Grazing-Induced Changes in circRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs Expression in Tibetan Sheep Biceps Femoris
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Experimental Animals and Sample Collection
2.2. IMF Content Measurements
2.3. RNA Extraction, Library Construction and Sequencing
2.4. Read Mapping and Transcript Assembly
2.5. Identification of circRNAs and miRNAs
2.6. Quantification and Differential Expression Analysis
2.7. Functional Annotation and Pathways Enrichment Analysis
2.8. Construction of the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network
3. Results
3.1. Differences in Meat Quality
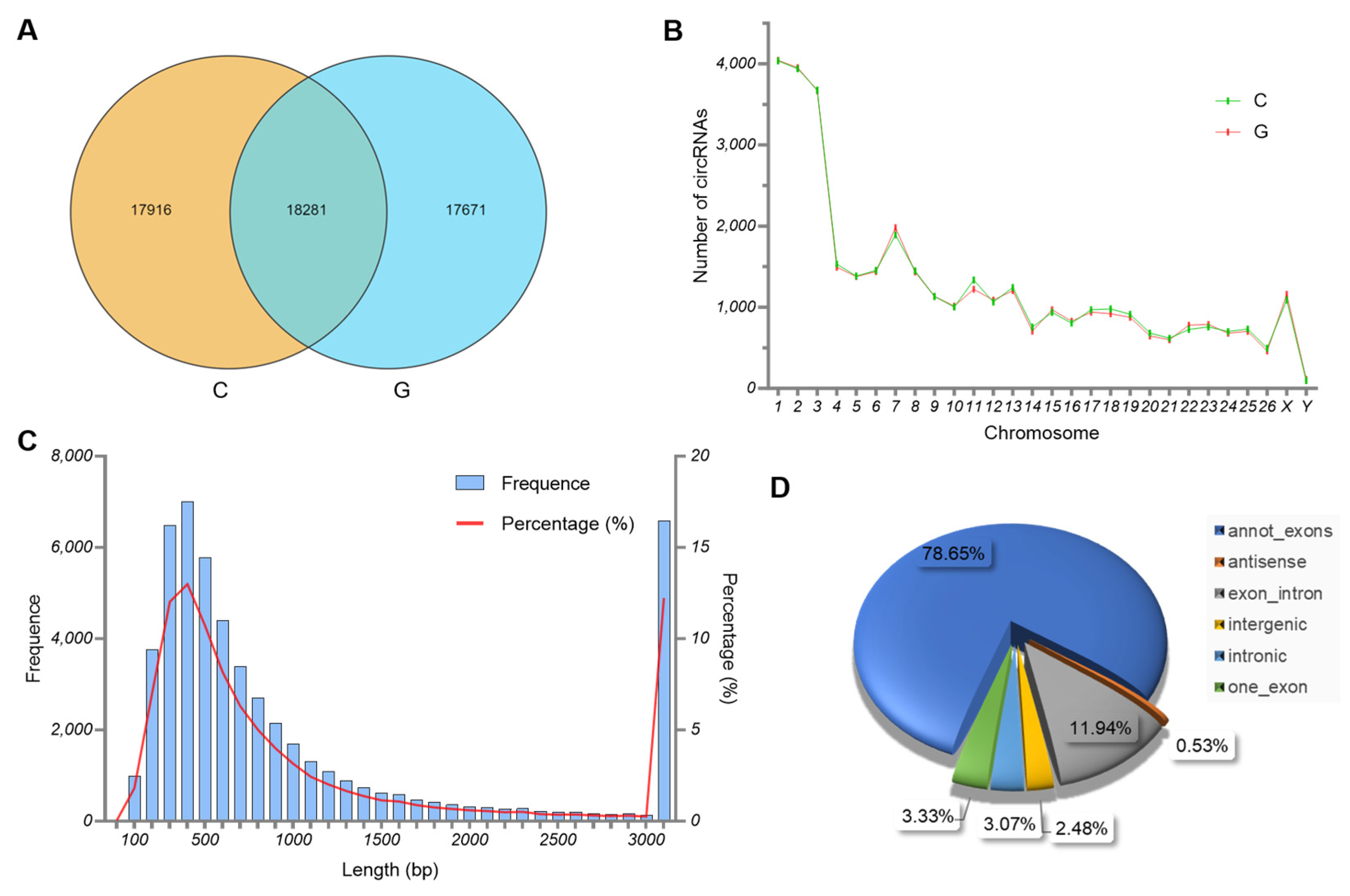
3.2. Characteristics of circRNAs
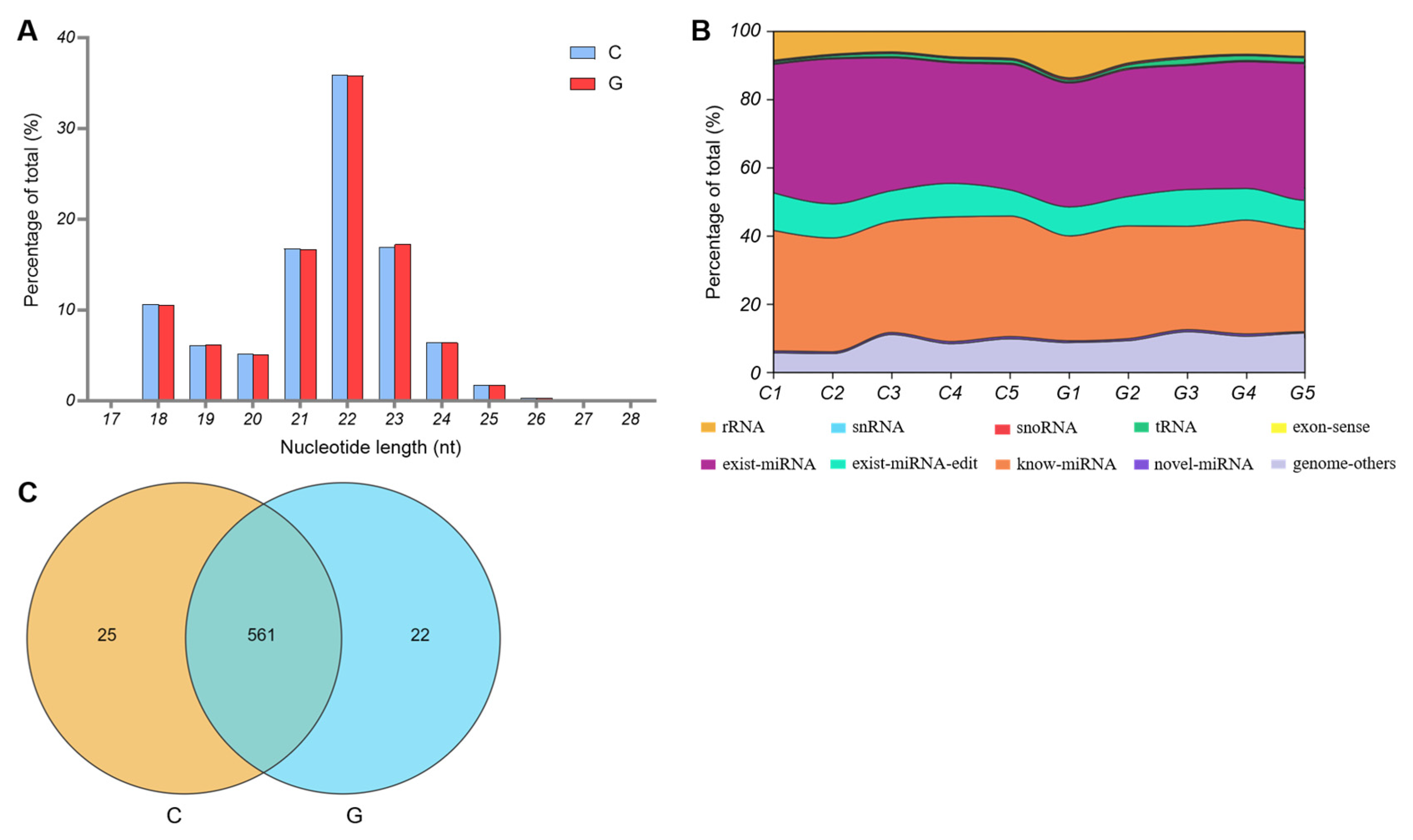
3.3. Characteristics of miRNAs
3.4. Differential Expression of circRNA and miRNA
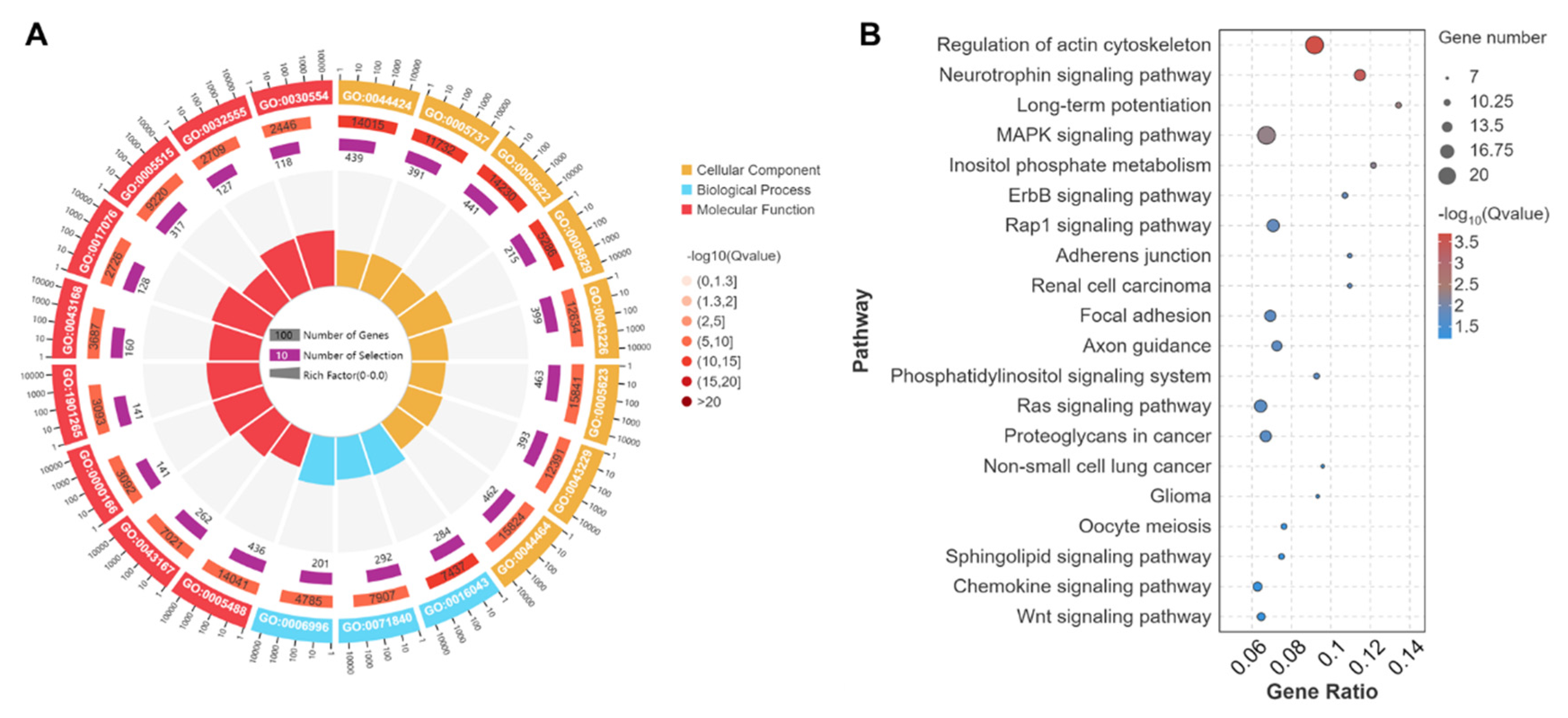
3.5. GO and KEGG Analyses of Source Genes of DEcircRNAs
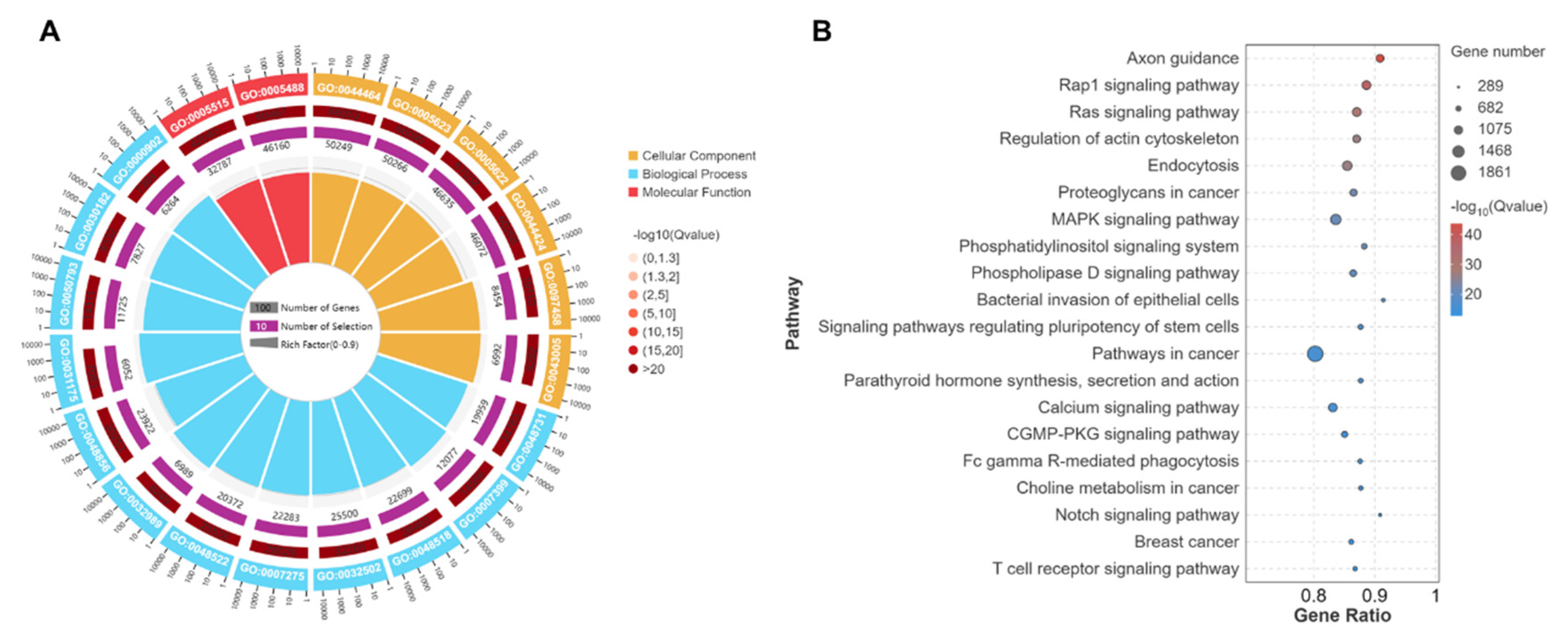
3.6. GO and KEGG Analyses of Target Genes of DEmiRNAs
3.7. Network Diagram of circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Regulatory Relationships
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| IMF | Intramuscular fat |
| G | Grazing group |
| C | Control group |
| RIN | RNA integrity number |
| cDNA | Complementary DNA |
| nt | Nucleotides |
| bp | Base pairs |
| DEcircRNAs | Differentially expressed circRNAs |
| DEmiRNAs | Differentially expressed miRNAs |
| GO | Gene ontology |
| KEGG | Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes |
| SCCs | Spearman’s rank correlation coefficient |
| PCCs | Pearson correlation coefficients |
| ceRNA | Competitive endogenous RNAs |
References
- Hu, X.-J.; Yang, J.; Xie, X.-L.; Lv, F.-H.; Cao, Y.-H.; Li, W.-R.; Liu, M.-J.; Wang, Y.-T.; Li, J.-Q.; Liu, Y.-G.; et al. The Genome Landscape of Tibetan Sheep Reveals Adaptive Introgression from Argali and the History of Early Human Settlements on the Qinghai-Tibetan Plateau. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2019, 36, 283–303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, L. Animal Genetic Resources in China: Sheep and Goats; China Agriculture Press: Beijing, China, 2011. [Google Scholar]
