Mechanistic Elucidation and Establishment of Drying Kinetic Models of Differential Metabolite Regulation in Rheum palmatum During Natural Sun Drying: An Integrated Physiology, Untargeted Metabolomics, and Enzymology Study
Simple Summary
Abstract
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Test Rhubarb
2.2. Experimental Design
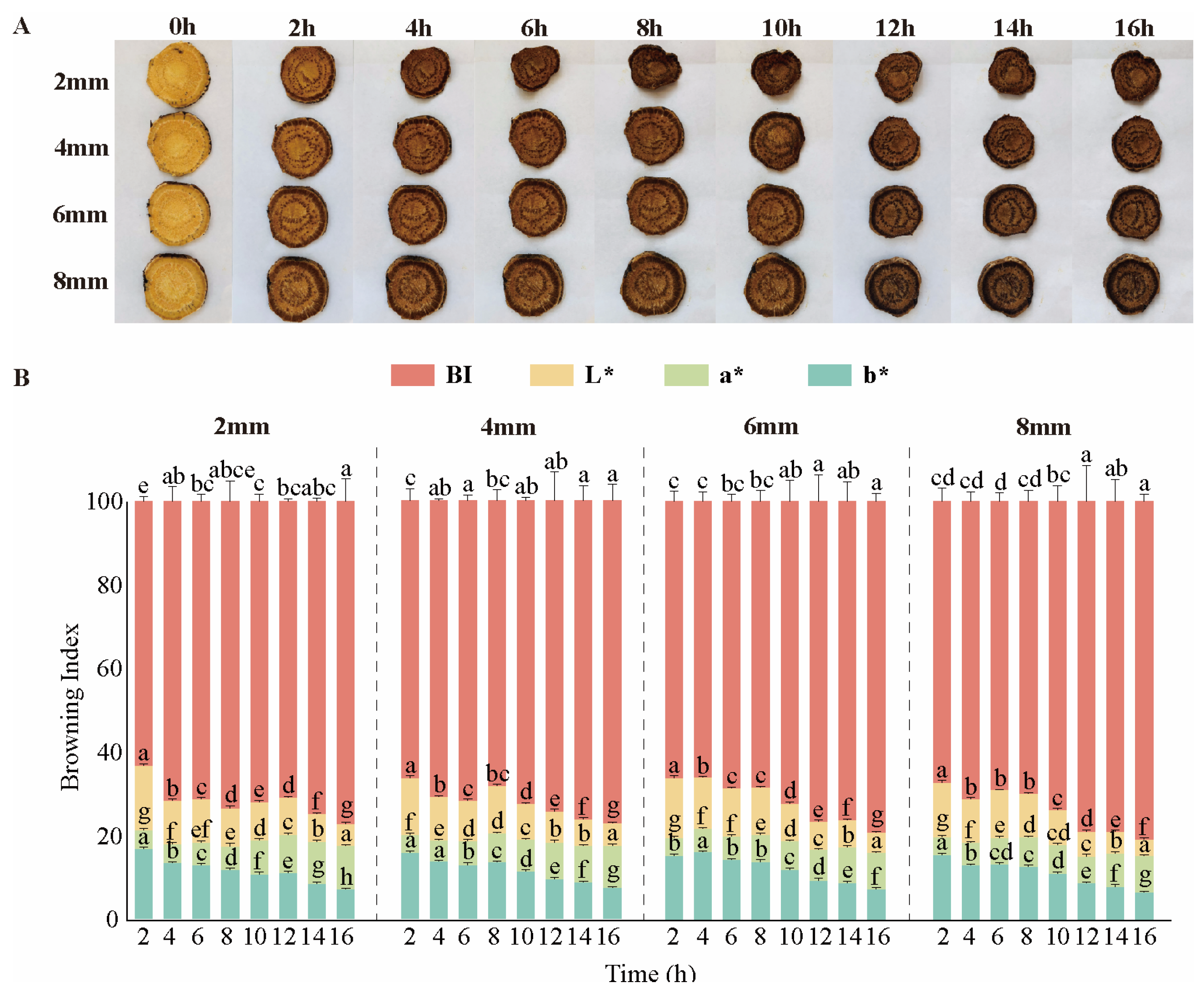
2.3. Determination of Color Difference
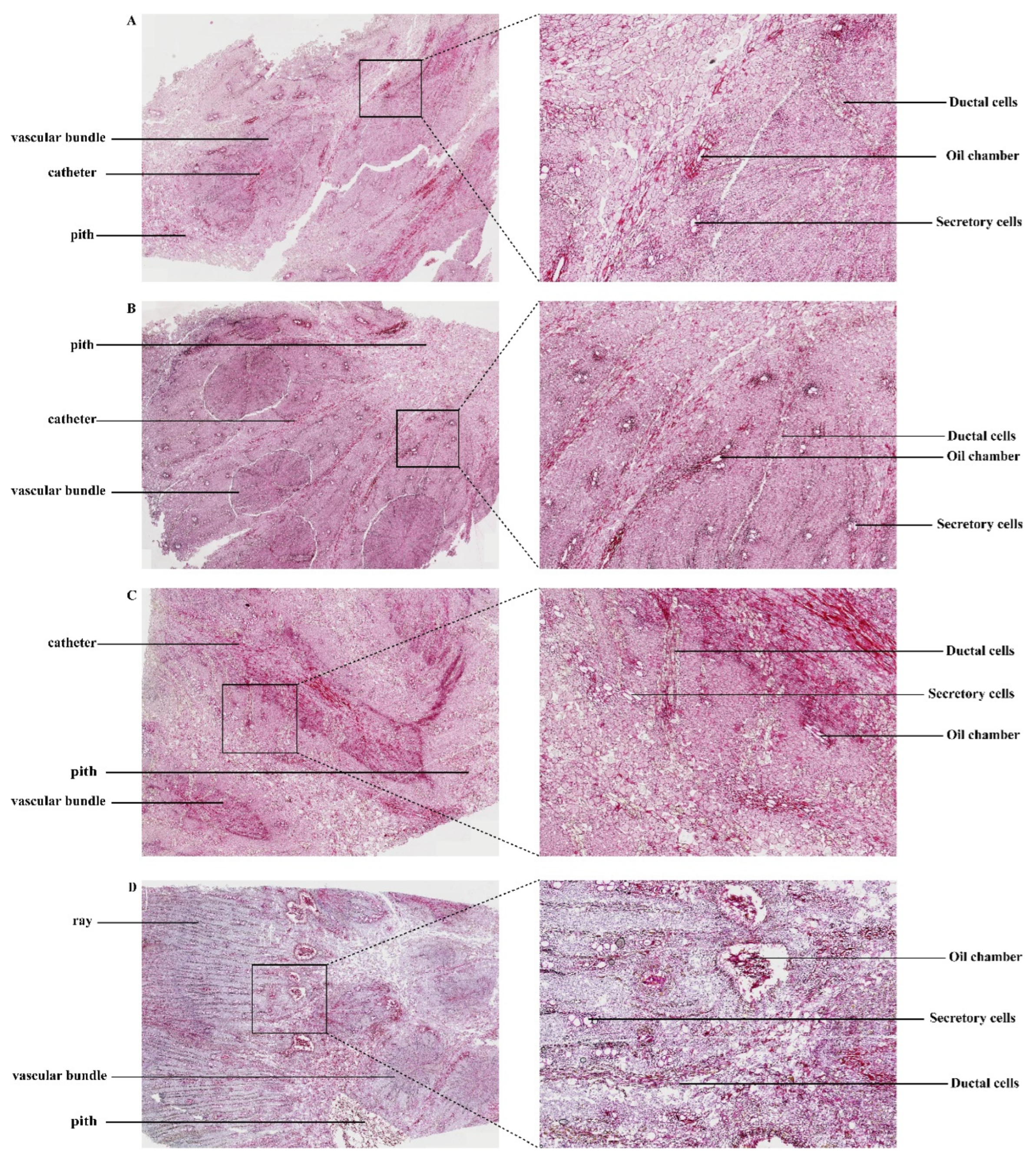
2.4. Preparation of Paraffin Sections
2.5. Determination of Anthraquinone Content
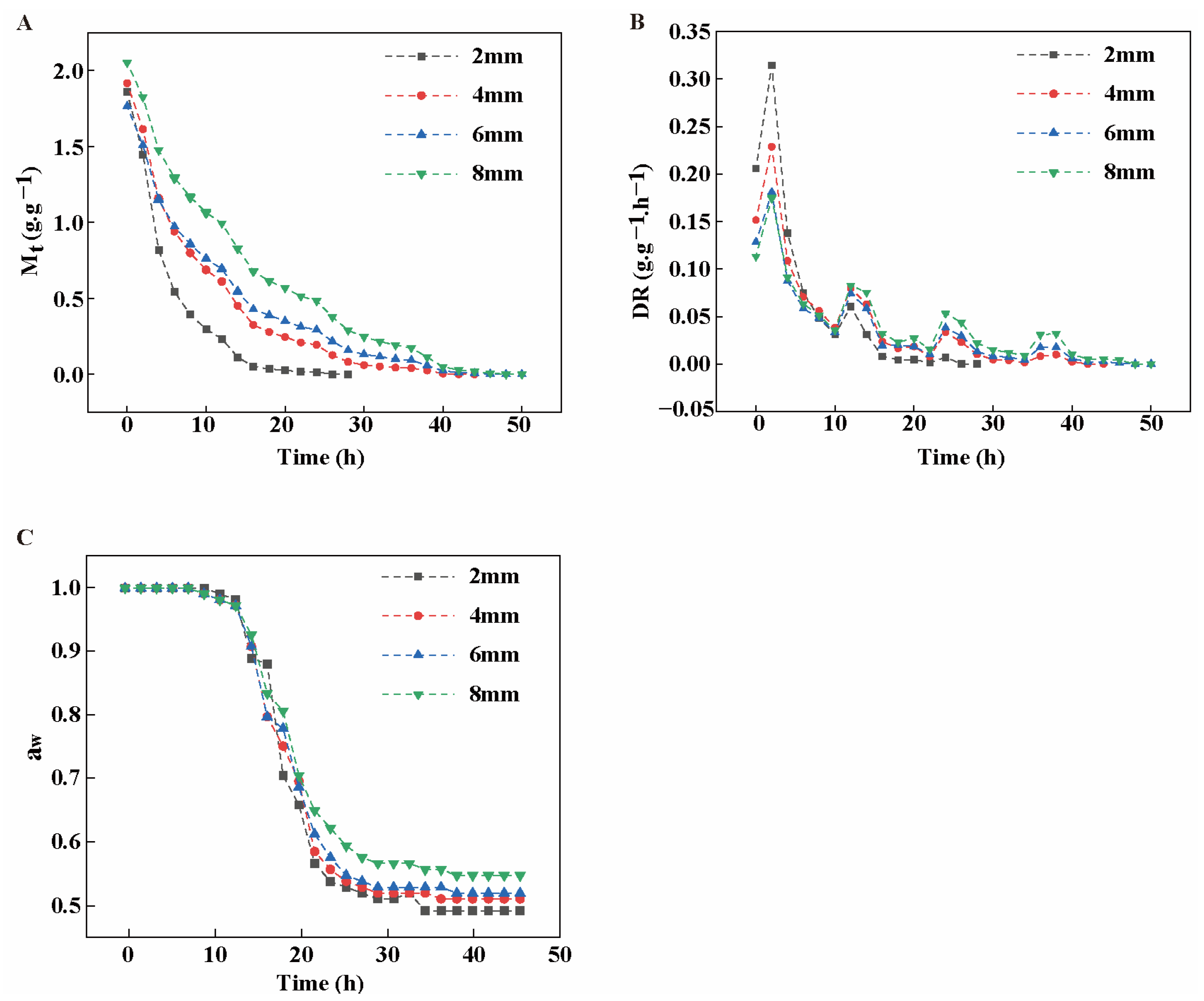
2.6. Determination of Drying Kinetic Parameters Including Dry Basis Moisture Content (Mt), Moisture Ratio (MR), Drying Rate (DR), and Water Activity (aw)
2.7. Metabolomics Analysis
2.7.1. Sample Processing Methods Required for Metabolomics
2.7.2. Mass Chromatography Acquisition Conditions
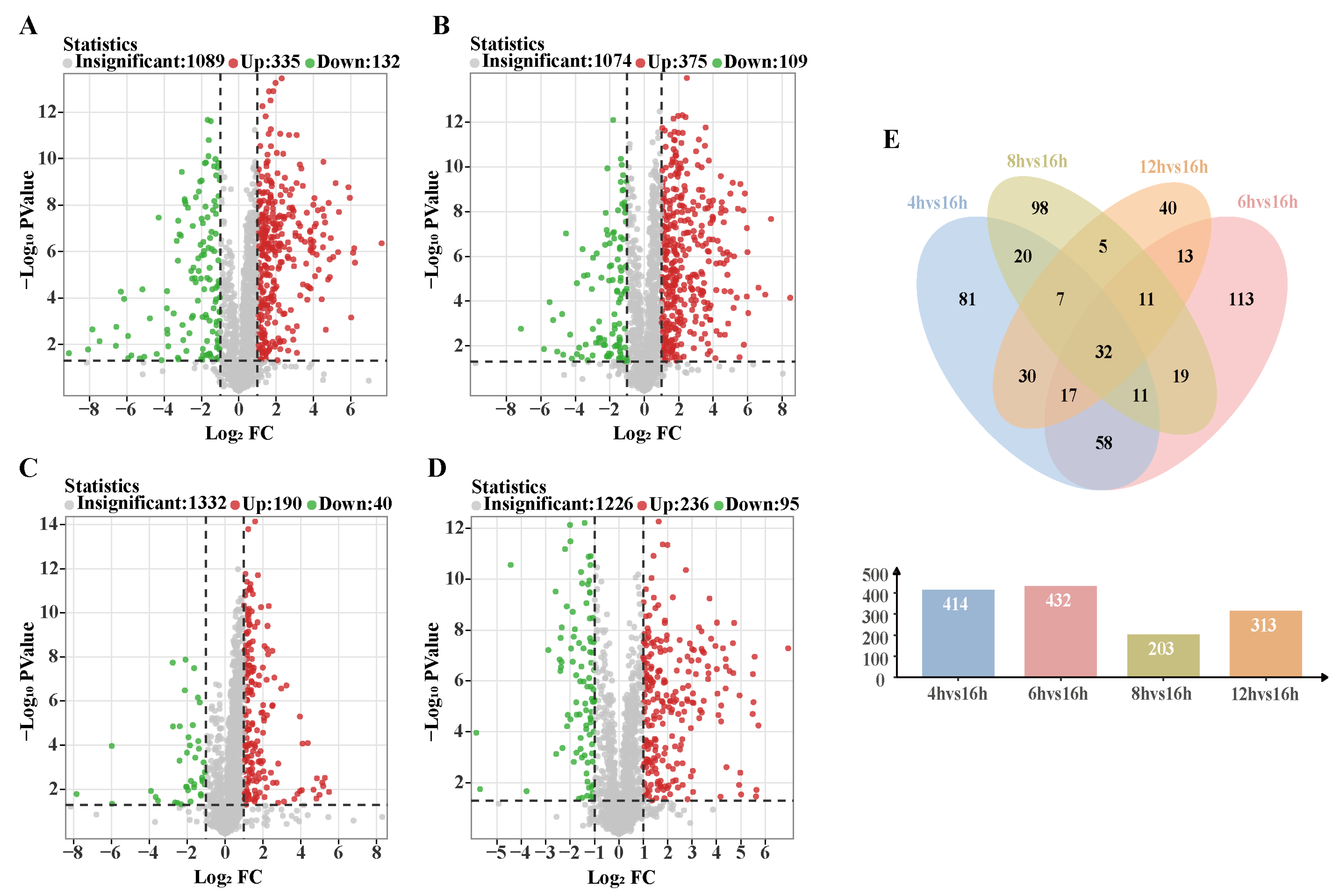
2.7.3. Differential Metabolite Analysis
2.8. Enzyme Activity Assay
2.8.1. Catalase (CAT)
2.8.2. Polyphenol Oxidase (PPO)
2.8.3. Key Enzymes in Metabolic Pathways
2.9. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
3.1. Macroscopic Analysis of Dried Rhubarb
3.2. Microscopic Analysis of Dried Rhubarb
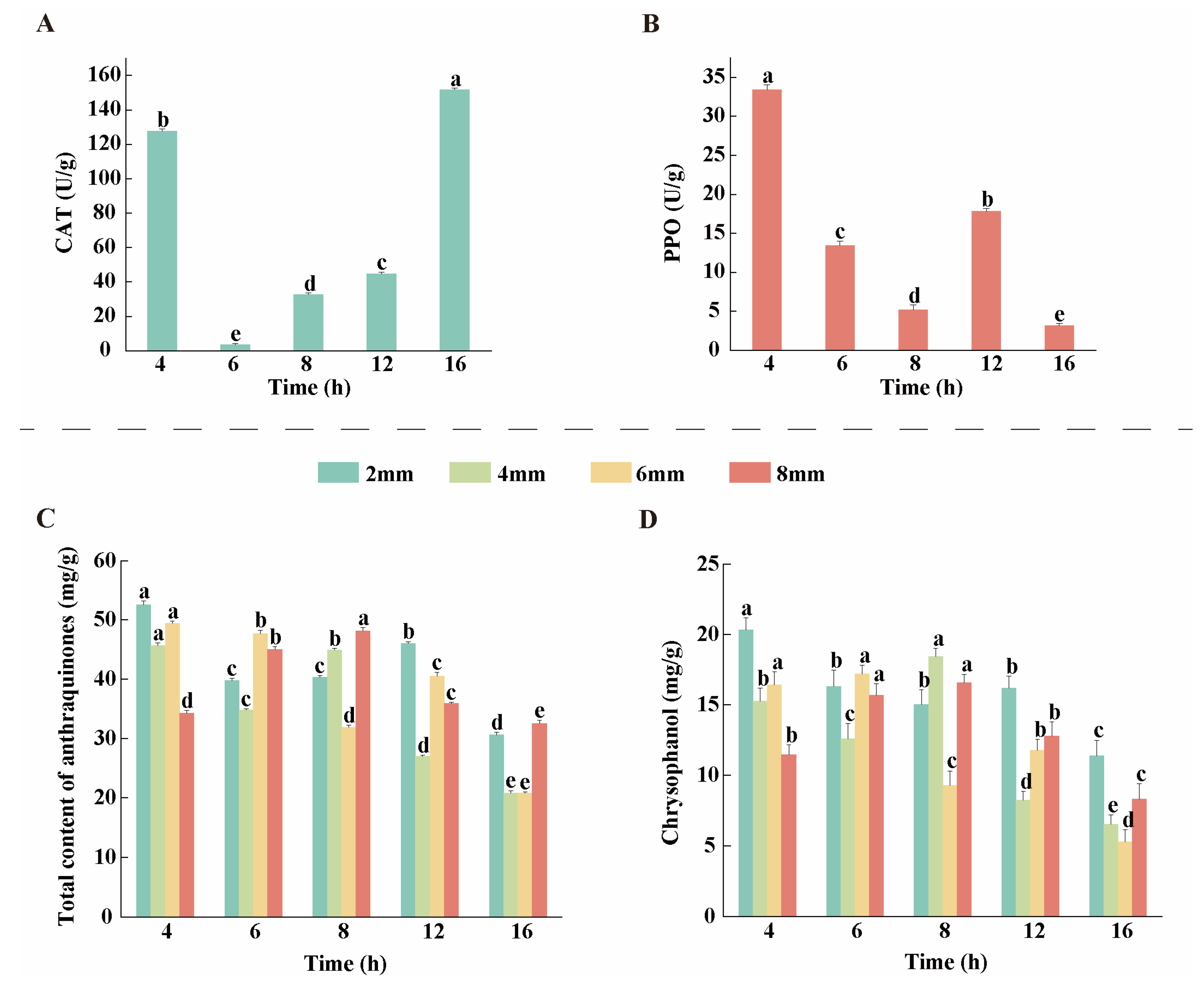
3.3. Changes in CAT and PPO Activities During the Drying Process of Rhubarb
3.4. Analysis of AQ Content
3.5. Drying Model and Data Fitting Analysis
3.5.1. Effect of Different Slice Thickness on the Drying Rate (DR) of Rhubarb
3.5.2. Comparison of Kinetic Models for Drying Rhubarb with Different Slice Thicknesses
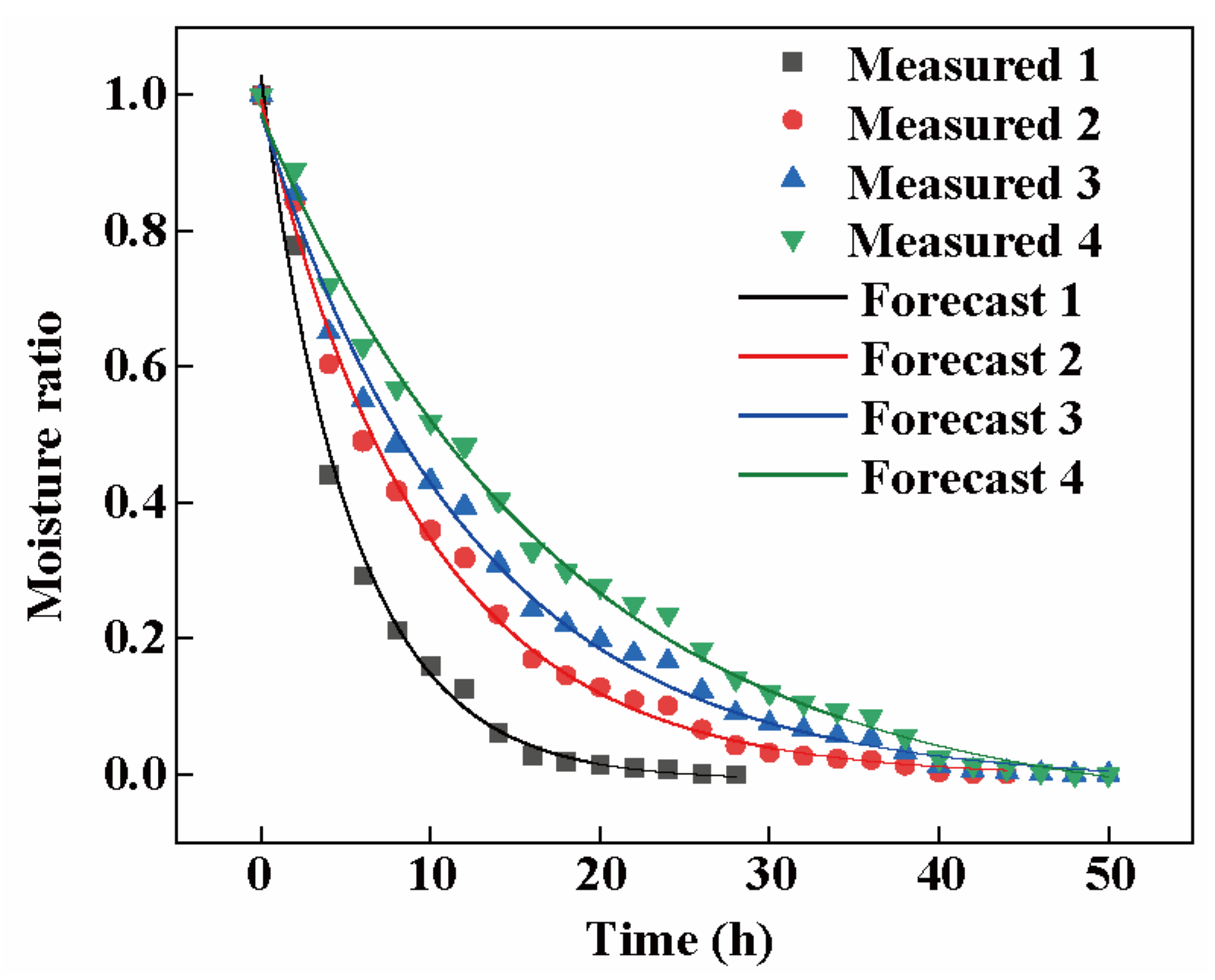
3.5.3. Logarithmic Model Simulation of Rhubarb with Different Slice Thicknesses
3.5.4. Logarithmic Model Validation
3.6. Metabolomics Analysis of Sun-Dried Rhubarb Decoction Pieces
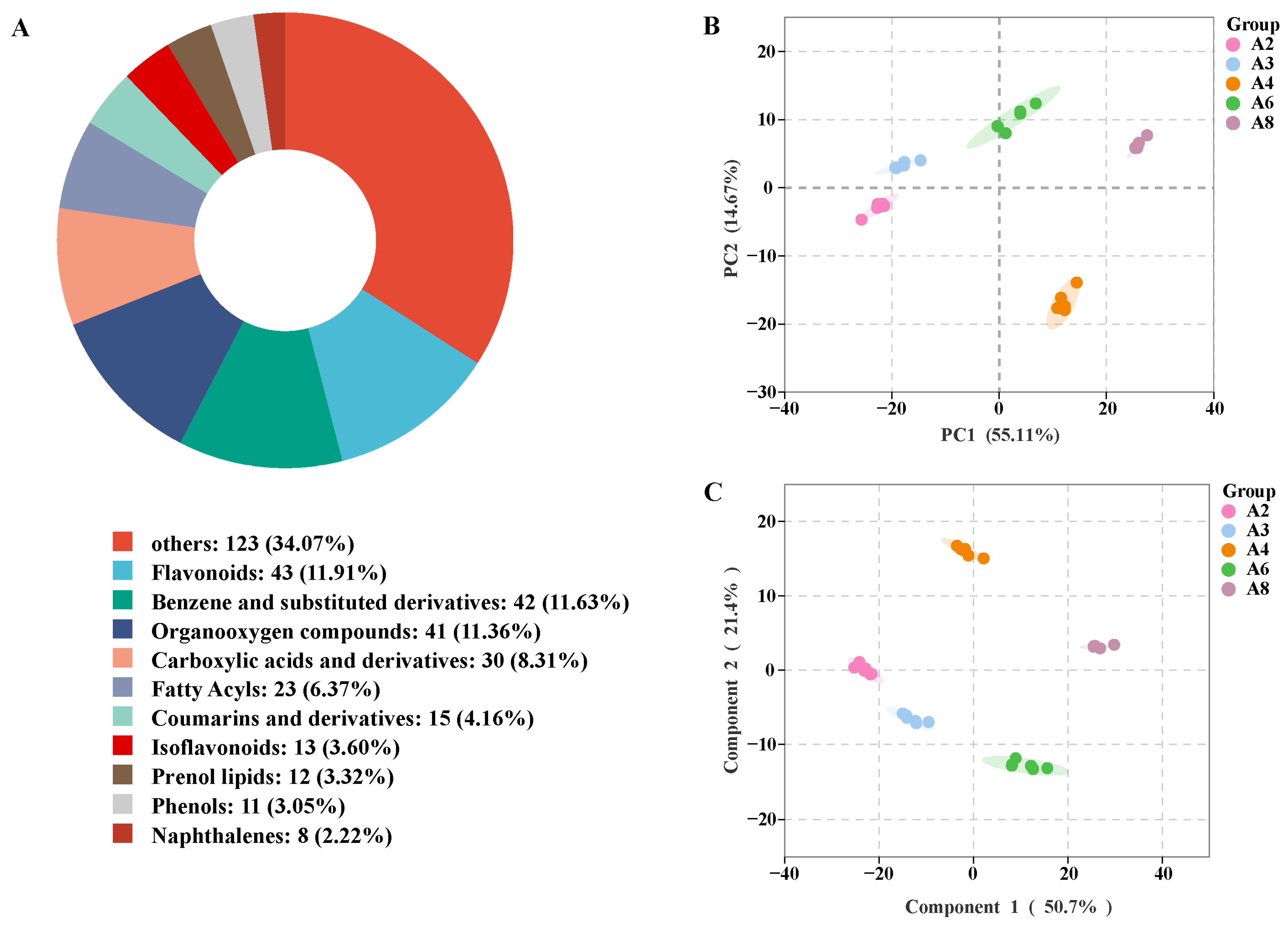
3.6.1. Metabolite Identification Results and Analysis
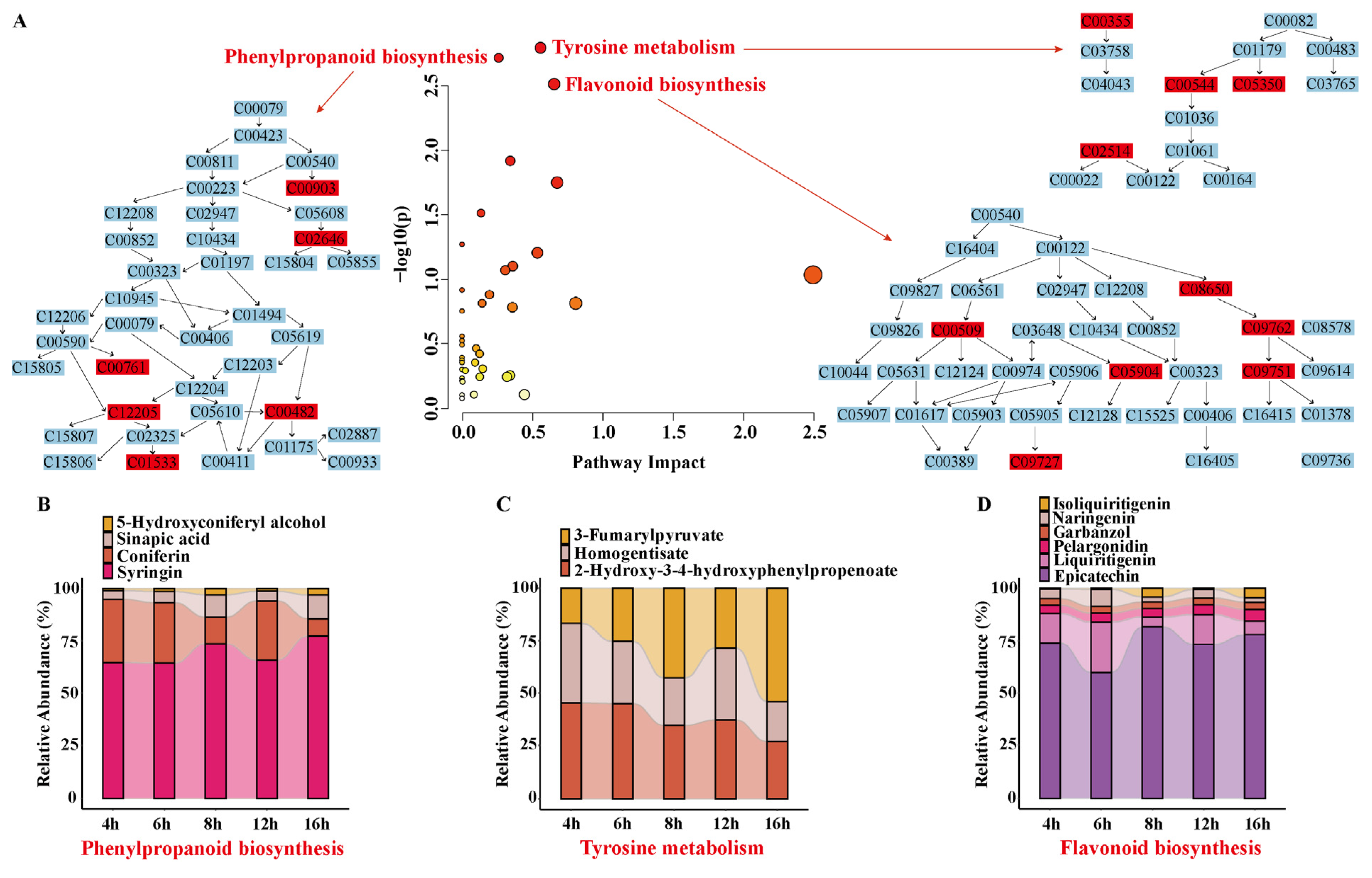
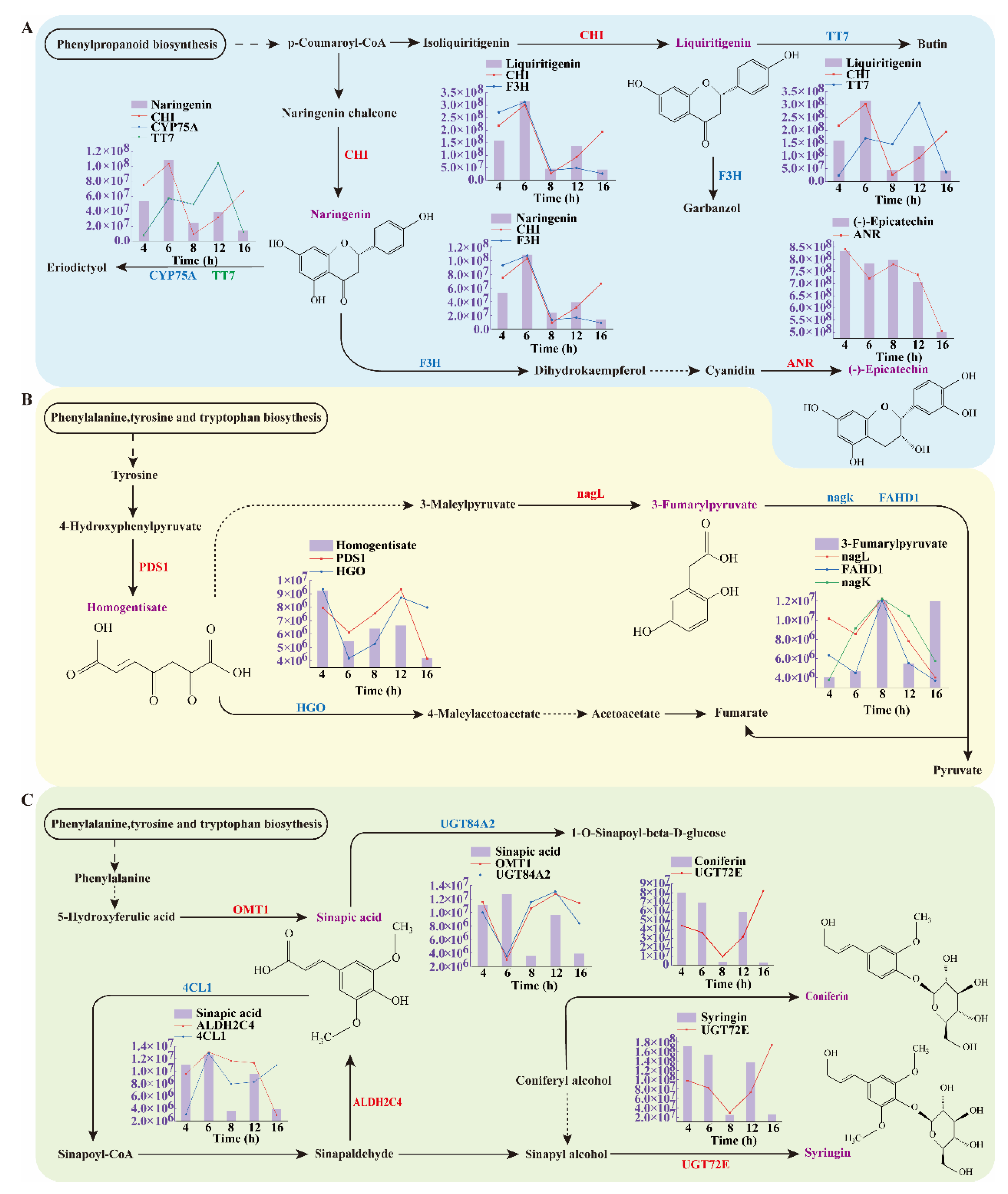
3.6.2. Analysis of Differential Metabolic Pathways
3.6.3. Changes in the Activities of Key Enzymes During Rhubarb Drying
