Hypoxia-Driven Extracellular Vesicles Promote Pro-Metastatic Signalling in LNCaP Cells via Wnt and EMT Pathways
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell Culture
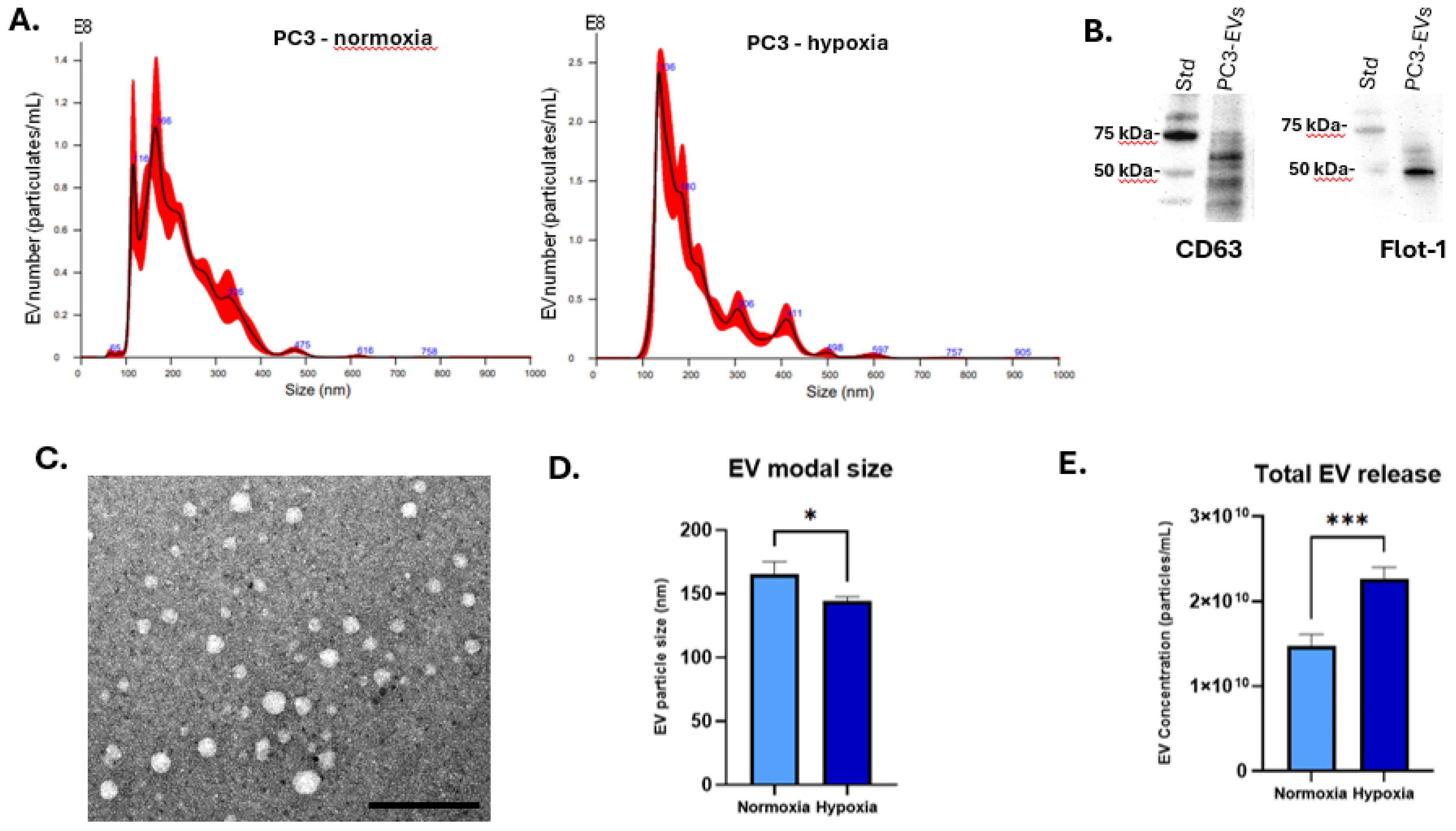
2.2. EV Isolation and Characterisation
2.3. RNA Extraction and qRT-PCR for Hypoxia, Wnt Signalling and EMT-Related Gene Expression Changes
2.4. Wound Healing and Invasion Assays
2.5. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Hypoxia Enhances EV Secretion and Alters EV Profiles
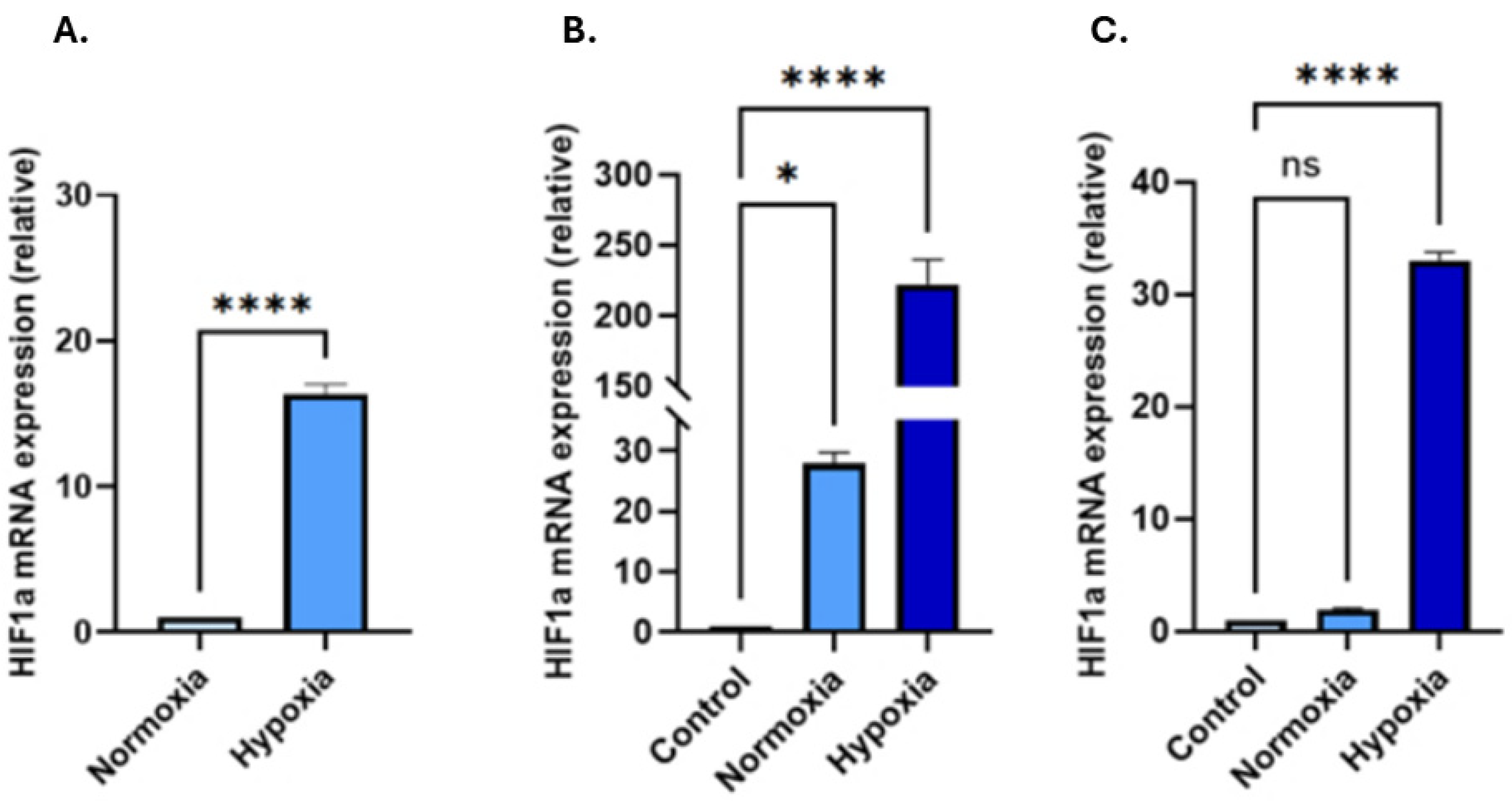
3.2. Hypoxic Treatment Increases HIF-1α in EVs and in Recipient Cells Following Hypoxia-EV Transplant
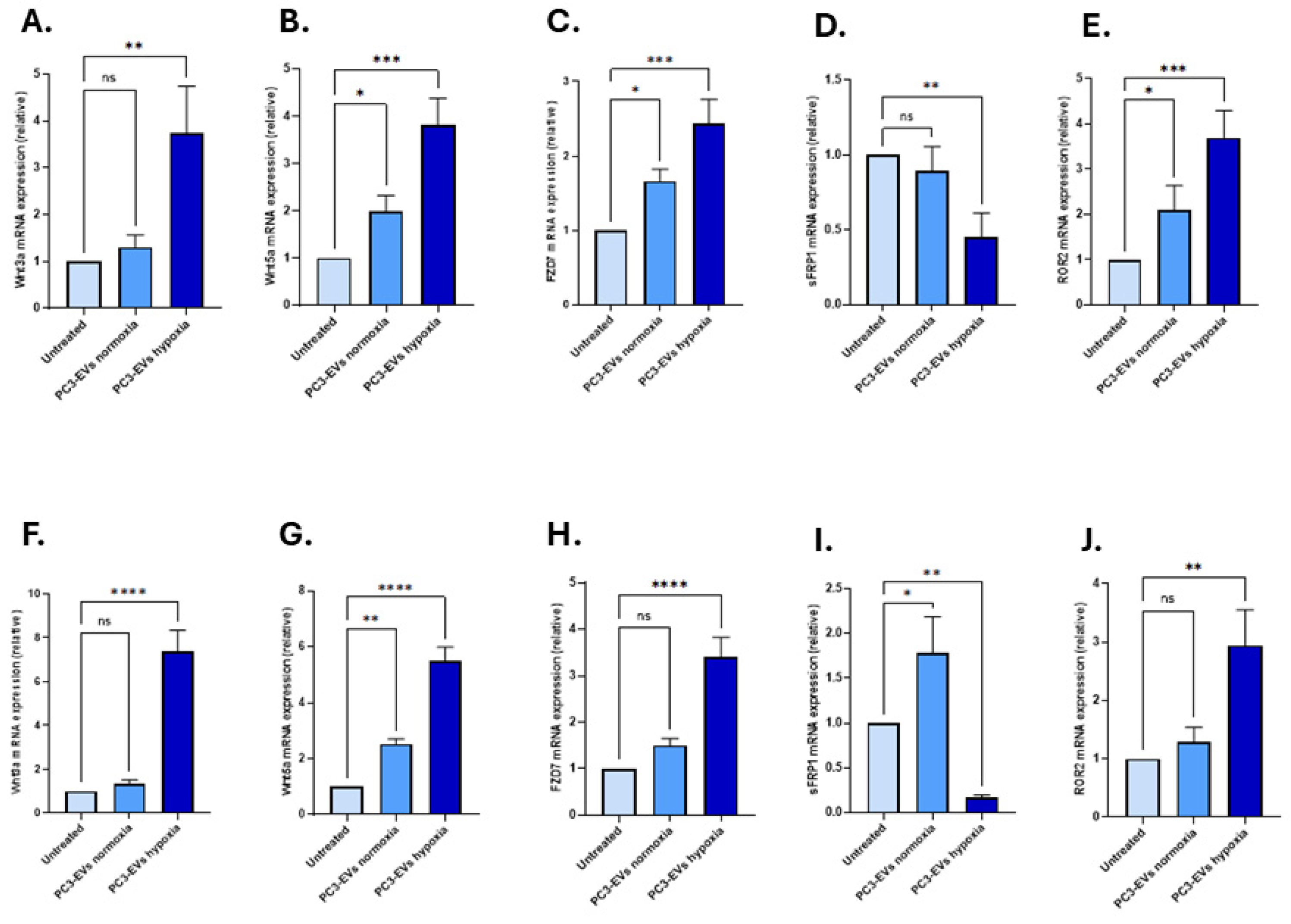
3.3. EVs from PC3 Hypoxia-Treated Cells Activate Wnt Signalling and Induce EMT in LNCaP and PNT2 Cells
Effects of PC3-Derived EVs from Hypoxia Conditions on EMT Markers
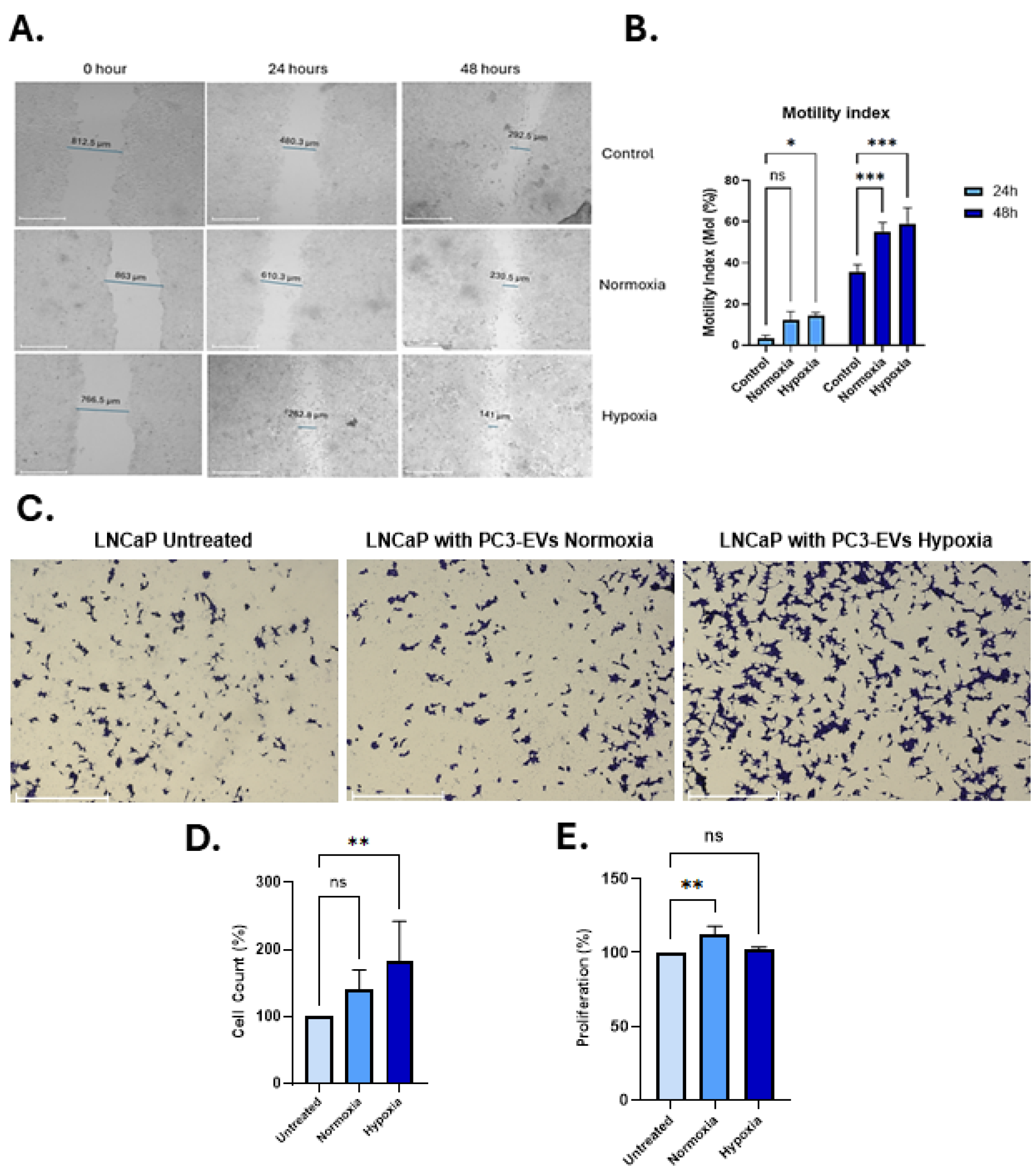
3.4. PC3-EVs from Hypoxia Conditions Enhance Motility and Invasion of LNCaP PCa Cells
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| ADT | Androgen Deprivation Therapy |
| AR | Androgen Receptor |
| CAFs | Cancer-Associated Fibroblasts |
| CSC | Cancer Stem Cell |
| CRPC | Castration-Resistant Prostate Cancer |
| CXCL8 | C-X-C Motif Chemokine Ligand 8 (also known as Interleukin-8) |
| DAPI | 4′,6-Diamidino-2-Phenylindole (a fluorescent DNA stain) |
| DMEM | Dulbecco’s Modified Eagle Medium |
| ECM | Extracellular Matrix |
| EMT | Epithelial-to-Mesenchymal Transition |
| EVs | Extracellular Vesicles |
| FBS | Fetal Bovine Serum |
| Fzd7 | Frizzled Class Receptor 7 |
| Glut1 | Glucose Transporter 1 |
| HIF-1α | Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1-alpha |
| lncRNA | Long Non-Coding RNA |
| LNCaP | Lymph Node Carcinoma of the Prostate (a prostate cancer cell line) |
| miRNA | MicroRNA |
| MMP2 | Matrix Metalloproteinase 2 |
| MMP9 | Matrix Metalloproteinase 9 |
| MTT | 3-(4,5-Dimethylthiazol-2-yl)-2,5-Diphenyltetrazolium Bromide (a cell viability assay) |
| N-cad | N-cadherin (Neural cadherin) |
| PBS | Phosphate-Buffered Saline |
| PC3 | Prostate Cancer Cell Line 3 |
| PCa | Prostate Cancer |
| PHD | Prolyl Hydroxylase Domain (enzymes) |
| PI3K | Phosphatidylinositol 3-Kinase |
| PNT2 | Prostate Normal Tissue 2 (non-tumorigenic prostate epithelial cell line) |
| qPCR | Quantitative Polymerase Chain Reaction |
| ROR2 | Receptor Tyrosine Kinase-Like Orphan Receptor 2 |
| sFRP1 | Secreted Frizzled-Related Protein 1 |
| VEGF | Vascular Endothelial Growth Factor |
| Vim | Vimentin |
| VHL | von Hippel–Lindau Protein |
| Wnt | Wingless/Integrated (signalling pathway) |
References
- Berenguer, C.V.; Pereira, F.; Câmara, J.S.; Pereira, J.A.M. Underlying Features of Prostate Cancer—Statistics, Risk Factors, and Emerging Methods for Its Diagnosis. Curr. Oncol. 2023, 30, 2300–2321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sung, H.; Ferlay, J.; Siegel, R.L.; Laversanne, M.; Soerjomataram, I.; Jemal, A.; Bray, F. Global Cancer Statistics 2020: GLOBOCAN Estimates of Incidence and Mortality Worldwide for 36 Cancers in 185 Countries. CA Cancer J. Clin. 2021, 71, 209–249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kania, E.; Janica, M.; Nesterowicz, M.; Modzelewski, W.; Cybulski, M.; Janica, J. Advances and Challenges in Prostate Cancer Diagnosis: A Comprehensive Review. Cancers 2025, 17, 2137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, M.; Koushyar, S.; Dart, D.A.; Uysal-Onganer, P. From Hypoxia to Bone: Reprogramming the Prostate Cancer Metastatic Cascade. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2025, 26, 7452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zhao, L.; Li, X.-F. Hypoxia and the Tumor Microenvironment. Technol. Cancer Res. Treat. 2021, 20, 15330338211036304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohamed, O.A.A.; Tesen, H.S.; Hany, M.; Sherif, A.; Abdelwahab, M.M.; Elnaggar, M.H. The Role of Hypoxia on Prostate Cancer Progression and Metastasis. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2023, 50, 3873–3884. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wicks, E.E.; Semenza, G.L. Hypoxia-Inducible Factors: Cancer Progression and Clinical Translation. J. Clin. Investig. 2022, 132, e159839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tirpe, A.A.; Gulei, D.; Ciortea, S.M.; Crivii, C.; Berindan-Neagoe, I. Hypoxia: Overview on Hypoxia-Mediated Mechanisms with a Focus on the Role of HIF Genes. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2019, 20, 6140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, X.; Liu, R.; Li, W.; Yu, Q.; Yang, Q.T.; Li, T. Advances in Research Regarding Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Prostate Cancer. Front. Cell Dev. Biol. 2025, 13, 1583255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, R.; Manzoor, M.; Hussain, A. Wnt Signaling Pathway: A Comprehensive Review. Cell Biol. Int. 2022, 46, 863–877. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, C.; Chu, Q.; Shi, Q.; Zeng, Y.; Lu, J.; Li, L. Wnt Signaling Pathways in Biology and Disease: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Advances. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2025, 10, 106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chang, W.H.; Lai, A.G. Pan-Cancer Genomic Amplifications Underlie a Wnt Hyperactivation Phenotype Associated with Stem Cell-like Features Leading to Poor Prognosis. Transl. Res. 2019, 208, 47–62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, K.; Ma, F.; Arai, S.; Wang, Y.; Varkaris, A.; Poluben, L.; Voznesensky, O.; Xie, F.; Zhang, X.; Yuan, X.; et al. WNT5a Signaling through ROR2 Activates the Hippo Pathway to Suppress YAP1 Activity and Tumor Growth. Cancer Res. 2023, 83, 1016–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, C.-F.; Chen, W.-Y.; Wu, C.-W. Upregulation of Wnt Signaling under Hypoxia Promotes Lung Cancer Progression. Oncol. Rep. 2017, 38, 1706–1714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Papanikolaou, S.; Vourda, A.; Syggelos, S.; Gyftopoulos, K. Cell Plasticity and Prostate Cancer: The Role of Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in Tumor Progression, Invasion, Metastasis and Cancer Therapy Resistance. Cancers 2021, 13, 2795. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koushyar, S.; Meniel, V.S.; Phesse, T.J.; Pearson, H.B. Exploring the Wnt Pathway as a Therapeutic Target for Prostate Cancer. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amiri-Farsani, M.; Taheri, Z.; Tirbakhsh Gouran, S.; Chabok, O.; Safarpour-Dehkordi, M.; Kazemi Roudsari, M. Cancer Stem Cells: Recent Trends in Cancer Therapy. Nucleosides Nucleotides Nucleic Acids 2024, 43, 1383–1414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, Y.; Wang, W.; Zhao, C. Frizzled Receptors in Tumors, Focusing on Signaling, Roles, Modulation Mechanisms, and Targeted Therapies. Oncol. Res. 2021, 28, 661–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, H.; Sun, X.; Xiu, S.; Zhang, X.; Wang, Z.; Gu, Y.; Yi, C.; Liu, J.; Dai, Y.; Yuan, X.; et al. Frizzled Receptors (FZDs) in Wnt Signaling: Potential Therapeutic Targets for Human Cancers. Acta