- Wei, C.; Wang, H.; Liu, G.; Wu, M.; Cao, J.; Liu, Z.; Liu, R.; Zhao, F.; Zhang, L.; Lu, J.; et al. Genome-wide analysis reveals population structure and selection in Chinese indigenous sheep breeds. BMC Genom. 2015, 16, 194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andersen, H.J. What is Pork Quality? Quality of Meat and Fat in Pigs as Affected by Genetics and Nutrition; EAAP Publication: Zurich, Switzerland, 2000. [Google Scholar]
- Li, R.; Li, B.; Jiang, A.; Cao, Y.; Hou, L.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Liu, H.; Kim, K.-H.; Wu, W. Exploring the lncRNAs Related to Skeletal Muscle Fiber Types and Meat Quality Traits in Pigs. Genes 2020, 11, 883. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogomolova, A.P.; Katrukha, I.A. Troponins and Skeletal Muscle Pathologies. Biochemistry 2024, 89, 2083–2106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, L.; Zhao, C.; Sun, B.; Dou, L.; Wang, C.; Yang, Z.; Li, T.; Jin, Y. Effects of exercise on muscle fiber conversion, muscle development and meat quality of Sunit sheep. Meat Sci. 2024, 211, 109440. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Wang, J.; Chen, H.; Su, H.; Wang, Z.; Wan, Y.; Huang, Y.; Jiang, R. Effects of exercise on carcass composition, meat quality, and mRNA expression profiles in breast muscle of a Chinese indigenous chicken breed. Poult. Sci. 2019, 98, 5241–5246. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frontera, W.R.; Ochala, J. Skeletal muscle: A brief review of structure and function. Calcif. Tissue Int. 2015, 96, 183–195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Song, S.; Ahn, C.H.; Kim, G.D. Muscle Fiber Typing in Bovine and Porcine Skeletal Muscles Using Immunofluorescence with Monoclonal Antibodies Specific to Myosin Heavy Chain Isoforms. Food Sci. Anim. Resour. 