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, T.; Yu, M.; Dai, Y.; Xiao, Y.; Li, L. Traditional method of rhubarb processing optimized by combining flavor analysis with anthraquinone content determination. Front. Nutr. 2024, 11, 1406430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, X.; Lei, G. Research Progress on Modern Pharmacological Action of Rhubarb. MEDS Chin. Med. 2023, 5, 138–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiang, H.; Zuo, J.; Guo, F.; Dong, D. What we already know about rhubarb: A comprehensive review. Chin. Med. 2020, 15, 88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, W.; Zhang, W.; Chen, Y.; Guo, F.; Sun, J.; Zhang, X.; Li, X.; Gao, W. Accumulation of functional metabolites and transcriptomics in postharvest fume-drying and air-drying process in rhubarb. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2022, 102, 5628–5641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhat, R. Bioactive Compounds of Rhubarb (Rheum Species). In Bioactive Compounds in Underutilized Vegetables and Legumes; Murthy, H.N., Paek, K.Y., Eds.; Reference Series in Phytochemistry; Springer International Publishing: Cham, Switzerland, 2021; pp. 239–254. ISBN 978-3-030-57414-7. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Leng, L.; Liu, Y.; Gao, H.; Yang, W.; Chen, S.; Liu, A. Identification and quantification of target metabolites combined with transcriptome of two rheum species focused on anthraquinone and flavonoids biosynthesis. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 20241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, L.; Geng, D.; Hu, F.; Dong, Q. Rapid Identification and Quantification of Natural Antioxidants in the Seeds of Rhubarb from Different Habitats in China Using Accelerated Solvent Extraction and HPLC-DAD-ESI–MSn-DPPH Assay. J. Chromatogr. Sci. 2016, 54, 48–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef][Green Version]
- Cao, Y.-J.; Pu, Z.-J.; Tang, Y.-P.; Shen, J.; Chen, Y.-Y.; Kang, A.; Zhou, G.-S.; Duan, J.-A. Advances in bio-active constituents, pharmacology and clinical applications of rhubarb. Chin. Med. 2017, 12, 36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cao, J.-L.; Li, X.-L.; Meng, F.; Gong, Y. Expert consensus on clinical application of Chinese herbal medicine decoction pieces. Zhongguo Zhong Yao Za Zhi 2020, 45, 3238–3244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Wang, Y.; Ma, X.; Li, M.; Kong, D.; Phavady, P.; Wang, Q.; Abdelkader, T.K. Chinese medicinal materials’ drying technologies advancements—Principles, energy performance, and influence on the bioactive components. Dry. Technol. 2024, 42, 1815–1845. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, J.; Wu, Y.; Dong, S.; Li, X.; Gao, W. Influence of the drying method on the bioactive compounds and pharmacological activities of rhubarb. J. Sci. Food Agric. 2018, 98, 3551–3562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Committee National Pharmacopoeia. Pharmacopoeia of People’s Republic of China—Part 4; China Medical Science Press: Beijing, China, 2020; ISBN 978-7-5214-1599-5. [Google Scholar]
- Polatci, H.; Taşova, M.; Şin, B. Effects of pre-treatments on drying kinetics and energy consumption, heat-mass transfer coefficients, micro-structure of jujube (Zizyphus jujuba L.) fruit. Food Sci. Technol. 2022, 42, e15721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hassoun, A.; Aït-Kaddour, A.; Dankar, I.; Safarov, J.; Ozogul, F.; Sultanova, S. The Significance of Industry 4.0 Technologies in Enhancing Various Unit Operations Applied in the Food Sector: Focus on Food Drying. Food Bioprocess Technol. 2025, 18, 109–128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahin, A.Z.; Dincer, I. Prediction of drying times for irregular shaped multi-dimensional moist solids. J. Food Eng. 2005, 71, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Doymaz, İ. Evaluation of some thin-layer drying models of persimmon slices (Diospyros kaki L.). Energy Convers. Manag. 2012, 56, 199–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wanderley, R.D.O.S.; De Figueirêdo, R.M.F.; Queiroz, A.J.D.M.; Dos Santos, F.S.; Paiva, Y.F.; Ferreira, J.P.D.L.; De Lima, A.G.B.; Gomes, J.P.; Costa, C.C.; Da Silva, W.P.; et al. The Temperature Influence on Drying Kinetics and Physico-Chemical Properties of Pomegranate Peels and Seeds. Foods 2023, 12, 286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menges, H.O.; Ertekin, C. Mathematical modeling of thin layer drying of Golden apples. J. Food Eng. 2006, 77, 119–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade, K.O.; Olurin, T.O.; Ike, E.A.; Aworh, O.C. Effect of pretreatment and temperature on air-drying of Dioscorea alata and Dioscorea rotundata slices. J. Food Eng. 2007, 80, 1002–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Manickam, S.; Rajagopalan, V.R.; Kambale, R.; Rajasekaran, R.; Kanagarajan, S.; Muthurajan, R. Plant Metabolomics: Current Initiatives and Future Prospects. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2023, 45, 8894–8906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, Y.; Zhu, X.; Yuan, B.; Chen, M.; Wang, J.; Zhu, L.; Jiang, Y.; Yuan, H.; Hua, J. Investigation of non-volatile metabolite variations during round green tea processing and effect of pan-frying degree using untargeted metabolomics and objective quantification. Food Chem. 2024, 457, 140067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ye, F.; Qiao, X.; Gui, A.; Wang, S.; Liu, P.; Wang, X.; Teng, J.; Zheng, L.; Feng, L.; Han, H.; et al. Metabolomics Provides A Novel Interpretation of the Changes in Main Compounds during Black Tea Processing through Different Drying Methods. Molecules 2021, 26, 6739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marinoni, L.; Cattaneo, T.M.P.; Vanoli, M.; Barzaghi, S. Real-time monitoring of solar drying of melon slices with a portable NIR spectrometer: A preliminary approach. Eur. Food Res. Technol. 2023, 249, 2151–2164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- ASTM E308-99; Standard Practice for Computing the Colors of Objects by Using the CIE System. ASTM Standards: West Conshohocken, PA, USA, 2001. Available online: https://standards.iteh.ai/catalog/standards/astm/c8a74a0f-0f89-4bc1-995b-01604592bd17/astm-e308-99?srsltid=AfmBOoof45xQQG7Veqn-L8DD1fByMphpN_YXbVWLTr19eyXJI7b0K5w3 (accessed on 13 May 2025).
- Ellison, M.A.; McMahon, M.B.; Bonde, M.R.; Palmer, C.L.; Luster, D.G. In situ hybridization for the detection of rust fungi in paraffin embedded plant tissue sections. Plant Methods 2016, 12, 37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kar, M.; Mishra, D. Catalase, Peroxidase, and Polyphenoloxidase Activities during Rice Leaf Senescence. Plant Physiol. 1976, 57, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jahan, A.; Khan, M.M.A.; Ahmad, B.; Ahmed, K.B.M.; Pandey, R.P.; Gulfishan, M. Hydrogen Peroxide: Regulator of Plant Development and Abiotic Stress Response. In Reactive Oxygen Species; Faizan, M., Hayat, S., Ahmed, S.M., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2023; pp. 213–228. ISBN 978-981-19-9793-8. [Google Scholar]
