 ± 4.90 c | 38.62 ± 9.18 c | 12.40 ± 2.33 c | 10.20 ± 0.90 c | 13.10 ± 4.09 c | |
| Submucosa thick/μm | Saline-alkali water | - | 29.06 ± 4.97 a | 79.52 ± 15.63 a | 68.02 ± 10.02 a | 20.62 ± 2.79 a | 6.73 ± 0.85 a | 8.92 ± 1.21 a | 9.22 ± 0.58 a |
| Freshwater | - | 48.09 ± 6.19 c | 58.47 ± 10.17 c | 52.77 ± 4.06 c | 26.47 ± 4.24 c | 9.75 ± 2.02 c | 5.00 ± 1.36 c | 9.59 ± 0.61 c | |
| Muscle layer thickness/μm | Saline-alkali water | - | 102.61 ± 11.88 a | 156.02 ± 33.23 a | 91.28 ± 4.29 a | 475.47 ± 41.51 a | 27.30 ± 2.71 a | 26.40 ± 1.62 a | 26.15 ± 3.57 a |
| Freshwater | - | 125.12 ± 48.96 c | 89.26 ± 6.88 c | 97.05 ± 3.38 c | 399.57 ± 32.85 c | 18.67 ± 0.98 c | 12.76 ± 1.24 c | 17.27 ± 1.31 c | |
| Goblet cell (cell number/100 μm) | Saline-alkali water | - | 104.42 ± 6.67 a | - | - | - | 82.00 ± 5.58 a | 72.50 ± 4.30 a | 21.50 ± 3.03 a |
| Freshwater | - | 59.94 ± 4.68 c | - | - | - | 41.20 ± 2.74 c | 39.40 ± 4.22 c | 19.90 ± 1.85 c | |
| The quantity of intestinal villi | Saline-alkali water | - | - | - | - | - | 12.70 ± 1.16 a | 12.60 ± 1.35 a | 12.40 ± 0.97 a |
| Freshwater | - | - | - | - | - | 6.80 ± 1.48 c | 10.20 ± 1.32 c | 8.20 ± 0.63 c |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Wang, Z.; Hao, Y.; Chen, Y.; Ji, Q.; Ai, T.; Zhang, S.; Wei, J.; Huang, Z.; Nie, Z. Histological Study on Digestive System of Triplophysa yarkandensis in Saline-Alkali and Freshwater Environments: Adaptive Mechanisms. Biology 2025, 14, 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091187
Wang Z, Hao Y, Chen Y, Ji Q, Ai T, Zhang S, Wei J, Huang Z, Nie Z. Histological Study on Digestive System of Triplophysa yarkandensis in Saline-Alkali and Freshwater Environments: Adaptive Mechanisms. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091187
Chicago/Turabian StyleWang, Zhengwei, Yichao Hao, Yinsheng Chen, Qing Ji, Tao Ai, Shijing Zhang, Jie Wei, Zhaohua Huang, and Zhulan Nie. 2025. "Histological Study on Digestive System of Triplophysa yarkandensis in Saline-Alkali and Freshwater Environments: Adaptive Mechanisms" Biology 14, no. 9: 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091187
APA StyleWang, Z., Hao, Y., Chen, Y., Ji, Q., Ai, T., Zhang, S., Wei, J., Huang, Z., & Nie, Z. (2025). Histological Study on Digestive System of Triplophysa yarkandensis in Saline-Alkali and Freshwater Environments: Adaptive Mechanisms. Biology, 14(9), 1187. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091187