Pharmacol. Sin. 2024, 45, 1556–1570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Surana, R.; Sikka, S.; Cai, W.; Shin, E.M.; Warrier, S.R.; Tan, H.J.G.; Arfuso, F.; Fox, S.A.; Dharmarajan, A.M.; Kumar, A.P. Secreted Frizzled Related Proteins: Implications in Cancers. Biochim. Biophys. Acta (BBA)—Rev. Cancer 2014, 1845, 53–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- García-Tobilla, P.; Solórzano, S.R.; Salido-Guadarrama, I.; González-Covarrubias, V.; Morales-Montor, G.; Díaz-Otañez, C.E.; Rodríguez-Dorantes, M. SFRP1 Repression in Prostate Cancer Is Triggered by Two Different Epigenetic Mechanisms. Gene 2016, 593, 292–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menck, K.; Heinrichs, S.; Baden, C.; Bleckmann, A. The WNT/ROR Pathway in Cancer: From Signaling to Therapeutic Intervention. Cells 2021, 10, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tse, S.W.; Tan, C.F.; Park, J.E.; Gnanasekaran, J.; Gupta, N.; Low, J.K.; Yeoh, K.W.; Chng, W.J.; Tay, C.Y.; McCarthy, N.E.; et al. Microenvironmental Hypoxia Induces Dynamic Changes in Lung Cancer Synthesis and Secretion of Extracellular Vesicles. Cancers 2020, 12, 2917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, S.; Huang, J.; Li, G.; Chen, W.; Li, Z.; Lei, J. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in Circulating Tumor Cell-Mediated Distant Metastasis. Mol. Cancer 2023, 22, 193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, M.A.; Baba, S.K.; Sadida, H.Q.; Marzooqi, S.A.; Jerobin, J.; Altemani, F.H.; Algehainy, N.; Alanazi, M.A.; Abou-Samra, A.-B.; Kumar, R.; et al. Extracellular Vesicles as Tools and Targets in Therapy for Diseases. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2024, 9, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, C.; Chen, Q.; Wu, T.; Du, X.; Dong, Y.; Peng, Z.; Xue, W.; Sunkara, V.; Cho, Y.-K.; Dong, L. The Role of Extracellular Vesicles in the Treatment of Prostate Cancer. Small 2024, 20, 2311071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Huo, M.; Li, W.; Zhang, H.; Liu, Q.; Jiang, J.; Fu, Y.; Huang, C. Exosomes in Tumor-Stroma Crosstalk: Shaping the Immune Microenvironment in Colorectal Cancer. FASEB J. 2024, 38, e23548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, Z.-W.; Yu, Z.-L.; Chen, G.; Jia, J. Extracellular Vesicles in Tumor Angiogenesis and Resistance to Anti-Angiogenic Therapy. Cancer Sci. 2023, 114, 2739–2749. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, R.; Baba, S.K.; Elfaki, I.; Algehainy, N.; Alanazi, M.A.; Altemani, F.H.; Tayeb, F.J.; Barnawi, J.; Husain, E.; Bedaiwi, R.I.; et al. Unlocking the Secrets of Extracellular Vesicles: Orchestrating Tumor Microenvironment Dynamics in Metastasis, Drug Resistance, and Immune Evasion. J. Cancer 2024, 15, 6383–6415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lian, M.; Mortoglou, M.; Uysal-Onganer, P. Impact of Hypoxia-Induced miR-210 on Pancreatic Cancer. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 9778–9792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Emami Nejad, A.; Najafgholian, S.; Rostami, A.; Sistani, A.; Shojaeifar, S.; Esparvarinha, M.; Nedaeinia, R.; Haghjooy Javanmard, S.; Taherian, M.; Ahmadlou, M.; et al. The Role of Hypoxia in the Tumor Microenvironment and Development of Cancer Stem Cell: A Novel Approach to Developing Treatment. Cancer Cell Int. 2021, 21, 62. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Wang, J. Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Prostate Cancer Immunometabolism. Biomolecules 2025, 15, 826. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kfoury, Y.; Baryawno, N.; Severe, N.; Mei, S.; Gustafsson, K.; Hirz, T.; Brouse, T.; Scadden, E.W.; Igolkina, A.A.; Kokkaliaris, K.; et al. Human Prostate Cancer Bone Metastases Have an Actionable Immunosuppressive Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2021, 39, 1464–1478.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ying, M.; Mao, J.; Sheng, L.; Wu, H.; Bai, G.; Zhong, Z.; Pan, Z. Biomarkers for Prostate Cancer Bone Metastasis Detection and Prediction. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todd, V.M.; Johnson, R.W. Hypoxia in Bone Metastasis and Osteolysis. Cancer Lett. 2020, 489, 144–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tripathi, K.; Bandari, S.K.; Sanderson, R.D. Extracellular Vesicles Released during Hypoxia Transport Heparanase and Enhance Macrophage Migration, Endothelial Tube Formation and Cancer Cell Stemness. Proteoglycan Res. 2023, 1, e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, B.; Zhu, Y.; Ni, J.; Thompson, J.; Malouf, D.; Bucci, J.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Extracellular Vesicles: The next Generation of Biomarkers for Liquid Biopsy-Based Prostate Cancer Diagnosis. Theranostics 2020, 10, 2309–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, H.Y.; Wang, Q.; Howie, A.; Bucci, J.; Graham, P.; Li, Y. Extracellular Vesicle Biomarkers Redefine Prostate Cancer Radiotherapy. Cancer Lett. 2025, 616, 217568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Chen, W.; Zeng, W.; Feng, K.; Zheng, Y.; Wang, P.; Chen, F.; Zhang, W.; Di, L.; Wang, R. Extracellular Vesicles as Biomarkers and Drug Delivery Systems for Tumor. Acta Pharm. Sin. B 2025, 15, 3460–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, H.-Y.; Su, G.-L.; Wu, Y.-X.; Chen, G.; Yu, Z.-L. Extracellular Vesicles in Anti-Tumor Drug Resistance: Mechanisms and Therapeutic Prospects. J. Pharm. Anal. 2024, 14, 100920. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Panigrahi, G.K.; Ramteke, A.; Birks, D.; Abouzeid Ali, H.E.; Venkataraman, S.; Agarwal, C.; Vibhakar, R.; Miller, L.D.; Agarwal, R.; Abd Elmageed, Z.Y.; et al. Exosomal microRNA Profiling to Identify Hypoxia-Related Biomarkers in Prostate Cancer. Oncotarget 2018, 9, 13894–13910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hosseini-Beheshti, E.; Choi, W.; Weiswald, L.-B.; Kharmate, G.; Ghaffari, M.; Roshan-Moniri, M.; Hassona, M.D.; Chan, L.; Chin, M.Y.; Tai, I.T.; et al. Exosomes Confer Pro-Survival Signals to Alter the Phenotype of Prostate Cells in Their Surrounding Environment. Oncotarget 2016, 7, 14639–14658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramteke, A.; Ting, H.; Agarwal, C.; Mateen, S.; Somasagara, R.; Hussain, A.; Graner, M.; Frederick, B.; Agarwal, R.; Deep, G. Exosomes Secreted under Hypoxia Enhance Invasiveness and Stemness of Prostate Cancer Cells by Targeting Adherens Junction Molecules. Mol. Carcinog. 2015, 54, 554–565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Deep, G.; Panigrahi, G.K. Hypoxia-Induced Signaling Promotes Prostate Cancer Progression: Exosomes Role as Messenger of Hypoxic Response in Tumor Microenvironment. Crit. Rev. Oncog. 2015, 20, 419–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shi, R.; Liao, C.; Zhang, Q. Hypoxia-Driven Effects in Cancer: Characterization, Mechanisms, and Therapeutic Implications. Cells 2021, 10, 678. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neophytou, C.M.; Panagi, M.; Stylianopoulos, T.; Papageorgis, P. The Role of Tumor Microenvironment in Cancer Metastasis: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Opportunities. Cancers 2021, 13, 2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Primary Prostate Epithelial Cells; Normal, Human (HPrEC)—PCS-440-010|ATCC. Available online: https://www.atcc.org/products/pcs-440-010 (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- LNCaP Clone FGC—CRL-1740|ATCC. Available online: https://www.atcc.org/products/crl-1740 (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- PC-3—CRL-1435|ATCC. Available online: https://www.atcc.org/products/crl-1435 (accessed on 9 July 2025).
- Dirimtekin, E.; Mortoglou, M.; Alavanda, C.; Benomar Yemlahi, A.; Arslan Ates, E.; Guney, I.; Uysal-Onganer, P. miR-34a-FOXP1 Loop in Ovarian Cancer. ACS Omega 2023, 8, 27743–27750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lange, S.; Inal, J.M.; Kraev, I.; Dart, D.A.; Uysal-Onganer, P. Low Magnetic Field Exposure Alters Prostate Cancer Cell Properties. Biology 2024, 13, 734. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Welsh, J.A.; Goberdhan, D.C.I.; O’Driscoll, L.; Buzas, E.I.; Blenkiron, C.; Bussolati, B.; Cai, H.; Di Vizio, D.; Driedonks, T.A.P.; Erdbrügger, U.; et al. Minimal Information for Studies of Extracellular Vesicles (MISEV2023): From Basic to Advanced Approaches. J. Extracell. Vesicles 2024, 13, e12404. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alavanda, C.; Dirimtekin, E.; Mortoglou, M.; Arslan Ates, E.; Guney, A.I.; Uysal-Onganer, P. BRCA Mutations and MicroRNA Expression Patterns in the Peripheral Blood of Breast Cancer Patients. ACS Omega 2024, 9, 17217–17228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lanning, B.; Webber, J.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Jiang, W.G.; Clayton, A.; Dart, D.A. Prostate Cancer Cell Extracellular Vesicles Increase Mineralisation of Bone Osteoblast Precursor Cells in an In Vitro Model. Biology 2021, 10, 318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arisan, E.D.; Rencuzogullari, O.; Cieza-Borrella, C.; Miralles Arenas, F.; Dwek, M.; Lange, S.; Uysal-Onganer, P. MiR-21 Is Required for the Epithelial–Mesenchymal Transition in MDA-MB-231 Breast Cancer Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 1557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Livak, K.J.; Schmittgen, T.D. Analysis of Relative Gene Expression Data Using Real-Time Quantitative PCR and the 2−ΔΔCT Method. Methods 2001, 25, 402–408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keleş, D.; Sipahi, M.; İnanç-Sürer, Ş.; Djamgoz, M.B.; Oktay, G. Tetracaine Downregulates Matrix Metalloproteinase Activity and Inhibits Invasiveness of Strongly Metastatic MDA-MB-231 Human Breast Cancer Cells. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2023, 385, 110730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mortoglou, M.; Miralles, F.; Arisan, E.D.; Dart, A.; Jurcevic, S.; Lange, S.; Uysal-Onganer, P. microRNA-21 Regulates Stemness in Pancreatic Ductal Adenocarcinoma Cells. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022, 23, 1275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sutera, P.; Shetty, A.C.; Hakansson, A.; Van der Eecken, K.; Song, Y.; Liu, Y.; Chang, J.; Fonteyne, V.; Mendes, A.A.; Lumen, N.; et al. Transcriptomic and Clinical Heterogeneity of Metastatic Disease Timing within Metastatic Castration-Sensitive Prostate Cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2023, 34, 605–614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, F.; Cherukuri, M.K.; Choyke, P.L. Metabolic Reprogramming in Prostate Cancer. Br. J. Cancer 2021, 125, 1185–1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, Z.; Yu, N.; Zhang, Y.; Jia, M.; Sun, Y.; Li, Y.; Zhao, L. The Potential Roles of HIF-1α in Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition and Ferroptosis in Tumor Cells. Cell. Signal. 