- Khattak, A.K.; Hassan, S.M.; Mughal, S.S. General Overview of Phytochemistry And Pharmacological Potential of Rheum palmatum (Chinese Rhubarb). Innovare J. Ayurvedic Sci. 2020, 8, 5–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perera, C. Selected Quality Attributes of Dried Foods. Dry. Technol. 2005, 23, 717–730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Z.-A.; Wang, S.-Y.; Wang, H.; Xiao, H.; Liu, Z.-L.; Pan, Y.-H.; Gao, L. Comparative Study on the Influence of Various Drying Techniques on Drying Characteristics and Physicochemical Quality of Garlic Slices. Foods 2023, 12, 1314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taghian Dinani, S.; Hamdami, N.; Shahedi, M.; Havet, M. Mathematical modeling of hot air/electrohydrodynamic (EHD) drying kinetics of mushroom slices. Energy Convers. Manag. 2014, 86, 70–80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Biswas, R.; Hossain, M.A.; Zzaman, W. Thin layer modeling of drying kinetics, rehydration kinetics and color changes of osmotic pre-treated pineapple (Ananas comosus) slices during drying: Development of a mechanistic model for mass transfer. Innov. Food Sci. Emerg. Technol. 2022, 80, 103094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Falade, K.O.; Solademi, O.J. Modelling of air drying of fresh and blanched sweet potato slices. Int. J. Food Sci. Technol. 2010, 45, 278–288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Chen, R.; Shi, Y.; Zhang, X.; Tian, C.; Xia, D. Antioxidant and Anti-Inflammatory Activities of Six Flavonoids from Smilax glabra Roxb. Molecules 2020, 25, 5295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orsavová, J.; Juríková, T.; Bednaříková, R.; Mlček, J. Total Phenolic and Total Flavonoid Content, Individual Phenolic Compounds and Antioxidant Activity in Sweet Rowanberry Cultivars. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yao, B.; Zhang, D.; Wu, X.; He, R.; Gao, H.; Chen, K.; Xiang, D.; Tang, Y. Exploring the impact of irradiation on the sensory quality of pork based on a metabolomics approach. Food Chem. X 2024, 22, 101460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, J.; Du, L.; Liang, W.; Qu, Z.; Zhao, H.; Guan, W. Effect of postharvest processing on quality traits of Radix Gentianae Macrophyllae: A integrative analysis of metabolomics and proteomics. Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 204, 108099. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, J.; Zhang, X.; Liu, W.; Zhang, Q.; Wu, L. Effect of different drying methods on color difference, microorganisms and volatile metabolites profiles of Ganpu Tea. Food Biosci. 