2020, 40, 132–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chaosap, C.; Sitthigripong, R.; Sivapirunthep, P.; Pungsuk, A.; Adeyemi, K.D.; Sazili, A.Q. Myosin heavy chain isoforms expression, calpain system and quality characteristics of different muscles in goats. Food Chem. 2020, 321, 126677. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lefaucheur, L. A second look into fibre typing—Relation to meat quality. Meat Sci. 2010, 84, 257–270. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alasnier, C.; Rémignon, H.; Gandemer, G. Lipid characteristics associated with oxidative and glycolytic fibres in rabbit muscles. Meat Sci. 1996, 43, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Renand, G.; Picard, B.; Touraille, C.; Berge, P.; Lepetit, J. Relationships between muscle characteristics and meat quality traits of young Charolais bulls. Meat Sci. 2001, 59, 49–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, P.; Li, P.; Zhou, W.; Fan, L.; Wang, B.; Liu, H.; Gao, C.; Du, T.; Pu, G.; Wu, C.; et al. Effects of various levels of dietary fiber on carcass traits, meat quality and myosin heavy chain I, IIa, IIx and IIb expression in muscles in Erhualian and Large White pigs. Meat Sci. 2020, 169, 108160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Folch, J.; Lees, M.; Sloane, S.G.H. A simple method for the isolation and purification of total lipides from animal tissues. J. Biol. Chem. 1957, 226, 497–509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Zhou, Y.; Chen, Y.; Gu, J. fastp: An ultra-fast all-in-one FASTQ preprocessor. Bioinformatics 2018, 34, i884–i890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, D.; Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. HISAT: A fast spliced aligner with low memory requirements. Nat. Methods 2015, 12, 357–360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertea, M.; Pertea, G.M.; Antonescu, C.M.; Chang, T.C.; Mendell, J.T.; Salzberg, S.L. StringTie enables improved reconstruction of a transcriptome from RNA-seq reads. Nat. Biotechnol. 