2024, 122, 111345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tam, S.Y.; Wu, V.W.C.; Law, H.K.W. Hypoxia-Induced Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in Cancers: HIF-1α and Beyond. Front. Oncol. 2020, 10, 486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, Z.; Tian, M.; Yang, G.; Tan, Q.; Chen, Y.; Li, G.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Y.; Wan, P.; Wu, J. Hypoxia Signaling in Human Health and Diseases: Implications and Prospects for Therapeutics. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2022, 7, 218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dong, S.; Liang, S.; Cheng, Z.; Zhang, X.; Luo, L.; Li, L.; Zhang, W.; Li, S.; Xu, Q.; Zhong, M.; et al. ROS/PI3K/Akt and Wnt/β-Catenin Signalings Activate HIF-1α-Induced Metabolic Reprogramming to Impart 5-Fluorouracil Resistance in Colorectal Cancer. J. Exp. Clin. Cancer Res. 2022, 41, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cameron, S.; Deblois, G.; Hawley, J.R.; Qamra, A.; Zhou, S.; Tonekaboni, S.A.M.; Murison, A.; Van Vliet, R.; Liu, J.; Locasale, J.W.; et al. Chronic Hypoxia Favours Adoption to a Castration-Resistant Cell State in Prostate Cancer. Oncogene 2023, 42, 1693–1703. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terzic, J.; Abu El Maaty, M.A.; Lutzing, R.; Vincent, A.; El Bizri, R.; Jung, M.; Keime, C.; Metzger, D. Hypoxia-Inducible Factor 1A Inhibition Overcomes Castration Resistance of Prostate Tumors. EMBO Mol. Med. 2023, 15, e17209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kuang, L.; Wu, L.; Li, Y. Extracellular Vesicles in Tumor Immunity: Mechanisms and Novel Insights. Mol. Cancer 2025, 24, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Shi, K.; Chen, Y.; Wu, X.; Chen, Z.; Cao, K.; Tao, Y.; Chen, X.; Liao, J.; Zhou, J. Exosomes and Their Role in Cancer Progression. Front. Oncol. 2021, 11, 639159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berumen Sánchez, G.; Bunn, K.E.; Pua, H.H.; Rafat, M. Extracellular Vesicles: Mediators of Intercellular Communication in Tissue Injury and Disease. Cell Commun. Signal. 2021, 19, 104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Han, F.; Du, Y.; Shi, H.; Zhou, W. Hypoxic Microenvironment in Cancer: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Interventions. Signal Transduct. Target. Ther. 2023, 8, 70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- King, H.W.; Michael, M.Z.; Gleadle, J.M. Hypoxic Enhancement of Exosome Release by Breast Cancer Cells. BMC Cancer 2012, 12, 421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Xu, S.; Yang, X. Hypoxia-Driven Changes in Tumor Microenvironment: Insights into Exosome-Mediated Cell Interactions. Int. J. Nanomed. 2024, 19, 8211–8236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Y.; Tan, X.; Du, Y.; Wei, Y.; Liu, S. Extracellular Vesicle-Mediated Pre-Metastatic Niche Formation via Altering Host Microenvironments. Front. Immunol. 2024, 15, 1367373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Venturella, M.; Criscuoli, M.; Carraro, F.; Naldini, A.; Zocco, D. Interplay between Hypoxia and Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer and Inflammation. Biology 2021, 10, 606. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, B.; Xiang, K.; Li, T.; Li, X.; Shi, F. The Signature of Extracellular Vesicles in Hypoxic Breast Cancer and Their Therapeutic Engineering. Cell Commun. Signal. 2024, 22, 512. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Capik, O.; Karatas, O.F. Pathways and Outputs Orchestrated in Tumor Microenvironment Cells by Hypoxia-Induced Tumor-Derived Exosomes in Pan-Cancer. Cell. Oncol. 2025, 48, 539–557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Minciacchi, V.R.; Freeman, M.R.; Di Vizio, D. Extracellular Vesicles in Cancer: Exosomes, Microvesicles and the Emerging Role of Large Oncosomes. Semin. Cell Dev. Biol. 2015, 40, 41–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irshad, S.; Bansal, M.; Castillo-Martin, M.; Zheng, T.; Aytes, A.; Wenske, S.; Le Magnen, C.; Guarnieri, P.; Sumazin, P.; Benson, M.C.; et al. A Molecular Signature Predictive of Indolent Prostate Cancer. Sci. Transl. Med. 2013, 5, 202ra122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Webber, J.; Steadman, R.; Mason, M.D.; Tabi, Z.; Clayton, A. Cancer Exosomes Trigger Fibroblast to Myofibroblast Differentiation. Cancer Res. 2010, 70, 9621–9630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Luo, G.; Zhang, K.; Cao, J.; Huang, C.; Jiang, T.; Liu, B.; Su, L.; Qiu, Z. Hypoxic Tumor-Derived Exosomal miR-301a Mediates M2 Macrophage Polarization via PTEN/PI3Kγ to Promote Pancreatic Cancer Metastasis. Cancer Res. 2018, 78, 4586–4598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baharudin, R.; Tieng, F.Y.F.; Lee, L.-H.; Ab Mutalib, N.S. Epigenetics of SFRP1: The Dual Roles in Human Cancers. Cancers 2020, 12, 445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, Q.-Y.; Zhao, G.-Q.; Tang, H.; Wa, Q.-D. Recent Advances in Understanding the Role of Wnt5a in Prostate Cancer and Bone Metastasis. Discov. Oncol. 2025, 16, 880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whiteside, T.L. Tumor-Derived Exosomes and Their Role in Cancer Progression. Adv. Clin. Chem. 2016, 74, 103–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huang, T.; Yu, Z.; Yu, Q.; Wang, Y.; Jiang, Z.; Wang, H.; Yang, G. Inhibition of Osteogenic and Adipogenic Potential in Bone Marrow-Derived Mesenchymal Stem Cells under Osteoporosis. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2020, 525, 902–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Wang, Q.; Yang, Y.; Zhou, S.; Zhang, P.; Feng, T. The Role of Exosomal lncRNAs in Cancer Biology and Clinical Management. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 1669–1673. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, W.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, J.; Tang, Y.; Tang, Y.; Liang, X. Extracellular Vesicle Long Non–Coding RNA-mediated Crosstalk in the Tumor Microenvironment: Tiny Molecules, Huge Roles. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 2726–2735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Z.; Wu, Y.; Xu, Y.; Li, G.; Li, Z.; Liu, T. Mesenchymal Stem Cell-Derived Exosomes in Cancer Therapy Resistance: Recent Advances and Therapeutic Potential. Mol. Cancer 2022, 21, 179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zuo, J.; Wen, J.; Lei, M.; Wen, M.; Li, S.; Lv, X.; Luo, Z.; Wen, G. Hypoxia Promotes the Invasion and Metastasis of Laryngeal Cancer Cells via EMT. Med. Oncol. 2016, 33, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dart, D.A.; Uysal-Onganer, P.; Jiang, W.G. Prostate-Specific PTen Deletion in Mice Activates Inflammatory microRNA Expression Pathways in the Epithelium Early in Hyperplasia Development. Oncogenesis 2017, 6, 400. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalluri, R.; LeBleu, V.S. The Biology, Function, and Biomedical Applications of Exosomes. Science 2020, 367, eaau6977. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, X.; Park, S.; Chen, Y.; Lee, H. Extracellular Vesicle-Associated miRNAs as a Biomarker for Lung Cancer in Liquid Biopsy. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2021, 8, 630718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raczkowska, J.; Bielska, A.; Krętowski, A.; Niemira, M. Extracellular Circulating miRNAs as Potential Non-Invasive Biomarkers in Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer Patients. Front. Oncol. 2023, 13, 1209299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kholia, S.; Ranghino, A.; Garnieri, P.; Lopatina, T.; Deregibus, M.C.; Rispoli, P.; Brizzi, M.F.; Camussi, G. Extracellular Vesicles as New Players in Angiogenesis. Vasc. Pharmacol. 2016, 86, 64–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosgodage, U.S.; Trindade, R.P.; Thompson, P.R.; Inal, J.M.; Lange, S. Chloramidine/Bisindolylmaleimide-I-Mediated Inhibition of Exosome and Microvesicle Release and Enhanced Efficacy of Cancer Chemotherapy. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2017, 18, 1007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jorfi, S.; Ansa-Addo, E.A.; Kholia, S.; Stratton, D.; Valley, S.; Lange, S.; Inal, J. Inhibition of Microvesiculation Sensitizes Prostate Cancer Cells to Chemotherapy and Reduces Docetaxel Dose Required to Limit Tumor Growth in Vivo. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 13006. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]

| Primer | Forward Sequence (5’-3’) | Reverse Sequence (5’-3’) |
|---|---|---|
| HIF1α | TTCACAAATCAGCACCAAGC | TGCAACATGGAAGGTATTGC |
| Wnt3a | GTTGGGCCACAGTATTCCTC | ATCCCACCAAACTCGATGTC |
| Wnt5a | TCTCAGCCCAAGCAACAAGG | GCCAGCATCACATCACAACAC |
| Fzd7 | GTCACGGATGCTGTTATTAAGG | CACATCGCCGTTATCATCATC |
| sFRP1 | CAATGCCACCGAAGCCTCCAAG | CAAACTCGCTGGCACAGAGATG |
| ROR2 | TTTGTGCGGCTGGGTCCAA | GTAAGGCTGGCAGAACCCAT |
| Ecad | AAGAAGCTGGCTGACATGTACGGA | CCACCAGCAACGTGATTTCTGCAT |
| Ncad | CCTCCAGAGTTTACTGCCATGAC | GTAGGATCTCCGCCACTGATTC |
| Vim | TACAGGAAGCTGCTGGAAGG | ACCAGAGGGAGTGAATCCAG |
| RPII | GCACCACGTCCAATGACAT | GTGCGGCTGCTTCCATAA |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Santos, M.; Bukhari, K.; Peker-Eyüboğlu, I.; Kraev, I.; Dart, D.A.; Lange, S.; Uysal-Onganer, P. Hypoxia-Driven Extracellular Vesicles Promote Pro-Metastatic Signalling in LNCaP Cells via Wnt and EMT Pathways. Biology 2025, 14, 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091135
Santos M, Bukhari K, Peker-Eyüboğlu I, Kraev I, Dart DA, Lange S, Uysal-Onganer P. Hypoxia-Driven Extracellular Vesicles Promote Pro-Metastatic Signalling in LNCaP Cells via Wnt and EMT Pathways. Biology. 2025; 14(9):1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091135
Chicago/Turabian StyleSantos, Melissa, Khansa Bukhari, Irem Peker-Eyüboğlu, Igor Kraev, Dafydd Alwyn Dart, Sigrun Lange, and Pinar Uysal-Onganer. 2025. "Hypoxia-Driven Extracellular Vesicles Promote Pro-Metastatic Signalling in LNCaP Cells via Wnt and EMT Pathways" Biology 14, no. 9: 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091135
APA StyleSantos, M., Bukhari, K., Peker-Eyüboğlu, I., Kraev, I., Dart, D. A., Lange, S., & Uysal-Onganer, P. (2025). Hypoxia-Driven Extracellular Vesicles Promote Pro-Metastatic Signalling in LNCaP Cells via Wnt and EMT Pathways. Biology, 14(9), 1135. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14091135