2023, 56, 103314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Glagoleva, A.Y.; Shoeva, O.Y.; Khlestkina, E.K. Melanin Pigment in Plants: Current Knowledge and Future Perspectives. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 770. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mertens, N.; Glomb, M. Mechanistische Untersuchungen zur enzymatischen Bräunung. Lebensmittelchemie 2023, 77, S2-043–S2-045. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, W.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Shan, Y. Effects of postharvest chilling and heating treatments on the sensory quality and antioxidant system of daylily flowers. Hortic. Environ. Biotechnol. 2018, 59, 671–685. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrés, C.M.C.; Pérez De La Lastra, J.M.; Juan, C.A.; Plou, F.J.; Pérez-Lebeña, E. Polyphenols as Antioxidant/Pro-Oxidant Compounds and Donors of Reducing Species: Relationship with Human Antioxidant Metabolism. Processes 2023, 11, 2771. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mittler, R.; Zandalinas, S.I.; Fichman, Y.; Van Breusegem, F. Reactive oxygen species signalling in plant stress responses. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2022, 23, 663–679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Korese, J.K.; Achaglinkame, M.A. Convective drying of Gardenia erubescens fruits: Effect of pretreatment, slice thickness and drying air temperature on drying kinetics and product quality. Heliyon 2024, 10, e25968. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yue, Y.; Zhang, Q.; Wan, F.; Ma, G.; Zang, Z.; Xu, Y.; Jiang, C.; Huang, X. Effects of Different Drying Methods on the Drying Characteristics and Quality of Codonopsis pilosulae Slices. Foods 2023, 12, 1323. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Amer, B.M.A.; Gottschalk, K.; Hossain, M.A. Integrated hybrid solar drying system and its drying kinetics of chamomile. Renew. Energy 2018, 121, 539–547. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, G.; Yu, Y.; Yao, C.; Zhou, L.; Zhu, G.; Lai, Y.; Niu, P. Effect of Far-Infrared Drying on Broccoli Rhizomes: Drying Kinetics and Quality Evaluation. Processes 2024, 12, 1674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Xu, H.; Liu, Q.; Ke, M.