2015, 33, 290–295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Yang, J.; Zhao, F. Accurate quantification of circular RNAs identifies extensive circular isoform switching events. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozomara, A.; Griffiths-Jones, S. miRBase: Annotating high confidence microRNAs using deep sequencing data. Nucleic Acids Res. 2014, 42, D68–D73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mackowiak, S.D. Identification of novel and known miRNAs in deep-sequencing data with miRDeep2. Curr. Protoc. Bioinform. 2011, 12, 12.10.1–12.10.15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anders, S.; Huber, W. Differential expression analysis for sequence count data. Genome Biol. 2010, 11, R106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, G.; Wang, L.; Han, Y.; He, Q. clusterProfiler: An R package for comparing biological themes among gene clusters. Omics A J. Integr. Biol. 2012, 16, 284–287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ashburner, M.; Ball, C.A.; Blake, J.A.; Botstein, D.; Butler, H.; Cherry, J.M.; Davis, A.P.; Dolinski, K.; Dwight, S.S.; Eppig, J.T.; et al. Gene ontology: Tool for the unification of biology. The Gene Ontology Consortium. Nat. Genet. 2000, 25, 25–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kanehisa, M.; Goto, S. KEGG: Kyoto encyclopedia of genes and genomes. Nucleic Acids Res. 2000, 28, 27–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Zhang, S.; Li, C.; Zhang, X.; Shan, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Bo, H.; Zhang, Y. Endurance exercise-induced histone methylation modification involved in skeletal muscle fiber type transition and mitochondrial biogenesis. Sci. Rep. 2024, 14, 