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, X.; Gao, Z.; Wu, R.; Yuan, Q.; Qian, C.; et al. Shoot-to-root communication via GMUVR8-GMSTF3 photosignaling and flavonoid biosynthesis fine-tunes soybean nodulation under UV-B light. New Phytol. 2024, 241, 209–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, M.; Dong, B.; Song, Z.; Qi, M.; Chen, T.; Du, T.; Cao, H.; Liu, N.; Meng, D.; Yang, Q.; et al. Molecular mechanism of naringenin regulation on flavonoid biosynthesis to improve the salt tolerance in pigeon pea (Cajanus cajan (Linn.) Millsp.). Plant Physiol. Biochem. 2023, 196, 381–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ezquerro, M.; Burbano-Erazo, E.; Rodriguez-Concepcion, M. Overlapping and specialized roles of tomato phytoene synthases in carotenoid and abscisic acid production. Plant Physiol. 2023, 193, 2021–2036. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gerna, D.; Arc, E.; Holzknecht, M.; Roach, T.; Jansen-Dürr, P.; Weiss, A.K.H.; Kranner, I. AtFAHD1a: A New Player Influencing Seed Longevity and Dormancy in Arabidopsis? Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2021, 22, 2997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Kim, J.I.; Pysh, L.; Chapple, C. Four isoforms of Arabidopsis thaliana 4-coumarate: CoA ligase (4CL) have overlapping yet distinct roles in phenylpropanoid metabolism. Plant Physiol. 2015, 169, 2409–2421. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hussain, S.; Zhang, R.; Liu, S.; Li, R.; Wang, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hou, H.; Dai, Q. Methyl Jasmonate Alleviates the Deleterious Effects of Salinity Stress by Augmenting Antioxidant Enzyme Activity and Ion Homeostasis in Rice (Oryza sativa L.). Agronomy 2022, 12, 2343. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazier-Hicks, M.; Gershater, M.; Dixon, D.; Edwards, R. Substrate specificity and safener inducibility of the plant UDP-glucose-dependent family 1 glycosyltransferase super-family. Plant Biotechnol. J. 2018, 16, 337–348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Model Name | Slice Thickness (mm) | Evaluation Metrics | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | RMSE | χ2 | ||
| Lewis | 2 | 0.99082 | 0.01969 | 0.00039 |
| 4 | 0.99087 | 0.02230 | 0.00050 | |
| 6 | 0.99345 | 0.02742 | 0.00075 | |
| 8 | 0.99504 | 0.02939 | 0.00086 | |
| Wang and Singh | 2 | 0.92138 | 0.04897 | 0.00240 |
| 4 | 0.92468 | 0.07239 | 0.00524 | |
| 6 | 0.93373 | 0.07854 | 0.00617 | |