21154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bao, G.; Zhao, F.; Wang, J.; Liu, X.; Hu, J.; Shi, B.; Wen, Y.; Zhao, L.; Luo, Y.; Li, S. Characterization of the circRNA-miRNA-mRNA Network to Reveal the Potential Functional ceRNAs Associated with Dynamic Changes in the Meat Quality of the Longissimus Thoracis Muscle in Tibetan Sheep at Different Growth Stages. Front. Vet. Sci. 2022, 9, 803758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, M.; Wei, X.; Song, M.; Jiang, R.; Huang, K.; Deng, Y.; Liu, Q.; Shi, D.; Li, H. Circular RNA circMYBPC1 promotes skeletal muscle differentiation by targeting MyHC. Mol. Ther.-Nucleic Acids 2021, 24, 352–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, K.; Chen, M.; Zhong, D.; Luo, X.; Feng, T.; Song, M.; Chen, Y.; Wei, X.; Shi, D.; Liu, Q.; et al. Circular RNA Profiling Reveals an Abundant circEch1 That Promotes Myogenesis and Differentiation of Bovine Skeletal Muscle. J. Agric. Food Chem. 2021, 69, 592–601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, M.; Zhang, N.; Zhang, W.; Hei, W.; Cai, C.; Yang, Y.; Lu, C.; Gao, P.; Guo, X.; Cao, G.; et al. Comprehensive analysis of differentially expressed circRNAs and ceRNA regulatory network in porcine skeletal muscle. BMC Genom. 2021, 22, 320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, K.; Liu, Y.; Li, C.; Li, X.; Li, X.; Wang, K.; Qiao, R.; Han, X. Construction of circRNA-related ceRNA networks in longissimus dorsi muscle of Queshan Black and Large White pigs. Mol. Genet. Genom. MGG 2022, 297, 101–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Shyamal, S.; Sinha, T.; Mishra, S.S.; Panda, A.C. Identification of Potential circRNA-microRNA-mRNA Regulatory Network in Skeletal Muscle. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 762185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, L.; Xu, D.; Li, W.; Wang, Y.; Cao, N.; Fu, X.; Tian, Y.; Li, Y.; Li, B. Non-coding RNA regulation of Magang geese skeletal muscle maturation via the MAPK signaling pathway. Front. Physiol. 