| 8 | 0.97205 | 0.08925 | 0.00797 | |
| Weibull | 2 | 0.99113 | 0.01966 | 0.00039 |
| 4 | 0.99308 | 0.02132 | 0.00045 | |
| 6 | 0.99425 | 0.02648 | 0.00070 | |
| 8 | 0.99528 | 0.02759 | 0.00076 | |
| Logarithmic | 2 | 0.99205 | 0.02047 | 0.00042 |
| 4 | 0.99433 | 0.02075 | 0.00043 | |
| 6 | 0.99513 | 0.02163 | 0.00047 | |
| 8 | 0.99519 | 0.02954 | 0.00087 | |
| Slice Thickness (mm) | Model Parameters | Evaluation Indicators | ||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| a | k | c | R2 | RMSE | χ2 | |
| 2 | 1.03643 | 0.18951 | −0.00856 | 0.99205 | 0.02954 | 0.00087 |
| 4 | 0.99628 | 0.10455 | −0.00406 | 0.99513 | 0.02047 | 0.00042 |
| 6 | 0.98489 | 0.08023 | −0.01325 | 0.99433 | 0.02163 | 0.00047 |
| 8 | 1.03497 | 0.05724 | −0.06299 | 0.99519 | 0.02075 | 0.00043 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2025 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).
Share and Cite
Luo, W.; Guo, J.; Zhou, J.; Yang, M.; Wang, Y. Mechanistic Elucidation and Establishment of Drying Kinetic Models of Differential Metabolite Regulation in Rheum palmatum During Natural Sun Drying: An Integrated Physiology, Untargeted Metabolomics, and Enzymology Study. Biology 2025, 14, 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080963
Luo W, Guo J, Zhou J, Yang M, Wang Y. Mechanistic Elucidation and Establishment of Drying Kinetic Models of Differential Metabolite Regulation in Rheum palmatum During Natural Sun Drying: An Integrated Physiology, Untargeted Metabolomics, and Enzymology Study. Biology. 2025; 14(8):963. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080963
Chicago/Turabian StyleLuo, Wen, Jinrong Guo, Jia Zhou, Mingjun Yang, and Yonggang Wang. 2025. "Mechanistic Elucidation and Establishment of Drying Kinetic Models of Differential Metabolite Regulation in Rheum palmatum During Natural Sun Drying: An Integrated Physiology, Untargeted Metabolomics, and Enzymology Study" Biology 14, no. 8: 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080963
APA StyleLuo, W., Guo, J., Zhou, J., Yang, M., & Wang, Y. (2025). Mechanistic Elucidation and Establishment of Drying Kinetic Models of Differential Metabolite Regulation in Rheum palmatum During Natural Sun Drying: An Integrated Physiology, Untargeted Metabolomics, and Enzymology Study. Biology, 14(8), 963. https://doi.org/10.3390/biology14080963