2024, 14, 1331974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kwon, I.; Kim, K.S.; Lee, Y. Relationships between endurance exercise training-induced muscle fiber-type shifting and autophagy in slow- and fast-twitch skeletal muscles of mice. Phys. Act. Nutr. 2024, 28, 23–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DiGirolamo, D.J.; Kiel, D.P.; Esser, K.A. Bone and skeletal muscle: Neighbors with close ties. J. Bone Miner. Res. 2013, 28, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, X.C.; Xia, B.; Zhang, J.F.; Zhang, R.X.; Zhang, D.Y.; Liu, H.; Xie, B.C.; Wang, Y.L.; Wu, J.W.; Hughes, S.M. Optineurin promotes myogenesis during muscle regeneration in mice by autophagic degradation of GSK3β. PLoS Biol. 2022, 20, e3001619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slot, I.G.; Schols, A.M.; Vosse, B.A.; Kelders, M.C.; Gosker, H.R. Hypoxia differentially regulates muscle oxidative fiber type and metabolism in a HIF-1α-dependent manner. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 1837–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karakilic, A.; Yuksel, O.; Kizildag, S.; Hosgorler, F.; Topcugil, B.; Ilgin, R.; Gumus, H.; Guvendi, G.; Koc, B.; Kandis, S.; et al. Regular aerobic exercise increased VEGF levels in both soleus and gastrocnemius muscles correlated with hippocampal learning and VEGF levels. Acta Neurobiol. Exp. 2021, 81, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tay, Y.; Rinn, J.; Pandolfi, P.P. The multilayered complexity of ceRNA crosstalk and competition. Nature 2014, 505, 344–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Z.; Tong, H.; Yan, Y.; Li, S. Effects of COL8A1 on the proliferation of muscle-derived satellite cells. Cell Biol. Int. 2018, 42, 1132–1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Somlyo, A.V.; Wang, H.; Choudhury, N.; Khromov, A.S.; Majesky, M.; Owens, G.K.; Somlyo, A.P. Myosin light chain kinase knockout. J. Muscle Res. Cell Motil. 2004, 25, 241–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youm, T.H.; Woo, S.H.; Kwon, E.S.; Park, S.S. NADPH Oxidase 4 Contributes to Myoblast Fusion and Skeletal Muscle Regeneration. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2019, 2019, 3585390. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cully, T.R.; Rodney, G.G. Nox4-RyR1-Nox2: Regulators of micro-domain signaling in skeletal muscle. Redox Biol. 2020, 36, 101557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, Y.M.; Kim, S.J.; Tatsunami, R.; Yamamura, H.; Fukai, T.; Ushio-Fukai, M. ROS-induced ROS release orchestrated by Nox4, Nox2, and mitochondria in VEGF signaling and angiogenesis. Am. J. Physiol.-Cell Physiol. 2017, 312, C749–C764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]



Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Ma, X.; Li, S.; Chen, Z.; He, Z.; Ren, J.; Tao, S.; Zhang, L.; Zhao, P. Grazing-Induced Changes in circRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs Expression in Tibetan Sheep Biceps Femoris. Biology 2025, 14, 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091143
Ma X, Li S, Chen Z, He Z, Ren J, Tao S, Zhang L, Zhao P. Grazing-Induced Changes in circRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs Expression in Tibetan Sheep Biceps Femoris. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091143
Chicago/Turabian StyleMa, Xiong, Shaobin Li, Zhanzhao Chen, Zhaohua He, Jianming Ren, Shiyu Tao, Lan Zhang, and Pengfei Zhao. 2025. "Grazing-Induced Changes in circRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs Expression in Tibetan Sheep Biceps Femoris" Biology 14, no. 9: 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091143
APA StyleMa, X., Li, S., Chen, Z., He, Z., Ren, J., Tao, S., Zhang, L., & Zhao, P. (2025). Grazing-Induced Changes in circRNAs, miRNAs and mRNAs Expression in Tibetan Sheep Biceps Femoris. Biology, 14(9), 1143. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091143






